Mental Health of Parents and Their Children: A Longitudinal Study of the Effects of Parents’ Negative Affect on Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Parents’ Negative Affect and Adolescents’ Mental Health
3. Pathological Gaming and Adolescents’ Mental Health
3.1. Aggression and Pathological Gaming
3.2. Adolescents’ Self-Control and Pathological Gaming
3.3. Adolescents’ ADHD and Pathological Gaming
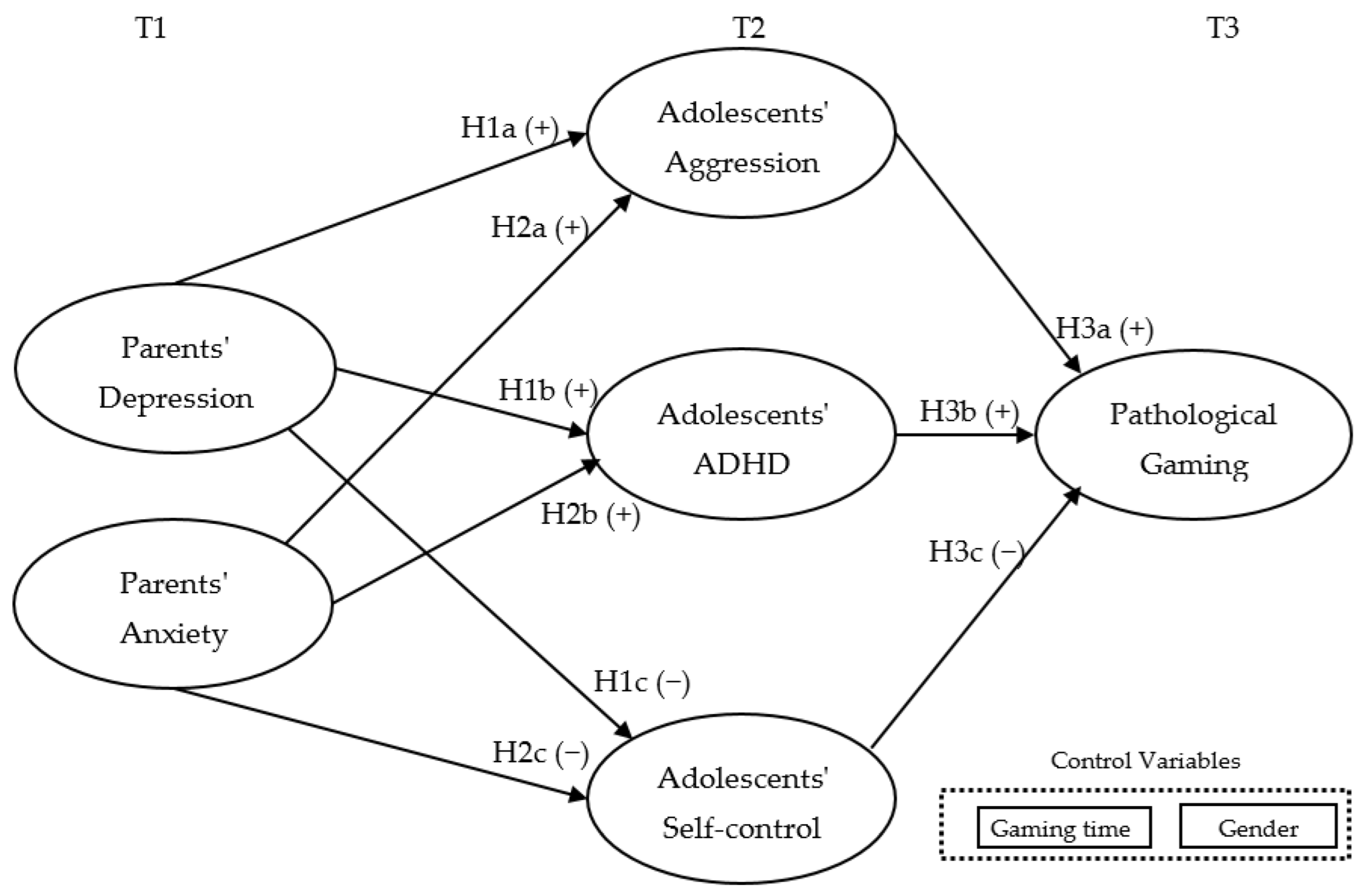
4. Research Model and Hypotheses
- H1. Parents’ depression is positively associated with adolescents’ aggression (H1a) and adolescents’ ADHD (H1b), while parents’ depression is negatively associated with adolescents’ self-control (H1c).
- H2. Parents’ anxiety is positively associated with adolescents’ aggression (H2a) and adolescents’ ADHD (H2b), while parents’ anxiety is negatively associated with adolescents’ self-control (H2c).
- H3. Adolescents’ aggression (H3a) and ADHD (H3b) is positively associated with pathological gaming, while adolescents’ self-control is negatively associated with pathological gaming (H3c).
- H4. Adolescents’ aggression (H4a) and self-control (H4b) mediate the effect of parents’ depression on the degree of pathological gaming.
5. Method
5.1. Data Collection
5.2. Measurement
5.2.1. Parents’ Depression
5.2.2. Parents’ Anxiety
5.2.3. Adolescents’ Aggression
5.2.4. Adolescents’ Self-Control
5.2.5. Adolescents’ ADHD
5.2.6. Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming
5.2.7. Daily Gaming Time
6. Results
6.1. Reliability and Validity Test
6.2. Research Model Test
6.3. Mediation Test (Parents’ Depression–Adolescents’ Aggression, Self-Control–Pathological Gaming)
7. Discussion
7.1. Findings
7.2. Theoretical and Practical Implications
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolicki, S.B.; Bitsko, R.H.; Cree, R.A.; Danielson, M.L.; Ko, J.Y.; Warner, L.; Robinson, L.R. Mental Health of Parents and Primary Caregivers by Sex and Associated Child Health Indicators. Advers. Resil. Sci. 2021, 2, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.; Hope, H.F.; Kolade, A.; Gellatly, J.; Osam, C.S.; Perchard, R.; Kosidou, K.; Dalman, C.; Morgan, V.; Di Prinzio, P.; et al. Effects of parental mental illness on children’s physical health: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 217, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.H.; Gotlib, I.H. Risk for psychopathology in the children of depressed mothers: A developmental model for understanding mechanisms of transmission. Psychol. Rev. 1999, 106, 458–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, E.; Bögels, S.M. Exposure to Parents’ Negative Emotions as a Developmental Pathway to the Family Aggregation of Depression and Anxiety in the First Year of Life. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 20, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Cheung, M.W.-L.; Wang, H.-Y. Multinational comparison of internet gaming disorder and psychosocial problems versus well-being: Meta-analysis of 20 countries. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 88, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bueso, V.; Santamaría, J.; Oliveras, I.; Fernández, D.; Montero, E.; Baño, M.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Del Pino-Gutiérrez, A.; Ribas, J. Internet Gaming Disorder Clustering Based on Personality Traits in Adolescents, and Its Relation with Comorbid Psychological Symptoms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.J.; Ferguson, C.J.; Lee, S.J. Pathological Gaming in Young Adolescents: A Longitudinal Study Focused on Academic Stress and Self-Control in South Korea. J. Youth Adolesc. 2019, 48, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Pontes, H.M.; Nie, Q.; Griffiths, M.D.; Guo, C. Depression and anxiety symptoms associated with internet gaming disorder before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal study. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 10, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, J.S.; Valkenburg, P.M.; Peter, J. Psychosocial causes and consequences of pathological gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.A.; Choo, H.; Liau, A.; Sim, T.; Li, D.; Fung, D.; Khoo, A. Pathological Video Game Use Among Youths: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e319–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L.; Delfabbro, P.H.; Zwaans, T.; Kaptsis, D. Clinical features and axis I comorbidity of Australian adolescent pathological Internet and video game users. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieris-Hirche, J.; Pape, M.; Wildt, B.T.T.; Kehyayan, A.; Esch, M.; Aicha, S.; Herpertz, S.; Bottel, L.; Dieris-Hirche, J.; Pape, M.; et al. Problematic gaming behavior and the personality traits of video gamers: A cross-sectional survey. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 106, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.J.; Ceranoglu, T.A. Attention Problems and Pathological Gaming: Resolving the ‘Chicken and Egg’ in a Prospective Analysis. Psychiatr. Q. 2014, 85, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, D.M. Why Do Some People Become Addicted to Digital Games More Easily? A Study of Digital Game Addiction from a Psychosocial Health Perspective. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2017, 33, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.; Griffiths, M. Internet Gaming Addiction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehroof, M.; Griffiths, M.D. Online Gaming Addiction: The Role of Sensation Seeking, Self-Control, Neuroticism, Aggression, State Anxiety, and Trait Anxiety. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2010, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, J.S.; Valkenburg, P.M.; Peter, J. The Effects of Pathological Gaming on Aggressive Behavior. J. Youth Adolesc. 2011, 40, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietglaiwansiri, T.; Chonchaiya, W. Pattern of video game use in children with attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder and typical development. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, A.K.; Neo, E.C.; Gentile, D.A.; Choo, H.; Sim, T.; Li, D.; Khoo, A. Impulsivity, self-regulation, and pathological video gaming among youth: Testing a mediation model. Asia-Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP2188–NP2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anxiety on Anxiety & Depression Association of America Home Page. Available online: https://adaa.org/understanding-anxiety/generalized-anxiety-disorder-gad (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- WHO. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; no.WHO/MSD/MER/2017.2; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/W?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Depression on American Psychological Association Home Page. Available online: https://www.apa.org/topics/depression/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Stein, D.J.; Kazdin, A.E.; Ruscio, A.M.; Chiu, W.T.; Sampson, N.A.; Ziobrowski, H.N.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Alonso, J.; Altwaijri, Y.; et al. Perceived helpfulness of treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: A World Mental Health Surveys report. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn-Waxler, C.; Cummings, E.M.; McKnew, D.H.; Radke-Yarrow, M. Mark Cummings, Altruism, Aggression, and Social Interactions in Young Children with a Manic-Depressive Parent. Child Dev. 1984, 55, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, D.; Vaske, J.; Taylor, J.; Wright, J.P. The Effects of Differential Parenting on Sibling Differences in Self-Control and Delinquency Among Brother–Sister Pairs. Crim. Justice Rev. 2012, 37, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, I. Online Social Networking and Mental Health. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbudak, E.; Evren, C.; Evren, B.; Topcu, M.; Kutlu, N. Relationship of Internet gaming disorder symptom severity with non-suicidal self-injury among young adults. Dusunen Adam 2020, 33, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bueso, V.; Santamaría, J.J.; Fernández, D.; Merino, L.; Montero, E.; Ribas, J. Association between Internet Gaming Disorder or Pathological Video-Game Use and Comorbid Psychopathology: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Bae, S.; Renshaw, P.F.; Anderson, J.S. Brain connectivity and psychiatric comorbidity in adolescents with Internet gaming disorder. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, G.J.; Han, D.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, K.D.; Yoo, S.K.; Chung, U.-S.; Renshaw, P.F. Risk factors associated with online game addiction: A hierarchical model. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 48, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.J.; A Anderson, C.; Bushman, B.J. The General Aggression Model. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2018, 19, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Yau, Y.H.C.; Chai, J.; Guo, J.; Potenza, M.N. Problematic Internet use, well-being, self-esteem and self-control: Data from a high-school survey in China. Addict. Behav. 2016, 61, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J. Internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: The effect of parental behavior and self-control. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Lachance, C.C.; Nincic, V.; Sharpe, J.P.; Ghassemi, M.; Straus, S.E.; Tricco, A.C. Exploring the prevalence of gaming disorder and Internet gaming disorder: A rapid scoping review. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylski, A.K.; Ryan, R.M.; Rigby, C.S. The Motivating Role of Violence in Video Games. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2009, 35, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, C.K. Children’s Motivations for Video Game Play in the Context of Normal Development. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2010, 14, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, S.; Saran, K.; A Green, D.; Hong, I. Electronic Media Use and Addiction among Youth in Psychiatric Clinic versus School Populations. Can. J. Psychiatry 2012, 57, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, C.J.; Coulson, M.; Barnett, J. A meta-analysis of pathological gaming prevalence and comorbidity with mental health, academic and social problems. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.J.; Giever, D.; Martin, J.S. Parental Management and Self-Control: An Empirical Test of Gottfredson and Hirschi’s General Theory. J. Res. Crime Delinq. 1998, 35, 40–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Caplan, S. Problematic Internet use and psychosocial well-being: Development of a theory-based cognitive–behavioral measurement instrument. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2002, 18, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ren, P.; Chiu, M.M.; Wang, C.; Lei, H. The Relationship Between Self-Control and Internet Addiction Among Students: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 735755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADHD on American Psychological Association Home Page. Available online: https://www.apa.org/topics/adhd (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Silverstein, M.J.; Faraone, S.V.; Leon, T.L.; Biederman, J.; Spencer, T.J.; Adler, L.A. The Relationship Between Executive Function Deficits and DSM-5-Defined ADHD Symptoms. J. Atten. Disord. 2020, 24, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupaul, G.J.; Anastopoulos, A.D.; Power, T.J.; Reid, R.; Ikeda, M.J.; McGoey, K.E. Parent Ratings of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms: Factor Structure and Normative Data. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 1998, 20, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, F.B.; Smith, B.D. Refining the Architecture of Aggression: A Measurement Model for the Buss–Perry Aggression Questionnaire. J. Res. Personal. 2001, 35, 138–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, A.H.; Perry, M. The aggression questionnaire. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 63, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangney, J.P.; Baumeister, R.; Boone, A.L. High Self-Control Predicts Good Adjustment, Less Pathology, Better Grades, and Interpersonal Success. J. Personal. 2004, 72, 271–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction—And a Winning Strategy for Recovery; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter, E.; Parzer, P.; Brunner, R.; Fischer, G.; Durkee, T.; Carli, V.; Hoven, C.W.; Wasserman, C.; Sarchiapone, M.; Wasserman, D.; et al. A 2-year longitudinal study of prospective predictors of pathological Internet use in adolescents. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 25, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartberg, L.; Kriston, L.; Zieglmeier, M.; Lincoln, T.; Kammerl, R. A longitudinal study on psychosocial causes and consequences of Internet gaming disorder in adolescence. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharkow, M.; Festl, R.; Quandt, T. Longitudinal patterns of problematic computer game use among adolescents and adults-a 2-year panel study. Addiction 2014, 109, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Constructs | No. of Measures | Mean (SD) | Cronbach’s Alpha | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression (P-t1 1) | 6 | 1.45 (2.359) | 0.835 | 0.861 | 0.510 |
| Anxiety (P-t1 1) | 6 | 3.60 (3.145) | 0.887 | 0.892 | 0.579 |
| Aggression (A-t2 2) | 5 | 9.17 (4.101) | 0.872 | 0.887 | 0.567 |
| ADHD (A-t2 2) | 6 | 3.00 (2.974) | 0.867 | 0.869 | 0.527 |
| Self-control (A-t2 2) | 9 | 41.48 (22.714) | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.930 |
| Pathological gaming (A-t3 3) | 19 | 41.82 (16.523) | 0.954 | 0.977 | 0.690 |
| Constructs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression (P-t1) | 0.714 | |||||
| Anxiety (P-t1) | 0.571 *** | 0.761 | ||||
| Aggression (A-t2) | 0.465 *** | 0.185 *** | 0.753 | |||
| ADHD (A-t2) | 0.189 *** | 0.186 *** | 0.229 *** | 0.726 | ||
| Self-control (A-t2) | 0.111 ** | −0.041 | −0.148 *** | 0.008 | 0.964 | |
| Pathological gaming (A-t3) | 0.215 *** | 0.099 ** | 0.304 *** | 0.115 *** | −0.657 *** | 0.831 |
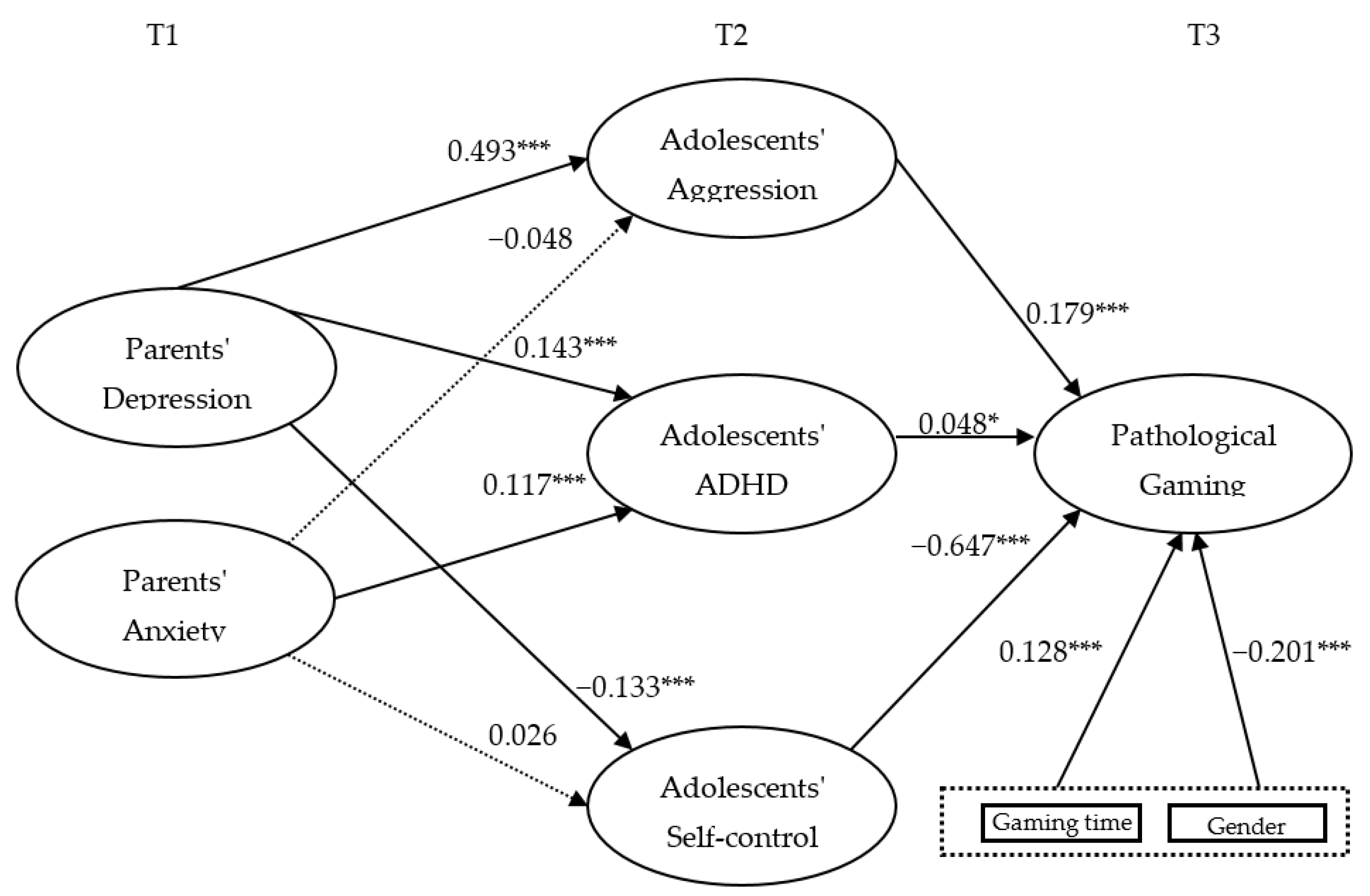
| Hypothesis | B | β | SE | CR | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1a. Parents’ depression → Adolescents’ aggression | 0.873 | 0.493 | 0.070 | 12.540 | Accepted |
| H1b. Parents’ depression → Adolescents’ ADHD | 0.145 | 0.143 | 0.037 | 3.955 | Accepted |
| H1c. Parents’ depression → Adolescents’ self-control | −0.952 | −0.133 | 0.242 | −3.929 | Accepted |
| H2a. Parents’ anxiety → Adolescents’ aggression | −0.068 | −0.048 | 0.045 | −1.513 | Rejected |
| H2b. Parents’ anxiety → Adolescents’ ADHD | 0.094 | 0.117 | 0.029 | 3.296 | Accepted |
| H2c. Parents’ anxiety → Adolescents’ self-control | 0.148 | 0.026 | 0.188 | 0.788 | Rejected |
| H3a. Adolescents’ aggression → Pathological gaming | 0.252 | 0.179 | 0.035 | 7.207 | Accepted |
| H3b. Adolescents’ ADHD → Pathological gaming | 0.118 | 0.048 | 0.059 | 2.009 | Accepted |
| H3c. Adolescents’ self-control → Pathological gaming | −0.224 | −0.647 | 0.009 | −23.661 | Accepted |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piao, M.Y.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, J.A. Mental Health of Parents and Their Children: A Longitudinal Study of the Effects of Parents’ Negative Affect on Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112233
Piao MY, Jeong EJ, Kim JA. Mental Health of Parents and Their Children: A Longitudinal Study of the Effects of Parents’ Negative Affect on Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming. Healthcare. 2022; 10(11):2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112233
Chicago/Turabian StylePiao, Mei Ying, Eui Jun Jeong, and Jeong Ae Kim. 2022. "Mental Health of Parents and Their Children: A Longitudinal Study of the Effects of Parents’ Negative Affect on Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming" Healthcare 10, no. 11: 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112233
APA StylePiao, M. Y., Jeong, E. J., & Kim, J. A. (2022). Mental Health of Parents and Their Children: A Longitudinal Study of the Effects of Parents’ Negative Affect on Adolescents’ Pathological Gaming. Healthcare, 10(11), 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112233






