Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
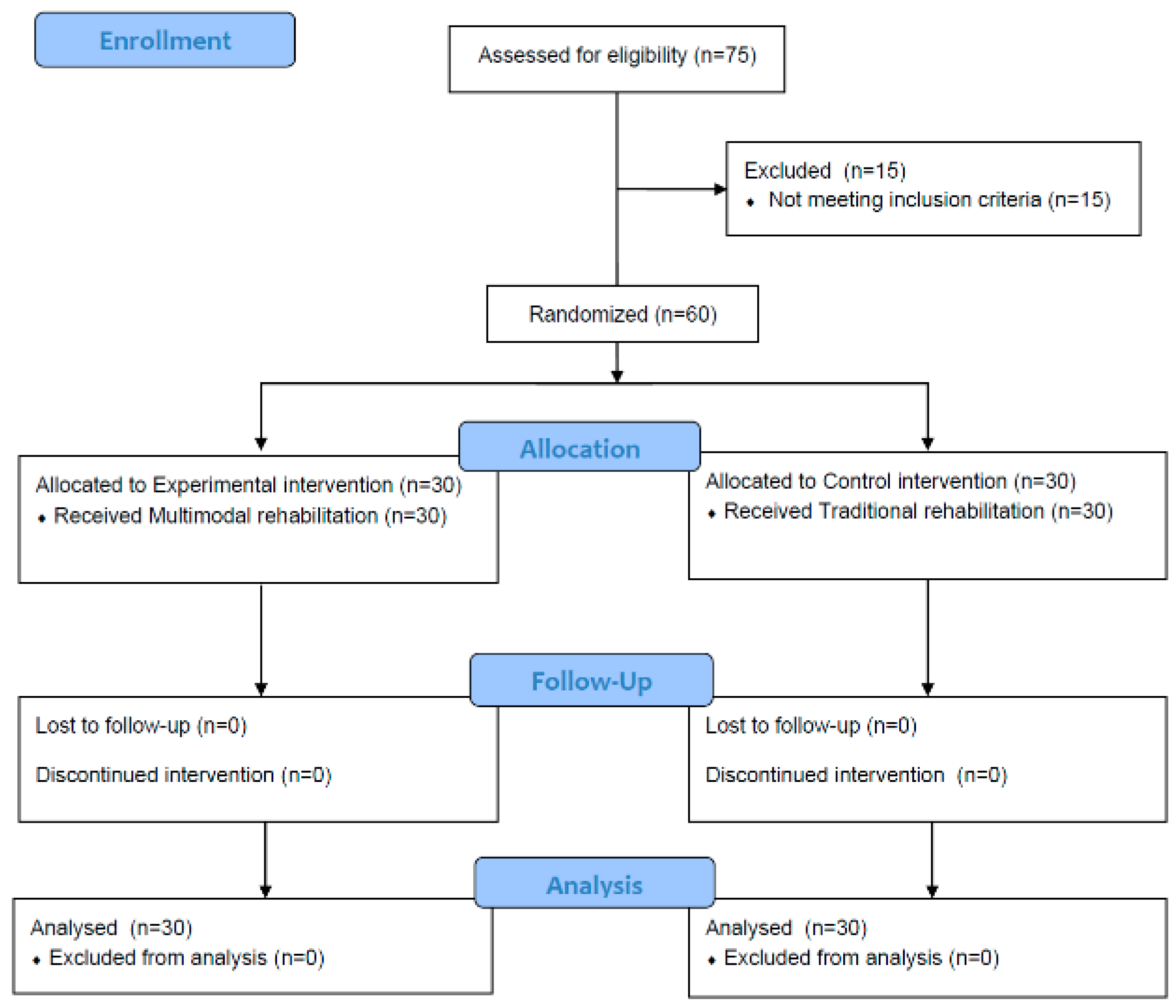
2.2. Participants and Procedures
2.3. Intervention Method
2.3.1. Multimodal Rehabilitation
2.3.2. Traditional Rehabilitation
2.3.3. Outcome Criteria
The New Activity Daily Living Questionnaire
Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire-39
Zarit Burden Interview Korean
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Multimodal Rehabilitation Changes
3.2. Traditional Rehabilitation Changes
3.3. Comparison the Experimental and Control Groups
3.4. Correlation between the Dependent Variable in the Experimental Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shulman, L.M.; Gruber-Baldini, A.L.; Anderson, K.E.; Vaughan, C.G.; Reich, S.G.; Fishman, P.S.; Weiner, W.J. The Evolution of Disability in Parkinson Disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martignoni, E.; Citterio, A.; Zangaglia, R.; Godi, L.; Pacchetti, C.; Fundaro, C.; Corengia, E.; Bono, G.; Nappi, G. How Parkinsonism Influences Life: The Patients’ Point of View. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, G.; Forsaa, E.B.; Pedersen, K.F.; Dreetz Gjerstad, M.; Larsen, J.P. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelb, D.J.; Oliver, E.; Gilman, S. Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, L.M. Understanding Disability in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, S131–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, C.; Rochon, P.; Lang, A.E. Predicting Motor Decline and Disability in Parkinson Disease: A Systematic Review. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1724–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, A.D.; Counsell, C.E. Predictors of Functional Dependency in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C.; McDermott, M.P.; Rochon, P.A.; Tanner, C.M.; Naglie, G.; Lang, A.E.; Investigators, P.S.G.D. Predictors of Deterioration in Health-Related Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease: Results from the DATATOP Trial. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Oudsten, B.L.; Lucas-Carrasco, R.; Green, A.M.; Whoqol-Dis Group, T. Perceptions of Persons with Parkinson’s Disease, Family and Professionals on Quality of Life: An International Focus Group Study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2011, 33, 2490–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.C.; Zonta, M.B.; Araújo, A.P.S.D.; Israel, V.L.; Teive, H.A. Quality of life in Parkinson’s disease patients: Progression markers of mild to moderate stage. Arq. Neuropsiquiat. 2017, 75, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, M.; Narita, Y.; Sakamoto, A.; Kawada, N.; Akiyama, M.; Kayama, M.; Suzukamo, Y.; Fukuhara, S. Health-Related Quality of Life among Community-Dwelling Patients with Intractable Neurological Diseases and Their Caregivers in Japan. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 65, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, P.E.; Moodie, R.; Dissanayaka, N. Caregiver Burden in Parkinson Disease: A Critical Review of Recent Literature. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2017, 30, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Doll, H.; Playford, D.; Jenkinson, C. Does Self-Reported Well-Being of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Influence Caregiver Strain and Quality of Life? Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, A.; Hovris, A.; Morley, D.; Quinn, N.; Jahanshahi, M. Caregiver-Burden in Parkinson’s Disease Is Closely Associated with Psychiatric Symptoms, Falls, and Disability. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2006, 12, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, K.H.; Choe, M.A.; Yi, M.; Hah, Y.S.; Chung, S.J.; Kwon, S.H. Subjective and Objective Caregiver Burden in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2007, 37, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caap-Ahlgren, M.; Dehlin, O. Factors of importance to the caregiver burden experienced by family caregivers of Parkinson’s disease patients. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 14, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, H.; Storey, L. Rehabilitation for Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Available Evidence. Clin. Rehabil. 2004, 18, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruzzese, G.; Marchese, R.; Avanzino, L.; Pelosin, E. Rehabilitation for Parkinson’s Disease: Current Outlook and Future Challenges. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 22, S60–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions (UK). Parkinson’s Disease: National Clinical Guideline for Diagnosis and Management in Primary and Secondary Care; National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Guidance; Royal College of Physicians (UK): London, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-1-86016-283-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.M.; da Costa Alves, W.M.G.; de Lima, T.A.; Alves, T.G.G.; Alves Filho, P.A.M.; Pimentel, C.P.; Sousa, E.C.; Cortinhas-Alves, E.A. The Effect of Resistance Training on the Anxiety Symptoms and Quality of Life in Elderly People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2018, 76, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciotta, M.; Maestri, R.; Ortelli, P.; Ferrazzoli, D.; Mastalli, F.; Frazzitta, G. Occupational Therapy for Parkinsonian Patients: A Retrospective study. Parkinsons Dis. 2019, 2019, 4561830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radder, D.L.; Sturkenboom, I.H.; van Nimwegen, M.; Keus, S.H.; Bloem, B.R.; de Vries, N.M. Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturkenboom, I.H.; Graff, M.J.; Hendriks, J.C.; Veenhuizen, Y.; Munneke, M.; Bloem, B.R.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W.; Group, O.S. Efficacy of Occupational Therapy for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, E.R.; Bedekar, M.; Tickle-Degnen, L. Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Occupational Therapy–Related Interventions for People with Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2014, 68, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Counsell, C.; Seidl, L. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: Status and recommendations the Movement Disorder Society Task Force on rating scales for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, A.; Kings, J. Occupational Therapy for People with Parkinson’s: Best Practice Guidelines; The Lavenham Press: Lavenham, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sturkenboom, I.; Thijssen, M.; Gons-van Elsacker, J.J.; Jansen, I.; Maasdam, A.; Schulten, M.; Vijver-Visser, D.; Steultjens, E.; Bloem, B.; Munneke, M. Guidelines for Occupational Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease Rehabilitation; Lemma Publishers: Nijmegen, Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Byl, N.; Zhang, W.; Coo, S.; Tomizuka, M. Clinical Impact of Gait Training Enhanced with Visual Kinematic Biofeedback: Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Patients Stable Post Stroke. Neuropsychologia 2015, 79, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, C.P.; Mattle, H.P.; Müri, R.M.; Heldner, M.R.; Blatter, V.; Bartlome, S.; Lüthy, J.; Imboden, D.; Pedrazzini, G.; Bohlhalter, S. Home-Based Training to Improve Manual Dexterity in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, M.; Ambrosini, E.; Laurini, A.; Rocca, B.; Foti, C. In-Patient Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation for Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, S.K.; Cheon, S.-M.; Seo, J.-W.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, J.W. Activities of Daily Living Questionnaire from Patients’ Perspectives in Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, C.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Peto, V.; Greenhall, R.; Hyman, N. The Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39): Development and Validation of a Parkinson’s Disease Summary Index Score. Age Ageing 1997, 26, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarit, S.H.; Todd, P.A.; Zarit, J.M. Subjective Burden of Husbands and Wives as Caregivers: A Longitudinal Study. Gerontologist 1986, 26, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.Y.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.M.; Yang, S.J.; Shin, H.Y.; Yoon, J.S. Care Burden of Caregivers According to Cognitive Function of Elderly Persons. J. Korean Soc. Biol. Ther. Psychiatry. 2006, 12, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Deane, K.; Ellis-Hill, C.; Dekker, K.; Davies, P.; Clarke, C. A Survey of Current Occupational Therapy Practice for Parkinson’s Disease in the United Kingdom. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2003, 66, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansa, J.; Aragon, A. Living with Parkinson’s and the Emerging Role of Occupational Therapy. Park. Dis. 2015, 2015, 196303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsby, E.; Berrigan, S.; Laver, K. Effectiveness of Occupational Therapy Intervention for People with Parkinson’s Disease: Systematic Review. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2019, 66, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, C.E.; Patel, S.; Ives, N.; Rick, C.E.; Dowling, F.; Woolley, R.; Wheatley, K.; Walker, M.F.; Sackley, C.M. others Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy vs No Therapy in Mild to Moderate Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tickle-Degnen, L.; Ellis, T.; Saint-Hilaire, M.H.; Thomas, C.A.; Wagenaar, R.C. Self-Management Rehabilitation and Health-Related Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderback, I. Occupational Therapy: Emphasis on Clinical Practice. In International Handbook of Occupational Therapy Interventions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Schell, B.A.; Gillen, G.; Scaffa, M.; Cohn, E.S. Willard and Spackman’s Occupational Therapy; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rajiah, K.; Maharajan, M.K.; Yeen, S.J.; Lew, S. Quality of Life and Caregivers’ Burden of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroepidemiology 2017, 48, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, A.; Marano, P.; Modugno, N.; Pontieri, F.E.; Tambasco, N.; Canesi, M.; Latorre, A.; Lopiano, L.; Sensi, M.; Quatrale, R.; et al. Caregiver Burden and Its Related Factors in Advanced Parkinson’s Disease: Data from the PREDICT Study. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, B.J.; Gasson, N.; Kane, R.; Bucks, R.S.; Loftus, A.M. Activities of Daily Living, Depression, and Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, Z.A.; Koljack, C.E.; Miyasaki, J.M.; Katz, M.; Galifianakis, N.; Prizer, L.P.; Sillau, S.H.; Kluger, B.M. Patient and caregiver characteristics associated with caregiver burden in Parkinson’s disease: A palliative care approach. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, S24–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner-Fisman, G.; Stern, M.B.; Fisman, D.N. Health-Related Quality of Life in Parkinson Disease: Correlation between Health Utilities Index III and Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) in US Male Veterans. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuther, M.; Spottke, E.; Klotsche, J.; Riedel, O.; Peter, H.; Berger, K.; Athen, O.; Köhne-Volland, R.; Dodel, R. Assessing Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease in a Prospective Longitudinal Study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2007, 13, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Han, H.; Cui, J.; Ge, X.; Qin, Y.; Yu, H.; Bai, W.; Yu, H. The path linking disease severity and cognitive function with quality of life in Parkinson’s disease: The mediating effect of activities of daily living and depression. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, D.-C.; Pahwa, R.; Mallya, U. Treatment Patterns and Associated Costs with Parkinson’s Disease Levodopa Induced Dyskinesia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 319, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, T.; Katz, D.I.; White, D.K.; DePiero, T.J.; Hohler, A.D.; Saint-Hilaire, M. Effectiveness of an Inpatient Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Program for People with Parkinson Disease. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Session | Multimodal Rehabilitation |
|---|---|
| 1A. Fine motor exercise (30 min) |
|
| 1B. Education (20 min) |
|
| 2A. Fine motor exercise (30 min) |
|
| 2B. ADL training (20 min) |
|
| 3~4A. Fall prevention exercise (30 min) |
|
| 3~4B. ADL training (20 min) |
|
| 5. Visiting home & Feedback |
|
| 6~9A. Fall prevention exercise or Fine motor exercise(30 min) |
|
| 6~9B. ADL training (20 min) |
|
| 10. Visiting home & Feedback |
|
| Items | M ± SD | t | p | Within Group Change 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | ||||
| The new ADL questionnaire | 57.1 ± 2.59 | 51.7 ± 2.55 | 16.076 | 0.000 *** | 5.4 (4.66, 6.03) |
| PDQ-39 | 43.5 ± 4.85 | 36.0 ± 3.82 | 19.888 | 0.000 *** | 7.5 (6.79, 8.36) |
| ZBI-K | 45.8 ± 3.58 | 37.7 ± 4.78 | 13.241 | 0.000 *** | 8.1 (6.82, 9.33) |
| Items | M ± SD | t | p | Within Group Change 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | ||||
| The new ADL questionnaire | 57.7 ± 3.16 | 54.1 ± 2.71 | 13.235 | 0.000 *** | 3.5 (2.98, 4.08) |
| PDQ-39 | 43.4 ± 4.55 | 39.6 ± 4.28 | 19.784 | 0.000 *** | 3.7 (3.34, 4.11) |
| ZBI-K | 46.6 ± 2.84 | 44.4 ± 2.36 | 9.311 | 0.000 *** | 2.2 (1.70, 2.67) |
| Items | Experimental Group | Control Group | t | p | Between Group Change (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The new ADL questionnaire | 5.3 ± 1.69 | 3.5 ± 1.36 | −4.236 | 0.001 ** | 1.8 (0.95, 2.66) |
| PDQ-39 | 7.5 ± 1.94 | 3.7 ± 0.96 | −9.048 | 0.000 *** | 3.8 (2.99, 4.70) |
| ZBI-K | 8.1 ± 3.11 | 2.2 ± 1.20 | −9.000 | 0.000 *** | 5.9 (4.55, 7.20) |
| The New ADL Questionnaire | ZBI-K | |
|---|---|---|
| ZBI-K | 0.259 | |
| PDQ-39 | 0.330 * | 0.578 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-S.; Cho, S.-H. Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101888
Choi H-S, Cho S-H. Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study. Healthcare. 2022; 10(10):1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101888
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyun-Se, and Seung-Hyun Cho. 2022. "Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study" Healthcare 10, no. 10: 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101888
APA StyleChoi, H.-S., & Cho, S.-H. (2022). Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study. Healthcare, 10(10), 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101888






