Robust Sensorless Model-Predictive Torque Flux Control for High-Performance Induction Motor Drives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
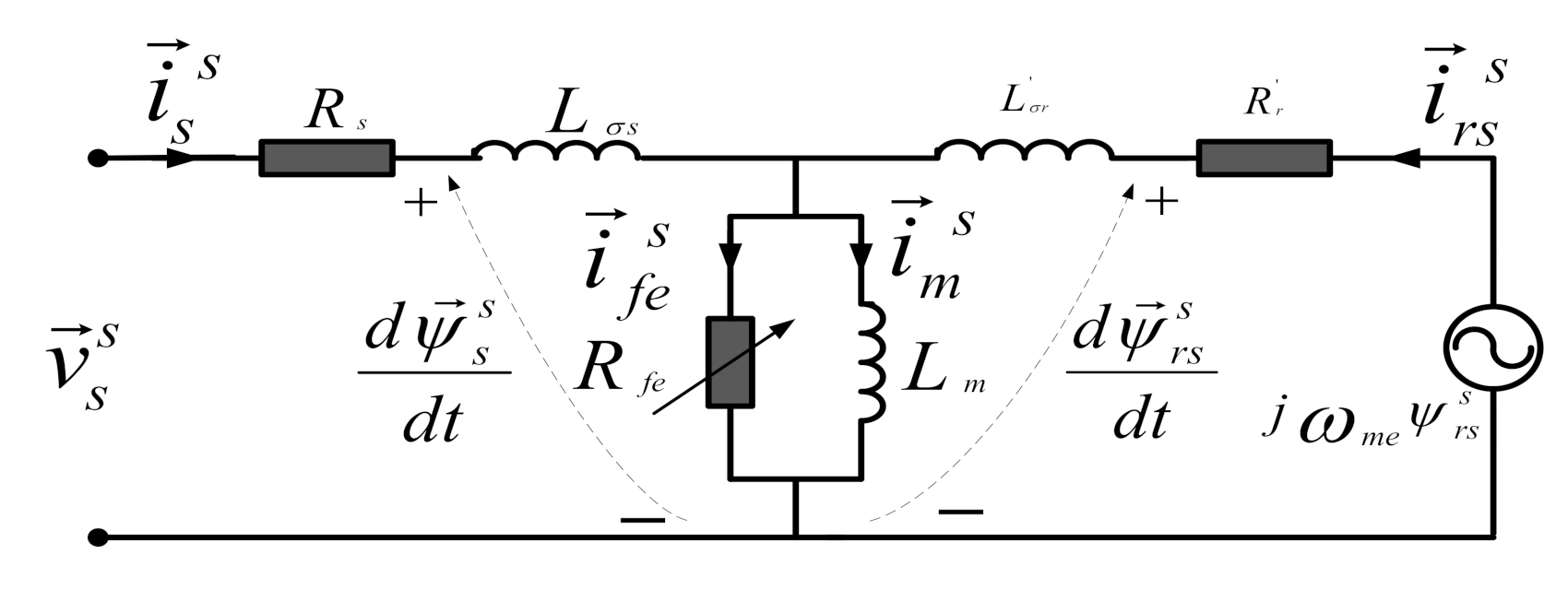
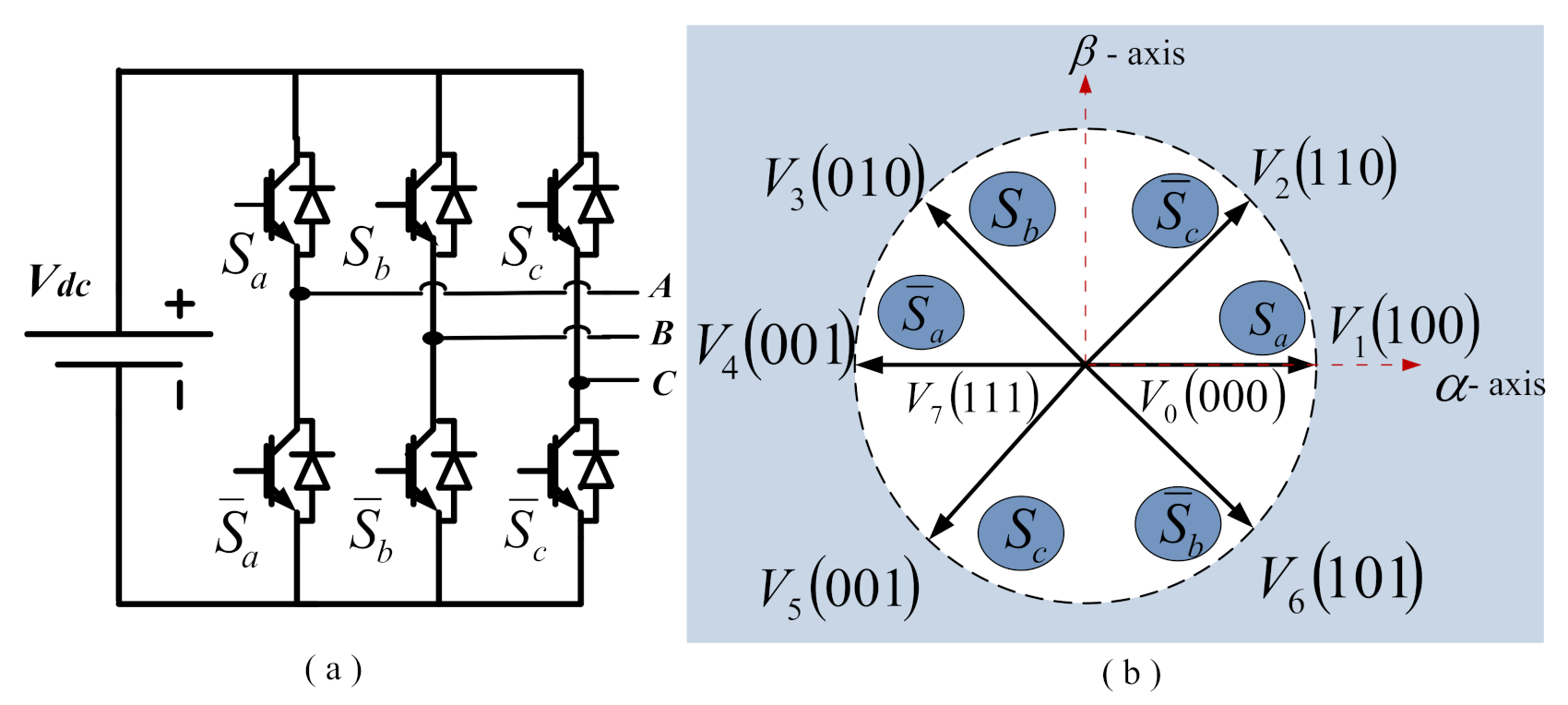
2. Mathematical Model of IM and Inverter
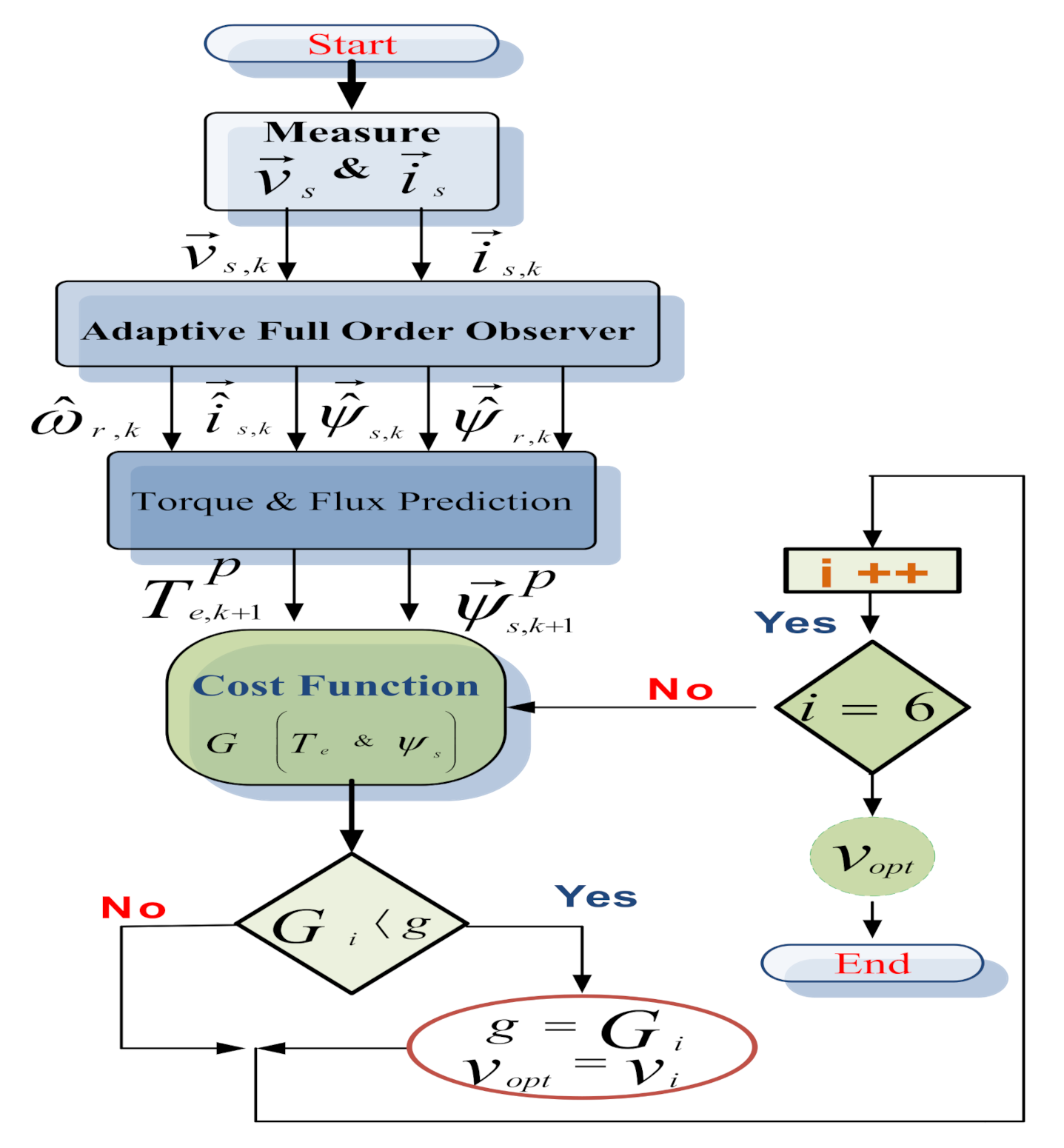
3. Adaptive Full Order Observer Modification
3.1. Stator Flux Estimation
3.2. Rotor Speed Estimation
3.3. Other Parameter Estimation
3.4. Torque Estimation
3.5. Conventional MPTC
3.6. Conventional MPFC
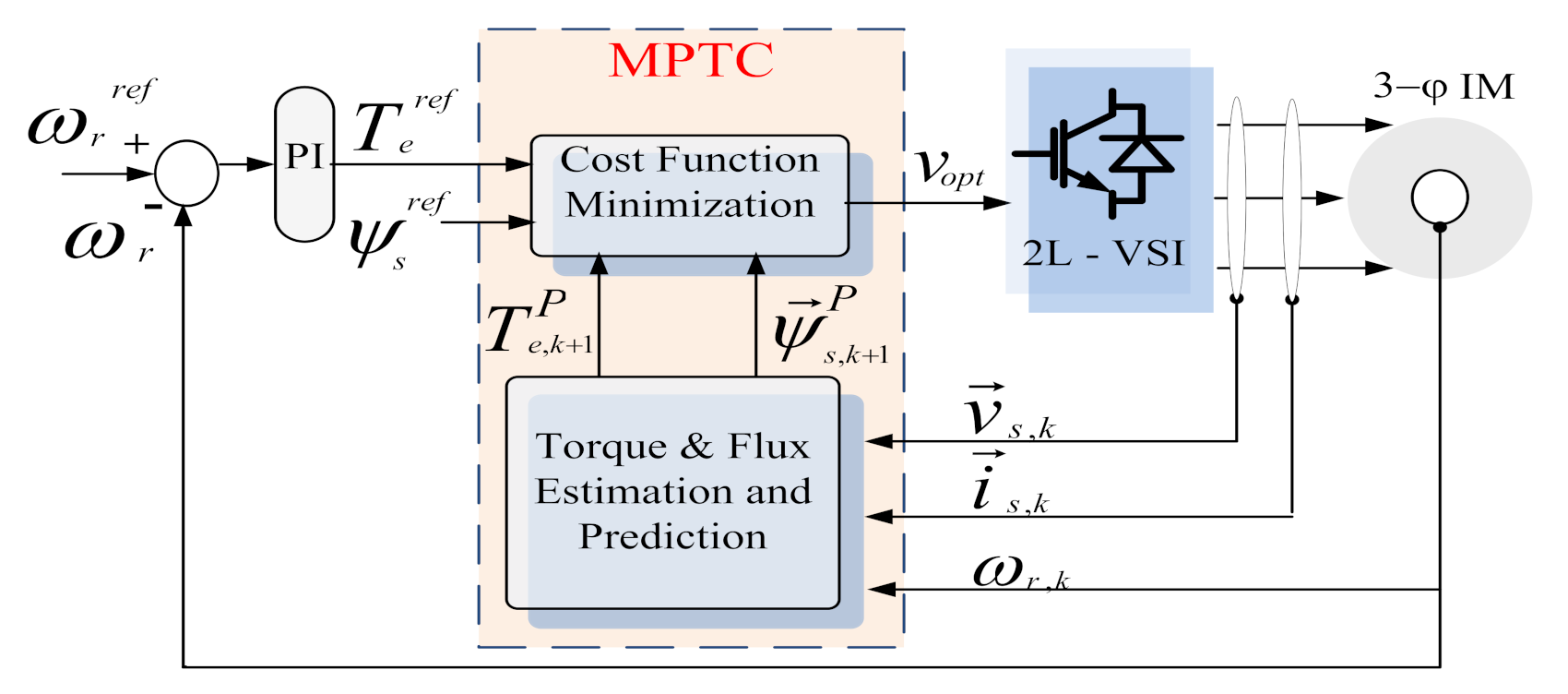
3.7. Proposed MPTFC
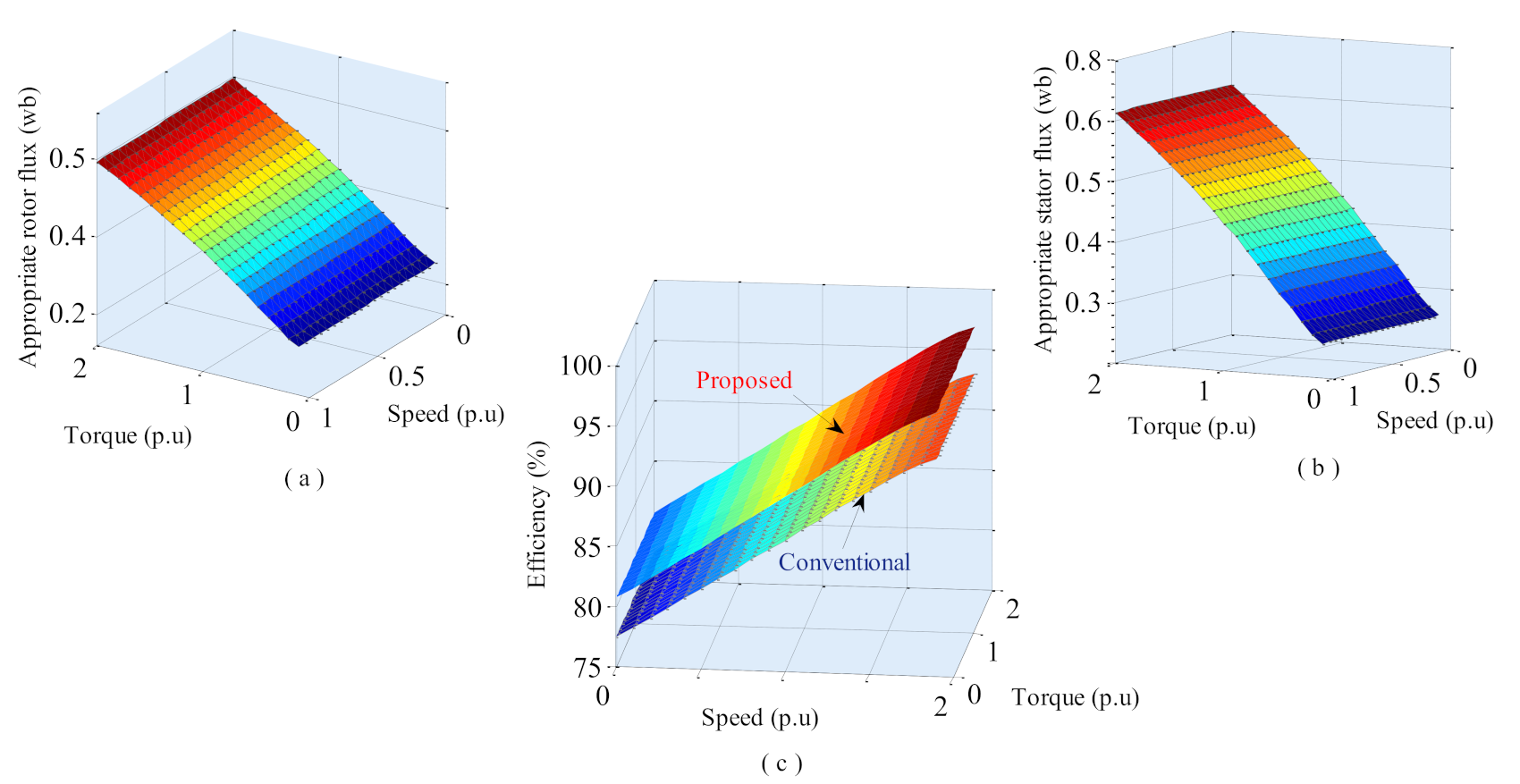
4. Optimal Steady-State Flux for Losses Minimization Criterion
5. System Layout
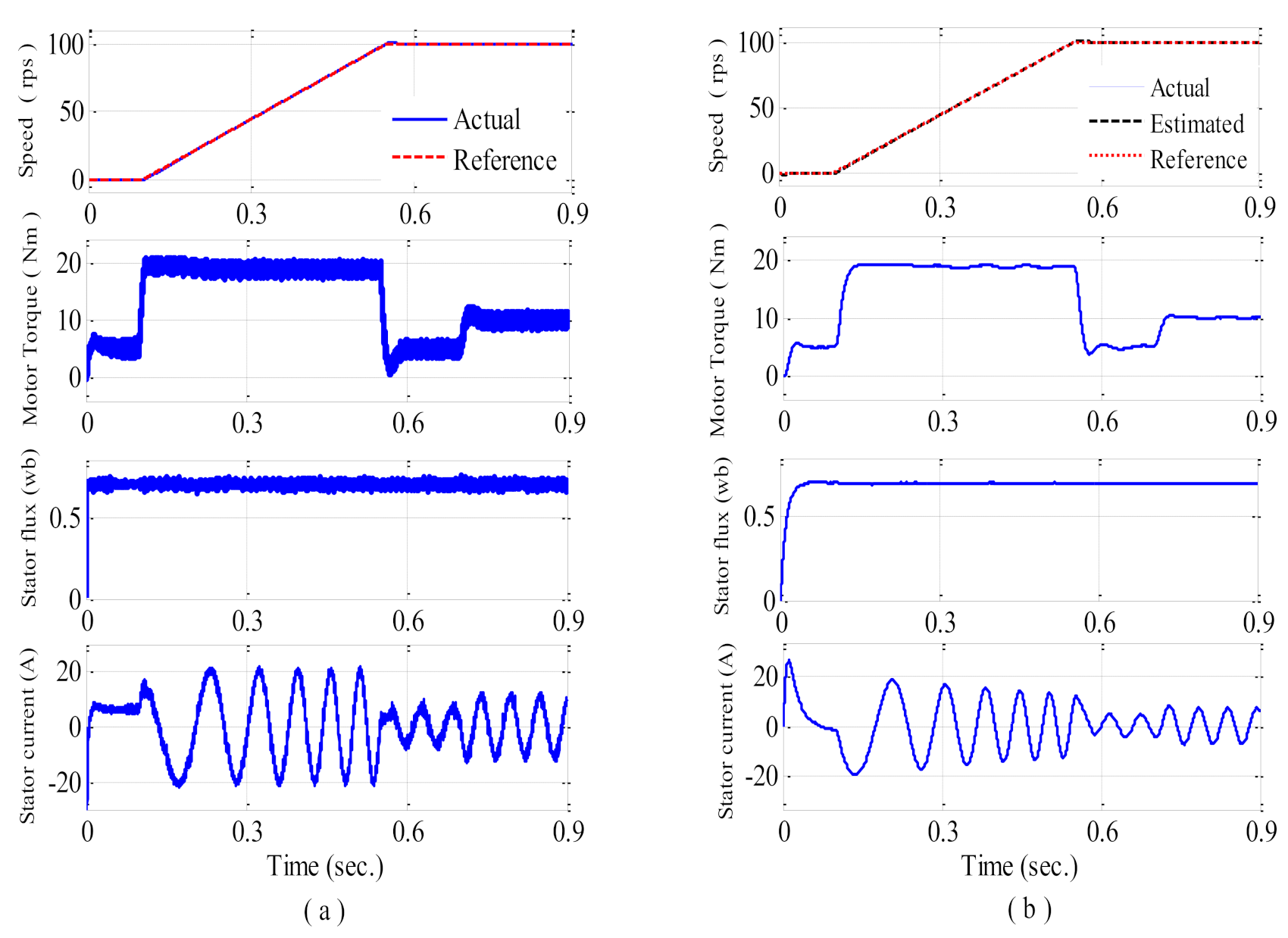
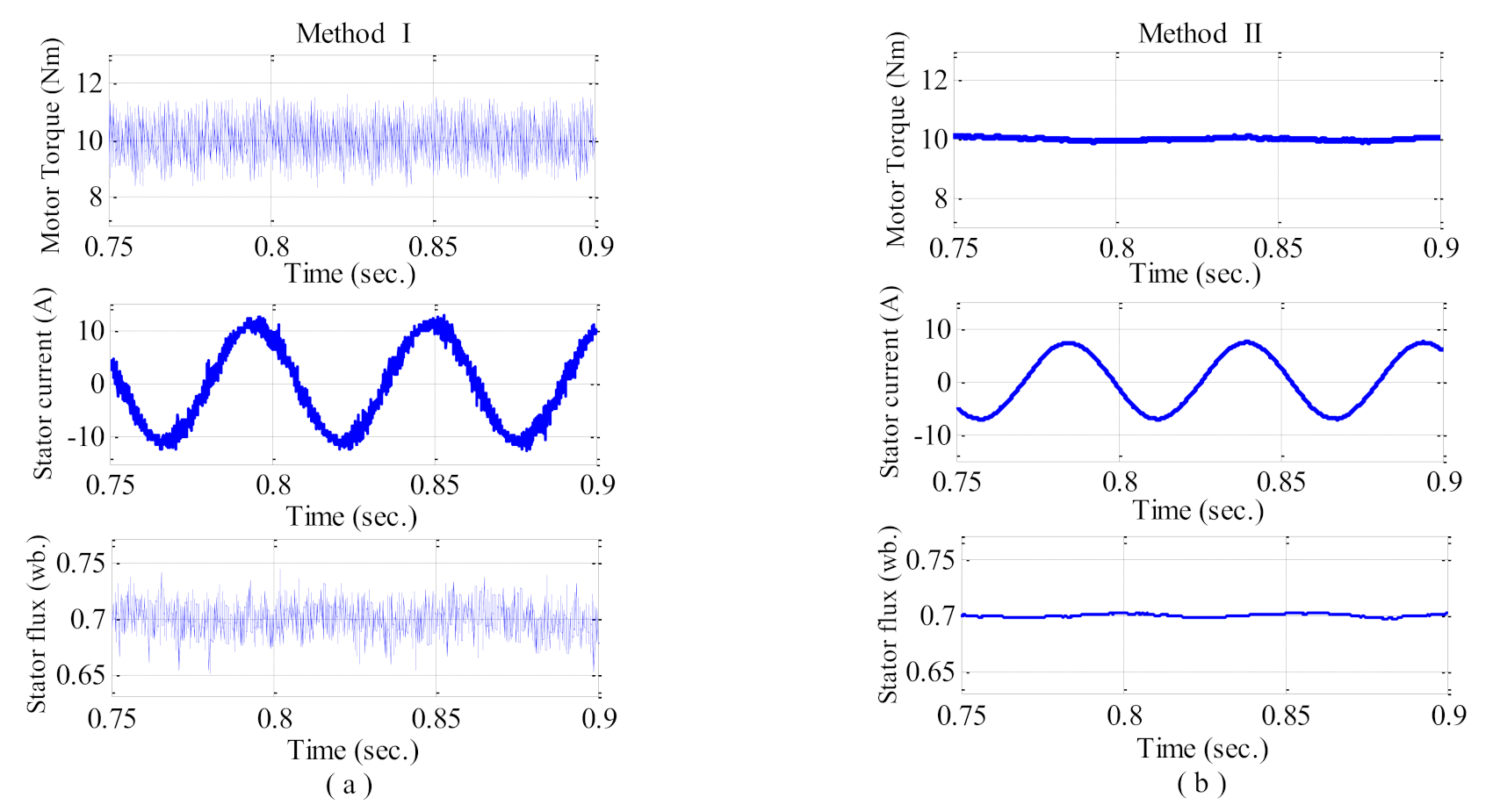
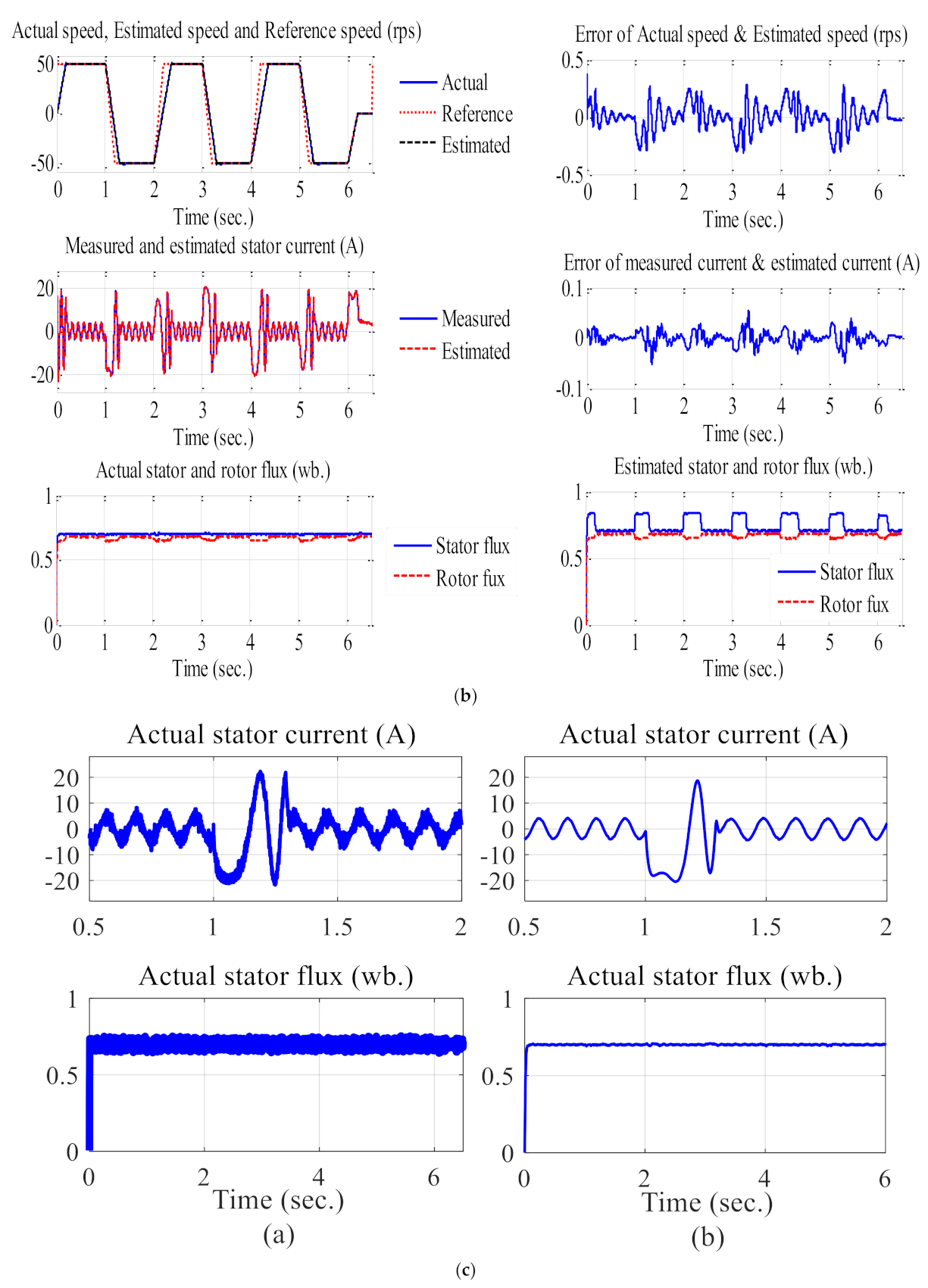
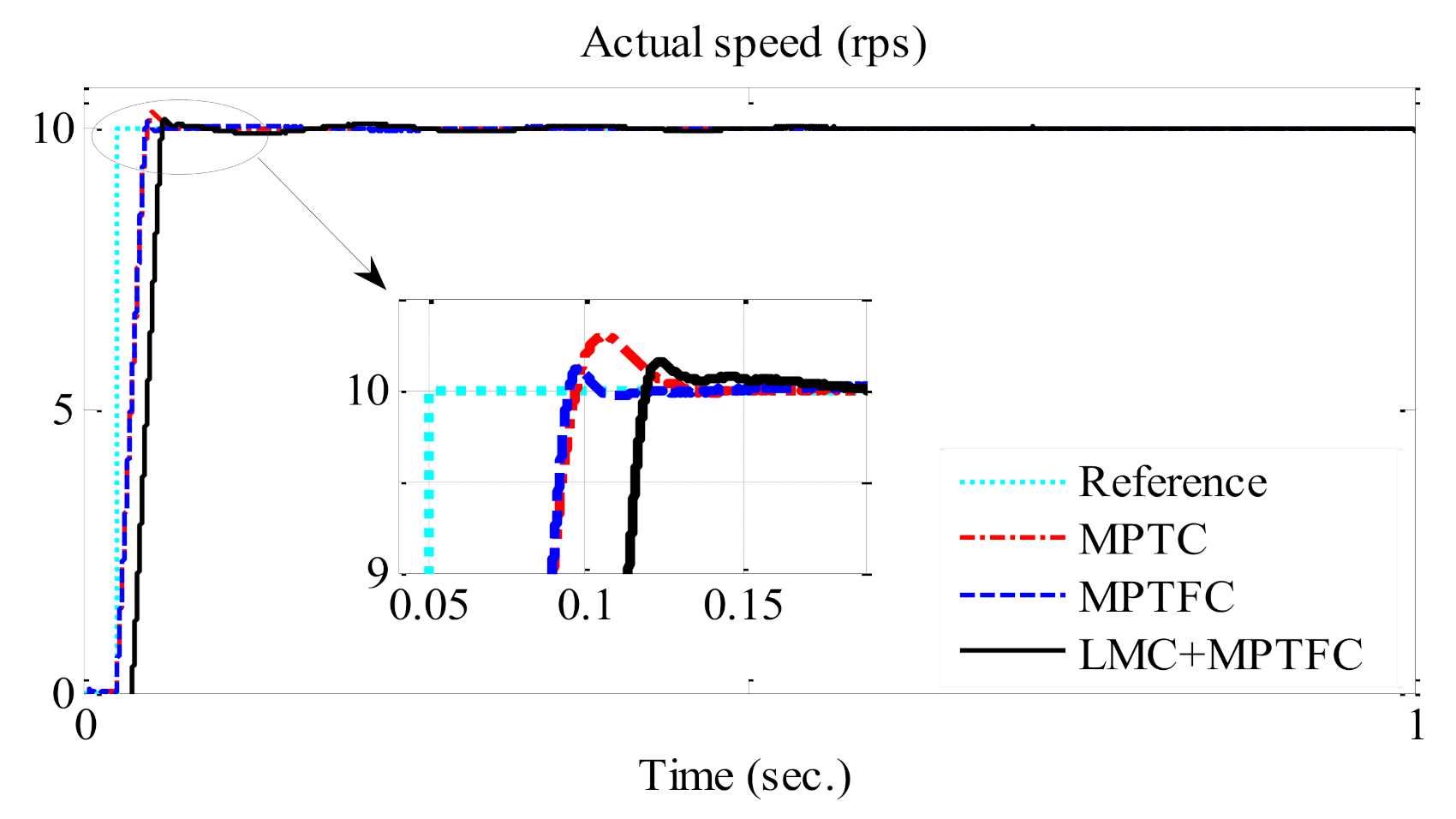
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Schauder, C. Adaptive speed identification for vector control of induction motors without rotational transducers. In Conference Record of the IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 493–499.
- Diab, A.A.Z. Novel robust simultaneous estimation of stator and rotor resistances and rotor speed to improve induction motor efficiency. Int. J. Power Electron. 2017, 8, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.K. Comparative assessment of two different model reference adaptive system schemes for speed-sensorless control of induction motor drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Gimenez, R.; Asher, G.; Sumner, M.; Bradley, K. Dynamic performance limitations for MRAS based sensorless induction motor drives. Part 1: Stability analysis for the closed loop drive. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 1996, 143, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Matsuse, K.; Nakano, T. DSP-based speed adaptive flux observer of induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, G.C.; Sanders, S.R. Observers for flux estimation in induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1988, 35, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnefors, L. Design and analysis of general rotor-flux-oriented vector control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2001, 48, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, D.; Profumo, F.; Serra, G.; Tani, A. FOC and DTC: Two viable schemes for induction motors torque control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diab, A.A.Z.; Selim, S.; Elnaghi, B.E. Particle swarm optimization based vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. In IEEE NW Russia Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Conference (EIConRusNW); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Alsofyani, I.M.; Idris, N.R.N. Simple flux regulation for improving state estimation at very low and zero speed of a speed sensorless direct torque control of an induction motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 3027–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.; Papafotiou, G.; Morari, M. Model predictive direct torque control—Part I: Concept, algorithm, and analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 56, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R.M.; Espinoza, J.R.; Trincado, M.; Silva, C.A.; Rojas, C.A. High-performance control strategies for electrical drives: An experimental assessment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Villarroel, F.; Espinoza, J.R.; Silva, C.A.; Trincado, M. Predictive torque and flux control without weighting factors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.A.Z.; Kotin, D.A.; Pankratov, V.V. Speed control of sensorless induction motor drive based on model predictive control. In 14th International Conference of Young Specialists on Micro/Nanotechnologies and Electron Devices; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Nacusse, M.A.; Romero, M.; Haimovich, H.; Seron, M.M. DTFC versus MPC for induction motor control reconfiguration after inverter faults. In Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol); IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, J. Finite-control-set model predictive direct torque control with extended set of voltage space vectors. In 2017. In 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W. Direct torque control strategy of induction motors based on predictive control and synthetic vector duty ratio control. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lunardi, A.; Sguarezi, A. Experimental results for predictive direct torque control for a squirrel cage induction motor. In Brazilian Power Electronics Conference (COBEP); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Rathore, V.; Yadav, K. Calculation of Torque Ripple and Derating Factor of a Symmetrical Six-Phase Induction Motor (SSPIM) Under the Loss of Phase Conditions. In Nanoelectronics. In Circuits and Communication Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 441–453. [Google Scholar]
- ML, P.; Eshwar, K.; Thippiripati, V.K. A modified duty-modulated predictive current control for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2021, 15, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, K.; Liu, C.; Lin, X. Discrete Dynamical Predictive Control on Current Vector for Three-Phase PWM Rectifier. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhimsetty, S.; Somasekhar, V.T. An Efficient Predictive Current Control Strategy for a Four-Level Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 6198–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Meng, D.; Yin, S.; Han, W.; Yan, X.; Shu, Z.; Diao, L. Vector-based model predictive hysteresis current control for asynchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8703–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, H.; Cortés, P.; Yuz, J.I.; Rodríguez, J. Predictive torque control of induction machines based on state-space models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.Z.; Kotin, D.; Anosov, V.; Pankratov, V. A comparative study of speed control based on MPC and PI-controller for Indirect Field oriented control of induction motor drive. In 12th International Conference on Actual Problems of Electronics Instrument Engineering (APEIE); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 728–732. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.; Cortes, P. Predictive Control of Power Converters and Electrical Drives; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Davari, S.A.; Khaburi, D.A.; Kennel, R. An improved FCS–MPC algorithm for an induction motor with an imposed optimized weighting factor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 27, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Model-predictive flux control of induction motor drives with switching instant optimization. J. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xia, B. Model-predictive control of induction motor drives: Torque control versus flux control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4050–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, P.; Geyer, T. Model predictive torque and flux control minimizing current distortions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T. Algebraic tuning guidelines for model predictive torque and flux control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 4464–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T. Model Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial Drives; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El Fadili, A.; Giri, F.; El Magri, A.; Lajouad, R.; Chaoui, F.Z. Towards a global control strategy for induction motor: Speed regulation, flux optimization and power factor correction. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 43, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diab, A.Z.; Vdovin, V.; Kotin, D.; Anosov, V.; Pankratov, V. Cascade model predictive vector control of induction motor drive. In 12th International Conference on Actual Problems of Electronics Instrument Engineering (APEIE); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Borisevich, A.; Schullerus, G. Energy efficient control of an induction machine under torque step changes. IEEE Transactions Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.-M.; Hori, Y. Convergence improvement of efficiency-optimization control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y. Flux Controlled Motor Management. U.S. Patent 20100090629A1, 14 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, A.A.Z. Robust simultaneous estimation of stator and rotor resistances and rotor speed for predictive maintenance of sensorless induction motor drives. Int. J. Power Energy Convers. 2017, 8, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.A.Z. Implementation of a novel full-order observer for speed sensorless vector control of induction motor drives. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuse, K.; Katsuta, S.; Tsukakoshi, M.; Ohta, M.; Huang, L.-p. Fast rotor flux control of direct-field-oriented induction motor operating at maximum efficiency using adaptive rotor flux observer. In IAS’95. Conference Record of the 1995 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Thirtieth IAS Annual Meeting; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Gao, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Robustness improvement of speed estimation in speed-sensorless induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 52, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Matsuse, K. Compensation for core loss of adaptive flux observer-based field-oriented induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the 1992 International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control, Instrumentation, and Automation; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wu, B. New integration algorithms for estimating motor flux over a wide speed range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1998, 13, 969–977. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Chin, T.-H. Adaptive-speed identification scheme for a vector-controlled speed sensorless inverter-induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.G.M.A.; Diab, A.A.Z.; Sattar, M.A.E. Speed sensorless vector controlled induction motor drive based stator and rotor resistances estimation taking core losses into account. In 2017 Nineteenth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1059–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Astrom, K.; Wittenmark, B. Computer Controlled Systems, Englewood Cliffs, NJ 07632; Prentice-Hall International, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yuz, J.I.; Goodwin, G.C. On sampled-data models for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Symbol | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage | ||
| No. pole pairs | ||
| Rated frequency | ||
| Stator resistance | ||
| Rotor resistance | ||
| Stator self-inductance | ||
| Rotor self-inductance | ||
| Magnetizing inductance | ||
| Moment of inertia | ||
| Nominal stator flux | ||
| Nominal torque | ||
| Core-resistance | ||
| Sampling-time |
| Method | Over Shot (%) | Rise Time | Settling Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPTC | |||
| MPTFC | |||
| MPTFC + LMC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, A.G.M.A.; Rez, H.; Diab, A.A.Z. Robust Sensorless Model-Predictive Torque Flux Control for High-Performance Induction Motor Drives. Mathematics 2021, 9, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040403
Aziz AGMA, Rez H, Diab AAZ. Robust Sensorless Model-Predictive Torque Flux Control for High-Performance Induction Motor Drives. Mathematics. 2021; 9(4):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040403
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Ahmed G. Mahmoud A., Hegazy Rez, and Ahmed A. Zaki Diab. 2021. "Robust Sensorless Model-Predictive Torque Flux Control for High-Performance Induction Motor Drives" Mathematics 9, no. 4: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040403
APA StyleAziz, A. G. M. A., Rez, H., & Diab, A. A. Z. (2021). Robust Sensorless Model-Predictive Torque Flux Control for High-Performance Induction Motor Drives. Mathematics, 9(4), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040403








