Abstract
In this article, we propose a novel mathematical model for the spread of COVID-19 involving environmental white noise. The new stochastic model was studied for the existence and persistence of the disease, as well as the extinction of the disease. We noticed that the existence and extinction of the disease are dependent on (the reproduction number). Then, a numerical scheme was developed for the computational analysis of the model; with the existing values of the parameters in the literature, we obtained the related simulations, which gave us more realistic numerical data for the future prediction. The mentioned stochastic model was analyzed for different values of and , and both the stochastic and the deterministic models were compared for the future prediction of the spread of COVID-19.
1. Introduction and Backgrounds
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a communicable respiratory disease. The disease is caused by a newly discovered virus strain, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) []. COVID-19 was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and spread quickly over four months. In a short period, more than 2.9 million people in 185 nations around the world were infected and 206 thousand people had died []. On March 11, 2020, The World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that the spread of this disease constituted a pandemic []. This disease can be spread primarily from droplets produced when coughing or sneezing, by person-to-person contact, or even through conversation. By contacting contaminated surfaces, susceptible individuals can also become infected. The most prevalent signs of this disease are fever, nausea, dry cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. All these signs constitute COVID-19 []. Some patients can have joint pain, nasal congestion, diarrhea, runny nose, or sore throat. The symptoms are typically mild, but can slowly worsen. In order to prevent infection, frequent hand washing, covering the nose and mouth when sneezing or coughing, avoiding touching the nose, mouth, or eyes, and other preventive steps are advised, including social distancing.
Due to the seriousness of the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries have taken extreme measures to curb its spread. In addition, they have evaluated and adapted their healthcare systems accordingly. Hence, they have canceled public events, closed public venues, schools, and borders, placed restrictions on travel, implemented lockdown measures, etc. While those measures have been helpful, lockdowns have led to negative socioeconomic impacts such as the bankruptcy of businesses, the loss of employment, etc. Furthermore, lockdowns have disrupted supply chains and decreased productivity. The shutdown of China’s drug-producing plants, which constitute the second largest pharmaceutical product exporters, has delayed the delivery of generic drugs []. The air transport, tourism, and oil sectors have been visibly affected. It is also expected that there will be unforeseen impacts irrespective of the duration of the pandemic. According to The International Monetary Fund, the worldwide economy was expected to shrink by 3% in 2020 [].
Governments must prevent the failure of the economy, taking measures to relax the lockdowns while preventing the spread of the disease. Some developed countries intend to or have already issued immunity identity cards. However, The World Health Organization has disapproved of this technique, since there is a lack of adequate scientific proof regarding reinfection, possibly rendering such measures ineffective. A risk-balancing strategy has been adopted by the South African government to lift the lockout restrictions progressively. We refer the readers to [,] for some scientific works performed on infectious diseases and, in particular, for several mathematical models related to abstract and real-world boundary problems via fractional operators, to [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,].
Brownian motion was discovered by the scholar Robert Brown in 1827. While Brown was studying pollen particles drifting in water in a microscope, he noticed that the particles exhibited an unsteady motion. After replicating the experiment, he concluded that the motion was due to the particles being alive; however, the initiation of the motion remained unexplained. The first to provide a theory of Brownian motion was Louis Bachelier in 1900 in his Ph.D. thesis. However, it was only in 1905 that Albert Einstein, using a probabilistic model, could adequately explain Brownian motion. He determined that the kinetic energy of fluids was the cause, in this case water molecules moving randomly. Thus, a small particle would receive a random number of impacts of random strength and from random directions in a short period of time. This random bombardment by the molecules of the fluid would cause a sufficiently small particle to move exactly as Brown described [].
In probability theory and associated fields, a stochastic or random process is a mathematical object, usually characterized as a group of random variables. In the 1930s, the first mathematical definition of a stochastic process as a family of random variables indexed by means of the change of the real line was given by Aleksandr Khinchin. Khinchin, Andrey Kolmogorov, Joseph Doob, and William Feller furthered the probability concept and stochastic techniques. In mathematics, the theory of stochastic processes is a significant aspect of probability theory and a subject of research for both theory and applications. The word stochastic is used to portray different terms and objects in mathematics. Few example, this includes a stochastic matrix, which describes a stochastic process known as a Markov process, and stochastic calculus, which includes differential equations and integrals depending on stochastic processes such as the Wiener process, also called the Brownian motion (white noise) process.
Stochastic processes are broadly used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appear to vary in a random manner, for example the growth of a bacterial population, an electrical flow fluctuating because of thermal noise, or the moment of gas particles []. Stochastic processes have applications in several fields such as biology, chemistry, physics, image processing, computer science, and cryptography. Stochastic processes consist of the Wiener process or Brownian motion technique, utilized by Louis Bachelier to study the value changes on the Paris Bourse, and the Poisson technique, used by A.K. Erlang to study the number of phone calls happening in a specific time frame. Stochastic processes can be arranged into different classes, which include random walks, martingales, and Markov processes [,]. Mathematical knowledge on probability, calculus, linear algebra, set theory, and topology, as well as branches of mathematical analysis such as real analysis and measure theory are used in the study of stochastic techniques. The theory of stochastic processes is viewed as a significant contribution to mathematics, and it continues to be an active topic of research for both theoretical reasons and applications. The Wiener process is a stochastic process with stationary and independent addition, which are typically dispersed depending on the size of the increments. The Wiener process is named after Norbert Wiener, who demonstrated its mathematical existence, but the process is also called the Brownian motion (white noises) process or just Brownian motion because of its historical association as a model for Brownian motion in liquids. Brownian motion (white noises) refers to either the physical phenomenon by which minute particles immersed in a fluid move around randomly or the mathematical models used to describe those random movements [].
Compartmental models are a type of general modeling tool that are frequently used in infectious diseases’ mathematical modeling. The population is divided into sections denoted by the letters , , or (susceptible, infectious, or recovered). The flow patterns between the sections are commonly indicated by the order of the abbreviations; for example, SEIS stands for susceptible, exposed, infected, and susceptible. Mathematical modeling begin with the well-known contributions of Ross [] in 1916, Ross and Hudson in 1917 [,], and Kermack and McKendrick in 1927 []. The work of Kermack and McKendrick, published in 1927, on inoculation against smallpox, had a major impact on the modeling of the system. Their SIR model is still used to model epidemics of infectious diseases. The SIR models are based on ordinary differential equations (which are deterministic), yet can likewise be utilized with a stochastic (random) structure, which is more sensible, yet substantially more challenging to investigate. The SIR model [,,] is the basic approach for a dynamical study, which can then be extended with further subcompartments.
The model comprises three classes: are the susceptible people. At the point when a susceptible and an infectious person come into “contact”, the susceptible becomes infected and advances to the infected class. is the class of infectious people. These are people who are infected and are able to infect uninfected people. stands for those who were infected, but are now immune or are now deceased, thus entering the removed compartment. It is expected that the quantity of deceased individuals will be negligible concerning the absolute population. This compartment may likewise be classified as “recovered” or “safe”.
The model predicts infections that are communicated from one person to another. These factors address the quantity of individuals in every compartment at a specific time. The quantity of susceptible, infected, and recovered people might differ over time (regardless of whether the absolute population size stays consistent), so we make the exact numbers a function of t (time): , , and . For a particular disease in a particular area, these compartments might be determined to anticipate possible outbreaks and bring them under control [].
As suggested by the variable function of t, the model is dynamic in that the numbers in every class might change over time. The significance of this unique perspective is generally clear in an endemic disease with a short infectious period, for example measles in the U.K. before the introduction of immunization in 1968. Such sicknesses will often happen in patterns of episodes due to the variation in the number of susceptibles over time. During an outbreak, the quantity of susceptible people falls quickly as a greater amount of them are infected and consequently enter the infectious and removed compartments. An outbreak cannot make an appearance again until the susceptible population has increased again, for example because of a future generation being naturally introduced to the susceptible compartment. Such models are still under consideration by the research community, and one can find some related work in [,,]. These aspects highlight some of the innovations in and contributions to the study of such models.
The notion of stochastic modeling can be investigated from different dimensions of engineering and science. For instance, stochastic models of financial markets are designed to analyze commodities, relative stock prices, and interest rates; in biological stochastic systems, we see that adding stochastic “noise” to internal links provides a balance and other noise interactions optimize function and behavior.It is believed that manufacturing processes have random structures. In fact, regarding both continuous and batch manufacturing processes, such a hypothesis is essentially valid. A process control chart represents a given parameter of process control in terms of time and is plotted to record and analyze the testing and monitoring of the relevant processes. Stochastic social science theory deals with subconscious processes. Since the number of involved variables is large, every event creates its own set of possibilities, which results in every event being unpredictable. The theory of stochastic models of different dynamical epidemic problems is of great interest among scientists. In the published literature, different aspects of theoretical analysis, including existence, extinction, persistence, and numerical simulations, can be observed in stochastic epidemic models. To better understand the subject, we recommend interested readers see [,,,,] and the references therein.
In this article, we considered that the fluctuations of and are random and and . With these considerations, we have the following new stochastic model for the spread of COVID-19:
Here, represents the class of uninfected susceptible people, represents the class of older people or those having other diseases, represents the class of people infected with COVID-19, represents the class of people who are undergoing treatment, and represents the class of recovered individuals. , are continuously increased with a constant ratio denoted by and , respectively. Furthermore, the parameters and are the ratios of the infection of and upon their contact with infected individuals . The infected individuals shift to the treated class with a ratio of , and the recovery rate is . represent the intensity of environmental white noise, and are the independent Brownian motions. For the case of , we have the following deterministic model []:
Our objectives were to study the analytical and computational approaches to the stochastic epidemic model (1). We compared our results with the deterministic model (2) numerically for different parametric values for the prediction of the future. Thus, the study can be helpful to the community regarding the awareness about the spread of the disease with a more realistic interpretation. Furthermore:
in which shows the total constant population for and .
The above equation has an exact solution, that is:
which implies that .
Furthermore, we have , , , , , implying that , , , . Therefore, the solution has a positive property.
2. Existence of the Solution
We made the following assumptions:
- Set ;
- Assume a complete probability space .
For the existence of the solution to our problem (1), we considered a general 5D stochastic differential equation, which takes the form:
via the initial value . Furthermore, an operator is defined as:
By operating on a function , then:
The existence of the solution is ensured by the following lemma.
Lemma 1.
For , a positive solution of (1) exists uniquely on in with probability equal to one.
Proof.
Since (1) fulfills the local Lipschitz criterion, in this case for:
we have as a unique local solution on in which is the explosion time. Now, our aim is to show for the global solution of (1). Let be very large so that lies in . For , define:
By assuming ∅ as the empty set, . Since is increasing for , set . Then, we have a.s.
Next, we aim to show a.s. If this claim is not true, then and such that . As a result, we have s.t. and for .
Now, consider the -function by the following formulation:
By Ito’s formula, we have:
where acts as:
Set the constant .
Then:
Now, integrate both sides of (11) between and calculate the expectation; then, we obtain the inequality:
where:
We take , which implies for every . We remark that for every , there exist at least , equaling the number ℏ or , such that:
From equation(12), we obtain the following relation:
in which stands for the indicator function. Furthermore, it is seen that when , then:
implies that a.s., which means that the solution is globally positive a.s. □
Theorem 1.
Let be the solution of the stochastic epidemic model (1). Then, for , we have:
Proof.
With the help of (1), we have:
This implies:
By the help of the large number approach in local martingales, studied in [], we have:
Thus, for , (16) yields:
We define . By (18), we have . This proves that the infection is bounded and controlled with .
Next, with the help of (1), for the infection, we have:
This yields the following:
By the arbitrariness of the , we have . Furthermore, on the other side,
Thus, there exists some constant, say , such that .
Next for , we have:
and so:
This implies:
Similarly, for , we have:
and for , we obtain:
However, due to the arbitrariness of the and , we have:
This completes the proof. □
Theorem 2.
Let be the solution of the stochastic epidemic model (1), via the initial values given by . Then, for , we have:
Proof.
In view of the first three equations of the proposed stochastic system (1), we obtain:
Integrating (19), we have:
This implies:
This further gives:
Ultimately, we have:
Next, for , we have:
Integrating (21), we have:
Thus:
This further gives:
Similarly, we have:
For , integrating the fourth equation in the system (1), we obtain:
This implies that:
Integrating the fifth equation of the system (1), we obtain:
Therefore:
With the help of (22), we reach:
This ends the proof. □
3. Numerical Scheme and Simulations
In this section, we provide a numerical scheme for the suggested stochastic COVID-19 epidemic model (1). We have the parametric values For the numerical values, we refer the readers to [,]. For the numerical results, we discretize the suggested stochastic mathematical model (1). The following discretization is based on the work given in [,] where the notion of the numerical scheme and its stability were discussed.
The graphical explanation of the model (1) is given onward. In Figure 1, a numerical solution of the model (1) is given for the zero noise, i.e., . In Figure 2, we give a numerical solution to the aforementioned epidemic stochastic model (1) for the zero noise, i.e., . For the zero noise, we have a numerical solution given by Figure 3 of the model (1), i.e., . In Figure 4, we give a numerical solution to (1) for the zero noise, i.e., . In Figure 5, another numerical solution is plotted to the model (1) for the zero noise, i.e., . The class is compared for different values of in Figure 6. Figure 7 represents a numerical analyses for the class keeping . These analyses show that there is a vital role of the noise in the spread of COVID-19. Next, we give the graphical presentation for the role of and for fixed and .
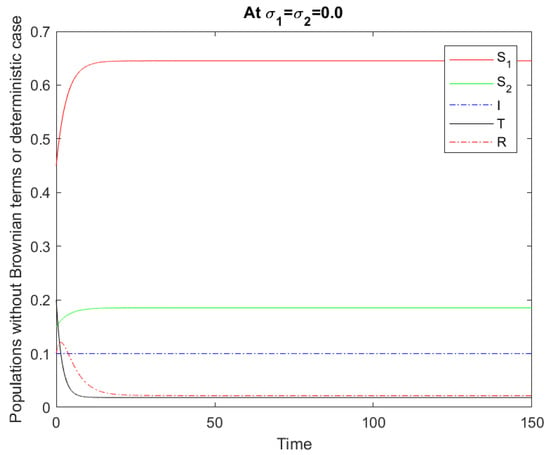
Figure 1.
Numerical solution of the model (1) for .
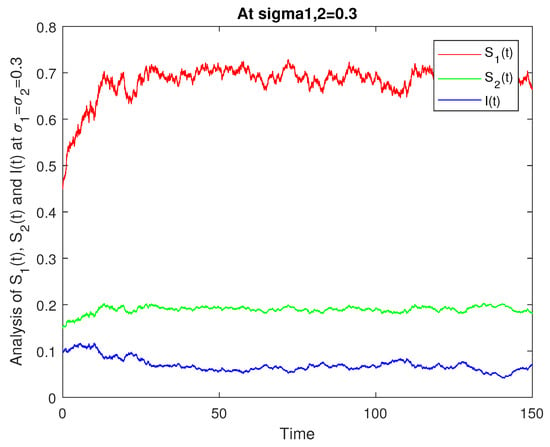
Figure 2.
Numerical solution of the model (1) for .
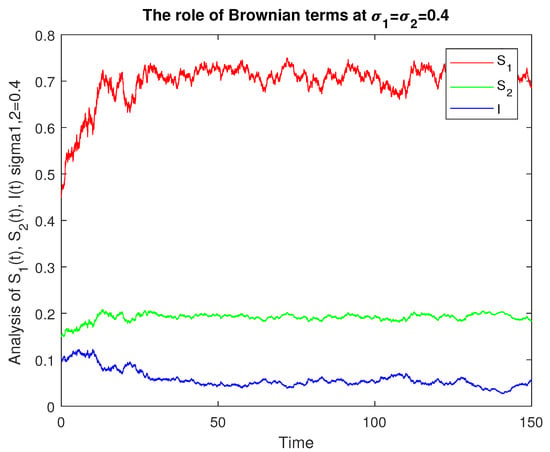
Figure 3.
Numerical solution of the model (1) for .
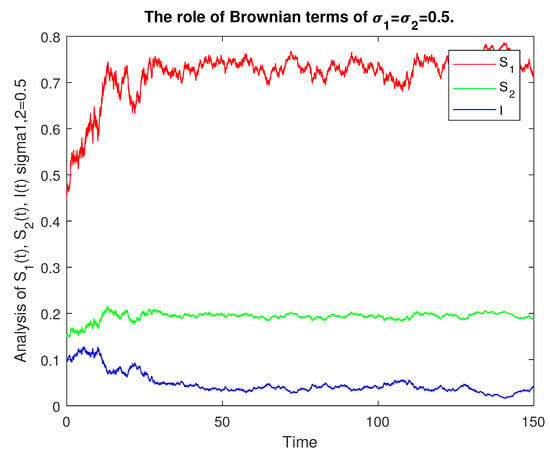
Figure 4.
Numerical solution of the model (1) for .
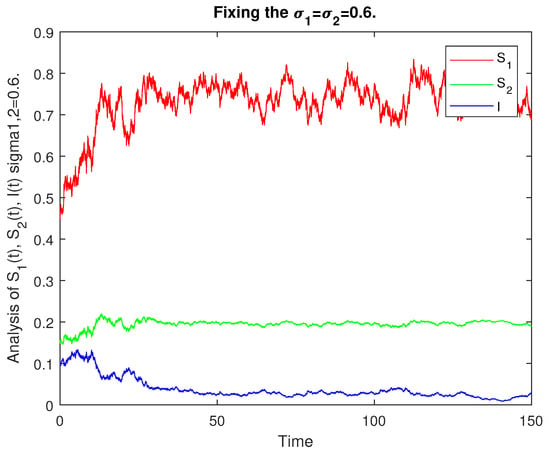
Figure 5.
Numerical solution of the model (1) for .
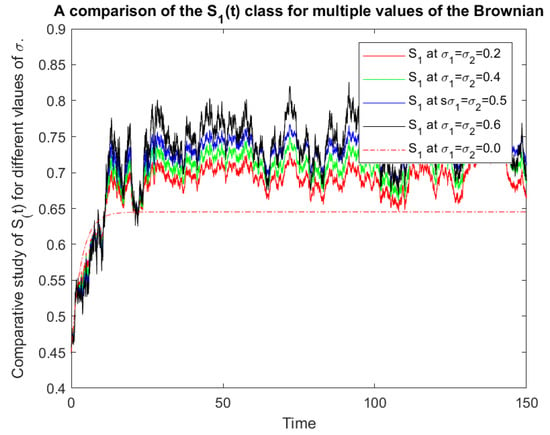
Figure 6.
Comparative analysis of for .
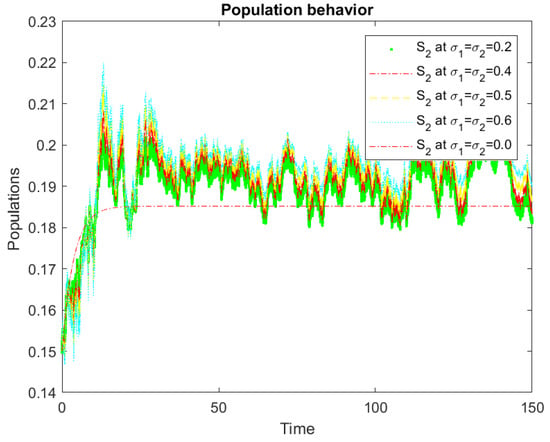
Figure 7.
Comparative analysis of for .
We give the numerical results with the help of graphs for the analysis of the stochastic model (1) based on and . In Figure 8, we give the numerical presentation of for the role of and such that keeping . In Figure 9, we have numerical data for the role of and with and . In Figure 10, we have numerical values for the role of and with and . In Figure 11, we have a numerical presentation of for the role of and with and . In Figure 12, we have a numerical presentation of the role of and with and and for the comparative analysis of the class. In Figure 13, we have a numerical presentation of the role of and with and and for the comparative analysis of the class.
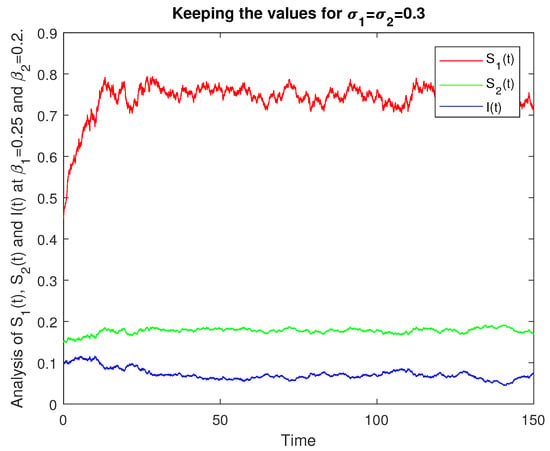
Figure 8.
Comparative analysis of , , for .
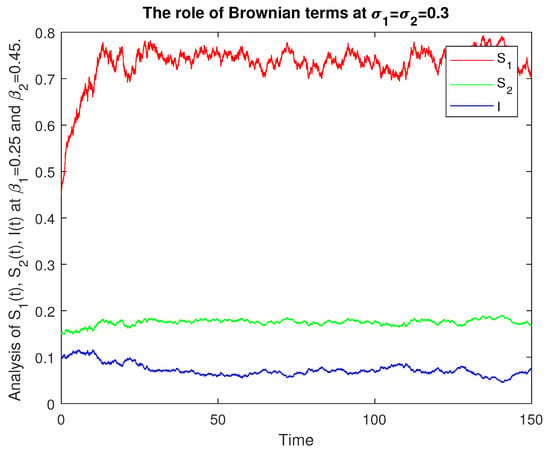
Figure 9.
Comparative analysis of , , for .
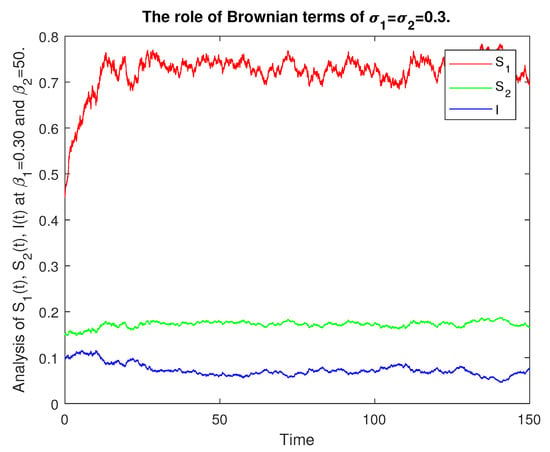
Figure 10.
Comparative analysis of , , for .
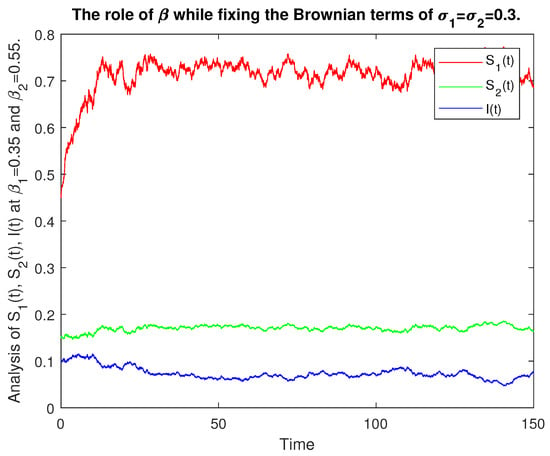
Figure 11.
Comparative analysis of , , for .
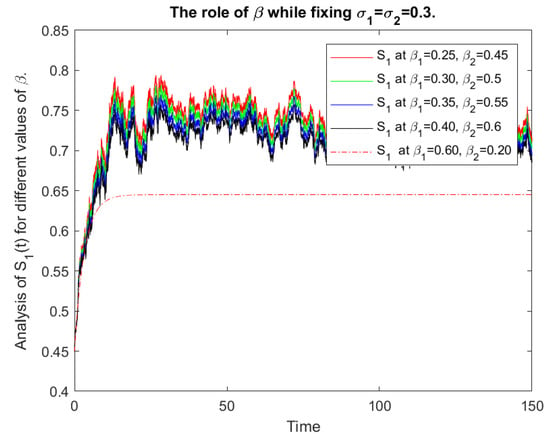
Figure 12.
Comparative analysis of .
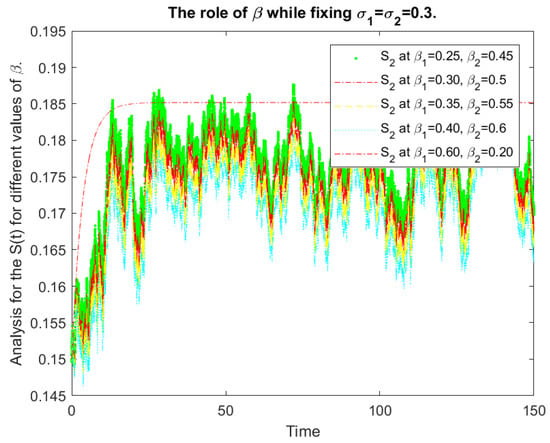
Figure 13.
Comparative analysis of .
4. Conclusions
In this article, we designed a new stochastic mathematical model for the spread of COVID-19 along with the white noise in the environment. The model was investigated mathematically in terms of the existence of the solution, the persistence of the disease, and the extinction of the disease. After the mathematical analysis of the model, we gave the numerical scheme for the computational analysis of the model, and the scheme was then tested for the available parametric and initial data in the literature. The computational results presented more realistic data for us. The numerical analysis was presented with the help of several graphs with respect to different noises , and the parameters , . These parametric values have important roles in the stochastic model (1). Our results showed that the disease dies out in the case of and persists if . In future works, we will aim to implement these criteria for different stochastic epidemic models of diseases. With the help of Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7, we observed that by increasing the values of and , an increase of the susceptible compartment occurs. Our presumed model is an model where the susceptible class is categorized into two classes: . In the future, the readers can follow the same technique to consider the epidemic models studied in [,,,] with a similar procedure as a continuation of the work and a further generalization of the study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., E.N.M. and H.K.; formal analysis, S.H., E.N.M., H.K., S.E., S.R., T.S. and N.P.; funding acquisition, N.P. and T.S.; methodology, S.H., E.N.M., H.K., S.E., S.R., T.S. and N.P.; software, S.H., H.K. and S.E.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok, Contract Number KMUTNB-64-KNOW-43.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable for this article as no datasets were generated nor analyzed during the current study.
Acknowledgments
The fourth and fifth authors would like to thank Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University. Furthermore, the authors would like to thank the reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments, which improved the quality of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W. Coronaviridae study group of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, S.A.; Jurak, G.; Starc, G. Responding to a global pandemic: Republic of Slovenia on maintaining physical activity during self-isolation. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 1546–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokudo, N.; Sugiyama, H. Call for international cooperation and collaboration to effectively tackle the COVID-19 pandemic. Global Health Med. 2020, 2, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, S.; Ali, S.; ud Din Babar, Z. Preventive measures and management of COVID-19 in pregnancy. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2020, 36, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, K.F.; Goufo, E.F.D.; Mugisha, S. Modelling intracellular delay and therapy interruptions within Ghanaian HIV population. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 401, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Mckee, M.; Mossialos, E. Developing a sustainable exit strategy for COVID-19: Health, economic and public policy implications. J. Roy. Soc. Med. 2020, 113, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, E.F.D.; Maritz, R. A note on Ebola’s outbreak and human migration dynamic. J. Hum. Ecol. 2015, 51, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djomegni, P.M.T.; Tekle, A.; Dawed, M.Y. Pre-exposure prophylaxis HIV/AIDS mathematical model with non classical isolation. Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 2020, 37, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Jarad, F.; Khan, A.; Khan, H. Nonlinear discrete fractional sum inequalities related to the theory of discrete fractional calculus with applications. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 100, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Alshehri, H.M.; Abdeljawad, T.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M.; Khan, H. Stability analysis of fractional nabla difference COVID-10 model. Res. Phys. 2021, 22, 103888. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, A.; Khan, H.; Gomez-Aguilar, J.F. Investigation of a system of nonlinear fractional order hybrid differential equations under usual boundary conditions for existence of solution. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Alqudah, M.A.; Jarad, F.; Abdeljawad, T. Semi-analytical study of pine wilt disease model with convex rate under Caputo-Febrizio fractional order derivative. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 135, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutiara, A.; Etemad, S.; Hussain, A.; Rezapour, S. The generalized U-H and U-H stability and existence analysis of a coupled hybrid system of integro-differential IVPs involving φ-Caputo fractional operators. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 95, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, A.; Etemad, S.; Rezapour, S. Topological degree theory and Caputo-Hadamard fractional boundary value problems. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 369, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Mamat, M.; Umar, A.O.; kamfa, K.; Madi, E.N. Some three-term conjugate gradient algorithms with descent condition for unconstrained optimization models. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2020, 12, 2494–2501. [Google Scholar]
- Madi, E.N.; Naim, S.; Yaafar, A.; Yaakob, A.M.; Yusoff, B. Agreement matrix based on fuzzy decision-making to rank ship Berthing criteria. Int. J. Eng. Trends Tech. 2020, 68, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad, S.; Rezapour, S.; Samei, M.E. α-ψ-contractions and solutions of a q-fractional differential inclusion with three-point boundary value conditions via computational results. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 218, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, H. A stochastic SIR epidemic model with density dependent birth rate. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2015, 330, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, H.; Kumar, S.; Rezapour, S.; Etemad, S. A theoretical study of the Caputo-Fabrizio fractional modeling for hearing loss due to Mumps virus with optimal control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 144, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Ntouyas, S.K.; Iqbal, M.Q.; Hussain, A.; Etemad, S.; Tariboon, J. An analytical survey on the solutions of the generalized double-order ϕ-integrodifferential equation. J. Funct. Spaces 2021, 6667757, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rezapour, S.; Etemad, S.; Mohammadi, H. A mathematical analysis of a system of Caputo-Fabrizio fractional differential equations for the anthrax disease model in animals. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 481, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongson, J.; Thaiprayoon, C.; Sudsutad, W. Analysis of a fractional model for HIV CD4+ T-cell with treatment under generalized Caputo fractional derivative. AIMS Math. 2021, 6, 7285–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, M.M.; Abbas, M.I.; Alzabut, J.; Kaabar, M.K.A.; Etemad, S.; Rezapour, S. Investigation of the p-Laplacian nonperiodic nonlinear boundary value problem via generalized Caputo fractional derivatives. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 68, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleanu, D.; Etemad, S.; Rezapour, S. On a fractional hybrid integro-differential equation with mixed hybrid integral boundary value conditions by using three operators. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R. XXVII. A brief account of microscopical observations made in the months of June, July and August 1827, on the particles contained in the pollen of plants; and on the general existence of active molecules in organic and inorganic bodies. Philos. Mag. 1828, 4, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doob, J.L. Stochastic Processes; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; 664p. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D. Probability with Martingales; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, L.C.G.; Williams, D. Diffusions, Markov Processes and Martingales: Volume 1, Foundations, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Burdzy, K. Brownian Motion and its Applications to Mathematical Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R. An application of the theory of probabilities to the study of a priori pathometry, Part I. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1916, 92, 204–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R.; Hudson, H.P. An application of the theory of probabilities to the study of a priori pathometry, Part II. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1917, 93, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R.; Hudson, H.P. An application of the theory of probabilities to the study of a priori pathometry, Part III. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1917, 93, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S.N.; Mak, M.K. Exact analytical solutions of the susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) epidemic model and of the SIR model with equal death and birth rates. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 236, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroger, M.; Schlickeiser, R. Analytical solution of the SIR-model for the temporal evolution of epidemics. Part A: Time-independent reproduction factor. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2020, 53, 505601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Kroger, M. Analytical solution of the SIR-model for the temporal evolution of epidemics: Part B. Semi-time case. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2021, 54, 175601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, D.; Peng, L.; Zhuge, C.; Hong, L. Rational evaluation of various epidemic models based on the COVID-19 data of China. Epidemics 2021, 37, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajbar, A.; Alqahtani, R.T.; Boumaza, M. Dynamics of an SIR-based COVID-19 model with linear incidence rate, nonlinear removal rate, and public awareness. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, S.A.; Kamruzzaman, M.M.; Alruwaili, M.; Alshammari, N.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Karime, A. Measuring and preventing COVID-19 using the SIR model and machine learning in smart health care. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8857346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, S.; Nickaeen, N.; Roointan, A.; Borhani, N.; Heidary, Z.; Javanmard, S.H.; Ghaisari, J.; Gheisari, Y. Inefficiency of SIR models in forecasting COVID-19 epidemic: A case study of Isfahan. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweilam, N.H.; Al-Mekhlafi, S.M.; Baleanu, D. A hybrid stochastic fractional order Coronavirus (2019-nCov) mathematical model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.; Jafari, H.; Banihashemi, S.; Ahmadi, M. Mathematical analysis of a stochastic model for spread of Coronavirus. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danane, J.; Allali, K.; Hammouch, Z.; Nisar, K.S. Mathematical analysis and simulation of a stochastic COVID-19 Levy jump model with isolation strategy. Res. Phys. 2021, 23, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moualkia, S.; Xu, Y. On the existence and uniqueness of solutions for multidimensional fractional stochastic differential equations with variable order. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, R.; Revathi, P.; Ren, Y. Existence of solutions for nonlinear fractional stochastic differential equations. Nonlilear Anal. 2013, 81, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Ali, J.; Riaz, M.B.; Awrejcewicz, J. Numerical analysis of a bi-modal COVID-19 sitr model. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, Y.G.; Sabir, Z.; Guirao, J.L.G. Design of a nonlinear SITR fractal model based on the dynamics of a novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). Fractals 2020, 28, 2040026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Sabir, Z.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shoaib, M.; Gupta, M.; Sanchez, Y.G. A stochastic intelligent computing with neuro-evolution heuristics for nonlinear SITR system of novel COVID-19 dynamics. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, D.J. An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 2001, 43, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, S. Survival and stationary distribution of a SIR epidemic model with stochastic perturbations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 244, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, K.M.A.; Risa, T.; Tanimoto, J. Prosocial behavior of wearing a mask during an epidemic: An evolutionary explanation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Kabir, K.M.A.; Tanimoto, J. How quarantine and social distancing policy can suppress the outbreak of novel coronavirus in developing or under poverty level countries: A mathematical and statistical analysis. Biom. Biostat. Int. J. 2021, 10, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto, J. Sociophysics Approach to Epidemics; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Madi, E.N.; Yusoff, B. Modelling perceptive-based information (words) for decision support system. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 7, 665–671. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).