Stability Analysis of SEIRS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Formulation
Equilibria of the Model
3. Stability Analysis of the Endemic Equilibria
3.1. Notations
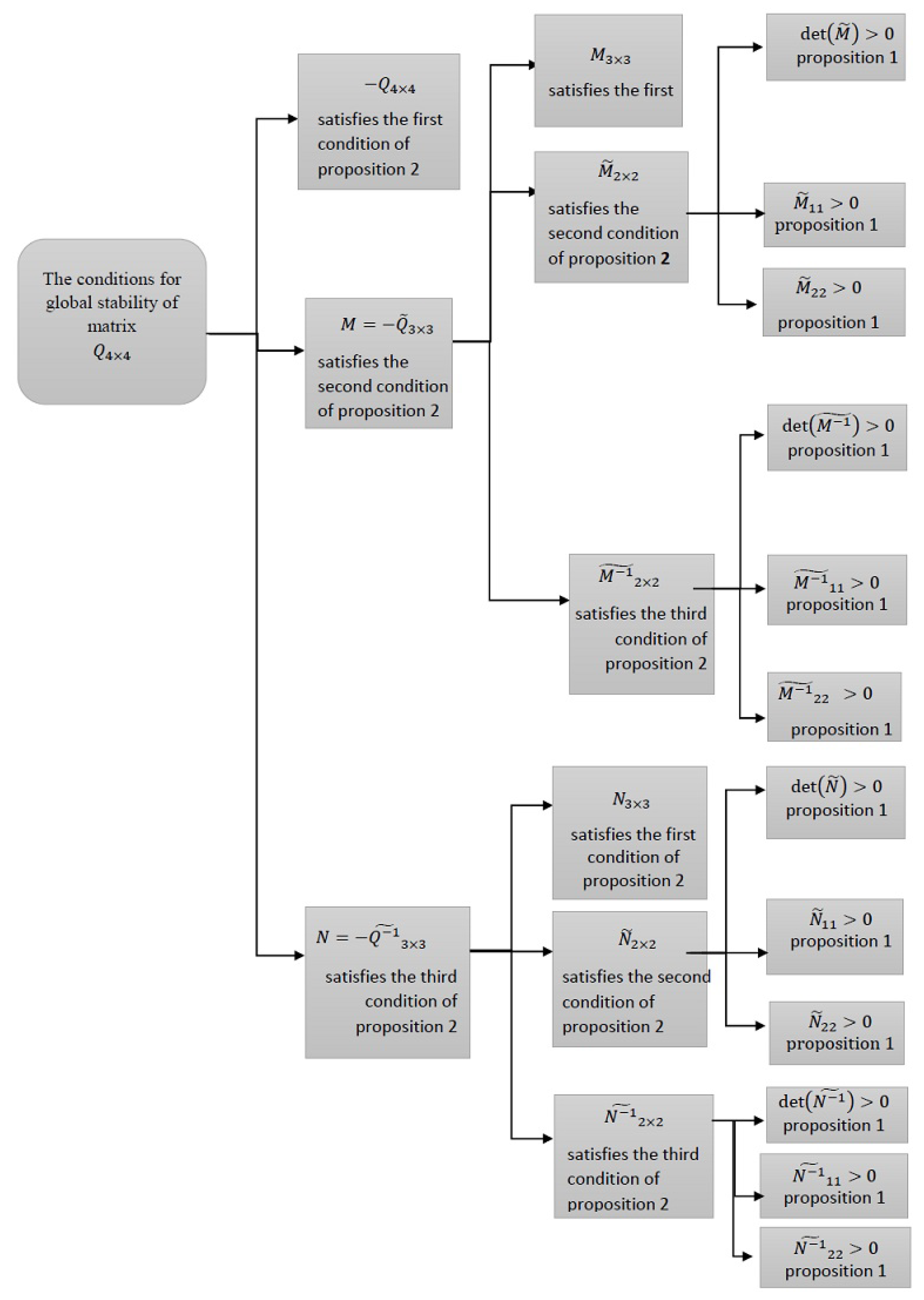
3.2. Global Stability of the Endemic Equilibrium
- (i)
- First, utilizing Proposition 1, they showed that is a Volterra-Lyapunov stable matrix.
- (ii)
- The second step was to evaluate the Volterra-Lyapunov stability of matrix They must specify the matrices and , such that
- (iii)
- Finally, they consideredand after some algebraic and matrix manipulations, it was concluded that
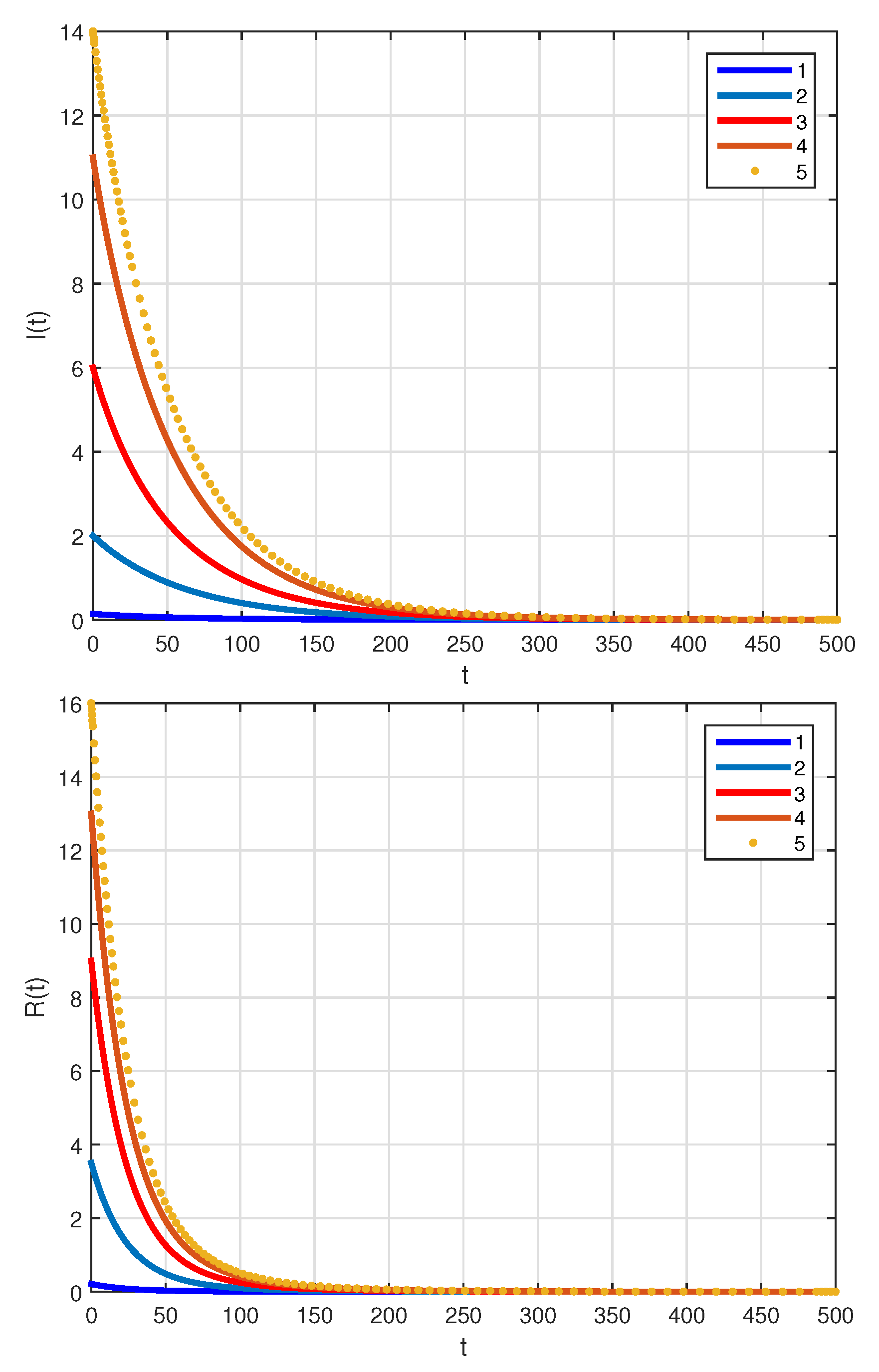
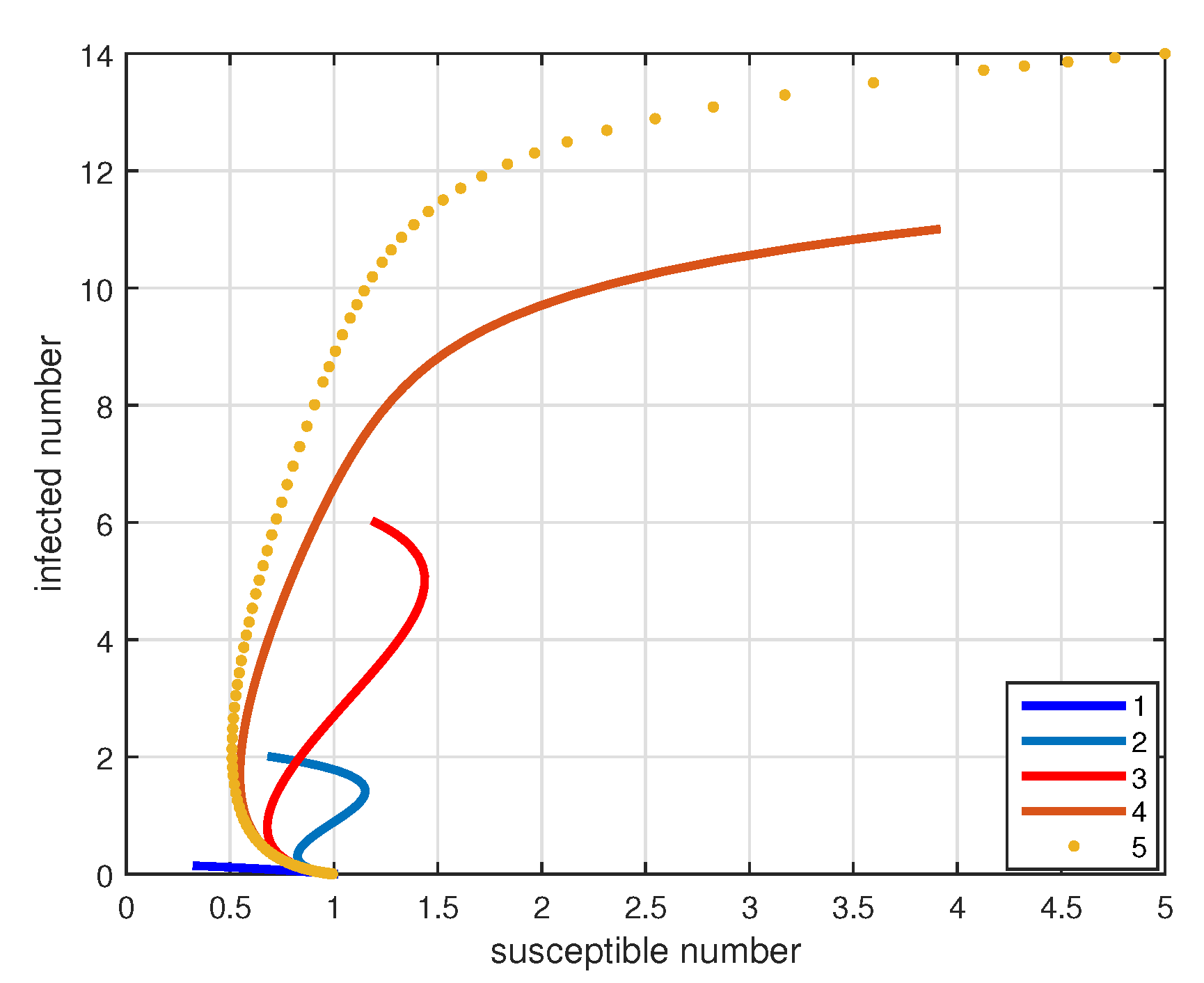
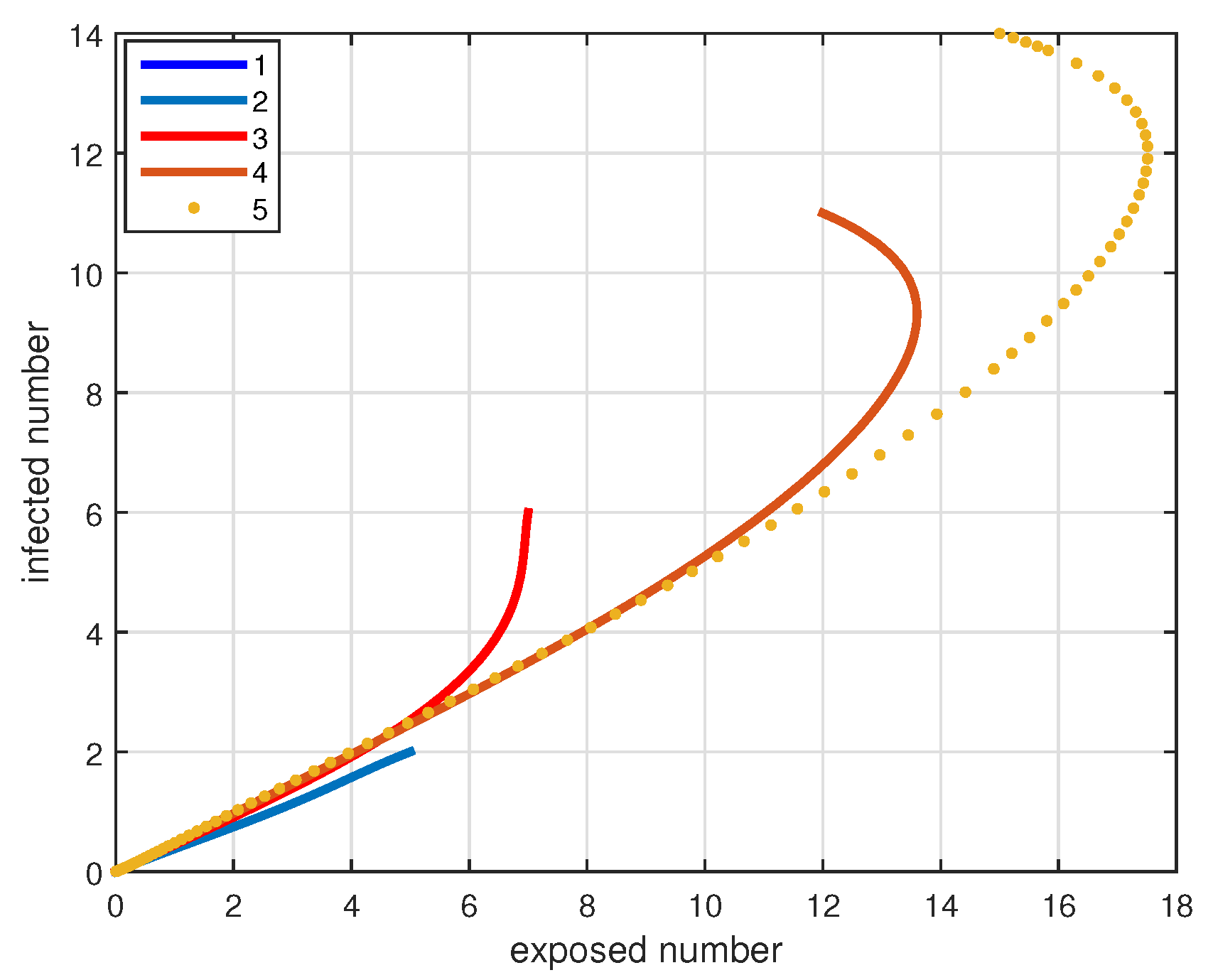
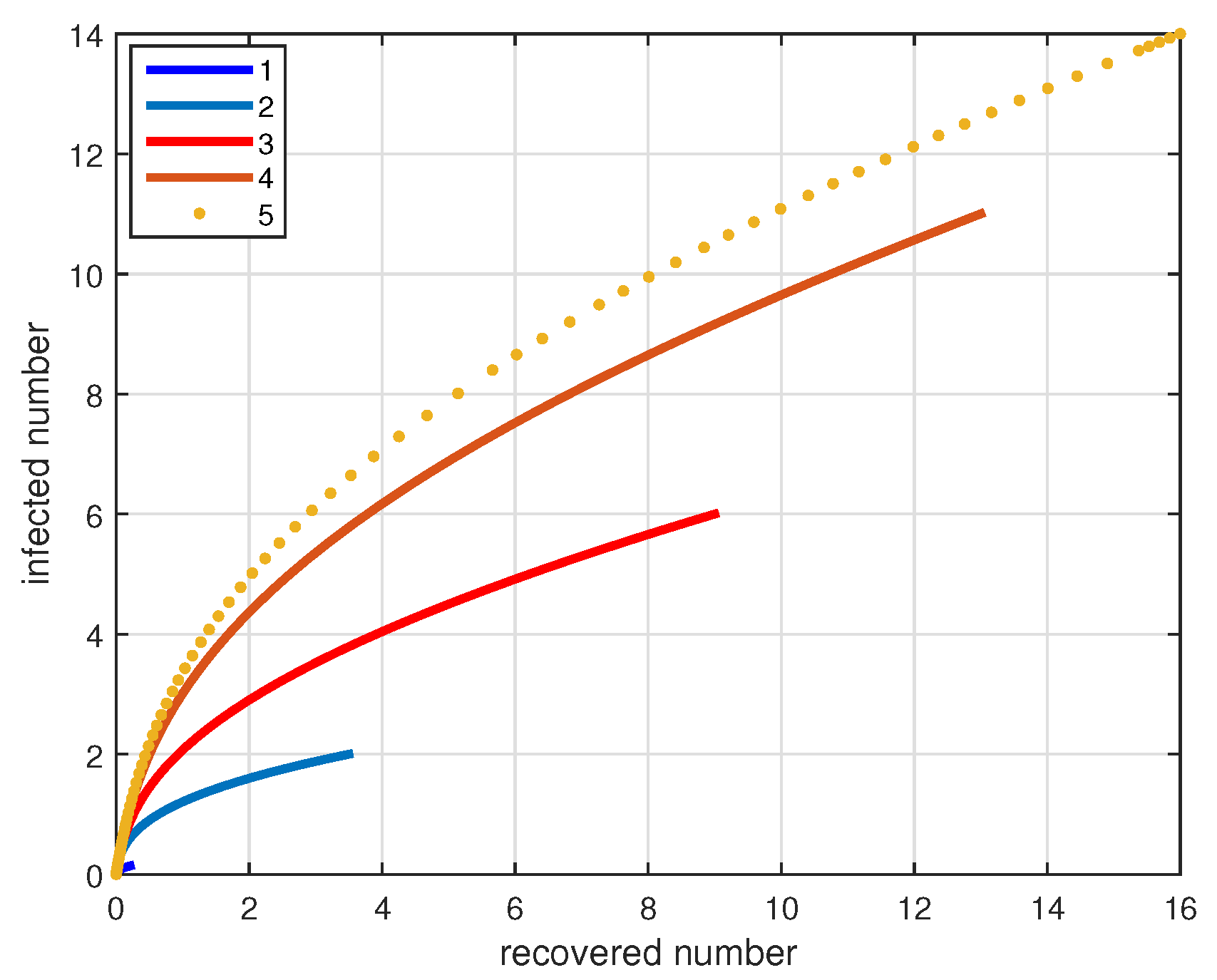
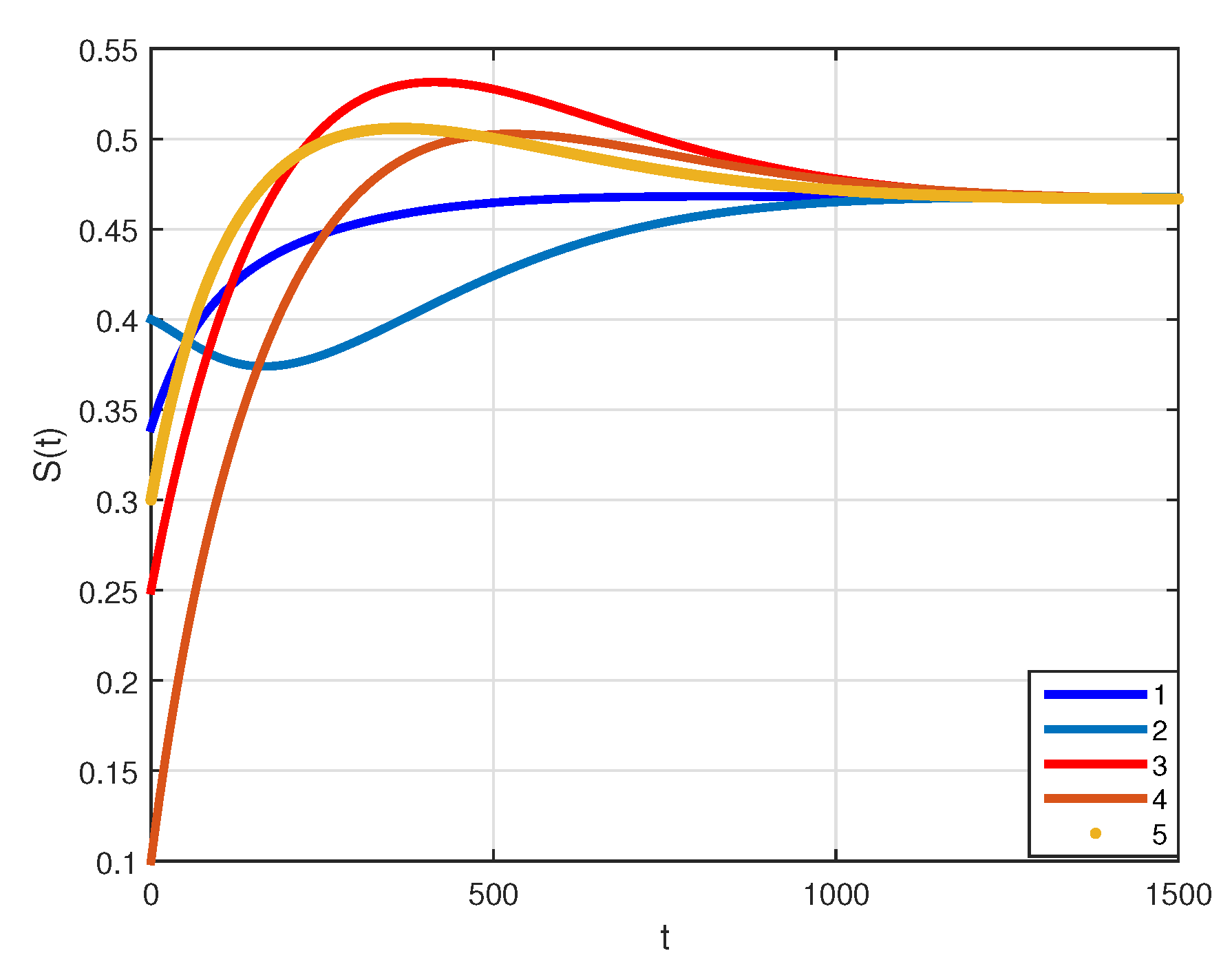
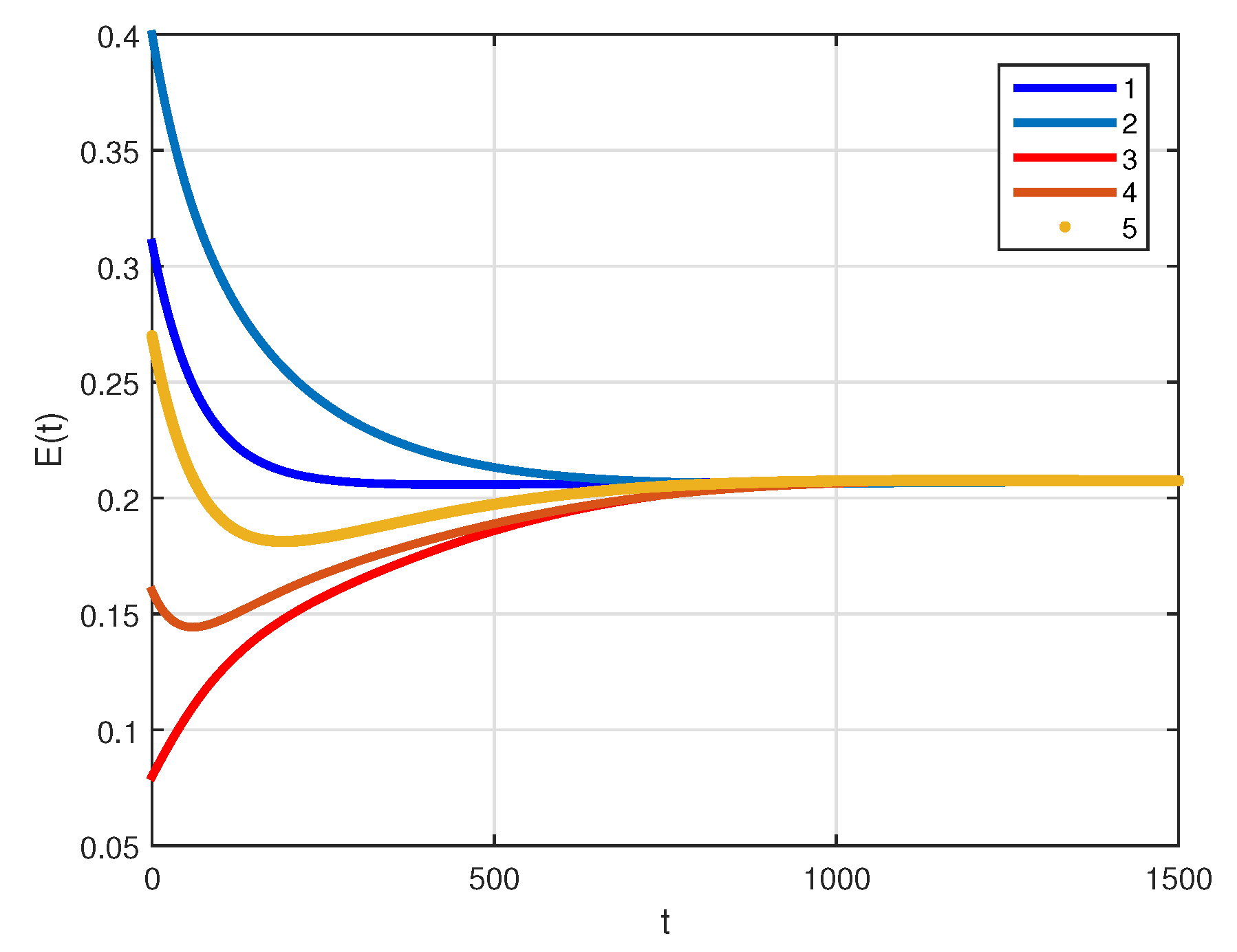
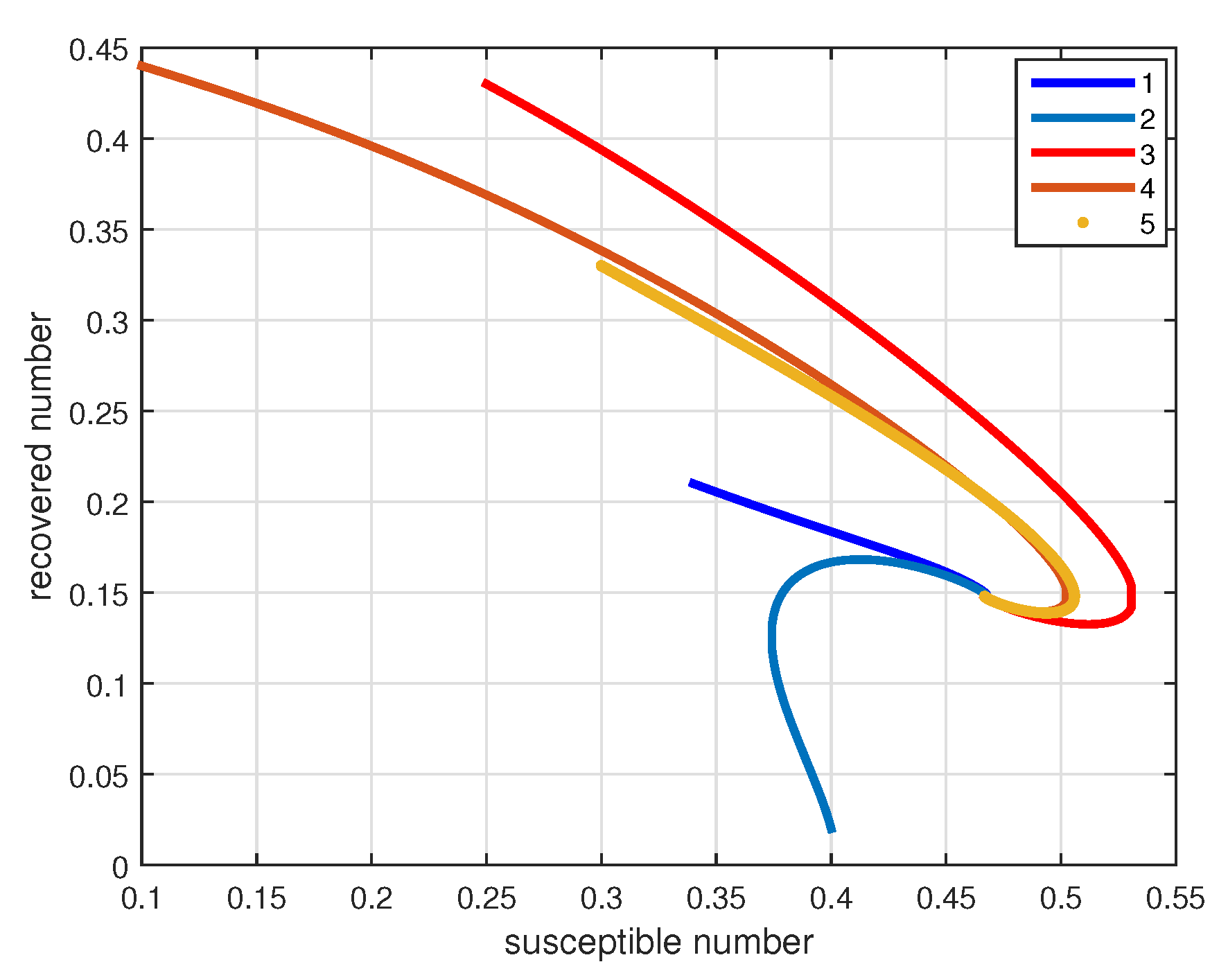
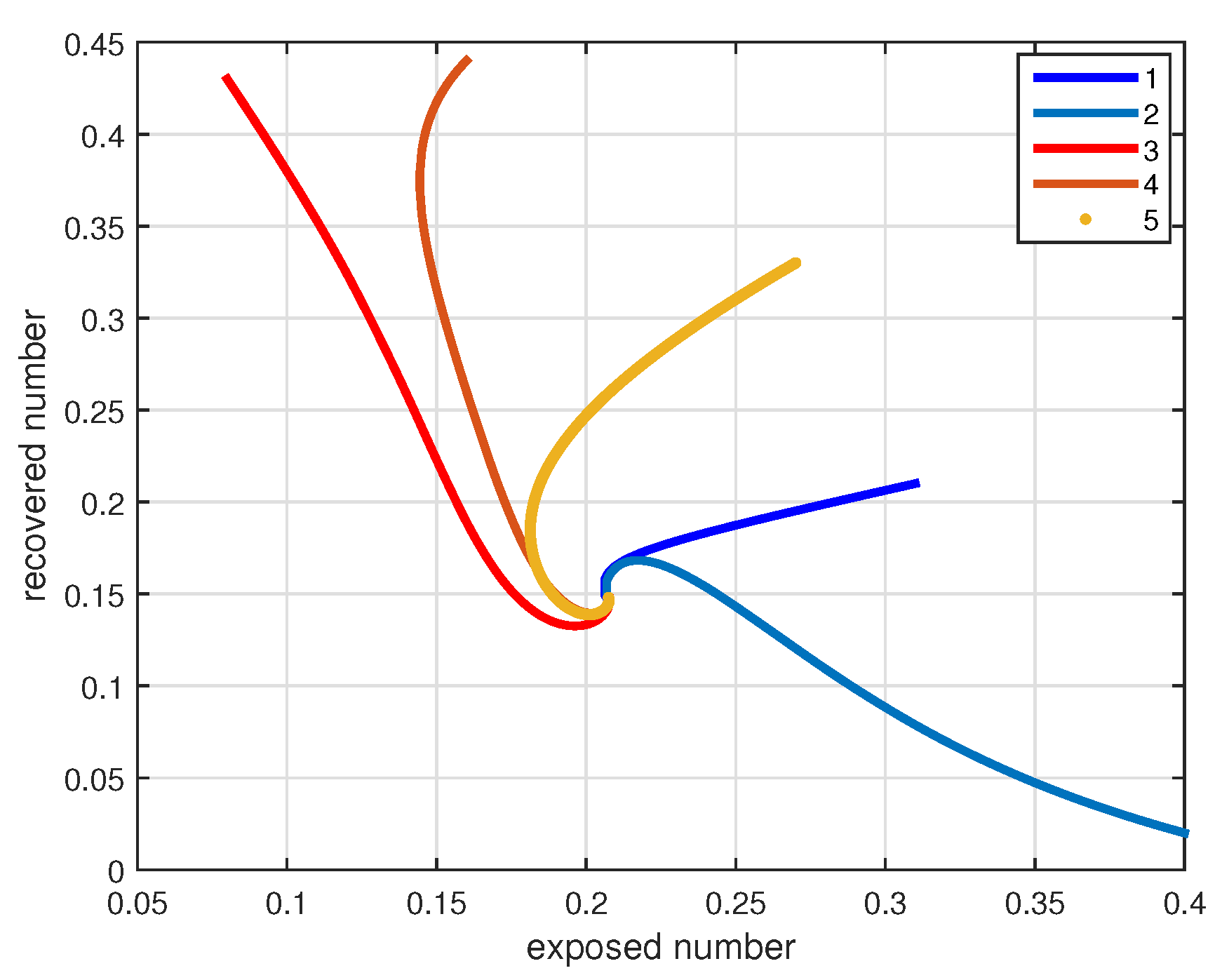
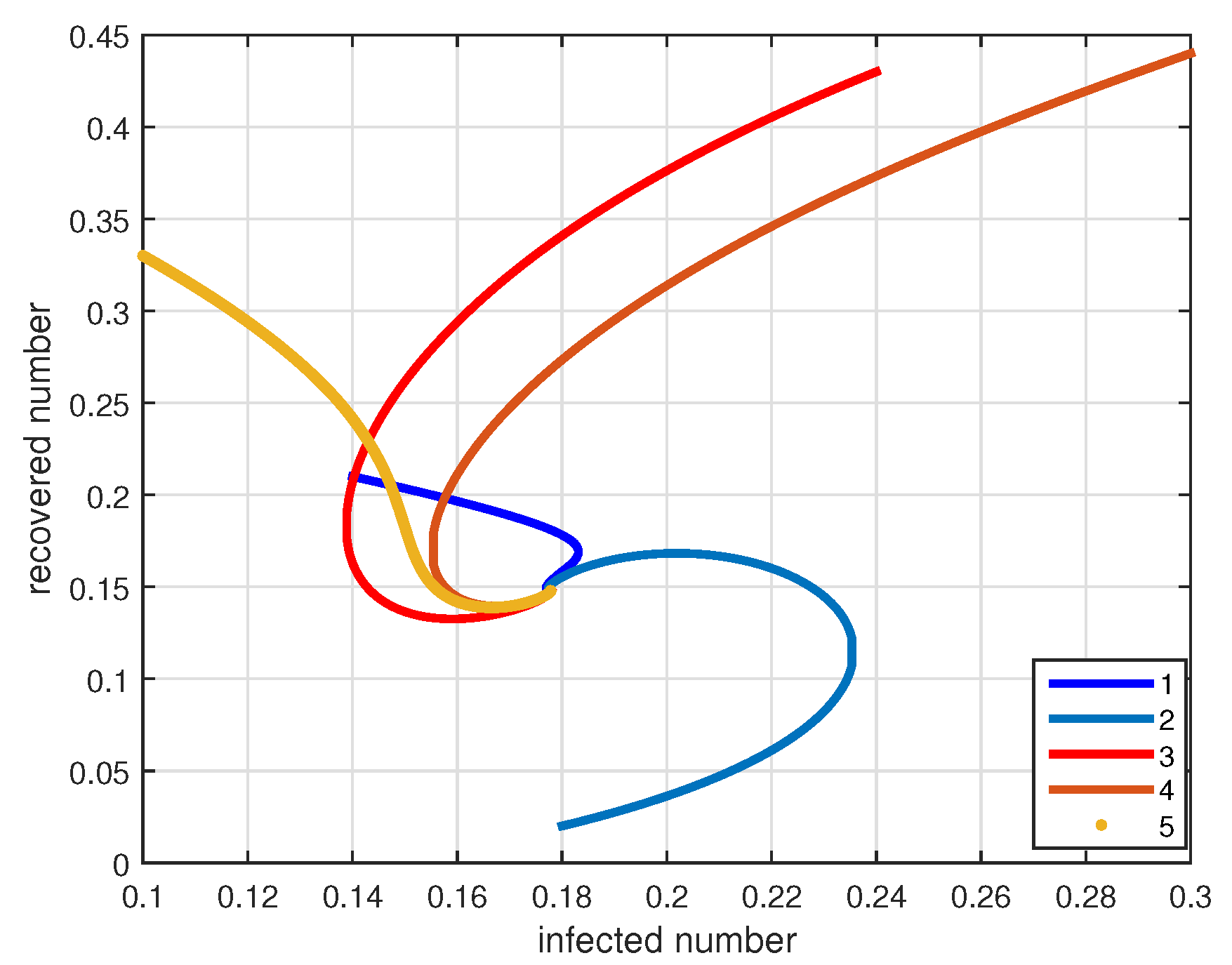
4. Numerical Simulations and Discussions
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
- and
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Kumar, A. Mathematical analysis of a delayed epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and treatment rates. J. Eng. Math. 2019, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, I.A.; Hincal, E. Global stability analysis of two-strain epidemic model with bilinear and non-monotone incidence rates. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J. Global stability of general cholera models with nonlinear incidence and removal rates. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 2464–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Xu, J. Stability preserving NSFD scheme for a multi-group SVIR epidemic model. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2017, 40, 4917–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Nie, C.; Dong, Y. Global stability for an SEI model of infectious diseases with immigration and age structure in susceptibility. Int. J. Biomath. 2019, 12, 1950042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, G. The asymptotic stability for an SIQS epidemic model with diffusion. Int. J. Biomath. 2016, 9, 1650015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eskandari, Z.; Alidousti, J. Stability and codimension 2 bifurcations of a discrete time SIR model. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 10937–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, A.A.; Alshehaiween, S.; Elaiw, A.; Alshaikh, M. A global analysis of delayed SARS-CoV-2/cancer model with immune response. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, S. A generalized cholera model and epidemic-endemic analysis. J. Biol. Dyn. 2012, 6, 568–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Ma, W.; Ruan, S. Analysis of SIR epidemic models with nonlinear incidence rate and treatment. Math. Biosci. 2012, 238, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hethcote, H.W.; van den Dreissche, P. Some epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence rate. J. Math. Biol. 1991, 29, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.Y.; Muldowney, J.S.; van den Dreissche, P. Global stability of the SEIRS model in epidemiology. Can. Appl. Math. Quart. 1999, 7, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, M.J.; Rohani, P.; Grenfell, B.T. Seasonally forced disease dynamics explored as switching between attractors. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2001, 148, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Ruan, S. Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 2007, 208, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.M.; Levin, S.A.; Iwasa, Y. Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 1986, 23, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohith, G.; Devika, K.B. Dynamics and control of COVID-19 pandemic with nonlinear incidence rates. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentaleb, D.; Amine, S. Lyapunov function and global stability for a two-strain SEIR model with bilinear and nonmonotone incidence. Int. J. Biomath. 2019, 12, 1950021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zou, S. Global dynamics of an epidemic model with relapse and nonlinear incidence. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2019, 42, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, J.; Georgescu, P. Multigroup deterministic and stochastic SEIRI epidemic models with nonlinear incidence rates and distributed delays: A stability analysis. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2017, 40, 6254–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. On global stability analysis for SEIRS models in epidemiology with nonlinear incidence rate function. Int. J. Biomath. 2017, 10, 1750019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Pal, A.K.; Kumari, S.; Roy, P. Dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and treatment rates. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 2351–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Ke, Q.; Li, K. Dynamic stability of an SIVS epidemic model with imperfect vaccination on scale-free networks and its control strategy. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 7092–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Wang, J. Global stability analysis of epidemiological models based on Volterra-Lyapunov stable matrices. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2012, 45, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaei, M.R.; Javidan, R.; Shayegh Kargar, N.; Saberi Nik, H. On the global stability of an epidemic model of computer viruses. Theory Biosci. 2017, 136, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumnezhad, M.; Rajabi, M.; Chapnevis, A.; Dorofeev, A.; Shateyi, S.; Karga, N.S.; Saberi Nik, H. An approach for the global stability of mathematical model of an infectious disease. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, M.S.; Kargar, N.S. The Volterra-Lyapunov matrix theory for global stability analysis of a model of the HIV/AIDS. Int. J. Biomath. 2017, 10, 1750002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P.; Wang, J. Global stability for cholera epidemic models. Math. Biosci. 2011, 232, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driessche, V.D.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, G.W. Three types of matrix stability. Linear Algebra Appl. 1978, 20, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinaldi, F. Global stability results for epidemic models with latent period. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 1990, 7, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redheffer, R. Volterra multipliers I. SIAM J. Algebraic Discret. Methods 1985, 6, 592–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redheffer, R. Volterra multipliers II. SIAM J. Algebraic Discret. Methods 1985, 6, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Rate of conversion of exposed population to infectious | |
| Rate of conversion of infectious to recovered | |
| Rate of conversion of immunity to recovered | |
| The birth (and death) rate | |
| The nonlinear transmission rate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, P.; Shateyi, S. Stability Analysis of SEIRS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate Function. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9212644
Shao P, Shateyi S. Stability Analysis of SEIRS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate Function. Mathematics. 2021; 9(21):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9212644
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Pengcheng, and Stanford Shateyi. 2021. "Stability Analysis of SEIRS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate Function" Mathematics 9, no. 21: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9212644
APA StyleShao, P., & Shateyi, S. (2021). Stability Analysis of SEIRS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate Function. Mathematics, 9(21), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9212644






