LAE-GAN-Based Face Image Restoration for Low-Light Age Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- It is the first study on age estimation considering low light;
- Without separately applying pre-processing to low-light facial images, images are enhanced using LAE-GAN, which is proposed in this study;
- In LAE-GAN, identity information of input data was preserved by removing an input random noise vector used in a conventional conditional GAN and adding an L2 loss function in the generator. Furthermore, high frequency information of the input image delivered through a skip-connection using a leaky rectified linear unit (ReLU) to the 6th and 7th decoder blocks of the generator was reinforced, and the ReLU was used in the 4th convolution layer of the discriminator;
- Through [20], the trained LAE-GAN and CNN for age estimation are disclosed to be fairly evaluated by other researchers in terms of performance.
2. Related Works
3. Proposed Method
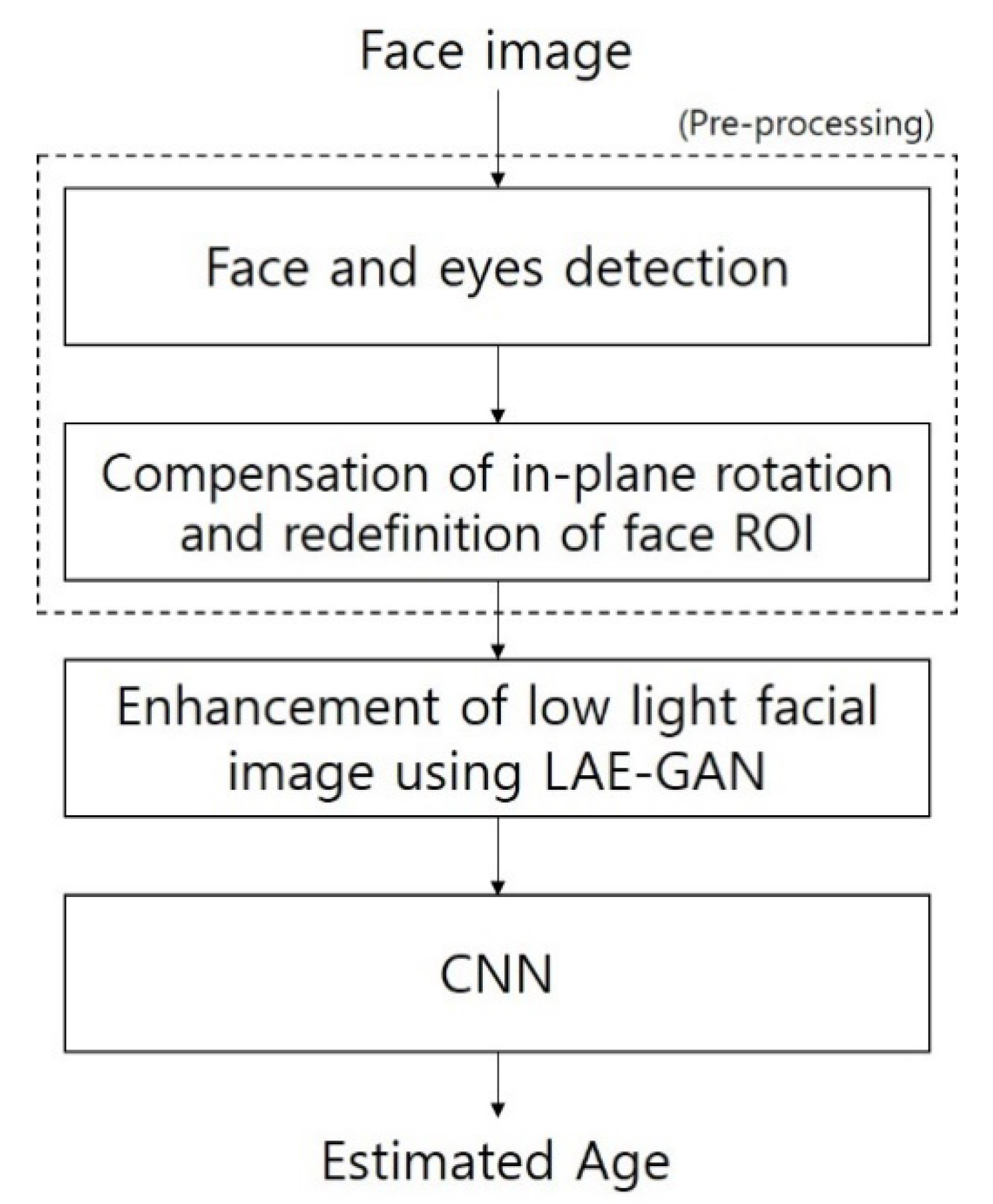
3.1. Overview of the Proposed Method
3.2. Pre-Processing
3.3. Enhancement of Low-Illuminated Face Image by LAE-GAN
3.3.1. Generator
3.3.2. Discriminator
3.4. Difference of Conditional GAN
- A random noise vector was used in the conventional conditional GAN for inducing image transformation, but it has been removed in this study as it has a stronger negative effect than noise in a 1:1 mapping structure between input data and target data for low-illumination image compensation;
- L2 loss function was used in the generator to preserve the identifiable information of the input data;
- Leaky ReLU was used in the 6th and 7th decoder blocks of the generator to strengthen the high frequency information of the input image delivered through skip connections;
- ReLU was used in the 4th convolution layer of the discriminator.
3.5. Age Estimation
3.5.1. VGG
3.5.2. DEX
3.5.3. ResNet
3.5.4. Age-Net
3.5.5. Inception with Random Forest
4. Experimental Results
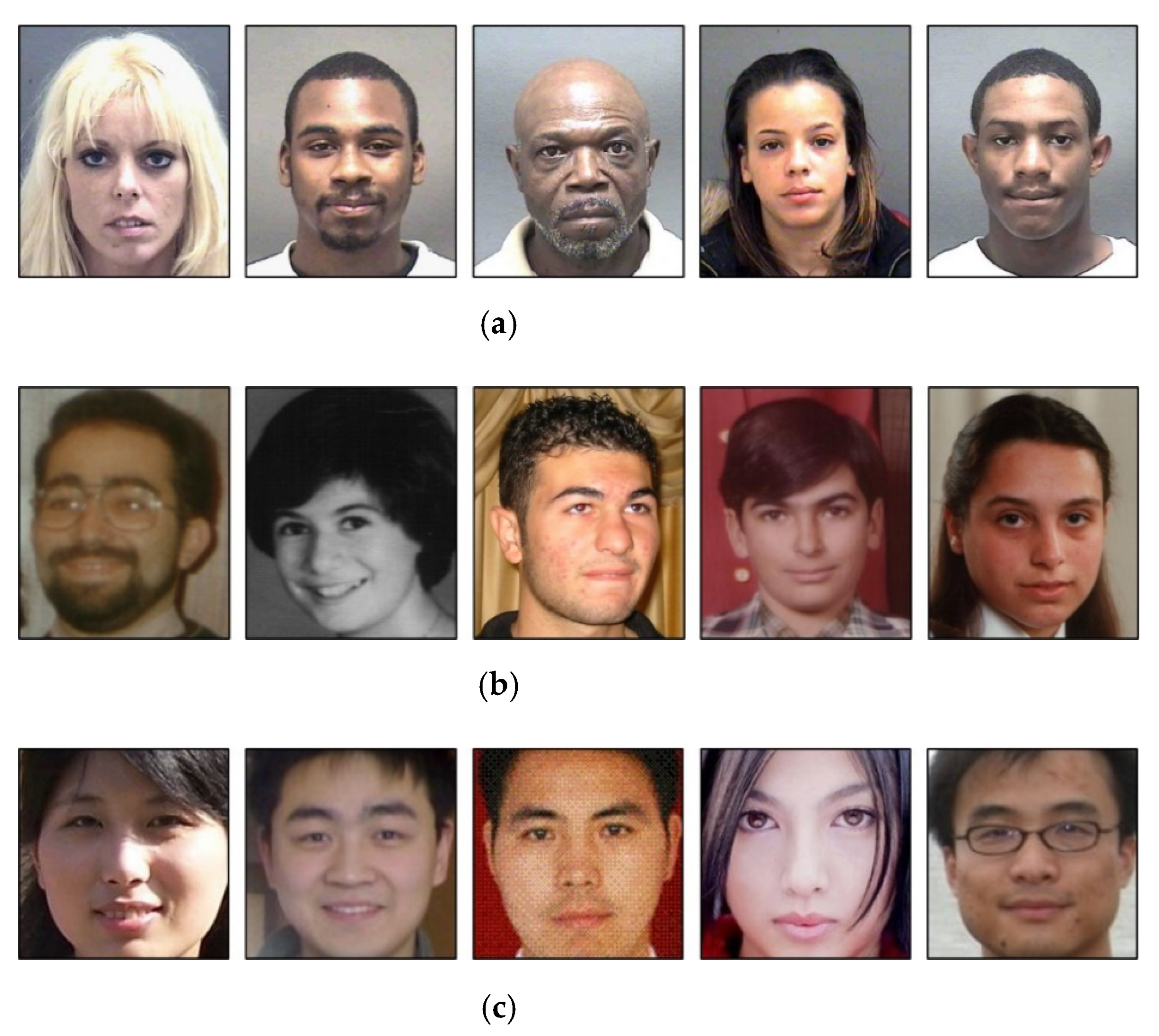
4.1. Experimental Data and Environment
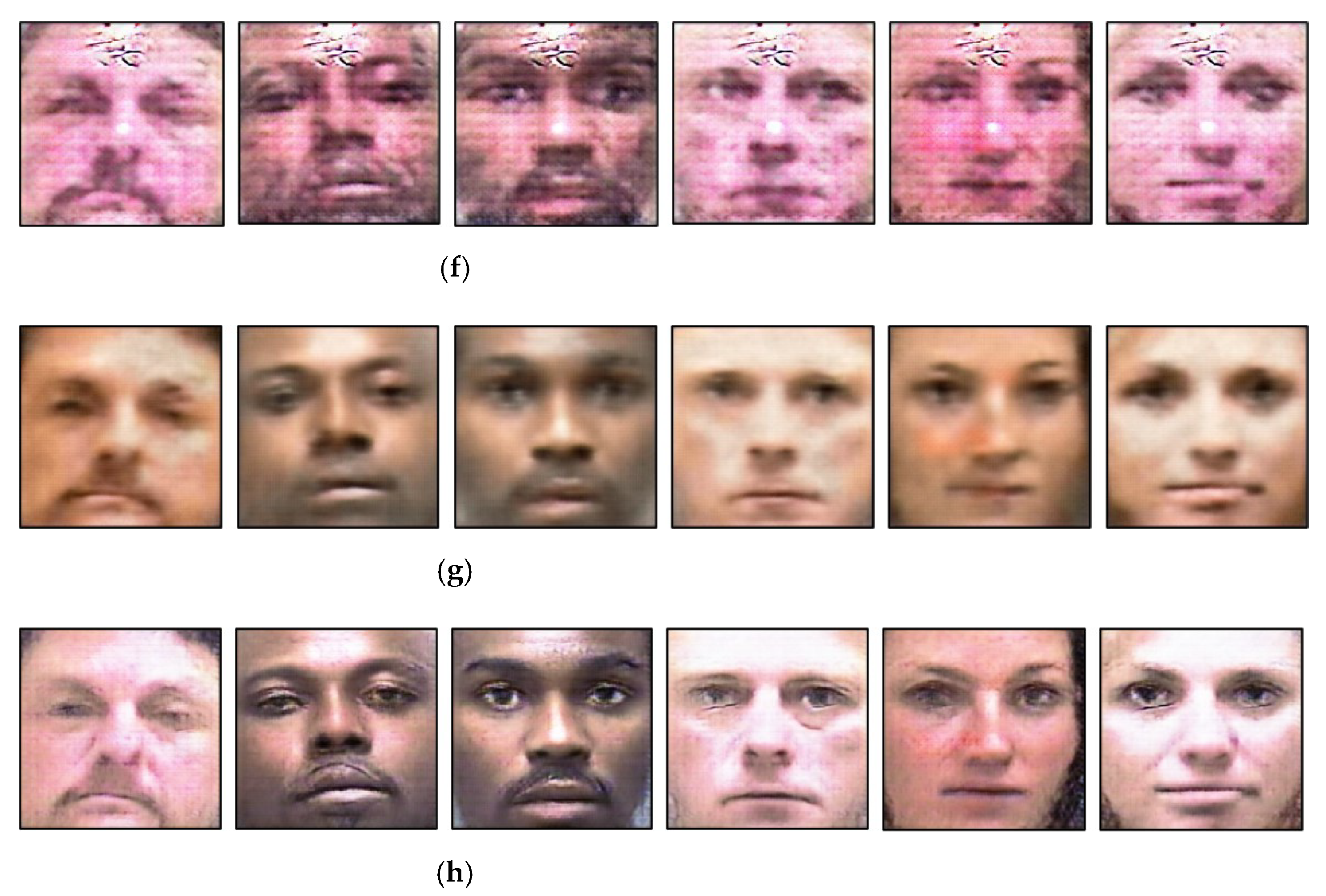
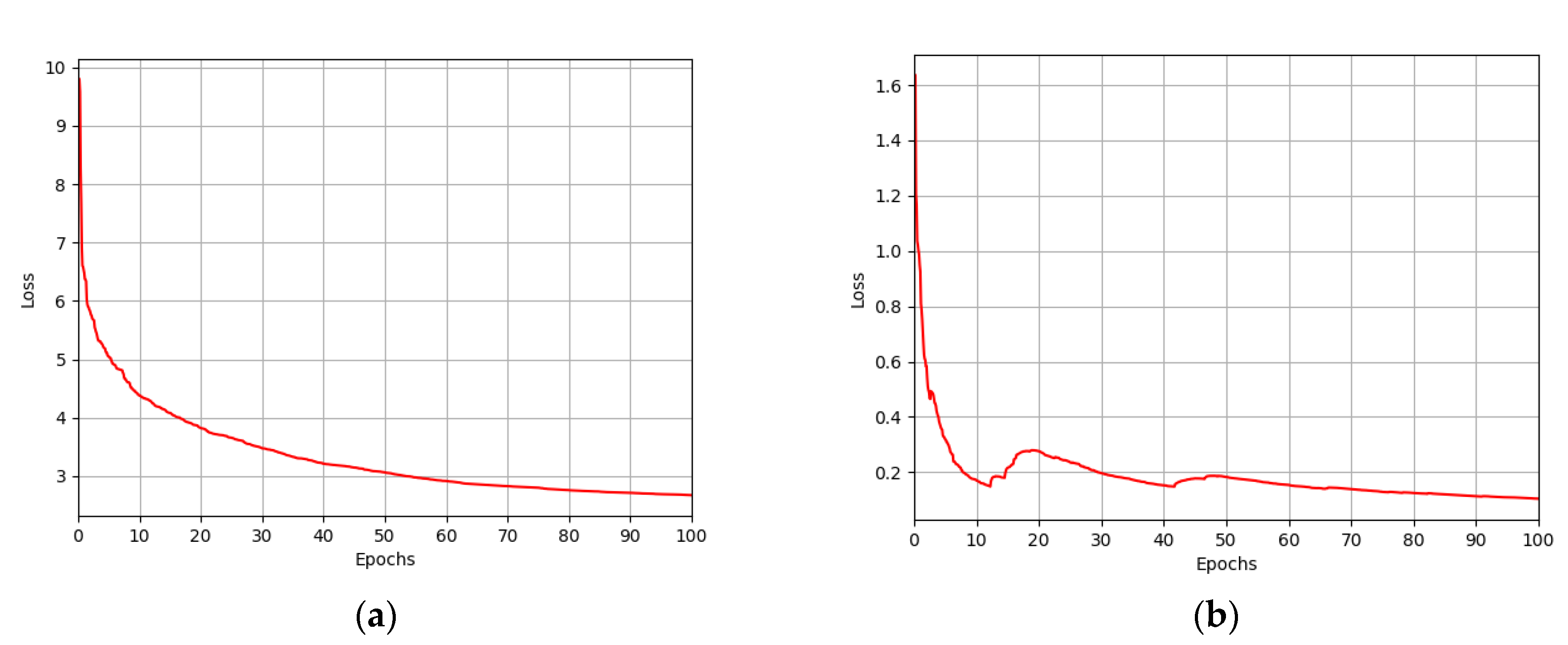
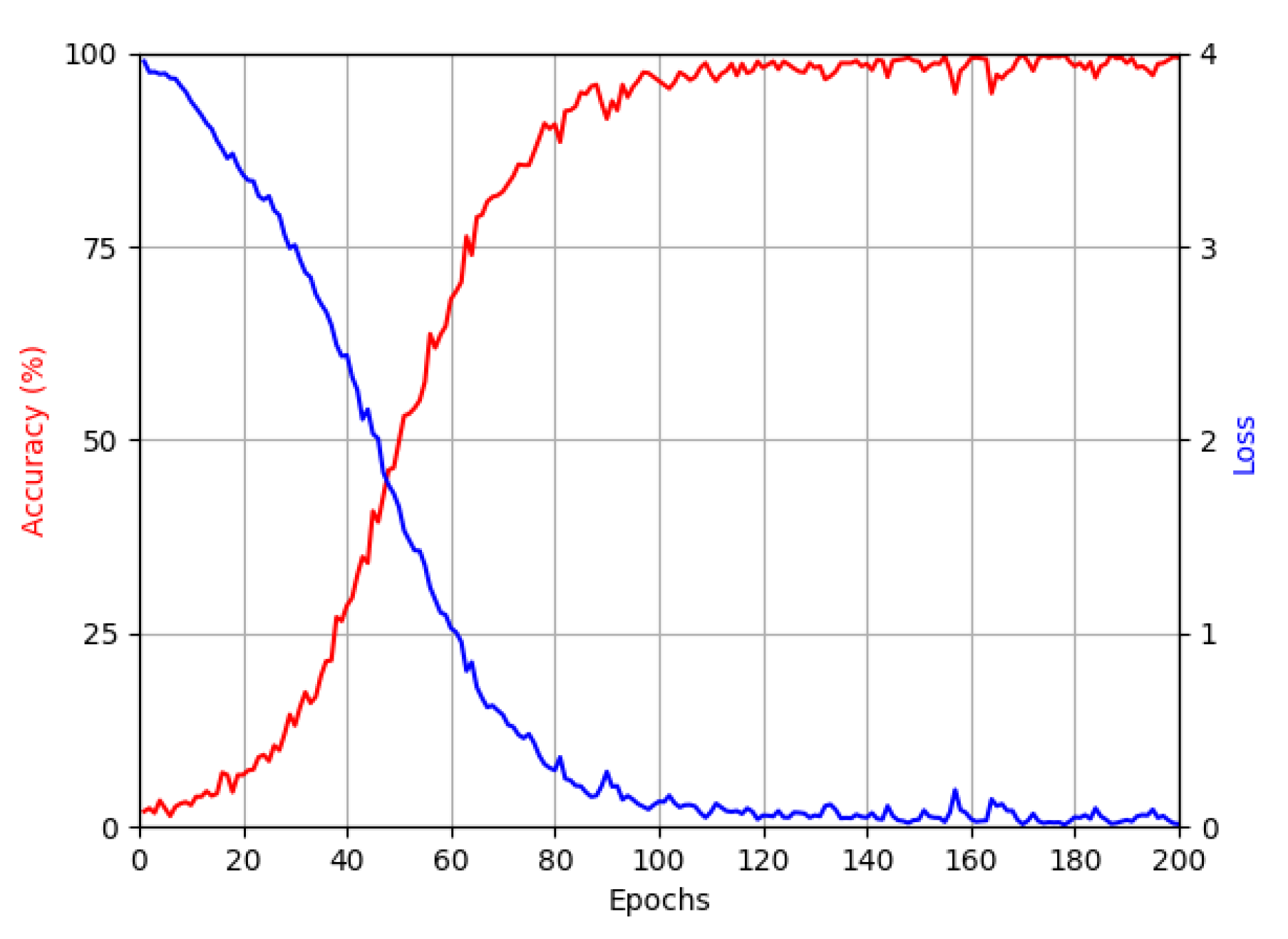
4.2. Training of LAE-GAN for Image Enhancement of Low Illumination and CNN for Age Estimation
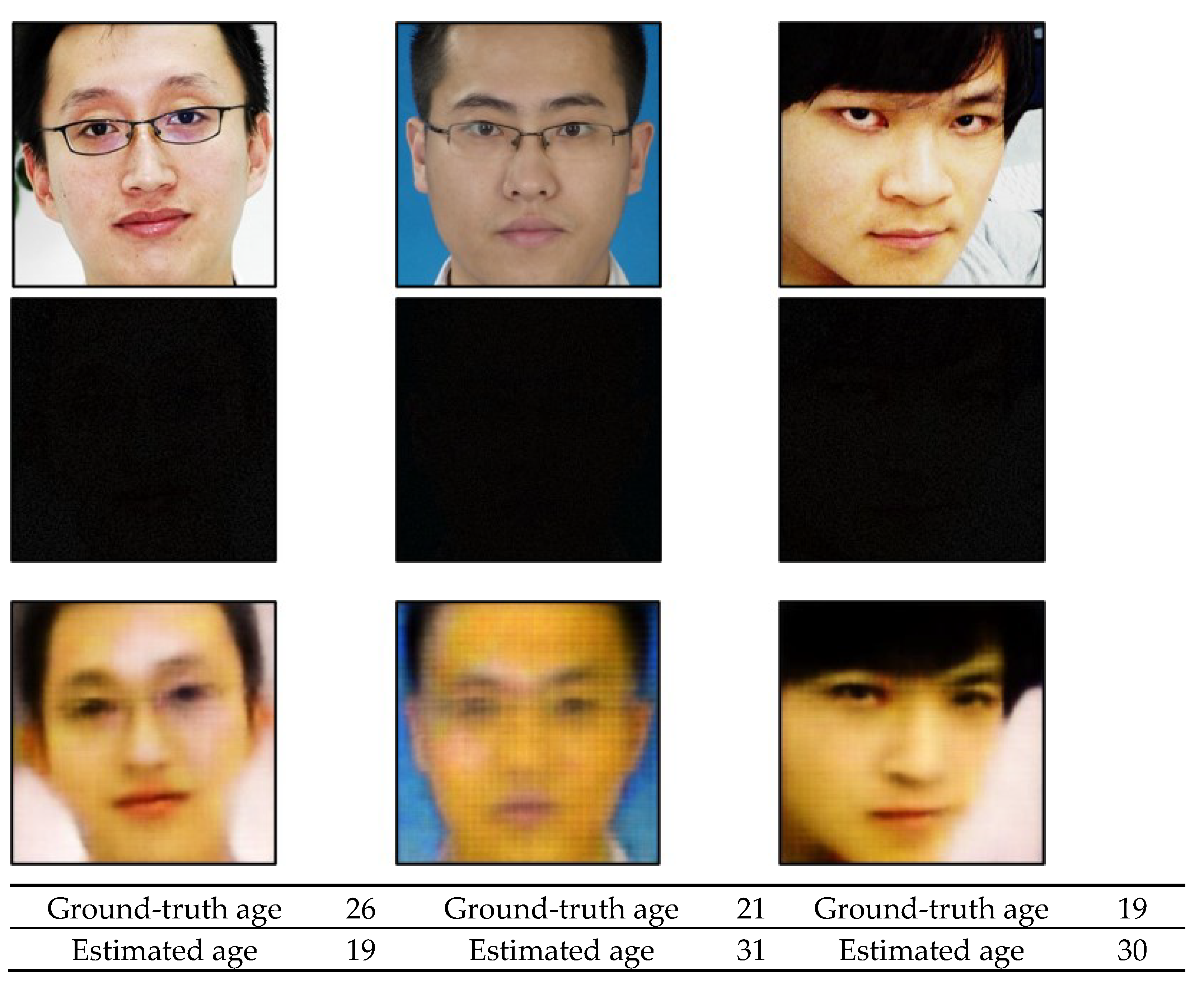
4.3. Testing with the MORPH Database
4.4. Testing with the AFAD Database
4.5. Testing with the FG-NET Database
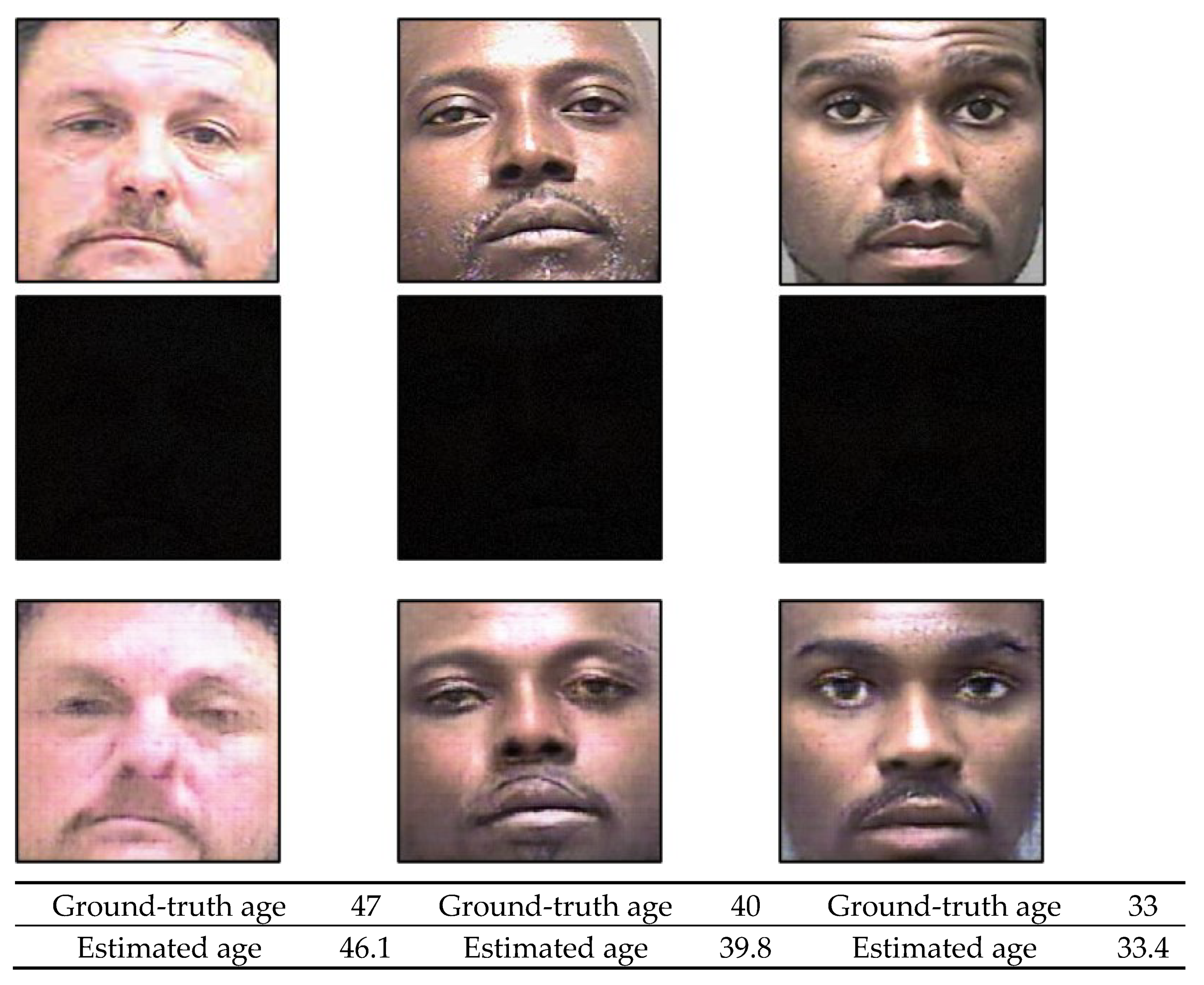
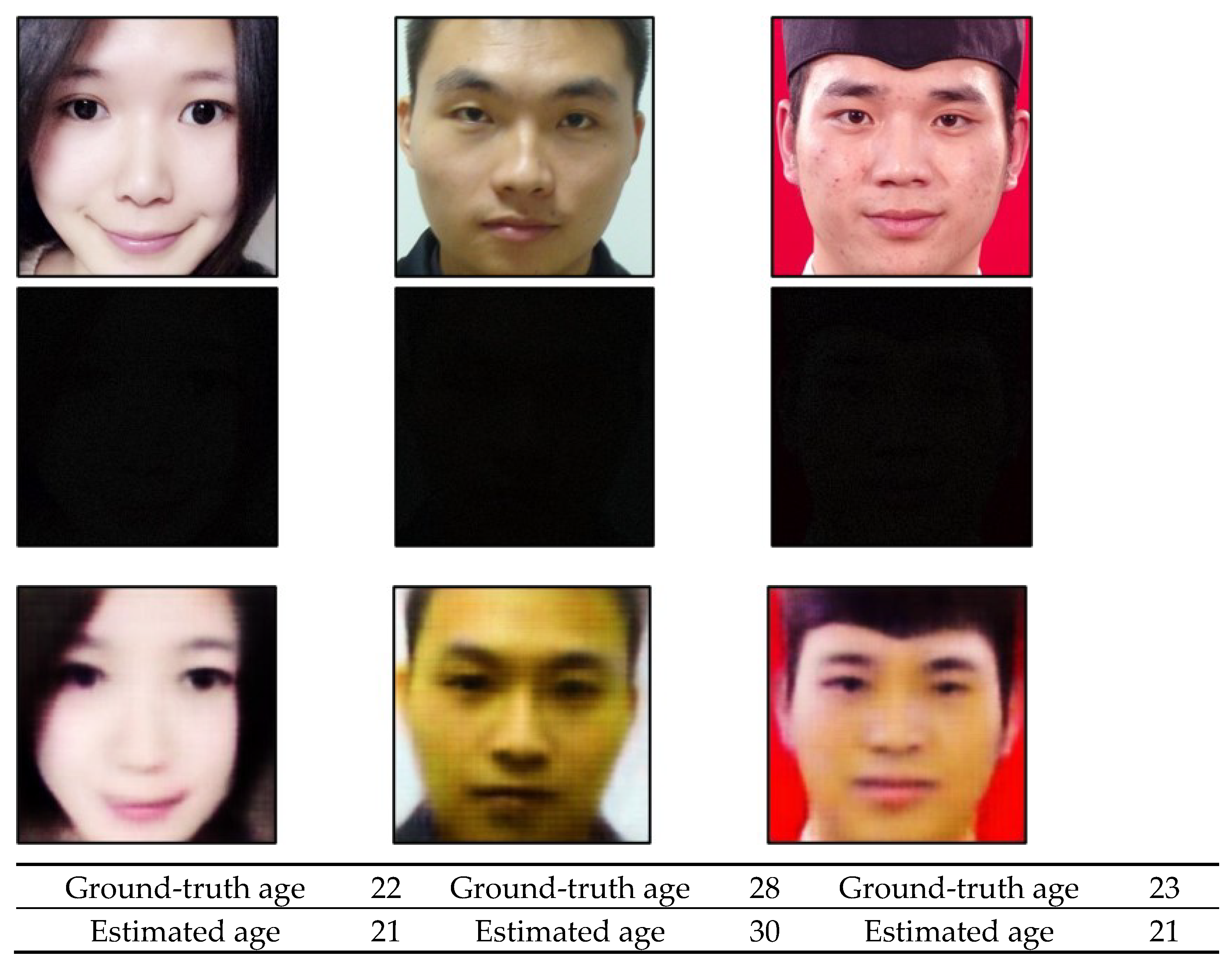
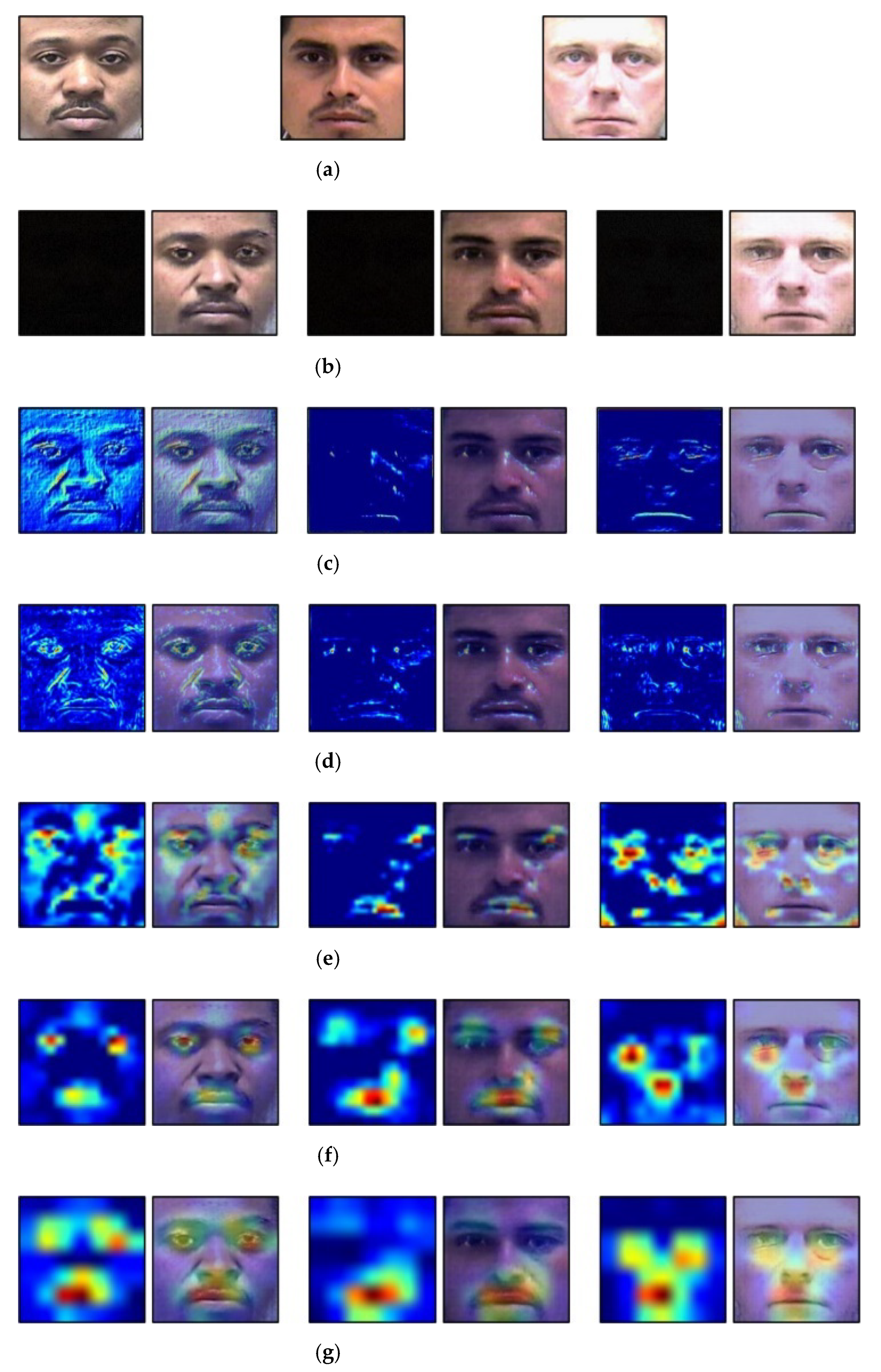
4.6. Discusion and Analysis of Grad CAM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, X.; Yap, M.H.; Palmer, I. Face recognition in the presence of expressions. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2012, 5, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyers, E.; Wolf, L. Using biologically inspired features for face processing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 76, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Gong, S.; McOwan, P.W. Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comp. 2009, 27, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ricanek, K.; Chen, C.; Chang, Y. Gender classification from infants to seniors. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications, Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 27–29 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alarifi, J.S.; Goyal, M.; Davison, A.K.; Dancey, D.; Khan, R.; Yap, M.H. Facial skin classification using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–7 July 2017; pp. 479–485. [Google Scholar]
- Punyani, P.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, A. Neural networks for facial age estimation: A survey on recent advances. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 3299–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Toygar, Ö. On the use of DAG-CNN architecture for age estimation with multi-stage features fusion. Neurocomputing 2019, 329, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cootes, T.F.; Taylor, C.J.; Cooper, D.H.; Graham, J. Active shape models-their training and application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1995, 61, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Smith-Miles, K. Automatic age estimation based on facial aging patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabor, D. Theory of communication. Part 1: The analysis of information. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. Part. III Radio. Commun. Eng. 1946, 93, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.A. The statistical utilization of multiple measurements. Ann. Eugen. 1938, 8, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, A.; Nabiyev, V.V. Automatic age classification with LBP. In Proceedings of the 23th International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences, Istanbul, Turkey, 27–29 October 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, K.R.; Kim, J. Age estimation using a hierarchical classifier based on global and local facial features. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 1262–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, M.H.; Zhang, B.; Kagawa, K.; Loffeld, O. Low-light image enhancement for multiaperture and multitap systems. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, K.P.; Reddy, V.K.; Ramasangu, H. Enhancement technique for improving the reliability of disparity map under low light condition. Procedia Technol. 2014, 14, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, M.; Yanyan, W.; Jiao, L.; Hongan, L.; Zhanli, L. Research on the improved Retinex algorithm for low illumination image enhancement. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2018, 39, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Yuan, X.; Gao, Z. An experiment-based review of low-light image enhancement methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87884–87917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAE-GAN with Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/nsh6473/LAE-GAN (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Chao, W.-L.; Liu, J.-Z.; Ding, J.-J. Facial age estimation based on label-sensitive learning and age-oriented regression. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, R.; Kambhamettu, C. Deeply-learned feature for age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2015; pp. 534–541. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, G.; Hassner, T. Age and gender classification using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 11–12 June 2015; pp. 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- RMalli, C.; Aygun, M.; Ekenel, H.K. Apparent age estimation using ensemble of deep learning models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-C.; Kumar, A.; Ranjan, R.; Patel, V.M.; Alavi, A.; Chellappa, R. A cascaded convolutional neural network for age estimation of unconstrained faces. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems, Niagara Falls, NY, USA, 6–9 September 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Dong, M.; Le, J.; Rao, M. Using ranking-CNN for age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5183–5192. [Google Scholar]
- Huerta, I.; Fernández, C.; Segura, C.; Hernando, J.; Prati, A. A deep analysis on age estimation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 68, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Kan, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Han, H.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Agenet: Deeply learned regressor and classifier for robust apparent age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Z.; Yang, X.; Xing, C.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Geng, X. Deep age distribution learning for apparent age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, J.; Zhao, T. Video system for human attribute analysis using compact convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 584–588. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Hua, G. Ordinal regression with multiple output CNN for age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4920–4928. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Hong, R.; Yan, S. Facial age estimation with age difference. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xing, J.; Hu, W.; Maybank, S.J. D2C: Deep cumulatively and comparatively learning for human age estimation. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 66, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qawaqneh, Z.; Mallouh, A.A.; Barkana, B.D. Age and gender classification from speech and face images by jointly fine-tuned deep neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 85, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; Cucurull, G.; Gonfaus, J.M.; Roca, F.X.; Gonzàlez, J. Age and gender recognition in the wild with deep attention. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 72, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Li, K.; Yang, C.; Li, K. A hybrid deep learning CNN–ELM for age and gender classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Tan, Z.; Lei, Z.; Guo, G.; Li, S.Z. Auxiliary demographic information assisted age estimation with cascaded structure. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghbani, S.; Boujneh, N.; Bouhlel, M.S. Age estimation using deep learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 68, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Kwak, Y.; Kim, Y.; Choi, C.; Kim, J. Deep facial age estimation using conditional multitask learning with weak label expansion. IEEE Signal. Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattani, A.; Reddy, N.; Derakhshani, R. Convolutional neural network for age classification from smart-phone based ocular images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics, Denver, CO, USA, 1–4 October 2017; pp. 756–761. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, S.; Toygar, Ö. Multi-stage age estimation using two level fusions of handcrafted and learned features on facial images. IET Biom. 2018, 8, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, V.P.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, M.N. A novel approach for face recognition using DCT coefficients re-scaling for illumination normalization. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communications, Guwahati, India, 18–21 December 2007; pp. 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Ward, R.K. Adaptive region-based image enhancement method for robust face recognition under variable illumination conditions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, V.; Farheen, N.; Manikantan, K.; Ramachandran, S. Face recognition using threshold based DWT feature extraction and selective illumination enhancement technique. Procedia Technol. 2012, 6, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, H.A.; Kakadiaris, I.A. SeLENet: A semi-supervised low light face enhancement method for mobile face unlock. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, H.H. Face recognition under low illumination via deep feature reconstruction network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 2161–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Quan, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Ling, H.; Xu, Y. Recurrent exposure generation for low-light face detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.10963v1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kwon, D.; Kwon, J. Low-lightgan: Low-light enhancement via advanced generative adversarial network with task-driven training. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 2811–2815. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatov, A.; Kobyshev, N.; Timofte, R.; Vanhoey, K.; Gool, L.V. Wespe: Weakly supervised photo enhancer for digital cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 691–700. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y. From night to day: GANs based low quality image enhancement. Neural Process. Lett. 2019, 50, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, H.; Liao, S.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.W.; Jain, A.K. Nighttime face recognition at long distance: Cross-distance and cross-spectral matching. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Daejeon, Korea, 5–9 November 2012; pp. 708–721. [Google Scholar]
- Baradarani, A.; Wu, Q.M.J.; Ahmadi, M. An efficient illumination invariant face recognition framework via illumination enhancement and DD-DTCWT filtering. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K.; Lee, S.W. Nighttime face recognition at large standoff: Cross-distance and cross-spectral matching. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 3750–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, G.; Yan, W.; Tao, W.; Xu, G.; Diao, D.; Green, P. Nighttime driving safety improvement via image enhancement for driver face detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 45625–45634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Baek, N.R.; Kim, M.C.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.R. Face detection in nighttime images using visible-light camera sensors with two-step faster region-based convolutional neural network. Sensors 2018, 18, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Wang, J.-G.; Yau, W.-Y.; Chua, X.L.; Tan, Y.P. Effects of facial alignment for age estimation. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision, Singapore, 7–10 December 2010; pp. 644–647. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Berg, T.L. Learning temporal transformations from time-lapse videos. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 262–277. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Rothe, R.; Timofte, R.; Gool, L.V. Dex: Deep expectation of apparent age from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 11–12 December 2015; pp. 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.R. The Regression Analysis of Binary Sequences. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Stat. Methodol. 1958, 20, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Sandiego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- MORPH Database. Available online: https://ebill.uncw.edu/C20231_ustores/web/store_main.jsp?STOREID=4 (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Mu, G.; Guo, G. A study on apparent age estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 11–12 December 2015; pp. 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- FGNET Database. Available online: https://yanweifu.github.io/FG_NET_data/index.html (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- AFAD Database. Available online: https://afad-dataset.github.io (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.W.; Baek, N.R.; Koo, J.H.; Park, K.R. Modified perceptual cycle generative adversarial network-based image enhancement for improving accuracy of low light image segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 6296–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.H.; Cho, S.W.; Baek, N.R.; Park, K.R. Multimodal human recognition in significantly low illumination environment using modified EnlightenGAN. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467v2. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-in/geforce/products/10series/geforce-gtx-1070/ (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Python. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- OpenCV. Available online: http://opencv.org (accessed on 17 May 2021).
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 24–27 October 2017; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Mejjati, Y.A.; Richardt, C.; Tompkin, J.; Cosker, D.; Kim, K.I. Unsupervised attention-guided image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 4–6 December 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Goodfellow, I.; Metaxas, D.; Odena, A. Self-attention generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.08318v2. [Google Scholar]
- Stathaki, T. Image Fusion: Algorithms and Applications; Academic: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Salomon, D. Data Compression: The Complete Reference, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. The accuracy of PSNR in predicting video quality for different video scenes and frame rates. Telecommun. Syst. 2012, 49, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 24–27 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]











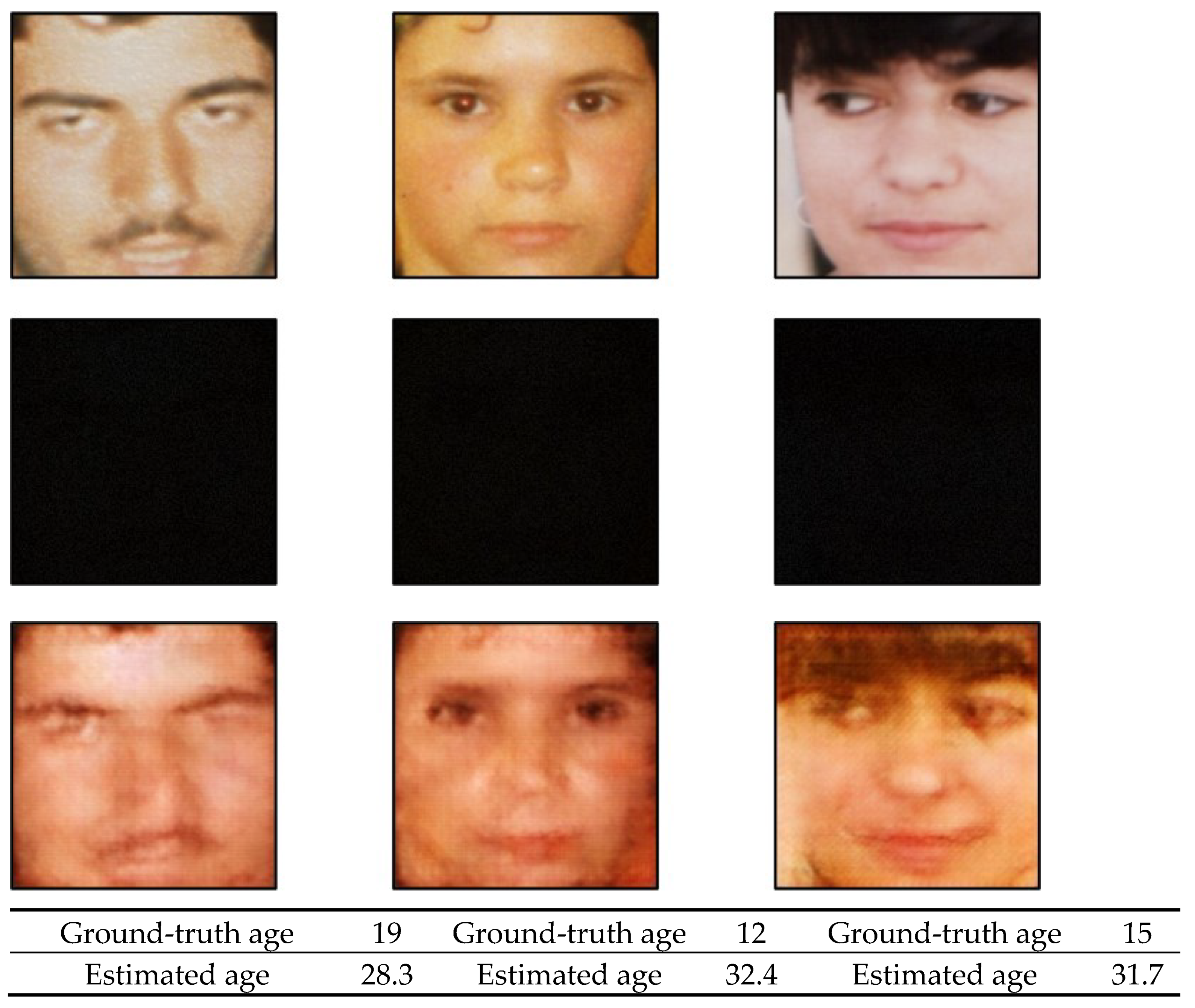


| Method | Database | MAE | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [22] | MORPH FG-NET | 4.77 4.26 | N.A. |
| Levi et al. [23] | Adience | N.A. | 84.7 |
| Huerta et al. [28] | MORPH II FRGC | 4.25 4.17 | N.A. |
| Liu et al. [29] | ICCV2015 | 3.33 | |
| Huo et al. [30] | ChaLearn LAP 2016 | 1.75 | |
| Chen et al. [26] | ICCV2015 FG-NET | N.A. 3.49 | 88.45 N.A. |
| Yang et al. [31] | MORPH II | 3.23 | 98.8 |
| Niu et al. [32] | MORPH II AFAD | 3.27 3.34 | N.A. |
| Hu et al. [33] | FG-NET MORPH | 2.8 2.78 | N.A. |
| Chen et al. [27] | MORPH | 2.96 | 92.9 |
| Li et al. [34] | MORPH II WebFace | 3.06 6.04 | N.A. |
| Qawaqneh et al. [35] | Adience | N.A. | 62.37 |
| Rodriguez et al. [36] | Adience MORPH II | N.A. 2.56 | 61.8 N.A. |
| Duan et al. [37] | MORPH II | 3.44 | N.A. |
| Wan et al. [38] | CACD MORPH II ChaLearn Lap 2016 | 5.22 2.93 3.30 | |
| Zaghbani et al. [39] | MORPH II FG-NET | 3.34 3.75 | |
| Yoo et al. [40] | MORPH II FG-NET | 2.89 3.46 | |
| Rattani et al. [41] | Adience | N.A. | 80.96 |
| Taheri et al. [42] | MORPH II FG-NET | 3.17 3.29 | N.A. |
| Taheri et al. [7] | MORPH II FG-NET | 2.81 3.05 |
| Categories | Method | Application | Database | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing -based techniques | Vishwakarma et al. [43] | Face recognition | Yale Face B | Face recognition is robust to the low-illumination problem | When the environment changes, parameters for enhancement of low-light images need to be manually revised. Does not consider low-illumination images for age estimation. |
| Du et al. [44] | Yale Face B, Carnegie Mellon database | ||||
| Vidya et al. [45] | ORL, UMIST, Yale Face B, Extended Yale B, and color FERET | ||||
| Maeng et al. [52] | LDHF database | ||||
| Baradarani et al. [53] | Yale Face B, Extended Yale B, CMU-PIE, FERET, AT&T, and Labeled Face in the Wild (LFW) | ||||
| Kang et al. [54] | LDHF database | ||||
| Machine learning -based techniques | Liang et al. [48] | Face detection | DARK FACE database | Face detection robust to the low illumination problem | Training data for restoration of low-light images, face detection, and recognition need to be trained. Does not consider low-illumination images for age estimation |
| Shen et al. [55] | Self-constructed database | ||||
| Deep learning -based techniques | Cho et al. [56] | Self-constructed database | |||
| Le et al. [46] | Face recognition | Self-constructed database | Face recognition robust to the low illumination problem | ||
| Huang et al. [47] | SoF database | ||||
| LAE-GAN (proposed method) | Age estimation | MORPH, FG-NET, and AFAD | Age estimation robust to the low illumination problem | Additional procedure for the training of LAE-GAN is necessary |
| Layer Name | Number of Filters | Size of Feature Map (Height × Width × Channel) | Filter Size (Height × Width) | Stride (Height × Width) | Padding (Height × Width) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input image | 256 × 256 × 3 | |||||
| Encoder | 1st convolutional layer Leaky ReLU layer | 64 | 128 × 128 × 64 | 4 × 4 × 3 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 |
| 2nd convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 128 | 64 × 64 × 128 | 4 × 4 × 64 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 3rd convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 256 | 32 × 32 × 256 | 4 × 4 × 128 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 4th convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 512 | 16 × 16 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 256 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 5th convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 512 | 8 × 8 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 6th convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 7th convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 512 | 2 × 2 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 8th convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layer | 512 | 1 × 1 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| Decoder | 1st deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation ReLU layer | 512 | 2 × 2 × 512 2 × 2 × 1024 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 |
| 2nd deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation ReLU layer | 512 | 4 × 4 × 512 4 × 4 × 1024 | 4 × 4 × 1024 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 3rd deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation ReLU layer | 512 | 8 × 8 × 512 8 × 8 × 1024 | 4 × 4 × 1024 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 4th deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation ReLU layer | 512 | 16 × 16 × 512 16 × 16 × 1024 | 4 × 4 × 1024 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 5th deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation ReLU layer | 256 | 32 × 32 × 256 32 × 32 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 1024 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 6th deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation Leaky ReLU layer | 128 | 64 × 64 × 128 64 × 64 × 256 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 7th deconvolutional layer Batch normalization Concatenation Leaky ReLU layer | 64 | 128 × 128 × 64 128 × 128 × 128 | 4 × 4 × 256 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| 8th deconvolutional layer Tanh | 3 | 256 × 256 × 3 | 4 × 4 × 128 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 | |
| Generated image | 256 × 256 × 3 | |||||
| Layer Name | Number of Filters | Size of Feature Map (Height × Width × Channel) | Filter Size (Height × Width) | Stride (Height × Width) | Padding (Height × Width) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input image | 256 × 256 × 3 | ||||
| Generated or target image | 256 × 256 × 3 | ||||
| Concatenation | 256 × 256 × 6 | ||||
| 1st convolutional layer Leaky ReLU layers | 64 | 128 × 128 × 64 | 4 × 4 × 6 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 |
| 2nd convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layers | 128 | 64 × 64 × 128 | 4 × 4 × 64 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 |
| 3rd convolutional layer Batch normalization Leaky ReLU layers | 256 | 32 × 32 × 256 | 4 × 4 × 128 | 2 × 2 | 1 × 1 |
| 4th convolutional layer Batch normalization ReLU layers | 512 | 31 × 31 × 512 | 4 × 4 × 256 | 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 |
| 5th convolutional layer | 1 | 30 × 30 × 1 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 |
| Sigmoid layer | 30 × 30 × 1 |
| Methods | SNR | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CycleGAN [79] | 1.2971 | 19.0120 | 0.5024 |
| Attention GAN [80] | 1.1808 | 16.3112 | 0.5011 |
| Attention cGAN [81] | 1.2734 | 18.5221 | 0.5631 |
| Conditional GAN [59] | 1.4802 | 19.8352 | 0.6207 |
| LAE-GAN | 1.3924 | 18.9404 | 0.6223 |
| Method | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| Age estimation using various age estimators with LAE-GAN | VGG-16 [25] | 13.99 |
| ResNet-50 [63] | 12.83 | |
| ResNet-152 [63] | 12.76 | |
| DEX [64] | 12.46 | |
| AgeNet [29] | 15.33 | |
| Inception with RF [68] | 15.01 | |
| Age estimation using original facial images or low -illuminated facial images without or with LAE-GAN | Original | 5.8 |
| Low illumination (without LAE-GAN) | 19.02 | |
| Enhanced by LAE-GAN (proposed) | 12.46 | |
| Age estimation by our network or the state-of-the-art methods | CycleGAN [79] | 16.97 |
| Attention GAN [80] | 19.00 | |
| Attention cGAN [81] | 18.60 | |
| Conditional GAN [59] | 13.01 | |
| LAE-GAN | 12.46 | |
| Method | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| Age estimation using various age estimators with LAE-GAN | VGG-16 [25] | 14.10 |
| ResNet-50 [63] | 16.31 | |
| ResNet-152 [63] | 14.35 | |
| DEX [64] | 14.12 | |
| AgeNet [29] | 15.17 | |
| Inception with RF [68] | 13.81 | |
| Age estimation using original facial images or low-illuminated facial images without or with LAE-GAN | Original | 7.08 |
| Low illumination (without LAE-GAN) | 16.10 | |
| Enhanced by LAE-GAN (proposed) | 13.81 | |
| Method | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| Age estimation using various age estimators with LAE-GAN | VGG-16 [25] | 10.22 |
| ResNet-50 [63] | 11.00 | |
| ResNet-152 [63] | 9.74 | |
| DEX [64] | 9.55 | |
| AgeNet [29] | 10.40 | |
| Inception with RF [68] | 10.14 | |
| Age estimation using original facial images or low-illuminated facial images without or with LAE-GAN | Original | 6.42 |
| Low illumination (without LAE-GAN) | 11.31 | |
| Enhanced by LAE-GAN (proposed) | 9.55 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, J.; Hong, S.B.; Owais, M.; Park, K.R. LAE-GAN-Based Face Image Restoration for Low-Light Age Estimation. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182329
Nam SH, Kim YH, Choi J, Hong SB, Owais M, Park KR. LAE-GAN-Based Face Image Restoration for Low-Light Age Estimation. Mathematics. 2021; 9(18):2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182329
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Se Hyun, Yu Hwan Kim, Jiho Choi, Seung Baek Hong, Muhammad Owais, and Kang Ryoung Park. 2021. "LAE-GAN-Based Face Image Restoration for Low-Light Age Estimation" Mathematics 9, no. 18: 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182329
APA StyleNam, S. H., Kim, Y. H., Choi, J., Hong, S. B., Owais, M., & Park, K. R. (2021). LAE-GAN-Based Face Image Restoration for Low-Light Age Estimation. Mathematics, 9(18), 2329. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182329







