Using the Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems to Compare the Impact of Speed and Space Perception on the Occurrence of Road Traffic Accidents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Experiment I
2.1.3. Experiment II
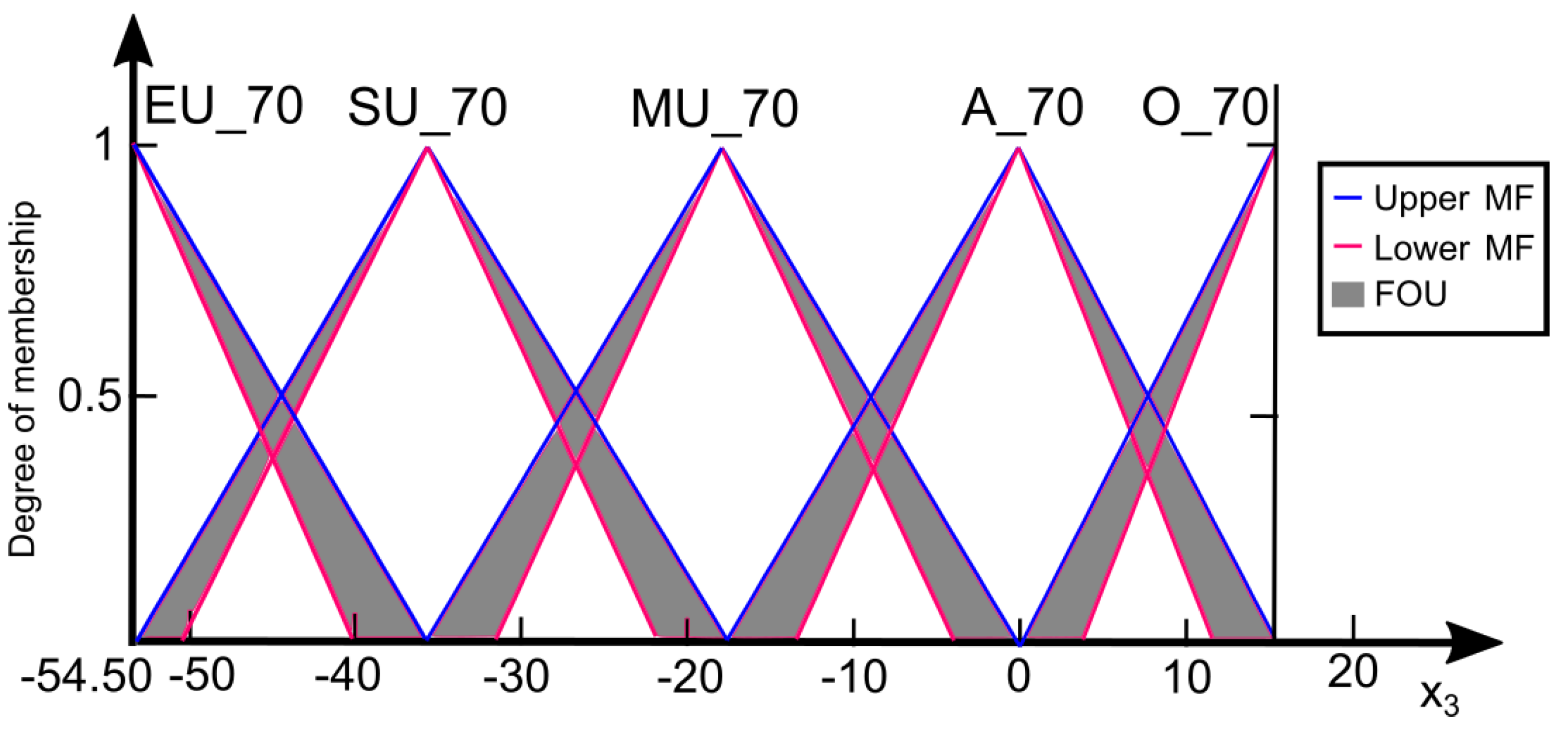
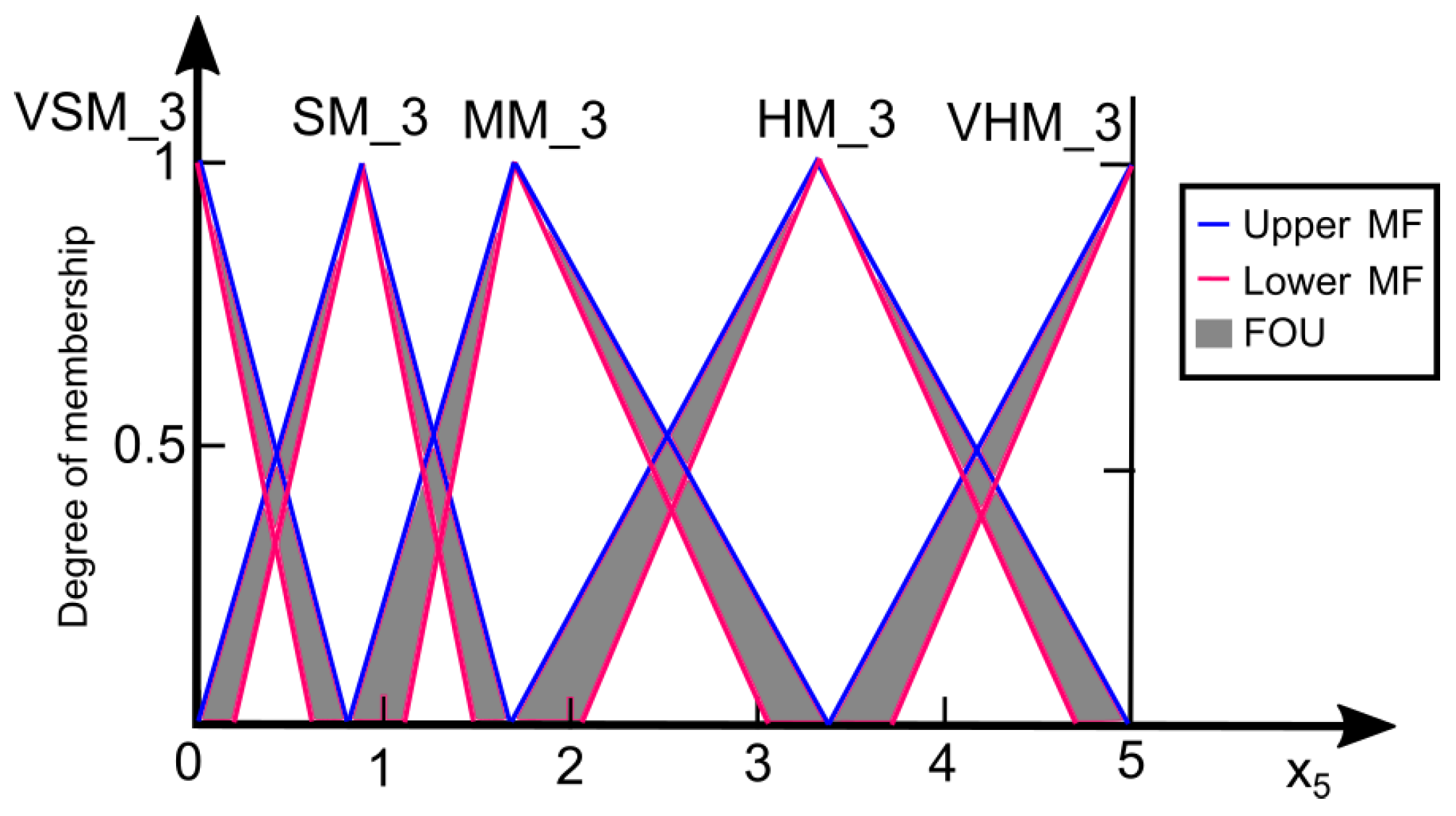
2.2. Model Development
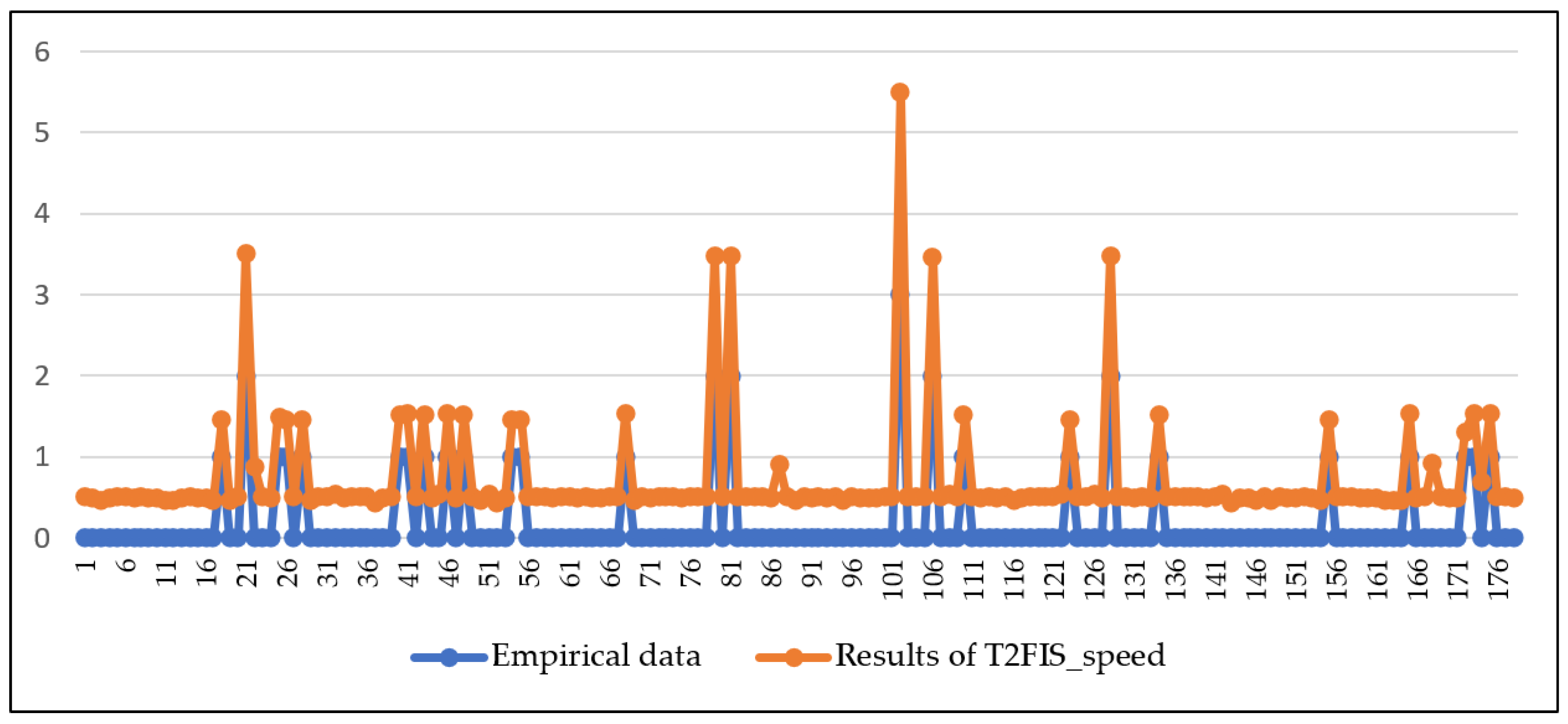
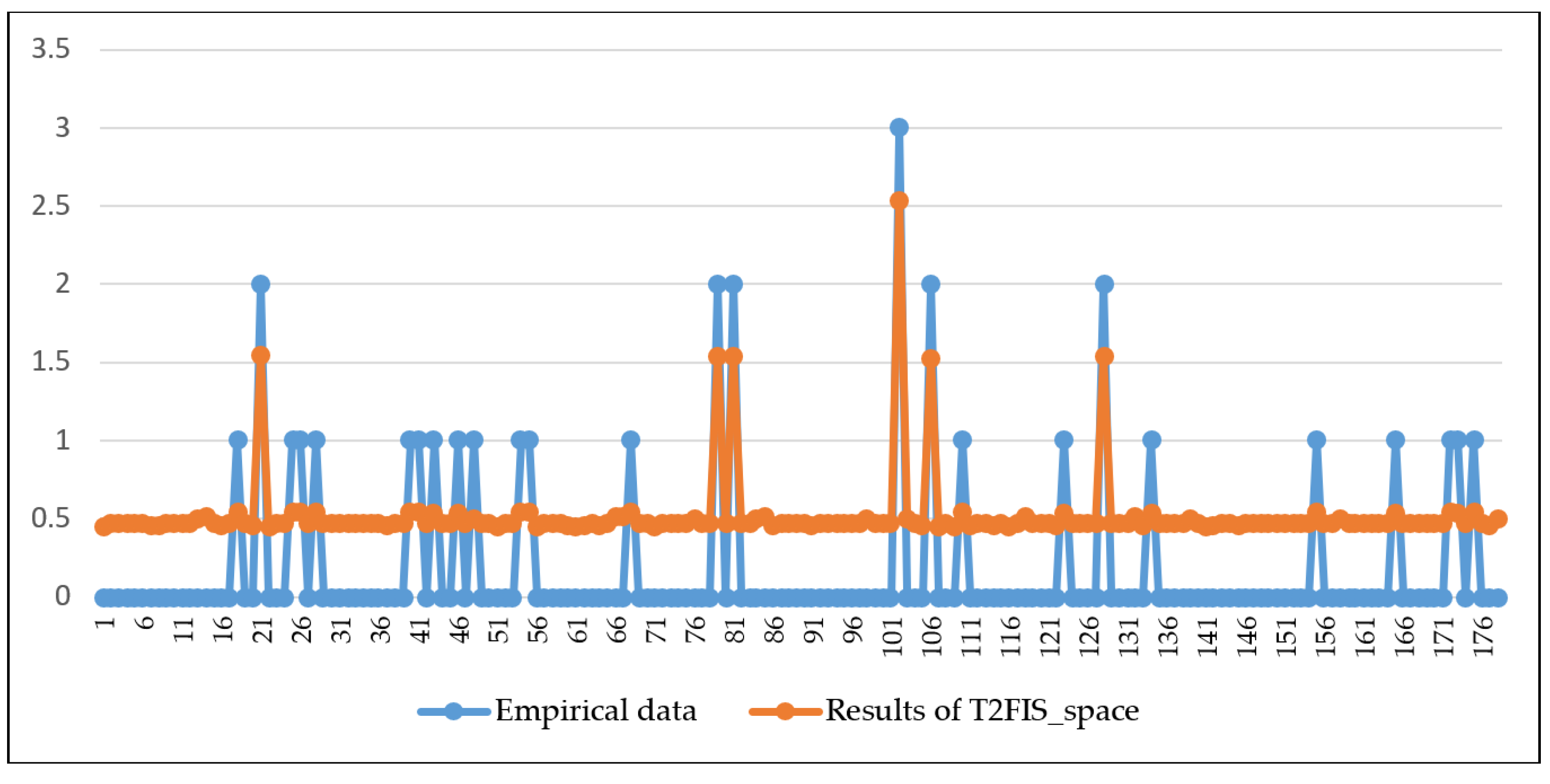
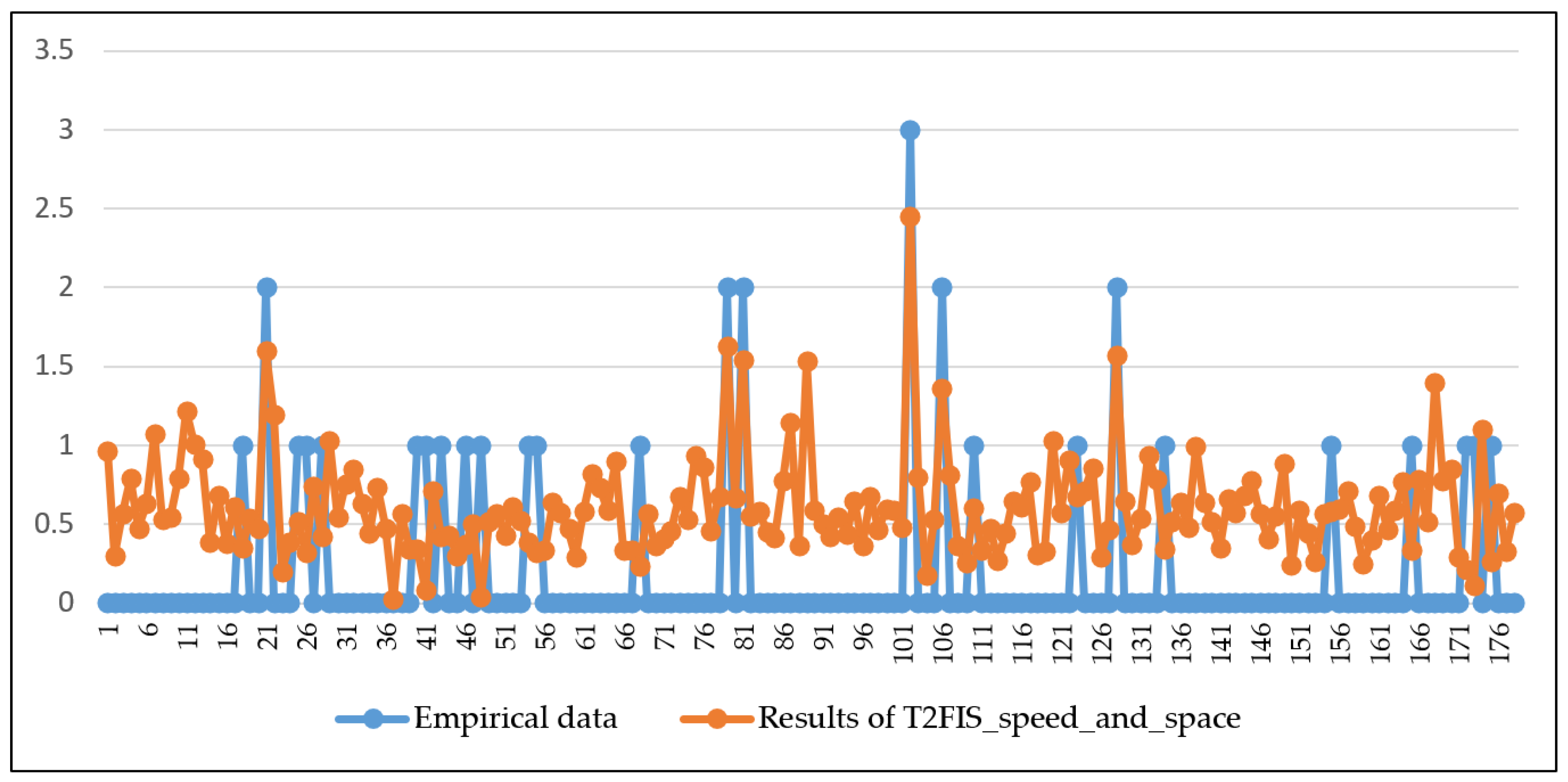
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| D(Rule) | Serial No. of MF for Variable x1 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x2 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x3 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x4 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x5 | Serial No. of MF for Variable y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.80239 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.30215 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.20504 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.23063 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.12946 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 0.29663 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.34355 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.32337 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.16547 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.30893 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.29847 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.25239 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.27987 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.55092 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.30552 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.33059 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.32500 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.20980 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.11413 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.15930 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.11327 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.22223 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.33499 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.32831 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.48439 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.28653 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.27443 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.39459 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.33644 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.31541 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.38599 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.35078 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.36788 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.31414 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 0.20192 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.24565 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.31204 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.28458 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.35178 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.40288 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.40232 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.54969 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.12764 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.55967 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.38411 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.49525 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.44577 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.59369 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.28958 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.51937 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.50663 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.40022 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.40399 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.28975 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| 0.40760 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.17203 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.34380 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.28869 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.51539 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.39328 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.33181 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.16842 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.23263 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.15876 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.16198 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.12092 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.21504 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.19945 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.14372 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.13577 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| 0.29205 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.26880 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.37232 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.38626 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.29795 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.30276 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.40495 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.28480 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.19056 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| 0.30128 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.33724 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.51798 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.07449 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 0.50251 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2013; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ihueze, C.C.; Onwurah, U.O. Road traffic accidents prediction modelling: An analysis of Anambra State, Nigeria. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 112, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.Y.; Jou, R.C. Using HLM to investigate the relationship between traffic accident risk of private vehicles and public transportation. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 119, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Aeron-Thomas, A.; Astrop, A. Estimating Global Road Fatalities; Department for International Development: London, UK, 2000.
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saccomanno, F.F.; Grossi, R.; Greco, D.; Mehmood, A. Identifying black spots along highway SS107 in Southern Italy using two models. J. Transp. Eng. 2001, 127, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, C.; Cai, D.; Yue, S. Research on black spot identification of safety in urban traffic accidents based on machine learning method. Saf. Sci. 2019, 118, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; Sadek, A.W. A novel variable selection method based on frequent pattern tree for real-time traffic accident risk prediction. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 55, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, Z.; Sayed, T. Traffic accident modeling: Some statistical issues. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Gómez, Á.; Lecumberry, F.; Pardo, Á.; Ramírez, I. Pattern recognition in Latin America in the “Big Data” era. Pattern Recogn. 2015, 48, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, B.; Dahlinger, A.; Gahr, B.; Zundritsch, P.; Wortmann, F.; Fleisch, E. Spatial prediction of traffic accidents with critical driving events–Insights from a nationwide field study. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 124, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, B.; Gahr, B.; Egolf, P.; Dahlinger, A.; Wortmann, F. Preventing traffic accidents with in-vehicle decision support systems-The impact of accident hotspot warnings on driver behavior. Decis. Support Syst. 2017, 99, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunović, A.; Pešić, D.; Čičević, S.; Antić, B. The importance of spatial orientation and knowledge of traffic signs for children’s traffic safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2017, 102, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornoldi, C.; Vecchi, T. Visuo-Spatial Working Memory and Individual Differences; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifunović, A.; Čičević, S.; Lazarević, D.; Dragović, M.; Vidović, N.; Mošić, M.; Otat, O. Perception of 3D virtual road markings: Based on estimation of vehicle speed. FME Trans. 2019, 47, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, L.; Van Schagen, I. Driving speed and the risk of road crashes: A review. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2006, 38, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakic, I.; Stevanovic, A. On development of arterial fundamental diagrams based on surrogate density measures from adaptive traffic control systems utilizing stop-line detection. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 94, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin-Brown, C.M. Vehicle height affects drivers’ speed perception: Implications for rollover risk. Transp. Res. Record. 2004, 1899, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloeden, C.N.; McLean, A.J.; Moore, V.M.; Ponte, G. Travelling Speed and the Risk of Crash Involvement Volume 2-Case and Reconstruction Details; NHMRC Road Accident Research Unit, The University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 1997.
- Kloeden, C.N.; McLean, J.; Glonek, G.F.V. Reanalysis of Travelling Speed and the Risk of Crash Involvement in Adelaide South Australia; Australian Transport Safety Bureau: Adelaide, Australia, 2002.
- Kloeden, C.N.; Ponte, G.; McLean, J. Travelling Speed and Risk of Crash Involvement on Rural Roads; Australian Transport Safety Bureau: Adelaide, Australia, 2001.
- Wang, C.; Quddus, M.; Ison, S. The effects of area-wide road speed and curvature on traffic casualties in England. J. Transp. Geogr. 2009, 17, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruya, A. Speed-accident relationships on European roads. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference “Road Safety in Europe”, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany, 21–23 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelman, V.; Doveh, E.; Bekhor, S. The relationship between free-flow travel speeds, infrastructure characteristics and accidents, on single-carriageway roads. Transp. Res. Proc. 2017, 25, 2026–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvik, R.; Christensen, P.; Amundsen, A.H. Speed and Road Accidents an Evaluation of the Power Model; Institute of Transport Economics (TØI): Oslo, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Quddus, M. Exploring the relationship between average speed, speed variation, and accident rates using spatial statistical models and GIS. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2013, 5, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Road Traffic Safety Agency. Statistical Report on the State of Traffic Safety in the Republic of Serbia in 2019; Road Traffic Safety Agency: Belgrade, Serbia, 2020.
- Road Traffic Safety Agency. On Line Statistical Report on the State of Traffic Safety in the Republic of Serbia for the Years from 2017 to 2019; Road Traffic Safety Agency: Belgrade, Serbia, 2020. Available online: http://195.222.99.60/ibbsPublic/ (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Endsley, M.R. Toward a theory of situation awareness in dynamic systems. Hum. Factors 1995, 37, 32–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.R.; Thompson, A.R.; Poulter, D.R.; Stride, C.B.; Rowe, R. Why do drivers become safer over the first three months of driving? A longitudinal qualitative study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 117, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddon, W., Jr. Advances in the epidemiology of injuries as a basis for public policy. Public Health Rep. 1980, 95, 411–421. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, B.D.; Haglund, K.; Ameh, E.A.; Olaomi, O.O.; Uthman, U.; Cassidy, L.D. Understanding Etiologies of Road Traffic Crashes, Injuries, and Death for Patients at National Hospital Abuja: A Qualitative Content Analysis Using Haddon’s Matrix. Qual. Rep. 2020, 25, 962–974. [Google Scholar]
- Čubranić-Dobrodolac, M.; Švadlenka, L.; Čičević, S.; Dobrodolac, M. Modelling driver propensity for traffic accidents: A comparison of multiple regression analysis and fuzzy approach. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2020, 27, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Donnell, E.T. Analysis of nighttime driver behavior and pavement marking effects using fuzzy inference system. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2007, 21, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentouh, C.; Nguyen, A.-T.; Rath, J.J.; Floris, J.; Popieul, J.-C. Human-machine shared control for vehicle lane keeping systems: A Lyapunov-based approach. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 13, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, F.; Khadim, S.; Rauf, R.; Ahmad, M.; Jabbar, S.; Chaudhry, J. A validated fuzzy logic inspired driver distraction evaluation system for road safety using artificial human driver emotion. Comput. Netw. 2018, 143, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Tsai, S.-F.; Ko, L.-W. EEG-based learning system for online motion sickness level estimation in a dynamic vehicle environment. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, D.; Grabengiesser, D.; Gauterin, F. Online driving style recognition using fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the IEEE 17th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Qingdao, China, 8–11 October 2014; pp. 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Aljaafreh, A.; Albdour, N. Fuzzy-based recognition model for driving styles. (IJEECS) Int. J. Electr. Electron. Comput. Syst. 2013, 16, 816–819. [Google Scholar]
- Bıçaksız, P.; Öztürk, İ.; Özkan, T. The differential associations of functional and dysfunctional impulsivity with driving style: A simulator study. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešić, D.; Trifunović, A.; Ivković, I.; Čičević, S.; Žunjić, A. Evaluation of the effects of daytime running lights for passenger cars. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 66, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Clark, J.R. Automobile running lights—A research report. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1964, 47, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlstedt, S.; Rumar, K. Vehicle Colour and Front Conspicuity in Some Simulated Rural Traffic Situations; Traffic Safety Research Group, Department of Psychology, University of Uppsala: Uppsala, Sweden, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Government of the Republic of Serbia. Law on Road Traffic Safety; Official Gazette: Belgrade, Serbia, 2019.
- Čičević, S.; Trifunović, A.; Mitrović, S.; Nešic, M. The usability analysis of a different presentation media design for vehicle speed assessment. In Ergonomic Design and Assessment of Products and Systems; Žunjić, A., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 195–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, P.U. Abutting Objects Warp the Three-Dimensional Curvature of Modally Completing Surfaces. i-Perception 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscani, M.; Valsecchi, M. Lightness discrimination depends more on bright rather than shaded regions of three-dimensional objects. i-Perception 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamdani, E.H.; Assilian, S. An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1975, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. The Concept of a Linguistic Variable and Its Application to Approximate Reasoning–1. Inform. Sci. 1975, 8, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Mendel, J.M. Generating fuzzy rules by learning from examples. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1992, 22, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovčić, S.; Průša, P.; Dobrodolac, M.; Švadlenka, L. A proposal for a decision-making tool in third-party logistics (3PL) provider selection based on multi-criteria analysis and the fuzzy approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čubranić-Dobrodolac, M.; Molkova, T.; Švadlenka, L. The impact of road characteristics assessment on the traffic accidents occurrence. In Proceedings of the Sinteza 2019-International Scientific Conference on Information Technology and Data Related Research, Belgrade, Serbia, 20 April 2019; Singidunum University: Belgrade, Serbia, 2019; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Uejima, S.; Asai, K. Linear regression analysis with fuzzy model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1982, 12, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H. Fuzzy data analysis by possibilistic linear models. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1987, 24, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukhrova, N.; Johannssen, A. Fuzzy regression analysis: Systematic review and bibliography. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 84, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Watada, J. Building a Type II Fuzzy Qualitative Regression Model. In Intelligent Decision Technologies; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Watada, J., Watanabe, T., Phillips-Wren, G., Howlett, R., Jain, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleshchuk, O.; Komarov, E. A Fuzzy Nonlinear Regression Model for Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets. Int. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2014, 8, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, E.; Hassanpour, H.; Arefi, M. A weighted goal programming approach to fuzzy linear regression with crisp inputs and type-2 fuzzy outputs. Soft Comput. 2015, 19, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.; Poleshchuk, O.; Komarov, E. A New Fuzzy Linear Regression Model for a Special Case of Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets. Appl. Math. Inform. Sci. 2016, 10, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Watada, J. Building a type-2 fuzzy regression model based on credibility theory and its application on Arbitrage Pricing theory. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2016, 11, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajestani, N.S.; Kamyad, A.V.; Zare, A. A piecewise type-2 fuzzy regression model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2017, 10, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajestani, N.S.; Kamyad, A.V.; Esfahani, E.N.; Zare, A. Prediction of retinopathy in diabetic patients using type-2 fuzzy regression model. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Gao, Y. Quadrilateral Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Regression Analysis for Data Outlier Detection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4914593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, I.; Yu, J.J.; Feng, J.; Marshman, J. Women match men when learning a spatial skill. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn 2009, 35, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, I.; Feng, J. Video Games and Spatial Cognitio. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2010, 14, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Spence, I.; Pratt, J. Playing an action video game reduces gender differences in spatial cognition. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, L.; Grumi, S.; Di Blasio, P. Positive Effects of Videogame Use on Visuospatial Competencies: The Impact of Visualization Style in Preadolescents and Adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.A.; Tayfour, A. Characteristics and prediction of traffic accident casualties in Sudan using statistical modeling and artificial neural networks. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
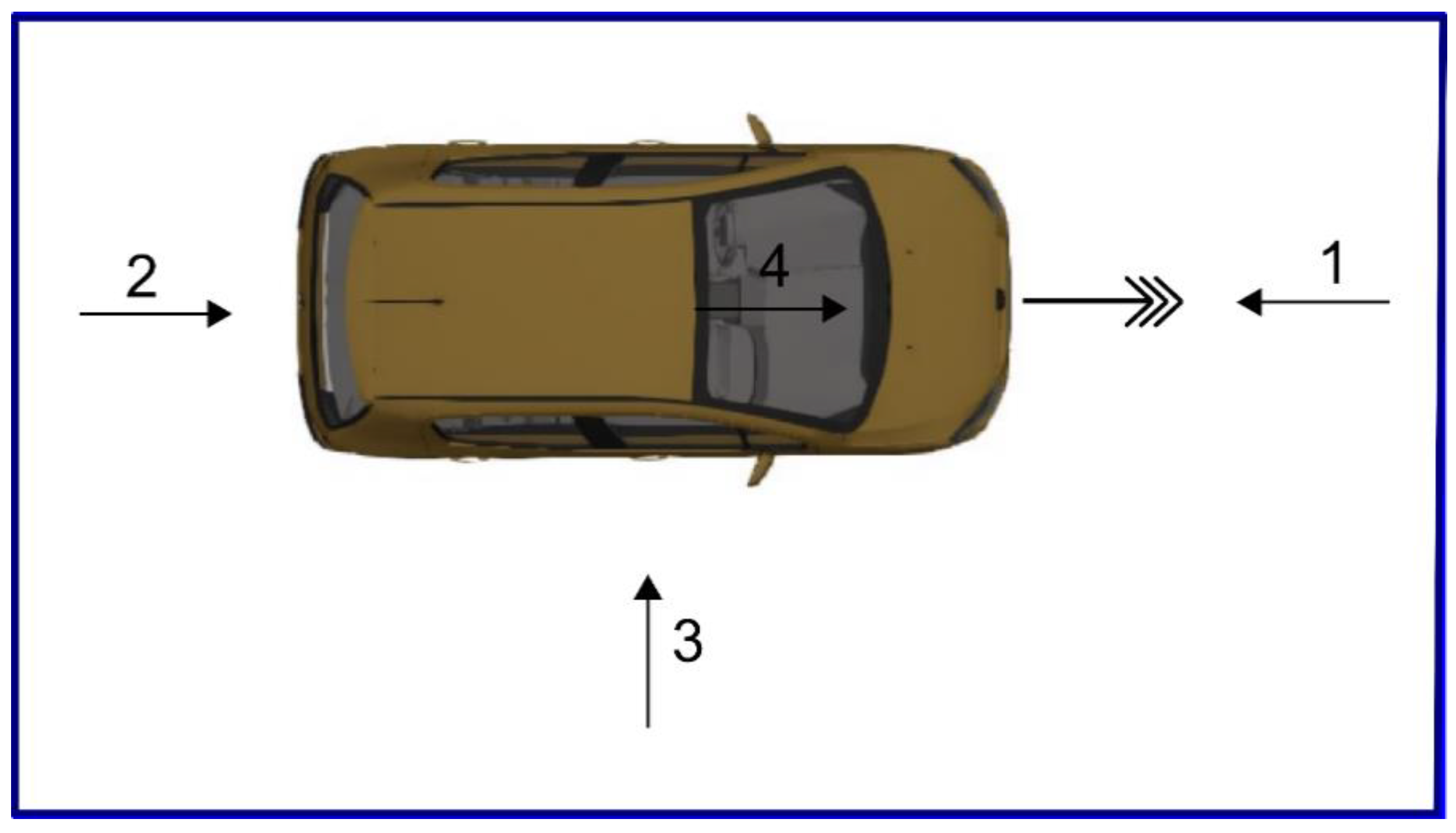





| Input Variable | Average Errors in Assessments from Four Different Positions [km/h] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Standard Deviation | |
| Average assessment of speed 30 km/h | −3.75 | 21.75 | 67.50 | 11.68 |
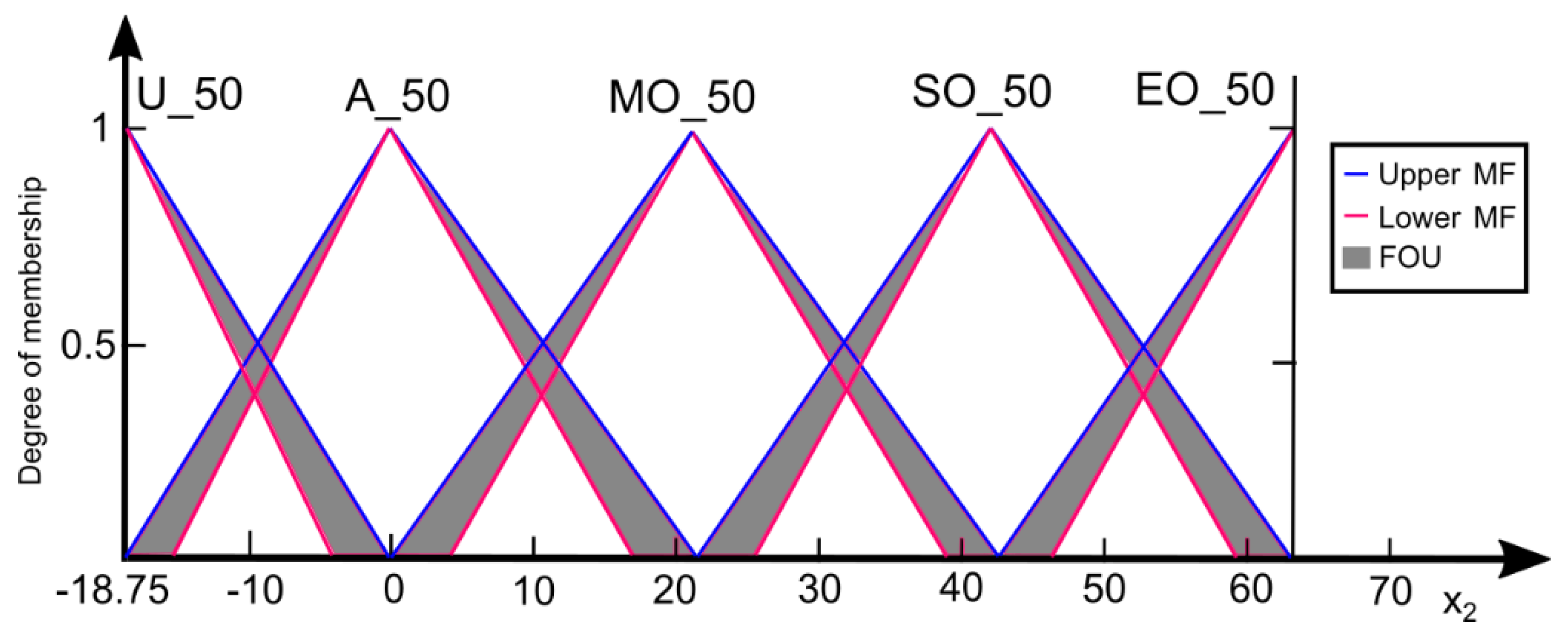
| Average assessment of speed 50 km/h | −18.75 | 13.57 | 62.50 | 13.51 |
| Average assessment of speed 70 km/h | −54.50 | −32.33 | 15.00 | 10.06 |
| Input Variable | Average Marks from the Space Assessments Tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Standard Deviation | |
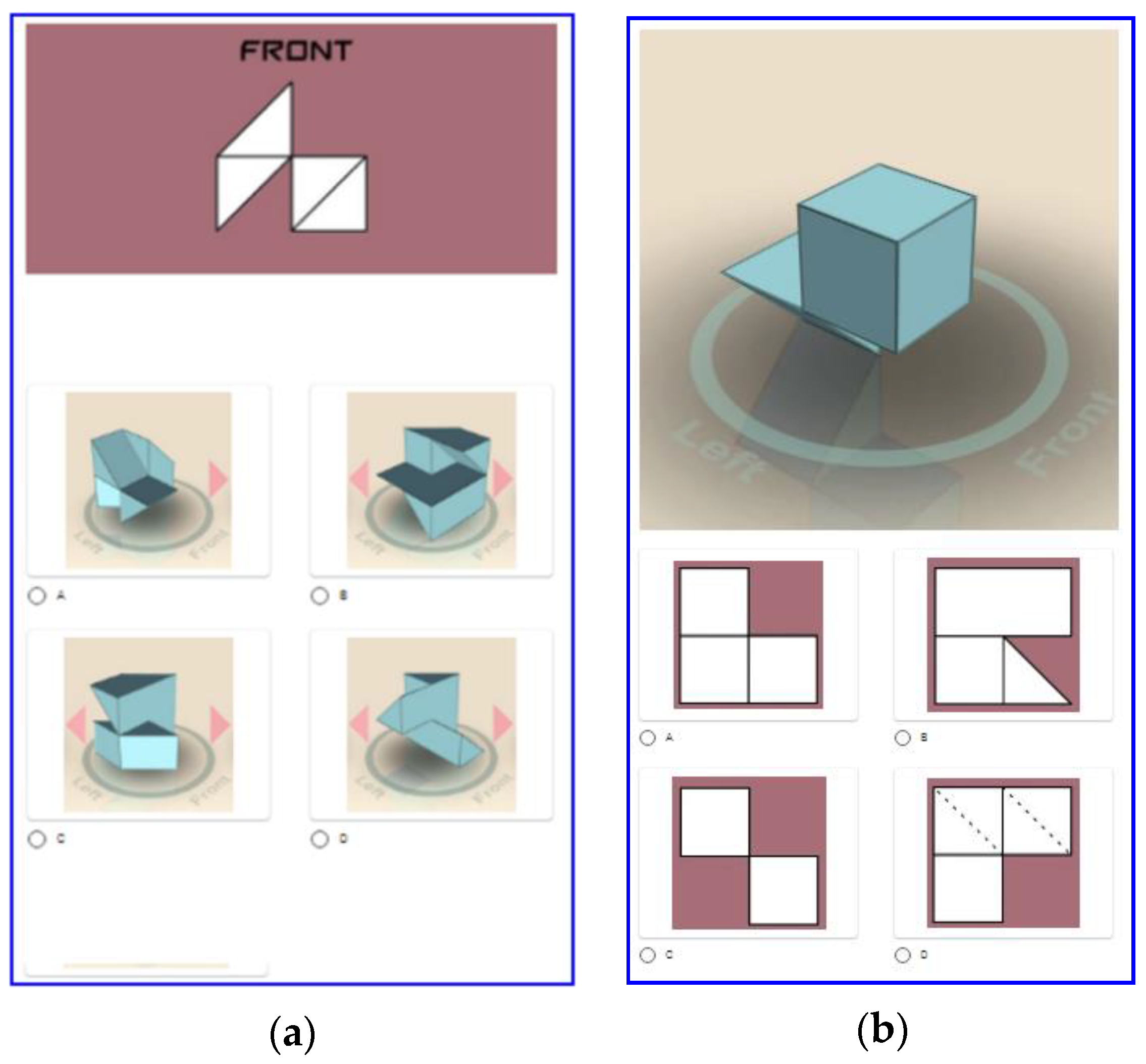
| Average assessment of 2D space | 0 | 1.81 | 5 | 1.12 |
| Average assessment of 3D space | 0 | 1.67 | 5 | 1.01 |
| D(Rule) | Serial No. of MF for Variable x1 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x2 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x3 | Serial No. of MF for Variable y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.42682 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.25945 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.54222 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.62963 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.29929 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.68531 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.47288 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.35178 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.85328 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.74074 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.33383 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.27160 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.24294 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.30423 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.48971 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.67901 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.50440 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.37940 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.65040 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| 0.10539 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| 0.72222 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| D(Rule) | Serial No. of MF for Variable x4 | Serial No. of MF for Variable x5 | Serial No. of MF for Variable y |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.79518 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.79640 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.80239 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.88888 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.70682 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.70791 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.71324 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.87500 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.69578 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.69685 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.70209 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 0.75000 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.59638 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0.59730 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.60179 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| T2FIS_Speed | T2FIS_Space | T2FIS_Speed_and_Space | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T2FIS_speed | - | ||
| T2FIS_space | 0.048 * | - | |
| T2FIS_speed_and_space | 0.059 | 0.049 * | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čubranić-Dobrodolac, M.; Švadlenka, L.; Čičević, S.; Trifunović, A.; Dobrodolac, M. Using the Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems to Compare the Impact of Speed and Space Perception on the Occurrence of Road Traffic Accidents. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091548
Čubranić-Dobrodolac M, Švadlenka L, Čičević S, Trifunović A, Dobrodolac M. Using the Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems to Compare the Impact of Speed and Space Perception on the Occurrence of Road Traffic Accidents. Mathematics. 2020; 8(9):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091548
Chicago/Turabian StyleČubranić-Dobrodolac, Marjana, Libor Švadlenka, Svetlana Čičević, Aleksandar Trifunović, and Momčilo Dobrodolac. 2020. "Using the Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems to Compare the Impact of Speed and Space Perception on the Occurrence of Road Traffic Accidents" Mathematics 8, no. 9: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091548
APA StyleČubranić-Dobrodolac, M., Švadlenka, L., Čičević, S., Trifunović, A., & Dobrodolac, M. (2020). Using the Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Inference Systems to Compare the Impact of Speed and Space Perception on the Occurrence of Road Traffic Accidents. Mathematics, 8(9), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091548








