Abstract
Presently, it is essential to increase customer service such that the Supply Chain Management (SCM) can earn more profit in a sustainable manner. In the supply chain, the manufacturer and the retailer are two players who try to maintain the joint profit of the Supply Chain (SC) without only thinking about their own respective profits. However, the retailer may not provide all information to the manufacturer. This research introduces the use of the advanced technology Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) in a retailer’s shop to obtain exact information about customer demand. A consignment policy is used to increase the manufacturer profit, and a fixed fee is offered to the retailer to generate more profit in coordination with the manufacturer. This study is conducted with and without the effect of RFID to show the benefit of SCM even when the retailer is unreliable. Both models are solved using the classical optimization technique. Numerical findings prove that SCM can benefit from the outcome of this study even for unreliability. Coordination within SCM can be maintained for a long time by using the proposed recommendations of this study.
1. Introduction
In the area of Supply Chain Management (SCM), an unreliable player is an important issue. Before observing customer demand, management needs to decide how many products need to be stocked. Sometimes, there is lead-time demand uncertainty, and the stockholder faces a situation called understock or overstock due to the lack of proper information exchange between the Supply Chain (SC) players. For overstock, the holding cost of the products is higher than usual. In this model, the retailer sends the wrong information to the manufacturer, such that understock or overstock happens. The manufacturer does not get actual demand or information about the inventory (Cárdenas-Barrón et al. []). Here, a consignment policy is applied. in this policy, two coalitions are contemplated—the consignee and the consignor. The manufacturer is denoted as the consignor, which means the upstream player, and the retailer is denoted as the consignee, which means the downstream player. Taleizadeh and Sadeghi [] introduced a unified pricing strategy for sustainable development to increase market share using different incentives such as reverse SC, where both the retailer and manufacturer propose a reward scheme to the customer.
According to Gautam et al. [], the consignor provides a certain amount of incentive to the consignee. A Stackelberg game approach is used, and more profit is generated for the manufacturer using a comprehensive analysis (Taleizadeh et al. []). In this research, the manufacturer acts as a leader and controls the inventory. In the consignment stock, products are stored in one location, such as a warehouse, but owned by the manufacturer. The consignment inventory is very common in manufacturing, where stock remains under the ownership of the manufacturer. There is a contract between two players, from stocking the products to selling them. In this paper, the retailer sells the product and sends to the manufacturer the revenue, from which the manufacturer generates profit. The retailer gets a certain amount of commission from the manufacturer after selling each product to the customer. The retailer gets a fixed fee from the manufacturer for implementing RFID. If the stocks are not sold or if the manufacturer and retailer mutually decide that the products are no longer needed, then the stock is returned to the legal owner. Yi and Sarker [] provided a summary of controllable lead-time under a consignment contract for an integrated inventory system. They discussed random lead-time demand, which did not follow any known distribution function. The stochastic demand pattern was discussed by Wangsa and Wee [].
Therefore, both players agree to a reasonable stock rolling agreement depending on market demand. To avoid stock disruption, the manufacturer production time and distribution of products are considered. Adopting smart technology in industry is a valuable business policy, since competition is very high. To improve production quality with minimum labor cost, RFID technology is introduced within SCM. An industry generates more profit with less production time by using this technology. RFID adoption within SCM is beneficial for the industry, even when remanufacturing (Tsao et al. []). Using this sensing technology, every movement of the product is tracked and traced in the inventory (Zhu et al. []). The deterministic coverage of each RFID scanner within a certain radius is as important as the number of RFID tags (Zhang and Hou []). Initially, RFID is implemented by the retailer, but the manufacturer pays the retailer a fixed amount for this advanced technology.
This study serves an economic purpose of profit maximization of the entire SC by reducing information asymmetry within the SC. Information asymmetry creates an unreliable SCM. The information hidden from the manufacturer amplifies the loss to the manufacturer. Thus, the purpose of this study is to improve the coordination between the manufacturer and the unreliable retailer, such that profit will be maximized and the effect of unreliability will be reduced. It may not always be possible to find a reliable SCM player for business. Thus, this study finds a way to improve coordination by using RFID and game policy.
2. Literature Review
In this research, the retailer is unreliable and does not provide proper information to the manufacturer. Therefore, the lead time demand is random, and it does not follow any kind of known distribution. Here comes the distribution free approach. The distribution free approach was first introduced by Scarf []. There, only the standard deviation along with the mean were considered without any other assumption about the distribution function. The model contained a lengthy mathematical approach, and for this reason, it was very difficult to understand the solution procedure. Scarf’s model was simplified by Gallego and Moon [] with a newly developed newsvendor model in which the distribution free approach was narrated in a simplified and understandable way. When the lead time demand does not follow any kind of known distribution, another newsvendor model of improved quality and reduced setup cost was developed by Ouyang et al. []. An extension of this inventory model was done by the same authors Ouyang et al. [] by integrating the distribution free approach with the controllable lead time. Being the leader, the manufacturer deals with the financial part. Operational components are being managed by the retailer since the retailer is the follower. The decision for controlling the inventory with the consignment policy within an SCM was described by Ru and Wang [].
Furthermore, the inventory holding cost can be nonlinear and was combined with the distribution free method by Pal et al. []. Moon et al. [] introduced an integrated inventory model considering a min-max approach with a controllable lead time and service level constraint. To improve the product quality, the process of manufacturing needed to be perfect. Quality improvement was done by reducing the setup cost with the introduction of a variable backorder cost with a distribution free approach, which was established for the reduction of the setup cost of the manufacturer. This model has proven that adding a service level constraint within an SC can improve the quality of the product. A model on continuous review inventory was introduced by Shin et al. [] with a variable lead time demand. A discount policy was introduced under the transportation cost to optimize the model along with the distribution free method.
A strategy on the consignment stock under an SCM was invented by Taleizadeh and Moshtagh [] where an imperfect manufacturing processes was discussed on the basis of remanufacturing. A typical warehouse has certain limitations like quality checking, unnecessary time consumption, and tracking and tracing the products properly within a certain time. The manufacturers sends the products to the warehouse, and the products are received by the staff on the receiving dock. After that, unloading those products and storing the inventory are done by checking the quality and quantity of products. Those products are then tagged with RFID tags. By scanning those tags, the detailed information of each product is stored in the system of the inventory. The database would be generated then and by using it, the status of each product could be tracked by the user. Storing the products with proper information in the inventory is called the inbound process. The proposed RFID based solution improved the receiving time by 90% and reduced the operating expenses by 30%. Earlier, updating the database of the inventory was a time-consuming process and was done manually. However, after using RFID, the process was transformed into an automatic process and also saved much paperwork.
All of the processes in an inventory system can be tracked by RFID, and the lot size is unequal (Hota et al. []). An automation policy for controlling the processes in a smart product manufacturing setup is an advanced idea. RFID gives the opportunity to reduce the human error due to inspection. RFID scanner does an automatic scan of all the RFID tags, which contain data on the product. Moreover, it is found that the tags are reusable in nature. This implies that the maintenance cost is reduced, and the real-time tracking of each product is possible (Sari []). For the outbound process, sales orders are generated with the minimum time where, without RFID, it takes a long time to calculate the inventory details. The fast processing is the advantage that the advanced technology has over the traditional process. The adoption of the RFID technology within an SCM can increase all the working abilities within the warehouse (Meguerdichian et al. []). As the traditional business policy suffers from unreliability, it gives less profit. Guchhait et al. [] described a brief approach on the RFID technology implementation to overcome the issue of unreliability and to optimize the overall SCM profit in a reliable way for generating more profit.
Within the supply chain, the decisions regarding loss minimization and profit maximization are the crucial decisions. Feng and Tan [] discussed coordinating the decisions regarding the pricing policy of the SCM. The scenario about loss aversion was discussed substantially. A discussion about the online and offline SCM was discussed by Lei et al. []. They studied the consumers’ strategies. The game strategy within the SCM comes forward whenever players of the SCM are not equal in power. In game theory, with two players, one is the leader, and the other one is the follower. The leader is the decision maker of the SCM. Chen et al. [] discussed a retailer Stackelberg SC where retailers made all the decisions. Wei and Jing [] studied the Stackelberg game policy within the SCM for backward integration. In this newsvendor model, a Stackelberg game policy is used where the manufacturer is the leader and the retailer is the follower. However, the follower has the priority to choose his/her optimum decisions. A Stackelberg game policy was discussed by Sarkar et al. [] within an integrated inventory model for setup cost reduction.
Table 1 shows the contribution of different authors and how this research addresses the existing gaps of previous research. A contribution table shows that within the supply chain model, even the distribution free approach is widely used for the unknown distribution probability function. However, the unreliability issue is not familiar to the literature. The unreliable retailer is hiding information from the manufacturer, and it creates an information asymmetry within the entire supply chain. RFID is the technology that can help to get over the unreliability problem by tracing the product. The utilization of RFID is the benchmark to reduce the information asymmetry issue. Moreover, the consignment policy works for stabilizing the unreliability issue by not giving the power to the retailer to sell the product. Instead, the manufacturer shares a fixed fee with the retailer for selling the product by the retailer on behalf of the manufacturer. Along with the fixed fee, a commission is provided to the retailer by the manufacturer for selling each product. This reduces the overall situation of the information asymmetry. Now, the unequal power of the manufacturer and retailer creates a game policy based on the leader-follower relationship. This study utilizes the Stackelberg game to stabilize the unequal power of the unreliable SCM. At last, the service to the customer is always beneficial to both the manufacturer and the retailer. The more product will be sold by the retailer, the more commission he/she can earn from the manufacturer. Thus, this study evolves around profit maximization by reducing the effect of the unreliability using various policies. Section 1 and Section 2 represent the Introduction and Literature Review of this study. The rest of the study is designed as follows: Section 3 signifies the problem definition and assumptions. The mathematical modeling part is in Section 4. The results of the numerical study are described in Section 5 followed by a sensitivity discussion on the parameters, and Section 6 concludes this research. The associated references are given in the references section.

Table 1.
Author contribution table.
3. Problem Definition, Assumptions, and Notation
The problem definition of this study is demonstrated in this segment. The assumptions and the notation are as follows to validate the proposed model mathematically.
3.1. Problem Definition
In this research, a differentiation between the traditional system and the consignment policy within an unreliable SCM is described where a single retailer and a single manufacturer are the two supply chain players with asymmetric power. The decision maker of this SC is determined by a Stackelberg game policy. A service dependent demand distribution is studied under a consignment contract because of the unreliable retailer. This unreliability is removed by using the RFID for tracking the inventory, as well as proper information sharing. In the consignment policy under RFID, a fixed fee is provided to the retailer by the manufacturer as support. This research follows a distribution free approach since it is difficult to estimate the probability distribution of the lead time demand. This research provides a new way to achieve more profit in an RFID based consignment policy over the traditional system policy, and also, the standard of service is improved.
3.2. Assumptions
The following assumptions are described for this research.
- A model of a two-echelon SC for a single type of product is considered under the newsvendor framework. The market demand is variable and is dependent on the service b provided by the retailer.
- In traditional system, only the manufacturer bears the cost for manufacturing, and the total cost of inventory is carried by the retailer. In the consignment policy, the manufacturer provides a contract on a consignment to the retailer under a custom-made production system. The retailer sells the product and sends the money to the manufacturer. The retailer gets a fixed fee from the manufacturer along with a certain amount of commission for selling each product to a customer (Sarkar et al. []).
- The total holding cost of the consignment policy is not only spent by the manufacturer or retailer alone. The holding cost is divided into two different segments. One is the operational part, which is carried by the retailer, and the other one is the financial part, which is incurred by the manufacturer.
- The lead time L is not negligible, and the demand during the lead time is random in nature. Any kind of specific probability distribution is not contemplated in the proposed model. The lead time demand follows an unknown probability distribution function with a known value of the standard deviation and mean () (Shin et al. []).
- As the retailer is not sharing proper information with the manufacturer, an information asymmetry is generated within the SCM. To solve this unreliability and to get the proper information, the manufacturer lets the retailer install the RFID technology (Guchhait et al. []). By the tracking facility of the RFID, the manufacturer becomes aware of all the information regarding the demand and the products.
- Along with the VMI, the consignment policy is used by the manufacturer. The retailer gets a commission for selling products and a fixed fee, that is a fixed amount of money for being a business partner of the manufacturer. A positive signed fixed fee denotes the process flow from the manufacturer to the retailer (Sarkar et al. []).
- For the asymmetric power of the supply chain players, game theory is used to find the decision maker. Using the Stackelberg game theoretic approach, the manufacturer acts as an SC leader, and the retailer acts as a follower. Thus, the manufacturer is the decision maker and gives the opportunity to the retailer to choose the optimal policy (Sarkar et al. []).
3.3. Notation
The notation associated with this study is given in the Appendix A.
4. Mathematical Model
This mathematical model is based on the newsvendor model. The mathematical model is described in two separate policies: one is the traditional policy, and the another is the RFID based consignment policy. A single manufacturer and a single retailer are involved in the two-echelon SCM for a single type of product. The retailer is unreliable such that he/she is not sharing the proper information with the manufacturer. Then, the SCM is converted into an unreliable SCM. For the unequal power in the SC, the Stackelberg game policy is utilized for finding the decision maker. In this study, the manufacturer acts as the Stackelberg leader, and the retailer acts as the Stackelberg follower. Thus, the manufacturer gives the opportunity to the retailer to optimize his/her decisions first. Based on those decisions, the manufacturer will make his/her decisions.
4.1. Traditional Policy
The traditional system is mainly based on the literature based process (Figure 1). All the costs of the manufacturer and the retailer are paid by the individuals. That is, the costs for the retailer are paid by the retailer and also those for the manufacturer. In the traditional model, both the profits of the retailer and the manufacturer under unreliability are mathematically described below. As on Stackelberg game, the retailer optimizes his/her decisions first.
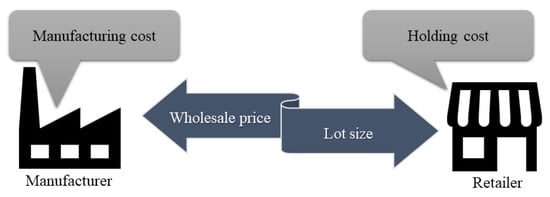
Figure 1.
Traditional system.
4.1.1. Retailer’s Model
The market demand of the retailer for a single type of product is , where a is the scaling parameter, is the shape parameter, and b is the provided service to the customers by the retailer. The corresponding costs of the retailer are described below:
The unit selling price of a product is p. If is the ordering quantity of the retailer, then the total revenue of the retailer is:
If the unit purchasing cost is , then the total purchasing cost is . The holding cost and the shortage cost are incurred based on the situation of the newsvendor model. If the unit holding cost per unit time of the retailer is and the unit shortage cost is , then the total cost of holding and shortage is:
The lead time L is a composition of n number of mutually independent lead time components . Every component has separate unit crashing cost , i.e., . The lead time component has a minimum duration and a normal duration , i.e., . Then, the lead time component is written as . Therefore, the lead time crashing cost can be written as . Thus, the total profit of the retailer as a follower under the traditional system is:
Distribution free approach
The necessity of the lead time on the basis of demand information is really essential for avoiding the shortage. Meanwhile, the lead time demand distribution function is unknown. According to the lemma of Gallego and Moon [], without having distribution information, one can easily calculate the expected shortage quantity during lead time demand for the least favorable distribution function , the set of cumulative distribution functions.
Lemma 1.
- (i)
- The expected overstock quantity is given by the following relation:The upper bound gives the maximum amount of the overstock quantity of the product.
- (ii)
- The expected quantity of shortage is given by the following expression:The upper bound gives the maximum quantity of the shortage amount.Using Equations (4) and (5), the expected profit of the retailer can be written as:
4.1.2. Manufacturer’s Model
The manufacturer is a Stackelberg leader and follows the optimized decision of the retailer. Thus, if is the per unit wholesale price, then the revenue of the manufacturer is . The production cost of the manufacturer is , where k is the unit production cost. Then, the expected profit of the manufacturer under the traditional policy is:
4.1.3. Joint Traditional Policy
Therefore, the joint expected total profit under the traditional policy is:
4.1.4. Solution Methodology
The optimum values of all the decision variables are found by the classical optimization procedure. By equating the first order derivatives to zero, the optimum values can be derivable. Hence, the first order derivative of Equation (8) with respect to gives:
Now, we obtain the optimum value by equating the above equation to zero, which gives:
Again, the first order derivative of Equation (8) with respect to L gives:
Now, the optimum value of L is given by:
Furthermore, the first order derivative of Equation (8) with respect to b describes:
Now, the optimum value of the above equation can be obtained by equating it with zero, which gives:
Thus, the maximum joint expected total profit of the traditional system under the Stackelberg game strategy is:
4.2. RFID-Based Consignment Policy
In the consignment policy, the manufacturer sends the product to the retailers, and the retailers hold the inventory. The retailer does not have to pay anything to the manufacturer until the products are sold. There are two different phases in the consignment. The first phase is for setting up and reserving the inventory, and the second phase starts after products are sold. The retailer hides information from the manufacturer. The improper information may cause a monetary loss of the total SCM, as well as the individual participants. Thus, the manufacturer insists that the RFID system be installed on the retailer’s side. As a support, the retailer earns a fixed fee and per unit commission per product selling from the manufacturer (Figure 2).
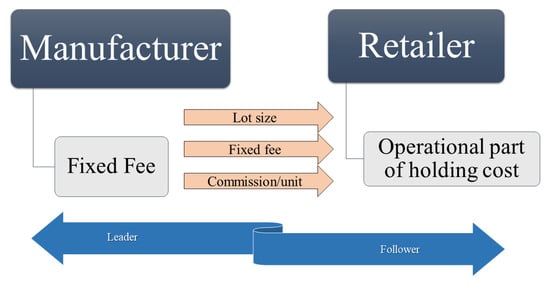
Figure 2.
Consignment policy.
4.2.1. Retailer’s Model
In the consignment policy, the retailer is not taking the responsibility of the product. All products are the full responsibility of the manufacturer, and the retailer sells the product on behalf of the manufacturer’s side. The retailer earns a per unit commission for the product selling. If the commission is , then the commission is:
For selling products for the manufacturer, the retailer gets a fixed fee A from the manufacturer. The lead time crashing cost of the retailer is , and the fixed cost for the installation of the RFID is T. As this installation amount is spent by the retailer, the fixed fee A is always positive for the retailer. If the unit passive tag cost is , then the RFID cost for the tag is . The operational part of the holding cost () is spent by the retailer, i.e., the total holding cost is , and the shortage cost is where is the unit shortage cost. Therefore, the retailer’s expected total profit as the Stackelberg follower for the consignment policy is:
Using Lemma 1, the expected profit of the retailer can be written as:
4.2.2. Manufacturer’s Model
As the manufacturer is a Stackelberg leader, the ownership of the warehouse merchandise is controlled by the manufacturer. The manufacturer controls the financial part of the holding cost (), and even a fixed fee (A) is given by the manufacturer to the retailer. The manufacturer generates the profit by selling the product through the retailer. The revenue of the manufacturer is:
For each unsold product, no fund is transferred to the manufacturer as a negative fixed fee. The production cost of the manufacturer is . Therefore, the manufacturer’s expected total profit as a Stackelberg leader for the consignment policy is:
indicates that decision variables are optimized by the retailer, and the manufacturer uses those values to optimize his/her profit. Again, using Lemma 1, the expected total profit of the manufacturer can be written as:
4.2.3. RFID Based Joint Consignment Policy
Therefore, adding both the profits of the manufacturer and the retailer, the joint expected total profit under consignment policy based on the Stackelberg game can be written as:
4.2.4. Solution Methodology
The maximum profit can be obtained after finding the optimum values of the decision variables. Doing the first order derivative of Equation (19) with respect to gives:
By equating the above equation to zero, the optimum values of is as follows:
Again, the first order derivative of Equation (19) with respect to L gives:
Now, the optimum value is obtained by equating the above equation to zero, i.e.,
Furthermore, the first order derivative of Equation (19) with respect to b obtains:
which gives the optimum value of b as:
5. Numerical Experiments
The numerical study gives the validation of the mathematical results numerically. Some supportive data were taken from Shin et al. [] and Sarkar et al. [] with some rational changes for the convergence of the objective function. For traditional system, the values of the parameters were used as follows: , unit, unit, , unit, , , unit, and unit. The lead time data are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Data for lead time demand.
The optimal solution for the traditional policy is summarized by using the above solution methodology, which is given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Optimal solutions for the traditional system.
For the consignment policy, the values of the parameters were used as follows: , unit, unit, , unit, , , unit, unit, unit, unit, unit, unit, , and . The optimal solution for the consignment policy is summarized by using the above solution methodology, which is given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Optimal solutions for the consignment policy.
In this numerical study, both the result for the traditional system and the consignment policy are given. Depending on the decision variables, this result depicts a very important scenario. In the traditional system, the system gave a good amount of profit. However, after using the consignment policy along with advanced technology RFID, the expected profit was much higher than the traditional policy. The consignment policy was clearly giving higher profit than the traditional one. The optimum lead time was three weeks. The lead time crashing cost was used to reduce this lead time duration. The service was more in the consignment policy than the traditional one. That is, the provided service to the customer by the retailer was more in the consignment policy. The overall result implied that the effect of the information sharing was reduced. This implied that the combination of the consignment policy and the RFID gave a profit goal within the unreliable SCM.
6. Sensitivity Analysis
In order to analyze the impact of the change due to key parameters p (retail price), (retailer’s holding cost for consignment policy), (retailer’s shortage cost for consignment policy), (shortage cost of manufacturer under consignment policy), (goodwill loss for manufacturer under consignment policy), k (manufacturing cost), T (fixed cost of RFID implementation), and (cost of one passive RFID tag), on the economic policies, in-depth sensitivity analysis were done numerically. The sensitivity analysis was done by varying to for the individual parameter by keeping all others unchanged. The most sensitive parameter was the retail price p. The positive changes brought more joint profit in the coordination case and vice versa for the negative percentage changes. The least sensitive parameter was the holding cost for manufacturer under the consignment policy , i.e., the changes in the joint total profit were much less for the changing of the parameter . As the unreliability was solved, the holding cost became less sensitive. Figure 3 interprets the sensitivity of the parameters graphically.
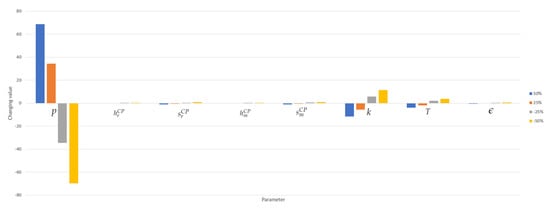
Figure 3.
Sensitivity analysis of the parameters between the range of to .
7. Managerial Implications
The Stackelberg game strategy gives the choice to the follower to optimize his/her decisions first. As the leader is more powerful than the follower, this policy helps the follower make his/her optimum decisions. Here, the manufacturer is the leader, and the retailer is the follower. Because of the power, the manufacturer can survive more easily than the retailer, thus providing more chance of survival to the retailer. This has a long-term effect for the SCM. The loss in the business can terminate the SCM contract between players as the player with less power does not have enough strength to survive the loss. Beside this, the consignment policy with the combination of RFID earns more joint total profit than the traditional one. The retailer only sells products on behalf of the manufacturer. Thus, if the retailer faces loss, the business will no longer exist because the retailer has some expenditure that he/she has to bear. The RFID technology succeeds in bringing the actual information regarding the products. The real-time tracking of each product, as well as availability help to gather the proper information about the product. Thus, information liability is completely emphasized in this SCM. Some insights are listed as follows:
- The chance for the first optimization of the decisions of the follower through the Stackelberg game policy is helpful for the long-term stability of the business between two players of the SCM. This is the strategic policy of the industry manager for a long-term profitable business. Table 3 and Table 4 provide the comparative scenario of the total profit.
- The RFID would help the industry manager reduce the effect of the unreliability of the retailers by tracking the products. The numerical study ensured that RFID implementation earned profit that was more than that of the traditional one. The service was increased in the consignment policy compared to the traditional policy. This implied that the consignment policy was beneficial for the industry.
- The consignment policy proved that the sharing policy of holding cost was effective for the industry. The total profit was increased. RFID provided more security to the industry along with more profit than the traditional policy of business with the Stackelberg policy. Thus, the combination established was more fruitful to the industry than the traditional policy.
- The fixed fee of the consignment policy was really helpful for the retailer. After paying the fixed fee, the joint total profit of the consignment policy was more than the traditional policy (Table 4). This proved that the industry could choose the consignment policy with the fixed fee strategy even if the retailer were unreliable. This earned more profit for the SCM.
8. Conclusions
The proposed model provided the major profit goal for the whole SCM though there was the unreliability issue from the retailer’s side. If the retailer was not giving the proper information of the market demand, the manufacturer could utilize the proposed strategy to obtain the profit in a sustainable way. The proposed model obtained the same results even with improving the standard of the service. The advanced technology was utilized to ensure the profit of the manufacturer. However, the retailer was benefited by the manufacturer through the fixed fee, offered by the manufacturer. It was found that the proposed Stackelberg game policy played an important role in gaining profit for the retailer. The degree of unreliability was not taken into consideration, which was a limitation of this whole research. The degree of unreliability was not considered in this study, which is an immediate future extension from this study. Apart from the domestic SCM, the effect of the RFID within the unreliable global SCM is an extension that is based on outsourcing. The demand, market size uncertainty, and carbon emission were not taken into consideration in this study. Uncertainty may occur in the market demand, which can be solved by using the fuzzy demand structure with the service. The emerging concern about the environment regards carbon emission, which can be considered as a future extension of this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S. & S.K.S.; methodology, B.S. & S.K.S.; software, B.S. & S.K.S.; validation, B.S.; formal analysis, B.S. & S.K.S.; investigation, B.S.; resources, B.S. & S.K.S.; data curation, B.S. & S.K.S.; writing, original draft preparation, B.S. & S.K.S.; writing, review and editing, B.S. & S.K.S.; visualization, B.S. & S.K.S.; supervision, B.S.; project administration, B.S.; funding acquisition, B.S. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| RFID | Radio Frequency IDentification |
| SCM | Supply Chain Management |
| SC | Supply Chain |
Appendix A
Notation
Decision variables
| retailer’s order quantity (units) | |
| b | service by the retailer |
| L | lead time (weeks) |
Parameters
| p | each product’s retail price ($/unit) |
| retailer’s holding cost for traditional policy ($/unit/unit time) | |
| retailer’s shortage cost ($/unit) | |
| retailer’s holding cost for consignment policy ($/unit/unit time) | |
| retailer’s shortage cost for consignment policy ($/unit) | |
| manufacturer’s holding cost for traditional policy ($/unit/unit time) | |
| manufacturer’s shortage cost ($/unit) | |
| manufacturer’s holding cost for consignment policy ($/unit/unit time) | |
| manufacturer’s shortage cost for consignment policy ($/unit) | |
| k | manufacturing cost ($/unit) |
| wholesale price ($/unit) | |
| standard deviation | |
| cost of one passive RFID tag ($/unit) | |
| T | fixed cost of RFID implementation ($) |
| a | scaling parameter |
| shape parameter | |
| lead time crashing cost | |
| A | fixed cost for retailer given by the manufacturer ($) |
| commission for each item sold ($/unit) | |
| unit crashing cost ($/day) | |
| normal duration of lead time | |
| minimum duration of lead time |
Other notation
| profit of retailer under traditional system | |
| profit of retailer under consignment policy | |
| profit of manufacturer under consignment policy | |
| profit of manufacturer under traditional system | |
| joint profit under consignment policy | |
| maximum value of x and 0 | |
| mathematical expectation |
References
- Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E.; González-Velarde, J.L.; Treviño-Garza, G.; Garza-Nuñez, D. Heuristic algorithm based on reduce and optimize approach for a selective and periodic inventory routing problem in a waste vegetable oil collection environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 211, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleizadeh, A.A.; Sadeghi, R. Pricing strategies in the competitive reverse supply chains with traditional and E-channels: A game theoretic approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 215, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Kishore, A.; Khanna, A.; Jaggi, C.K. Strategic defect management for a sustainable green supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleizadeh, A.A.; Yadegari, M.; Sana, S.S. Production models of multiple products using a single machine under quality screening and reworking policies. J. Model. Manag. 2019, 14, 232–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Sarker, B.R. An operational policy for an integrated inventory system under consignment stock policy with controllable lead time and buyers’ space limitation. Comput. Oper. Res. 2013, 40, 2632–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darma Wangsa, I.; Wee, H.M. An integrated vendor–buyer inventory model with transportation cost and stochastic demand. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2018, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, Y.C.; Linh, V.T.; Lu, J.C. Closed-loop supply chain network designs considering RFID adoption. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 113, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Kurata, H. A review of RFID technology and its managerial applications in different industries. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2012, 29, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hou, J.C. Maintaining sensing coverage and connectivity in large sensor networks. Ad Hoc Sens. Wirel. Netw. 2005, 1, 89–124. [Google Scholar]
- Scarf, H. A min-max solution of an inventory problem. Stud. Math. Theory Invent. Prod. 1958. Available online: https://www.rand.org/pubs/papers/P910.html (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Gallego, G.; Moon, I. The distribution free newsboy problem: Review and extensions. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1993, 44, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Chang, H.C. Quality improvement, setup cost and lead-time reductions in lot size reorder point models with an imperfect production process. Comput. Oper. Res. 2002, 29, 1701–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.Y.; Wu, K.S.; Ho, C.H. Integrated vendor–buyer cooperative models with stochastic demand in controllable lead time. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2004, 92, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, Y. Consignment contracting: Who should control inventory in the supply chain? Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 201, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Sana, S.S.; Chaudhuri, K. A distribution-free newsvendor problem with nonlinear holding cost. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2013, 46, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.; Shin, E.; Sarkar, B. Min–max distribution free continuous-review model with a service level constraint and variable lead time. Appl. Math. Comp. 2014, 229, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Guchhait, R.; Sarkar, B.; Mittal, M. Controllable lead time, service level constraint, and transportation discounts in a continuous review inventory model. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 2016, 50, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleizadeh, A.A.; Moshtagh, M.S. A consignment stock scheme for closed loop supply chain with imperfect manufacturing processes, lost sales, and quality dependent return: Multi levels structure. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 217, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, S.K.; Sarkar, B.; Ghosh, S.K. Effect of unequal lot size and variable transportation in an unreliable supply chain management. Mathematics 2020, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, K. Exploring the impacts of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology on supply chain performance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 217, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguerdichian, S.; Koushanfar, F.; Potkonjak, M.; Srivastava, M.B. Coverage problems in wireless ad-hoc sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2001, Anchorage, AK, USA, 22–26 April 2001; Volume 22, pp. 1380–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Guchhait, R.; Pareek, S.; Sarkar, B. How does a radio frequency identification optimize the profit in an unreliable supply chain management? Mathematics 2019, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Tan, C. Pricing, green degree and coordination decisions in a green supply chain with loss aversion. Mathematics 2019, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; He, J.; Huang, F. Impacts of online and offline channel structures on two-period supply chains with strategic consumers. Mathematics 2020, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. Optimal decisions in a retailer Stackelberg supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 187, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jing, C. Backward integration strategy in a retailer Stackelberg supply chain. Omega 2018, 75, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Saren, S.; Sarkar, M.; Seo, Y. A Stackelberg game approach in an integrated inventory model with carbon-emission and setup cost reduction. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.C.Q.; Calado, J.M.F.; Luís Osório, L.F.; Morgado, L.F. RFID together with multi-agent systems to control global value chains. Annu. Rev. Control. 2009, 33, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefeeda, M.; Ahmadi, H. A probabilistic coverage protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Network Protocols, Beijing, China, 16–19 October 2007; Volume 16, pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Glock, C.H. On the use of RFID in the management of reusable containers in closed-loop supply chains under stochastic container return quantities. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 64, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, A.; Absi, N.; Dauzère-Pérès, S. A literature review on the impact of RFID technologies on supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2010, 128, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Zhang, C.; Majumder, A.; Sarkar, M.; Seo, Y.W. A distribution free newsvendor model with consignment policy and retailer’s royalty reduction. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 5025–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).