Integrated Production and Distribution Problem of Perishable Products with a Minimum Total Order Weighted Delivery Time
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
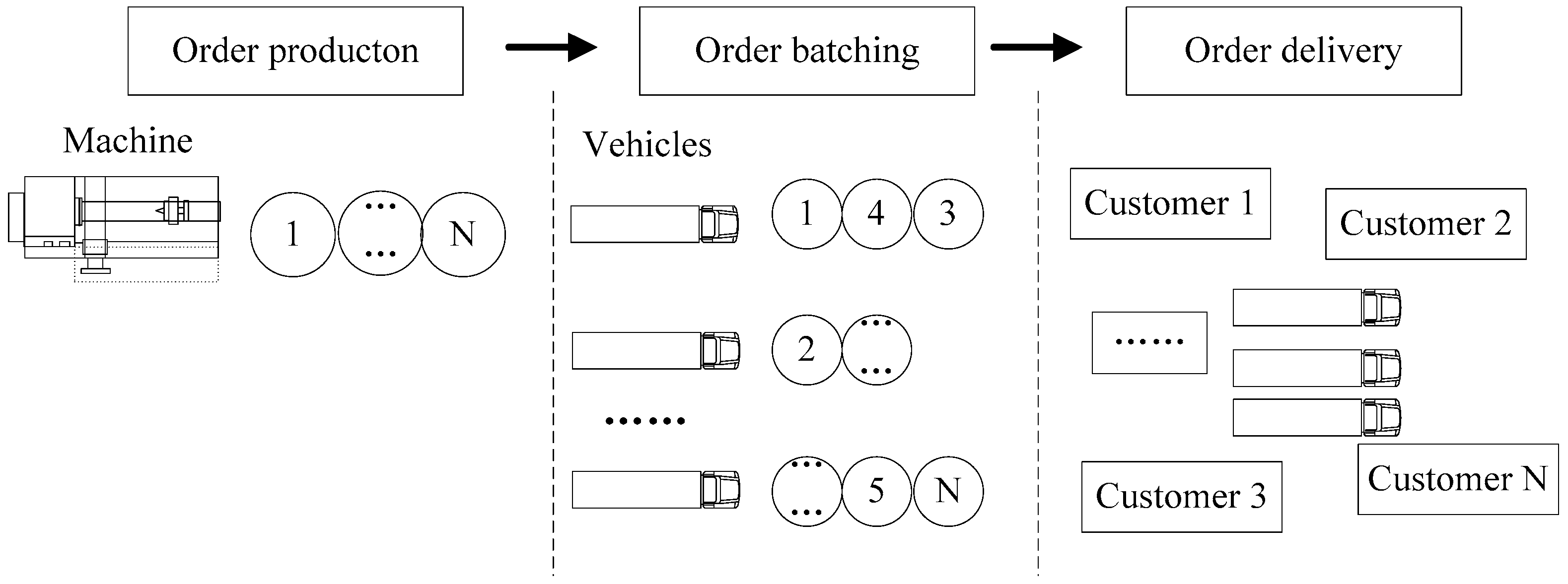
3. Problem and Model Definition
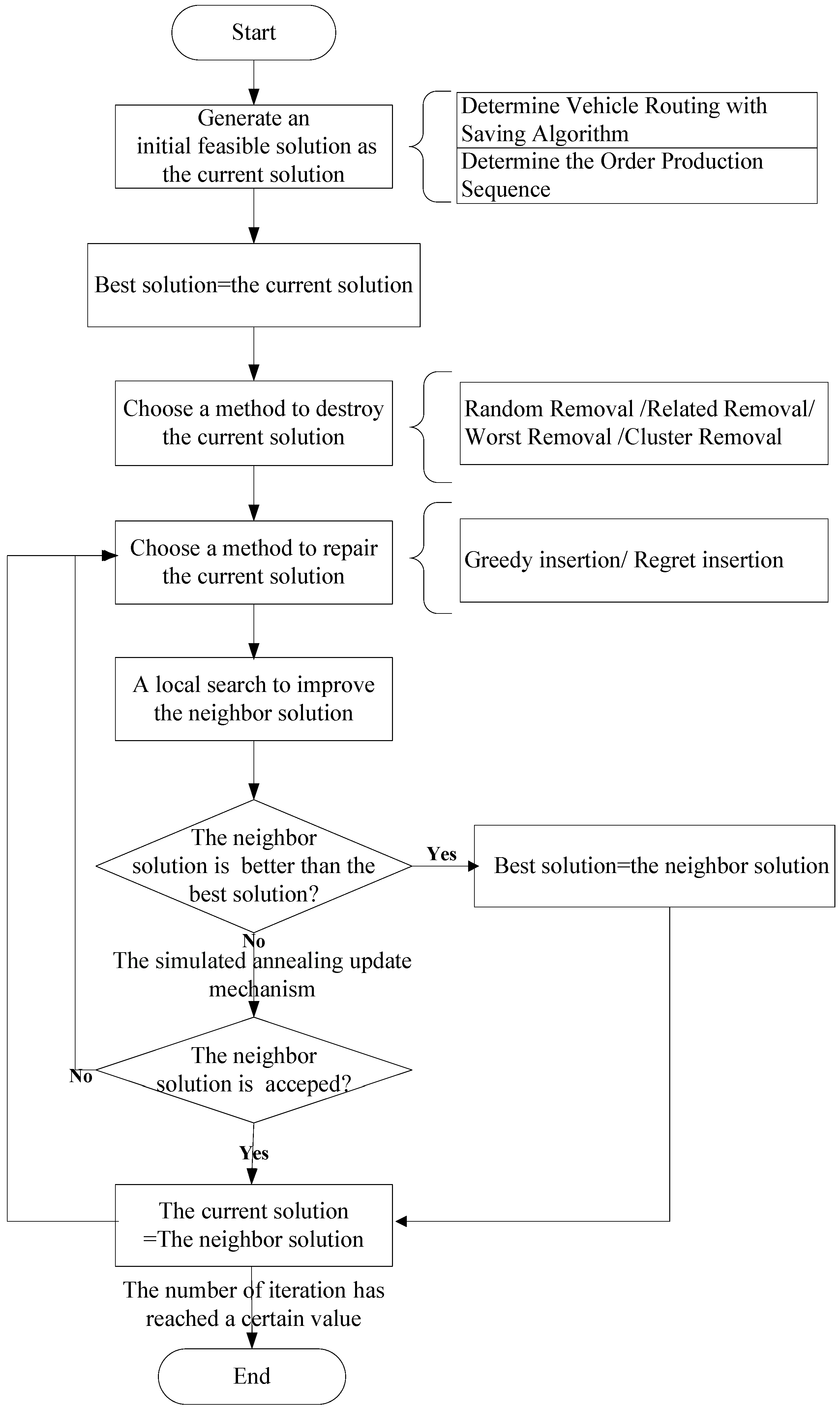
4. An Improved Large Neighborhood Search Algorithm
4.1. Construction of an Initial Solution
4.1.1. Determine Vehicle Routing with a Saving Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Saving Algorithm |
| Set X = 1, C = {1,2, …, n}, S = {sij: i,jC} Insert n customers into n empty routes. Calculate the savings sij between any two customers Sequence sij in S in non-increasing order While S is not empty do Mark the largest savings sij If the onboard quantity of vehicle X does not exceed its capacity when i and j are loaded, then Append the arc (i,j) to the end of route X Remove arc (i,j) and other arcs that contain point i or j from set S else X = X + 1 For each customer c in C, do If customer c is not loaded to any route, then Load the order of customer c into the route that has the largest remaining capacity Return to the route of each vehicle |
4.1.2. Determine the Order Production Sequence
| Algorithm 2: Determine the Order Production Sequence |
|
4.2. Neighborhood Search
4.2.1. Four Removal Heuristics
4.2.2. Two Insertion Heuristics
4.3. A Local Search for Improving the Neighbor Solution
4.4. Acceptance Rule
4.5. Stopping Criterion
5. Computational Results
5.1. Instances Generation
5.2. Results for Small-Sized Instances
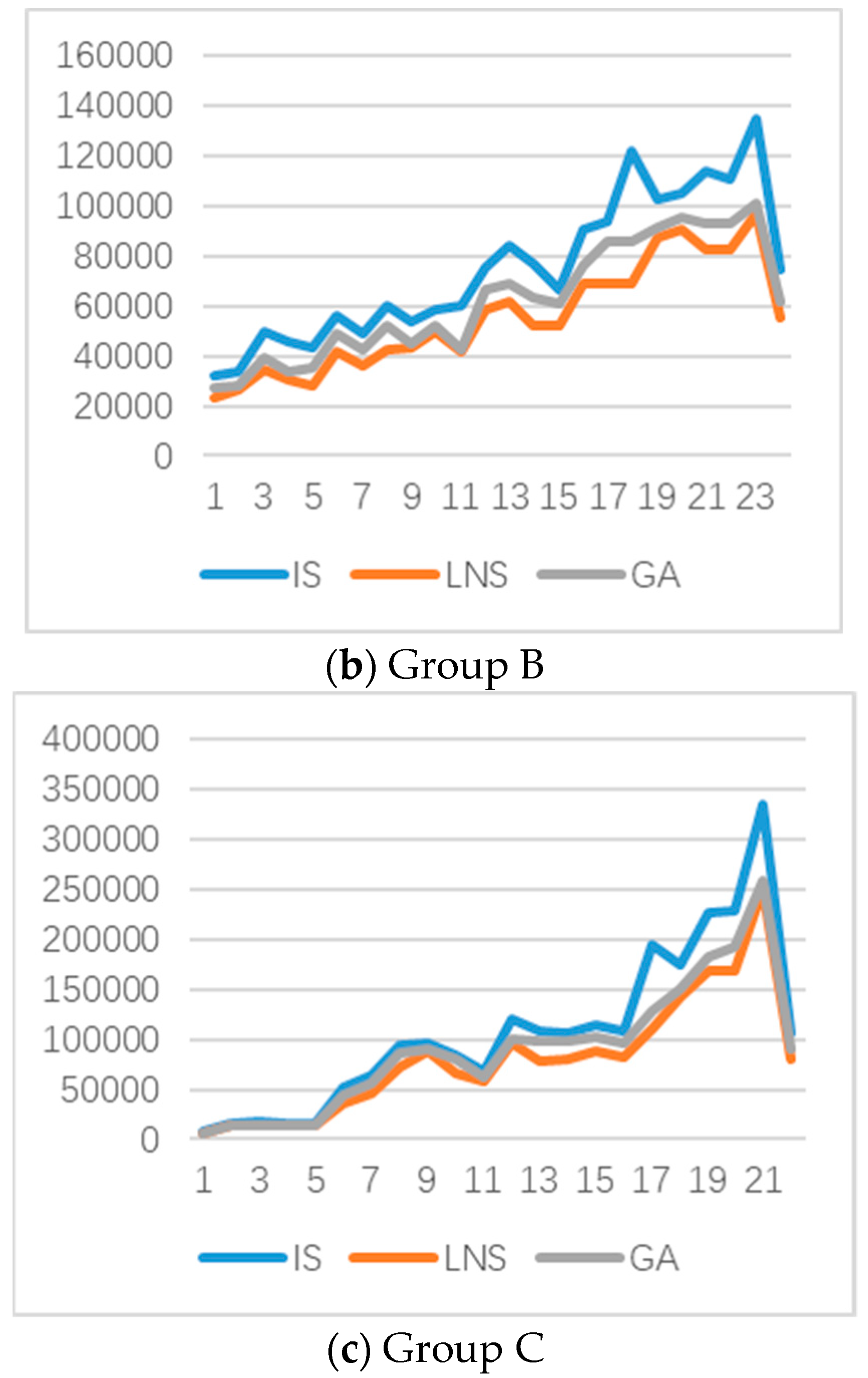
5.3. Results for Larger-Sized Instances
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amorim, P.; Meyr, H.; Almeder, C.; Almada-Lobo, B. Managing perishability in production-distribution planning: A discussion and review. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2013, 25, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoğlan, İ.; Kesen, S.E. The coordinated production and transportation scheduling problem with a time-sensitive product: A branch-and-cut algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 55, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bashiri, M.; Badri, H.; Talebi, J. A new approach to tactical and strategic planning in production–distribution networks. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 1703–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundoor, G.; Chen, Z.L. Scheduling a production-distribution system to optimize the tradeoff between delivery tardiness and total distribution cost. Naval Res. Logist. 2005, 52, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Pundoor, G. Order assignment and scheduling in a supply chain. Oper. Res. 2006, 54, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.P.; Sivakumar, A.I.; Ganesan, V.K. Complexities and algorithms for synchronized scheduling of parallel machine assembly and air transportation in consumer electronics supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 187, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Vairaktarakis, G.L. Integrated scheduling of production and distribution operations. Manag. Sci. 2005, 51, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sel, C.; Bilgen, B. Hybrid simulation and mip based heuristic algorithm for the production and distribution planning in the soft drink industry. J. Manuf. Syst. 2014, 33, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.; Chiang, W.C.; Zepeda, D. Integrating multi-product production and distribution in newspaper logistics. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.C.; Russell, R.; Xu, X.J.; Zepeda, D. A simulation/metaheuristic approach to newspaper production and distribution supply chain problems. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 121, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R. A constraint programming approach to designing a newspaper distribution system. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 145, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yuan, B.; Jiang, Z. Mathematical model and exact algorithm for the home care worker scheduling and routing problem with lunch break requirements. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 558–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Al-e-Hashem, S.M.J.; Rekik, Y. An integrated production scheduling and delivery route planning with multi-purpose machines: A case study from a furniture manufacturing company. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.; Gao, S.; Lei, L. A zero-inventory production and distribution problem with a fixed customer sequence. Ann. Oper. Res. 2008, 159, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismar, H.N.; Laporte, G.; Lei, L.; Sriskandarajah, C. The integrated production and transportation scheduling problem for a product with a short lifespan. J. Comput. 2008, 20, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.K.; Hsueh, C.F.; Chang, M.S. Production scheduling and vehicle routing with time windows for perishable food products. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viergutz, C.; Knust, S. Integrated production and distribution scheduling with lifespan constraints. Ann. Oper. Res. 2014, 213, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo-Filho, M.A.F.; Amorim, P.; Almada-Lobo, B. An adaptive large neighbourhood search for the operational integrated production and distribution problem of perishable products. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devapriya, P.; Ferrell, W.; Geismar, N. Integrated Production and Distribution Scheduling with a Perishable Product. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 259, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacomme, P.; Moukrim, A.; Quilliot, A.; Vinot, M. Supply chain optimisation with both production and transportation integration: Multiple vehicles for a single perishable product. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 4313–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L. Integrated production and outbound distribution scheduling: Review and extensions. Oper. Res. 2010, 58, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Liu, L.; Li, K.; Li, W. A coordinated algorithm for integrated production scheduling and vehicle routing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 5005–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Banerjee, A.; Yang, L. An integrated production–distribution model for a deteriorating inventory item. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 133, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.M.; Lozano, S.; Canca, D. Coordinated scheduling of production and delivery from multiple plants. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2004, 20, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.M.; Lozano, S. Production and delivery scheduling problem with time windows. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2005, 48, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbach, L.; Dorndorf, U.; Pesch, E. Analysis, modeling and solution of the concrete delivery problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 193, 820–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, V.; Doerner, K.F.; Hartl, R.F.; Stoecher, S.W. A hybrid solution approach for ready-mixed concrete delivery. Transp. Sci. 2009, 43, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmid, V.; Doerner, K.F.; Hartl, R.F.; Salazar-González, J.J. Hybridization of very large neighborhood search for ready-mixed concrete delivery problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2010, 37, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Leung, Y.T.; Wang, X. Integrated production and delivery scheduling with disjoint windows. Discret. Appl. Math. 2009, 158, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Geismar, H.N.; Dawande, M.; Sriskandarajah, C. Pool-point distribution of zero-inventory products. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2011, 20, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, P.; Günther, H.O.; Almada-Lobo, B. Multi-objective integrated production and distribution planning of perishable products. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 138, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, P.; Grunow, M.; Günther, H.-O. Integrated production and distribution planning for perishable food products. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2012, 24, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanos, G.M.; Puigjaner, L.; Georgiadis, M.C. Simultaneous production and logistics operations planning in semicontinuous food industries. Omega 2012, 40, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, B.I.; Johnson, A.L.; Lee, K. The nuclear medicine production and delivery problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 236, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismar, H.N.; Murthy, N.M. Balancing Production and Distribution in Paper Manufacturing. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2015, 24, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergosien, Y.; Gendreau, M.; Billaut, J.C. A Benders decomposition-based heuristic for a production and outbound distribution scheduling problem with strict delivery constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves-Moreira, F.; Almada-Lobo, B.; Cordeau, J.F.; Guimarães, L. Solving a large multi-product production-Routing problem with delivery time windows. Omega 2019, 86, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaei, A.; Jolai, F. A Pareto approach for the multi-factory supply chain scheduling and distribution problem. Oper. Res. 2019, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawik, B.; Faulin, J.; Pérez-Bernabeu, E. Multi-Criteria Optimization for Fleet Size with Environmental Aspects. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 27, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizys, R.; Juan, A.A.; Sawik, B.; Calvet, L. A Biased-Randomized Iterated Local Search Algorithm for Rich Portfolio Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.H. Cat swarm optimization for solving flexible job shop scheduling problem. Computer Engineering and Applications. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2018, 54, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.L.; Nagano, M.S. Heuristics for the mixed no-idle flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2019, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres-Cruz, J.; Arias, O.; Guimarans, D.; Riera, D.; Angel, A.J. Rich vehicle routing problem: Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, K.; Liu, Z. A capacitated vehicle routing problem with order available time in e-commerce industry. Eng. Optim. 2017, 49, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehipour, A.; Sörensen, K.; Goos, P.; Bräysy, O. Efficient GRASP+VND and GRASP+VNS metaheuristics for the traveling repairman problem. 4OR 2011, 9, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, W.L.; Li, K.P.; Zou, X.X. A coordinated production and transportation scheduling problem with minimum sum of order delivery times. J. Heuristics 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, G.M.; Laporte, G. An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; Imeson, F. Glns: An effective large neighborhood search heuristic for the generalized traveling salesman problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 87, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimault, A.; Bostel, N.; Lehuédé, F. An adaptive large neighborhood search for the full truckload pickup and delivery problem with resource synchronization. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 88, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, A.P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Dawal, S.Z.M. Multi-objective adaptive large neighborhood search for distributed reentrant permutation flow shop scheduling. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; de Weerdt, M.; Yorke-Smith, N. Time/sequence-dependent scheduling: The design and evaluation of a general purpose tabu-based adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithm. J. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarpour, M.; Dejax, P.; Péton, O. A large neighborhood search heuristic for supply chain network design. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 80, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, X.L.; Laporte, G.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, Y.G. An improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for multiple agile satellites scheduling. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 100, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, S.; Cheraitia, M. Iterated local and very-large-scale neighborhood search for a novel uncapacitated exam scheduling model. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2018, 13, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Wright, J.W. Scheduling of vehicles from a central depot to a number of delivery points. Oper. Res. 1964, 12, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropke, S.; Pisinger, D. A unified heuristic for a large class of vehicle routing problems with backhauls. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 171, 750–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, M.E.; Askin, R.G. Heuristic scheduling of parallel machines with sequence-dependent set-up times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2001, 39, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmelmayr, V.C. Sequential and parallel large neighborhood search algorithms for the periodic location routing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 243, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CPLEX | ILNS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSTANCE CPLEX | Objective | Time (s) | Objective | Time (s) | Optimal? |
| Small-n5-k2 | 302 | 5 | 302 | 3 | Yes |
| Small-n6-k2 | 349 | 5 | 349 | 3 | Yes |
| Small-n7-k2 | 397 | 7 | 397 | 3 | Yes |
| Small-n8-k2 | 720 | 9 | 720 | 3 | Yes |
| Small-n9-k2 | 1116 | 210 | 1116 | 3 | Yes |
| Small-n10-k2 | 1225 | 1381 | 1225 | 3 | Yes |
| IS | ILNS | GA | Gap1 | Gap2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSTANCE | S1 | T1 (s) | S2 | T2 (s) | S3 | (S1-S2)/S1 × 100% | (S3-S2)/S3 × 100% |
| A-n32-k5 | 39,950 | 0.1 | 26,793 | 21 | 30,560 | 32.93% | 12.33% |
| A-n33-k5 | 36,365 | 0.1 | 27,038 | 27 | 27,104 | 25.65% | 0.24% |
| A-n33-k6 | 38,089 | 0.1 | 27,500 | 25 | 28,257 | 27.80% | 2.68% |
| A-n34-k5 | 39,784 | 0.1 | 27,097 | 26 | 27,953 | 31.89% | 3.06% |
| A-n36-k5 | 41,233 | 0.1 | 28,538 | 30 | 29,629 | 30.79% | 3.68% |
| A-n37-k5 | 49,801 | 0.1 | 27,846 | 30 | 31,928 | 44.09% | 12.79% |
| A-n37-k6 | 45,931 | 0.1 | 37,024 | 33 | 37,389 | 19.39% | 0.98% |
| A-n38-k5 | 51,750 | 0.1 | 34,040 | 33 | 35,199 | 34.22% | 3.29% |
| A-n39-k5 | 48,215 | 0.1 | 36,046 | 35 | 39,128 | 25.24% | 7.88% |
| A-n39-k6 | 47,778 | 0.1 | 33,226 | 36 | 35,404 | 30.46% | 6.15% |
| A-n44-k6 | 63,887 | 0.1 | 46,951 | 40 | 47,775 | 26.51% | 1.72% |
| A-n45-k6 | 67,183 | 0.1 | 52,041 | 40 | 56,139 | 22.54% | 7.30% |
| A-n45-k7 | 60,960 | 0.1 | 44,569 | 41 | 45,427 | 26.89% | 1.89% |
| A-n46-k7 | 65,123 | 0.1 | 44,634 | 51 | 47,779 | 31.46% | 6.58% |
| A-n48-k7 | 72,441 | 0.1 | 50,220 | 52 | 54,918 | 30.67% | 8.55% |
| A-n53-k7 | 79,839 | 0.1 | 57,642 | 52 | 66,360 | 27.80% | 13.14% |
| A-n54-k7 | 81,834 | 0.1 | 65,353 | 53 | 65,671 | 20.14% | 0.48% |
| A-n55-k9 | 88,571 | 0.1 | 67,390 | 56 | 79,548 | 23.91% | 15.28% |
| A-n60-k9 | 105,298 | 0.1 | 77,041 | 56 | 93,972 | 26.84% | 18.02% |
| A-n61-k9 | 107,332 | 0.1 | 95,840 | 58 | 96,831 | 10.71% | 1.02% |
| A-n62-k8 | 112,022 | 0.1 | 79,393 | 58 | 92,145 | 29.13% | 13.84% |
| A-n63-k9 | 126,931 | 0.1 | 103,647 | 58 | 111,543 | 18.34% | 7.08% |
| A-n63-k10 | 109,440 | 0.1 | 82,116 | 60 | 97,488 | 24.97% | 15.77% |
| A-n64-k9 | 106,569 | 0.1 | 83,404 | 60 | 95,853 | 21.74% | 12.99% |
| A-n65-k9 | 115,155 | 0.1 | 99,977 | 65 | 102,061 | 13.18% | 2.04% |
| A-n69-k9 | 112,302 | 0.1 | 88,760 | 68 | 96,742 | 20.96% | 8.25% |
| A-n80-k10 | 177,768 | 0.1 | 126,095 | 70 | 136,001 | 29.07% | 7.28% |
| Average | 77,465 | 0.1 | 58,156 | 46 | 63,289 | 26.20% | 7.20% |
| IS | ILNS | GA | GA | Gap2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSTANCE | S1 | T1 (s) | S2 | T2 (s) | S3 | (S1-S2)/S1 × 100% | (S3-S2)/S3 × 100% |
| B-n31-k5 | 32,037 | 0.1 | 23,086 | 20 | 27,400 | 27.94% | 15.74% |
| B-n34-k5 | 34,005 | 0.1 | 26,357 | 21 | 27,840 | 22.49% | 5.33% |
| B-n35-k5 | 49,824 | 0.1 | 34,661 | 21 | 38,894 | 30.43% | 10.88% |
| B-n38-k6 | 45,343 | 0.1 | 30,791 | 22 | 33,623 | 32.09% | 8.42% |
| B-n39-k5 | 43,406 | 0.1 | 28,290 | 24 | 35,428 | 34.82% | 20.15% |
| B-n41-k6 | 56,097 | 0.1 | 41,899 | 24 | 48,512 | 25.31% | 13.63% |
| B-n43-k6 | 49,010 | 0.1 | 36,450 | 25 | 42,848 | 25.63% | 14.93% |
| B-n44-k7 | 59,878 | 0.1 | 42,445 | 27 | 51,955 | 29.11% | 18.30% |
| B-n45-k5 | 53,701 | 0.1 | 43,150 | 24 | 44,859 | 19.65% | 3.81% |
| B-n45-k6 | 58,183 | 0.1 | 50,010 | 24 | 52,044 | 14.05% | 3.91% |
| B-n50-k7 | 59,880 | 0.1 | 41,784 | 28 | 42,563 | 30.22% | 1.83% |
| B-n50-k8 | 75,327 | 0.1 | 58,666 | 31 | 66,615 | 22.12% | 11.93% |
| B-n51-k7 | 84,392 | 0.1 | 61,684 | 32 | 69,275 | 26.91% | 10.96% |
| B-n52-k7 | 76,791 | 0.1 | 52,150 | 34 | 63,476 | 32.09% | 17.84% |
| B-n56-k7 | 66,308 | 0.1 | 51,942 | 31 | 61,185 | 21.67% | 15.11% |
| B-n57-k7 | 90,875 | 0.1 | 69,093 | 35 | 76,394 | 23.97% | 9.56% |
| B-n57-k9 | 93,921 | 0.1 | 69,093 | 43 | 85,416 | 26.43% | 19.11% |
| B-n63-k10 | 121,647 | 0.1 | 68,553 | 48 | 85,632 | 43.65% | 19.94% |
| B-n64-k9 | 102,957 | 0.1 | 87,335 | 53 | 91,611 | 15.17% | 4.67% |
| B-n66-k9 | 105,353 | 0.1 | 90,749 | 51 | 95,558 | 13.86% | 5.03% |
| B-n67-k10 | 113,652 | 0.1 | 82,307 | 52 | 93,042 | 27.58% | 11.54% |
| B-n68-k9 | 110,826 | 0.1 | 82,378 | 61 | 92,653 | 25.67% | 11.09% |
| B-n78-k10 | 134,927 | 0.1 | 97,012 | 66 | 100,653 | 28.10% | 3.62% |
| AVERAGE | 74,710 | 0.1 | 55,212 | 35 | 62,064 | 26.04% | 11.19% |
| IS | ILNS | GA | Gap1 | Gap2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSTANCE | S1 | T1 (s) | S1 | T2 (s) | S3 | (S1-S2)/S1 × 100% | (S3-S2)/S3 × 100% |
| P-n16-k8 | 7375 | 0.1 | 5814 | 2 | 6673 | 21.17% | 12.87% |
| P-n19-k2 | 15,717 | 0.1 | 13,190 | 2 | 13,679 | 16.08% | 3.57% |
| P-n20-k2 | 17,867 | 0.1 | 13,616 | 2 | 14,814 | 23.79% | 8.09% |
| P-n21-k2 | 16,059 | 0.1 | 13,420 | 3 | 14,113 | 16.43% | 4.91% |
| P-n22-k2 | 16,968 | 0.1 | 13,272 | 3 | 14,427 | 21.78% | 8.01% |
| P-n40-k5 | 52,858 | 0.1 | 36,417 | 26 | 44,662 | 31.10% | 18.46% |
| P-n45-k5 | 63,627 | 0.1 | 46,808 | 25 | 55,816 | 26.43% | 16.14% |
| P-n50-k7 | 93,494 | 0.1 | 71,981 | 31 | 86,726 | 23.01% | 17.00% |
| P-n50-k8 | 95,320 | 0.1 | 87,236 | 34 | 89,506 | 8.48% | 2.54% |
| P-n50-k10 | 83,723 | 0.1 | 65,187 | 45 | 79,185 | 22.14% | 17.68% |
| P-n51-k10 | 68,048 | 0.1 | 58,944 | 47 | 62,206 | 13.38% | 5.24% |
| P-n55-k7 | 119,836 | 0.1 | 95,366 | 52 | 100,486 | 20.42% | 5.10% |
| P-n55-k8 | 108,155 | 0.1 | 78,880 | 56 | 97,682 | 27.07% | 19.25% |
| P-n55-k10 | 105,705 | 0.1 | 79,318 | 56 | 97,313 | 24.96% | 18.49% |
| P-n60-k10 | 114,276 | 0.1 | 87,847 | 51 | 102,735 | 23.13% | 14.49% |
| P-n60-k15 | 107,808 | 0.1 | 82,345 | 52 | 95,938 | 23.62% | 14.17% |
| P-n65-k10 | 194,119 | 0.1 | 111,145 | 55 | 128,938 | 42.74% | 13.80% |
| P-n70-k10 | 174,502 | 0.1 | 143,062 | 55 | 151,189 | 18.02% | 5.38% |
| P-n76-k4 | 227,017 | 0.1 | 167,543 | 60 | 182,731 | 26.20% | 8.31% |
| P-n76-k5 | 228,876 | 0.1 | 168,409 | 62 | 192,277 | 26.42% | 12.41% |
| P-n101-k4 | 334,428 | 0.1 | 249,633 | 91 | 258,090 | 25.36% | 3.28% |
| AVERAGE | 106,942 | 0.1 | 80,449 | 39 | 89,961 | 22.94% | 10.91% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Liu, S. Integrated Production and Distribution Problem of Perishable Products with a Minimum Total Order Weighted Delivery Time. Mathematics 2020, 8, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020146
Liu L, Liu S. Integrated Production and Distribution Problem of Perishable Products with a Minimum Total Order Weighted Delivery Time. Mathematics. 2020; 8(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ling, and Sen Liu. 2020. "Integrated Production and Distribution Problem of Perishable Products with a Minimum Total Order Weighted Delivery Time" Mathematics 8, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020146
APA StyleLiu, L., & Liu, S. (2020). Integrated Production and Distribution Problem of Perishable Products with a Minimum Total Order Weighted Delivery Time. Mathematics, 8(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8020146






