A Delayed Epidemic Model for Propagation of Malicious Codes in Wireless Sensor Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Positivity and Boundedness
3. Lyapunov Stability Analysis
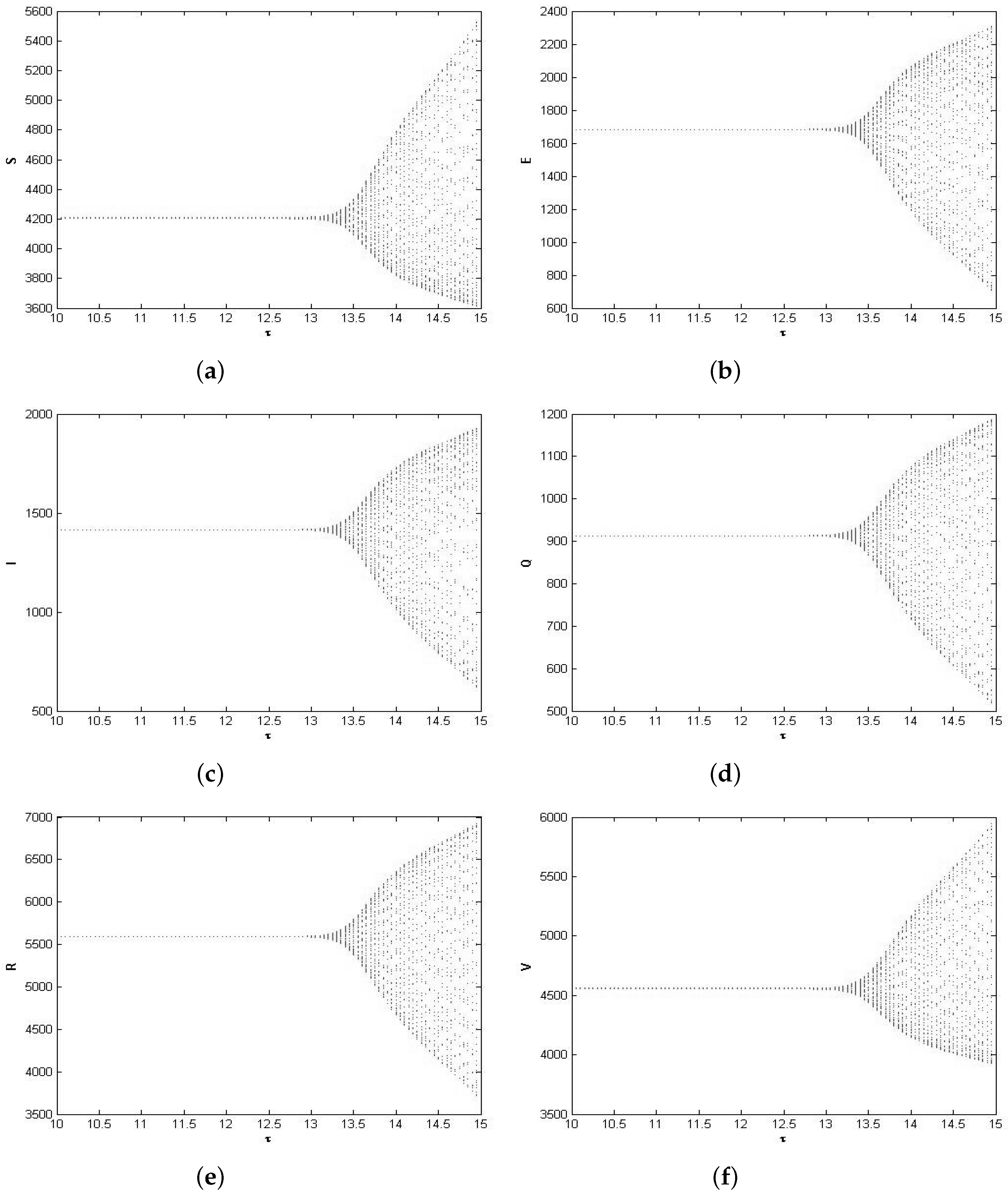
4. Existence of Hopf Bifurcation
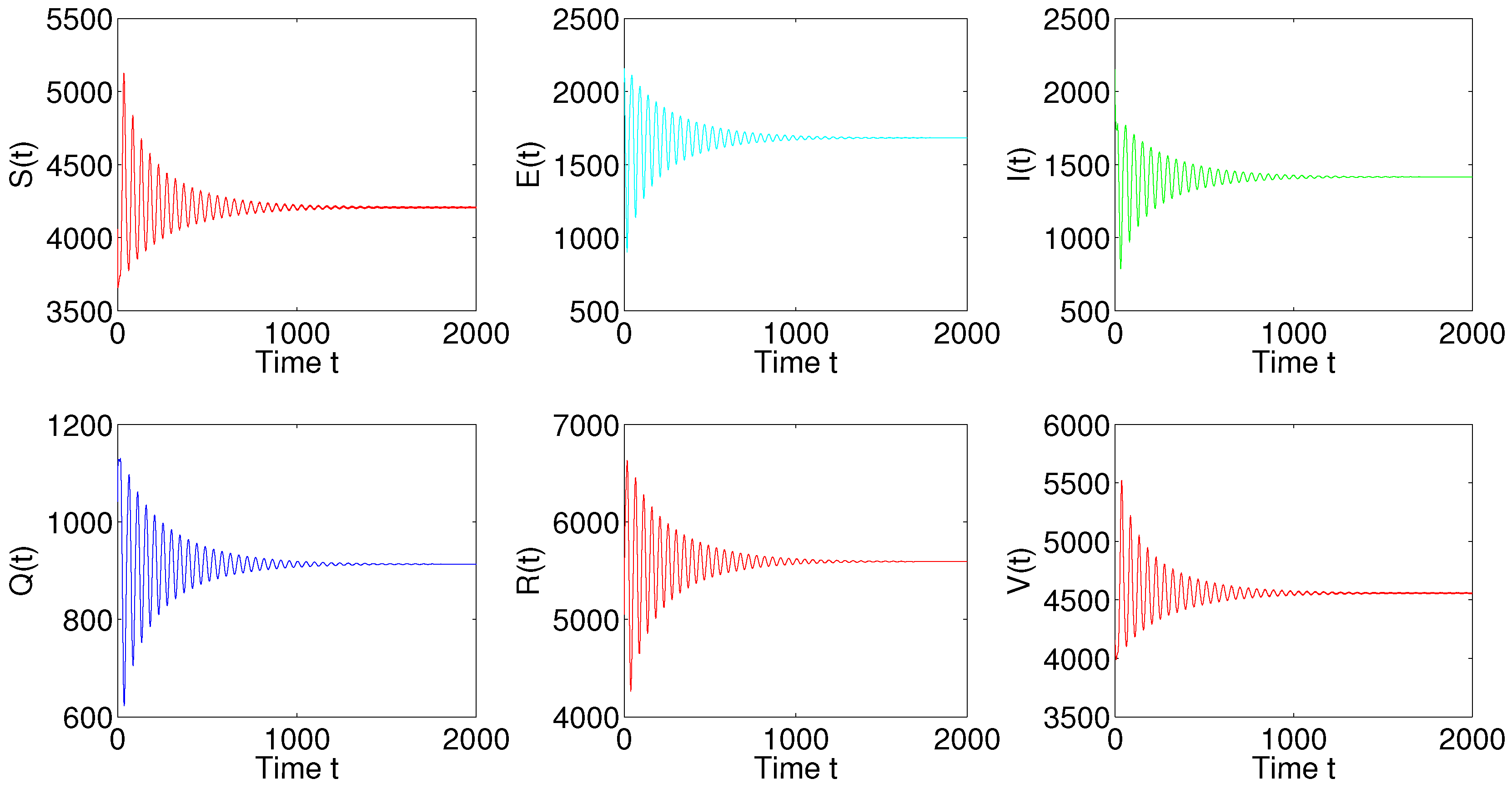
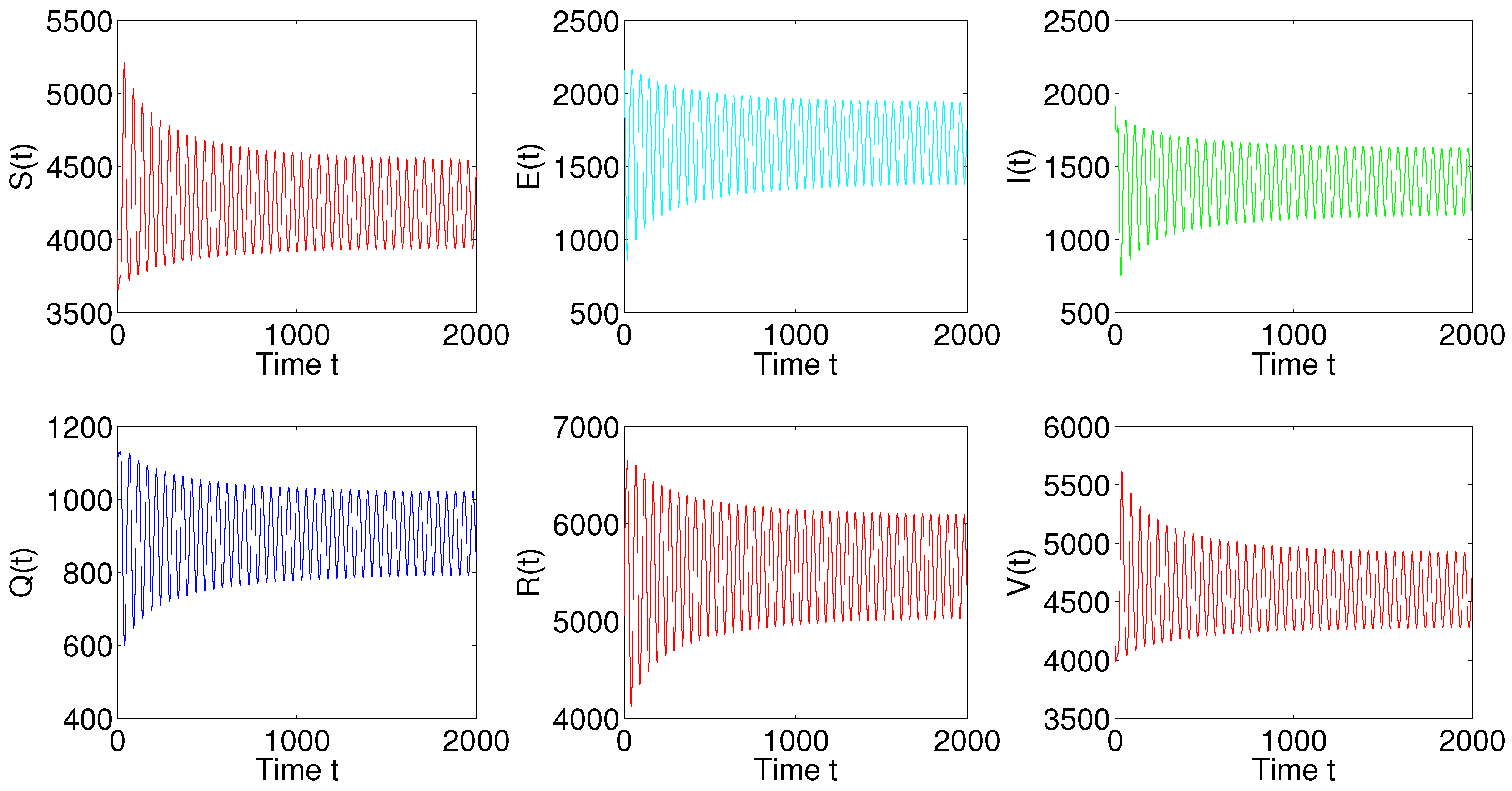
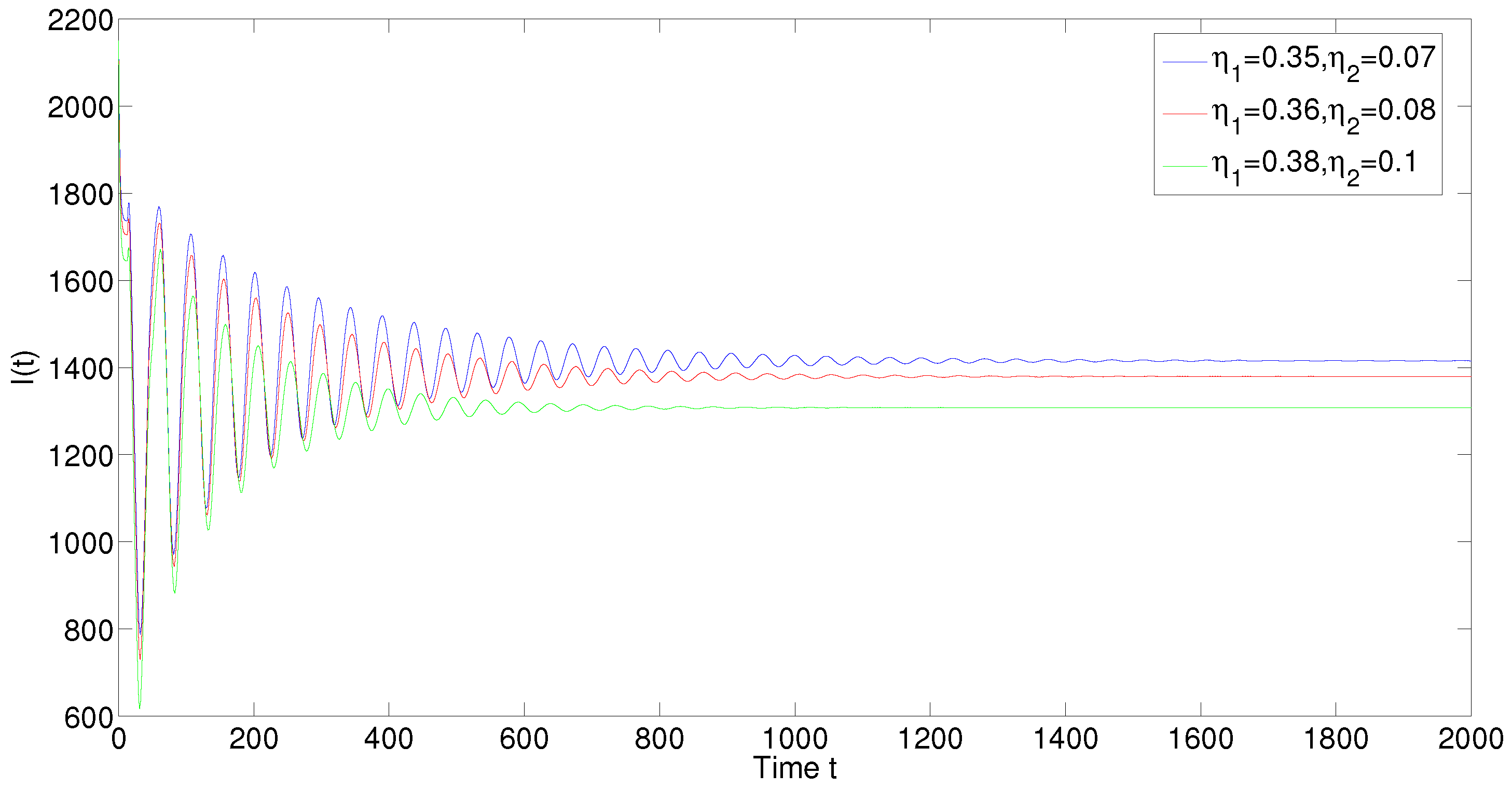
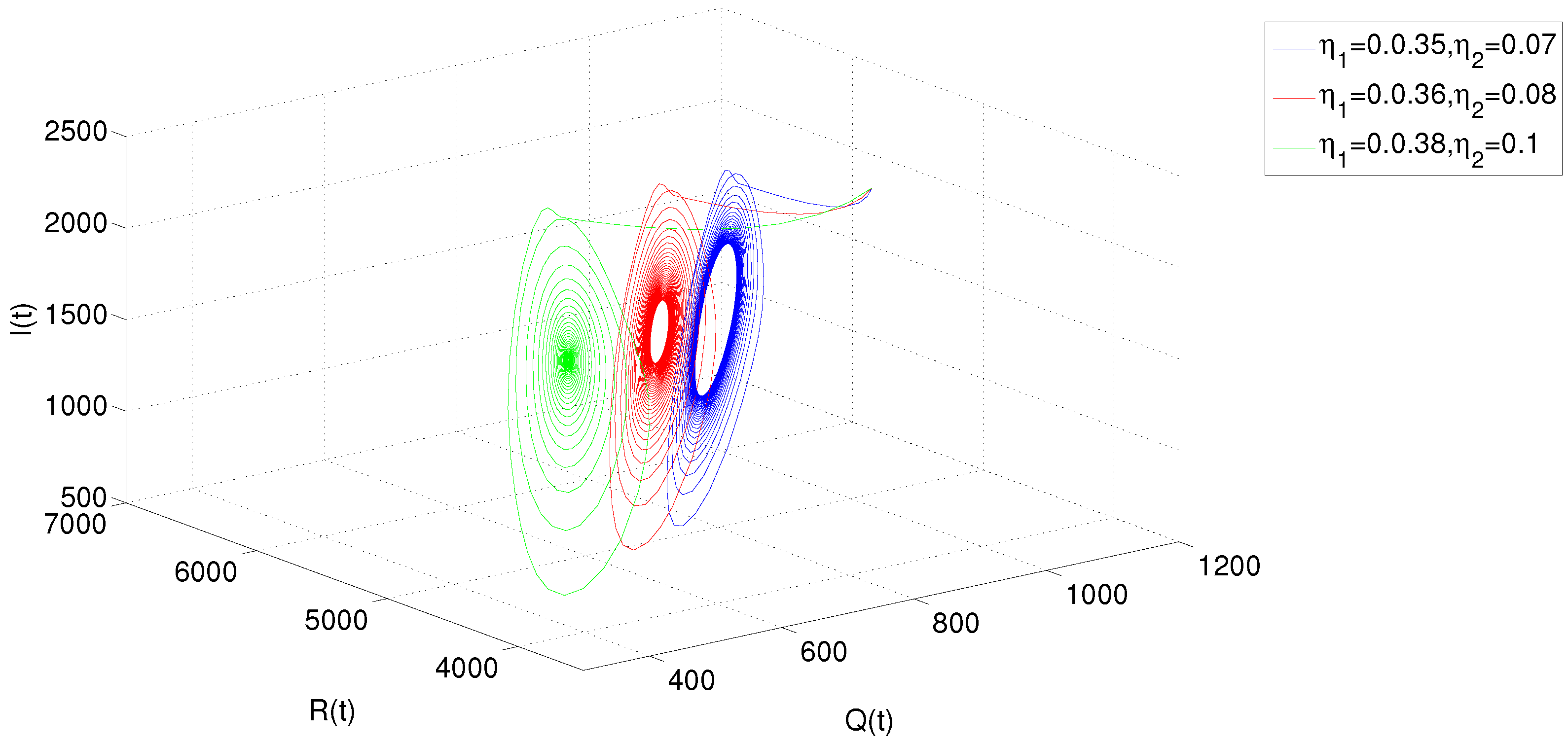
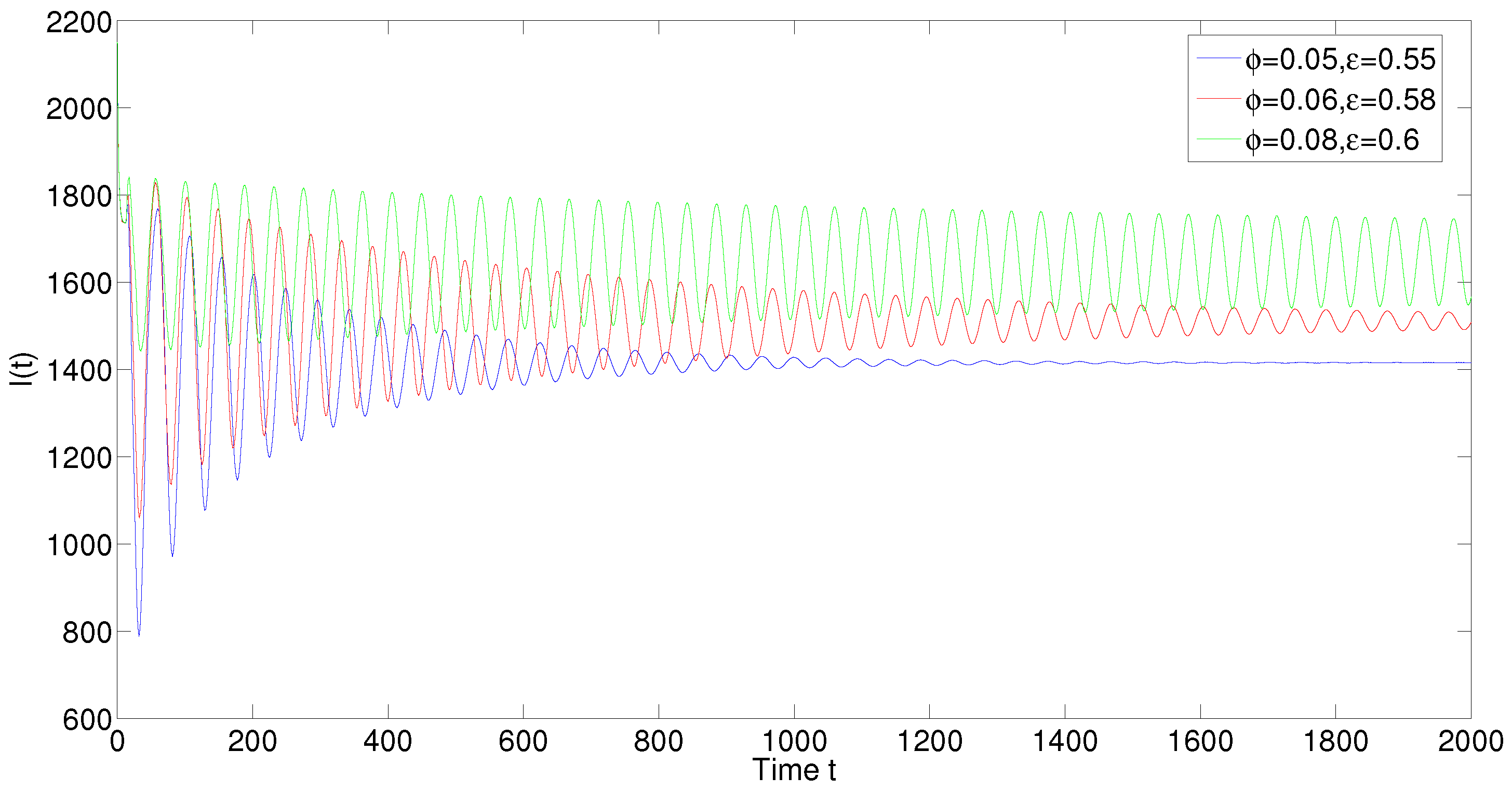
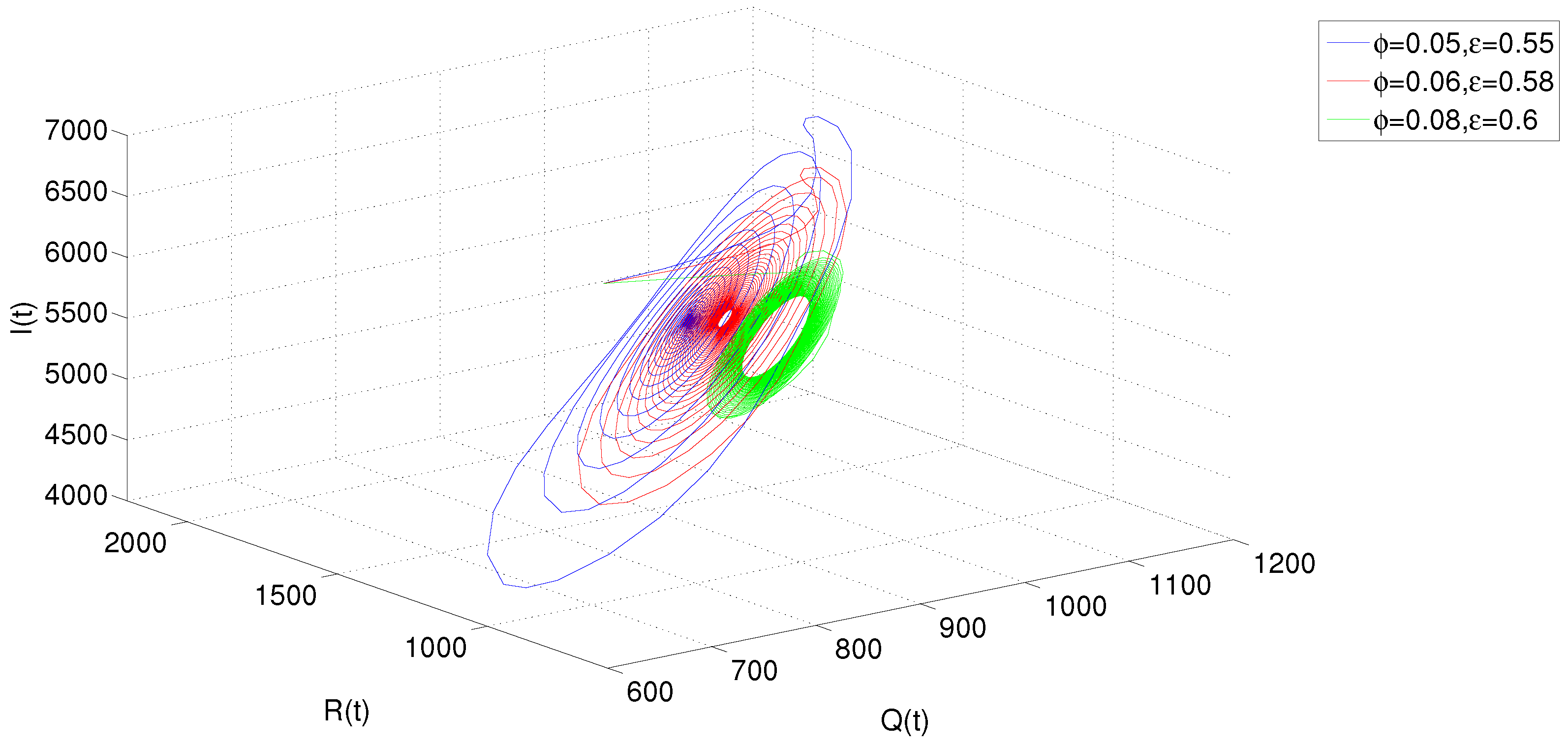
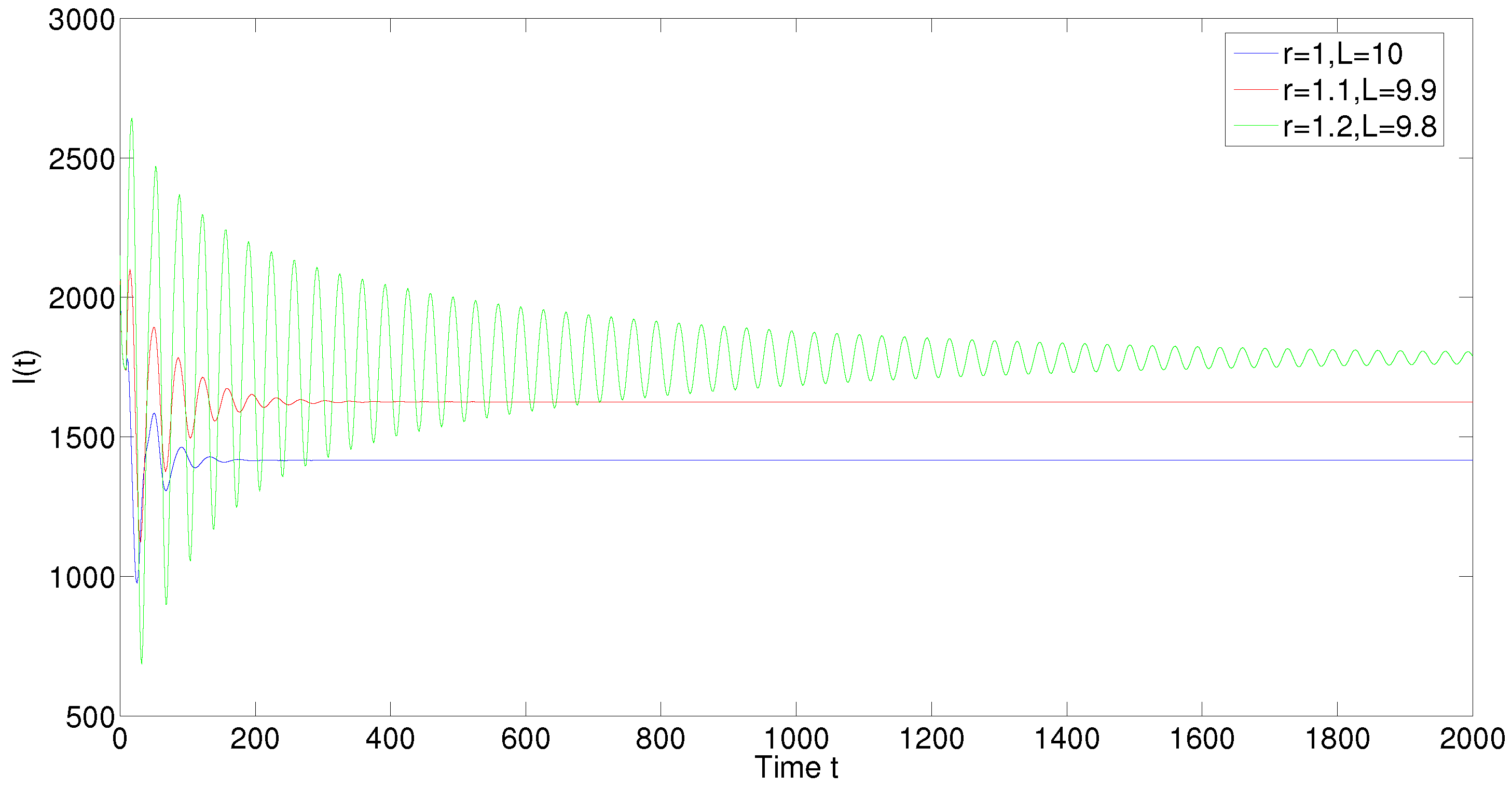
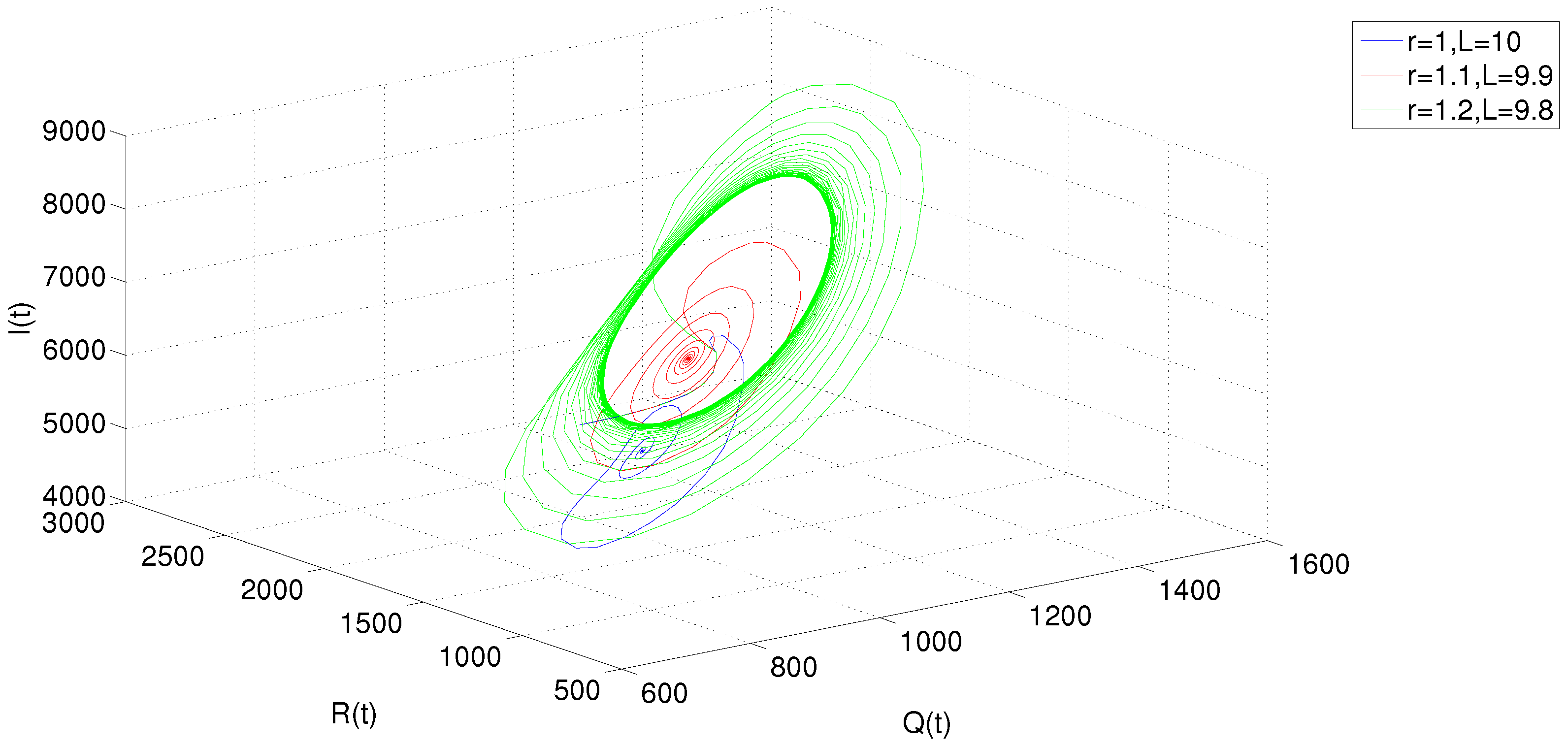
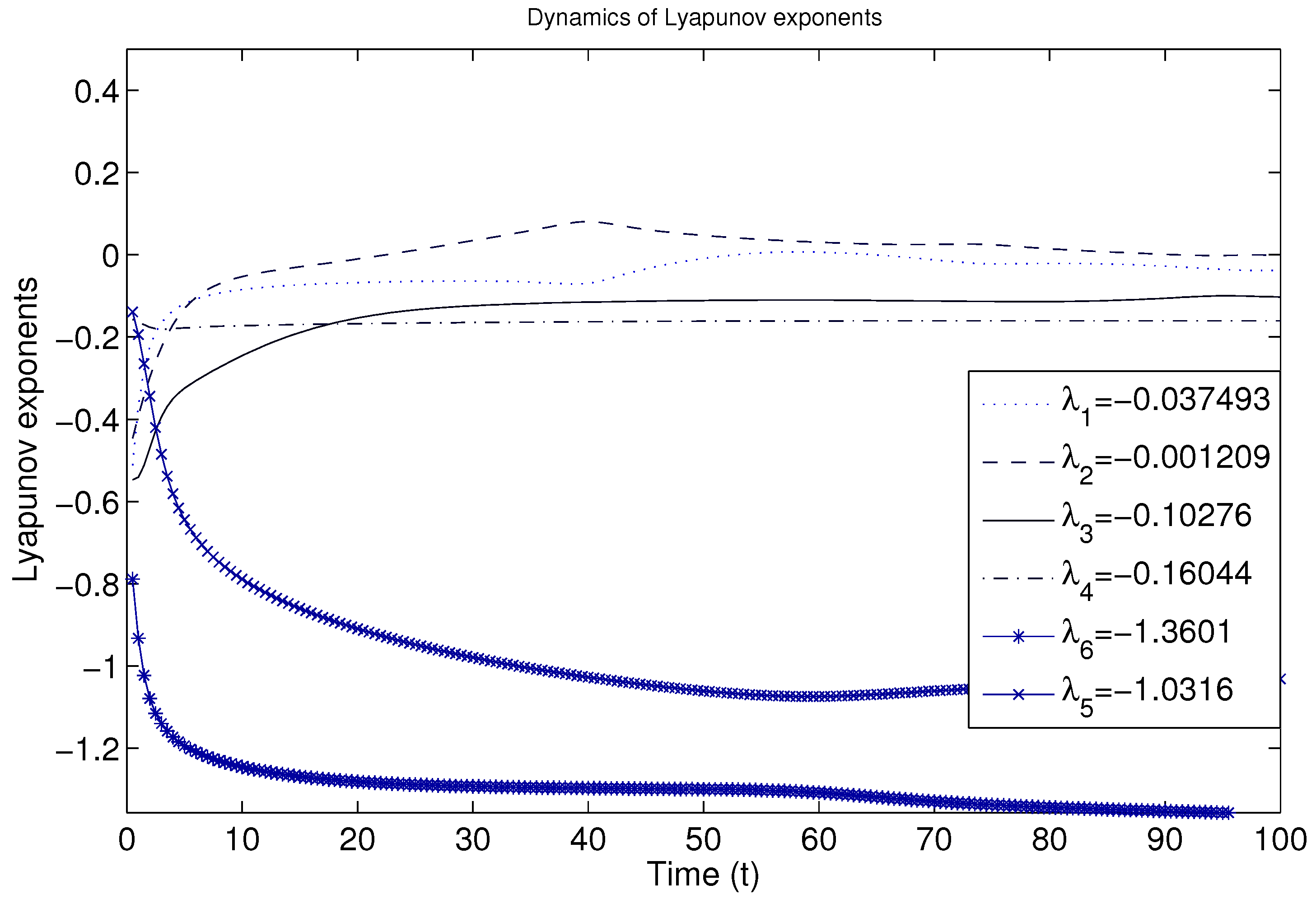
5. Numerical Simulations
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Keshri, A.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Mallick, D.K. Library formation of known malicious attacks and their future variants. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, D.; Hammouch, Z.; Atangana, A. A fractional epidemiological model for computer viruses pertaining to a new fractional derivative. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 316, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, A.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Mallick, D.K. A predator-prey model on the attacking behavior of malicious objects in wireless nanosensor networks. Nano Commun. Netw. 2018, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybercrime-Report. Available online: http://cyberseurityventures.com/2015-wp/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/2017-Cybercrime-Report.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Khanh, N.H. Dynamics of a worm propagation model with quarantine in wireless sensor networks. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2016, 10, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Kershi, N. Mathematical model on the transmission of worms in wireless sensor network. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 3, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Pandey, S.K. Dynamic model of worms with vertical transmission in computer network. Appl. Math. Comput. 2011, 217, 8438–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Fu, P.; Dou, C.S.; Li, Q.; Hu, G.W.; Xia, S.T. Design and analysis of SEIQR worm propagation model in mobile internet. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 43, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, N.; Mishra, B.K. Stability analysis of a predator-prey model in wireless sensor network. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2014, 91, 928–943. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.X.; Yang, X.F. The spread of computer viruses under the influence of removable storage devices. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 3914–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroya, Y.; Li, H.X.; Kuziya, T. On global stabiity of a nonresident computer virus model. Acta Math. Sci. 2014, 34B, 1427–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.W.; Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, C.G.; Ma, J.F. Stability analysis of an e-SEIAR model with point-to-group worm propagation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 20, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Q.; Wu, Y.H. Global exponential stability of nonresident computer virus models. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2017, 34, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, U.; Ali, M.; Ahmed, N.; Rafiq, M. Numerical modeling of susceptible latent breaking-out quarantine computer virus epidemic dynamics. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Li, C.D. A novel computer virus model with generic nonlinear burst rate. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Complex Systems and Networks, Doha, Qatar, 8–10 December 2017; pp. 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.F.; Liu, B.; Gan, C.Q. Global stability of an epidemic model of computer virus. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 456320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Hattaf, K.; Sun, J.T. Optimal control of a delayed SLBS computer virus model. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2015, 427, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroya, Y.; Kuniya, T. Global stability of nonresident computer virus models. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2015, 38, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.X.; Guo, W. A stochastic worm model. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 64, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, J. The stochastic SIRA model for computer viruses. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 232, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafazzoli, T.; Sadeghiyan, B.A. Stochastic model for the size of worm origin. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2016, 9, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarabadi, A.; Azgomi, M.A. A stochastic epidemiological model for the propagation of active worms considering the dynamicity of network topology. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2015, 8, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Deng, S.W. A stochastic dynamic model of computer viruses. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, 2012, 264874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, N.; Gupta, A.; Mishra, B.K. Impact of reduced scale free network on wireless sensor network. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 463, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Azgomi, M.A.; Rahmani, A.T. Malware propagation modeling considering software diversity andimmunization. J. Comput. Sci. 2016, 13, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.M.; Huang, H.T. Optimal control strategy for a novel computer virus propagation model on scale-free networks. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 451, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.P.; Song, L.P.; Zhao, Q.S.; Wang, H.B. Modeling and stability analysis of worm propagation in wireless sensor network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 129598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.P.; Awasthi, S.; Ojha, R.P.; Srivastava, P.K.; Katiyar, S. Stability analysis of SIDR model for worm propagation in wireless sensor network. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokoye, C.H.; Ejiofor, W.E.; Orji, R. Investigating the effect of uniform random distribution of nodes in wireless sensor networks usingan epidemic worm model. In Proceedings of the CORI’16, Ibadan, Nigeria, 7–9 September 2016; pp. 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Awasthi, A.K.; Singh, K.; Srivastava, P.K. Modeling and analysis of worm propagation in wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 98, 2535–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, R.P.; Sanyal, G.; Srivastava, P.K.; Sharma, K. Design and analysis of modified SIQRS model for performance study of wireless sensor network. Scalable Comput. 2017, 18, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Tyagi, I. Defending against malicious threats in wireless sensor network: A mathematical model. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 2014, 6, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokoye, C.H.; Umeh, I.I. The SEIQR-V Model: On a More Accurate Analytical Characterization of Malicious Threat Defense. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 2017, 12, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keshri, N.; Mishra, B.K. Two time-delay dynamic model on the transmission of malicious signals in wireless sensor network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2014, 68, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Bi, D.J. Bifurcation analysis in a delayed computer virus model with the effect of external computers. Adv. Differ. Equat. 2015, 317, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Bi, D.J. Hopf bifurcation of a computer virus spreading model in the network with limited anti-virus ability. Adv. Differ. Equat. 2017, 183, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Chai, S.X. Hopf bifurcation of an SEIRS epidemic model with delays and vertical transmission in the network. Adv. Differ. Equat. 2016, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.X.; Lin, Y.P.; Zhao, H.T.; Khalique, C.M. Global stability and Hopf bifurcation of a delayed computer virus propagation model with saturation incidence rate and temporary immunity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2016, 30, 1640009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.J.; Kundu, S.; Maitra, S. Dynamics of a delayed SEIQ epidemic model. Adv. Differ. Equat. 2018, 336, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassard, B.D.; Kazarinoff, N.D.; Wan, Y.H. Theory and Applications of Hopf Bifurcation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.G.; Yang, X.F.; Yang, L.X.; Xu, Y.H.; Yang, F.Z. A delayed computer virus propagation model and its dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2012, 45, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Song, L.M. Dynamics of a delayed worm propagation model with quarantine. Adv. Differ. Equat. 2017, 155, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Kumari, S. Bifurcation analysis of an e-epidemic model in wireless sensor network. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2018, 95, 1775–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Kundu, S.; Wei, R. A Delayed Epidemic Model for Propagation of Malicious Codes in Wireless Sensor Network. Mathematics 2019, 7, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050396
Zhang Z, Kundu S, Wei R. A Delayed Epidemic Model for Propagation of Malicious Codes in Wireless Sensor Network. Mathematics. 2019; 7(5):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050396
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zizhen, Soumen Kundu, and Ruibin Wei. 2019. "A Delayed Epidemic Model for Propagation of Malicious Codes in Wireless Sensor Network" Mathematics 7, no. 5: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050396
APA StyleZhang, Z., Kundu, S., & Wei, R. (2019). A Delayed Epidemic Model for Propagation of Malicious Codes in Wireless Sensor Network. Mathematics, 7(5), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050396




