Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm for Linear Difference Equation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- By defining internal state variables, the difference equation model is rewritten in the form of the state-space model.
- A Kalman filter based VB (VB-KF) estimation algorithm is provided to estimate both the model states and parameters interactively. Based on the estimated states, the VB algorithm calculates the system parameters and the noise variance. Then the states are updated by means of the Kalman filter with new obtained parameters and noise variance.
- Different from the existing point parameter estimation methods, the proposed algorithm can give the distributions of the system parameters and noise variance to reflect the uncertainties of their estimates.
2. Transformation of the Difference Equation
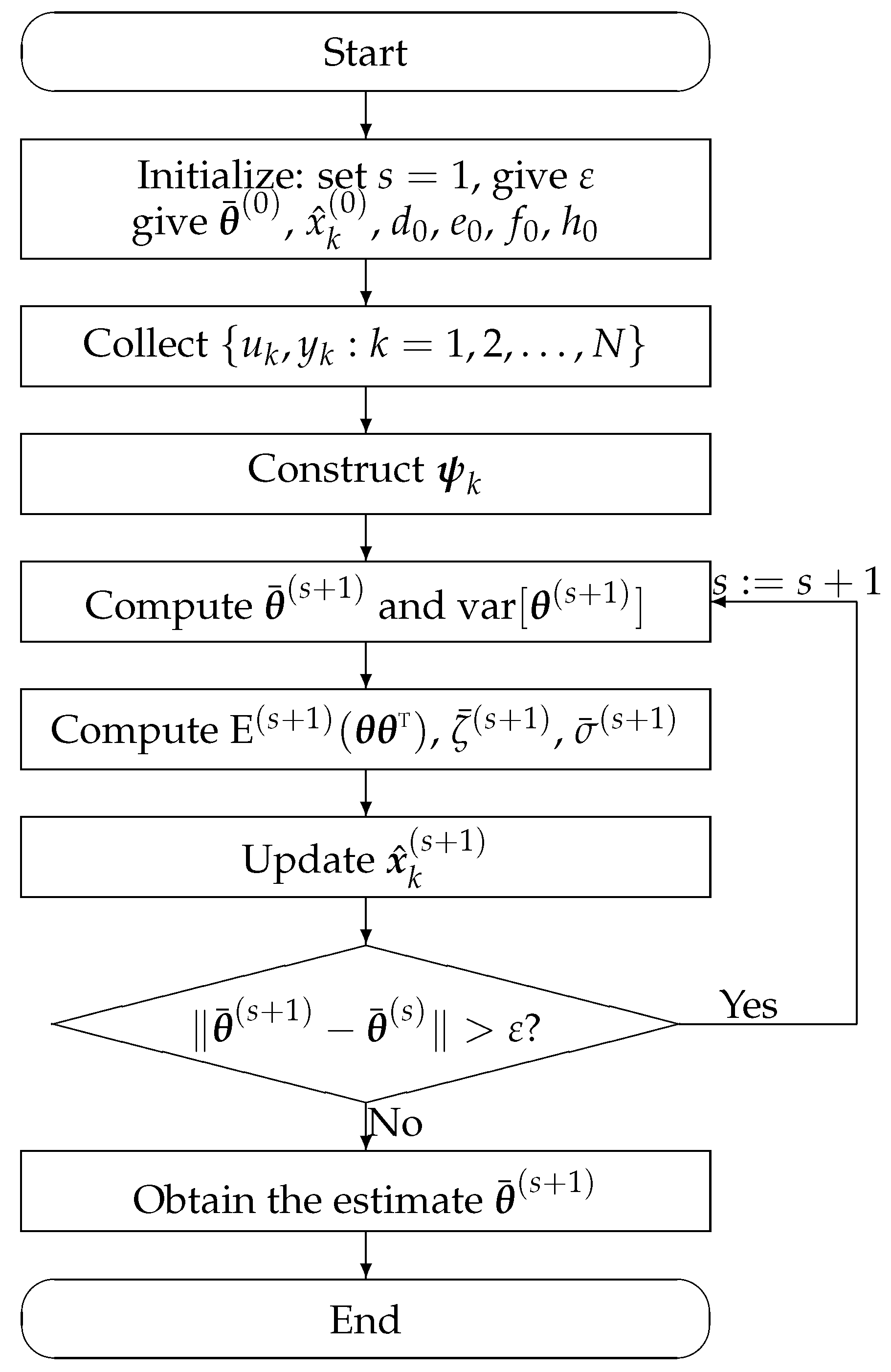
3. The Kalman Filter-Based Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm
3.1. The Variational Bayesian Parameter Estimation Algorithm
3.2. The State Estimation Algorithm
- (1)
- Initialization: set , , , and give a group of random positive values to parameters and a small positive value to .
- (2)
- Collect input-output data , and contract information vector with Equation (10).
- (3)
- (4)
- Update noise variance with Equation (22).
- (5)
- (6)
- Evaluate the relative change between and , if ( means L2-norm), for a very small positive number , then stop the iteration procedure and get the parameter estimates ; or else, let and go to Step 3.
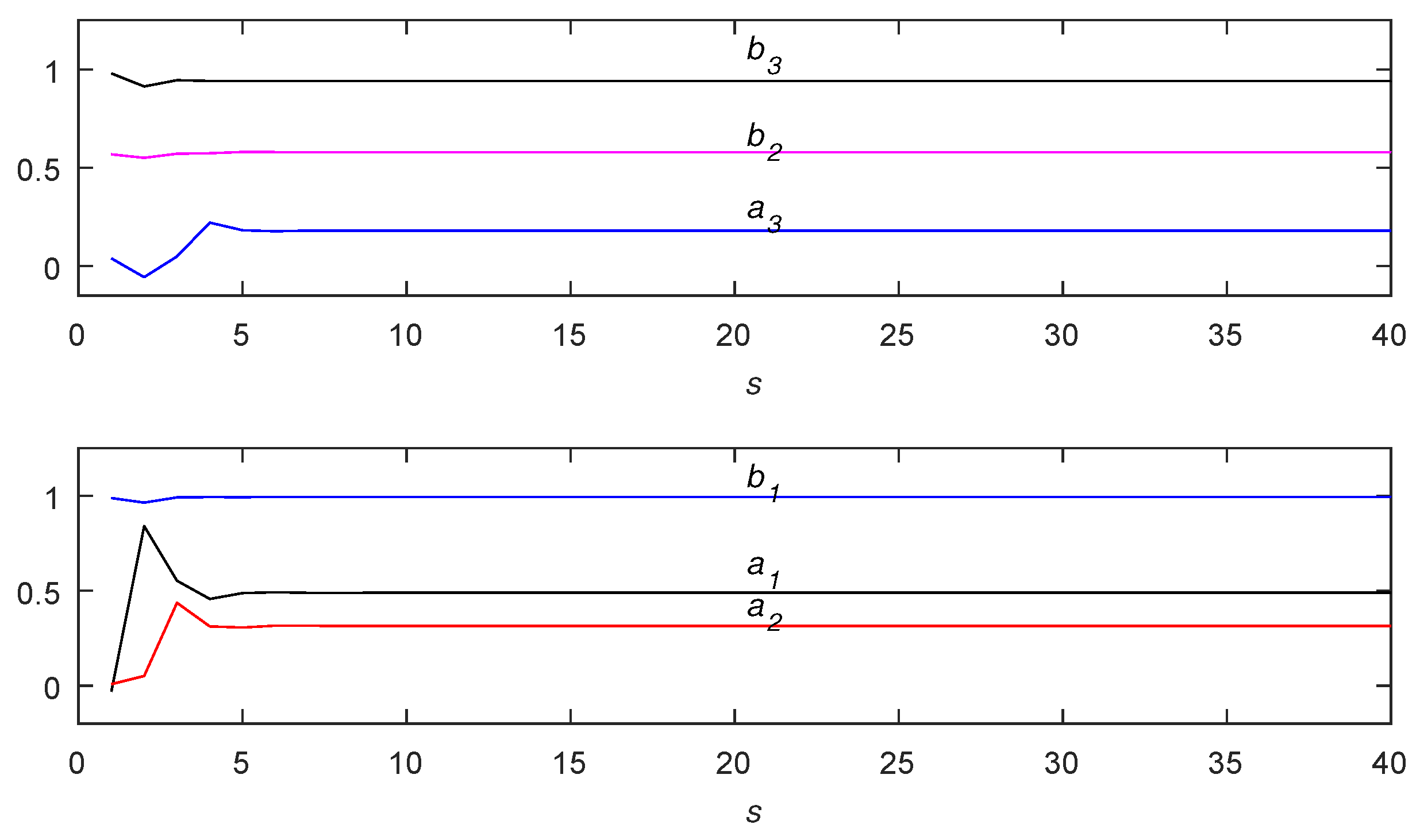
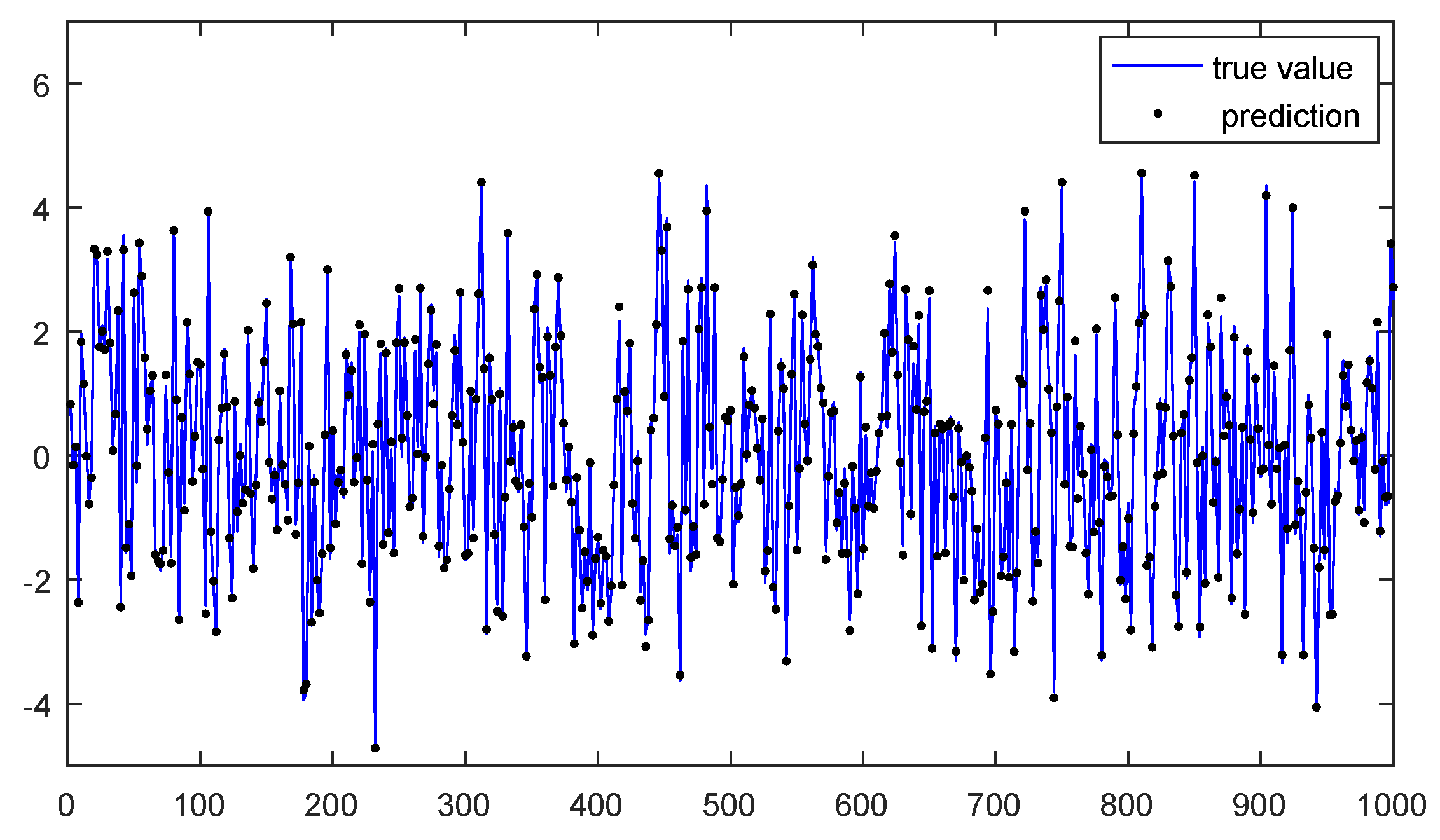
4. Simulation Example
5. Conclusions
- The parameter estimation errors are generally becoming smaller with iteration s increasing and with the noise variance decreasing. The estimated parameters are very close to the real values.
- The estimated noise variances in Table 2 show that variance estimates are relatively large in the previous period because of the inaccurate parameters and states, but with the increasing of the iteration s, the noise variance estimates can converge to their true value.
- Under the same batch of date and noise variance, the estimation accuracy of the proposed VB algorithm is higher than that of VB-SO and VB-KF2 algorithms.
- The predicted outputs fit well with true outputs, which indicates the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dallon, J.C.; Evans, E.J.; Grant, C.P.; Smith, W.V. Results from a differential equation model for cell motion with random switching show that the model cell velocity is asymptotically independent of force. J. Differ. Equ. 2019, 268, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, R.; Janarthanan, K.; Prakash, J. Nonlinear state estimation using fuzzy Kalman filter. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8678–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizawa, S.; Inagaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Tsuchida, N.; Tsuda, T.; Fujinami, H. Modeling and Recognition of Driving Behavior Based on Stochastic Switched ARX Model. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2007, 8, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garus, D.; Gogolla, T.; Krebber, K.; Schliep, F. Brillouin optical-fiber frequency-domain analysis for distributed temperature and strain measurements. J. Light. Technol. 1997, 15, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, V.; Ye, Z.; Kolwalkar, A. Investigation of anti-islanding protection of power converter based distributed generators using frequency domain analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, K.; Hickey, D.; Haroon, M.; Adams, D.E. Nonlinear system identification of automotive dampers: A time and frequency-domain analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Parameter estimation algorithms for dynamical response signals based on the multi-innovation theory and the hierarchical principle. IET Signal Process. 2017, 11, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Xiong, W.L. Parameter estimation and controller design for dynamic systems from the step responses based on the Newton iteration. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. The damping iterative parameter identification method for dynamical systems based on the sine signal measurement. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, G. Gradient based and least-squares based iterative identification methods for OE and OEMA systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Jiang, X.; Wan, X.K.; Ding, W. A filtering based multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariable control systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Decomposition based fast least squares algorithm for output error systems. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for CARARMA system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 4798–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.J.; Ding, F. Decomposition- and gradient-based iterative identification algorithms for multivariable systems using the multi-innovation theory. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 2971–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Pan, J.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Gradient-based iterative parameter estimation algorithms for dynamical systems from observation data. Mathematics 2019, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Hayat, T. Hierarchical principle-based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for dual-frequency signals. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 3251–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, Y.J.; Bao, B. Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2012, 226, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Zhu, Q.M. Hierarchical Newton and least squares iterative estimation algorithm for dynamic systems by transfer functions based on the impulse responses. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2019, 50, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunizeau, J.; Friston, K.J.; Kiebel, S.J. Variational Bayesian identification and prediction of stochastic nonlinear dynamic causal models. Phys. D 2009, 238, 2089–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibisepehr, S.; Huang, B. Dealing with irregular data in soft sensors: Bayesian method and comparative study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8713–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yin, S. Variational Bayesian inference for FIR models with randomly missing measurements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. State filtering and parameter estimation for state space systems with scarce measurements. Signal Process. 2014, 104, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Ding, F.; Shi, Y. An efficient hierarchical identification method for general dual-rate sampled-data systems. Automatica 2014, 50, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Combined state and least squares parameter estimation algorithms for dynamic systems. Appl. Math. Modell. 2014, 38, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, M. Subspace-based methods for the identification of linear time-invariant systems. Automatica 1995, 21, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y. A state space force identification method based on Markov parameters precise computation and regularization technique. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 300–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.P. Partially coupled stochastic gradient identification methods for non-uniformly sampled systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 1976–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F.; Yang, E.F. State estimation for bilinear systems through minimizing the covariance matrix of the state estimation errors. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2019, 33, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Shan, L.; Xia, J. Hierarchical recursive least squares parameter estimation of non-unifoimly sampled Hammerstein nonlinear systems based on Kalman filter. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 4231–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkka, S.; Nymmenmaa, A. Recursive noise adaptive Kalman filtering by variational Bayesian approximations. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 2009, 54, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Chambers, J. A robust Gaussian approximate fixed-interval smoother for nonlinear systems with heavy-tailed process and measurement noises. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Liu, X.M.; Ding, F. The filtering-based maximum likelihood iterative estimation algorithms for a special class of nonlinear systems with autoregressive moving average noise using the hierarchical identification principle. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2019, 33, 1189–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. The parameter estimation algorithms based on the dynamical response measurement data. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pan, J.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Ding, W. Partially-coupled least squares based iterative parameter estimation for multi-variable output-error-like autoregressive moving average systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Application of the Newton iteration algorithm to the parameter estimation for dynamical systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 288, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Gu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. A multi-innovation state and parameter estimation algorithm for a state space system with d-step state-delay. Signal Process. 2017, 140, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzikas, D.G.; Likas, A.C.; Galatsanos, N.P. The variational approximation for Bayesian inference. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latouche, P.; Birmele, E.; Ambroise, C. Variational Bayesian inference and complexity control for stochastic block models. Stat. Model. 2012, 12, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.X.; Xiong, W.L.; Chen, J.; Feng, D. Hierarchical identification for multivariate Hammerstein systems by using the modified Kalman filter. IET Control Theory Appl. 2017, 11, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.P. Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 2011, 47, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, J.Z.; Lin, J.X.; Wan, L.J. Particle filtering based parameter estimation for systems with output-error type model structures. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 5521–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, J.Z.; Lin, J.X.; Jiang, G.P. Particle filtering-based recursive identification for controlled auto-regressive systems with quantised output. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Ding, F.; Wu, M.H. Recursive parameter estimation algorithm for multivariate output- error systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 5163–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Wang, F.F.; Xu, L.; Wu, M.H. Decomposition based least squares iterative identification algorithm for multivariate pseudo-linear ARMA systems using the data filtering. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 1321–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Wang, C.W. The perturbed compound Poisson risk process with investment and debit interest. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. 2010, 12, 391–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Yuen, K.C. Optimality of the threshold dividend strategy for the compound Poisson model. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2011, 81, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Wen, Y.Z. Optimal dividend problem with a terminal value for spectrally positive Levy processes. Insur. Math. Econom. 2013, 53, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Wen, Y.Z. Exit problems for jump processes with applications to dividend problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2013, 245, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.P. Control algorithms of magnetic suspension systems based on the improved double exponential reaching law of sliding mode control. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2018, 16, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.X.; Ding, F. Filtering-based multistage recursive identification algorithm for an input nonlinear output-error autoregressive system by using the key term separation technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Ding, F. New gradient based identification methods for multivariate pseudo-linear systems using the multi-innovation and the data filtering. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 1568–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.K.; Li, Y.; Xia, C.; Wu, M.H.; Liang, J.; Wang, N. A T-wave alternans assessment method based on least squares curve fitting technique. Measurement 2016, 86, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N. Joint Optimization of cooperative spectrum sensing and resource allocation in multi-channel cognitive radio sensor networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 2563–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Liu, F.; Fu, B.; Na, F. Reliability analysis of hybrid multi-carrier energy systems based on entropy-based Markov model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2016, 230, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liang, Y.; Pei, Y. Dynamic contract incentive mechanism for cooperative wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10970–10982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Kalman state filtering based least squares iterative parameter estimation for observer canonical state space systems using decomposition. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2016, 301, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Wen, Y.Z. An extension of Paulsen-Gjessing’s risk model with stochastic return on investments. Insur. Math. Econom. 2013, 52, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Wen, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.X. On the optimal dividend problem for a spectrally positive levy process. Astin Bull. 2014, 44, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Yuen, K.C. Exact joint laws associated with spectrally negative Levy processes and applications to insurance risk theory. Front. Math. China 2014, 9, 1453–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.C.; Yuen, K.C. Optimal dividend problems for a jump-diffusion model with capital injections and proportional transaction costs. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2015, 11, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.C.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, F.C.; Cheung, H. Sparsity-aware transmit beamspace design for FDA-MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2018, 144, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Fu, B.; He, L.; Na, F. Research on automatic generation control with wind power participation based on predictive optimal 2-degree-of-freedom PID strategy for multi-area interconnected power system. Energies 2018, 11, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Fu, B.; He, L.; Li, C.S. Research on the predictive optimal PID plus second order derivative method for AGC of power system with high penetration of photovoltaic and wind power. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 14, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.X.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Y.M.; Cao, X.A. Effects of postannealing on the characteristics and reliability of polyfluorene organic light-emitting diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Z.; Shi, X.; Liao, L.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhou, H.; Su, Y.H. A capacity configuration control strategy to alleviate power fluctuation of hybrid energy storage system based on improved particle swarm optimization. Energies 2019, 12, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| s | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01016 | −0.02289 | −0.03700 | 1.00397 | 0.53194 | 0.97784 | 40.69214 | |
| 2 | −0.07361 | 0.00728 | 0.89702 | 0.94687 | 0.52043 | 0.96392 | 35.08236 | |
| 5 | 0.17474 | 0.30156 | 0.49471 | 0.97522 | 0.55029 | 0.99253 | 2.40308 | |
| 10 | 0.17243 | 0.31521 | 0.49920 | 0.97571 | 0.54883 | 0.99432 | 2.19306 | |
| 20 | 0.17246 | 0.31520 | 0.49918 | 0.97571 | 0.54883 | 0.99432 | 2.19278 | |
| 40 | 0.17246 | 0.31520 | 0.49918 | 0.97571 | 0.54883 | 0.99432 | 2.19278 | |
| 1 | −0.05182 | −0.05809 | 0.04132 | 1.00842 | 0.54880 | 0.99711 | 39.39494 | |
| 2 | −0.11574 | 0.04963 | 0.90089 | 0.93849 | 0.52609 | 0.97003 | 35.19921 | |
| 5 | 0.17688 | 0.31997 | 0.49349 | 0.96759 | 0.56015 | 1.00064 | 2.85674 | |
| 10 | 0.17674 | 0.32778 | 0.49767 | 0.96774 | 0.55874 | 1.00189 | 2.90030 | |
| 20 | 0.17676 | 0.32777 | 0.49764 | 0.96774 | 0.55874 | 1.00189 | 2.90017 | |
| 40 | 0.17676 | 0.32777 | 0.49764 | 0.96774 | 0.55874 | 1.00189 | 2.90017 | |
| 1 | −0.01785 | 0.06661 | −0.15694 | 0.98365 | 0.51835 | 1.01729 | 45.26212 | |
| 2 | −0.01462 | −0.04935 | 0.75665 | 0.89482 | 0.48419 | 0.96419 | 31.18481 | |
| 5 | 0.17291 | 0.28867 | 0.46187 | 0.91682 | 0.50836 | 0.98695 | 6.59330 | |
| 10 | 0.17082 | 0.29553 | 0.46557 | 0.91739 | 0.50776 | 0.98825 | 6.41325 | |
| 20 | 0.17083 | 0.29553 | 0.46556 | 0.91739 | 0.50776 | 0.98825 | 6.41343 | |
| 40 | 0.17083 | 0.29553 | 0.46556 | 0.91739 | 0.50776 | 0.98825 | 6.41343 | |
| true values | 0.18000 | 0.32000 | 0.50000 | 1.00000 | 0.55000 | 0.97000 | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 40 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2000 | 0.7509 | 0.0356 | 0.0280 | 0.0108 | 0.0108 | 0.0108 | |
| 0.2000 | 0.9935 | 0.3010 | 0.2748 | 0.2664 | 0.2664 | 0.2664 | |
| 0.2000 | 1.6252 | 1.0241 | 1.0097 | 0.9950 | 0.9950 | 0.9950 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Fei, Q.; Guo, F.; Xiong, W. Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm for Linear Difference Equation Systems. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7121143
Ma J, Fei Q, Guo F, Xiong W. Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm for Linear Difference Equation Systems. Mathematics. 2019; 7(12):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7121143
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Junxia, Qiuling Fei, Fan Guo, and Weili Xiong. 2019. "Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm for Linear Difference Equation Systems" Mathematics 7, no. 12: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7121143
APA StyleMa, J., Fei, Q., Guo, F., & Xiong, W. (2019). Variational Bayesian Iterative Estimation Algorithm for Linear Difference Equation Systems. Mathematics, 7(12), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7121143





