Effects of Nanolayer and Second Order Slip on Unsteady Nanofluid Flow Past a Wedge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation of the Problem
2.1. Mathematical Modeling Analysis
2.2. Application of HAM
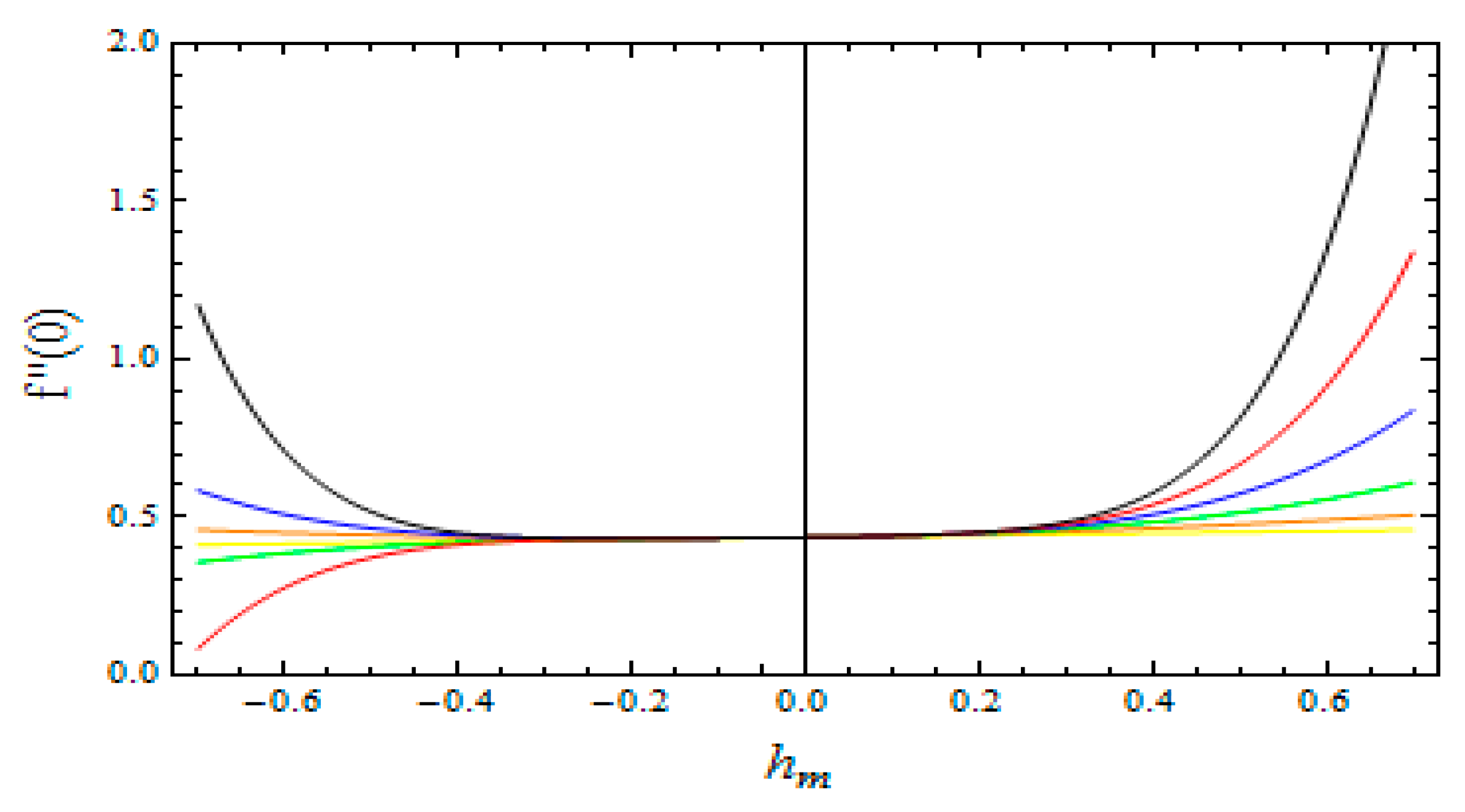
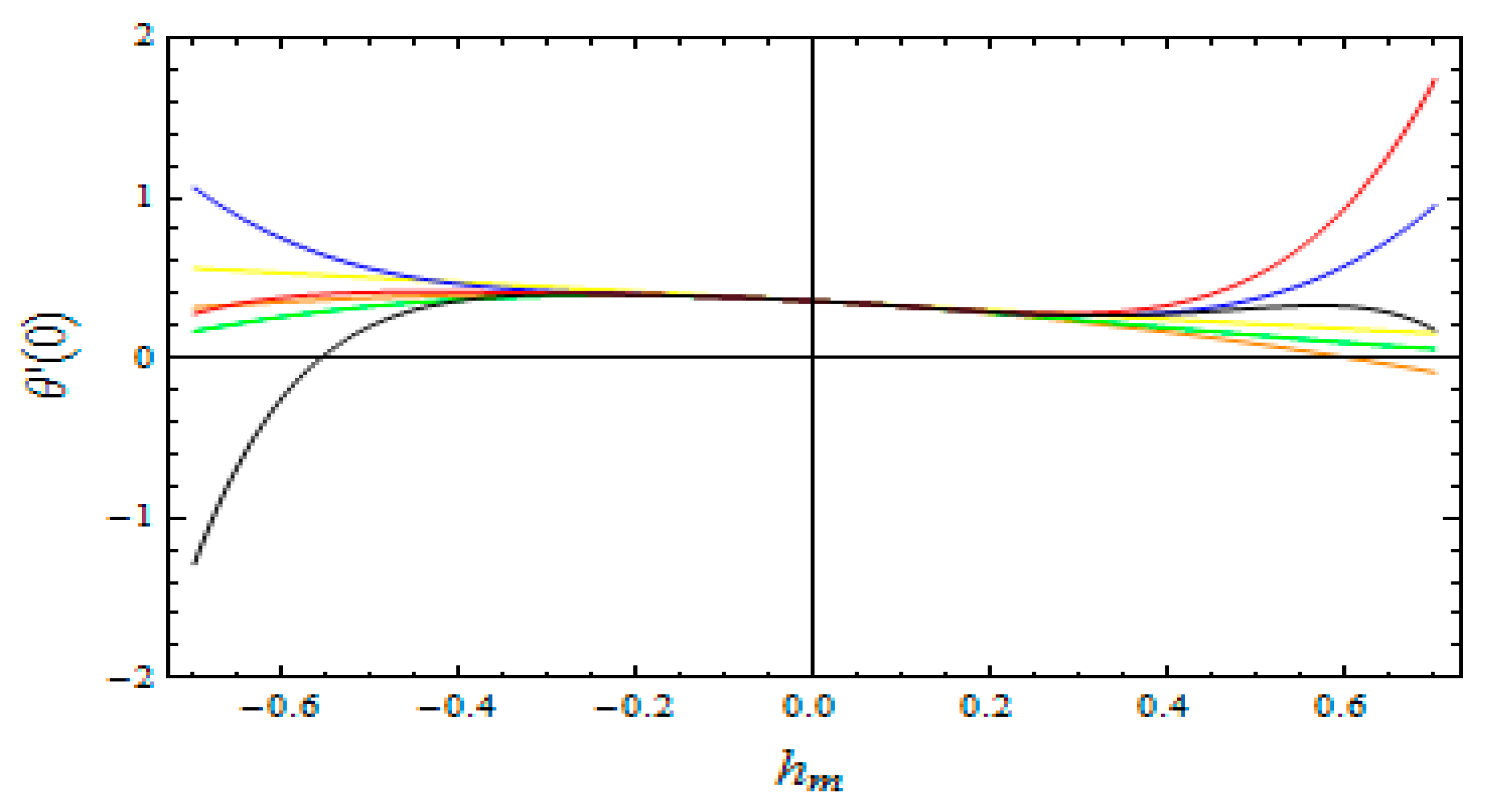
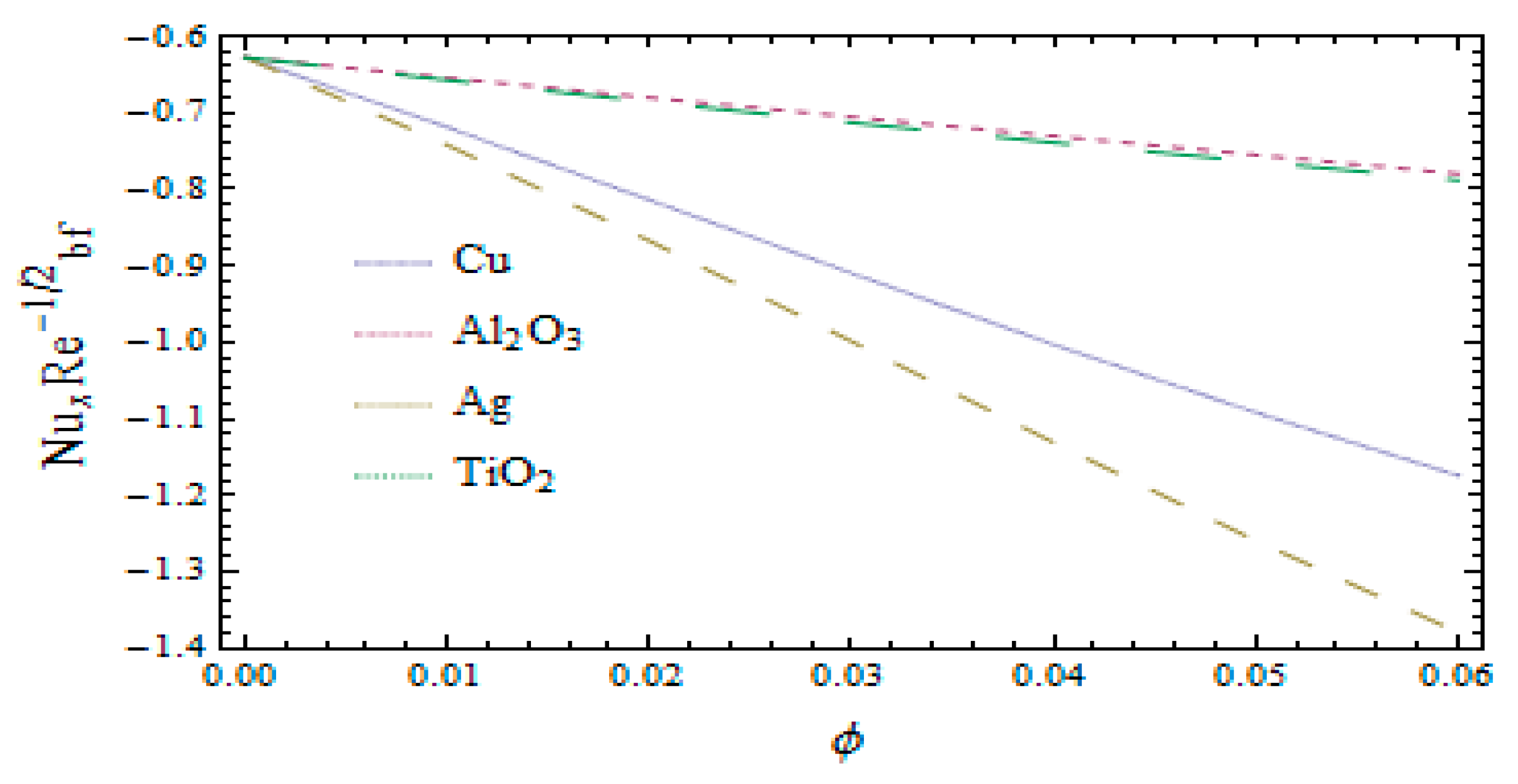
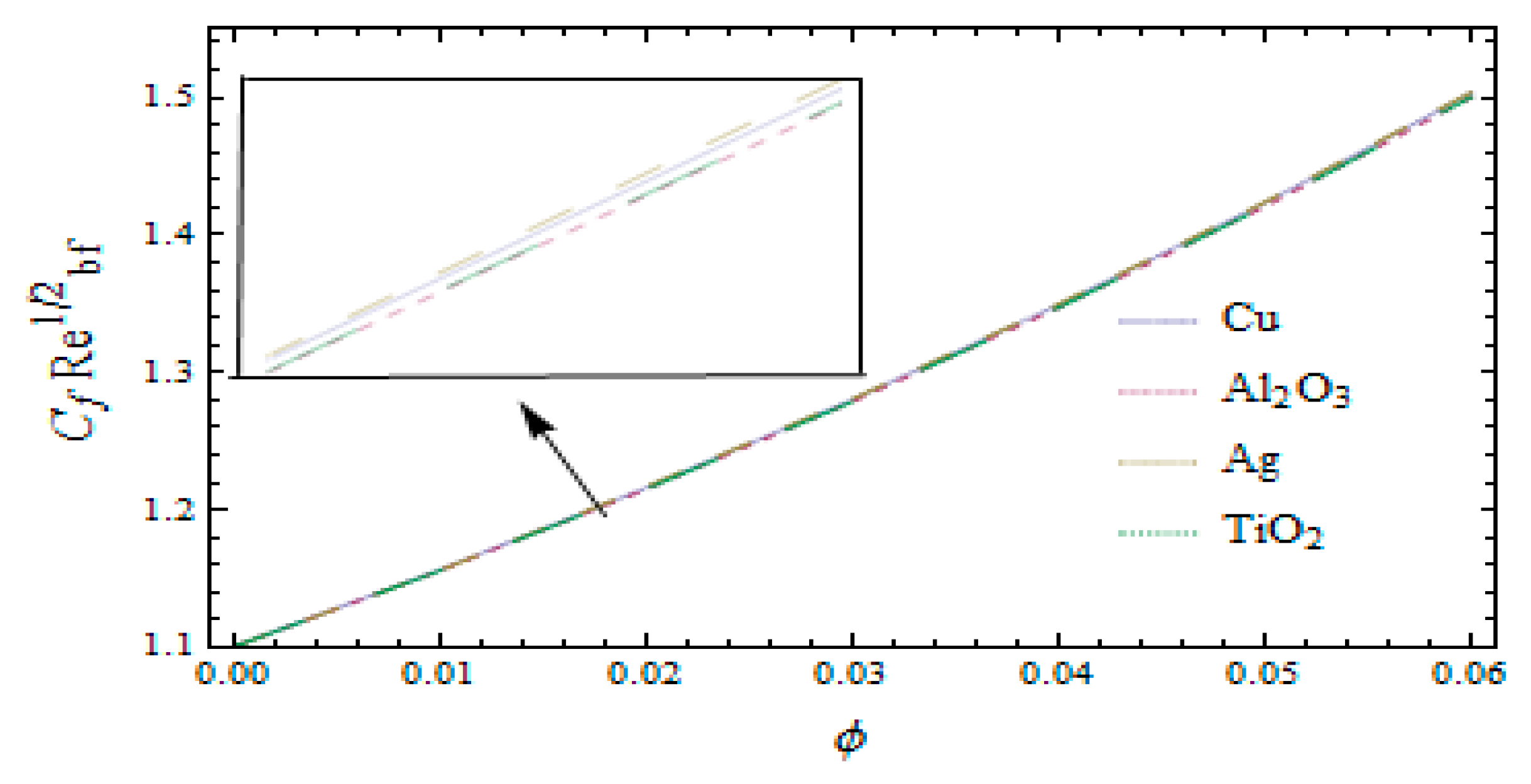
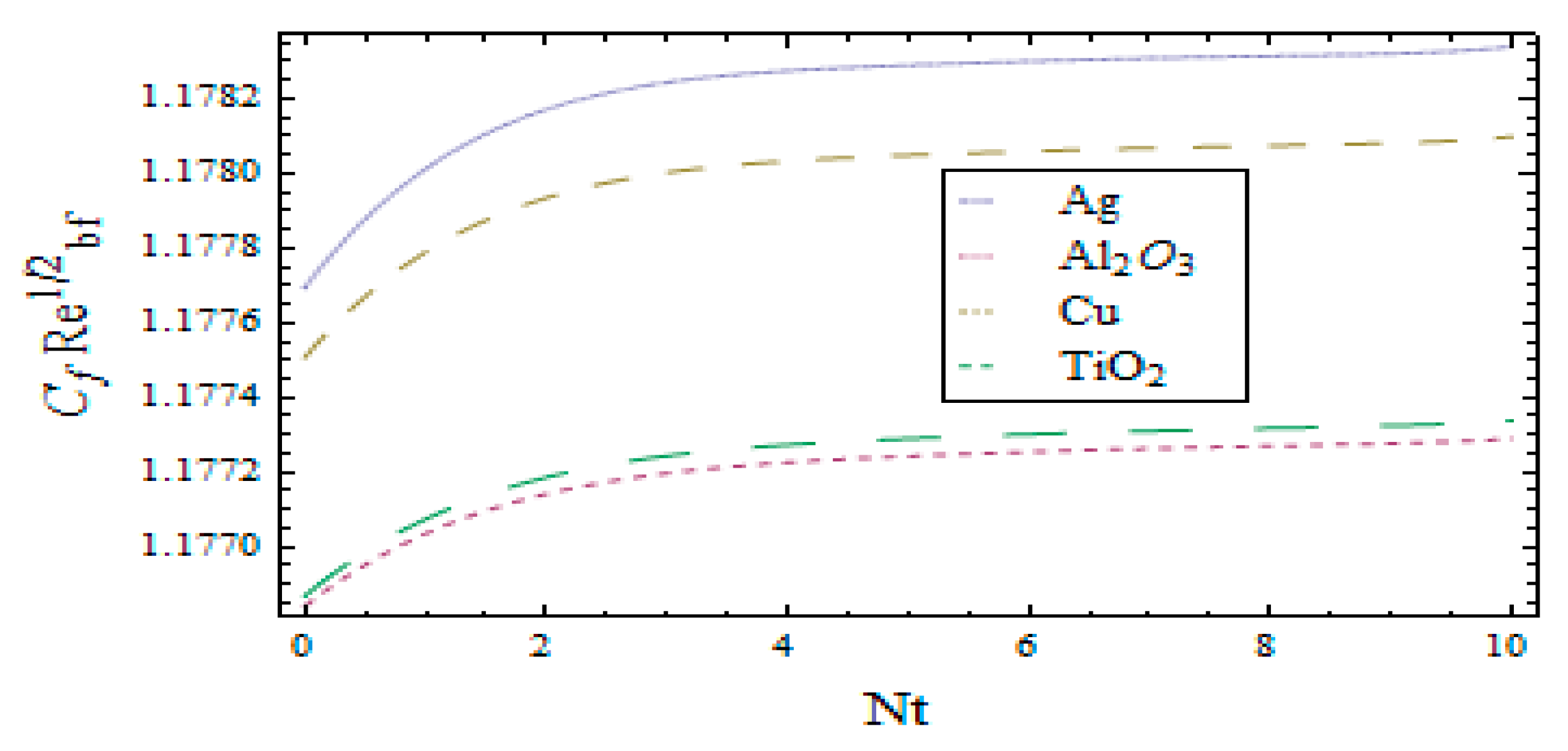
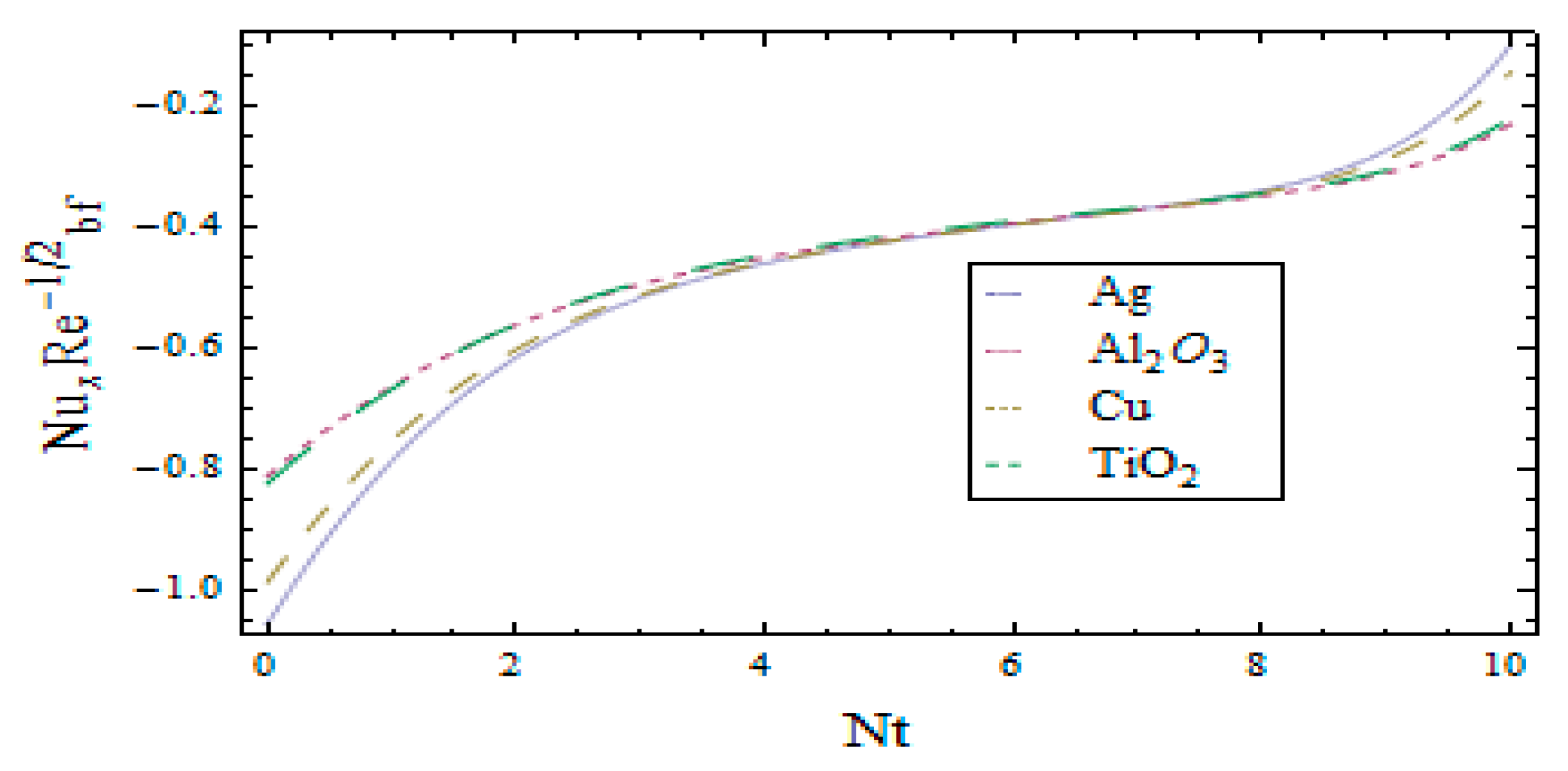
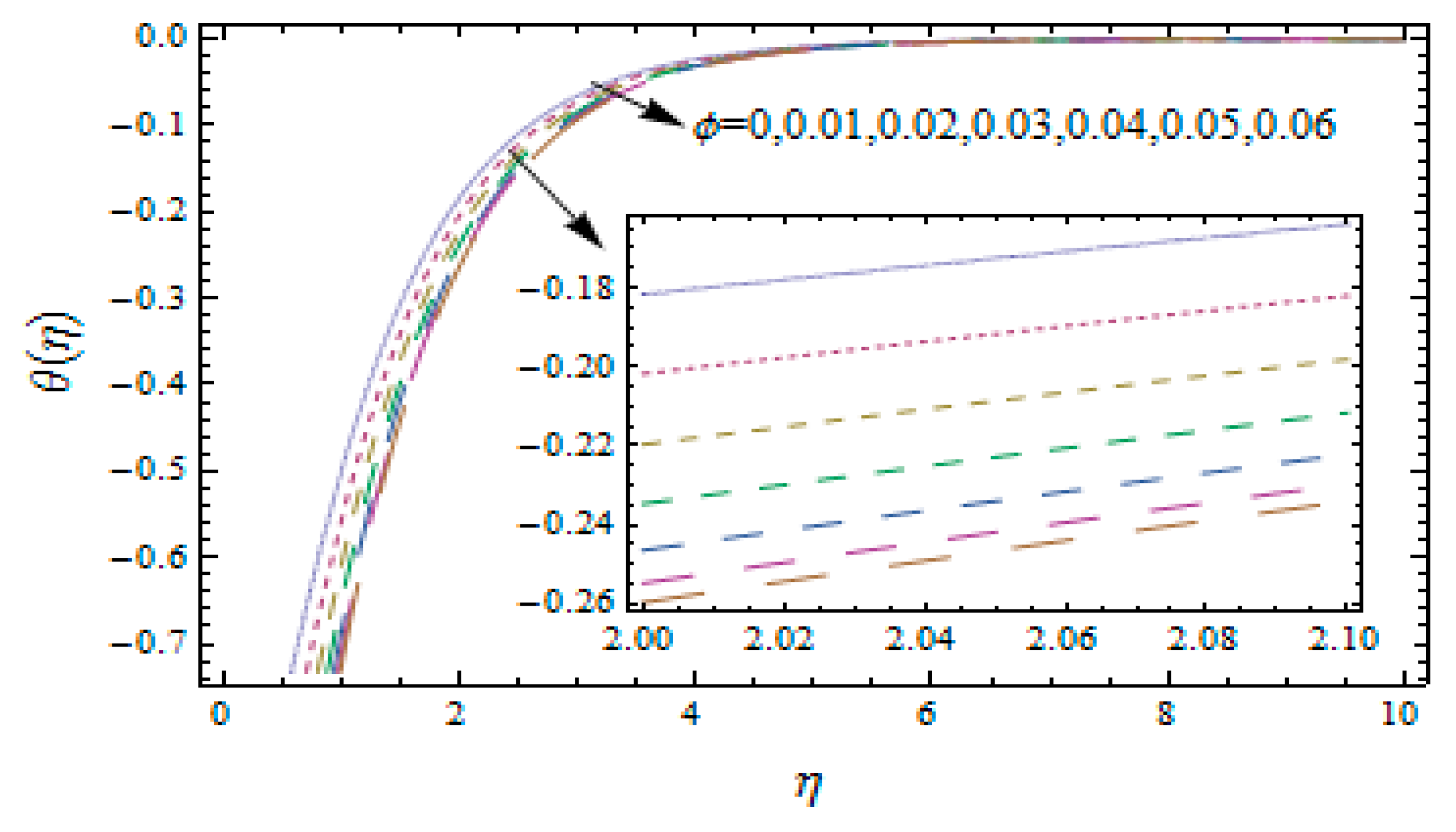
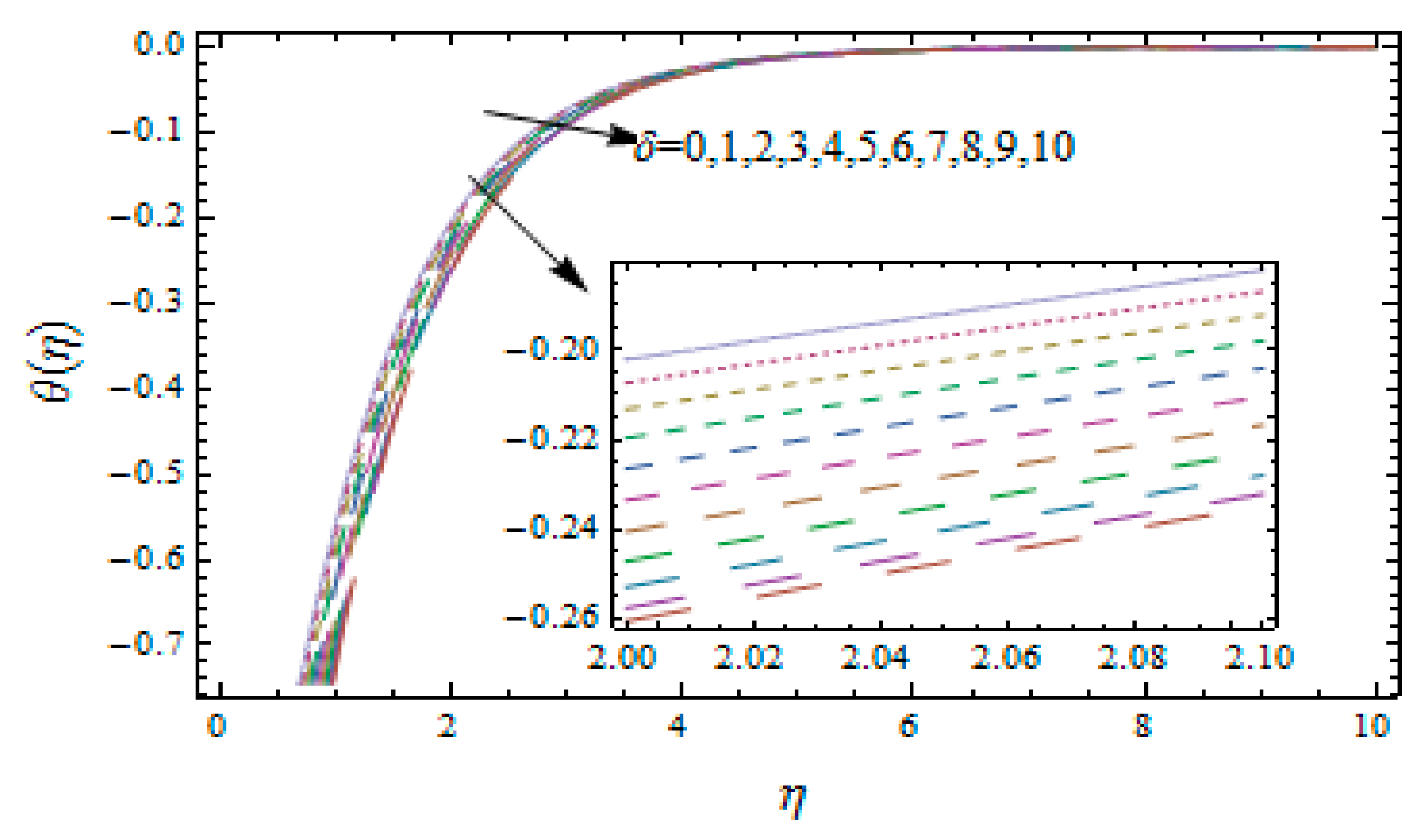
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.U.S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Publ. Fed 1995, 231, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.A.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S. Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zhou, J.E.; Tung, S.; Schneider, E.; Xi, S.Q. A review on development of nanofluid preparation and characterization. Powder Technol. 2009, 196, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Choi, S.U.S. The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: A renovated Hamilton–Crosser model. J. Nanopart. Res. 2004, 5, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, R.; Doroodchi, E.; Moghtaderi, B. Influence of controlled aggregation on thermal conductivity of nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2016, 138, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, M.B.; Fasano, M.; Cardellini, A.; Chiavazzo, E.; Asinari, P. A review on the heat and mass transfer phenomena in nanofluid coolants with special focus on automotive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1615–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.G. A note on the unsteady boundary layers over a flat plate. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 2008, 43, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Shafie, S.; Makinde, O.D.; Khan, I. Unsteady MHD Falkner-Skan flow of Casson nanofluid with generative/destructive chemical reaction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 172, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, S.E.; Khan, Z.A.; Awais, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Raja, M.A.Z. Numerical treatment for hydro-magnetic unsteady channel flow of nanofluid with heat transfer. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Sakidin, H.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid: A revised model with stability and regression analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Sajjad, R.; Muhammad, T. On MHD nonlinear stretching flow of Powell–Eyring nanomaterial. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Li, B.W.; Hu, Z.M. Convective stagnation point flow of a MHD non-Newtonian nanofluid towards a stretching plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.L. Combined Electrical MHD Heat Transfer Thermal Extrusion System Using Maxwell Fluid with Radiative and Viscous Dissipation Effects. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.J.; Sandeep, N. Three-dimensional MHD slip flow of nanofluids over a slendering stretching sheet with thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Soomro, F.A.; Haq, R.U.; Wang, W.; Defterli, O. Thermal and velocity slip effects on Casson nanofluid flow over an Inclined permeable stretching cylinder via collocation method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Saleem, S.; Nadeem, S.; Alderremy, A.A.; Khan, A.U. On stagnation point flow of a micro polar nanofluid past a circular cylinder with velocity and thermal slip. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Ullah, N. Partial slip effect in the flow of MHD micropolar nanofluid flow due to a rotating disk—A numerical approach. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, G.S.; Mishra, M.K. Analysis of transient flow of MHD nanofluid past a non-linear stretching sheet considering Navier’s slip boundary condition. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Troian, S.M. A general boundary condition for liquid flow at solid surfaces. Nature 1997, 389, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, L.C.; Zhang, X.X. Effects of second order velocity slip and nanoparticles migration on flow of Buongiorno nanofluid. Appl. Math. Lett. 2016, 52, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Zhu, J.; Bandar, B.M.; Zheng, L.C. Hydromagnetic flow and heat transfer with various nanoparticles additives past a wedge with high order velocity slip and temperature jump. Can. J. Phys. 2017, 95, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobamowo, M.G.; Jayesimi, L.O.; Waheed, M.A. Magnetohydrodynamic squeezing flow analysis of nanofluid under the effect of slip boundary conditions using variation of parameter method. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2018, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, V.M.; Gunakala, S.R. Unsteady MHD free convection nanofluid flows within a wavy trapezoidal enclosure with viscous and Joule dissipation effects. Numer. Heat Transf. Appl. 2015, 69, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.J. Beyond perturbation: The basic concepts of the homotopy analysis method and its applications. Adv. Mech. 2008, 38, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.Q.; Fujii, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of interfacial nanolayer on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, T.; Nithyadevi, N.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. MHD mixed convective heat transfer in a lid-driven enclosure filled with Ag-water nanofluid with center heater. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 142, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Hakeem, A.K.; Raja, K.; Ganga, B.; Ganesh, N.V. Nanofluid slip flow through porous medium with elastic deformation and uniform heat source/sink effects. Comput. Therm. Sci. Int. J. 2019, 11, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseland, S. Astrophysik und Atom-Theoretische Grundlagen; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1931; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kandasamy, R.; Muhaimin, I.; Khamis, A.B. Unsteady Hiemenz flow of Cu-nanofluid over a porous wedge in the presence of thermal stratification due to solar energy radiation: Lie group transformation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 65, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
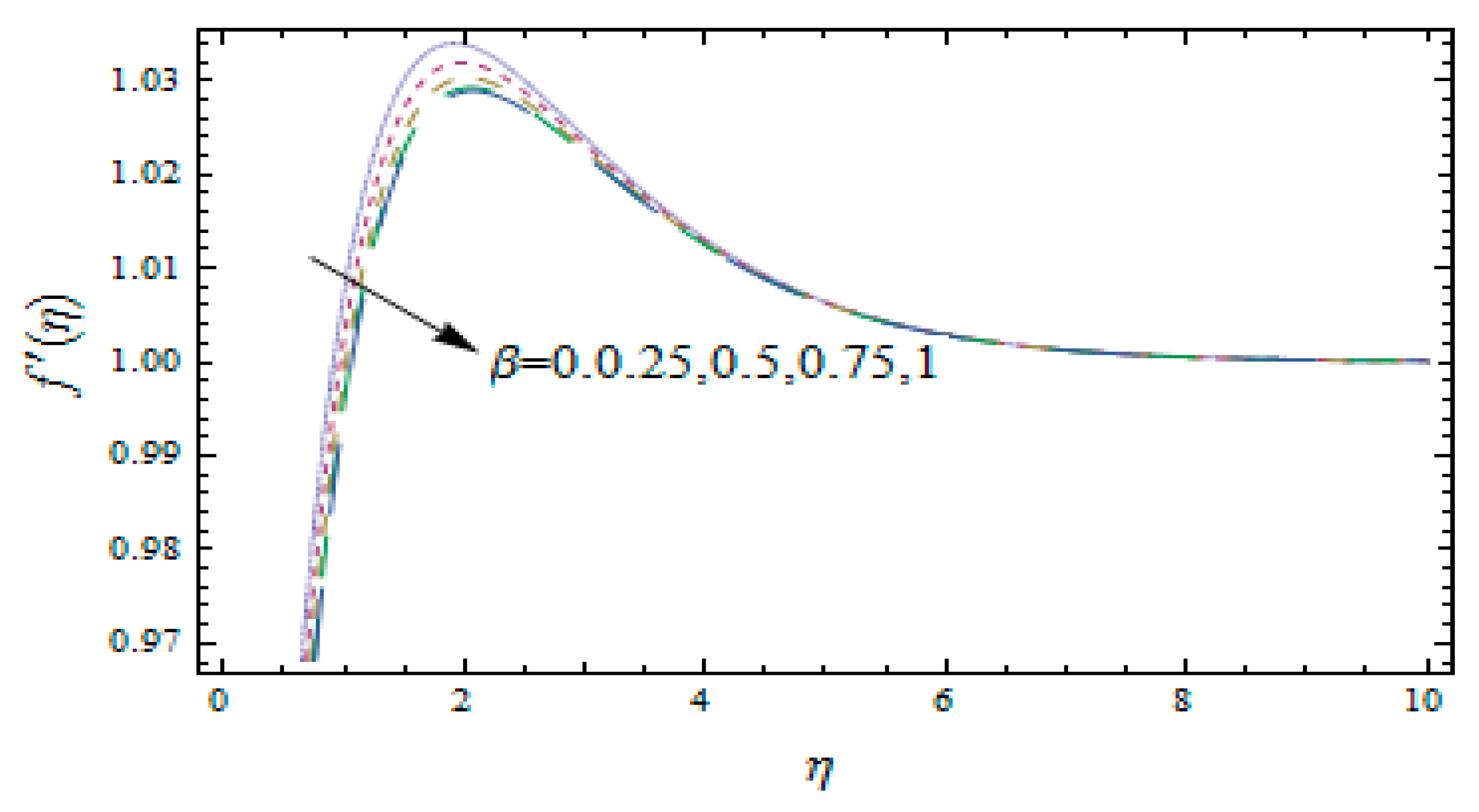
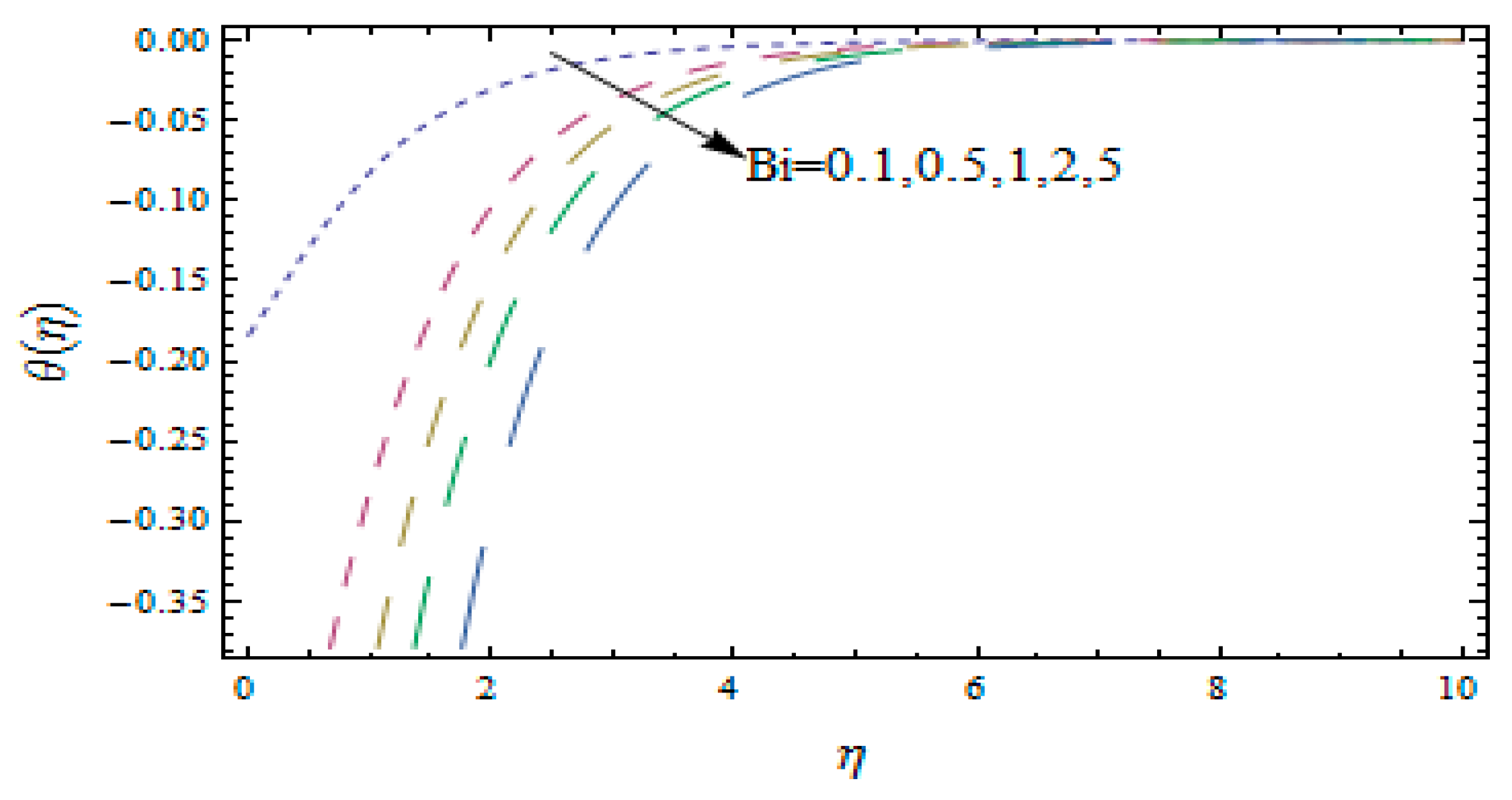
| Order | Same hm | Different hm |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.09804597363984649 | 0.10971050115341624 |
| 4 | 0.01695228455734058 | 0.01987321691368215 |
| 6 | 0.00149718658281736 | 0.00111284953763120 |
| 8 | 0.00092006200460696 | 0.00103228583202702 |
| 10 | 0.00016652968112583 | 0.00023106953667965 |
| 12 | 0.00028937817232142 | 0.00018686850247371 |
| 14 | 0.00004625312077364 | 0.00003407739648355 |
| 16 | 0.00004411186515886 | 0.00003247720532823 |
| 18 | 0.00004138348805906 | 0.00003498110747688 |
| 20 | 0.00000913314203849 | 0.00000687359503864 |
| Radius | NuxRe−1/2bf | CfRe1/2bf |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | −0.891502 | 1.26755 |
| 6 | −0.854912 | 1.24286 |
| 7 | −0.830858 | 1.22730 |
| 8 | −0.813950 | 1.21633 |
| 9 | −0.801466 | 1.20772 |
| 10 | −0.791884 | 1.20219 |
| 11 | −0.784313 | 1.19735 |
| 12 | −0.778192 | 1.19350 |
| Thickness | NuxRe−1/2bf | CfRe1/2bf |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | −0.721204 | 1.15796 |
| 1 | −0.747387 | 1.17419 |
| 2 | −0.778192 | 1.1935 |
| 3 | −0.81395 | 1.21633 |
| 4 | −0.854912 | 1.24286 |
| 5 | −0.901176 | 1.27453 |
| 6 | −0.952644 | 1.31082 |
| 7 | −1.00893 | 1.35419 |
| 8 | −1.06935 | 1.40348 |
| 9 | −1.13284 | 1.46137 |
| 10 | −1.19796 | 1.52895 |
| Parameter | Value | NuxRe−1/2bf | CfRe1/2bf |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −0.739726 | 1.279140 | |
| 0.5 | −0.737890 | 0.987631 | |
| 1 | −0.736706 | 0.810298 | |
| 1.5 | −0.735953 | 0.678731 | |
| 2 | −0.735382 | 0.586453 | |
| −1 | −0.736851 | 0.829446 | |
| −0.5 | −0.739202 | 1.184720 | |
| 0 | −0.744404 | 1.996120 | |
| 0.3 | −0.752506 | 3.308360 | |
| 0.5 | −0.767527 | 5.848600 | |
| 0 | −1.060260 | 0.944702 | |
| 1 | −0.471135 | 0.944367 | |
| 2 | −0.407875 | 0.944307 | |
| 3 | −0.302604 | 0.944202 | |
| −2 | −0.210557 | 0.918785 | |
| −1 | −0.372054 | 0.918769 | |
| −0.5 | −0.603914 | 0.918768 | |
| 0 | −1.839810 | 0.916633 | |
| 0.5 | 2.405830 | 0.914590 | |
| 1 | 0.681384 | 0.918776 | |
| 2 | 0.294131 | 0.918839 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Cao, J. Effects of Nanolayer and Second Order Slip on Unsteady Nanofluid Flow Past a Wedge. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111043
Zhu J, Cao J. Effects of Nanolayer and Second Order Slip on Unsteady Nanofluid Flow Past a Wedge. Mathematics. 2019; 7(11):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111043
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jing, and Jiahui Cao. 2019. "Effects of Nanolayer and Second Order Slip on Unsteady Nanofluid Flow Past a Wedge" Mathematics 7, no. 11: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111043
APA StyleZhu, J., & Cao, J. (2019). Effects of Nanolayer and Second Order Slip on Unsteady Nanofluid Flow Past a Wedge. Mathematics, 7(11), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7111043




