Generalized Synchronization of a Novel Hyperchaotic System and Application in Secure Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A generalized synchronization framework is rigorously formulated for identical hyperchaotic systems by defining appropriate error dynamics with diagonal scaling matrices. This formulation provides a unified mathematical setting that encompasses complete and anti-synchronization as special cases.
- A control law is analytically derived to stabilize the resulting error system. By constructing a quadratic Lyapunov function, sufficient conditions are established to ensure that the synchronization error dynamics are globally asymptotically stable for arbitrary initial conditions and nonzero scaling factors.
- The proposed synchronization framework is further exploited to generate high-quality chaotic sequences from the drive-system trajectories. These sequences are systematically incorporated into a permutation diffusion image encryption algorithm, thereby demonstrating the practical applicability of the theoretical results.
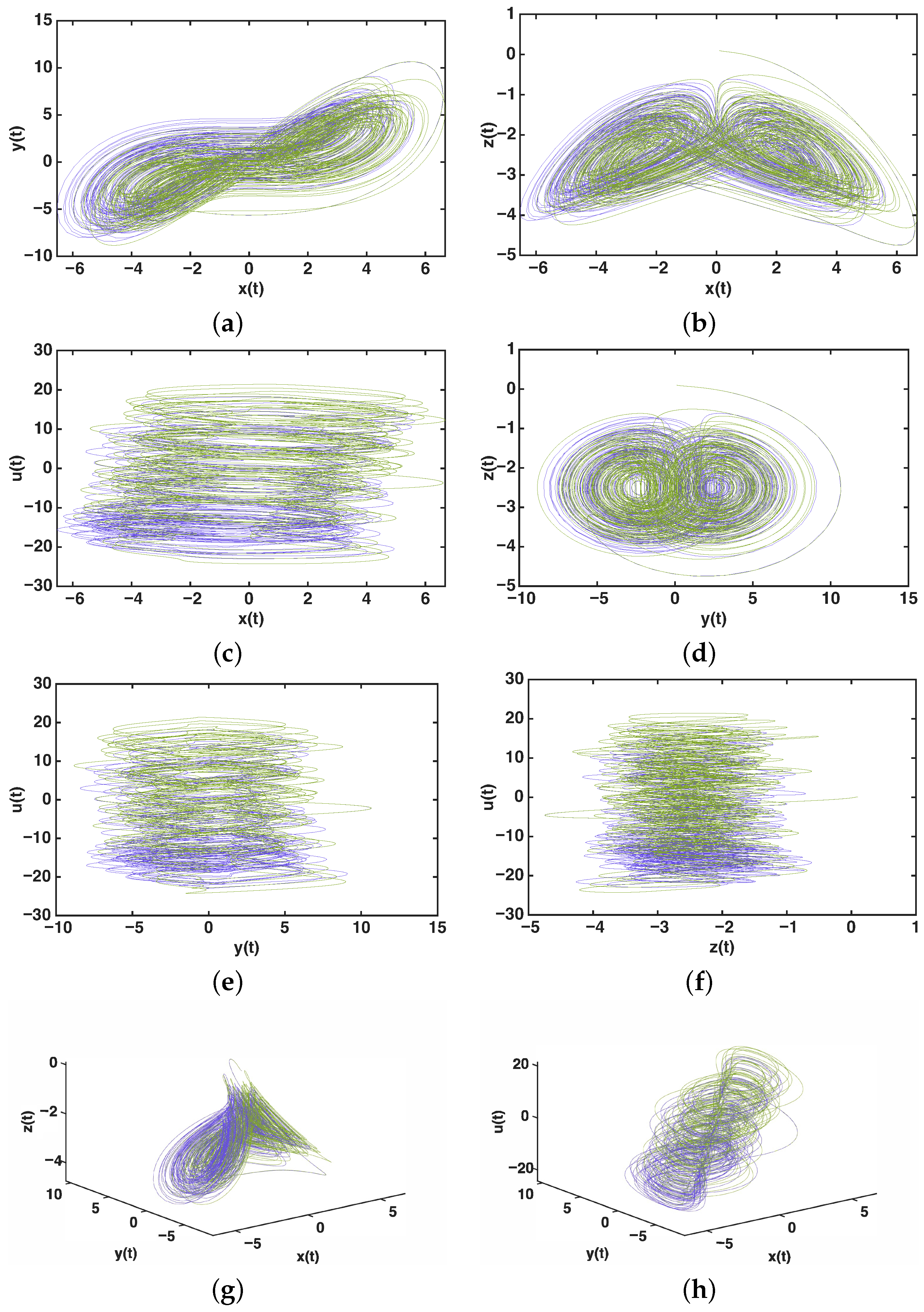
2. The Novel Hyperchaotic System
3. The Scheme of General Synchronization
- If , where denotes the identity matrix, the generalized synchronization reduces to complete synchronization, that is,
- If , the generalized synchronization becomes anti-synchronization, where the state variables of the drive and response systems evolve in opposite directions, i.e.,
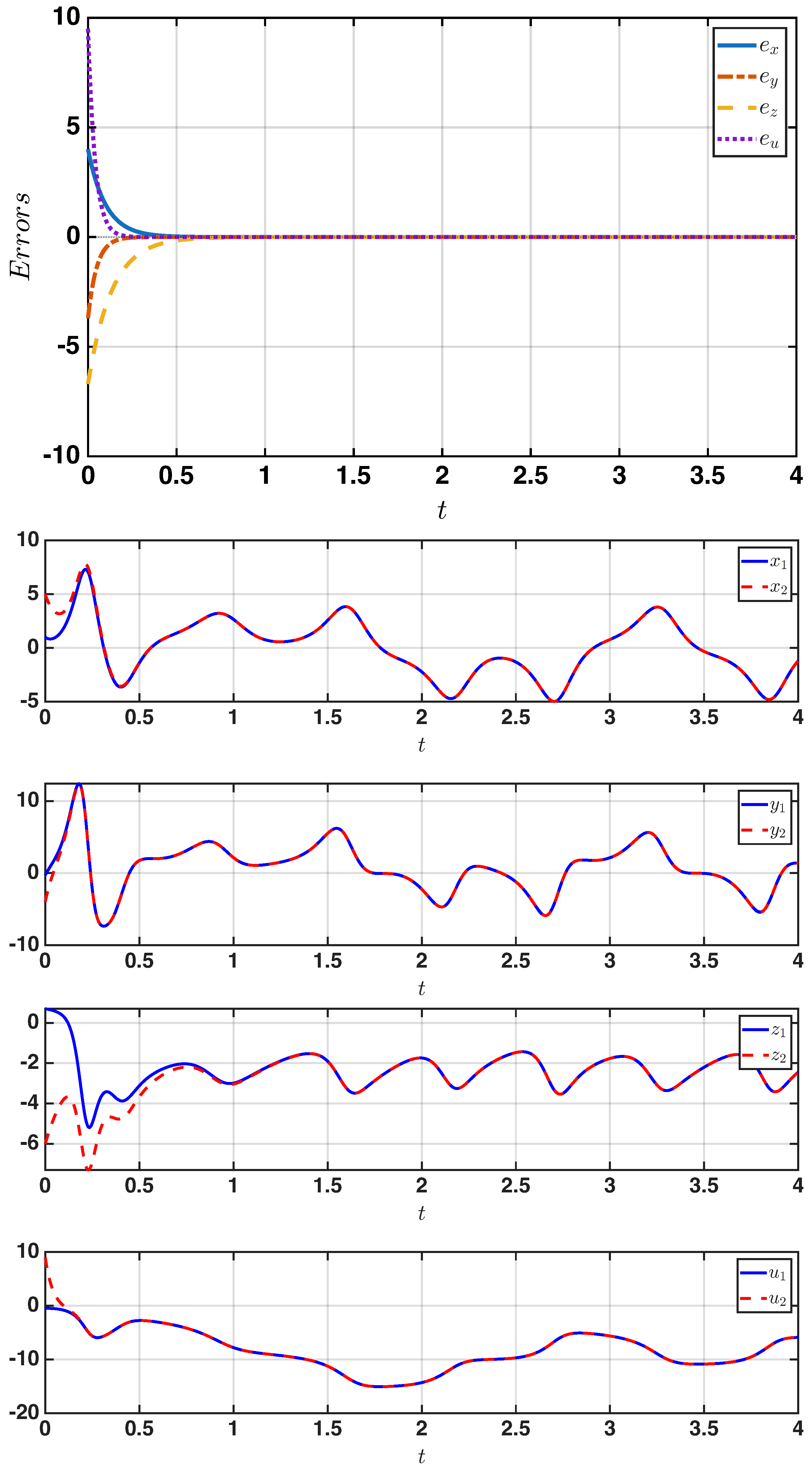
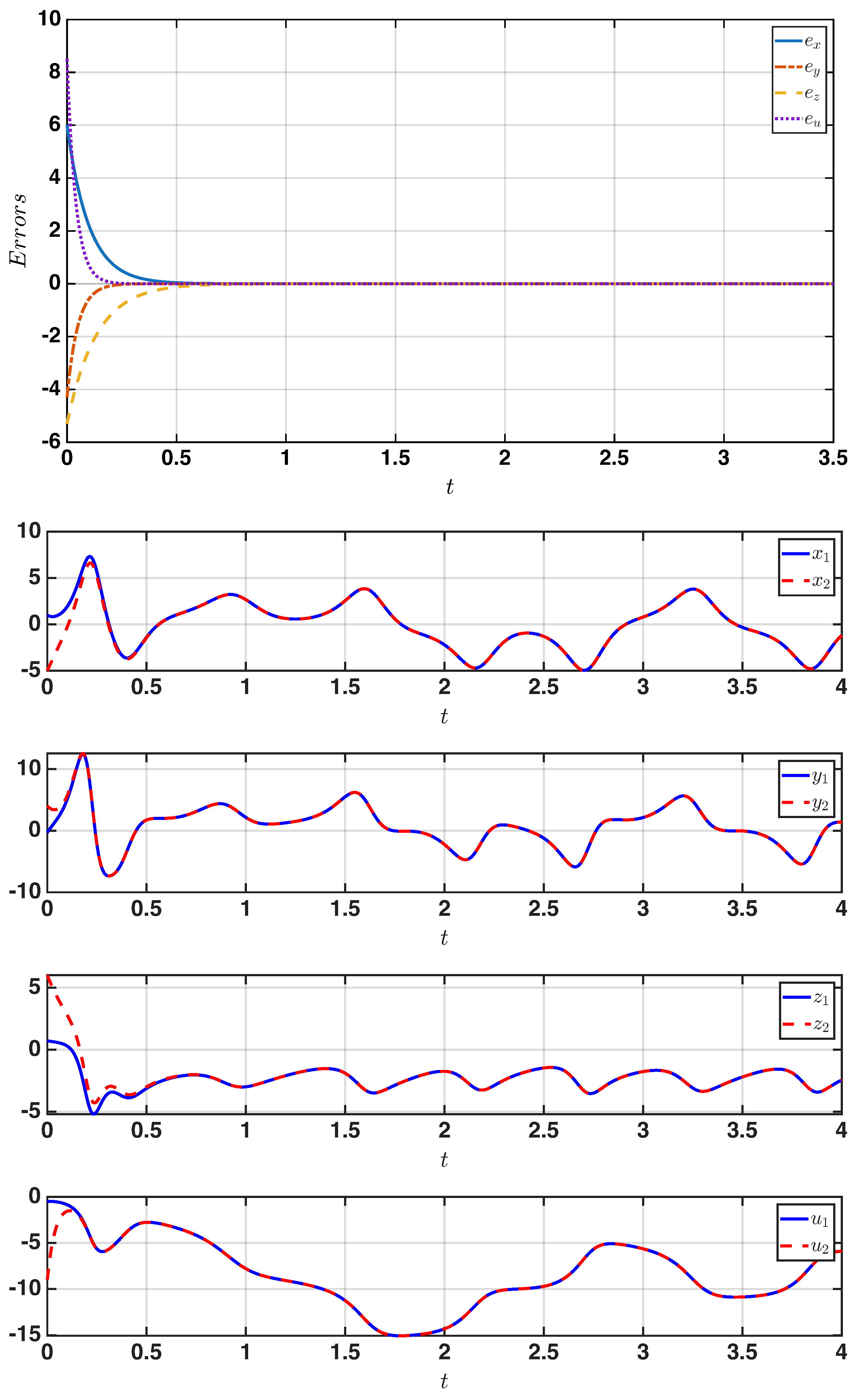
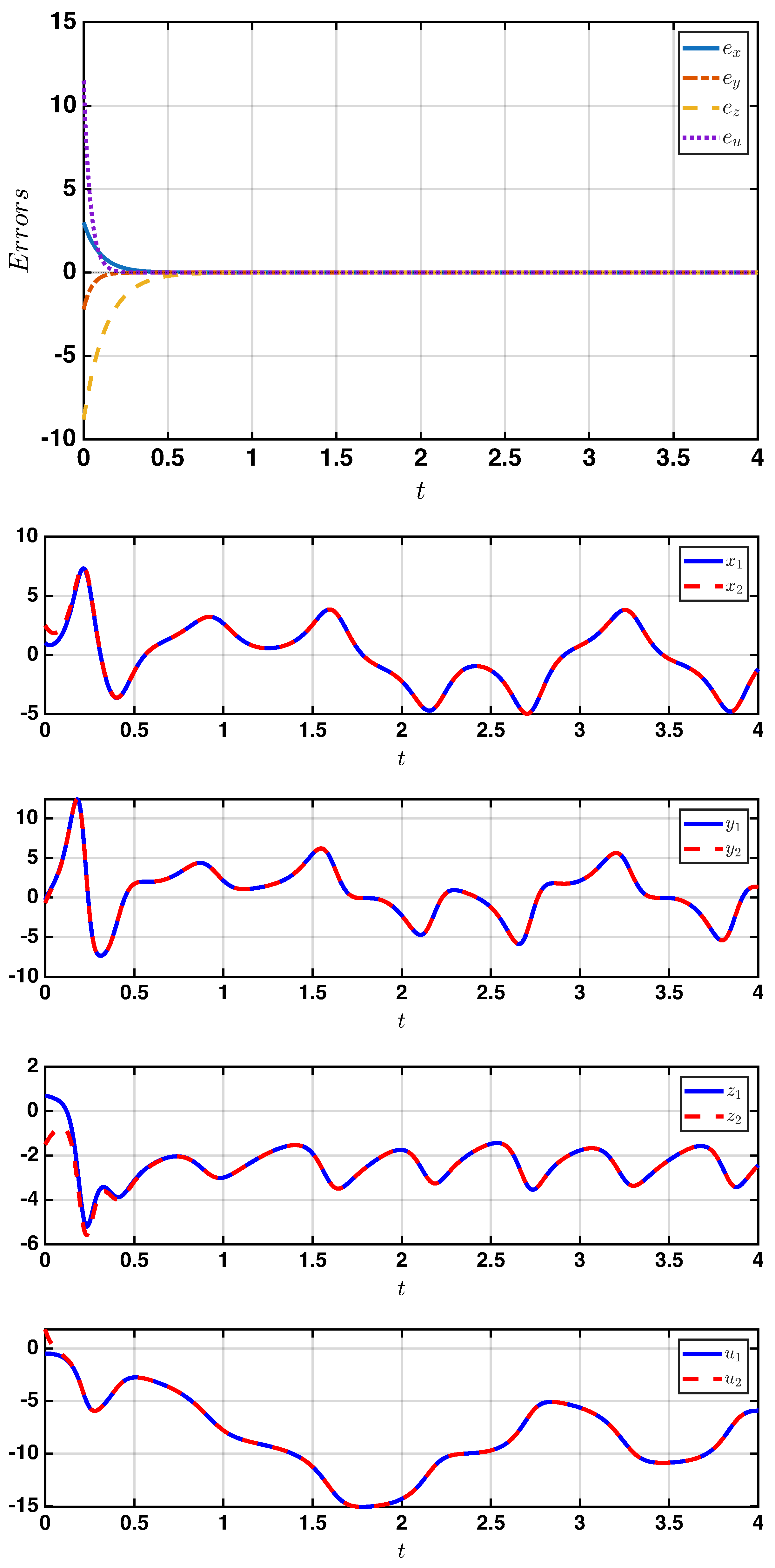
4. Generalized Synchronization Between Two Identical Systems
5. Numerical Simulations
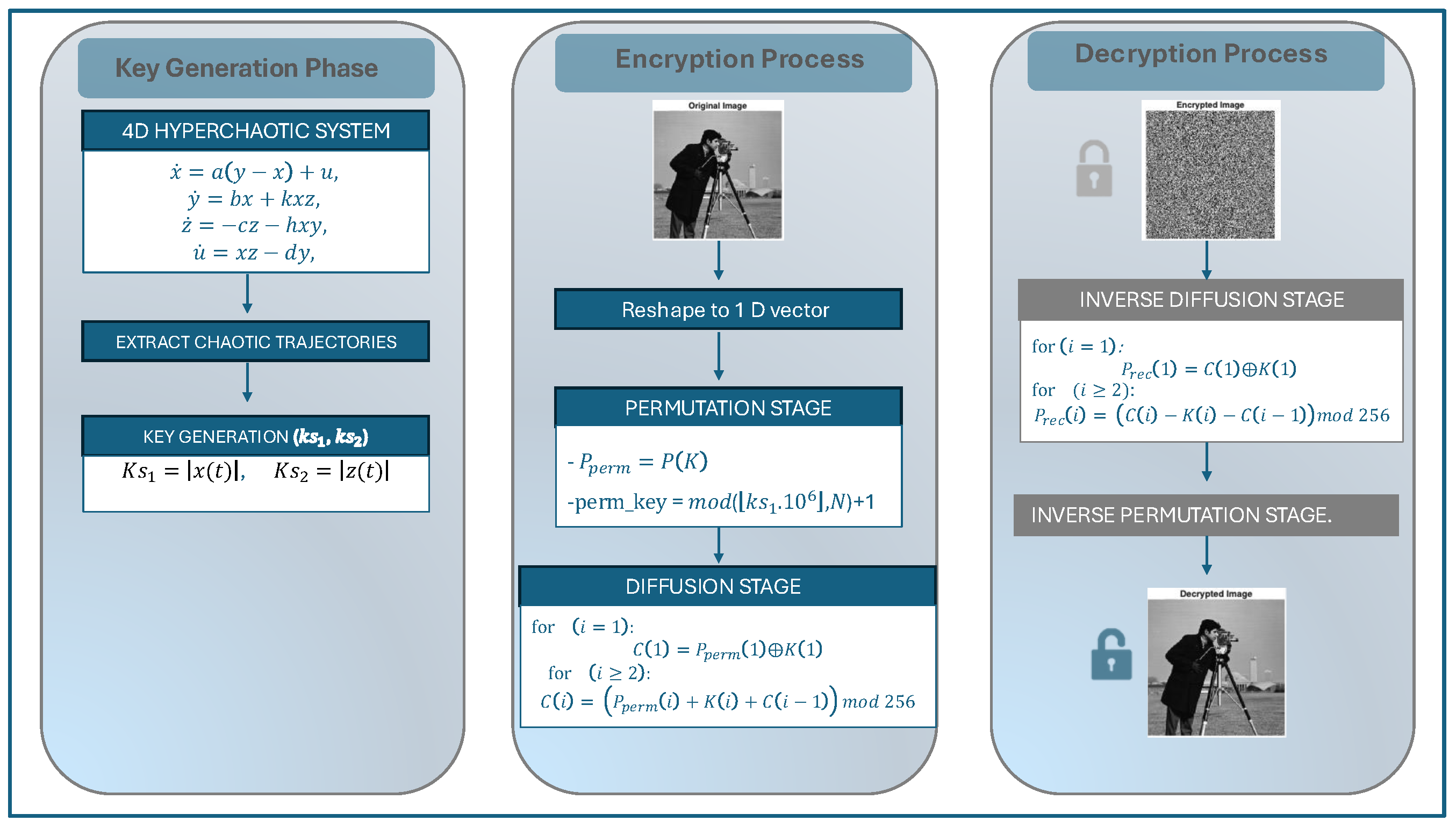
6. Chaotic Image Encryption and Decryption Process
6.1. Novel Hyperchaotic System Modeling
6.2. Key Generation
Image Preprocessing
- Permutation Key GenerationA permutation key is generated from the chaotic sequence () as follows:By sorting the permutation key in ascending order, a permutation index vector () is obtained, which determines the scrambling order of pixel positions. The permuted pixel sequence is given byThis permutation stage effectively disrupts the strong spatial correlation among adjacent pixels in the original image.
- Diffusion Key GenerationA diffusion key stream is derived from the second chaotic sequence aswhere is an 8-bit integer sequence used to modify pixel intensities during the diffusion process.
6.3. Diffusion Stage
6.4. Decryption Process
- Inverse Diffusion:
- Inverse Permutation: Construct the inverse index such that
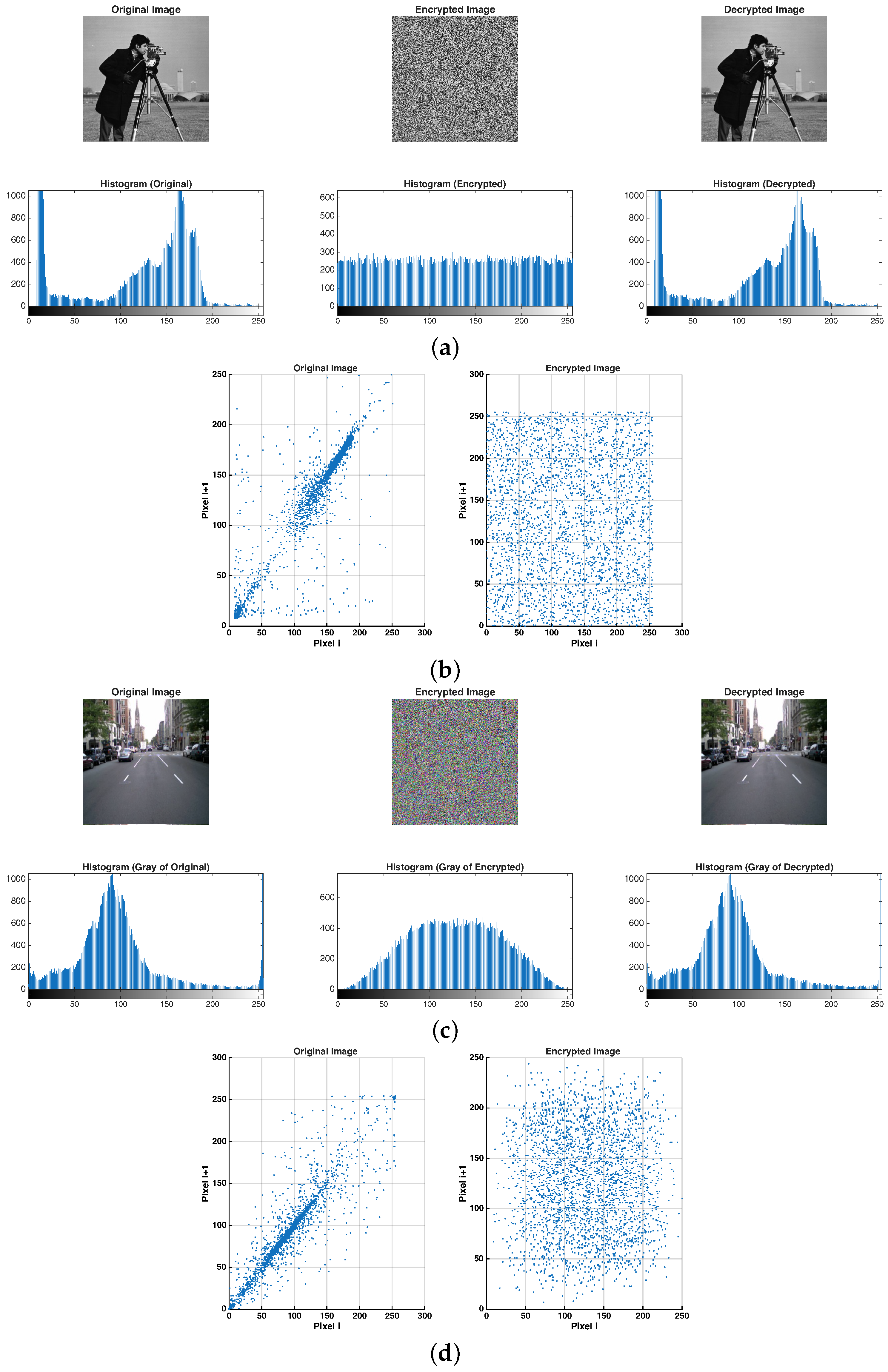
6.5. Validation
- Histogram Analysis: Encrypted images exhibit uniform distributions.
- Correlation Coefficient: Near-zero correlation for adjacent pixels in encrypted images.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H. Adaptive modified projective synchronization of a unified chaotic system with an uncertain parameter. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 34, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Adaptive synchronization between different hyperchaotic systems with fully uncertain parameters. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 372, 4799–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runzi, L.; Zhengmin, W. Adaptive function projective synchronization of unified chaotic systems with uncertain parameters. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.X. Adaptive generalized function projective synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Dong, G.; Bi, Q. Adaptive modified function projective synchronization of hyperchaotic systems with unknown parameters. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 3547–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S. Adaptive modified function projective synchronization of unknown chaotic systems with different order. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 218, 5891–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessoky, M.M.; Alzahrani, E.; Almohammadi, N. Function projective synchronization for four scroll attractor by nonlinear control. Appl. Math. Sci. 2017, 11, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessoky, M.M.; Alzahrani, E.; Almohammadi, N. Control and adaptive modified function projective synchronization of Liu chaotic dynamical system. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2019, 9, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohammadi, N.; Alzahrani, E.; El-Dessoky, M.M. Combined modified function projective synchronization of different systems through adaptive control. Arch. Control Sci. 2019, 29, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessoky, M.M.; Alzahrani, E.; Almohammadi, N. Adaptive modified function projective synchronization of chaotic dynamical system with different order. J. Comput. Anal. Appl. 2020, 28, 354–363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, P.; Qin, J.; Mu, C.; Xu, F. Dynamics of a Generalized Lorenz-Like Chaos Dynamical Systems. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2021, 11, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessoky, M.M.; Almohammadi, N.; Alzahrani, E. Control and adaptive modified function projective synchronization of different hyperchaotic dynamical systems. AIMS Math. 2023, 8, 23621–23634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Chen, F. Global Stability, Bifurcations and Chaos Control in a Discrete Amensalism Model With Cover and Saturation Effect. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2025, 15, 2977–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Chen, S. Feedback Control of Chaos in The Modified KdV–Burgers–Kuramoto Equation Via a Single Time-Delay. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2026, 16, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, S. Image Encryption Technique Combining Compressive Sensing with Double Random-Phase Encoding. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 6764052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Di, X.; Zhou, J.; Man, Z. Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Bit-level Permutation and Dynamic Overlap Diffusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 160004–160024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, Y.; Wang, D. A Fast Chaotic Image Encryption Scheme with Simultaneous Permutation and Diffusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27361–27374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Peng, C.; Tan, W.; Li, L. An Effective Chaos-Based Image Encryption Scheme Using Imitating Jigsaw Method. Complexity 2021, 2021, 8824915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvanshi, A.; Budhia, M.; Patro, K.; Acharya, B. FSR-SPD: An efficient chaotic multi-image encryption system based on flip-shift-rotate synchronous-permutation-diffusion operation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 57011–57057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wei, D.; Deng, Y. A Novel Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Compressive Sensing and a Two-Dimensional Linear Canonical Transform. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wei, D. Fast Encryption Algorithm Based on Chaotic System and Cyclic Shift in Integer Wavelet Domain. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.; Sravan, J.V.; Potnuru, D.J.R.; Patro, K.A.K. MIE-SPD: A New and Highly Efficient Chaos-Based Multiple Image Encryption Technique With Synchronous Permutation Diffusion. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 62773–62797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.; Tayeb, H. A secure communication scheme based on generalized modified projective synchronization of a new 4-D fractional-order hyperchaotic system. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 095203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Kong, X.; Yao, W.; Zhang, J.; Cai, S.; Lin, H.; Jin, J. Dynamics analysis, synchronization and FPGA implementation of multiscroll Hopfield neural networks with non-polynomial memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 179, 114440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Zhou, L.; Zong, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Shangguan, X. Fixed Time Control for Interlayer Synchronism Under DDMNNs and Application in Secure Communication. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 10827–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, R.; Arumugam, V.; Pathmanaban, S. Mittag–Leffler synchronization of fractional order disturbed chaotic neural networks with varying time-delay using hybrid controller and its application to biometric image encryption. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2026, 152, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cai, G.; Zheng, S. A Novel Hyperchaotic System and Its Control. J. Uncertain Syst. 2009, 3, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Generalized projective synchronization between Lorenz system and Chen’s system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 32, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
El-Dessoky, M.M.; Almohammadi, N.; Alsulami, M. Generalized Synchronization of a Novel Hyperchaotic System and Application in Secure Communication. Mathematics 2026, 14, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14010111
El-Dessoky MM, Almohammadi N, Alsulami M. Generalized Synchronization of a Novel Hyperchaotic System and Application in Secure Communication. Mathematics. 2026; 14(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Dessoky, Mohamed M., Nehad Almohammadi, and Mansoor Alsulami. 2026. "Generalized Synchronization of a Novel Hyperchaotic System and Application in Secure Communication" Mathematics 14, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14010111
APA StyleEl-Dessoky, M. M., Almohammadi, N., & Alsulami, M. (2026). Generalized Synchronization of a Novel Hyperchaotic System and Application in Secure Communication. Mathematics, 14(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14010111






