Identification and Empirical Likelihood Inference in Nonlinear Regression Model with Nonignorable Nonresponse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Penalized Semiparametric Likelihood Estimation
2.2. Construction of Estimating Equations
2.3. MELEs of Model Parameters
3. Main Results
3.1. Asymptotic Properties
- (A1)
- The nonresponse mechanism almost surely and almost surely; in a neighborhood of , , and exists and is bounded by an integrable function.
- (A2)
- The probability density function is bounded away from ∞ in the support of ; the first and second derivatives of are continuous, smooth and bounded; and and are finite.
- (A3)
- is twice continuously differentiable in the neighborhood of .
- (A4)
- The function is continuous with respect to , where lies in a compact set; and exist; has full column rank.
- (A5)
- has full column rank.
- (A6)
- The kernel function is a probability density function such that (a) it is bounded and has a compact support; (b) it is symmetric with ; (c) for some in some closed interval centered at zero; and (d) the bandwidth h satisfies and as .
- (A7)
- As , , and the tuning parameter satisfies as and .
- (A8)
- The penalty function satisfies and , where .
- (A9)
- The moment conditionsandhold for , , and , where with ℵ being the compact set, and is defined in (A1). The notation denotes the k-th component of .
- (1)
- Asymptotic normality:
- (2)
- Likelihood ratio convergence:where are independent chi-squared variates with 1 degree of freedom, and () are eigenvalues of .
3.2. Double Robustness
3.3. Dimension Reduction
3.4. Asymptotic Variance Estimation
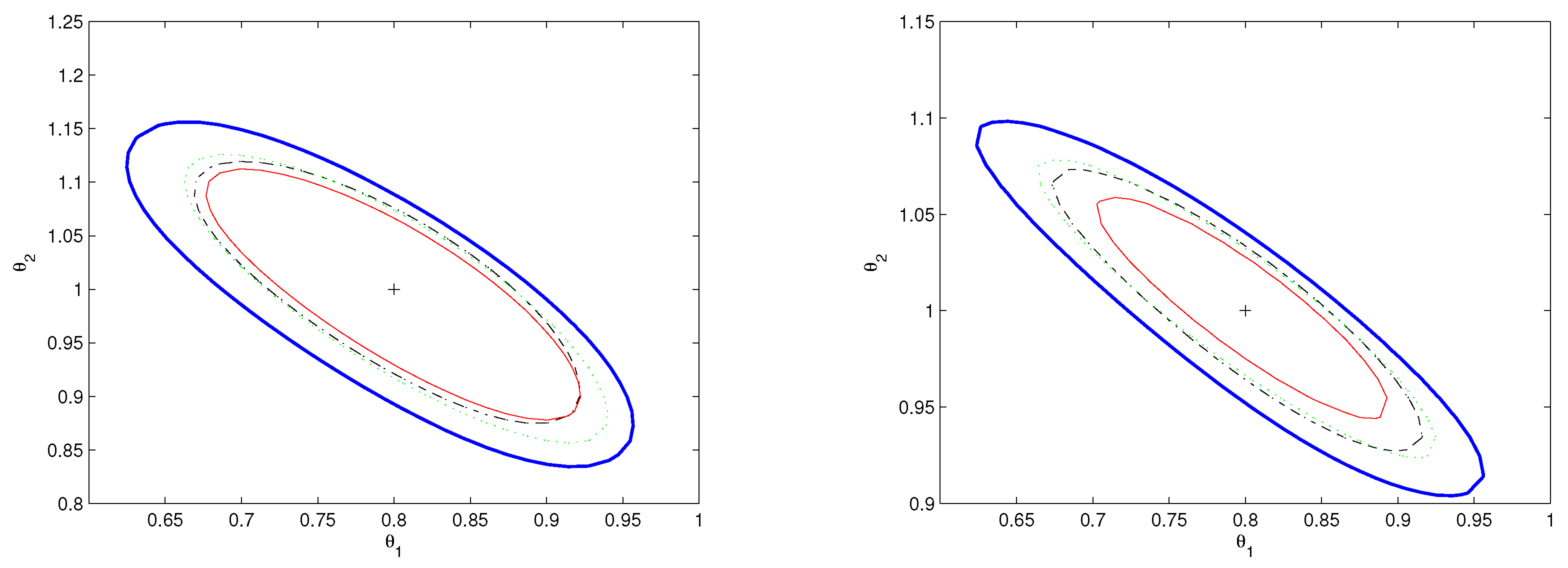
4. Simulation Study
4.1. Simulation 1
4.2. Simulation 2
5. Application to the ACTG 175 Data
- Treatment assignment (: 0 = ZDV monotherapy)
- Baseline CD4 count (: )
- Demographic covariates: age (), weight (), race (: 0 = White), gender (: 0 = Female)
- Clinical covariates: antiretroviral history (: 0 = naive), early treatment termination (: 0 = completed)
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jennrich, R.I. Asymptotic properties of non-linear least squares estimators. Ann. Math. Stat. 1969, 40, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F. Asymptotic theory of nonlinear least squares estimation. Ann. Stat. 1981, 9, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekedulegn, D.; Mac Siurtain, M.P.; Colbert, J.J. Parameter estimation of nonlinear growth models in forestry. Silva Fenn 1999, 33, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V. Asymptotic Theory of Nonlinear Regression; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Little, R.J.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz, D.G.; Thompson, D.J. A generalization of sampling without replacement from a finite universe. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, J.M.; Rotnitzky, A.; Zhao, L. Estimation of regression coefficients when some regressors are not always observed. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 846–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P. Multiply robust estimation in regression analysis with missing data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2014, 109, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xie, J. Efficient robust estimation for single-index mixed effects models with missing observations. Stat. Pap. 2024, 65, 827–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, S.; Stoll, K.; Ning, W. Statistical inferences for missing response problems based on modified empirical likelihood. Stat. Pap. 2024, 65, 4079–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, S.; Xu, W. Calibrated regression estimation using empirical likelihood under data fusion. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2024, 190, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhao, P. Empirical likelihood-based inference in nonlinear regression models with missing responses at random. Statistics 2013, 47, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.B. Empirical likelihood ratio confidence regions. Ann. Stat. 1990, 18, 90–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, N. Empirical likelihood for nonlinear regression models with nonignorable missing responses. Can. J. Stat. 2020, 48, 386–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, J.; Kim, J.K. An instrumental variable approach for identification and estimation with nonignorable nonresponse. Stat. Sin. 2014, 24, 1097–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shao, J.; Fang, F. Propensity model selection with nonignorable nonresponse and instrument variable. Stat. Sin. 2021, 31, 647–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shao, J.; Fang, F. Instrument search in pseudo-likelihood approach for nonignorable nonresponse. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 2021, 73, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, Y.; Cui, X. Identification and estimation of generalized additive partial linear models with nonignorable missing response. Commun. Math. Stat. 2024, 12, 113–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, K.; Morikawa, K. Verifiable identification condition for nonignorable nonresponse data with categorical instrumental variables. Stat. Theory Relat. Fields. 2024, 8, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, R. Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2001, 96, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Leung, D.; Shao, J. Estimation with survey data under nonignorable nonresponse or informative sampling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Lawless, J.F. Empirical likelihood and general estimating equations. Ann. Stat. 1994, 22, 300–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, H. Empirical likelihood for estimating equations with nonignorably missing data. Stat. Sin. 2014, 24, 723–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Tang, N. Adjusted empirical likelihood estimation of distribution function and quantile with nonignorable missing data. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2018, 31, 820–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Kano, Y. Statistical inference with different missing-data mechanisms. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.4971. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, W.; Tchetgen, E.J. On varieties of doubly robust estimators under missingness not at random with a shadow variable. Biometrika 2016, 103, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yuan, X. Doubly robust augmented-estimating-equations estimation with nonignorable nonresponse data. Stat. Pap. 2020, 61, 2241–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, N.; Zhu, H. Generalized empirical likelihood inferences for nonsmooth moment functions with nonignorable missing values. Stat. Sin. 2020, 30, 217–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Follmann, D.A.; Qin, J. Semiparametric dimension reduction estimation for mean response with missing data. Biometrika 2010, 97, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, N.; Qu, A.; Jiang, D. Semiparametric estimating equations inference with nonignorable missing data. Stat. Sin. 2017, 27, 89–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Zhao, P.; Tang, N. A propensity score adjustment method for regression models with nonignorable missing covariates. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2016, 94, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wan, A.T.K.; Wang, X. Estimating equations inference with missing data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 103, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, S.M.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Hughes, M.D.; Gundacker, H.; Schooley, R.T.; Haubrich, R.H.; Henry, W.K.; Lederman, M.M.; Phair, J.P.; Niu, M.; et al. A trial comparing nucleoside monotherapy with combination therapy in HIV-infected adults with CD4 cell counts from 200 to 500 per cubic millimeter. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidian, M.; Tsiatis, A.A.; Leon, S. Semiparametric estimation of treatment effect in a pretest–posttest study with missing data. Statist. Sci. 2005, 20, 261–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiatis, A.A.; Davidian, M.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X. Covariate adjustment for two-sample treatment comparisons in randomized clinical trials: A principled yet flexible approach. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 4658–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, X. Variable selection using penalized empirical likelihood. Sci. China Math. 2011, 54, 1829–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Est. | Bias | SD | RMS | T | F | Bias | SD | RMS | T | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0549 | 0.1021 | 0.1158 | 3.69 | 0 | 0.0447 | 0.0703 | 0.0833 | 3.79 | 0 | |
| 0.0211 | 0.2313 | 0.2321 | – | – | 0.0038 | 0.1612 | 0.1612 | – | – | |
| 0.0031 | 0.1397 | 0.1397 | – | – | 0.0118 | 0.0984 | 0.0990 | – | – | |
| IPW | AIPW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Est. | Bias | SD | RMS | Bias | SD | RMS | |
| 150 | 0.0014 | 0.0442 | 0.0443 | 0.0007 | 0.0439 | 0.0439 | |
| 0.0015 | 0.0519 | 0.0520 | 0.0012 | 0.0520 | 0.0522 | ||
| 0.0015 | 0.0569 | 0.0570 | 0.0008 | 0.0576 | 0.0576 | ||
| 0.0006 | 0.0596 | 0.0596 | 0.0001 | 0.0601 | 0.0601 | ||
| 0.0023 | 0.0573 | 0.0574 | 0.0020 | 0.0574 | 0.0574 | ||
| 0.0011 | 0.0305 | 0.0305 | 0.0009 | 0.0305 | 0.0305 | ||
| 250 | 0.0006 | 0.0382 | 0.0382 | 0.0008 | 0.0379 | 0.0379 | |
| 0.0012 | 0.0399 | 0.0399 | 0.0012 | 0.0401 | 0.0402 | ||
| 0.0015 | 0.0466 | 0.0466 | 0.0013 | 0.0466 | 0.0466 | ||
| 0.0010 | 0.0450 | 0.0450 | 0.0013 | 0.0449 | 0.0449 | ||
| 0.0016 | 0.0409 | 0.0409 | 0.0021 | 0.0409 | 0.0409 | ||
| 0.0005 | 0.0227 | 0.0227 | 0.0007 | 0.0225 | 0.0225 | ||
| Est. | Estimate | p-Value | Est. | Estimate | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.64 | <0.001 | 0.0068 | <0.001 | ||
| −0.0007 | <0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.002 | ||
| 0.0011 | 0.003 | 0.0010 | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 0.574 | −0.6299 | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 0.191 | −0.0010 | <0.001 |
| Complete-Case Analysis | Han’s Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | s.e. | p-Value | Estimate | s.e. | p-Value | |
| Intercept | 21.50 | 27.44 | 0.433 | 65.53 | 34.06 | 0.054 |
| Trt | 63.68 | 9.09 | <0.001 | 52.72 | 10.34 | <0.001 |
| 0.76 | 0.04 | <0.001 | 0.73 | 0.05 | <0.001 | |
| Age | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.816 | 0.14 | 0.55 | 0.796 |
| Weight | 0.54 | 0.28 | 0.054 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.417 |
| Race | −20.60 | 8.51 | 0.015 | −18.30 | 9.66 | 0.058 |
| Gender | −10.73 | 10.79 | 0.320 | −16.54 | 11.34 | 0.145 |
| History | −42.02 | 7.62 | <0.001 | −41.45 | 8.65 | <0.001 |
| Offtrt | −80.72 | 9.62 | <0.001 | −86.87 | 10.31 | <0.001 |
| IPW | AIPW | |||||
| Estimate | s.e. | p-Value | Estimate | s.e. | p-Value | |
| Intercept | 33.15 | 30.66 | 0.2796 | 34.28 | 30.77 | 0.2651 |
| Trt | 62.14 | 9.52 | <0.001 | 61.77 | 9.60 | <0.001 |
| 0.76 | 0.05 | <0.001 | 0.76 | 0.05 | <0.001 | |
| Age | 0.18 | 0.53 | 0.7278 | 0.18 | 0.54 | 0.7326 |
| Weight | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.1797 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.1884 |
| Race | −22.07 | 10.10 | 0.0288 | −22.01 | 10.13 | 0.0297 |
| Gender | −9.38 | 12.07 | 0.4369 | −9.33 | 12.10 | 0.4402 |
| History | −41.34 | 8.67 | <0.001 | −41.24 | 8.70 | <0.001 |
| Offtrt | −74.74 | 11.62 | <0.001 | −74.44 | 11.64 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Li, X. Identification and Empirical Likelihood Inference in Nonlinear Regression Model with Nonignorable Nonresponse. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091388
Ding X, Li X. Identification and Empirical Likelihood Inference in Nonlinear Regression Model with Nonignorable Nonresponse. Mathematics. 2025; 13(9):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091388
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xianwen, and Xiaoxia Li. 2025. "Identification and Empirical Likelihood Inference in Nonlinear Regression Model with Nonignorable Nonresponse" Mathematics 13, no. 9: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091388
APA StyleDing, X., & Li, X. (2025). Identification and Empirical Likelihood Inference in Nonlinear Regression Model with Nonignorable Nonresponse. Mathematics, 13(9), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091388





