Single-Source and Multi-Source Cross-Subject Transfer Based on Domain Adaptation Algorithms for EEG Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Investigate the effect of domain shifts between EEG recordings that contribute to significant variations in EEG characteristics from subject to subject;
- Assess the performance of domain adaptation methods—including ML algorithms implemented through a traditional BCI—under STS and MTS transfer learning paradigms based on a cross-subject EEG classification scenario;
- Conduct an extensive comparative performance analysis among MMFT, MEKT, K-NN, and NB. The results acquired from the experiments illustrated that domain adaptation algorithms yield superior performance under both the STS and MTS transfer learning paradigms compared to classical ML algorithms for cross-subject EEG classification.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
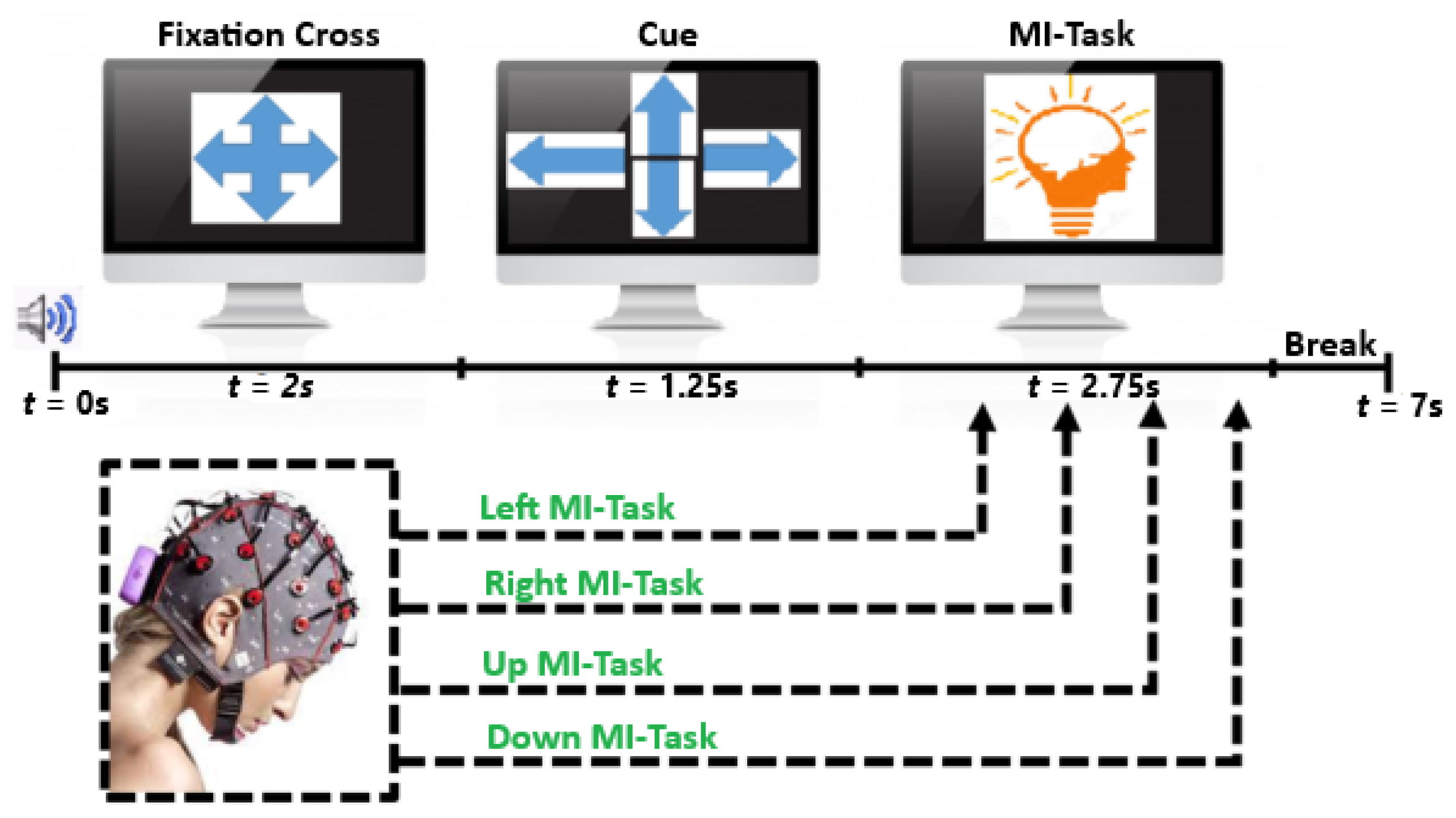
3.1. EEG Signal Acquisition
3.1.1. Dataset IIa of BCI Competition IV-a
3.1.2. Recorded MI and SSVEP Datasets
3.2. Domain Adaptation Algorithms Based on Cross-Subject EEG Classification
3.2.1. Manifold Embedded Knowledge Transfer Framework (MEKT)
3.2.2. Multi-Source Manifold Feature Transfer Learning (MMFT)
3.3. Proposed Traditional BCI Framework Based on Cross-Subject Classification
3.3.1. EEG Signal Pre-Processing
Filtering of EEG Signals
Decomposition of EEG Signals
3.3.2. Extraction of EEG Signal Features
3.3.3. Selection of EEG Signal Features
3.3.4. Classification of EEG Signal Features
K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN)
4. Implementation of Domain Adaptation and ML Algorithms Based on STS, MTS Transfer Paradigm
5. Results
5.1. Experiment Setup for STS and MTS Transfer Paradigms
5.2. Setup for SD Increment Experiment
5.3. Experimental Results
5.3.1. Single-Source-to-Single-Target (STS) Transfer Paradigm
Performance Evaluation Under STS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing BCI Competition IV-a Dataset
Performance Evaluation Under STS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing the Recorded MI Dataset
Performance Evaluation Under STS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing the Recorded SSVEP Dataset
5.3.2. Multi-Source-to-Single-Target (MTS) Transfer Learning Paradigm
Performance Evaluation Under MTS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing BCI Competition IV-a Dataset
Performance Evaluation Under MTS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing the Recorded MI Dataset
Performance Evaluation Under MTS Transfer Paradigm Utilizing the Recorded SSVEP Dataset
5.3.3. Impacts of Hyper Parameters
Performance Evaluation for Different Numbers of Source Domains
- (1)
- Source-domain increment experiment utilizing BCI Competition IV-a dataset
- (2)
- Source-domain increment experiment utilizing the recorded MI dataset
- (3)
- Source-domain increment experiment utilizing the recorded SSVEP dataset
5.3.4. Computational Complexity
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maswanganyi, C.; Tu, C.; Owolawi, P.; Du, S. Overview of artifacts detection and elimination methods for BCI using EEG. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chongqing, China, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 832–836. [Google Scholar]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Ani, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. Feature subset selection using differential evolution and a statistical repair mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 11515–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanganyi, C.; Tu, C.; Owolawi, P.; Du, S. Discrimination of motor imagery task using wavelet based EEG signal features. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Computing Applications (ICONIC), Mon Tresor, Mauritius, 6–7 December 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Myrden, A.; Chau, T. A passive EEG-BCI for single-trial detection of changes in mental state. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Ahmed, K.I.; Mostafa, R.; Khandoker, A.H.; Hadjileontiadis, L. Enhanced inter-subject brain computer interface with associative sensorimotor oscillations. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Chu, M. TDLNet: Transfer data learning network for cross-subject classification based on multiclass upper limb motor imagery EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 3958–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Zhang, C.; Fang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multisource Associate Domain Adaptation for Cross-Subject and Cross-Session EEG Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2515512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, P.; Chowdhury, A.; McCreadie, K.; Pachori, R.B.; Wang, H. Logistic Regression with Tangent Space-Based Cross-Subject Learning for Enhancing Motor Imagery Classification. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cui, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. A Cross-Scale Transformer and Triple-View Attention Based Domain-Rectified Transfer Learning for EEG Classification in RSVP Tasks. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zuo, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, P.Z. Evolutionary Ensemble Learning for EEG-based Cross-Subject Emotion Recognition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 3872–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. Artificial Intelligence with Great Potential in Medical Informatics: A Brief Review. Medinformatics 2024, 1, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.-W. Motor imagery classification using inter-task transfer learning via a channel-wise variational autoencoder-based convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Cao, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. Cross-subject assistance: Inter-and intra-subject maximal correlation for enhancing the performance of SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Xiong, B.; Wang, Q.; Wan, B.; Li, F.; Yang, P. Cross-subject transfer method based on domain generalization for facilitating calibration of SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 3307–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S. Decoding Medical Diagnosis with Machine Learning Classifiers. Medinformatics 2024. Available online: https://ojs.bonviewpress.com/index.php/MEDIN/article/view/2583/905 (accessed on 24 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Jeng, P.-Y.; Wei, C.-S.; Jung, T.-P.; Wang, L.-C. Low-dimensional subject representation-based transfer learning in EEG decoding. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Yang, R.; Huang, M.; Ni, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Sub-band cascaded csp-based deep transfer learning for cross-subject lower limb motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2023, 16, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhah, L.; Sarno, R.; Fatichah, C. Cross-subject channel selection using modified relief and simplified CNN-based deep learning for EEG-based emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 110136–110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, E.; Jin, M.; Fan, C.; He, H.; Cai, T.; Li, J. Dynamic domain adaptation for class-aware cross-subject and cross-session EEG emotion recognition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 5964–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Ahmed, K.I.U.; Mostafa, R.; Hadjileontiadis, L.; Khandoker, A. Evidence of variabilities in EEG dynamics during motor imagery-based multiclass brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 26, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ortega, P.; Faisal, A.A. Inter-subject deep transfer learning for motor imagery EEG decoding. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Sorrento, Italy, 4–6 May 2021; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xu, T.; Zhou, T.; Hu, H. MDTL: A Novel and Model-Agnostic Transfer Learning Strategy for Cross-Subject Motor Imagery BCI. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Chauhan, M.; Shaikh, M.A.; Chu, J.; Srihari, S. Ultra efficient transfer learning with meta update for cross subject EEG classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.06113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, H.; Yu, Z.; Yu, T.; Gu, Z.; Yang, J. A multi-domain convolutional neural network for EEG-based motor imagery decoding. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 3988–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Corralejo, R.; Gomez-Pilar, J.; Álvarez, D.; Hornero, R. Adaptive stacked generalization for multiclass motor imagery-based brain computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, D.; Raza, H.; Prasad, G.; Cecotti, H. Current source density estimation enhances the performance of motor-imagery-related brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuagwu, B.A.; Zych, M.; Vuckovic, A. Is implicit motor imagery a reliable strategy for a brain–computer interface? IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Gu, Z.; Cichocki, A.; Li, Y. Enhanced motor imagery training using a hybrid BCI with feedback. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanganyi, R.C.; Tu, C.; Owolawi, P.A.; Du, S. Statistical Evaluation of Factors Influencing Inter-Session and Inter-Subject Variability in EEG-Based Brain Computer Interface. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 96821–96839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Gao, S. A benchmark dataset for SSVEP-based brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, S.Q.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.-Q. Cross-subject transfer learning for boosting recognition performance in SSVEP-based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, X.; Ma, C.; Ma, K.; Hui, P. A deep learning method for improving the classification accuracy of SSMVEP-based BCI. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3447–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, D. Manifold embedded knowledge transfer for brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Cai, Y.; Du, S.; Chen, Y. Multi-source manifold feature transfer learning with domain selection for brain-computer interfaces. Neurocomputing 2022, 514, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoomi, R.; Khadem, A. Enhancing LDA-based discrimination of left and right hand motor imagery: Outperforming the winner of BCI Competition II. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI), Tehran, Iran, 5–6 November 2015; pp. 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, J.; Lee, D.D. Grassmann discriminant analysis: A unifying view on subspace-based learning. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 376–383. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Jin, X.; Hu, H.; Zhu, L.; Ozawa, K.; Pan, G.; Kong, W. Dynamic distribution alignment with dual-subspace mapping for cross-subject driver mental state detection. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Xu, G.; Tao, T.; Wu, Q. Class-imbalance adversarial transfer learning network for cross-domain fault diagnosis with imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 3501111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, S.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Liu, C.-L.; He, H. Multisource transfer learning for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 3281–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, F.P.A.; Pane, E.S.; Suprapto, Y.K.; Purnomo, M.H. Wavelet based-analysis of alpha rhythm on eeg signal. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 6–7 March 2018; pp. 719–723. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, N.; Afrakhteh, S.; Mosavi, M.R. Multi-task EEG signal classification using correlation-based IMF selection and multi-class CSP. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 52712–52725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castañeda, E.F.; Torres-García, A.A.; Reyes-García, C.A.; Villaseñor-Pineda, L. Sonification and textification: Proposing methods for classifying unspoken words from EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 37, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, V.; Das, S.; Jamal, W.; Maharatna, K. Hybrid wavelet and EMD/ICA approach for artifact suppression in pervasive EEG. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 267, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, R.; Huang, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Single-source to single-target cross-subject motor imagery classification based on multisubdomain adaptation network. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Yin, G. Motion control of a four-wheel-independent-drive electric vehicle by motor imagery EEG based BCI system. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 5449–5454. [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik, P.K.; Sarraf, J. Brain Computer Interface issues on hand movement. J. King Saud Univ.—Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 30, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Guan, C. Bayesian learning for spatial filtering in an EEG-based brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Wang, G. Improvement in EEG source imaging accuracy by means of wavelet packet transform and subspace component selection. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bong, S.Z.; Wan, K.; Murugappan, M.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Rajamanickam, Y.; Mohamad, K. Implementation of wavelet packet transform and non linear analysis for emotion classification in stroke patient using brain signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 36, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alickovic, E.; Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduallatif, N.A.; Elsherbini, S.G.; Boshra, B.S.; Yassine, I.A. Brain-Computer Interface controlled functional electrical stimulation system for paralyzed arm. In Proceedings of the 2016 8th Cairo International Biomedical Engineering Conference (CIBEC), Cairo, Egypt, 15–17 December 2016; pp. 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bak, S.; Jeong, J. User biometric identification methodology via EEG-based motor imagery signals. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 41303–41314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, C.Y.; Mokhtar, N.; Arof, H.; Cumming, P.; Iwahashi, M. Automated classification and removal of EEG artifacts with SVM and wavelet-ICA. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, R.; Rakshit, P.; Konar, A. Evolutionary perspective for optimal selection of EEG electrodes and features. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 36, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, S.; Rajkumar, K.; Ravichander, J. EEG based Motor Imagery BCI using Four Class Iterative Filtering & Four Class Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Advances in Electronics, Communication, Computing and Intelligent Information Systems (ICAECIS), Bangalore, India, 19–21 April 2023; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Lai, X.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. Cluster embedding joint-probability-discrepancy transfer for cross-subject seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 31, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-S.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Jung, T.-P. Toward drowsiness detection using non-hair-bearing EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, W.-J.; Chen, C.-C. Multiclass Classification of EEG Motor Imagery Signals Based on Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Applied System Innovation (ICASI), Nantou, Taiwan, 22–23 April 2022; pp. 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Chung, F.-L.; Wang, S. Recognition of multiclass epileptic EEG signals based on knowledge and label space inductive transfer. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.Z.; Aslam, N.; Shum, H.P.; Zhang, L. Differential evolution algorithm as a tool for optimal feature subset selection in motor imagery EEG. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 90, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Guarneros, M.; Fuentes-Pineda, G. Cross-subject EEG-based emotion recognition via semi-supervised multi-source joint distribution adaptation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2523911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanganyi, C.; Tu, C.; Owolawi, P.; Du, S. Factors influencing low intension detection rate in a non-invasive EEG-based brain computer interface system. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. (IJEECS) 2020, 20, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Methods | Source Domains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
| MMFT | 89 (9.6) | 89 (10.5) | 88 (11.6) | 82 (16.5) | 79 (13.4) | 82 (13.2) | 68 (9.4) | 51 (2.8) | 75 (10) |
| MEKT | 75 (13.8) | 51 (5.2) | 84 (13.1) | 64 (6.1) | 53 (3.2) | 64 (5.7) | 60 (9.8) | 87 (7.3) | 74 (4.7) |
| K-NN | 38 (4.5) | 37 (5.3) | 37 (4.6) | 36 (3.6) | 37 (3.2) | 33 (3.7) | 37 (3.04) | 36 (2.7) | 37 (3.9) |
| NB | 36 (6.9) | 37 (7.1) | 34 (2.6) | 33 (2.5) | 35 (3.5) | 34 (2.7) | 35 (2.1) | 34 (3) | 35 (2.1) |
| Methods | Source Domains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
| MMFT | 54 (15.8) | 57 (16.6) | 56 (16.3) | 59 (12.9) | 41 (18.5) | 60 (18.5) | 63 (14.2) | 47 (13.4) | 49 (19.5) |
| MEKT | 53 (17.2) | 55 (13.6) | 60 (18.7) | 67 (14.6) | 45 (19.8) | 62 (20.8) | 67 (17.2) | 43 (11.9) | 51 (8.2) |
| K-NN | 36 (4.9) | 35 (5.7) | 39 (6.2) | 38 (5.4) | 45 (6.4) | 40 (6.1) | 43 (12.1) | 42 (9.3) | 43 (4.6) |
| NB | 33 (4.7) | 42 (7.4) | 37 (6.6) | 45 (13.5) | 42 (6) | 43 (13.5) | 41 (4.2) | 45 (3.9) | 41 (4.9) |
| Methods | Source Domains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
| MMFT | 77 (31.2) | 73 (17.4) | 65 (32.4) | 67 (21.9) | 75 (26.4) | 73 (23.7) | 78 (16.9) | 59 (23.7) | 42 (14.1) |
| MEKT | 77 (30.5) | 68 (23) | 65 (34.4) | 69 (16) | 76 (21.7) | 73 (18.7) | 82 (18.9) | 62 (18.3) | 42 (15.3) |
| K-NN | 45 (7.9) | 40 (6.3) | 43 (9.9) | 37 (7.7) | 50 (3.1) | 43 (4.9) | 41 (8.6) | 44 (8.5) | 40 (6.3) |
| NB | 52 (6.5) | 34 (10.2) | 36 (12.5) | 37 (11.1) | 49 (3.9) | 34 (10.5) | 40 (6.2) | 51 (4.5) | 40 (5.9) |
| Methods | BCI Competition IV-a | Recorded SSVEP Dataset | Recorded MI Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMFT | 83 (14.4) | 83 (24.6) | 62 (21.0) |
| MEKT | 76 (16.8) | 73 (27.7) | 63 (13.8) |
| K-NN | 40 (4.8) | 46 (5.0) | 51 (10.4) |
| NB | 34 (4.2) | 42 (11.1) | 46 (10.2) |
| Computational Time | ||
|---|---|---|
| Methods | STS | MTS |
| NB | 1586.4 s | 214.6 s |
| K-NN | 1994.4 s | 224.2 s |
| MEKT | 16.7 s | 9.4 s |
| MMFT | 14.8 s | 9.1 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maswanganyi, R.C.; Tu, C.; Owolawi, P.A.; Du, S. Single-Source and Multi-Source Cross-Subject Transfer Based on Domain Adaptation Algorithms for EEG Classification. Mathematics 2025, 13, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050802
Maswanganyi RC, Tu C, Owolawi PA, Du S. Single-Source and Multi-Source Cross-Subject Transfer Based on Domain Adaptation Algorithms for EEG Classification. Mathematics. 2025; 13(5):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050802
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaswanganyi, Rito Clifford, Chunling Tu, Pius Adewale Owolawi, and Shengzhi Du. 2025. "Single-Source and Multi-Source Cross-Subject Transfer Based on Domain Adaptation Algorithms for EEG Classification" Mathematics 13, no. 5: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050802
APA StyleMaswanganyi, R. C., Tu, C., Owolawi, P. A., & Du, S. (2025). Single-Source and Multi-Source Cross-Subject Transfer Based on Domain Adaptation Algorithms for EEG Classification. Mathematics, 13(5), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13050802







