Scalar Field and Quintessence in Late-Time Cosmic Expansion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Field Equations
3. Parametrization of Hubble Parameter
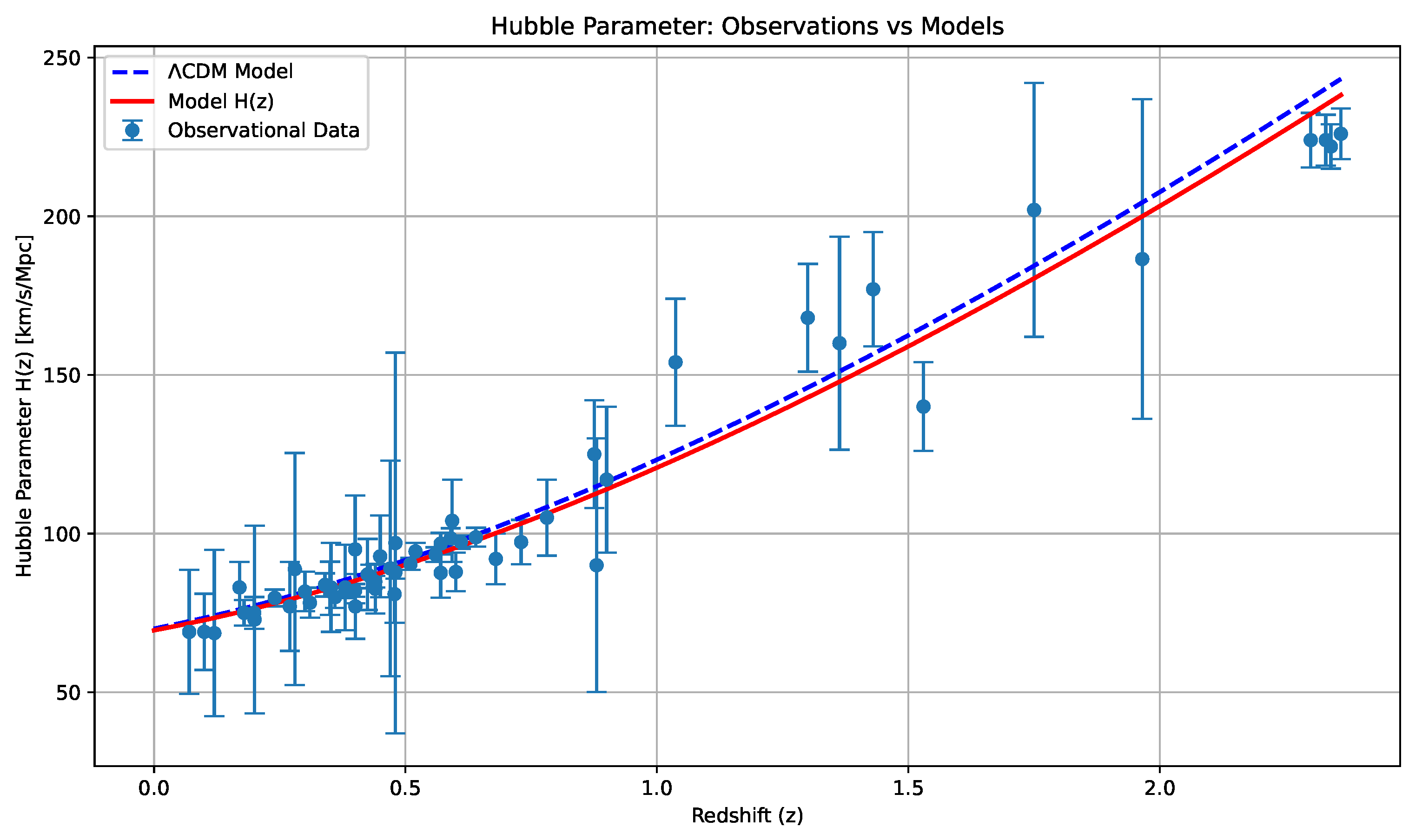
4. Datasets and Observational Framework
5. Cosmographic Parameters
5.1. Deceleration Parameter
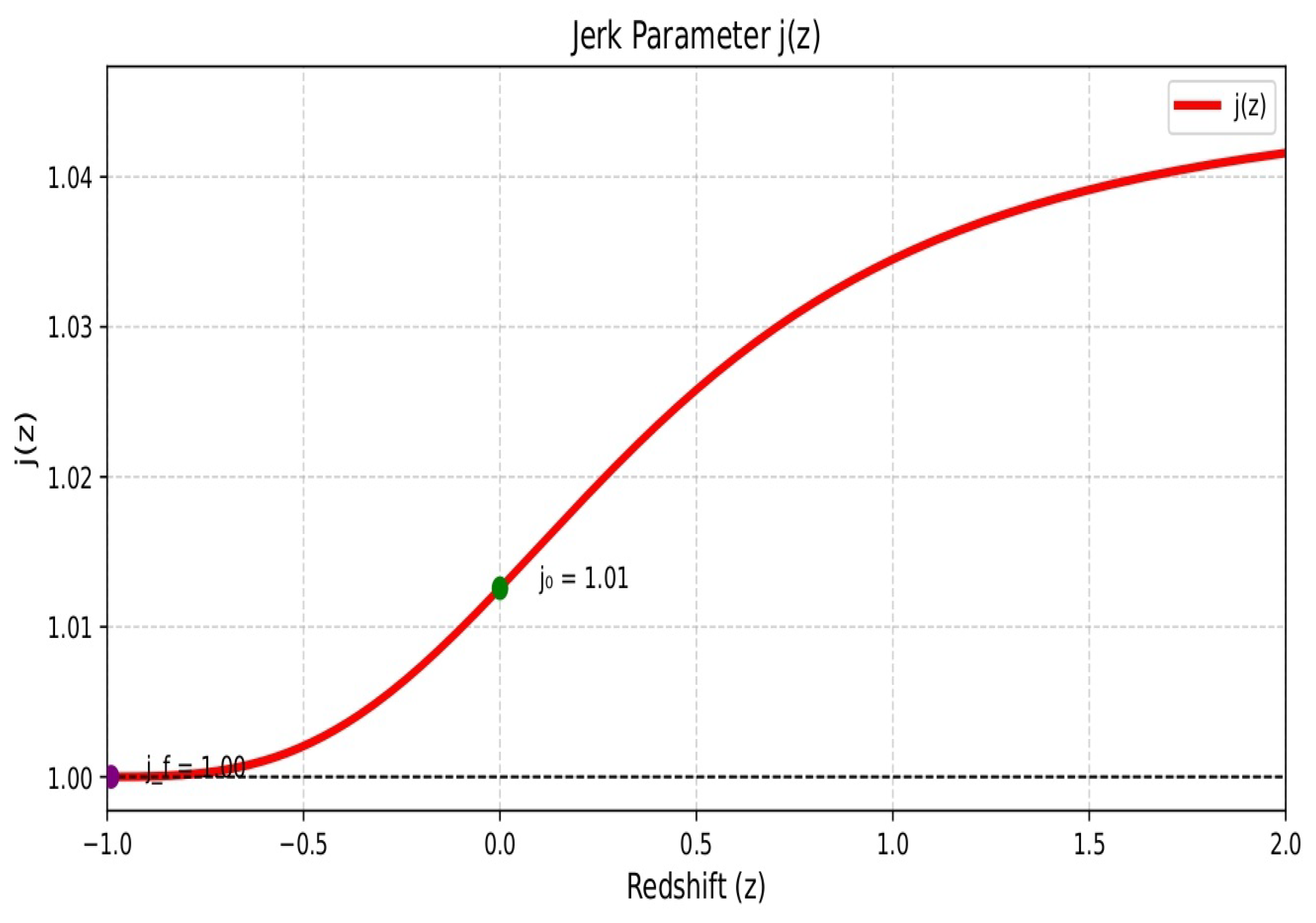
5.2. Jerk Parameter
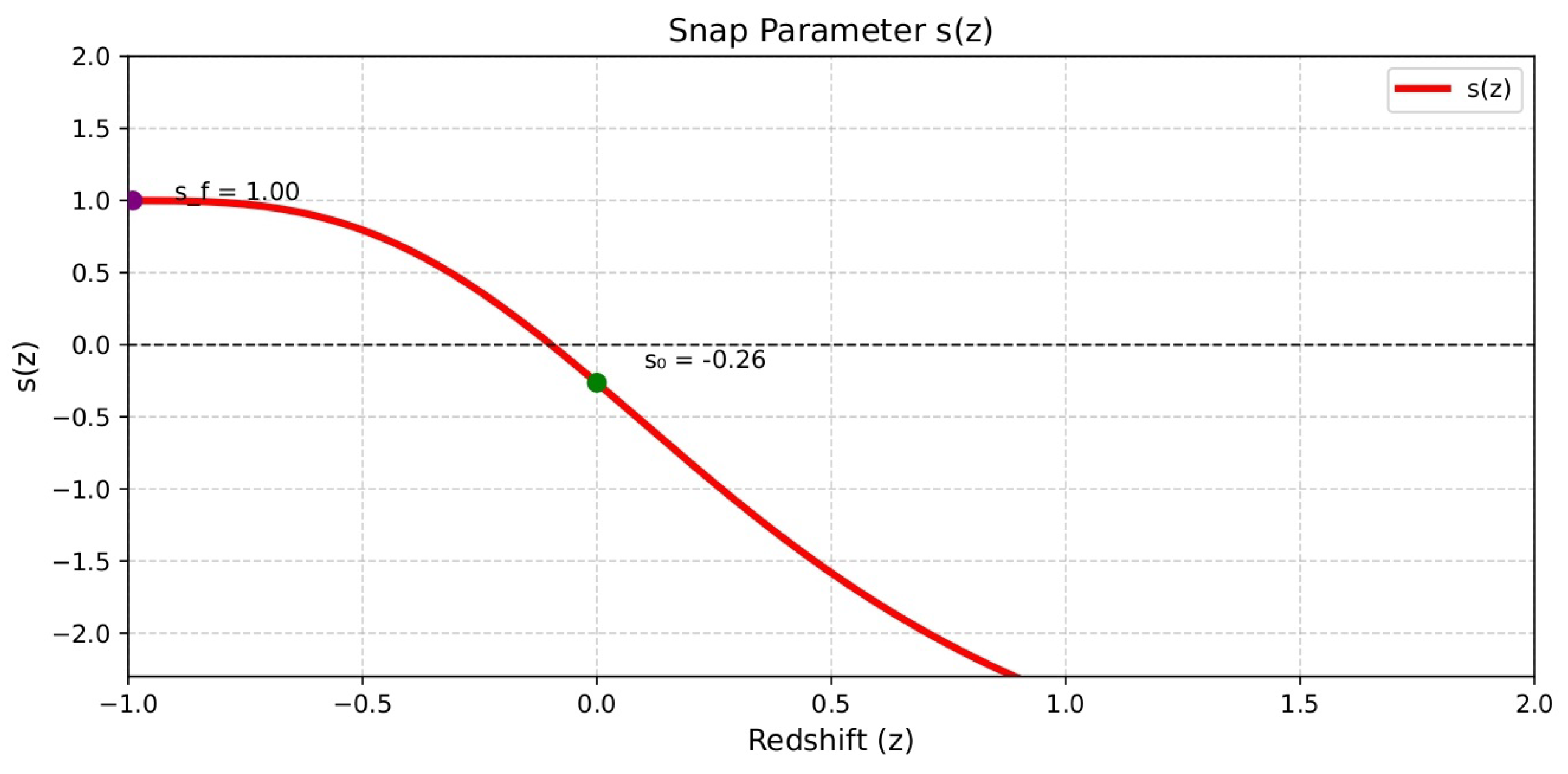
5.3. Snap Parameter
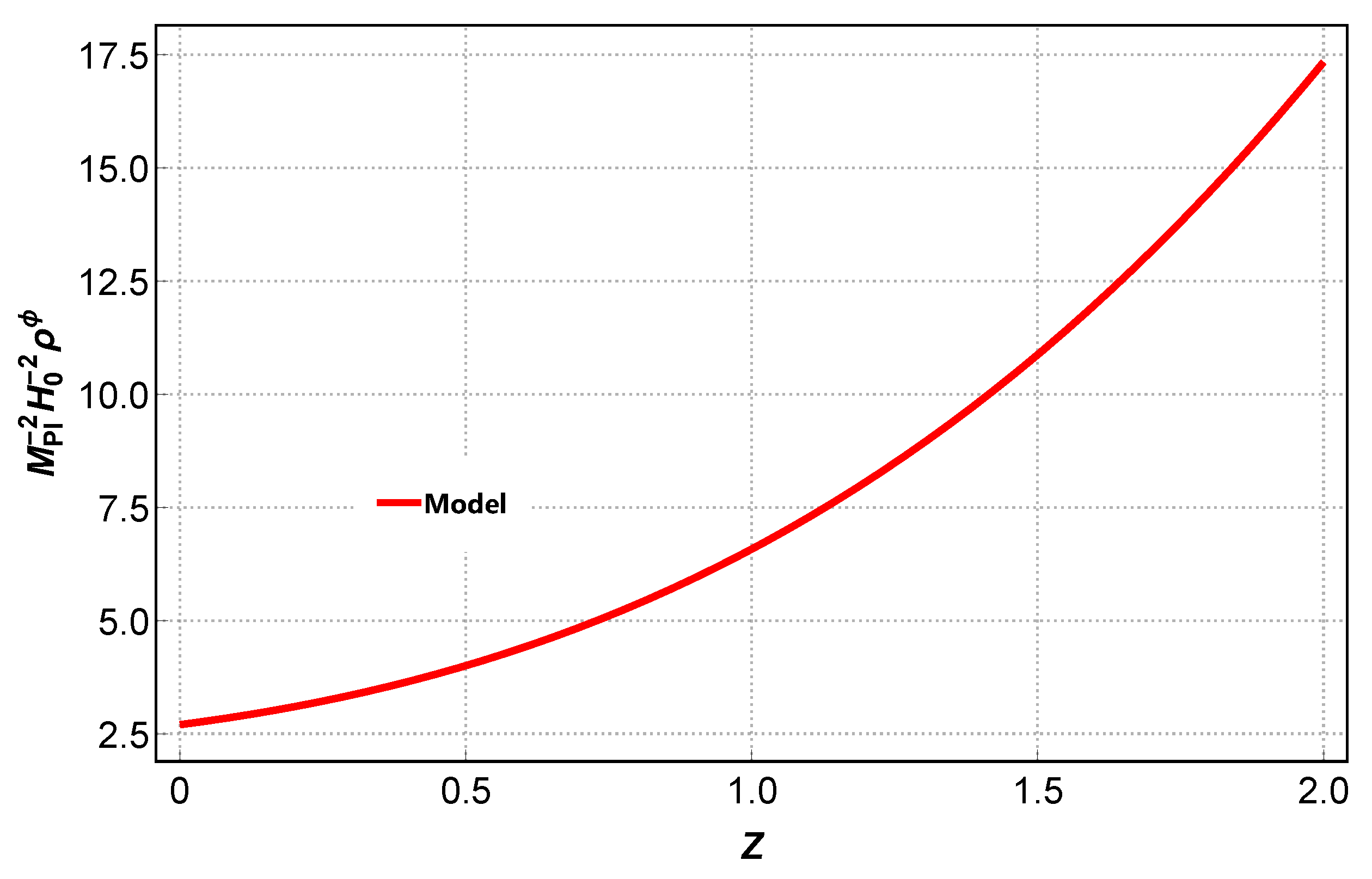
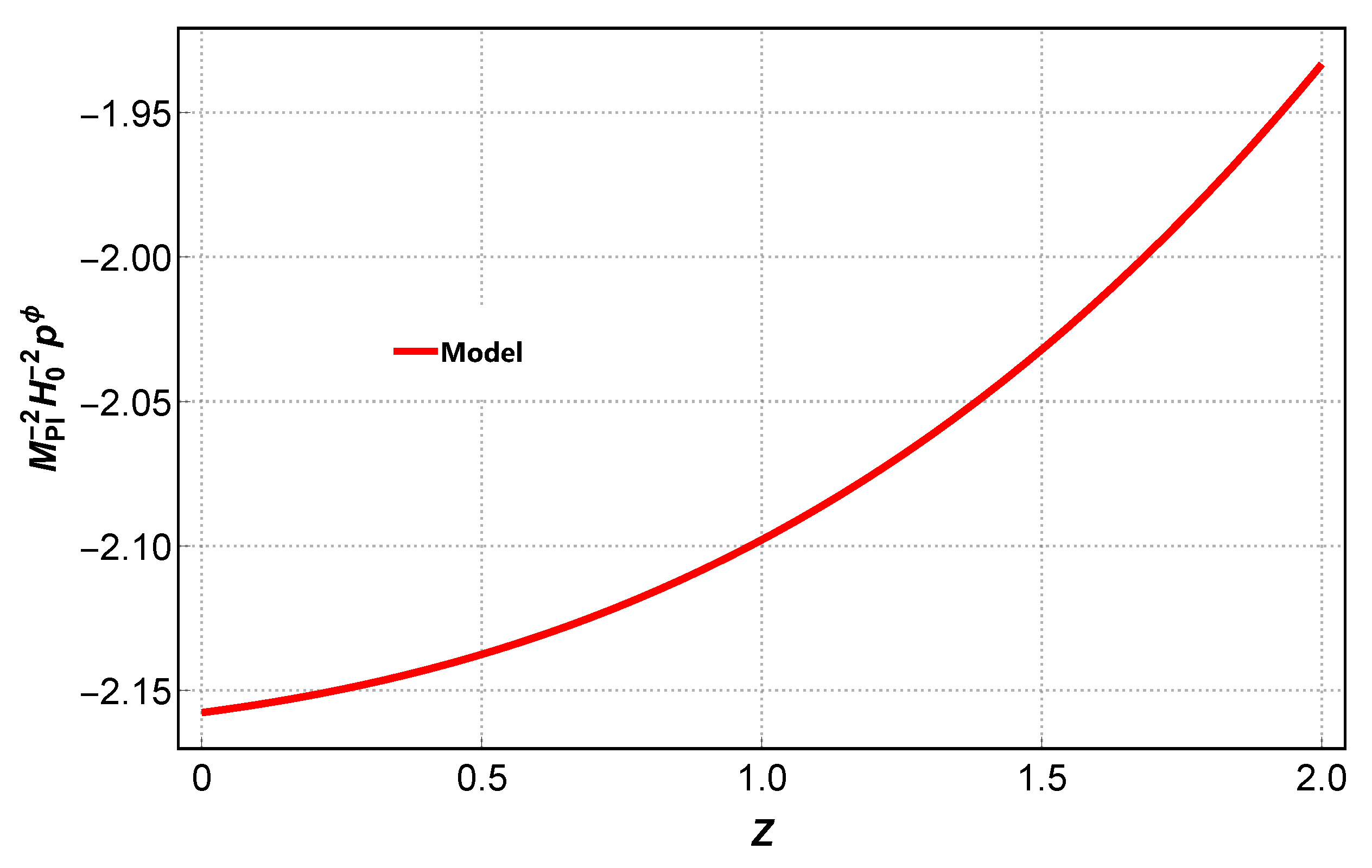
6. Physical Characteristics of Quintessence as a Dark Energy Source: Cosmic Evolution
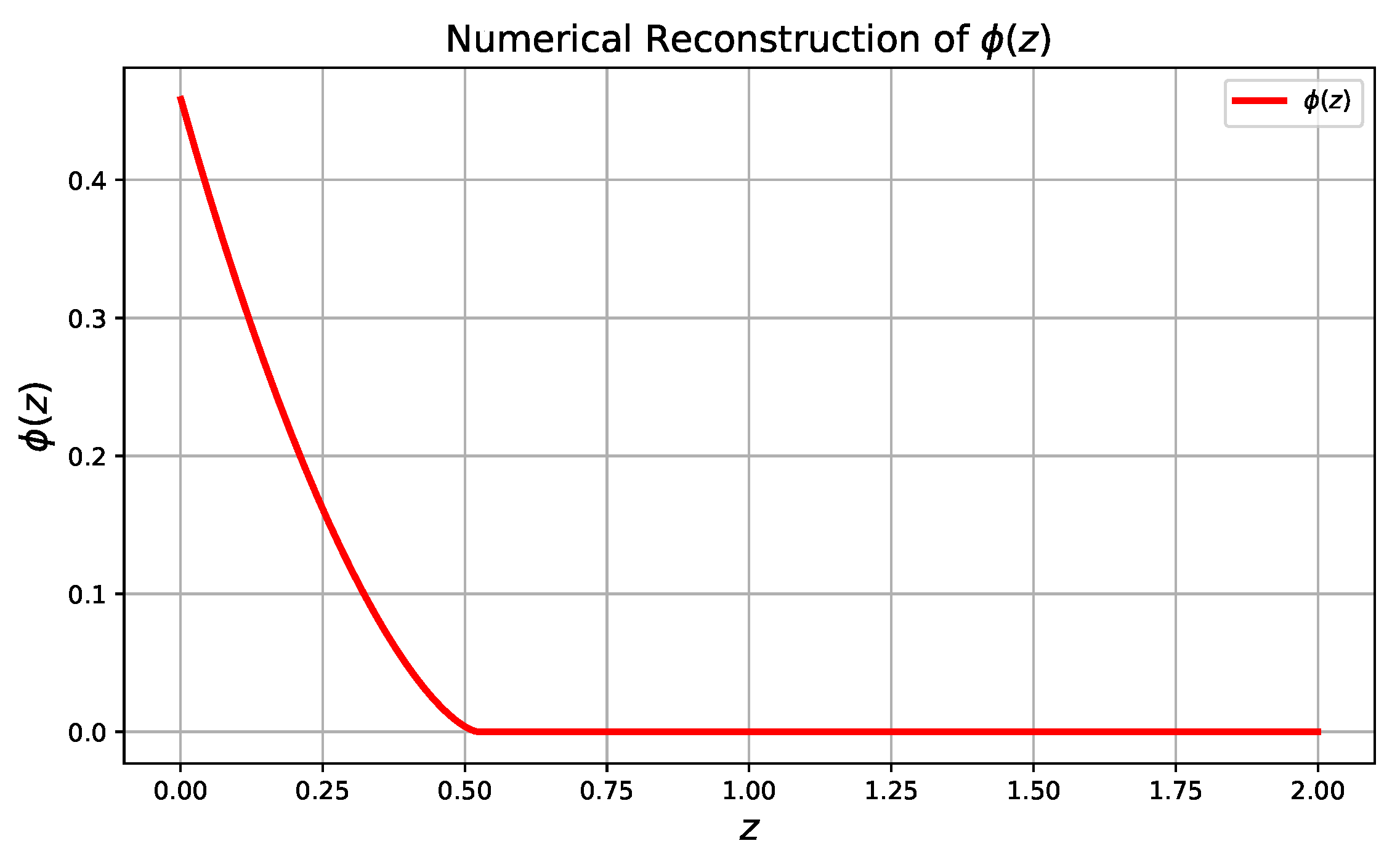
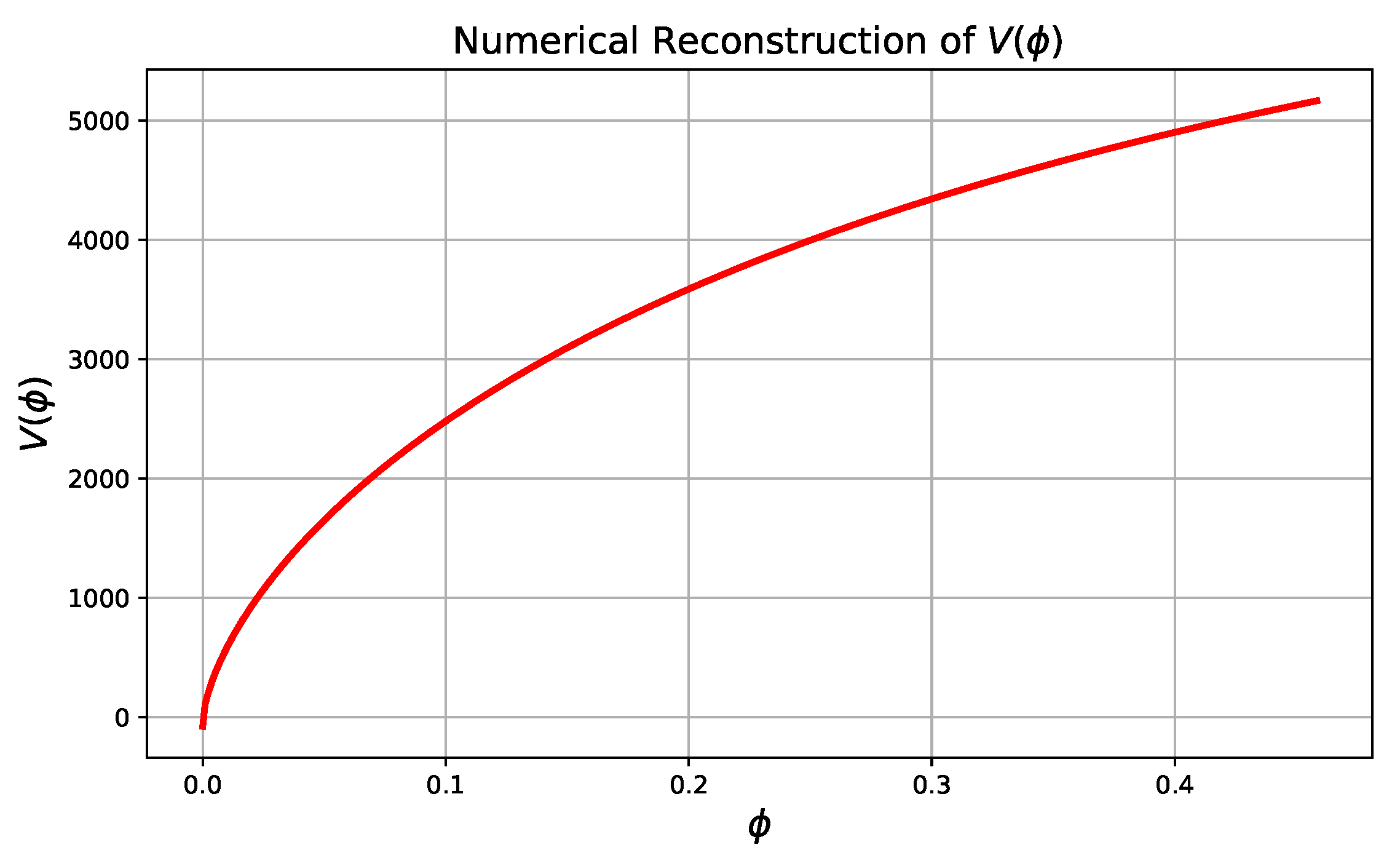
Kinetic and Potential Terms of the Scalar Field
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, P. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.L.; Scolnic, D.; Casertano, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; Tucker, B.E.; Reid, M.J.; Jones, D.O.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A 2.4% determination of the local value of the Hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Bowers, J.B.; Macri, L.; Zinn, J.C.; Scolnic, D. Cosmic distances calibrated to 1% precision with Gaia EDR3 parallaxes and Hubble Space Telescope photometry of 75 Milky Way Cepheids confirm tension with ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylor, K.; Joy, M.; Knox, L.; Millea, M.; Raghunathan, S.; Story, K. Sounds Discordant: Classical distance ladder and ΛCDM–based determinations of the cosmological sound horizon. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, L.; Millea, M. Hubble constant hunter’s guide. Phys. Rep. 2021, 913, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, S.; Battye, R. Do Consistent F(R) Models Mimic General Relativity plus Lambda? Phys. Lett. B 2007, 654, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Gannouji, R.; Polarski, D.; Tsujikawa, S. Conditions for the cosmological viability of f(R) dark energy models. Phys. Rev. D. 2007, 75, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, R.; Rahvar, S. Consistency Condition of Spherically Symmetric Solutions in f(R) Gravity. Phys. Rev. D. 2008, 77, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashe, G. Energy Conditions of Built-In Inflation Models in f(T) Gravitational Theories. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Setare, M.; Mohammadipour, N. Can f(T) gravity theories mimic ΛCDM cosmic history. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 2013, 015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S.N.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. f(R,T) gravity. Phys. Rev. D. 2011, 84, 024020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlu, S.; Alfedeel, A.H.A.; Abebe, A. The cosmology of f(R,Lm) gravity: Constraining the background and perturbed dynamics. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.08303. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, J.B.; Heisenberg, L.; Koivisto, T. Coincident general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.B.; Heisenberg, L.; Koivisto, T.; Pekar, S. Cosmology in f(Q) geometry. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Harko, T.; Liang, S.D. f(Q,T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horndeski, G.W. Second-Order Scalar-Tensor Field Equations in a Four-Dimensional Space. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1974, 10, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, D. Dark energy and modified gravity in degenerate higher-order scalar–tensor (DHOST) theories: A review. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1942006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratra, B.; Peebles, P.J.E. Cosmological consequences of a rolling homogeneous scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 3406–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of Dark Energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1753–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, I.; Wang, L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Quintessence, Cosmic Coincidence, and the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.J.; Wang, L.; Zlatev, I. Cosmological tracking solutions. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, V.B. Genesis of cosmological tracker fields. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tocchini-Valentini, D. Stationary dark energy: The present universe as a global attractor. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 043509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M.; Piazza, F.; Veneziano, G. Quintessence as a runaway dilaton. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 65, 023508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. Dynamical Solution to the Problem of a Small Cosmological Constant and Late-Time Cosmic Acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 4438–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, L.A.; Caldwell, R.R.; Kamionkowski, M. Spintessence! New models for dark matter and dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 545, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Majeed, A. Correspondence of pilgrim dark energy with scalar field models. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 356, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Okabe, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Kinetically driven quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 023511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, H.M.; Alimohammadi, M. Transition from quintessence to the phantom phase in the quintom model. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 043506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Battaner, E.; et al. Planck2015 results: XXVIII. ThePlanckCatalogue of Galactic cold clumps. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A28. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenshchik, A.; Moschella, U.; Pasquier, V. An alternative to quintessence. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 511, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieloo, A.; Kim, A.G.; Linder, E.V. Gaussian process cosmography. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 123530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieloo, A.; Kim, A.G.; Linder, E.V. Model independent tests of cosmic growth versus expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 023520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.R. Model independent parametrization of the late time cosmic acceleration: Constraints on the parameters from recent observations. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 043528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corasaniti, P.S.; Copeland, E.J. Model independent approach to the dark energy equation of state. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 063521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics beyond ΛCDM. Ap. J. 2019, 876, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, A.; Chaudhary, H.; Mehrotra, A.; Pacif, S.K.J. Model-independent study for a quintessence model of dark energy: Analysis and observational constraints. Fortschritte Der Phys. 2023, 71, 2300086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, W.; Pavón, D. Statefinder parameters for interacting dark energy. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2004, 36, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolami, O.; Martins, P.J. Nonminimal coupling and quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Pavón, D. Cosmic acceleration without quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overduin, J.; Cooperstock, F. Evolution of the scale factor with a variable cosmological term. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 043506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, T.D.; Raychaudhury, S.; Sahni, V.; Starobinsky, A.A. Reconstructing the cosmic equation of state from supernova distances. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.; Verde, L.; Jimenez, R. Constraints on the redshift dependence of the dark energy potential. Phys. Rev. D—Part. Fields Gravit. Cosmol. 2005, 71, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Das, R.K.; Pan, S. Parametrizing the Hubble function instead of dark energy: Many possibilities. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 112, 043542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisty, D.; Pan, S.; Staicova, D.; Valentino, E.D.; Nunes, R.C. Late-time constraints on interacting dark energy: Analysis independent of H0, rd, and MB. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 688, A156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chakraborty, S. An analytic model for interacting dark energy and its observational constraints. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Sharov, G.S. A model with interaction of dark components and recent observational data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 4736–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.Y.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Han, Z.W.; Yang, R.J. A new parametrization of Hubble function and Hubble tension. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 2024, 028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharov, G.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Pan, S.; Nunes, R.C.; Chakraborty, S. A new interacting two-fluid model and its consequences. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 466, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, W. Curvature tension: Evidence for a closed universe. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, L041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, E.D.; Melchiorri, A.; Silk, J. Cosmic discordance: Planck and luminosity distance data exclude ΛCDM. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04935. [Google Scholar]
- Cuceu, A.; Farr, J.; Lemos, P.; Font-Ribera, A. Baryon acoustic oscillations and the Hubble constant: Past, present and future. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Motloch, P.; Hu, W.; Raveri, M. Hubble constant difference between CMB lensing and BAO measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 023510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, F.; Blake, C.; Colless, M.; Jones, D.H.; Staveley-Smith, L.; Campbell, L.; Parker, Q.; Saunders, W.; Watson, F. The 6dF Galaxy Survey: Baryon acoustic oscillations and the local Hubble constant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 3017–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.J.; Samushia, L.; Howlett, C.; Percival, W.J.; Burden, A.; Manera, M. The clustering of the SDSS DR7 main galaxy sample–I. A 4 per cent distance measure at z = 0.15. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, J.A.; McEwen, J.E.; Hirata, C.M. Streaming velocities and the baryon acoustic oscillation scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellejero-Ibanez, M.; Chuang, C.H.; Rubiño-Martín, J.; Cuesta, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ross, A.J.; Rodríguez-Torres, S.; Prada, F.; Slosar, A.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Double-probe measurements from BOSS galaxy clustering & Planck data–towards an analysis without informative priors. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.03152. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, C.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; Croton, D.; Davis, T.M.; Drinkwater, M.J.; Forster, K.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: Joint measurements of the expansion and growth history at z < 1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.J.; Ho, S.; White, M.; Cuesta, A.J.; Ross, A.J.; Saito, S.; Reid, B.; Padmanabhan, N.; Percival, W.J.; Putter, R.D.; et al. Acoustic scale from the angular power spectra of SDSS-III DR8 photometric luminous galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumagnac, M.; Barkana, R.; Sabiu, C.; Loeb, A.; Ross, A.; Abdalla, F.; Balan, S.; Lahav, O. Large scale distribution of total mass versus luminous matter from baryon acoustic oscillations: First search in the SDSS-III BOSS data release 10. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.01839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Song, Y.S.; Ross, A.J.; Zhou, R.; Newman, J.A.; Chuang, C.H.; Blum, R.; Gaztanaga, E.; Landriau, M.; Prada, F. Clustering of LRGs in the DECaLS DR8 footprint: Distance constraints from baryon acoustic oscillations using photometric redshifts. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.E.; Vargas-Magaña, M.; Dawson, K.S.; Percival, W.J.; Brinkmann, J.; Brownstein, J.; Camacho, B.; Comparat, J.; Gil-Marín, H.; Mueller, E.M.; et al. The SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Baryon acoustic oscillations at redshift of 0.72 with the DR14 luminous red galaxy sample. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Monroy, M.; Avila, S.; Porredon, A.; Chan, K.; Camacho, H.; Weaverdyck, N.; Sevilla-Noarbe, I.; Sanchez, E.; Cipriano, L.T.S.; et al. Dark Energy Survey: Galaxy sample for the baryonic acoustic oscillation measurement from the final dataset. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sánchez, A.G.; Ross, A.J.; Smith, A.; Neveux, R.; Bautista, J.; Burtin, E.; Zhao, C.; Scoccimarro, R.; Dawson, K.S.; et al. The completed SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: BAO and RSD measurements from anisotropic clustering analysis of the quasar sample in configuration space between redshift 0.8 and 2.2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 500, 1201–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, N.G.; Delubac, T.; Rich, J.; Bailey, S.; Font-Ribera, A.; Kirkby, D.; Goff, J.M.L.; Pieri, M.M.; Slosar, A.; Aubourg, É.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations in the Ly-α forest of BOSS quasars. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1211.2616. [Google Scholar]
- de Sainte Agathe, V.; Balland, C.; Bourboux, H.D.M.D.; Blomqvist, M.; Guy, J.; Rich, J.; Font-Ribera, A.; Pieri, M.M.; Bautista, J.E.; Dawson, K.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations at z = 2.34 from the correlations of Lyα absorption in eBOSS DR14. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 629, A85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.; Beutler, F.; Percival, W.J.; Blake, C.; Koda, J.; Ross, A.J. Low redshift baryon acoustic oscillation measurement from the reconstructed 6-degree Field Galaxy Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2371–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazin, E.A.; Koda, J.; Blake, C.; Padmanabhan, N.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; Croton, D.J.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: Improved distance measurements to z = 1 with reconstruction of the baryonic acoustic feature. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 3524–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Verde, L.; Pozzetti, L.; Jimenez, R.; Cimatti, A. New constraints on cosmological parameters and neutrino properties using the expansion rate of the Universe to z∼1.75. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Pozzetti, L.; Zamorani, G.; Bolzonella, M.; Dunlop, J.; Lamareille, F.; Mignoli, M.; Pearce, H.; et al. Improved constraints on the expansion rate of the Universe up to z∼1.1 from the spectroscopic evolution of cosmic chronometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M. Raising the bar: New constraints on the Hubble parameter with cosmic chronometers at z∼2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 450, L16–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Pozzetti, L.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Maraston, C.; Verde, L.; Thomas, D.; Citro, A.; Tojeiro, R.; Wilkinson, D. A 6% measurement of the Hubble parameter at z∼0.45: Direct evidence of the epoch of cosmic re-acceleration. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.A.; Sullivan, M.; Nugent, P.E.; Ellis, R.S.; Conley, A.J.; Borgne, D.L.; Carlberg, R.G.; Guy, J.; Balam, D.; Basa, S.; et al. The type Ia supernova SNLS-03D3bb from a super-Chandrasekhar-mass white dwarf star. Nature 2006, 443, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.M.; Jones, D.; Rest, A.; Pan, Y.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.; Huber, M.; Kessler, R.; Narayan, G.; Riess, A.; et al. The complete light-curve sample of spectroscopically confirmed SNe Ia from Pan-STARRS1 and cosmological constraints from the combined Pantheon sample. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, F.K.; Basilakos, S.; Saridakis, E.N. Observational constraints on Barrow holographic dark energy. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Horne, K.; Hodson, A.O.; Leggat, A.D. Tests of ΛCDM and conformal gravity using GRB and quasars as standard candles out to z∼8. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.10369. [Google Scholar]
- Demianski, M.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Sawant, D.; Amati, L. Cosmology with gamma-ray bursts—I. The Hubble diagram through the calibrated Ep,i–Eiso correlation. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, L.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Evolution of the fσ8 tension with the Planck15/ΛCDM determination and implications for modified gravity theories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, D.; Abdul-Karim, M.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Allen, L.; Prieto, C.A.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; et al. DESI DR2 Results II: Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations and Cosmological Constraints. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 112, 083515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
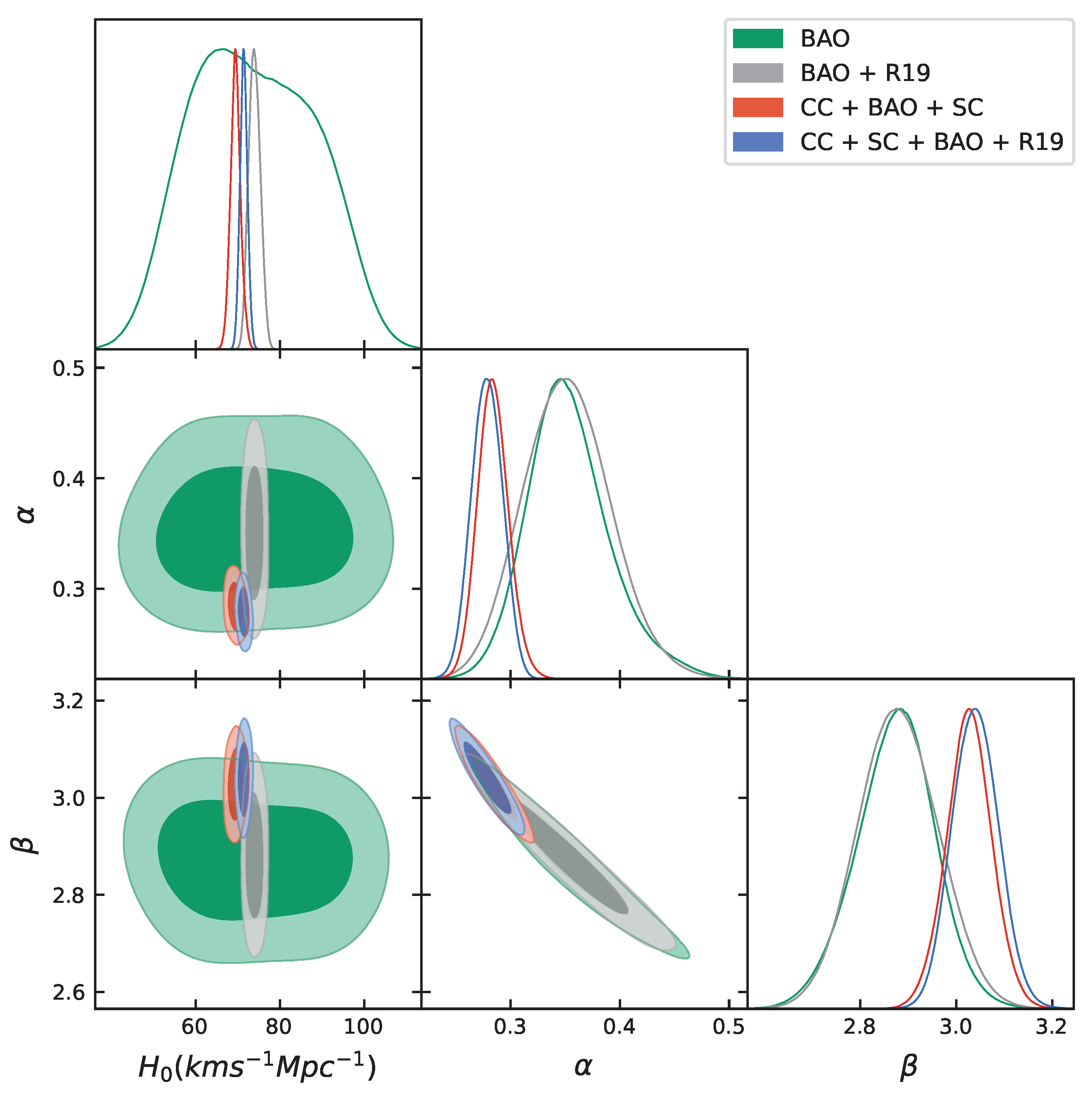
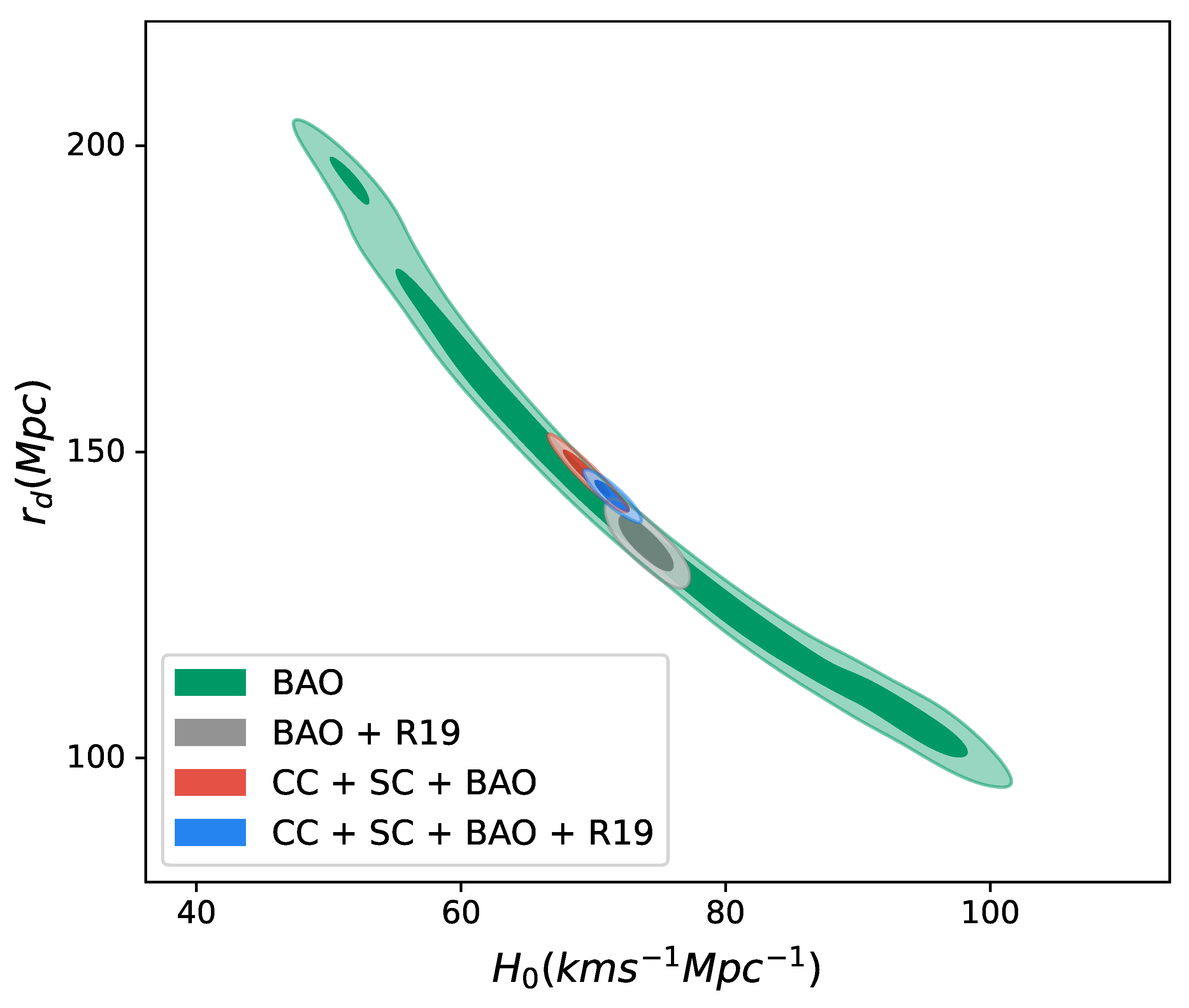


| MCMC Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Parameters | Priors | BAO | BAO + R19 | CC + BAO + SC | CC + SC + BAO + R19 |
| CDM Model | [50, 100] | |||||
| [0, 1] | ||||||
| [0, 1] | ||||||
| [100, 200] | ||||||
| [0.9, 1.1] | ||||||
| Proposed Model | [50, 100] | |||||
| [0, 0.6] | ||||||
| [2, 4] | ||||||
| [100, 200] | ||||||
| [0.9, 1.1] | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beesham, A. Scalar Field and Quintessence in Late-Time Cosmic Expansion. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13243917
Beesham A. Scalar Field and Quintessence in Late-Time Cosmic Expansion. Mathematics. 2025; 13(24):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13243917
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeesham, Aroonkumar. 2025. "Scalar Field and Quintessence in Late-Time Cosmic Expansion" Mathematics 13, no. 24: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13243917
APA StyleBeesham, A. (2025). Scalar Field and Quintessence in Late-Time Cosmic Expansion. Mathematics, 13(24), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13243917






