Comparing Weighted RMSD, Weighted MD, Infit, and Outfit Item Fit Statistics Under Uniform Differential Item Functioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Weighted RMSD and Weighted MD Under DIF
2.1. Weighted RMSD and Weighted MD
2.2. Distribution-Weighted RMSD and MD Statistics
2.3. Difficulty-Weighted RMSD and MD
2.4. Information-Weighted RMSD and MD
2.5. Uniformly Weighted RMSD and MD
2.6. Estimation of Weighted RMSD and Weighted MD
3. Infit and Outfit Under DIF
3.1. Expected Value of Outfit Statistic
3.2. Expected Value of Infit Statistic
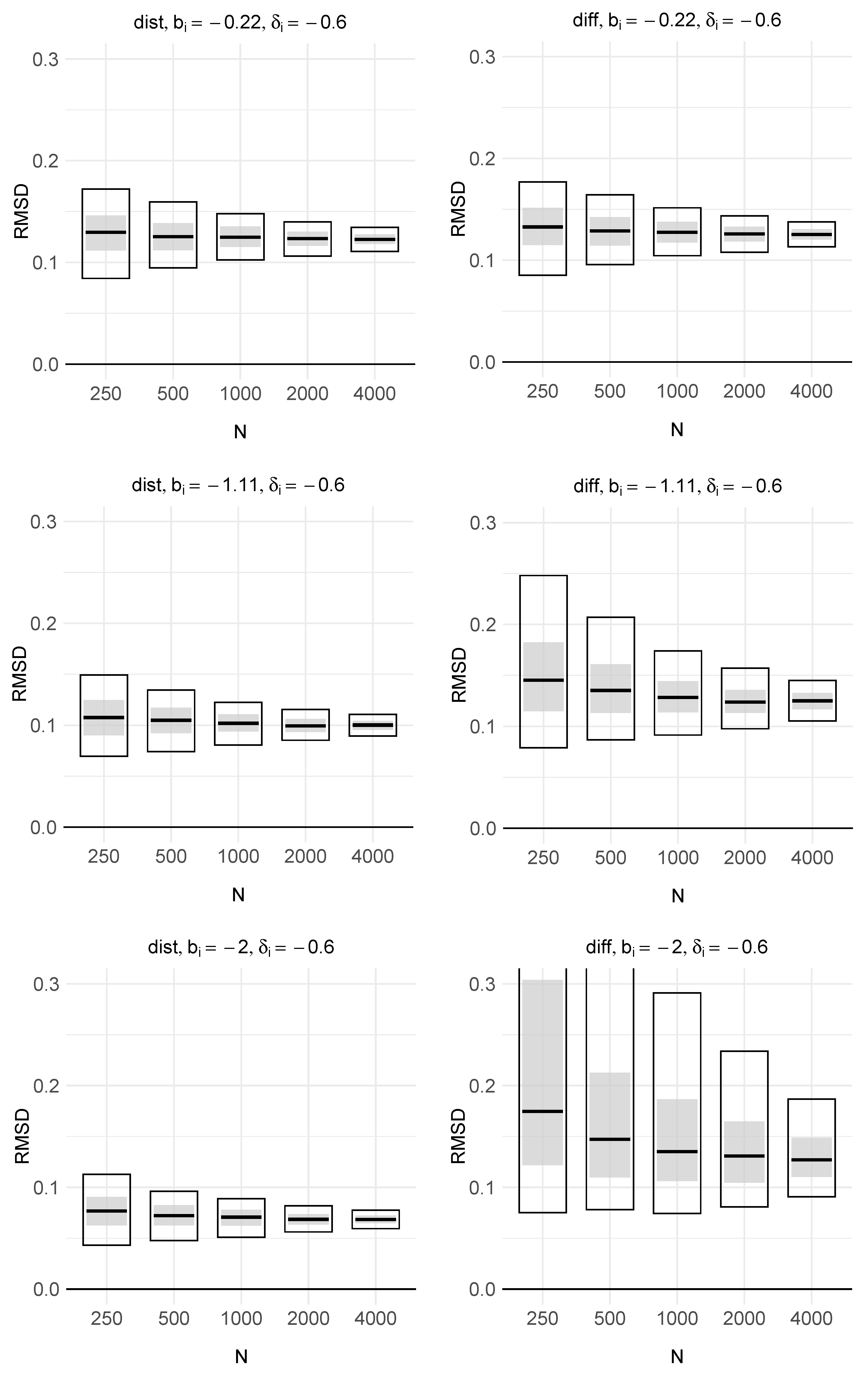
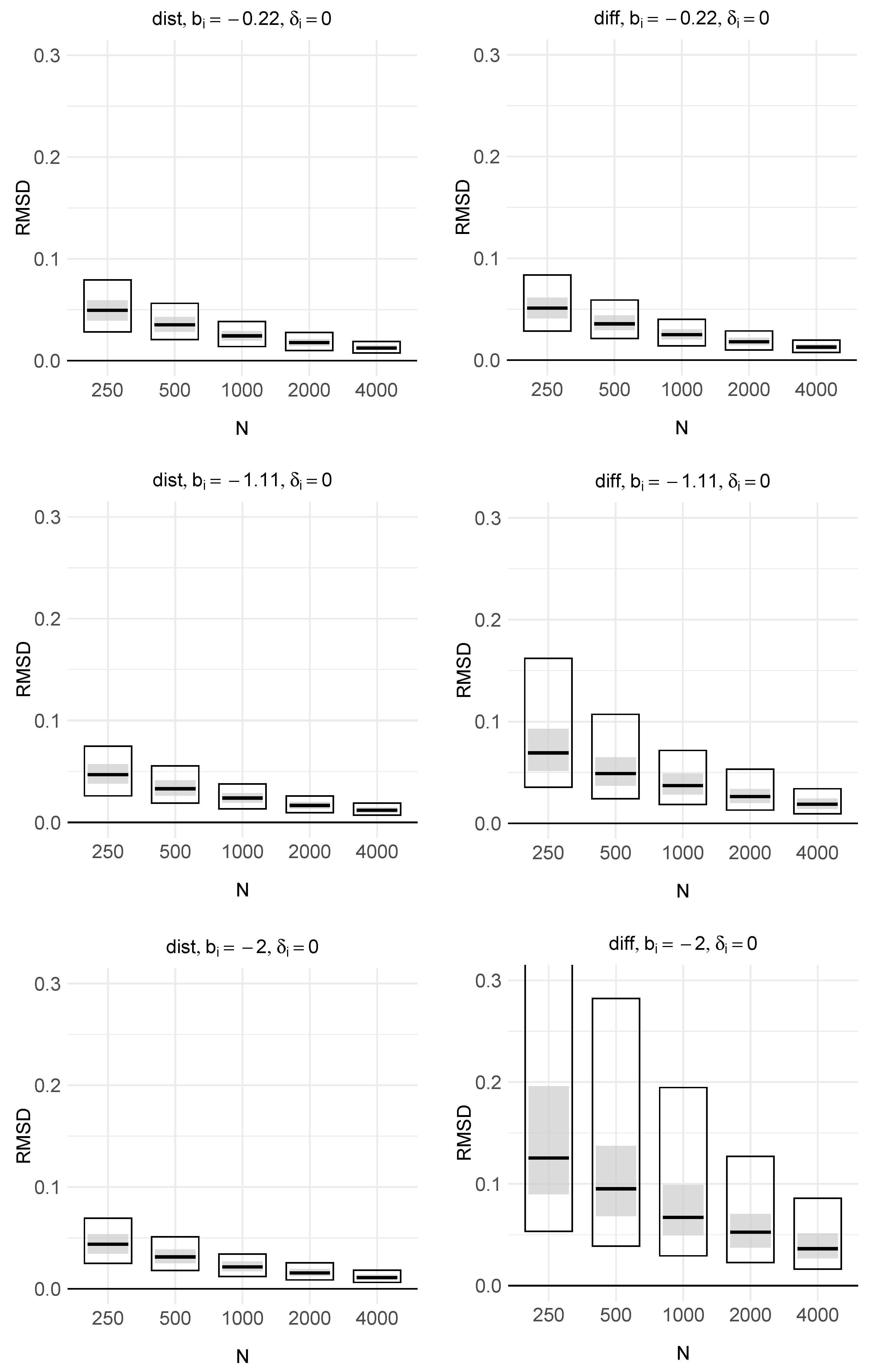
4. Simulation Study
4.1. Method
4.2. Results
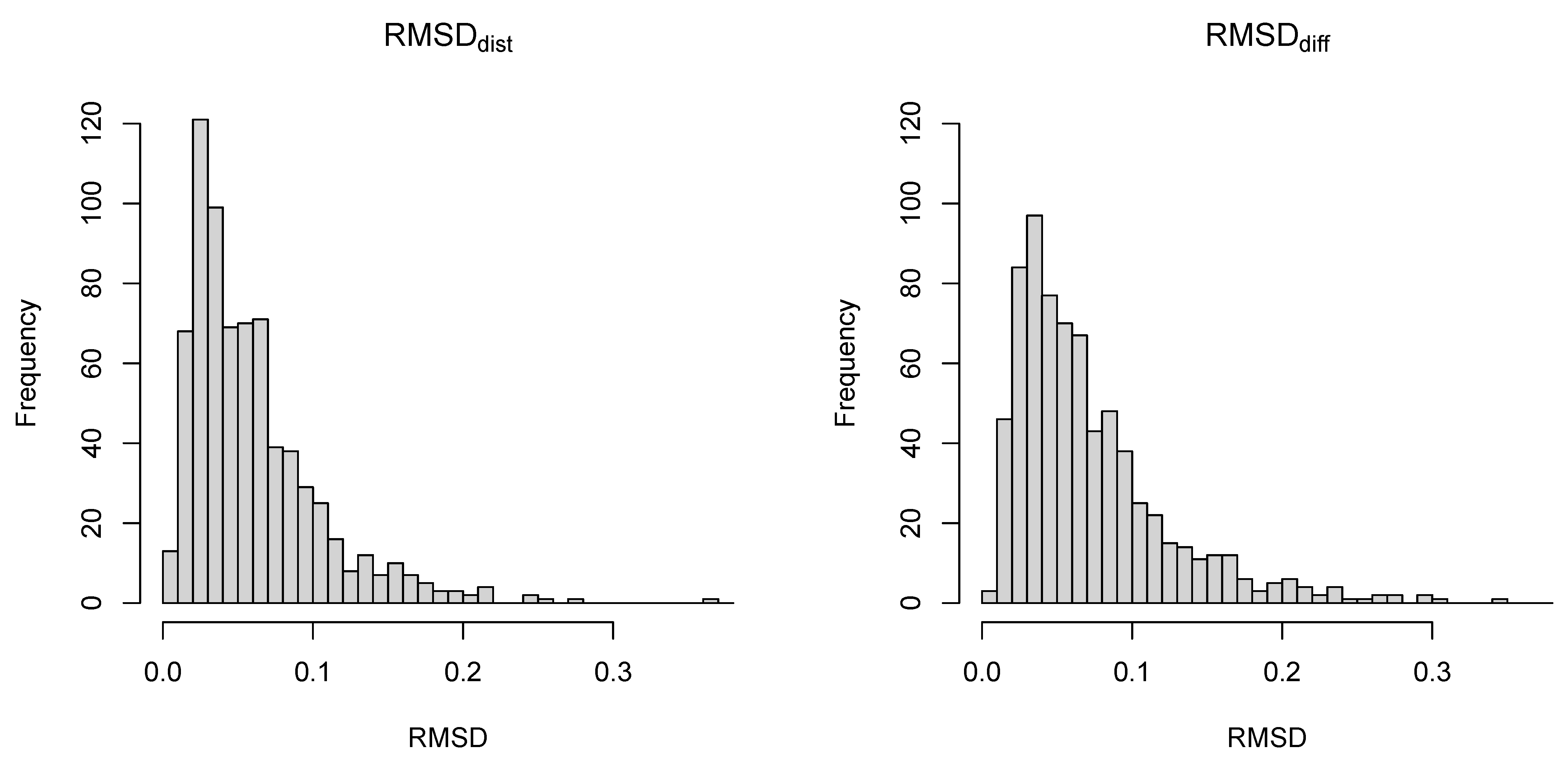
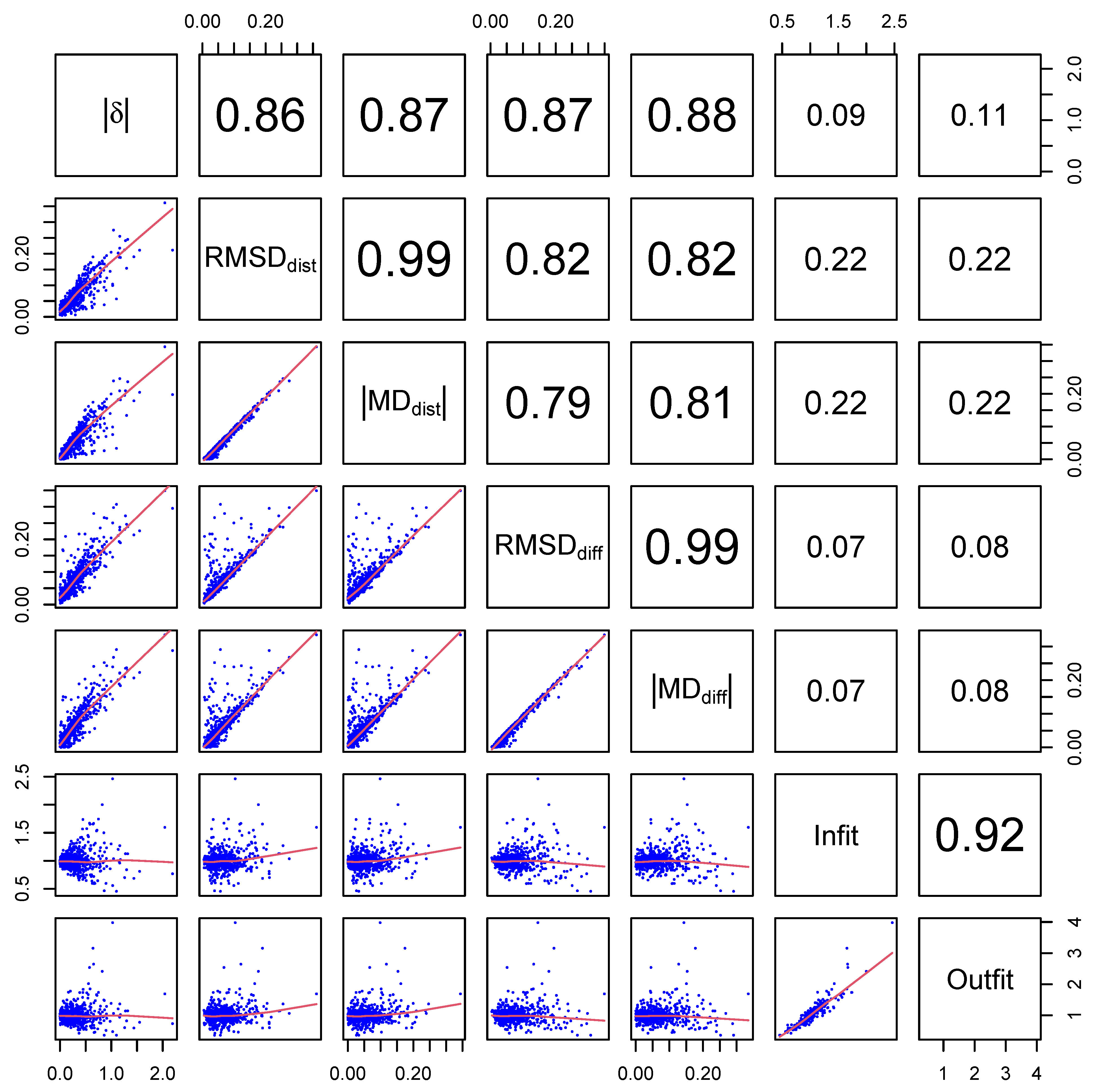
5. Empirical Example
5.1. Method
5.2. Results
6. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2PL | two-parameter logistic |
| DIF | differential item functioning |
| IRF | item response function |
| IRT | item response theory |
| LSA | large-scale assessment |
| MD | mean deviation |
| MML | marginal maximum likelihood |
| NLD | the Netherlands |
| PISA | programme for international student assessment |
| RMSD | root mean square deviation |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SE | standard error |
Appendix A. Integral Identities for the Normal Distribution
Appendix B. Approximation Error in the Computation of the RMSD Statistic
Appendix C. Country Labels for PISA 2006 Reading Study
References
- Baker, F.B.; Kim, S.H. Item Response Theory: Parameter Estimation Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.D.; Moustaki, I. 15 item response theory in a general framework. In Handbook of Statistics: Psychometrics; Rao, C.R., Sinharay, S., Eds.; North Holland (Elsiver): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 26, pp. 469–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.D.; Gibbons, R.D. Item Response Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Ying, Z. Item response theory—A statistical framework for educational and psychological measurement. Stat. Sci. 2025, 40, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutz, G. A Short Guide to Item Response Theory Models; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, W.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.R. Item response theory. In Educational Measurement; Brennan, R.L., Ed.; Praeger Publishers: Westport, CT, USA, 2006; pp. 111–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lietz, P.; Cresswell, J.C.; Rust, K.F.; Adams, R.J. (Eds.) Implementation of Large-Scale Education Assessments; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, L.; von Davier, M.; Rutkowski, D. (Eds.) A Handbook of International Large-Scale Assessment: Background, Technical Issues, and Methods of Data Analysis; Chapman Hall/CRC Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.; Hartig, J.; Rupp, A.A. An NCME instructional module on booklet designs in large-scale assessments of student achievement: Theory and practice. Educ. Meas. 2009, 28, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, H.; von Davier, M. The use of test scores from large-scale assessment surveys: Psychometric and statistical considerations. Large-Scale Assess. Educ. 2017, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, W.J. Unidimensional logistic response models. In Handbook of Item Response Theory: Models; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, A. Some latent trait models and their use in inferring an examinee’s ability. In Statistical Theories of Mental Test Scores; Lord, F.M., Novick, M.R., Eds.; MIT Press: Reading, MA, USA, 1968; pp. 397–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rasch, G. Probabilistic Models for Some Intelligence and Attainment Tests; Danish Institute for Educational Research: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.; Yan, Z.; Heene, M. Applying the Rasch Model; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glas, C.A.W. Maximum-likelihood estimation. In Handbook of Item Response Theory: Statistical Tools; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A. A note on a computationally efficient implementation of the EM algorithm in item response models. Quant. Comput. Methods Behav. Sc. 2021, 1, e3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkin, M. Expectation maximization algorithm and extensions. In Handbook of Item Response Theory: Statistical Tools; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.D.; Aitkin, M. Marginal maximum likelihood estimation of item parameters: Application of an EM algorithm. Psychometrika 1981, 46, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. PISA 2018; Technical Report; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://bit.ly/3zWbidA (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Holland, P.W.; Wainer, H. (Eds.) Differential Item Functioning: Theory and Practice; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, R.D.; Camilli, G. Differential item functioning and item bias. In Handbook of Statistics: Psychometrics; Rao, C.R., Sinharay, S., Eds.; North Holland (Elsiver): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 26, pp. 125–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellenbergh, G.J. Item bias and item response theory. Int. J. Educ. Res. 1989, 13, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.; Cohen, A. Nonparametric item response function estimation for assessing parametric model fit. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2001, 25, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharay, S.; Haberman, S.J. How often is the misfit of item response theory models practically significant? Educ. Meas. 2014, 33, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, H.; Hambleton, R.K.; Rogers, H.J. Assessing the fit of item response theory models. In Handbook of Statistics: Psychometrics; Rao, C.R., Sinharay, S., Eds.; North Holland (Elsiver): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 26, pp. 683–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, J.; Hartig, J. Comparing attitudes across groups: An IRT-based item-fit statistic for the analysis of measurement invariance. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2019, 43, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, J.; Hartig, J. Measurement invariance testing in questionnaires: A comparison of three multigroup-CFA and IRT-based approaches. Psychol. Test Assess. Model. 2020, 62, 29–53. Available online: https://bit.ly/38kswHh (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Khorramdel, L.; Shin, H.J.; von Davier, M. GDM software mdltm including parallel EM algorithm. In Handbook of Diagnostic Classification Models; von Davier, M., Lee, Y.S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 603–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Cai, L.; Kim, Y. Evaluation of item fit with output from the EM algorithm: RMSD index based on posterior expectations. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.; Robitzsch, A.; Hartig, J. A bias-corrected RMSD item fit statistic: An evaluation and comparison to alternatives. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2020, 45, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.; Robitzsch, A.; Fährmann, K.; von Davier, M.; Hartig, J. A semiparametric approach for item response function estimation to detect item misfit. Brit. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2021, 74, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunina-Habenicht, O.; Rupp, A.A.; Wilhelm, O. A practical illustration of multidimensional diagnostic skills profiling: Comparing results from confirmatory factor analysis and diagnostic classification models. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2009, 35, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Khorramdel, L.; Yamamoto, K.; Shin, H.J.; Robin, F. Evaluating item fit statistic thresholds in PISA: Analysis of cross-country comparability of cognitive items. Educ. Meas. 2021, 40, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Ali, U.; Robin, F.; Shin, H.J. Impact of differential item functioning on group score reporting in the context of large-scale assessments. Large-Scale Assess. Educ. 2022, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A. Statistical properties of estimators of the RMSD item fit statistic. Foundations 2022, 2, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueiro, M.J.; Abad, F.J. Assessing goodness of fit in item response theory with nonparametric models: A comparison of posterior probabilities and kernel-smoothing approaches. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2011, 71, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijmstra, J.; Bolsinova, M.; Liaw, Y.L.; Rutkowski, L.; Rutkowski, D. Sensitivity of the RMSD for detecting item-level misfit in low-performing countries. J. Educ. Meas. 2020, 57, 566–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Davier, M.; Bezirhan, U. A robust method for detecting item misfit in large scale assessments. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2023, 83, 740–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.D.; Stone, M.H. Best Test Design; Mesa Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1979; Available online: https://bit.ly/38jnLMX (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Wu, M.; Tam, H.P.; Jen, T.H. Educational Measurement for Applied Researchers; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fährmann, K.; Köhler, C.; Hartig, J.; Heine, J.H. Practical significance of item misfit and its manifestations in constructs assessed in large-scale studies. Large-Scale Assess. Educ. 2022, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Davier, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Shin, H.J.; Chen, H.; Khorramdel, L.; Weeks, J.; Davis, S.; Kong, N.; Kandathil, M. Evaluating item response theory linking and model fit for data from PISA 2000–2012. Assess. Educ. 2019, 26, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Valdivia, M.; Svetina Valdivia, D.; Rutkowski, L. Alternatives to weighted item fit statistics for establishing measurement invariance in many groups. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2024, 49, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, L.; Sabanés Bové, D. Applied Statistical Inference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilli, G. Origin of the scaling constant d = 1.7 in item response theory. J. Educ. Stat. 1994, 19, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilli, G. The scaling constant D in item response theory. Open J. Stat. 2017, 7, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savalei, V. Logistic approximation to the normal: The KL rationale. Psychometrika 2006, 71, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A.; Lüdtke, O. A review of different scaling approaches under full invariance, partial invariance, and noninvariance for cross-sectional country comparisons in large-scale assessments. Psychol. Test Assess. Model. 2020, 62, 233–279. Available online: https://bit.ly/3ezBB05 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Raju, N.S. The area between two item characteristic curves. Psychometrika 1988, 53, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Lee, P. Detecting differential item functioning using posterior predictive model checking: A comparison of discrepancy statistics. J. Educ. Meas. 2022, 59, 442–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linacre, J.M. Understanding Rasch measurement: Estimation methods for Rasch measures. J. Outcome Meas. 1999, 3, 382–405. Available online: https://bit.ly/2UV6Eht (accessed on 4 October 2025). [PubMed]
- van der Linden, W.J.; Hambleton, R.K. (Eds.) Handbook of Modern Item Response Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.J.; Wu, M.L. The mixed-coefficients multinomial logit model: A generalized form of the Rasch model. In Multivariate and Mixture Distribution Rasch Models; von Davier, M., Carstensen, C.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Adams, R.J. Properties of Rasch residual fit statistics. J. Appl. Meas. 2013, 14, 339–355. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.; Wu, M. (Eds.) PISA 2000 Technical Report; OECD: Paris, France, 2003; Available online: https://tinyurl.com/y79c3kmp (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Lamprianou, I. Applying the Rasch Model in Social Sciences Using R and BlueSky Statistics; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M. Constructing Measures: An Item Response Modeling Approach; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Diaz, J.A.; Köhler, C.; Hartig, J. Performance of infit and outfit confidence intervals calculated via parametric bootstrapping. Appl. Meas. Educ. 2022, 35, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterlind, S.J.; Everson, H.T. Differential Item Functioning; Sage: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Robitzsch, A.; Kiefer, T.; Wu, M. TAM: Test Analysis Modules. R Package Version 4.3-25. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/TAM/index.html (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; van den Brand, T.; et al. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. R Package Version 4.0.0. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/index.html (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. PISA 2006 Technical Report; OECD: Paris, France, 2009; Available online: https://bit.ly/38jhdzp (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Robitzsch, A. sirt: Supplementary Item Response Theory Models. R Package Version 4.2-133. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/sirt/index.html (accessed on 27 September 2025).
- Kolenikov, S. Resampling variance estimation for complex survey data. Stata J. 2010, 10, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.N.K.; Wu, C.F.J. Resampling inference with complex survey data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longford, N.T.; Holland, P.W.; Thayer, D.T. Stability of the MH D-DIF statistics across populations. In Differential Item Functioning; Holland, P.W., Wainer, H., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; pp. 171–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, T.A.; Ma, Y. Examining differential item functioning from a multidimensional IRT perspective. Psychometrika 2024, 89, 4–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Davier, M.; Khorramdel, L.; He, Q.; Shin, H.J.; Chen, H. Developments in psychometric population models for technology-based large-scale assessments: An overview of challenges and opportunities. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2019, 44, 671–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilli, G. The case against item bias detection techniques based on internal criteria: Do item bias procedures obscure test fairness issues? In Differential Item Functioning: Theory and Practice; Holland, P.W., Wainer, H., Eds.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 397–417. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.J. Comments on Kreiner 2011: Is the Foundation Under PISA Solid? A Critical Look at the Scaling Model Underlying International Comparisons of Student Attainment; Technical Report; OECD: Paris, France, 2011; Available online: https://bit.ly/3wVUKo0 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Robitzsch, A.; Lüdtke, O. Some thoughts on analytical choices in the scaling model for test scores in international large-scale assessment studies. Meas. Instrum. Soc. Sci. 2022, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.J. Enhancing measurement validity in diverse populations: Modern approaches to evaluating differential item functioning. Brit. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2023, 76, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, J.; Zeileis, A.; Strobl, C. Anchor selection strategies for DIF analysis: Review, assessment, and new approaches. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2015, 75, 22–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, F.M. Applications of Item Response Theory to Practical Testing Problems; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.; Hanke, K.; He, J. On detecting systematic measurement error in cross-cultural research: A review and critical reflection on equivalence and invariance tests. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2018, 49, 713–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Barrera-Pedemonte, F.; Buchholz, J. Cross-cultural comparability of noncognitive constructs in TIMSS and PISA. Assess. Educ. 2019, 26, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, L.; Svetina, D. Assessing the hypothesis of measurement invariance in the context of large-scale international surveys. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2014, 74, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A. On the choice of the item response model for scaling PISA data: Model selection based on information criteria and quantifying model uncertainty. Entropy 2022, 24, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.B. A table of normal integrals. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 1980, 9, 389–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean | SD | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dist | Diff | Infit | Outfit | Dist | Diff | Infit | Outfit | |||||||
| RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | |||||||
| −0.22 | −0.6 | 250 | 0.129 | 0.117 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.982 | 0.975 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.047 | 0.066 |
| 500 | 0.126 | 0.118 | 0.129 | 0.121 | 0.983 | 0.977 | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.020 | 0.033 | 0.046 | ||
| 1000 | 0.125 | 0.119 | 0.128 | 0.122 | 0.981 | 0.973 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.023 | 0.032 | ||
| 2000 | 0.123 | 0.118 | 0.126 | 0.121 | 0.982 | 0.974 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.016 | 0.022 | ||
| 4000 | 0.123 | 0.118 | 0.125 | 0.121 | 0.982 | 0.974 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.016 | ||
| 0.6 | 250 | 0.134 | −0.123 | 0.133 | −0.122 | 1.064 | 1.088 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.051 | 0.076 | |
| 500 | 0.131 | −0.123 | 0.129 | −0.122 | 1.063 | 1.086 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.036 | 0.053 | ||
| 1000 | 0.129 | −0.124 | 0.128 | −0.123 | 1.064 | 1.087 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.026 | 0.038 | ||
| 2000 | 0.127 | −0.123 | 0.126 | −0.122 | 1.063 | 1.085 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.017 | 0.025 | ||
| 4000 | 0.127 | −0.123 | 0.126 | −0.122 | 1.064 | 1.086 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.019 | ||
| −1.11 | −0.6 | 250 | 0.108 | 0.092 | 0.152 | 0.125 | 0.839 | 0.791 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.052 | 0.048 | 0.056 | 0.085 |
| 500 | 0.104 | 0.092 | 0.139 | 0.123 | 0.841 | 0.793 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.037 | 0.035 | 0.041 | 0.062 | ||
| 1000 | 0.102 | 0.092 | 0.130 | 0.120 | 0.836 | 0.786 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.025 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.041 | ||
| 2000 | 0.100 | 0.091 | 0.125 | 0.118 | 0.839 | 0.790 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.018 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.032 | ||
| 4000 | 0.100 | 0.092 | 0.125 | 0.120 | 0.839 | 0.791 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.022 | ||
| 0.6 | 250 | 0.126 | −0.112 | 0.142 | −0.120 | 1.237 | 1.323 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.042 | 0.080 | 0.136 | |
| 500 | 0.121 | −0.112 | 0.132 | −0.119 | 1.237 | 1.322 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.028 | 0.057 | 0.099 | ||
| 1000 | 0.119 | −0.111 | 0.128 | −0.120 | 1.235 | 1.322 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.040 | 0.070 | ||
| 2000 | 0.118 | −0.112 | 0.126 | −0.120 | 1.237 | 1.324 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.028 | 0.048 | ||
| 4000 | 0.117 | −0.111 | 0.124 | −0.120 | 1.236 | 1.322 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.021 | 0.036 | ||
| −2.00 | −0.6 | 250 | 0.077 | 0.057 | 0.215 | 0.145 | 0.731 | 0.670 | 0.021 | 0.019 | 0.118 | 0.118 | 0.096 | 0.154 |
| 500 | 0.072 | 0.057 | 0.174 | 0.126 | 0.729 | 0.671 | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.087 | 0.085 | 0.063 | 0.102 | ||
| 1000 | 0.070 | 0.058 | 0.154 | 0.124 | 0.727 | 0.668 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.067 | 0.062 | 0.046 | 0.073 | ||
| 2000 | 0.069 | 0.057 | 0.140 | 0.121 | 0.730 | 0.671 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.048 | 0.044 | 0.032 | 0.052 | ||
| 4000 | 0.069 | 0.058 | 0.132 | 0.120 | 0.729 | 0.671 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.031 | 0.028 | 0.022 | 0.037 | ||
| 0.6 | 250 | 0.101 | −0.083 | 0.177 | −0.107 | 1.416 | 1.537 | 0.027 | 0.026 | 0.067 | 0.097 | 0.143 | 0.260 | |
| 500 | 0.094 | −0.080 | 0.150 | −0.111 | 1.400 | 1.522 | 0.019 | 0.018 | 0.046 | 0.062 | 0.102 | 0.182 | ||
| 1000 | 0.091 | −0.080 | 0.137 | −0.113 | 1.401 | 1.525 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.068 | 0.125 | ||
| 2000 | 0.091 | −0.081 | 0.129 | −0.116 | 1.404 | 1.527 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.024 | 0.029 | 0.049 | 0.092 | ||
| 4000 | 0.090 | −0.080 | 0.124 | −0.115 | 1.404 | 1.528 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.022 | 0.035 | 0.063 | ||
| Mean | SD | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dist | Diff | Infit | Outfit | Dist | Diff | Infit | Outfit | ||||||
| RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | ||||||
| −0.22 | 250 | 0.051 | 0.000 | 0.053 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.016 | 0.028 | 0.017 | 0.029 | 0.047 | 0.066 |
| 500 | 0.036 | 0.000 | 0.037 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.011 | 0.020 | 0.012 | 0.020 | 0.033 | 0.046 | |
| 1000 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.026 | −0.001 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.023 | 0.032 | |
| 2000 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.016 | 0.023 | |
| 4000 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.016 | |
| −1.11 | 250 | 0.048 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.001 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.015 | 0.025 | 0.039 | 0.044 | 0.068 | 0.109 |
| 500 | 0.035 | −0.001 | 0.055 | −0.003 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.011 | 0.018 | 0.027 | 0.033 | 0.048 | 0.079 | |
| 1000 | 0.025 | −0.001 | 0.040 | −0.002 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.022 | 0.034 | 0.055 | |
| 2000 | 0.017 | −0.001 | 0.028 | −0.002 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.023 | 0.036 | |
| 4000 | 0.012 | −0.001 | 0.020 | −0.002 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.028 | |
| −2.00 | 250 | 0.045 | 0.000 | 0.158 | 0.023 | 1.003 | 1.005 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.098 | 0.114 | 0.112 | 0.191 |
| 500 | 0.033 | −0.001 | 0.116 | 0.008 | 1.003 | 0.999 | 0.010 | 0.015 | 0.073 | 0.081 | 0.081 | 0.133 | |
| 1000 | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.082 | 0.005 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.052 | 0.055 | 0.056 | 0.092 | |
| 2000 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.060 | 0.001 | 0.999 | 0.993 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.034 | 0.038 | 0.042 | 0.067 | |
| 4000 | 0.011 | −0.001 | 0.042 | −0.002 | 1.002 | 1.000 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.028 | 0.046 | |
| Item | Dist | Diff | Infit | Outfit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSD | MD | RMSD | MD | ||||||
| R055Q01 | 1.394 | −1.487 | 0.655 (0.054) | 0.122 (0.012) | −0.118 (0.011) | 0.133 (0.014) | −0.128 (0.013) | 1.666 (0.008) | 2.645 (0.030) |
| R055Q02 | 1.378 | 0.043 | 0.288 (0.048) | 0.073 (0.012) | −0.070 (0.011) | 0.072 (0.012) | −0.070 (0.011) | 1.057 (0.005) | 1.113 (0.011) |
| R055Q03 | 1.619 | −0.334 | 0.176 (0.043) | 0.048 (0.010) | −0.042 (0.011) | 0.055 (0.010) | −0.049 (0.011) | 0.989 (0.004) | 1.030 (0.009) |
| R055Q05 | 2.116 | −0.779 | −0.055 (0.043) | 0.037 (0.008) | 0.018 (0.008) | 0.042 (0.008) | 0.003 (0.011) | 0.850 (0.002) | 0.719 (0.003) |
| R067Q01 | 1.226 | −2.073 | 0.523 (0.064) | 0.077 (0.013) | −0.064 (0.010) | 0.108 (0.033) | −0.093 (0.048) | 1.572 (0.009) | 1.724 (0.011) |
| R067Q04 | 0.832 | 0.723 | 0.723 (0.093) | 0.123 (0.013) | −0.118 (0.013) | 0.132 (0.015) | −0.130 (0.015) | 0.934 (0.003) | 0.919 (0.003) |
| R067Q05 | 1.087 | −0.307 | 0.304 (0.060) | 0.072 (0.013) | −0.069 (0.013) | 0.076 (0.014) | −0.072 (0.014) | 1.051 (0.003) | 1.087 (0.007) |
| R102Q04A | 1.460 | 0.669 | −0.371 (0.047) | 0.094 (0.012) | 0.090 (0.011) | 0.094 (0.013) | 0.088 (0.012) | 1.103 (0.004) | 1.215 (0.009) |
| R102Q05 | 1.330 | 0.244 | −0.611 (0.048) | 0.151 (0.012) | 0.145 (0.011) | 0.150 (0.012) | 0.144 (0.011) | 1.046 (0.004) | 1.086 (0.008) |
| R102Q07 | 1.417 | −1.494 | 0.823 (0.047) | 0.177 (0.011) | −0.153 (0.010) | 0.179 (0.016) | −0.153 (0.021) | 2.000 (0.010) | 2.415 (0.019) |
| R104Q01 | 1.626 | −1.322 | 0.087 (0.072) | 0.017 (0.014) | −0.012 (0.012) | 0.021 (0.021) | −0.018 (0.028) | 1.044 (0.004) | 0.959 (0.006) |
| R104Q02 | 0.584 | 1.334 | 0.157 (0.112) | 0.025 (0.010) | −0.017 (0.013) | 0.018 (0.011) | 0.000 (0.021) | 0.969 (0.001) | 0.960 (0.001) |
| R104Q05 | 1.133 | 3.129 | 0.622 (0.147) | 0.034 (0.008) | −0.024 (0.004) | 0.175 (0.087) | −0.166 (0.078) | 0.639 (0.004) | 0.594 (0.003) |
| R111Q01 | 1.365 | −0.604 | 0.470 (0.039) | 0.113 (0.009) | −0.108 (0.009) | 0.112 (0.011) | −0.101 (0.014) | 1.228 (0.004) | 1.408 (0.012) |
| R111Q02B | 1.047 | 1.912 | −0.324 (0.065) | 0.048 (0.010) | 0.046 (0.010) | 0.038 (0.016) | 0.035 (0.019) | 1.228 (0.004) | 1.341 (0.006) |
| R111Q06B | 1.588 | 0.542 | 0.162 (0.044) | 0.042 (0.011) | −0.039 (0.010) | 0.046 (0.012) | −0.044 (0.011) | 0.990 (0.004) | 0.973 (0.007) |
| R219Q01E | 1.633 | −0.250 | −0.236 (0.054) | 0.074 (0.014) | 0.058 (0.013) | 0.081 (0.015) | 0.067 (0.014) | 1.021 (0.006) | 1.008 (0.010) |
| R219Q01T | 1.860 | −0.664 | −0.246 (0.062) | 0.077 (0.017) | 0.054 (0.013) | 0.099 (0.023) | 0.081 (0.020) | 1.023 (0.006) | 1.049 (0.013) |
| R219Q02 | 1.533 | −1.179 | −0.120 (0.055) | 0.031 (0.011) | 0.020 (0.009) | 0.038 (0.016) | 0.026 (0.016) | 0.921 (0.002) | 1.048 (0.013) |
| R220Q01 | 1.761 | 0.305 | 0.170 (0.033) | 0.058 (0.008) | −0.053 (0.008) | 0.058 (0.009) | −0.054 (0.008) | 0.981 (0.005) | 0.986 (0.009) |
| R220Q02B | 1.520 | −0.376 | 0.102 (0.047) | 0.050 (0.010) | −0.029 (0.012) | 0.058 (0.012) | −0.032 (0.016) | 1.006 (0.004) | 1.060 (0.010) |
| R220Q04 | 1.301 | −0.312 | −0.260 (0.055) | 0.062 (0.011) | 0.054 (0.012) | 0.060 (0.012) | 0.051 (0.014) | 0.888 (0.003) | 0.854 (0.004) |
| R220Q05 | 1.976 | −1.145 | −0.007 (0.050) | 0.023 (0.011) | −0.002 (0.009) | 0.029 (0.017) | −0.013 (0.019) | 0.920 (0.004) | 0.701 (0.004) |
| R220Q06 | 1.166 | −0.675 | −0.110 (0.061) | 0.032 (0.008) | 0.018 (0.012) | 0.038 (0.014) | 0.015 (0.018) | 0.917 (0.003) | 0.882 (0.004) |
| R227Q01 | 0.778 | −0.151 | −0.778 (0.066) | 0.131 (0.010) | 0.129 (0.010) | 0.131 (0.011) | 0.129 (0.011) | 0.942 (0.002) | 0.937 (0.003) |
| R227Q02T | 0.993 | 0.793 | −0.907 (0.066) | 0.194 (0.013) | 0.184 (0.013) | 0.193 (0.013) | 0.183 (0.013) | 1.230 (0.004) | 1.289 (0.006) |
| R227Q03 | 1.664 | −0.183 | −0.159 (0.043) | 0.057 (0.012) | 0.046 (0.011) | 0.063 (0.013) | 0.054 (0.012) | 1.042 (0.005) | 1.094 (0.011) |
| R227Q06 | 1.765 | −0.777 | −0.286 (0.053) | 0.082 (0.012) | 0.064 (0.009) | 0.100 (0.017) | 0.088 (0.015) | 0.903 (0.004) | 0.876 (0.007) |
| Flagged Items | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 65.1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.8 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5.5 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7.3 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.3 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1.1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 13.5 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3.0 |
| Flagged Items | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cnt | |||||
| AUS | 28 | 7.1 | 21.4 | 25.0 | 0.0 |
| AUT | 27 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 18.5 | 0.0 |
| BEL | 28 | 14.3 | 7.1 | 17.9 | 10.7 |
| CAN | 28 | 17.9 | 21.4 | 32.1 | 3.6 |
| CHE | 28 | 25.0 | 17.9 | 28.6 | 7.1 |
| CZE | 28 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 28.6 | 3.6 |
| DEU | 28 | 21.4 | 21.4 | 28.6 | 7.1 |
| DNK | 27 | 29.6 | 37.0 | 44.4 | 3.7 |
| ESP | 28 | 17.9 | 32.1 | 39.3 | 7.1 |
| EST | 28 | 17.9 | 35.7 | 42.9 | 10.7 |
| FIN | 28 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 17.9 | 3.6 |
| FRA | 28 | 14.3 | 25.0 | 39.3 | 3.6 |
| GBR | 28 | 25.0 | 35.7 | 42.9 | 7.1 |
| GRC | 28 | 25.0 | 28.6 | 35.7 | 3.6 |
| HUN | 28 | 21.4 | 17.9 | 32.1 | 3.6 |
| IRL | 28 | 17.9 | 21.4 | 28.6 | 3.6 |
| ISL | 28 | 21.4 | 17.9 | 21.4 | 10.7 |
| ITA | 28 | 25.0 | 21.4 | 25.0 | 7.1 |
| JPN | 28 | 25.0 | 35.7 | 42.9 | 17.9 |
| KOR | 27 | 25.9 | 33.3 | 51.9 | 11.1 |
| LUX | 27 | 14.8 | 11.1 | 18.5 | 7.4 |
| NLD | 28 | 32.1 | 32.1 | 46.4 | 14.3 |
| NOR | 28 | 25.0 | 32.1 | 42.9 | 3.6 |
| POL | 28 | 21.4 | 25.0 | 39.3 | 3.6 |
| PRT | 28 | 32.1 | 32.1 | 35.7 | 3.6 |
| SWE | 28 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 25.0 | 7.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robitzsch, A. Comparing Weighted RMSD, Weighted MD, Infit, and Outfit Item Fit Statistics Under Uniform Differential Item Functioning. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233752
Robitzsch A. Comparing Weighted RMSD, Weighted MD, Infit, and Outfit Item Fit Statistics Under Uniform Differential Item Functioning. Mathematics. 2025; 13(23):3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233752
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobitzsch, Alexander. 2025. "Comparing Weighted RMSD, Weighted MD, Infit, and Outfit Item Fit Statistics Under Uniform Differential Item Functioning" Mathematics 13, no. 23: 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233752
APA StyleRobitzsch, A. (2025). Comparing Weighted RMSD, Weighted MD, Infit, and Outfit Item Fit Statistics Under Uniform Differential Item Functioning. Mathematics, 13(23), 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233752






