Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds Under Regime Switching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Framework
3. Esscher Transform for 2FMMSVDEJ–MMGBM Dynamics
4. Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds
4.1. Simplified Condition: The Corporate Bond May Default Only at Maturity
4.2. Generalized Condition: The Bond May Default at or Before Maturity
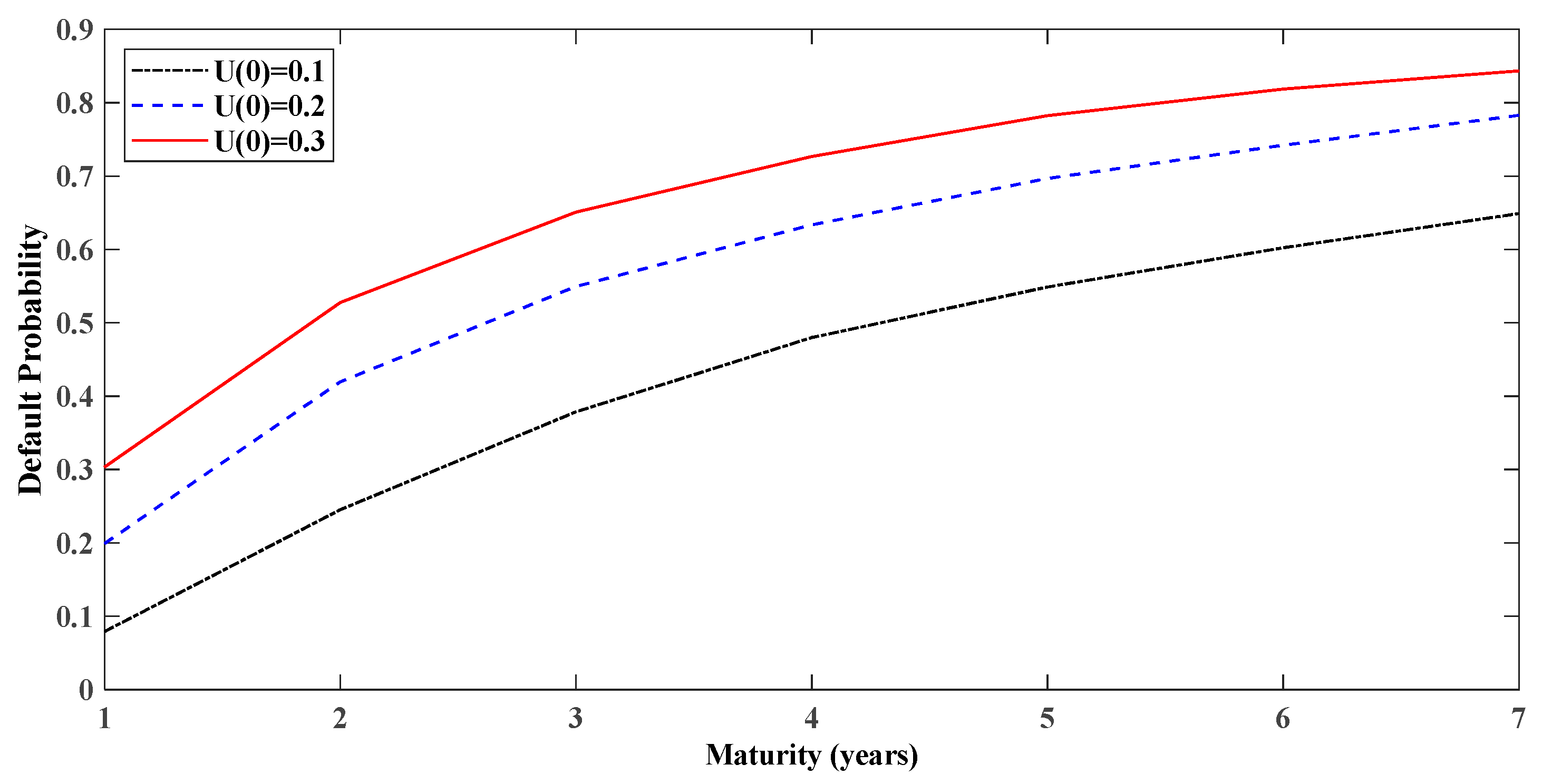
5. Numerical Illustrations
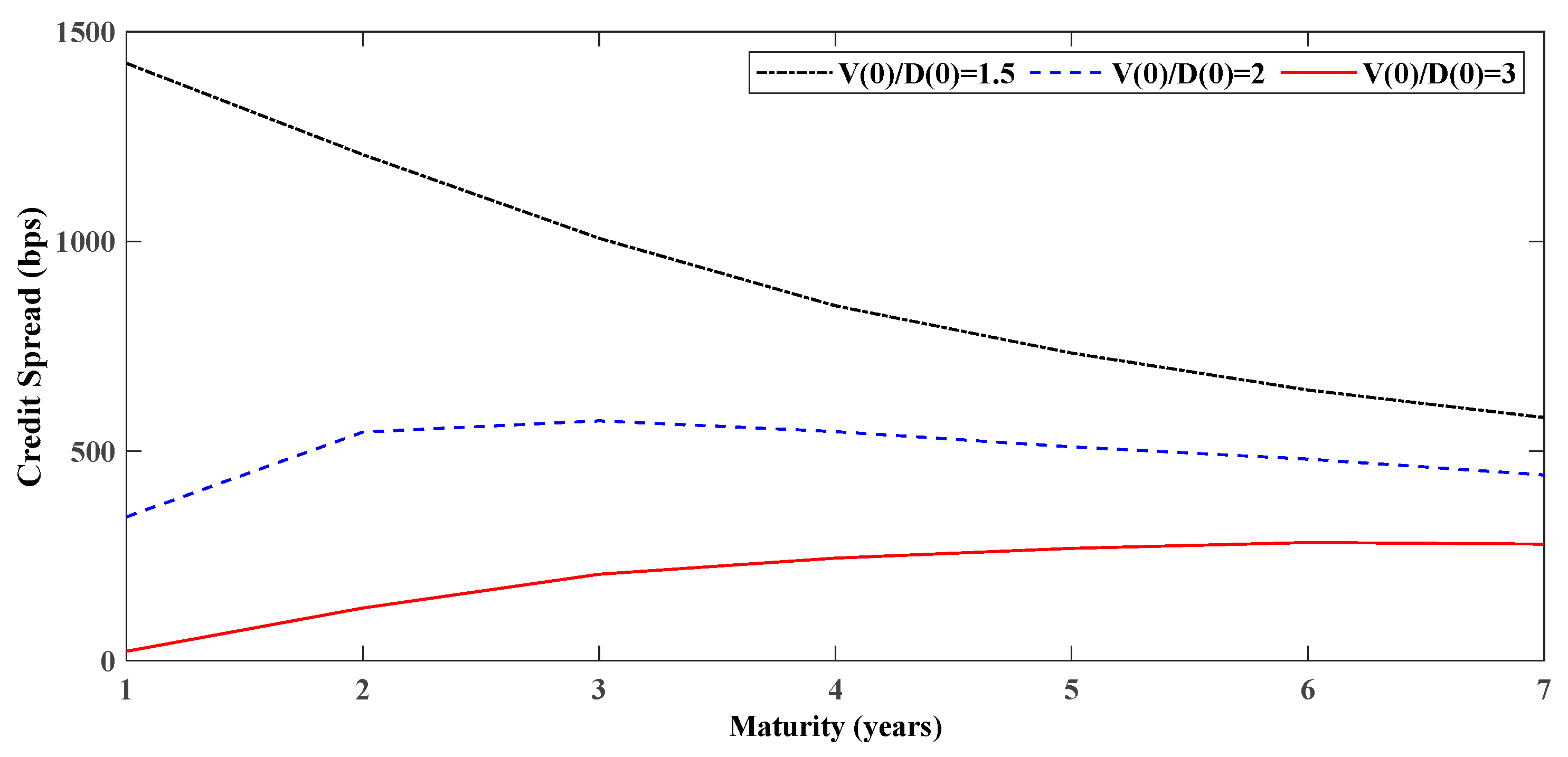
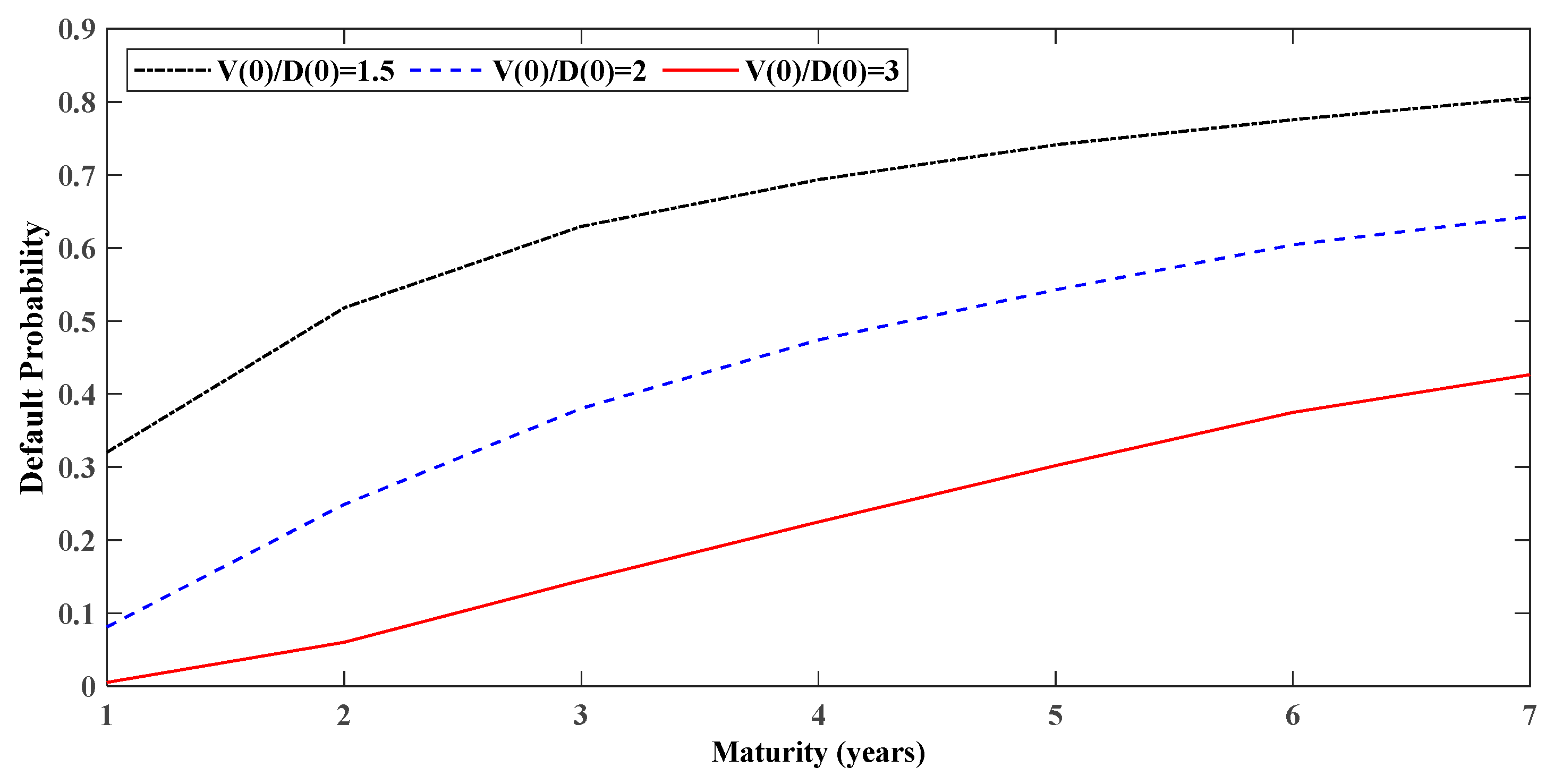
5.1. Generalized Condition Analytics
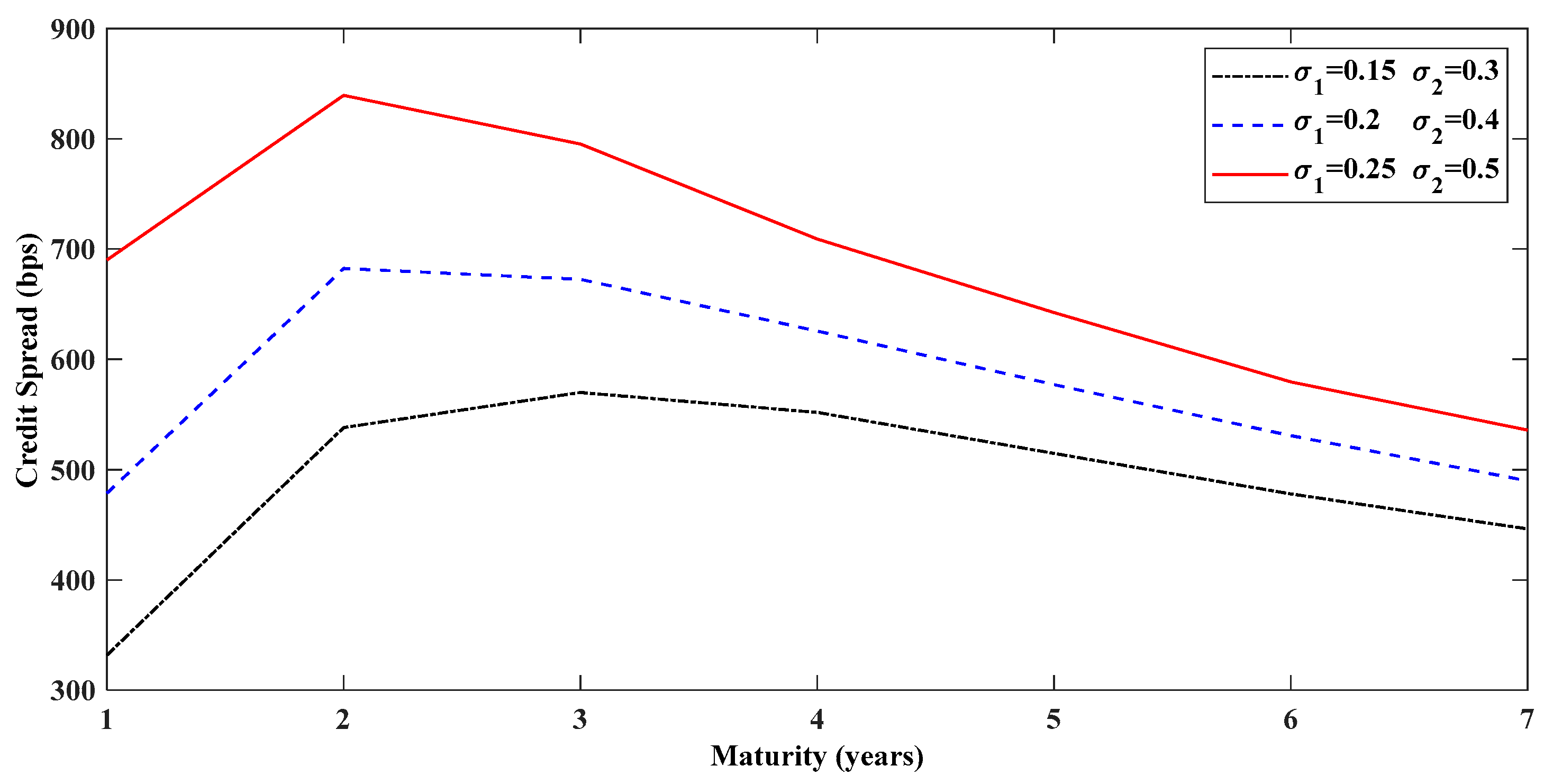
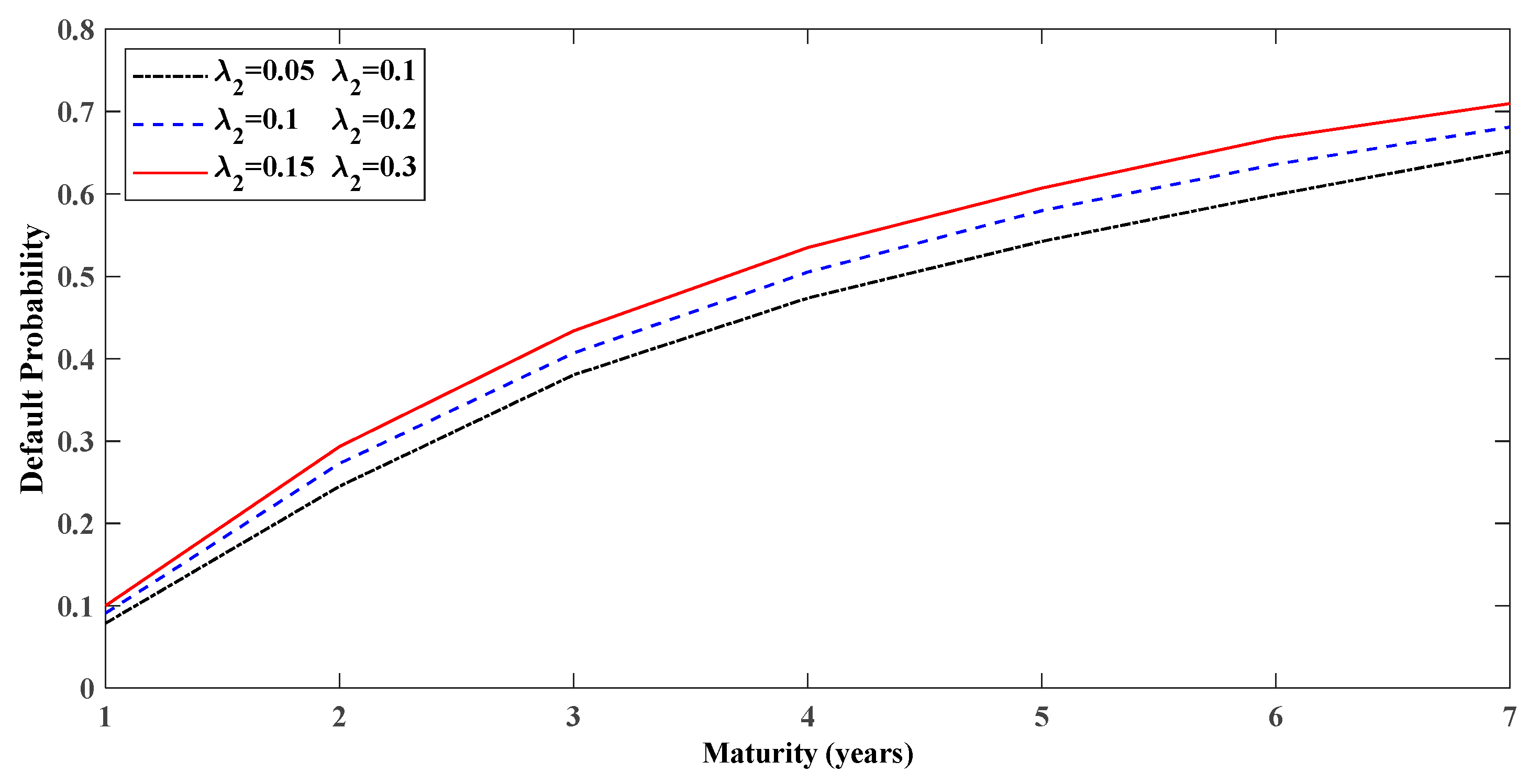
5.2. Comparison of the Simplified and Generalized Conditions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Martingale Condition
Appendix B. Derivation of the Defaultable Corporate Bond Pricing Formula
References
- Gebhardt, W.R.; Hvidkjaer, S.; Swaminathan, B. The cross-section of expected corporate bond returns: Betas or characteristics? J. Financ. Econ. 2005, 75, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Binsbergen, J.H.; Diamond, W.F.; Grotteria, M. Risk-free interest rates. J. Financ. Econ. 2022, 143, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, A.; Mueller, P.; Robotti, C. Priced risk in corporate bonds. J. Financ. Econ. 2023, 150, 103707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Binsbergen, J.H.; Nozawa, Y.; Schwert, M. Duration-based valuation of corporate bonds. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2025, 38, 158–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, F.; Scholes, M. The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. J. Political Econ. 1973, 81, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merton, R.C. On the pricing of corporate debt: The risk structure of interest rates. J. Financ. 1974, 29, 449–470. [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff, F.; Schwartz, E.S. A simple approach to valuing risky fixed and floating rate debt. J. Financ. 1995, 50, 789–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T.S.; Kounchev, O.; Savov, M. Two frameworks for pricing defaultable derivatives. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 123, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.; Ju, N.; Leland, H. An EBIT-based model of dynamic capital structure. J. Bus. 2001, 74, 483–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, D.T.; Shumway, T. Forecasting default with the Merton distance to default model. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2008, 21, 1339–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhamra, H.S.; Kuehn, L.-A.; Strebulaev, I.A. The levered equity risk premium and credit spreads: A unified framework. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2010, 23, 645–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Chen, L.J.; Fuh, C.D. The pricing of risk and sentiment: A study of executive stock options. Financ. Manag. 2013, 42, 79–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.S. A Jump-Diffusion Approach to Modeling Credit Risk and Valuing Defaultable Securities. 1997. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=39800 (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Zhou, C.S. The term structure of credit spreads with jump risk. J. Bank. Financ. 2001, 25, 2015–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilberink, B.; Rogers, C. Optimal capital structure and endogenous default. Financ. Stoch. 2002, 6, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tang, Q.M. Does default risk of the listed company increase since the global financial crisis: Analysis based on the jump changes in Chinese company’s asset value. Manag. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S.G. A jump-diffusion model for option pricing. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.G.; Wang, H. Option pricing under a double exponential jump-diffusion model. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 1178–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Kou, S.G. Credit spreads, optimal capital structure, and implied volatility with endogenous default and jump risk. Math. Financ. 2009, 19, 343–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, C.D.; Luo, S.F.; Yen, J.F. Pricing discrete path-dependent options under a double exponential jump diffusion model. J. Bank. Financ. 2013, 37, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraker, B.; Johannes, M.; Polson, N. The impact of jumps in volatility and returns. J. Financ. 2003, 58, 1269–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.H.; Li, C.Y.; Chen, S.N. Pricing currency options under double exponential jump diffusion in a Markov-modulated HJM economy. Rev. Quant. Financ. Account. 2016, 46, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Hsu, P.P. Pricing and hedging barrier options under a Markov-modulated double exponential jump diffusion-CIR model. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2018, 56, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.J.; Chan, L.; Siu, T.K. Option pricing and Esscher transform under regime switching. Ann. Financ. 2005, 1, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.U.; Shiu, E.S.W. Option pricing by Esscher transforms (with discussions). Trans. Soc. Actuar. 1994, 46, 99–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hubalek, F.; Sgarra, C. On the Esscher transforms and other equivalent martingale measures for Barndorff-Nielsen and Shephard stochastic volatility models with jumps. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 2009, 119, 2353–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, T.K.; Yang, H.; Lau, J.W. Pricing currency options under two-factor Markov-modulated stochastic volatility models. Insur. Math. Econ. 2008, 43, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Markov-modulated jump-diffusions for currency option pricing. Insur. Math. Econ. 2010, 46, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swishchuk, A.; Tertychnyi, M.; Elliott, R. Pricing currency derivatives with Markov-modulated Lévy dynamics. Insur. Math. Econ. 2014, 57, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.M.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, J.H. State-dependent jump risks for American gold futures option pricing. North Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2015, 33, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.M.; Chen, J.H. Joint dynamic modeling and option pricing in incomplete derivative-security market. North Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2020, 51, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.M.; Chen, J.H. Valuation of chooser options with state-dependent risks. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 52, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.M.; Chen, J.H.; Liao, S.L. Pricing derivatives on foreign assets using Markov-modulated cojump-diffusion dynamics. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 93, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.J.; Osakwe, C.-J.U. Option pricing for pure jump processes with Markov switching compensators. Financ. Stoch. 2006, 10, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.M.; Pliska, S.R. Martingales and stochastic integrals in the theory of continuous trading. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 1981, 11, 215–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.M.; Pliska, S.R. A stochastic calculus model of continuous trading: Complete markets. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 1983, 15, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.G.; Wang, H. First passage times of a jump diffusion process. Adv. Appl. Probab. 2003, 35, 504–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter Name | Value in Boom State | Value in Recession State |
|---|---|---|
| Asset value volatility () | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Annual jump intensity () | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| Double exponential upward jump probability () | 0.3 | |
| Double exponential parameter () | 1/0.5 | |
| Double exponential parameter () | 1/0.2 | |
| Initial value of | 0.1 | |
| Drift term of () | 0.03 | |
| Volatility term of () | 0.02 | |
| Debt volatility () | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Correlation coefficient between asset value and () | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Correlation coefficient between asset value and debt () | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| Risk-free rate () | 0.05 | 0.025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, Y.-M.; Chen, J.-H. Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds Under Regime Switching. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223628
Lian Y-M, Chen J-H. Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds Under Regime Switching. Mathematics. 2025; 13(22):3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Yu-Min, and Jun-Home Chen. 2025. "Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds Under Regime Switching" Mathematics 13, no. 22: 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223628
APA StyleLian, Y.-M., & Chen, J.-H. (2025). Valuation of Defaultable Corporate Bonds Under Regime Switching. Mathematics, 13(22), 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223628





