Abstract
Urban infrastructure planning is central to advancing sustainable cities, but project success increasingly depends on public acceptance as well as technical, economic, and environmental performance. This study develops a fuzzy–grey multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) framework that embeds public opinion as a formal evaluation dimension. A novel POI, derived from online discourse data, integrates multi-dimensional emotions, polarization, and participation intensity to capture societal legitimacy. The framework employs entropy weighting and applies three established MCDM methods: TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS, to evaluate project alternatives under uncertainty and incomplete information. An empirical case study in Nanjing demonstrates that incorporating Public Opinion Index (POI) significantly alters decision outcomes: the ecological park gained priority due to strong public support, while the wastewater treatment plant declined in ranking despite environmental benefits. These results underscore the decisive role of societal legitimacy in shaping sustainable infrastructure decisions. The framework contributes to sustainable urban planning by providing a replicable tool for balancing technical feasibility, environmental responsibility, and social acceptance in future infrastructure projects.
Keywords:
sustainable urban planning; urban infrastructure; fuzzy–grey multi-criteria decision-making; public opinion; social acceptance; entropy weighting MSC:
90B50; 90C70; 91B10
1. Introduction
Urban infrastructure planning and sustainable environmental management are increasingly recognized as complex decision-making problems that involve balancing economic efficiency, ecological protection, technological feasibility, and social well-being. In recent decades, multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods have been widely applied to support such complex choices, offering structured approaches to integrate heterogeneous criteria and stakeholder preferences [1,2]. Techniques such as the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS), and VlseKriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) have been employed in diverse environmental applications, including land use allocation, renewable energy site selection, and water resource management [3,4]. Within the scope of environmental systems research, such methods have provided important insights into integrating ecological, technical, and economic perspectives for sustainable development [5]. However, despite the progress, the dimension of public opinion and societal acceptance has often remained underexplored in MCDM-based environmental planning
Previous studies addressing public perception have mainly relied on questionnaire surveys and stakeholder interviews to capture citizens’ preferences and concerns [6,7]. Even in articles published in Environmental Systems Research, survey-based approaches have been adopted to evaluate local communities’ attitudes toward planning alternatives. While valuable, these approaches face several limitations: small sample sizes restrict representativeness; social desirability bias may lead respondents to provide “polite” rather than truthful answers in face-to-face settings; and static survey designs cannot fully capture the evolving dynamics of social opinion. In contrast, online platforms such as social media, forums, and digital news outlets provide massive, timely, and relatively anonymous data sources where individuals are more willing to express genuine concerns, especially on controversial infrastructure projects [8,9]. Consequently, online public opinion data not only enhance scalability and efficiency in collection and processing, but also more authentically reflect collective attitudes, making them a promising input for environmental decision-making frameworks.
Nevertheless, even when public opinion has been incorporated in decision models, it is usually represented in a simplistic manner, for instance as an average sentiment score or a positive–negative ratio [10,11]. Such aggregate measures fail to capture the complexity of collective attitudes, particularly the presence of polarization (i.e., strong divisions between support and opposition) and the degree of public engagement. These factors are crucial in determining whether a technically and economically sound project can gain sufficient legitimacy to be implemented. To address this gap, this study develops a novel POI that integrates three dimensions: (i) multi-dimensional emotions (e.g., anger, fear, joy, anticipation) extracted from online discourse, (ii) polarization of opinions, measured using an entropy-based index, and (iii) participation intensity, reflecting the scale of societal attention. The POI is normalized and incorporated as an explicit criterion into a fuzzy–grey MADM framework, alongside economic, environmental, and technical criteria. By designing comparative experiments between models with and without POI, and between traditional sentiment-based indices and the proposed POI, we aim to demonstrate the necessity and added value of incorporating social acceptance into sustainable infrastructure planning.
The main contributions of this study are threefold. First of all, we integrate public opinion as an explicit and independent criterion into the fuzzy–grey MADM framework for infrastructure planning, thereby extending the scope of decision-making beyond conventional technical and economic dimensions. Secondly, we propose a novel POI that moves beyond simplistic sentiment averages by combining multi-dimensional emotions, polarization, and participation intensity into a single quantitative measure. Thirdly, we validate the effectiveness of this approach through comparative experiments, showing how incorporating POI can significantly alter the ranking of alternatives and provide more socially robust decisions. Together, these contributions advance both the methodological toolkit of environmental systems research and the practical agenda of embedding societal legitimacy into sustainable decision-making processes.
The novelty of this study lies in three interrelated dimensions that extend conventional fuzzy–grey multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) frameworks toward a socially grounded and dynamically adaptive form of urban governance:
Interdisciplinary integration:
The proposed framework bridges quantitative decision science and social science by embedding societal legitimacy—captured through public opinion—into the fuzzy–grey MCDM process. This integration transforms traditional sustainability assessment, which focuses mainly on technical, economic, and environmental factors, into a framework that explicitly accounts for public sentiment and collective acceptance.
Data-driven legitimacy measurement:
Instead of relying on static expert surveys or small-sample questionnaires that often suffer from social desirability bias, this study introduces large-scale online opinion crawling as a normative and efficient means to quantify public attitudes. The approach ensures higher authenticity, timeliness, and representativeness, as individuals express genuine perspectives in online spaces without the constraints typical of formal survey environments.
Temporal adaptability:
Public opinion inherently possesses a time dimension that allows decision-makers to monitor legitimacy dynamics in real time. By leveraging the temporal evolution of online discourse, the framework can be extended into a dynamic decision-support system that adapts to shifts in public sentiment, thereby enhancing the transparency, interpretability, and long-term acceptance of government decisions.
Collectively, these innovations reposition the fuzzy–grey MCDM paradigm from a purely technical optimization tool to a participatory and legitimacy-oriented mechanism for sustainable urban infrastructure planning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Notation and Assumptions
To enhance the mathematical rigor and clarity of the proposed framework, the main symbols and assumptions are summarized in Table 1. Table 1 summarizes all mathematical symbols and assumptions used throughout the methodology. To ensure consistency, the same notation is applied across Section 2.5, Section 2.6, Section 2.7 and Section 2.8, where and represent alternatives and criteria, respectively, and specifically denotes the Public Opinion Index (POI) introduced in this study. This unified definition facilitates the understanding of subsequent formulations and their empirical implementation.

Table 1.
Notations.
- Assumptions:
- All criteria can be transformed into benefit-type indicators; cost-type criteria are directionally adjusted before normalization.
- Grey intervals and TFNs are unified through a defuzzification and confidence rule (Equations (7) and (8)).
- The POI consists of three normalized components: emotion polarity, polarization, and participation intensity with corresponding weights.
All variables appearing in the following equations are defined in Table 1 for clarity and reference.
2.2. Research Framework
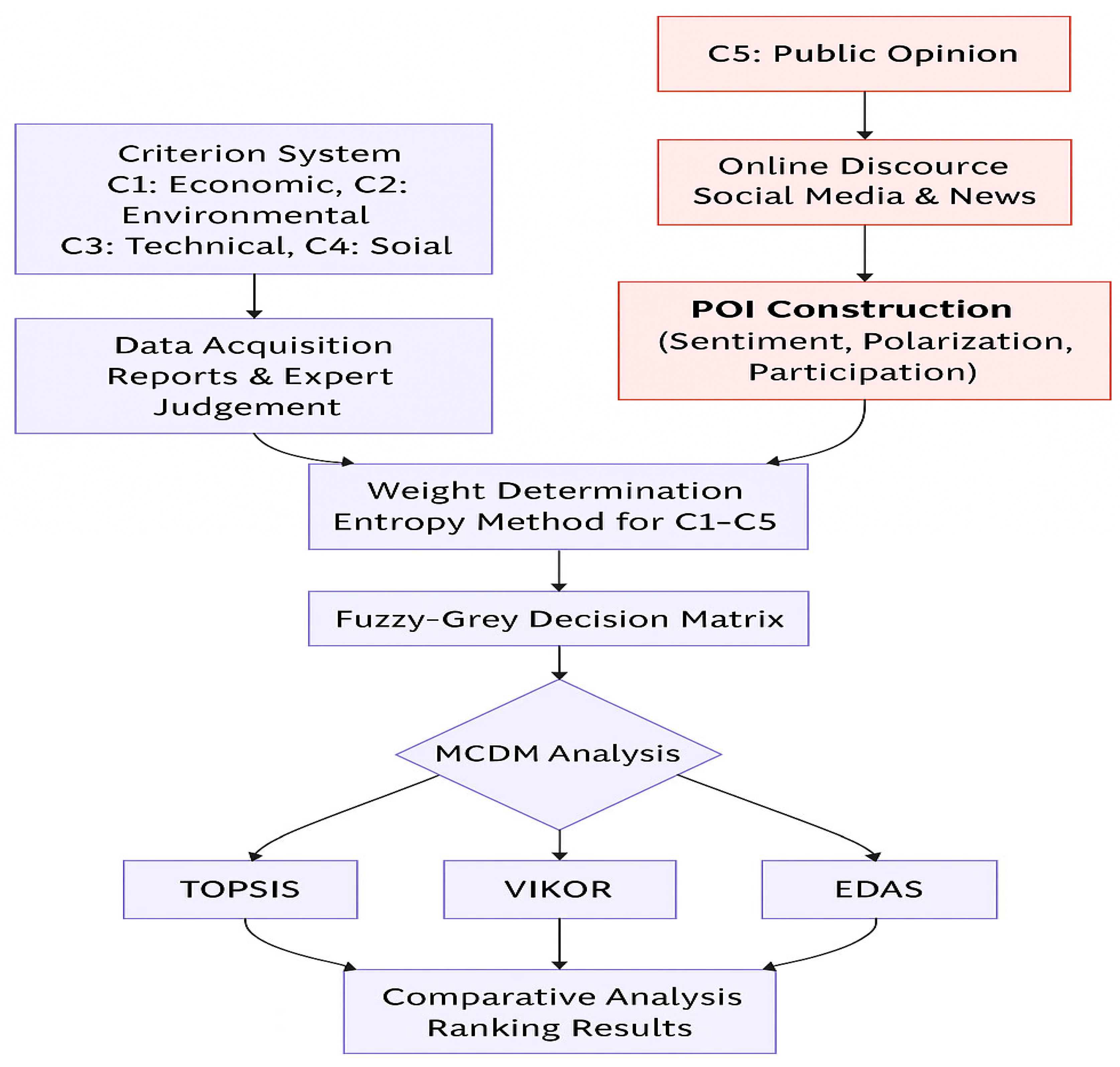
To provide a systematic overview of the methodological design and highlight the integration of the POI, this section introduces the overall research framework (Figure 1). The framework combines conventional sustainability assessment with a novel societal legitimacy dimension, ensuring that both technical and social aspects are explicitly incorporated into the evaluation process.
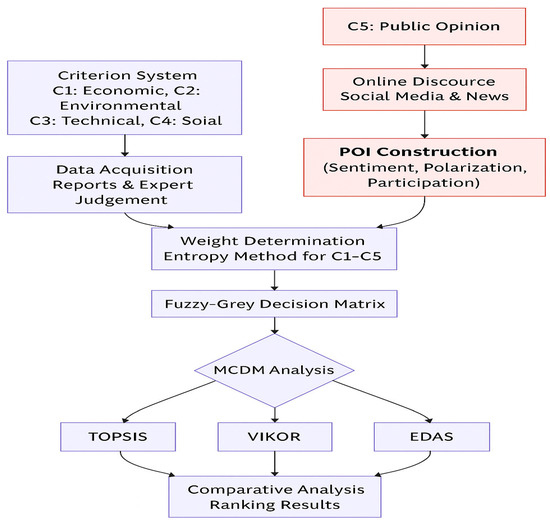
Figure 1.
Research framework.
The framework begins with the formulation of a comprehensive criteria system. Four conventional dimensions, including economic, environmental, technical, and social, constitute the foundation of sustainability evaluation, while the POI is added as a fifth criterion to represent collective societal attitudes expressed in online discourse. This extension reflects the recognition that infrastructure projects cannot be regarded as sustainable without adequate public legitimacy.
Data are then acquired from both conventional and online sources. For the first four dimensions, information is obtained from governmental reports, feasibility studies, planning documents, and expert consultations, expressed in either quantitative form or linguistic assessments. For the public opinion dimension, text data are collected from social media and digital news platforms. After preprocessing procedures such as text cleaning, sentiment and emotion classification, and the measurement of polarization and participation intensity, the results are normalized to generate POI values that are comparable with other criteria.
The relative importance of the criteria is subsequently determined through the entropy weighting method. Unlike subjective weighting approaches, this technique objectively reflects the discriminative power of each criterion based on the variability of evaluation data. By including the POI in this process, the influence of societal legitimacy is formally embedded within the weighting structure.
A fuzzy–grey decision matrix is then constructed to accommodate the uncertainty of linguistic judgments and the incompleteness of available information. Expert assessments are represented as triangular fuzzy numbers, missing or imprecise values are modeled as grey intervals, and POI values serve as direct quantitative indicators. This hybrid representation provides a realistic modeling of decision environments where vagueness and incomplete information coexist, while also balancing expert-based inputs with data-driven social measures.
Finally, the weighted fuzzy–grey decision matrix is analyzed using three mainstream MCDM methods: TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS. The use of multiple methods enhances robustness through cross-validation of results, while comparative analysis between models with and without POI explicitly demonstrates the role of public opinion in shaping decision outcomes.
Figure 1 presents the overall research framework, showing the sequential process from criteria formulation to comparative analysis. The integration of the POI is emphasized as the central innovative component of this study.
2.3. Decision Criteria System
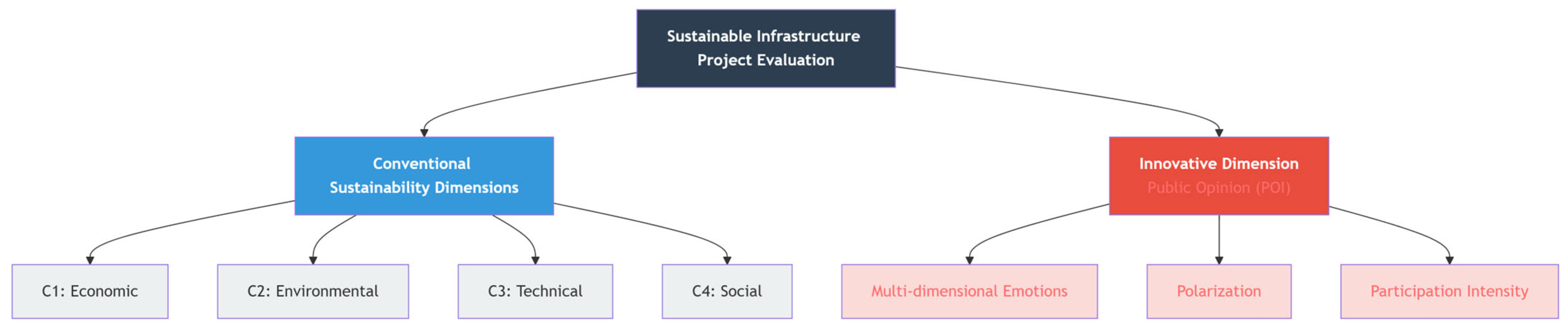
The evaluation of sustainable infrastructure projects requires a multidimensional set of criteria that adequately captures technical feasibility, economic viability, ecological protection, social benefits, and societal legitimacy. Drawing on previous studies in environmental decision-making [1,2], this study adopts a five-dimensional criteria system (Figure 2). The conventional pillars of sustainability assessment are represented by four dimensions: economic, environmental, technical, and social. The fifth dimension, public opinion, explicitly aims to incorporate societal acceptance into the decision-making process.
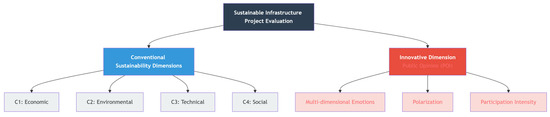
Figure 2.
The Integrated Sustainability Evaluation Framework.
Economic (C1): investment cost, operational efficiency.
Environmental (C2): ecological impacts, including carbon emissions, pollution control, ecological footprint.
Technical (C3): feasibility and reliability of project implementation, adaptability to future needs.
Social (C4): equity, inclusiveness, and accessibility of services.
Public Opinion (C5): quantified through the POI, integrating multi-dimensional emotions, polarization, and participation intensity.
The hierarchical structure of the criteria is shown in Figure 2, with representative sub-indicators summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Decision criteria and representative sub-indicators.
2.4. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
Reliable and comprehensive data acquisition is a prerequisite for applying the proposed fuzzy–grey MCDM framework. This study combines conventional sources of evaluation data with online public opinion data to construct a balanced decision matrix.
For C1–C4, data are obtained from governmental reports, planning documents, and domain experts. Quantitative indicators such as investment, operating efficiency, and emission levels are collected from official statistics and technical studies. Qualitative assessments such as feasibility and social equity are elicited through expert consultation. These linguistic terms are converted into TFNs, preserving vagueness while maintaining computational tractability [3,4].
For C5, data are retrieved from online platforms such as social media, news comments, and forums. Preprocessing includes:
Text cleaning and tokenization
Sentiment and emotion classification (anger, fear, joy, anticipation, etc.)
Aggregation and normalization to [0, 1]
In addition, participation intensity is measured by discourse frequency, while distributions of supportive versus opposing opinions are used to compute polarization. These three components form the POI [5,6,7].
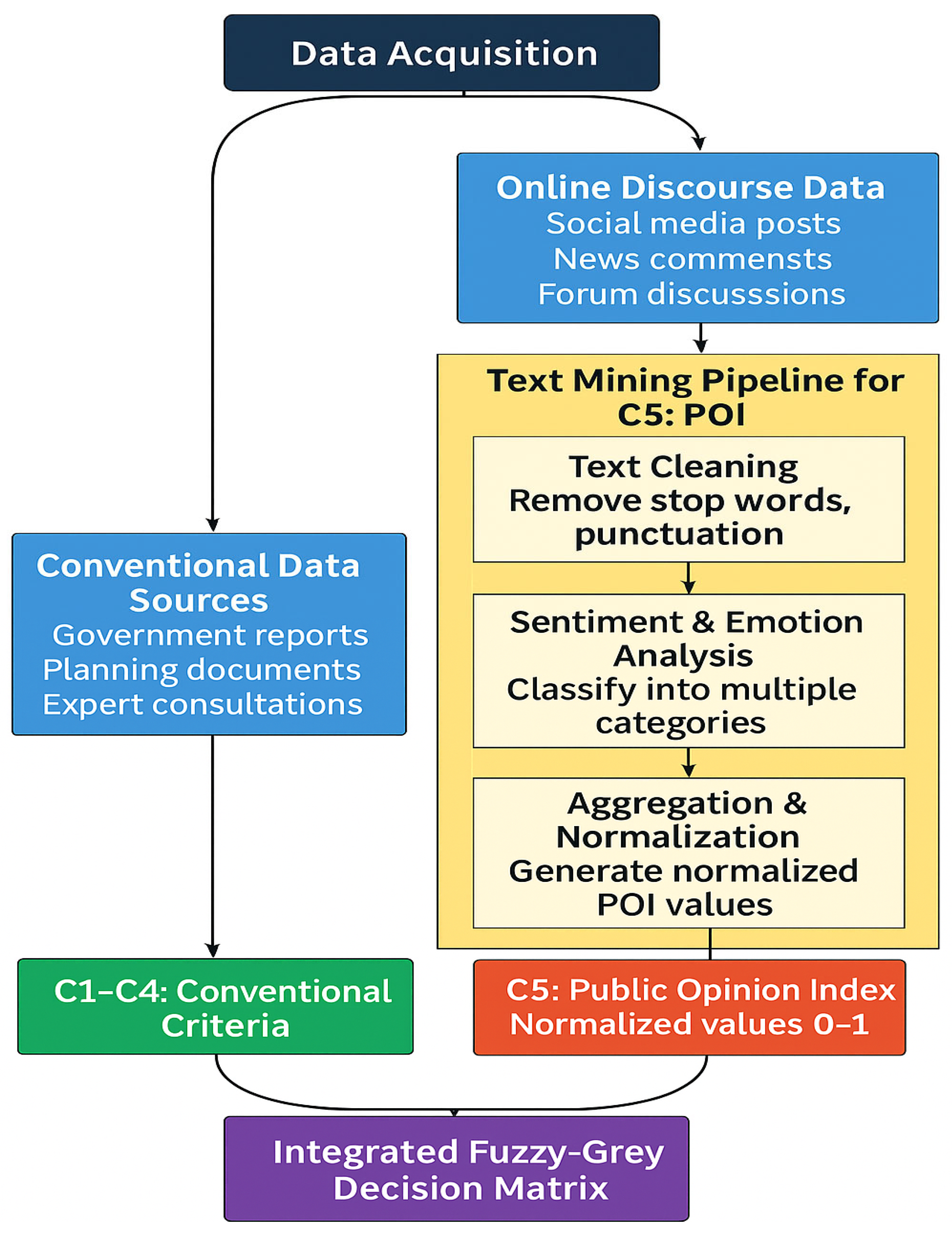
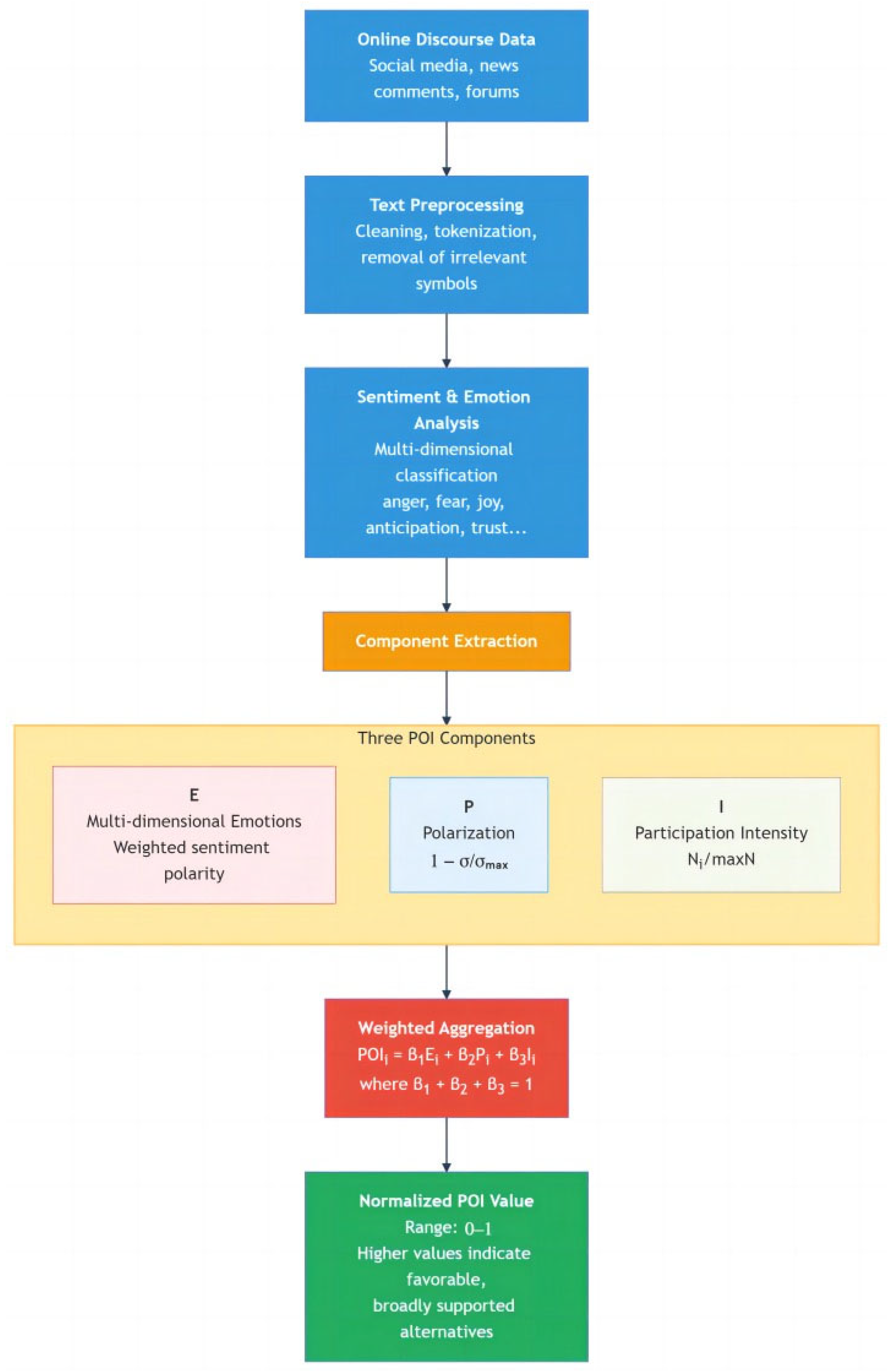
The overall data acquisition and preprocessing workflow is shown in Figure 3.
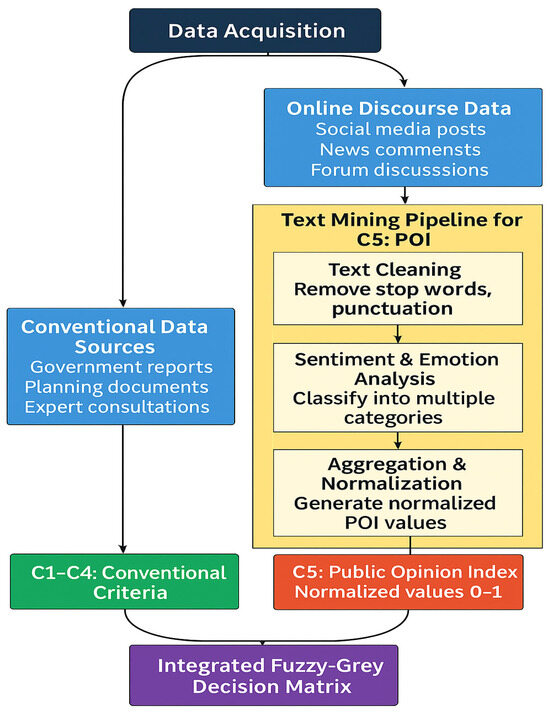
Figure 3.
Preprocessing workflow.
This figure illustrates the workflow for constructing the Public Opinion Index (POI) from large-scale online discourse data. It depicts the sequential procedures of text collection, data cleaning, tokenization, sentiment classification, and normalization. Each stage transforms raw comments into structured information that quantitatively represents citizens’ emotional tendencies toward infrastructure alternatives.
To ensure transparency and reproducibility, additional details of data collection are clarified. For C1–C4, expert judgments were obtained from a panel of domain specialists with backgrounds in construction management, urban planning, and environmental engineering. Each expert provided linguistic evaluations, later transformed into triangular fuzzy numbers, covering the economic feasibility, environmental impact, social acceptance, and technical reliability of the alternatives. For C5, public opinion data were collected from the Bilibili video platform, where a total of 421 comments were retrieved between Year 2024 Month 11 and Month 12 using a dedicated Python 3.12.3 crawler. After removing duplicates, irrelevant messages, and spam, 361 valid comments (emtion not conclude) were retained for sentiment analysis. The emotional polarity, polarization, and participation intensity were then derived using a lexicon-based classifier and engagement metrics. Missing values were handled through grey intervals, while extreme outliers were truncated at the 5th and 95th percentiles to improve robustness.
2.5. Entropy Weight Determination
The entropy weighting method is adopted to obtain objective weights. Unlike subjective assignment methods such as AHP, entropy weighting avoids expert bias and ensures criteria with greater discriminative information receive higher weights [9,10].
Let denote the normalized performance value of alternative with respect to criterion where and . The entropy of criterion is computed as:
The degree of diversification of criterion is:
Finally, the entropy weight of criterion is obtained as:
The entropy of each criterion is calculated, followed by diversification and weight determination. All five criteria (C1–C5) are included in the process, guaranteeing that public opinion is integrated into the structure. Expert linguistic judgments are mapped to TFNs before normalization (Table 3).

Table 3.
Entropy-based weights of the five evaluation criteria.
Compared with subjective weighting techniques such as AHP or BWM, the entropy method relies on the intrinsic variability of data and avoids potential biases from expert judgment, making it particularly suitable for the context of this study.
2.6. Fuzzy–Grey Decision Matrix Construction
After weight determination, the fuzzy–grey decision matrix is constructed. C1–C4 expert judgments are expressed as TFNs, while C5 values are derived from the POI. Incomplete or uncertain data are represented by grey intervals. This ensures the decision matrix reflects real-world uncertainty [11,12,13].
After determining the criteria weights, the next step is to construct the fuzzy–grey decision matrix that integrates both conventional sustainability dimensions (C1–C4) and public opinion (C5). This representation accounts for two main sources of uncertainty: linguistic vagueness in expert evaluations and incompleteness of data arising from limited or imprecise information [11,12,13].
Let denote the set of alternatives under consideration, and the evaluation criteria. Expert judgments with respect to criteria C1–C4 are expressed as TFNs:
Here, and represent the lower, most likely, and upper values of the linguistic evaluation, respectively. This formulation captures the inherent imprecision of linguistic terms and ensures that expert subjectivity is preserved in computational form.
For public opinion (C5), the value assigned to each alternative is given by the POI derived in Section 3.4. Unlike expert evaluations, POI is data-driven and directly quantifies collective attitudes by integrating emotional intensity, polarization, and participation. Thus, the decision matrix explicitly balances traditional expert-driven inputs with large-scale social feedback.
To handle incomplete or uncertain data, the fuzzy decision matrix is extended with a grey system representation. When the available information for an alternative–criterion pair is incomplete, the evaluation is expressed as a grey interval: .
In constructing the unified decision matrix, the POI is directly incorporated as criterion C5 alongside the conventional dimensions, ensuring its consistent role in the subsequent evaluation procedures.
By combining fuzzy numbers with grey intervals, the final decision matrix is expressed as:
where each element may be a TFN, a grey interval, or (in the case of C5) a normalized POI value.
The hybrid use of fuzzy and grey systems is not an arbitrary combination: fuzzy numbers capture subjective vagueness in expert assessments, while grey intervals address missing or incomplete information. Their integration therefore enables the framework to simultaneously represent cognitive uncertainty and data incompleteness, which are typical characteristics of large-scale decision-making.
The incorporation of both fuzzy and grey elements ensures that the decision matrix faithfully represents real-world conditions, where data may be uncertain, imprecise, or incomplete. In particular, the integration of the POI as criterion C5 provides a novel mechanism to embed public acceptance into a rigorous MCDM framework, thereby enhancing the societal relevance of the evaluation results.
2.7. Evaluation Methods
Instead of developing an entirely new MCDM method, this study introduces a novel criterion, the POI, and embeds it into three mainstream fuzzy–grey MCDM techniques: TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS. This design choice reflects two key considerations. First, the selected methods are widely recognized and frequently applied in environmental decision-making, which ensures methodological familiarity for both scholars and practitioners [6,7,14]. Second, by incorporating the POI as a formal criterion (C5) alongside conventional sustainability dimensions (C1–C4), the proposed framework highlights the innovative contribution of integrating societal legitimacy into project evaluation.
Through this embedded approach, the evaluation process remains transparent and replicable, while at the same time extending existing methods to account for public acceptance. The use of multiple methods further enhances the robustness of results, as consistent rankings across techniques strengthen confidence, whereas discrepancies reveal methodological sensitivity.
2.7.1. Fuzzy–Grey TOPSIS
The selection of TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS is motivated by their complementary perspectives on multi-criteria evaluation. TOPSIS emphasizes proximity to the ideal solution, VIKOR highlights compromise solutions balancing group utility and individual regret, while EDAS assesses deviations from average performance. Applying these three methods in parallel enhances the robustness and credibility of the final ranking results.
The fuzzy–grey TOPSIS method ranks alternatives according to their relative closeness to the positive ideal solution (PIS) and distance from the negative ideal solution (NIS). For each criterion the fuzzy–grey normalized values are compared against the ideal benchmarks. The closeness coefficient of alternative is defined as:
where and are the distances of alternative from the PIS and NIS, respectively. Alternatives are ranked in descending order of
In this framework, POI (C5) is incorporated as a normalized and weighted criterion. Alternatives that receive strong public support and low polarization are positioned closer to the PIS, highlighting the role of societal legitimacy in decision outcomes [15,16].
2.7.2. Fuzzy–Grey VIKOR
The fuzzy–grey VIKOR method emphasizes compromise solutions by considering both group utility and individual regret. For each alternative , the following indices are computed:
where and are the best and worst values across all alternatives for criterion The overall compromise index is then:
With typically set to 0.5. Alternatives are ranked in ascending order of .
By including POI (C5) in the weighting and normalization process, VIKOR explicitly integrates public attitudes into the compromise solution, balancing technical efficiency with social legitimacy [13,17].
2.7.3. Fuzzy–Grey EDAS
The EDAS method evaluates alternatives based on their positive distance from average (PDA) and negative distance from average (NDA) across all criteria. For alternative
where is the average performance of criterion . The appraisal score of alternative is:
Alternatives are ranked in descending order of .
In this study, the POI dimension contributes to both PDA and NDA calculations. Alternatives that align with favorable public sentiment achieve higher appraisal scores, thereby reinforcing the importance of societal legitimacy in sustainability assessments [14,18].
2.7.4. Comparative Advantage of Using Multiple Methods
By employing TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS simultaneously, this framework enables a robust evaluation (Table 4). While TOPSIS emphasizes proximity to ideal solutions, VIKOR highlights compromise under conflicting objectives, and EDAS provides an intuitive assessment relative to average performance. Consistency across these methods enhances the reliability of results, whereas discrepancies reveal sensitivity to methodological assumptions. Importantly, in all three approaches, the integration of the POI criterion ensures that societal legitimacy is explicitly embedded into the ranking process [19,20].

Table 4.
Improvements of classical MCDM methods after embedding POI [21,22].
2.8. POI Formulation
In order to systematically embed societal legitimacy into the evaluation framework, this study proposes a novel POI as criterion C5. The POI captures the collective attitudes of stakeholders as expressed through online platforms, reflecting not only the average emotional polarity but also the diversity and intensity of participation. This design ensures that alternatives with broader and stronger public support are favored in the decision-making process, while those facing polarized or limited engagement are penalized.
The POI is constructed from three complementary components:
Multi-dimensional emotions ()
Sentiment analysis provides the probability distribution of emotions (e.g., joy, trust, fear, anger) for alternative . The aggregated sentiment polarity score is computed as:
where is the proportion of emotion category k associated with alternative , and is the weight assigned to each emotion (positive emotions > 0, negative emotions < 0). This yields a normalized sentiment value in [23].
Polarization
To account for disagreement within public discourse, polarization is measured by the variance of sentiment polarity across individuals:
where is the standard deviation of sentiment scores for alternative , and is the maximum observed deviation across all alternatives. Higher values of indicate greater consensus, whereas lower values suggest divisive opinions [24].
Participation intensity
Public legitimacy also depends on the level of civic engagement. Participation intensity is proxied by the normalized volume of online discourse:
where is the number of opinion instances collected for alternative , and max is the maximum count among alternatives [25].
The overall POI for alternative is then defined as a weighted aggregation of the three components:
Weights are assigned according to the relative importance of emotion, polarization, and intensity in the specific decision context. In this study, equal weights are adopted for simplicity, but the framework allows flexibility for stakeholders to adjust these parameters [26].
The resulting is a continuous value in the range [0, 1], where higher values indicate alternatives that are more positively perceived, broadly supported, and less divisive among the public. By including POI as criterion C5 in the decision matrix, the framework provides a transparent and reproducible mechanism for integrating social legitimacy into sustainable infrastructure evaluation.
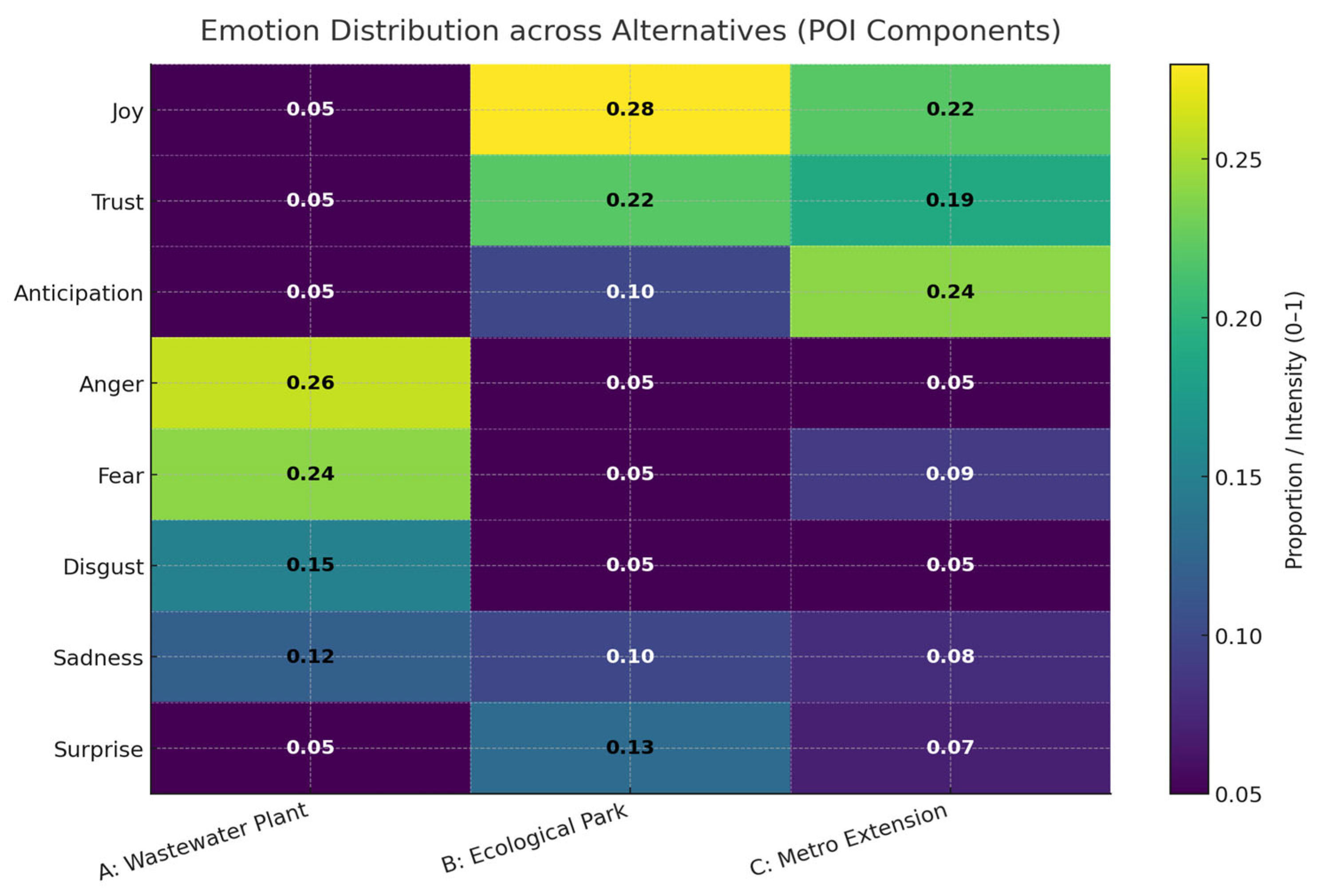
Figure 4 illustrates the distribution of eight basic emotions: joy, trust, anticipation, anger, fear, disgust, sadness, and surprise across the three candidate infrastructure projects. The heatmap highlights distinct emotional profiles for each alternative, reflecting the heterogeneity of public discourse. Specifically, Alternative A (wastewater treatment plant) is predominantly associated with negative emotions such as anger, fear, and disgust, which aligns with common concerns over environmental risks and health hazards. In contrast, Alternative B (ecological park) exhibits higher levels of joy and trust, indicating broad societal support rooted in perceived ecological and recreational benefits. Alternative C (metro extension) is characterized by strong anticipation and joy, suggesting positive expectations regarding improved mobility and urban connectivity. These differentiated emotional patterns provide empirical evidence that public attitudes toward infrastructure projects extend beyond a simple polarity of positive versus negative sentiment. By incorporating such multi-dimensional emotional information into the POI, the proposed framework captures not only the overall orientation of public opinion but also its underlying affective drivers, thereby offering a more nuanced and socially grounded basis for sustainable infrastructure decision-making.
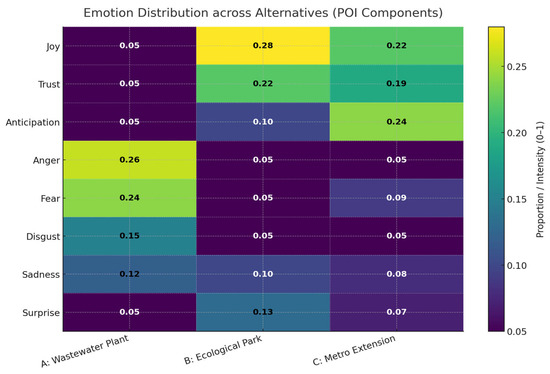
Figure 4.
Distribution of emotion.
This figure presents the distribution of eight basic emotions which are joy, trust, anticipation, anger, fear, disgust, sadness, and surprise—across the considered infrastructure alternatives. The color gradient denotes the relative intensity of each emotion (lighter shades indicate higher proportions). The figure highlights distinct emotional patterns among alternatives, revealing how collective sentiment shapes the perceived legitimacy of each option.
2.9. Integration and Implementation Procedure
To ensure logical consistency, the overall methodological procedure can be summarized in four sequential steps: Criteria system construction: Five dimensions (C1–C5) are defined, integrating conventional sustainability criteria with the novel POI. Weighting and representation: Entropy weighting (Section 2.5) is applied to determine the objective importance of each criterion, and the fuzzy–grey decision matrix (Section 2.6) is constructed by combining TFNs, grey intervals, and POI values. Evaluation through multiple methods: The weighted decision matrix is analyzed using three well-established multi-criteria decision-making methods: TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS, each embedding POI as an explicit criterion to highlight societal legitimacy. Comparative analysis: By contrasting results with and without POI, and by performing sensitivity tests on POI weights, the framework demonstrates both the methodological contribution and the robustness of outcomes.
This integration ensures that the proposed framework is not a simple collection of techniques, but a coherent decision-making process in which societal legitimacy is systematically embedded. The next section applies this procedure to the Nanjing case study to validate its feasibility and practical implications. In this way, the methodological framework forms a complete toolchain, which directly supports the empirical validation presented in Section 3.
3. Results
3.1. Case Background
Nanjing, the capital city of Jiangsu Province in eastern China, is undergoing rapid urban expansion and faces mounting challenges related to environmental sustainability and social well-being. With a population exceeding nine million and an ambitious agenda to achieve carbon peaking before 2030, the city has prioritized investments in green infrastructure projects such as wastewater treatment, ecological restoration, and sustainable urban transport [27]. These projects are not only technically demanding and financially intensive but also subject to diverse societal expectations and public scrutiny.
In this study, three candidate projects were selected to represent alternative options for sustainable infrastructure development in Nanjing:
- Alternative A: Construction of a large-scale wastewater treatment facility.
- Alternative B: Development of a new urban ecological park.
- Alternative C: Extension of a metro line.
3.2. Data Collection and Processing
To evaluate the three candidate projects, data were collected for each of the five criteria (C1–C5). For C1–C4, information was gathered from government planning documents, technical feasibility reports, and domain experts. Expert judgments were elicited using linguistic terms (Very Low to Very High) and subsequently converted into triangular fuzzy numbers, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Data Sources and Processing Methods for Evaluation Criteria.
For C5, online public opinion data were retrieved from major Chinese social media platforms and digital news portals. Preprocessing included text cleaning, sentiment/emotion classification, and computation of polarization and participation intensity [28]. These steps generated normalized POI values for each project (Figure 5).
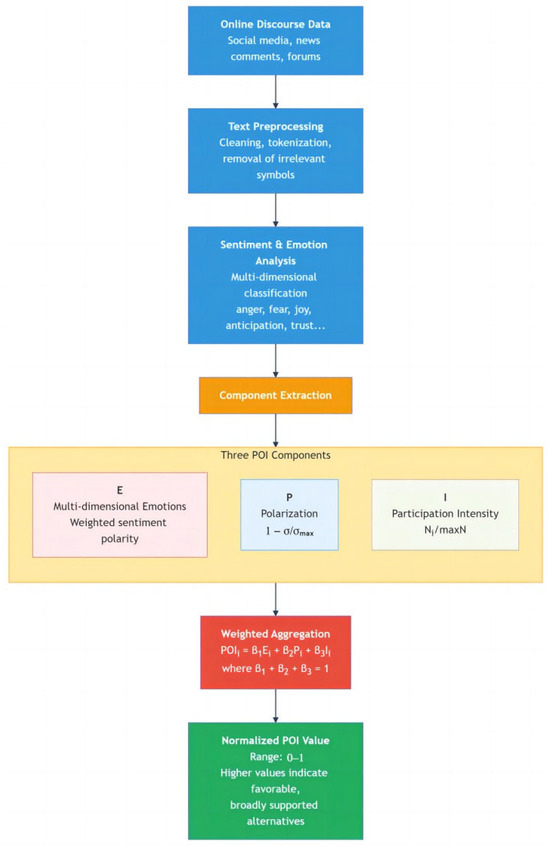
Figure 5.
Workflow of POI construction from online discourse data.
This figure depicts the integrated construction process of the Public Opinion Index (POI). It combines three complementary dimensions: emotional polarity, polarization, and participation intensity. The visualization demonstrates how these sub-indices are synthesized into a unified legitimacy metric that reflects both the emotional direction and the diversity of public attitudes. The proposed POI, together with the conventional sustainability dimensions, forms an integrated decision-making framework. In the next section, this framework is applied to a real-world case study to demonstrate its feasibility and practical implications.
3.3. Computation Process
Using the collected data, entropy weights were calculated for the five criteria (Table 2). Next, the fuzzy–grey decision matrix was constructed, integrating both expert-derived TFNs and POI values. The evaluation process was carried out using the three methods: TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS.
- In TOPSIS, each alternative’s closeness coefficient was computed by measuring its distance to the PIS and NIS.
- In VIKOR, compromise solutions were derived based on group utility and individual regret, incorporating POI into the normalization process.
- In EDAS, appraisal scores were calculated from positive and negative distances to the average, with POI contributing directly to PDA and NDA values.
The integration of POI into all three methods ensured that societal legitimacy was explicitly embedded in the evaluation results [29,30].
3.4. Impact of Public Opinion on Rankings
3.4.1. Comparative Ranking Outcomes
The evaluation framework was applied to the three candidate projects in Nanjing under the five-dimensional criteria system. The entropy weighting method was first used to determine the relative importance of criteria. When only C1–C4 were considered, environmental and economic criteria received relatively higher weights, reflecting the salience of cost efficiency and ecological performance in conventional sustainability assessments. After the inclusion of C5, the weight distribution shifted, with POI contributing nearly 20% of the overall importance, thereby elevating the influence of societal legitimacy in the decision process.
The rankings of alternatives obtained from the three fuzzy–grey MCDM methods are summarized in Table 6.

Table 6.
Rankings of alternatives using fuzzy–grey TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS with POI included.
All three methods produced a consistent ranking:
- Alternative C (Metro extension) ranked first, benefiting from strong economic efficiency, technical feasibility, and widespread public support captured by the POI.
- Alternative B (Ecological park) was ranked second, as its high social acceptance and favorable online sentiment compensated for relatively modest economic returns.
- Alternative A (Wastewater treatment plant) was ranked lowest, despite strong environmental performance, due to high investment costs and negative public perceptions reflected in online discourse.
To highlight the added value of POI integration, a baseline model was constructed using only C1–C4. The comparison between the two models is presented in Table 7.

Table 7.
Comparison of average ranks with and without POI integration.
In the baseline model (without POI), Alternatives A and C were close in performance: A gained advantages from its environmental benefits, while C scored highly on economic and technical grounds. Alternative B lagged behind because its ecological and social benefits were not sufficient to outweigh weaker economic performance. However, once POI was introduced, the ranking pattern changed substantially:
- C (Metro extension) was consistently reinforced as the top-ranked alternative, with strong online support consolidating its leading position.
- B (Ecological park) improved significantly, moving ahead of A, as public sentiment strongly favored the ecological park.
- A (Wastewater treatment plant) fell to the lowest rank, as widespread online opposition to wastewater facility construction outweighed its environmental merits.
This reversal demonstrates that excluding POI could lead to misleading conclusions, whereas the proposed framework explicitly captures the decisive role of societal legitimacy.
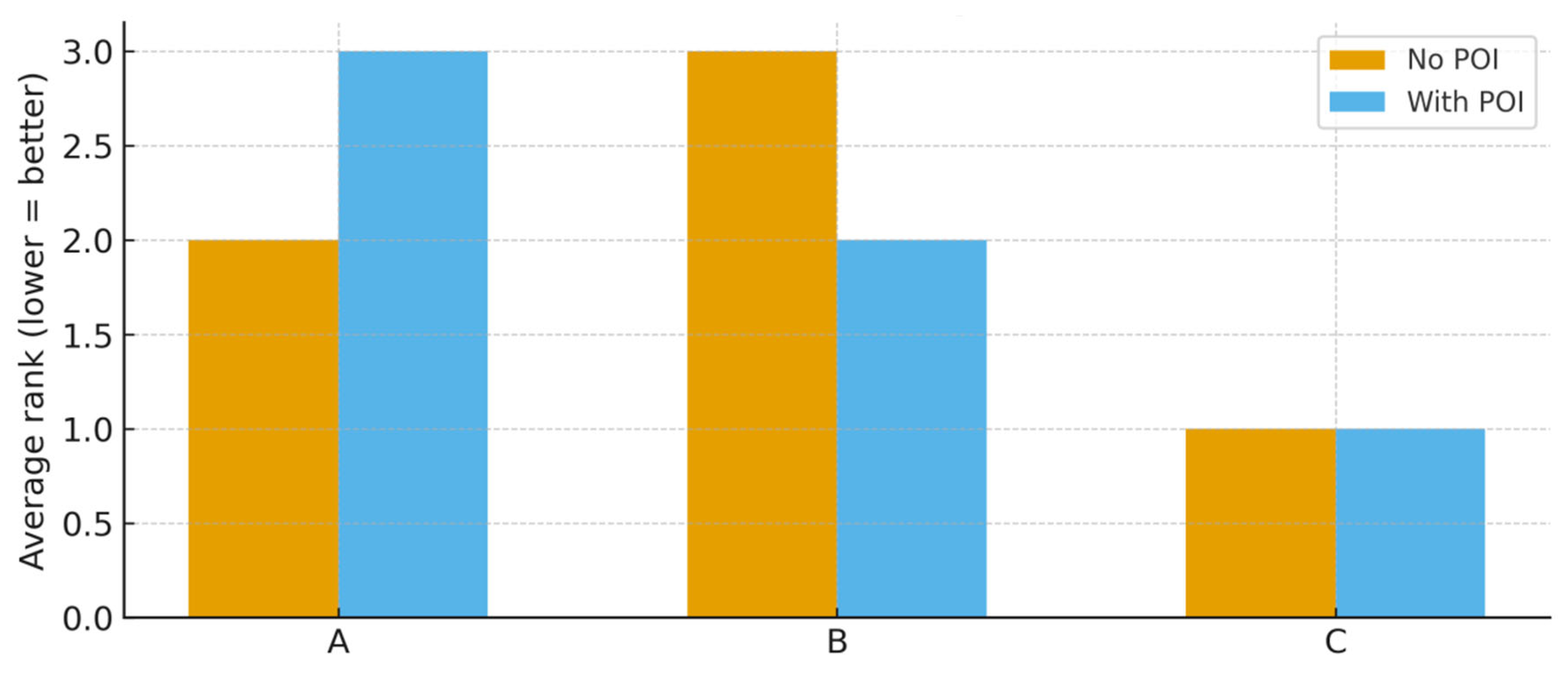
Figure 6 compares the ranking results of the three candidate infrastructure projects under two evaluation settings: one excluding the POI and one embedding POI as an explicit criterion. The comparison highlights the decisive influence of societal legitimacy on sustainable decision outcomes.
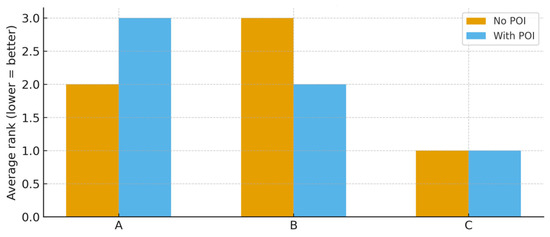
Figure 6.
Comparative average rankings of alternatives with and without POI integration.
This figure compares the average ranking results of alternatives under models with and without the POI. The comparison indicates that incorporating the POI alters the relative priorities of certain alternatives, signifying the tangible influence of social legitimacy on decision outcomes. The figure underscores that public opinion can reshape the final sustainability assessment when integrated into the MCDM framework.
Specifically, in the baseline model without POI, the wastewater treatment facility (Alternative A) obtained a relatively favorable position due to its strong environmental benefits, while the ecological park (Alternative B) was penalized for limited economic returns. However, once POI was introduced, the ranking of Alternative A declined substantially, reflecting the strong opposition expressed in online discourse. In contrast, Alternative B improved in rank, supported by high levels of joy and trust identified in the public sentiment analysis. The metro extension (Alternative C) maintained its top position across both models, indicating a convergence of technical feasibility, economic efficiency, and positive societal perception.
This comparative result demonstrates that conventional sustainability criteria (C1–C4) are insufficient to capture the full complexity of infrastructure legitimacy [21,22]. By incorporating POI, the framework accounts for negative externalities arising from public resistance, which can undermine technically sound but socially contested projects [23,24]. Moreover, the shift in ranking underscores the methodological contribution of the fuzzy–grey MCDM approach with POI: the ability to integrate heterogeneous data sources—expert judgments and large-scale online discourse—into a unified evaluation matrix [12,13].
From a broader perspective, the results emphasize that excluding public opinion may lead to misleading policy recommendations, as projects that are environmentally responsible but socially rejected are unlikely to succeed in practice. Conversely, including POI ensures that evaluation outcomes align more closely with societal legitimacy and long-term governance feasibility [14,19,31]. Hence, Figure 6 not only visualizes the outcome differences between the two models but also illustrates the theoretical necessity of embedding legitimacy into sustainable decision-making frameworks.
The shift in rankings after incorporating the Public Opinion Index (POI) reflects the divergence that often exists between expert-driven evaluations and the collective voice of citizens. In real-world governance, such divergence cannot—and should not—be eliminated, as it embodies the pluralistic nature of sustainable decision-making. Ignoring public sentiment may lead to technically sound yet socially fragile outcomes. In contrast, incorporating POI not only makes the evaluation more inclusive but also exposes the social legitimacy dimension that conventional MCDM frameworks overlook.
Compared with the baseline model without POI, the proposed approach better captures the trade-offs between technical optimization and social acceptance. The results show that alternatives with greater public endorsement tend to rank higher despite lower economic or technical scores, suggesting that legitimacy acts as a compensatory factor balancing short-term efficiency and long-term governance feasibility. This improvement is not merely quantitative but interpretive: by linking decisions to collective emotions, polarization, and participation intensity, the model yields rankings that policymakers can more easily justify and communicate to the public. Hence, the integration of POI transforms a purely analytical evaluation into a socially grounded decision framework—one that acknowledges public voice as an indispensable foundation of sustainable and democratic governance.
3.4.2. Robustness and Sensitivity Analysis
While Figure 6 provides a static comparison between the models with and without the POI, further robustness tests are required to examine whether these results hold under varying parameter settings. To this end, we conducted a sensitivity analysis by adjusting the relative weight of POI from 10% to 30% of the total criteria weight.
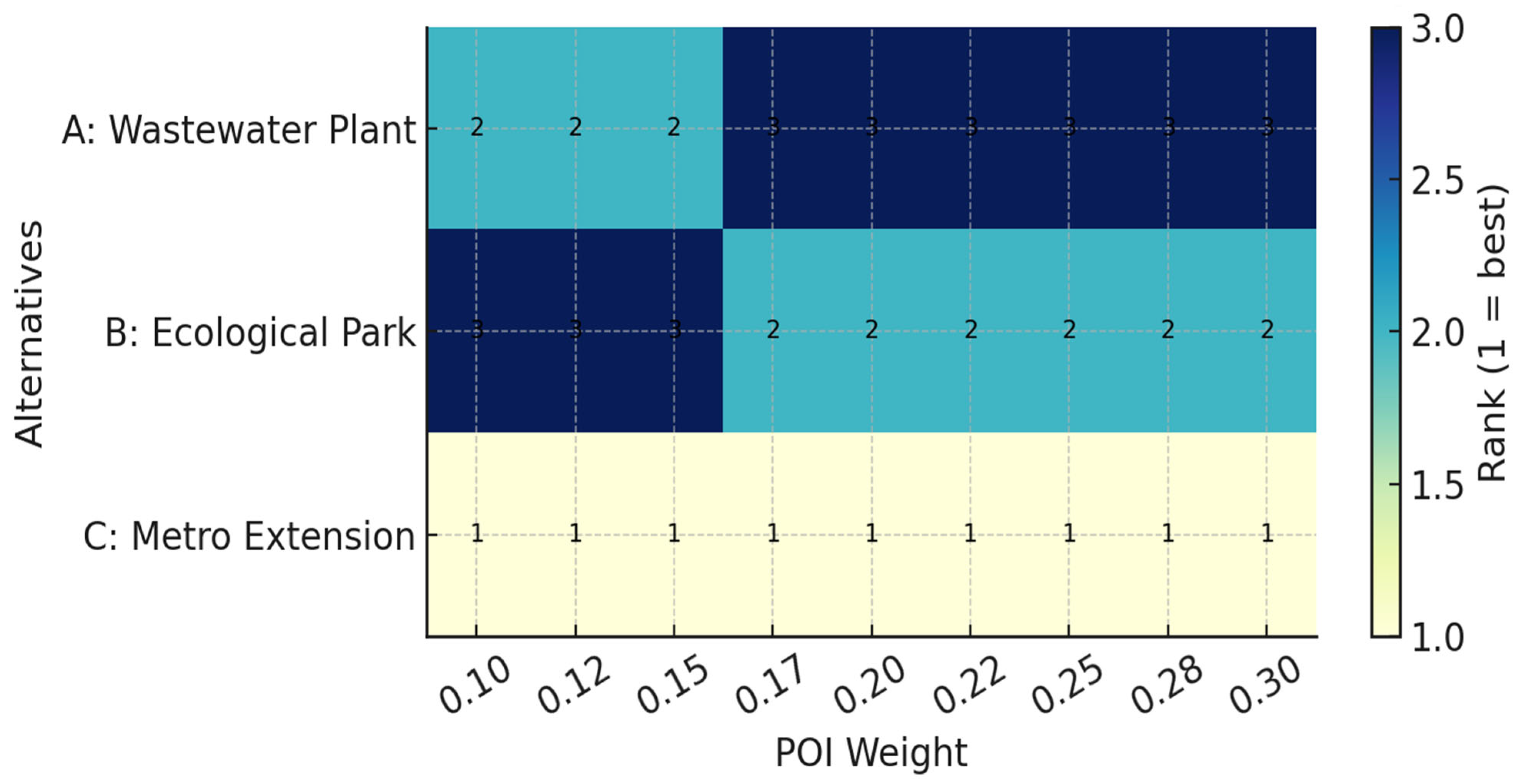
Figure 7 illustrates the ranking outcomes of the three alternatives across different weighting scenarios. The results reveal several consistent patterns. First, the metro extension (Alternative C) maintains the top position in all cases, suggesting strong robustness of its superiority. Second, the ecological park (Alternative B) steadily improves its ranking as the weight of POI increases, reflecting the positive contribution of broad public support captured in the sentiment analysis. By contrast, the wastewater treatment facility (Alternative A) consistently declines in rank under higher POI weights, indicating that its low legitimacy driven by negative emotions and high polarization, cannot be compensated for by environmental benefits alone.
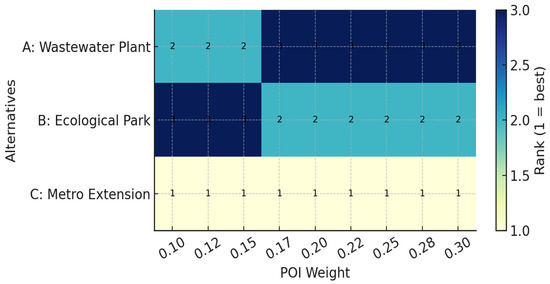
Figure 7.
Sensitivity of ranking outcomes.
This figure presents the sensitivity analysis of final ranking outcomes with respect to variations in the POI weighting coefficient (γ). The results show that the ranking of the top alternatives remains relatively stable, while the positions of lower-ranked options fluctuate with increasing γ. This stability demonstrates the robustness of the proposed model and the moderate yet consistent role of the POI in shaping decision preferences.
These findings confirm that the integration of POI systematically reshapes the ranking structure and that the results are not artifacts of arbitrary weight assignments. The persistence of Alternative C at the top and the downward trajectory of Alternative A underscore the methodological soundness of embedding legitimacy as an explicit criterion. Moreover, this robustness analysis strengthens the credibility of the fuzzy–grey MCDM framework, demonstrating its ability to produce stable and interpretable outcomes under different parameter assumptions.
4. Discussion
The case study in Nanjing provides valuable insights that go beyond the simple ranking of infrastructure projects. The results clearly show how the inclusion of public opinion can reshape quantitative evaluations. When the assessment only considered traditional sustainability factors such as economic, environmental, technical, and social aspects, the wastewater treatment plant ranked relatively high because of its environmental contribution. After the POI was introduced, its ranking declined significantly, revealing strong public opposition in online discussions. This change demonstrates that technical excellence alone cannot guarantee social legitimacy. It also supports the idea that legitimacy should be treated as an independent criterion rather than as a secondary effect of social or environmental factors.
In addition, the case reveals how emotions play a complex role in shaping collective preferences. The POI, which combines emotional polarity, polarization, and participation intensity, showed distinct patterns among the three projects. For example, the metro extension generated positive emotions such as anticipation and joy, reflecting expectations for better mobility and urban connectivity. In contrast, the wastewater treatment project triggered fear, anger, and disgust, emotions often linked to perceived risk and opposition. These findings suggest that emotion-related data from social media can serve as early signals of acceptance or resistance. For planners, such information offers an early warning tool to identify projects that may face legitimacy challenges before implementation.
Moreover, the comparison of results from TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS shows that incorporating POI not only changes the order of rankings but also improves the consistency across different methods. This consistency increases confidence in the conclusions and highlights the importance of legitimacy as a decision factor. Ignoring public opinion can lead to strategies that seem efficient from a technical and economic perspective but lack social stability. Integrating legitimacy into multi-criteria decision frameworks helps reduce the risk of project delays, public protests, or policy reversals. Compared with traditional fuzzy–grey MCDM models, the proposed approach provides both methodological and practical advantages. Conventional models rely heavily on expert judgment or small-scale surveys, which cannot reflect the dynamic nature of social attitudes. By contrast, the POI-based framework incorporates large-scale online discussions, allowing legitimacy to be measured more objectively and updated over time. This result shows that social legitimacy is not an optional addition to sustainability evaluation but a key factor that determines whether a project can actually be implemented.
Another important point is the tension between environmental responsibility and social legitimacy. The wastewater treatment facility contributes greatly to environmental sustainability, yet its low legitimacy score caused by negative public sentiment lowered its overall priority. This finding highlights a common dilemma in urban planning: projects that bring long-term environmental benefits may encounter short-term social resistance, while projects that are popular in the short term may have limited ecological value. By considering both aspects together, the fuzzy–grey MCDM framework with POI provides a structured tool to balance these competing goals. Future studies could extend this approach by reassessing projects over time as public attitudes evolve.
Finally, the experience from Nanjing shows that this framework can be applied in other rapidly growing cities. Urban areas often face tension between expert-driven sustainability goals and community-driven legitimacy concerns. The results demonstrate that large-scale online discourse can be systematically integrated into decision-making, reducing dependence on traditional surveys that are static and narrow in scope. This approach also bridges quantitative analysis with participatory governance. Beyond urban infrastructure, the framework could be adapted to other fields such as renewable energy, waste management, or transportation planning, where public legitimacy often determines the ultimate success or failure of projects.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
The comparison between the proposed model and traditional fuzzy–grey MCDM approaches shows that introducing the POI can fundamentally change evaluation outcomes and make them more socially meaningful. This highlights the importance of integrating public sentiment and legitimacy dynamics into sustainable infrastructure assessment.
This study brings social legitimacy into a multi-criteria decision-making framework, thereby advancing sustainable infrastructure planning both methodologically and practically. Our core innovation lies in proposing the POI, which systematically extracts sentiment, polarization, and engagement intensity from large-scale online discussions. Compared to traditional sentiment averages, POI provides a more nuanced and accurate portrayal of public attitudes. This enables decision models to consider not only the positive or negative orientation of opinions but also their intensity, diversity, and level of engagement.
Integrating the POI into the fuzzy grey MCDM framework provides a more complete way to support complex infrastructure decisions. This approach combines expert judgment with large-scale public data, allowing analysis to proceed even when information is uncertain or incomplete. Comparative results from TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS show that including the POI changes the nature of evaluation itself rather than simply adding another factor. Once public sentiment is considered, the rankings become more stable across methods, and the final decisions are clearer and more socially credible.
The Nanjing case demonstrates how these effects appear in practice. Projects that performed well on technical or environmental grounds, such as the wastewater treatment plant, dropped in priority after legitimacy was considered. In contrast, projects with strong public support, including the ecological park and the metro extension, rose in the ranking. This outcome reflects a common dilemma in urban planning: projects that bring long-term environmental benefits often face short-term resistance, while initiatives that attract quick approval may offer limited ecological value. Sustainable decision-making therefore requires balancing environmental goals with public expectations that continue to evolve over time.
Beyond this case, the findings suggest several directions for future research. The POI can be updated continuously to monitor changes in public sentiment during a project’s entire life cycle, enabling decision-makers to respond more effectively to shifts in opinion. Comparative studies conducted in different cultural and institutional contexts could further test the flexibility of the framework. Linking the POI with models of trust, communication, and social consensus may also help explain how legitimacy develops and spreads among communities. In parallel, advances in natural language processing and machine learning could improve the accuracy of emotion and polarization analysis, making public opinion integration both more precise and more timely.
Although the proposed fuzzy-grey MCDM framework with the POI shows great potential, there are several meaningful directions that can be explored in future research:
- (1)
- Multi-source public opinion measurement and improved emotion analysisFuture research can expand data sources beyond a single social media platform. It may include information from news websites, online forums, community feedback systems, and short-video platforms. At the same time, emotion analysis can be improved by using advanced machine learning and deep learning methods. These tools can better identify mixed emotions, sarcasm, and contextual meanings. Such progress would make the POI more accurate and more representative of overall public attitudes.
- (2)
- Dynamic modeling and continuous monitoring of legitimacyA one-time evaluation can only reflect public sentiment at a single moment. Future studies should build dynamic models that follow how public opinions change over time and how these changes influence policy decisions. Including time factors, feedback effects, and variables such as trust, information flow, and communication networks can help create a real-time decision system that tracks and adjusts legitimacy continuously.
- (3)
- Spatio-temporal and socio-cultural differencesPublic attitudes and perceptions of legitimacy differ between regions because of variations in culture, governance, and civic participation. Future work can add spatial and cultural factors to the framework to understand how local conditions affect public support, participation, and responses to planning projects. This approach would make POI-based evaluation more general and more useful for explaining local patterns.
- (4)
- Broader applications in decision-makingThe proposed framework can be applied to more complex planning problems beyond basic site selection or ranking. It can help address issues such as urban redevelopment, relocation, demolition, transport network planning, or the placement of industrial facilities near housing areas. By adapting the POI to these cases and including related economic and environmental variables, the model can support more realistic and participatory urban planning decisions.
Overall, this study shows that including public opinion in fuzzy grey MCDM frameworks is not only practical but also essential. It gives policymakers a way to design infrastructure decisions that are technically reliable, environmentally responsible, and socially accepted. By connecting decision science with social legitimacy, the research contributes to a more flexible, transparent, and participatory model of sustainable urban governance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.; Methodology, H.M.; Validation, H.M.; Formal analysis, Y.C.; Investigation, H.M.; Writing—original draft, H.M.; Writing—review & editing, H.M. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data set available on request from the authors. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R.E.; Zadeh, L.A. Decision-Making in a Fuzzy Environment. Manag. Sci. 1970, 17, B141–B164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Öztayşi, B.; Çevik Onar, S. A Comprehensive Literature Review of 50 Years of Fuzzy Set Theory. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9 (Suppl. S1), 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Jusoh, A.; Zavadskas, E.K. Fuzzy Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Techniques and Applications—Two Decades Review from 1994 to 2014. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 4126–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Gupta, N.; Mahmood, T.; Tripathy, B.C.; Das, R.; Das, S. An Innovative Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model for Analyzing Anthropogenic Influences on Urban River Water Quality. Iran J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 8, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Labella, Á.; Martínez, L. An Overview on Fuzzy Modelling of Complex Linguistic Preferences in Decision Making. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peneva, V.; Popchev, I. Aggregation of Fuzzy Preference Relations to Multicriteria Decision Making. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2007, 6, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantud, J.C.R.; Santos-García, G.; Torra, V. Ranked Hesitant Fuzzy Sets for Multi-Criteria Multi-Agent Decisions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, V. Hesitant Fuzzy Sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2010, 25, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Sets for Decision Making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, B.; Kahraman, C.; Kaya, İ. A Comprehensive Review of the Novel Weighting Methods in MCDM. Information 2023, 14, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, E.; Kusterka-Jefmańska, M.; Jefmański, B. Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS as a Method for Assessing Socioeconomic Phenomena on the Basis of Survey Data. Entropy 2021, 23, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q. A Consensus Model for Large-Scale Group Decision-Making Based on the Trust Relationship Considering Leadership Behaviors and Non-Cooperative Behaviors. Group Decis. Negot. 2021, 30, 2213–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.T.; Felfernig, A.; Le, V.M. An Overview of Consensus Models for Group Decision-Making and Group Recommender Systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 489–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xu, Z.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Consensus-Based Group Decision Making under Hesitant Fuzzy Environment. Inf. Fusion 2019, 52, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtan, S.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Zaidan, A.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; AlSattar, H.A.; Qahtan, S.; Albahri, Q.S.; Talal, M.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Mohammed, R.T. Toward Sustainable Transportation: A Pavement Strategy Selection Based on the Extension of Dual-Hesitant Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 31, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chiclana, F.; Fujita, H.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A Visual Interaction Consensus Model for Social Network Group Decision Making with Trust Propagation. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 122, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kou, G.; Li, G.; Peng, Y. Consensus Reaching Process in Large-Scale Group Decision Making Based on Bounded Confidence and Social Network. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 303, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhu, J.; Cabrerizo, F.J.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A Cyclic Dynamic Trust-Based Consensus Model for Large-Scale Group Decision Making with Probabilistic Linguistic Information. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Olfat, L.; Turskis, Z. Multi-Criteria Inventory Classification Using a New Method of Evaluation Based on Distance from Average Solution (EDAS). Informatica 2015, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.B.; Keisler, J.; Linkov, I. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in Environmental Sciences: Ten Years of Applications and Trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3578–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Niu, D.; Wang, H. Multiple Attribute Grey Target Decision Making Model Based on Linear Combination Weights Determining and Entropy. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2008, 3, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Zuo, X.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Urban Sustainability Assessment Based on Sentiment Analysis and Entropy Weight Method: Case Study in Liaoning, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 7973–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Medina, B.; Ordoñez, J.; Romana, M.G.; Alcaraz Carrillo de Albornoz, V. Achieving Sustainable Urban Mobility with a Modified VIKOR Method to Improve the Selection of a Park and Ride System. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2025, 31, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxano, I.; Villalba-Eguiluz, U. Twenty-Five Years of Social Multi-Criteria Evaluation (SMCE) in the Search for Sustainability: Analysis of Case Studies. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 188, 107131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluskens, N.; Alkemade, F.; Höffken, J. Beyond a Checklist for Acceptance: Understanding the Dynamic Process of Community Acceptance. Sustain. Sci. 2024, 19, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, E.M.; Reagan, A.J.; Mitchell, L.; Dodds, P.S.; Danforth, C.M. Climate Change Sentiment on Twitter: An Unsolicited Public Opinion Perspective. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnstein, S.R. A Ladder of Citizen Participation. J. Am. Inst. Plann. 1969, 35, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, T. Social Media Data in Urban Design and Landscape Research: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Land 2022, 11, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X. Natural Language Processing in Urban Planning: A Research Agenda. J. Plan. Lit. 2024, 39, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görg, C. Landscape Governance: The “Politics of Scale” and the “Natural” Conditions of Places. Geoforum 2007, 38, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).