Underwater Image Enhancement with a Hybrid U-Net-Transformer and Recurrent Multi-Scale Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The proposed hybrid U-Net-Transformer architecture synergizes the local feature extraction proficiency of convolutional neural networks with the global context modeling capacity of Transformers, enabling a more effective method for processing complex underwater scenes.
- (2)
- The architecture incorporates a Recurrent Multi-Scale Feature Modulation (R-MSFM) mechanism that iteratively refines features during the decoding process, thereby preserving critical spatial and textural details to significantly enhance the final image quality.
- (3)
- On standard underwater benchmarks, the proposed method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in key metrics, including PSNR, SSIM, and UIQM. This superior performance is achieved while maintaining a high degree of computational efficiency, thereby demonstrating the method’s suitability for real-time applications.
2. Methodology
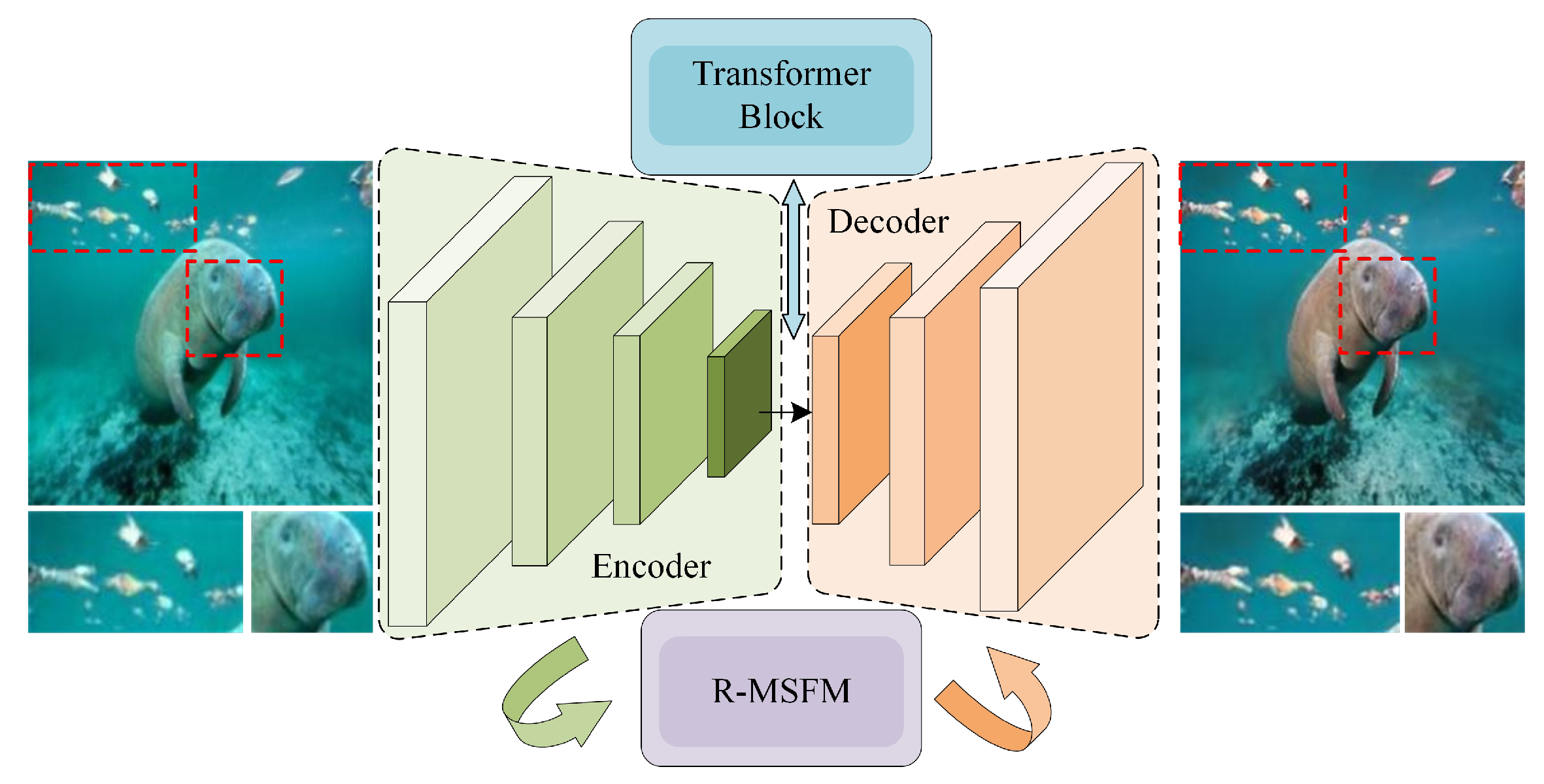
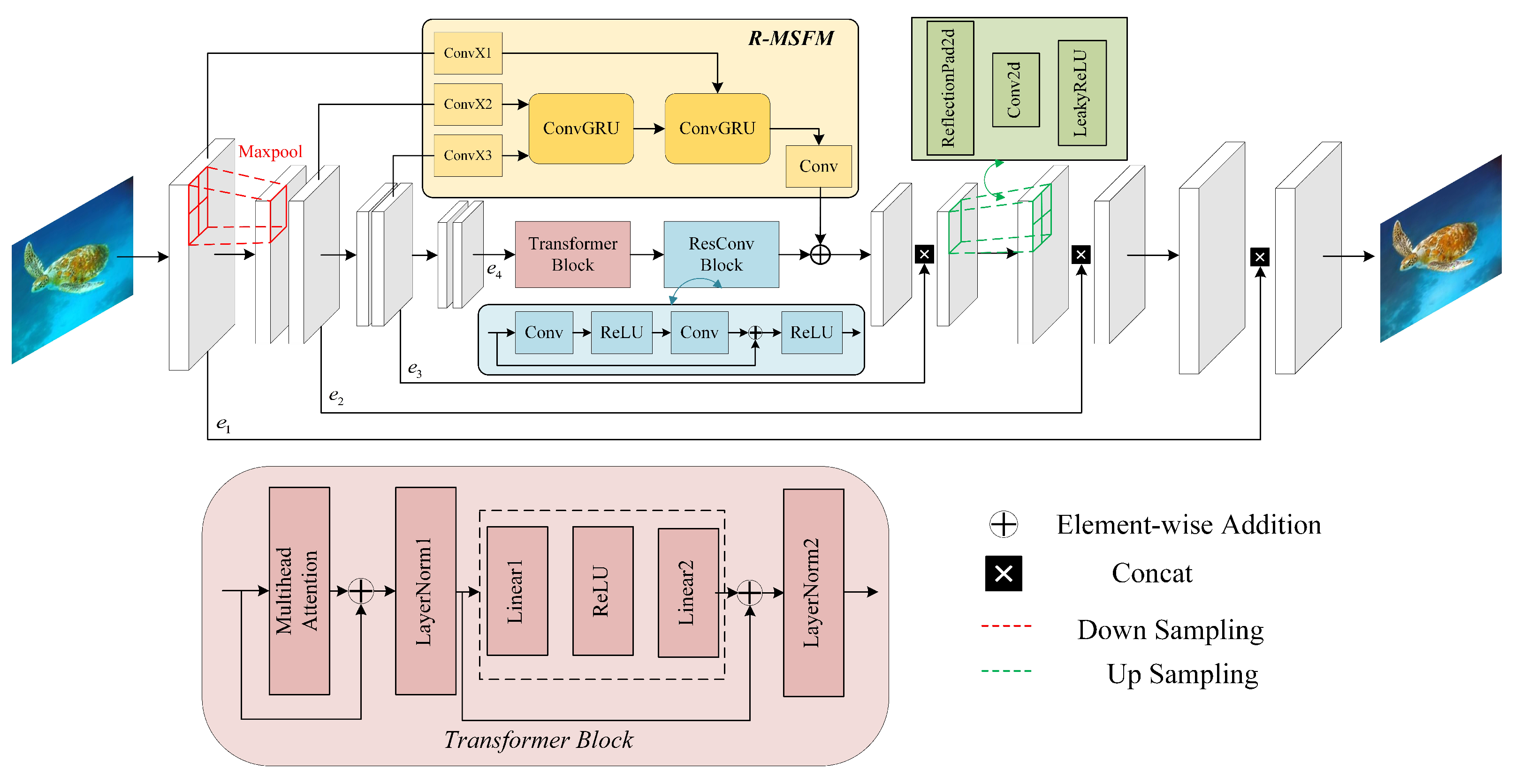
2.1. Overall Framework
- Encoder (E): The encoder, a U-Net-based CNN, extracts multi-scale local features. It progressively downsamples the input, producing a set of feature maps at resolutions of , , , and the original image size, respectively. Thus, .
- Core Network (T): The deepest feature map, , is flattened and processed by a Transformer network to model global dependencies, producing a contextually enriched feature map . This approach differs from standard Vision Transformers (ViT), as the proposed do not perform patch embedding on the input image but instead tokenize the feature map from a convolutional backbone.
- Decoder (D): The decoder generates the enhanced image through progressive upsampling and refinement. At each upsampling stage, it fuses the feature map from the previous decoder stage with the corresponding skip-connection feature map from the encoder. This fusion is followed by an iterative refinement process governed by the R-MSFM module, which updates the state of the feature map to restore fine details. Schematically, .
2.2. U-Net-Transformer
2.3. R-MSFM Mechanism
2.4. Loss Function
3. Experiment and Discussions
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Comparative Methods and Datasets
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.5. Ablation Study
3.6. Application Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Q.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H. Underwater image enhancement based on zero-shot learning and level adjustment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, K.; Wang, X.; Song, W.; Wang, H. Lightweight underwater image adaptive enhancement based on zero-reference parameter estimation network. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1378817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z. MCRNet: Underwater image enhancement using multi-color space residual network. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2024, 4, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S. Adaptive Underwater Image Enhancement Guided by Generalized Imaging Components. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Mazhar, S. HIFI-Net: A Novel Network for Enhancement to Underwater Optical Images. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guan, F.; Zhang, H.; Lai, H. Underwater image enhancement method based on denoising diffusion probabilistic model. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 96, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhou, S.; Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, J. LLaVA-based semantic feature modulation diffusion model for underwater image enhancement. Inf. Fusion 2026, 126, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yang, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y. Two-stage underwater image restoration algorithm based on physical model and causal intervention. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 30, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaynak, D.; Treibitz, T. Sea-thru: A method for removing water from underwater images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sohn, K.; Min, D. Unsupervised low-light image enhancement using bright channel prior. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y. An Underwater Image Enhancement Method Based on Balanced Adaption Compensation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hao, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R. Joint luminance and chrominance learning for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Integrating Cross-Domain Feature Representation and Semantic Guidance for Underwater Image Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Manzar, J.; Shivani; Garg, S. Underwater image enhancement using deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 46789–46809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhu, C.; Bian, L. U-shape transformer for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3066–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, W.; Xu, Y. Ghost-U-Net: Lightweight model for underwater image enhancement. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Xia, Y.; Sattar, J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Fan, X.; Shi, P.; Xin, Y.; Duan, D.; Yang, L. Recurrent Multiscale Feature Modulation for Geometry Consistent Depth Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 9551–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5637–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Guo, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, C. Synergistic Multiscale Detail Refinement via Intrinsic Supervision for Underwater Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 7033–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Anwar, S.; Porikli, F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement. Pattern Recogn. 2020, 98, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Luo, P.; Sattar, J. Simultaneous enhancement and super-resolution of underwater imagery for improved visual perception. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.01155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lei, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Pun, C.-M. Uwformer: Underwater image enhancement via a semi-supervised multi-scale transformer. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Yokohama, Japan, 30 June–5 July 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Ren, W.; Cong, R.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Tao, D. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Swarnakar, A.; Mittal, K. Shallow-uwnet: Compressed model for underwater image enhancement (student abstract). In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 15853–15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Anwar, S.; Hou, J.; Cong, R.; Guo, C.; Ren, W. Underwater image enhancement via medium transmission-guided multi-color space embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4985–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhuang, P.; Sun, H.-H.; Li, G.; Kwong, S.; Li, C. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3997–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image Quality Metrics: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, K.; Gao, C.; Agaian, S. Human-Visual-System-Inspired Underwater Image Quality Measures. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, M.; Creuze, V.; Moras, J.; Trouvé-Peloux, P. AQUALOC: An underwater dataset for visual–inertial–pressure localization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2019, 38, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teed, Z.; Deng, J. Droid-slam: Deep visual slam for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 16558–16569. [Google Scholar]
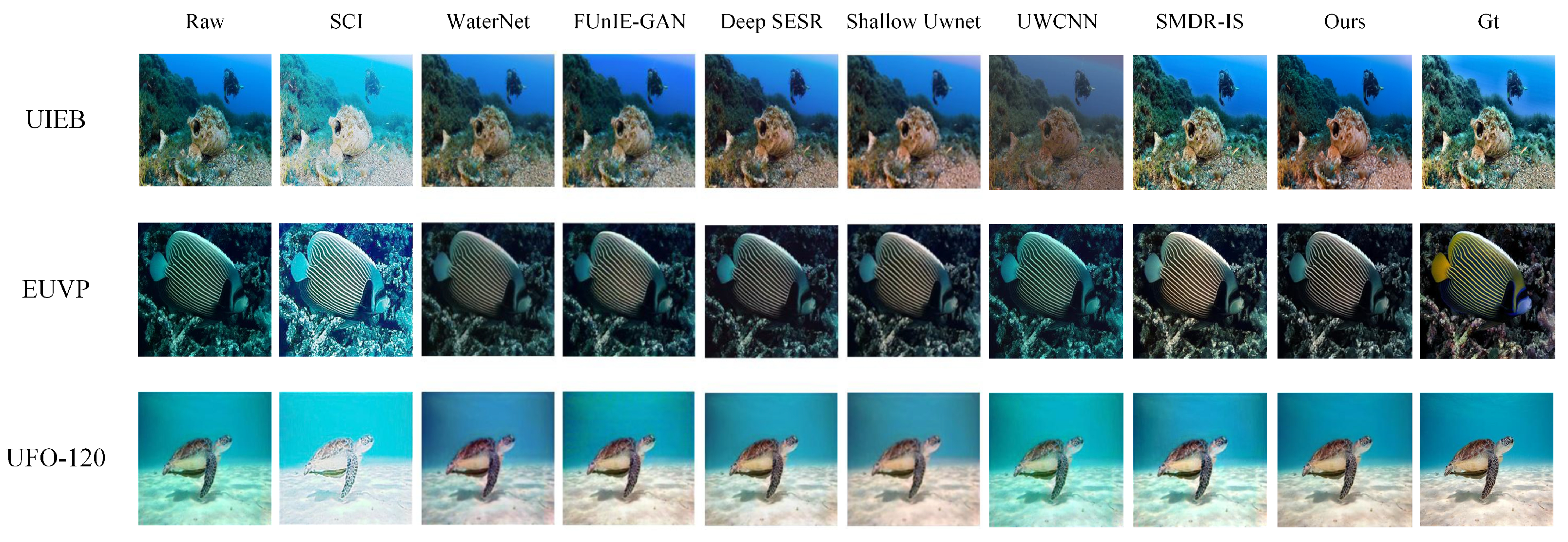



| MSE (103) ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | UIQM ↑ | A-UIQM →0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep SESR | 0.192 | 25.300 | 0.780 | 2.950 | 0.137 |
| FUnIE-GAN | 0.156 | 26.190 | 0.740 | 2.840 | 0.027 |
| MMLE | 2.037 | 15.040 | 0.623 | 2.737 | −0.076 |
| Shallow-UWnet | 0.127 | 27.101 | 0.812 | 2.886 | 0.073 |
| SMDR-IS | 0.427 | 21.827 | 0.798 | 2.887 | 0.074 |
| U-Net | 0.393 | 22.190 | 0.802 | 2.485 | −0.328 |
| Ucolor | 0.557 | 20.670 | 0.786 | 2.824 | 0.011 |
| UWCNN | 0.664 | 19.906 | 0.715 | 2.895 | 0.082 |
| UWFormer | 0.236 | 24.400 | 0.845 | 2.745 | −0.068 |
| Water-Net | 0.234 | 24.430 | 0.820 | 2.970 | 0.157 |
| UTR (Proposed) | 0.095 | 28.347 | 0.850 | 2.809 | −0.004 |
| MSE (103) ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | UIQM ↑ | A-UIQM →0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep SESR | 0.771 | 19.260 | 0.730 | 2.950 | 0.013 |
| FUnIE-GAN | 0.794 | 19.130 | 0.730 | 2.990 | 0.053 |
| MMLE | 0.975 | 18.240 | 0.767 | 2.197 | −0.740 |
| SCI | 5.344 | 10.852 | 0.596 | 2.566 | −0.371 |
| Shallow-UWnet | 0.802 | 19.087 | 0.668 | 2.853 | −0.084 |
| SMDR-IS | 0.277 | 23.710 | 0.922 | 3.015 | 0.078 |
| U-Net | 1.047 | 17.930 | 0.692 | 2.406 | −0.531 |
| Ucolor | 1.002 | 18.120 | 0.573 | 2.700 | −0.237 |
| UWCNN | 2.451 | 14.237 | 0.572 | 2.814 | −0.123 |
| Water-Net | 0.798 | 19.110 | 0.790 | 3.020 | 0.083 |
| UTR (Proposed) | 0.619 | 20.211 | 0.797 | 3.059 | 0.122 |
| MSE (103) ↓ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | UIQM ↑ | A-UIQM →0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle-GAN | 0.462 | 21.480 | 0.748 | 2.873 | 0.078 |
| Deep SESR | 0.147 | 26.460 | 0.780 | 2.980 | 0.185 |
| FUnIE-GAN | 0.219 | 24.720 | 0.740 | 2.880 | 0.085 |
| Fusion-Based | 0.569 | 20.580 | 0.770 | 2.886 | 0.091 |
| HIFI-Net | 0.151 | 26.330 | 0.882 | 2.910 | 0.115 |
| SCI | 5.761 | 10.526 | 0.557 | 2.664 | −0.131 |
| Shallow-UWnet | 0.201 | 25.092 | 0.731 | 2.866 | 0.071 |
| SMDR-IS | 0.481 | 21.306 | 0.746 | 2.889 | 0.094 |
| UWCNN | 0.241 | 24.309 | 0.728 | 2.740 | −0.055 |
| Water-Net | 0.317 | 23.120 | 0.730 | 2.940 | 0.145 |
| UTR(Proposed) | 0.148 | 26.423 | 0.792 | 2.754 | −0.041 |
| Method | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ |
|---|---|---|
| U-Net (CNN Baseline) | 22.190 | 0.802 |
| UWFormer (Transformer-based SOTA) | 24.400 | 0.845 |
| UTR (Proposed: U-Net + Trans. + R-MSFM) | 28.347 | 0.850 |
| Metrics | Raw | Enhanced |
|---|---|---|
| ATE RMSE (m) 1 | 0.2615 ± 0.112 | 0.1366 ± 0.065 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Shi, P. Underwater Image Enhancement with a Hybrid U-Net-Transformer and Recurrent Multi-Scale Modulation. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213398
Geng Z, Huang J, Wang X, Zhang Y, Fan X, Shi P. Underwater Image Enhancement with a Hybrid U-Net-Transformer and Recurrent Multi-Scale Modulation. Mathematics. 2025; 13(21):3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213398
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Zaiming, Jiabin Huang, Xiaotian Wang, Yu Zhang, Xinnan Fan, and Pengfei Shi. 2025. "Underwater Image Enhancement with a Hybrid U-Net-Transformer and Recurrent Multi-Scale Modulation" Mathematics 13, no. 21: 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213398
APA StyleGeng, Z., Huang, J., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Fan, X., & Shi, P. (2025). Underwater Image Enhancement with a Hybrid U-Net-Transformer and Recurrent Multi-Scale Modulation. Mathematics, 13(21), 3398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13213398






