Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor UAV Trajectory
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The development of a dynamic model for a Quadrotor UAV (QUAV).
- The design of a BSMC strategy that reduces chattering while ensuring robust performance and stability.
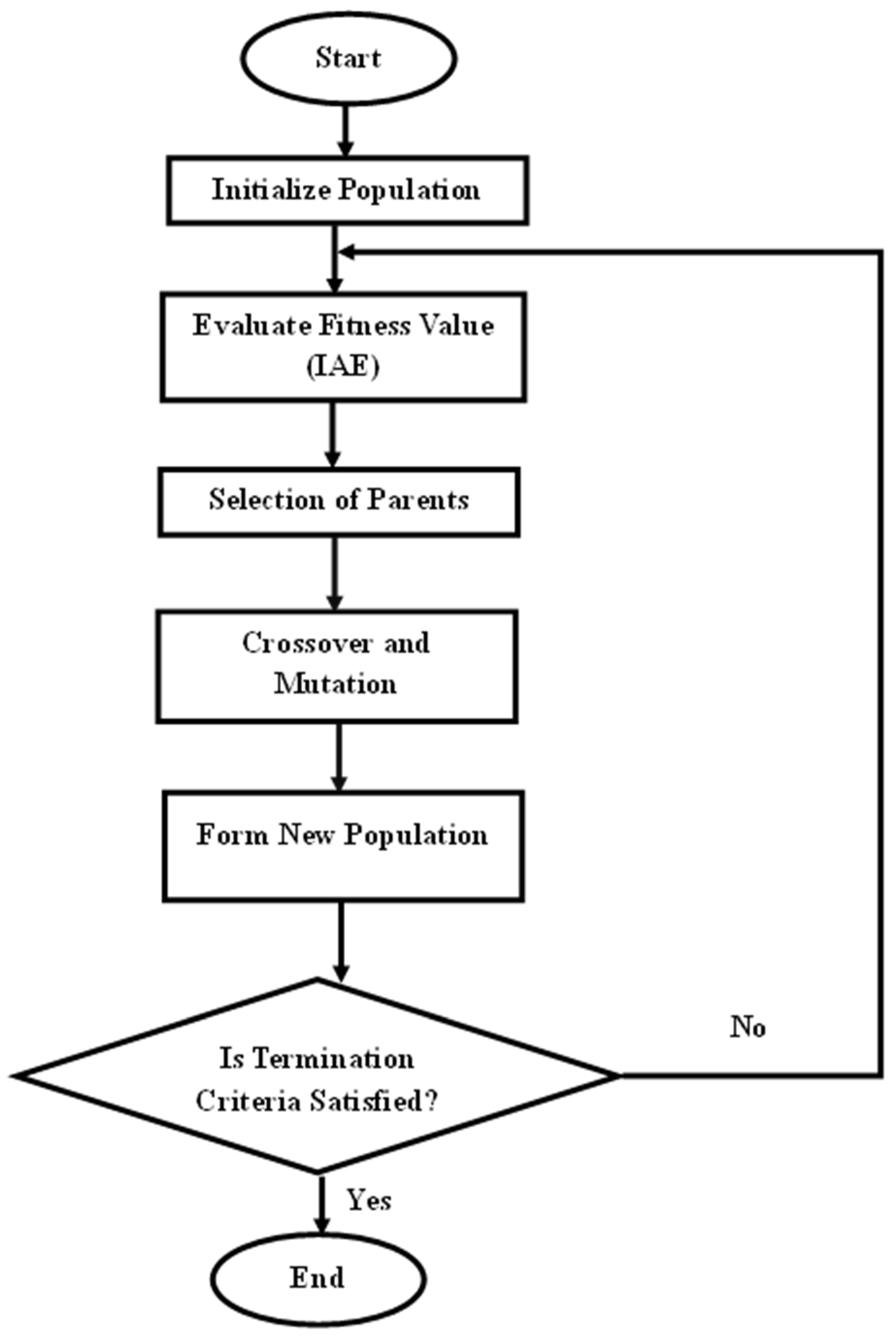
- The optimization of the controller parameters using a GA.
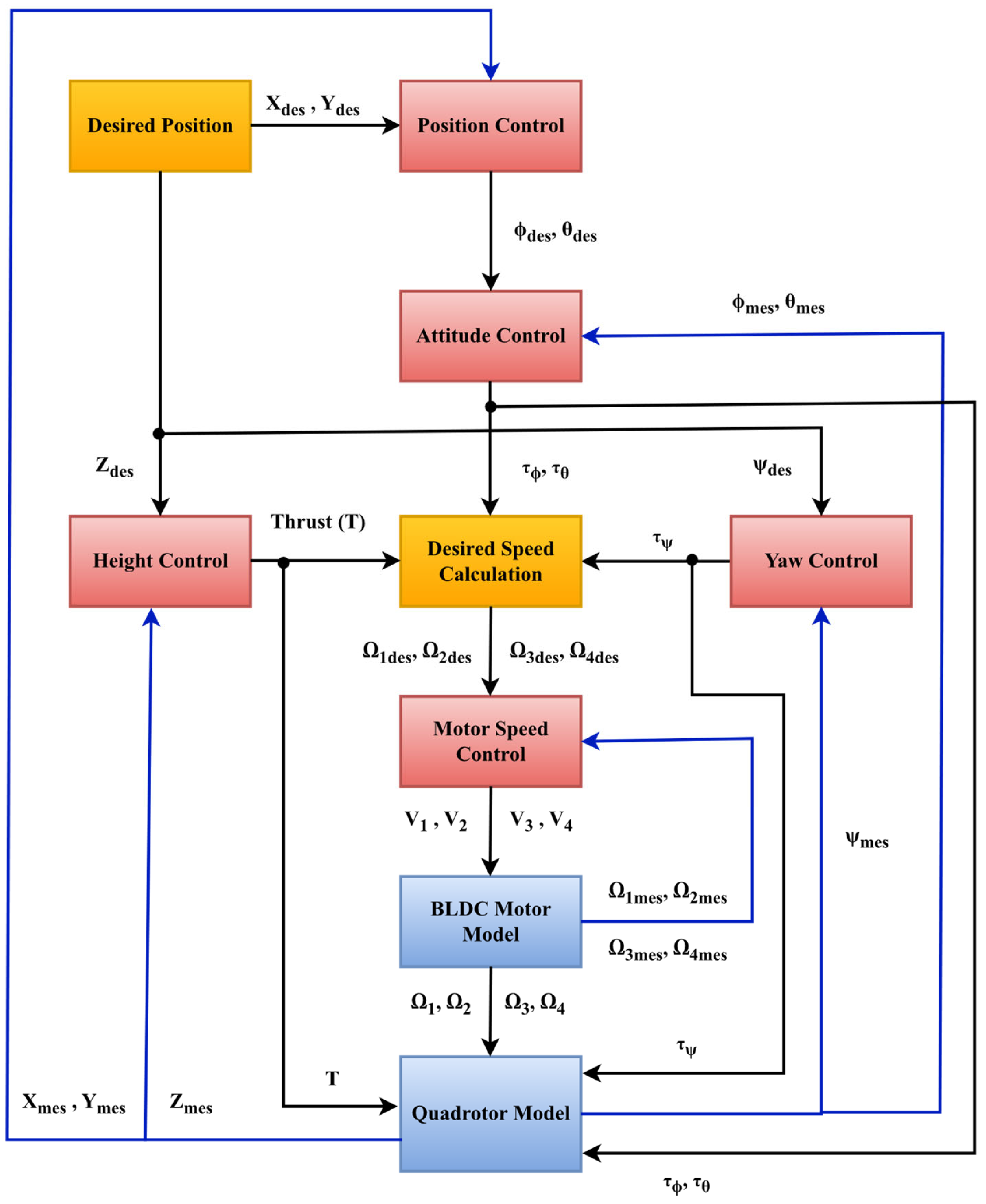
2. Modeling Approach of a Quadrotor UAV
2.1. Kinematic Model
2.1.1. Reference Frame Alignment
2.1.2. Rotation and Transformation Matrix
2.2. Rigid Body Dynamics
- The structure is assumed to be completely symmetrical and rigid.
- The center of mass of the quadrotor aligns with the origin of the body-fixed reference frame.
- Complex phenomena that are difficult to accurately simulate, such as ground effect, blade flapping, and other minor aerodynamic or inertial influences, are disregarded.
2.2.1. Rotational Equation of Motion
2.2.2. Translational Equation of Motion
2.3. State Space Representation of the Model
2.4. Calculation of the Desired Roll and Pitch Angle
3. Design of a Backstepping Sliding Mode Controller
3.1. Height Control
3.2. Attitude Control
3.3. Trajectory Control
3.4. Tuning of the Controller Parameters
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Results Under Normal Conditions
4.1.1. Setpoint Tracking Performance at m = 1.5 Kg
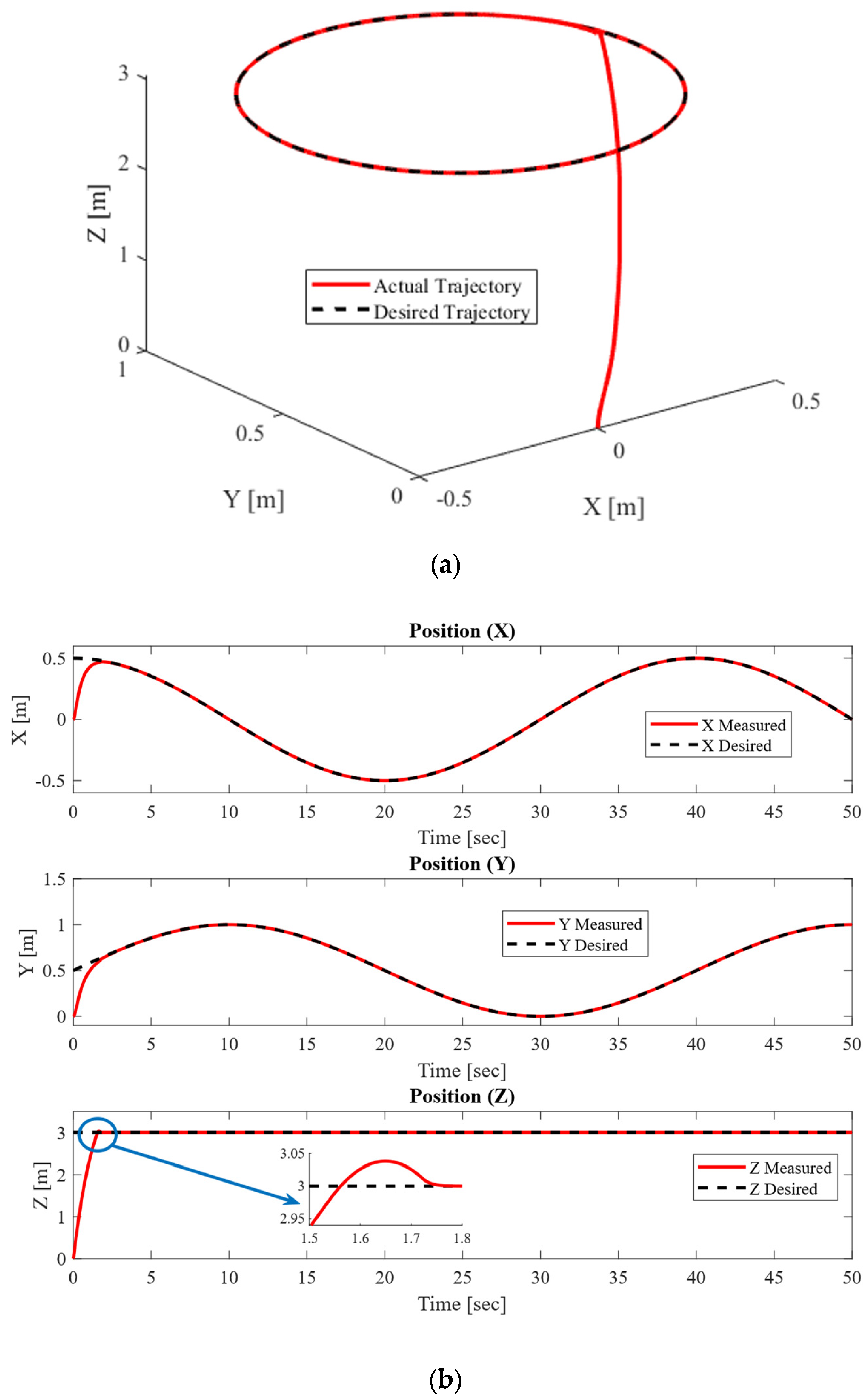
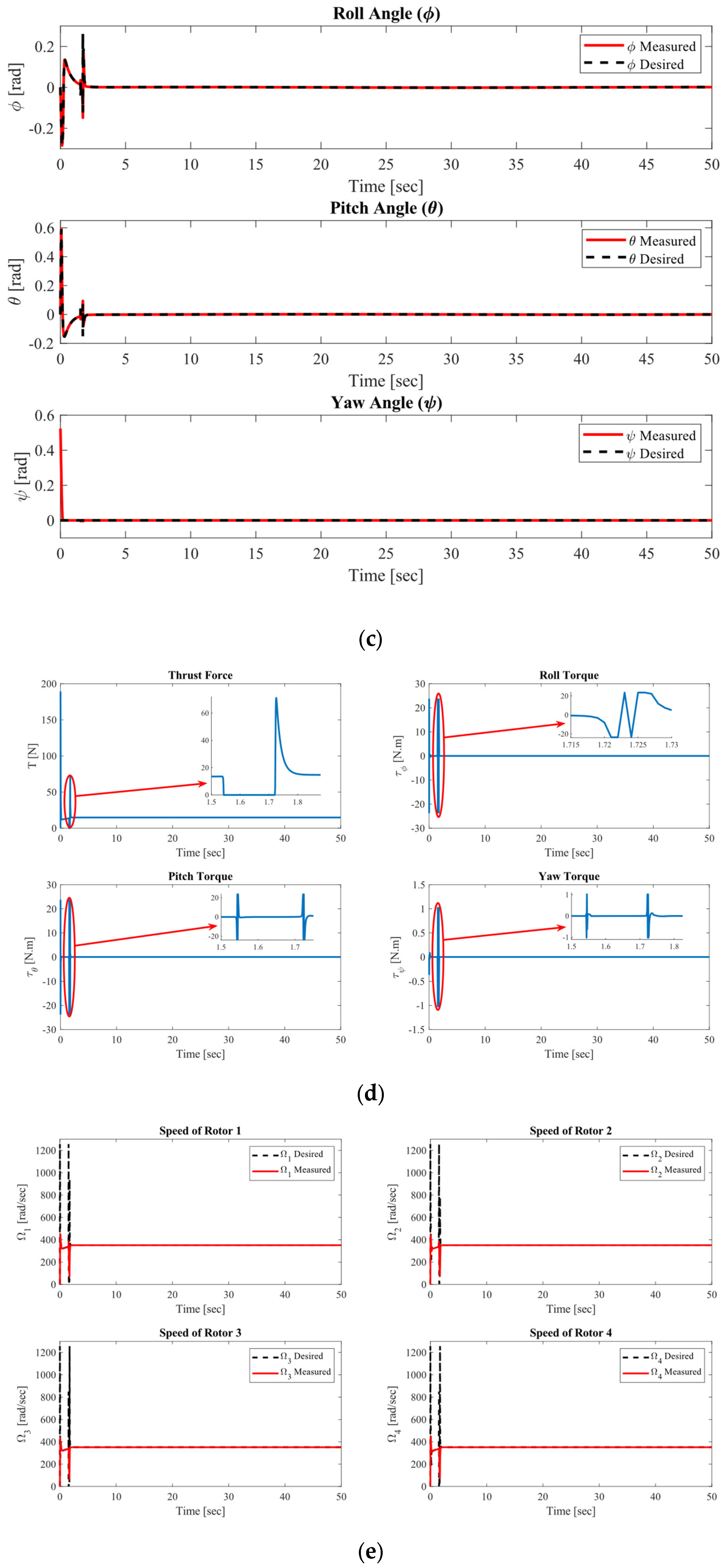
4.1.2. Circular Trajectory Tracking Performance at m = 1.5 Kg
4.1.3. Figure-of-Eight-Shaped Trajectory Tracking Performance at m = 1.5 Kg
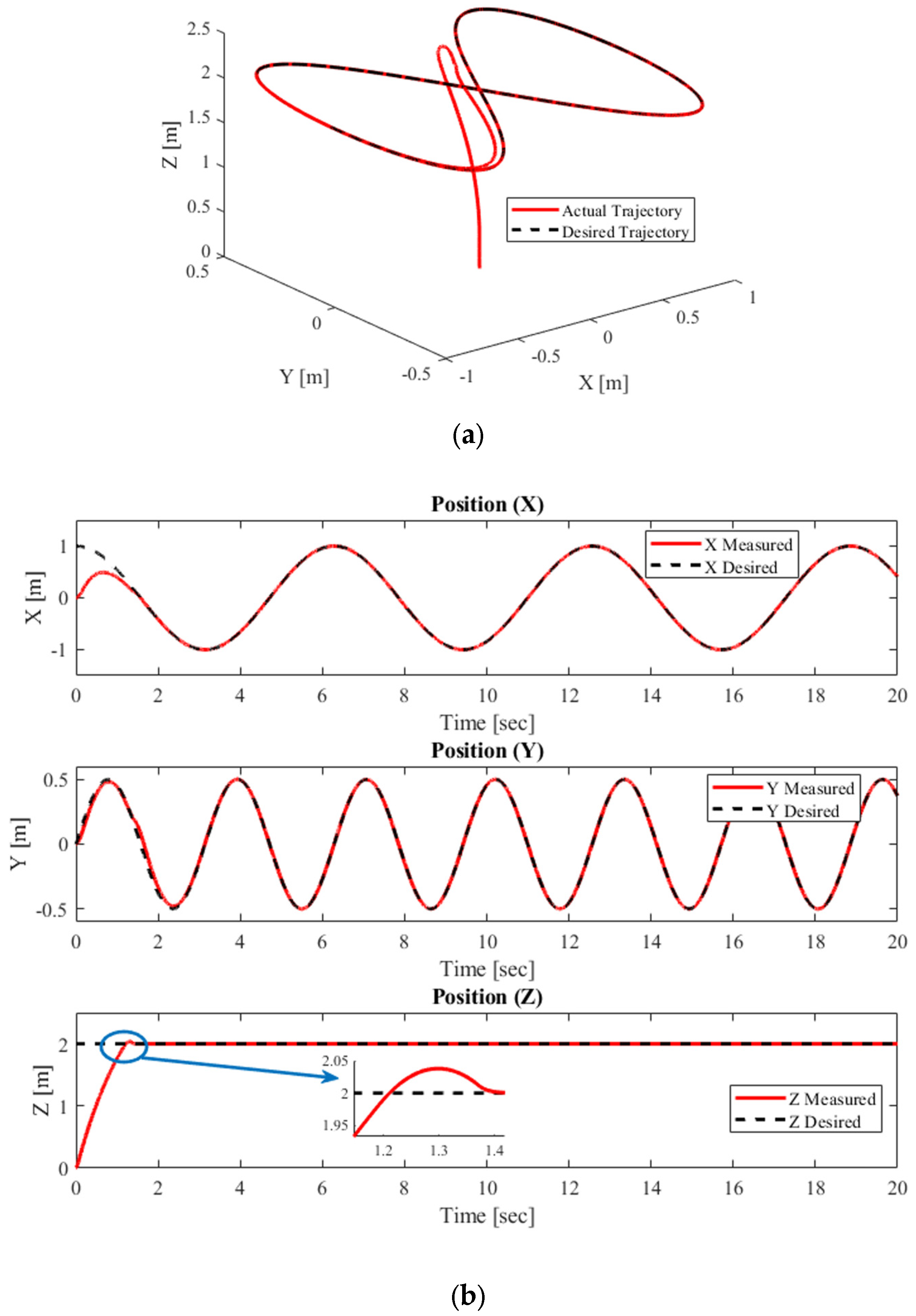
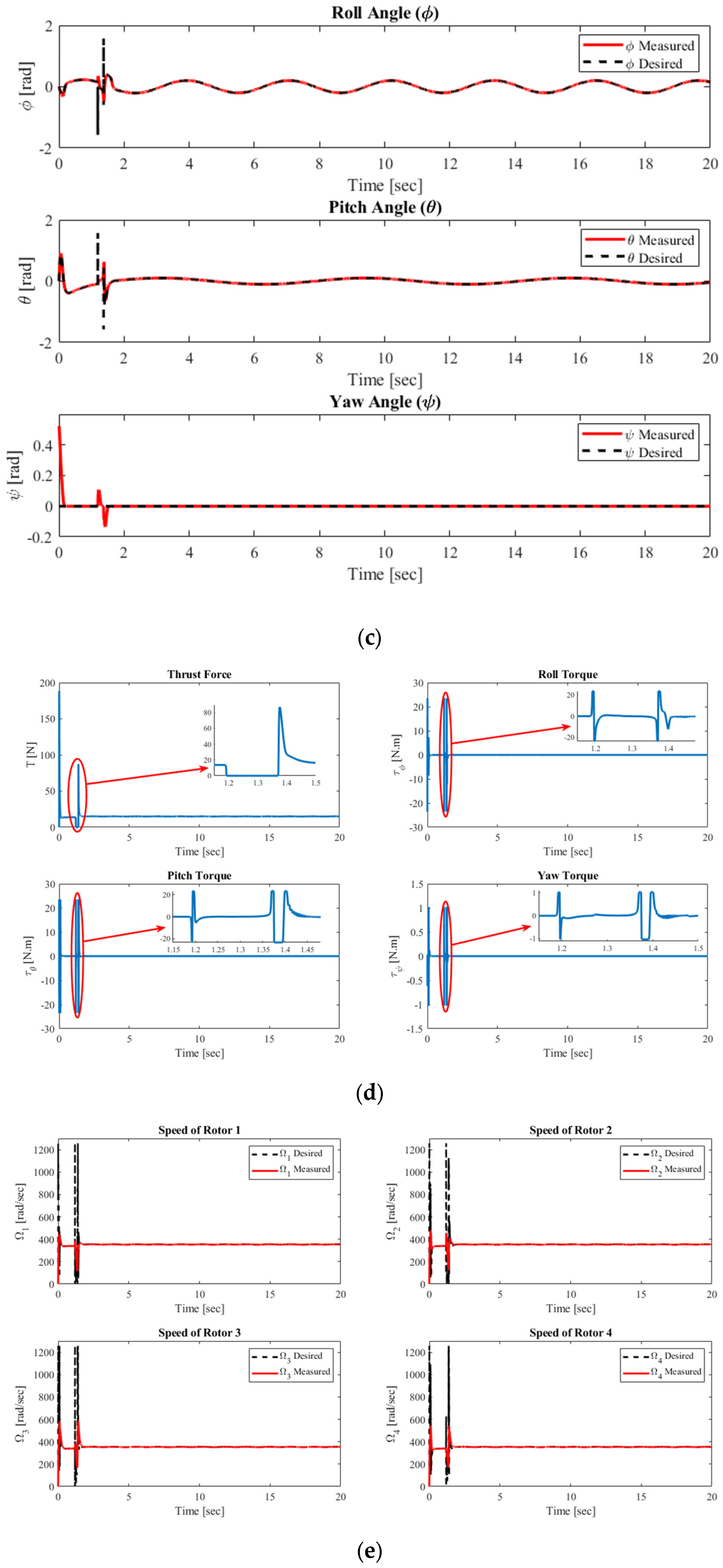
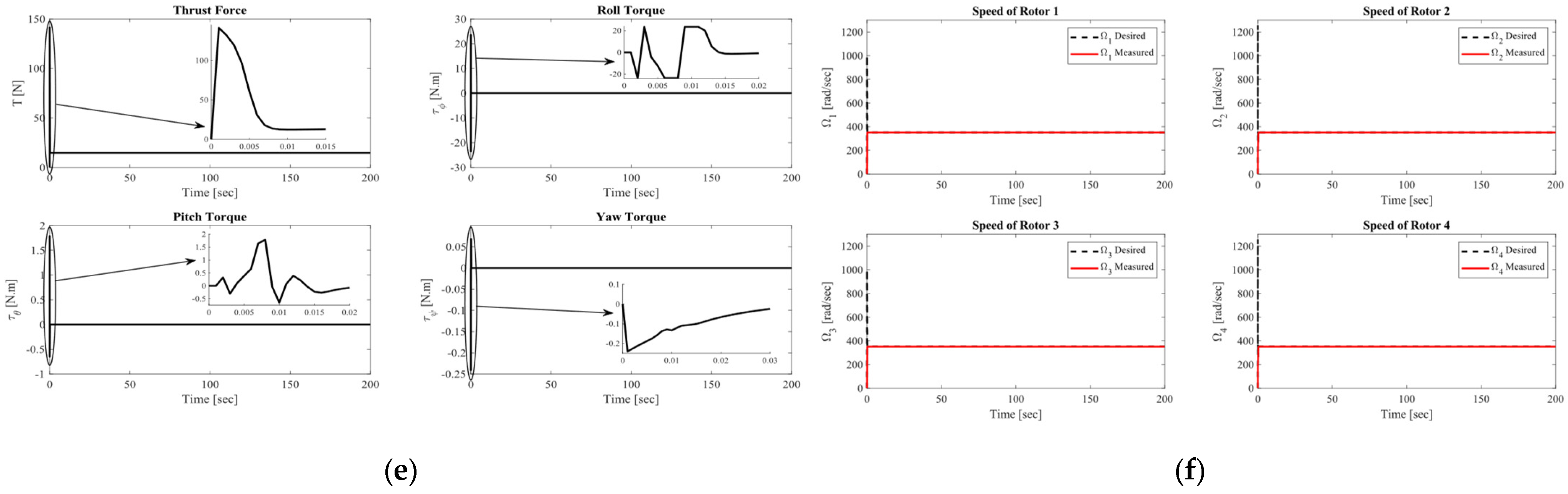
4.1.4. Complex Helix Trajectory Tracking Performance at m = 1.5 Kg
4.2. Simulation Result for Quadrotor Subjected to Time-Varying External Disturbance and Parameter Uncertainties
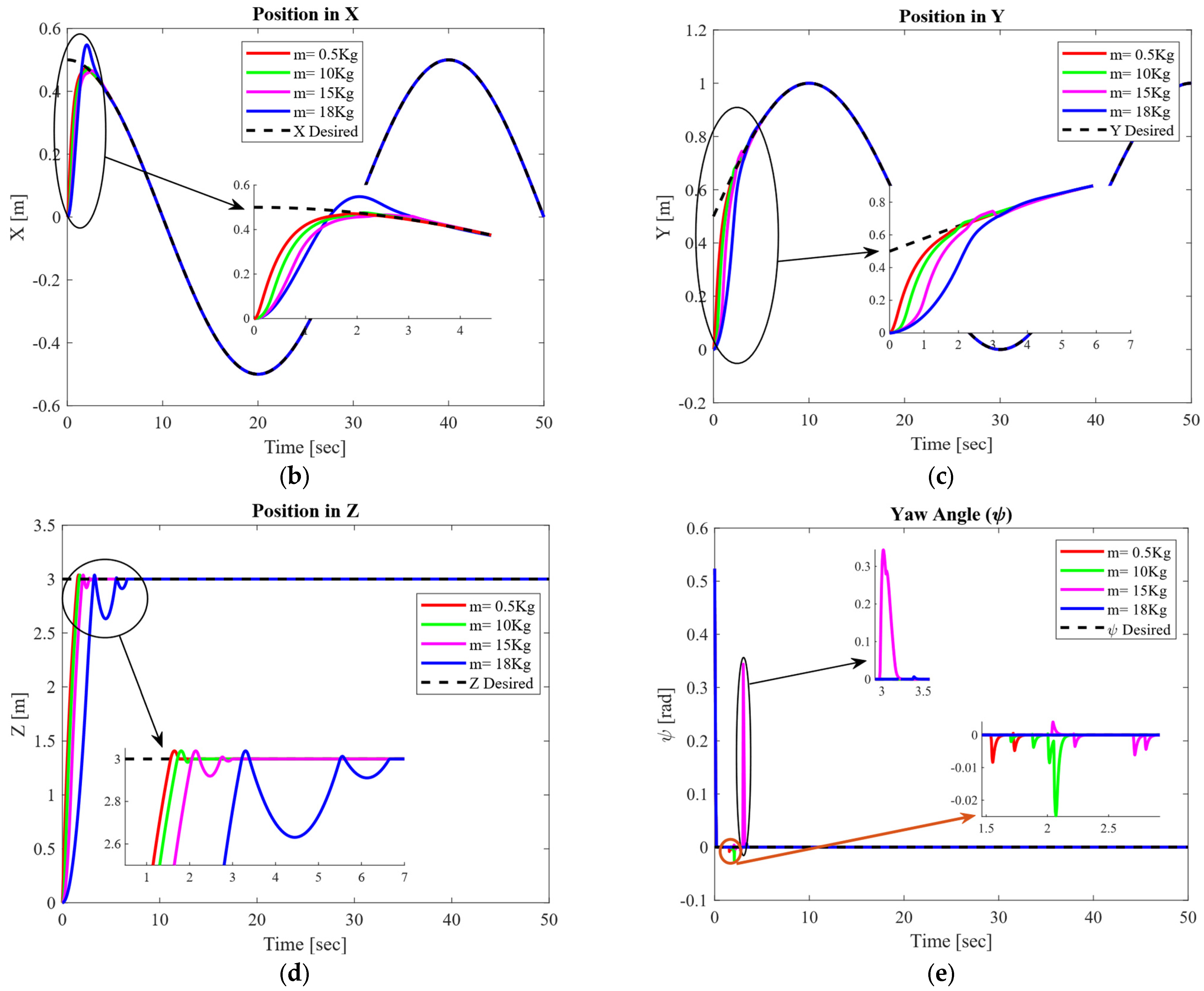
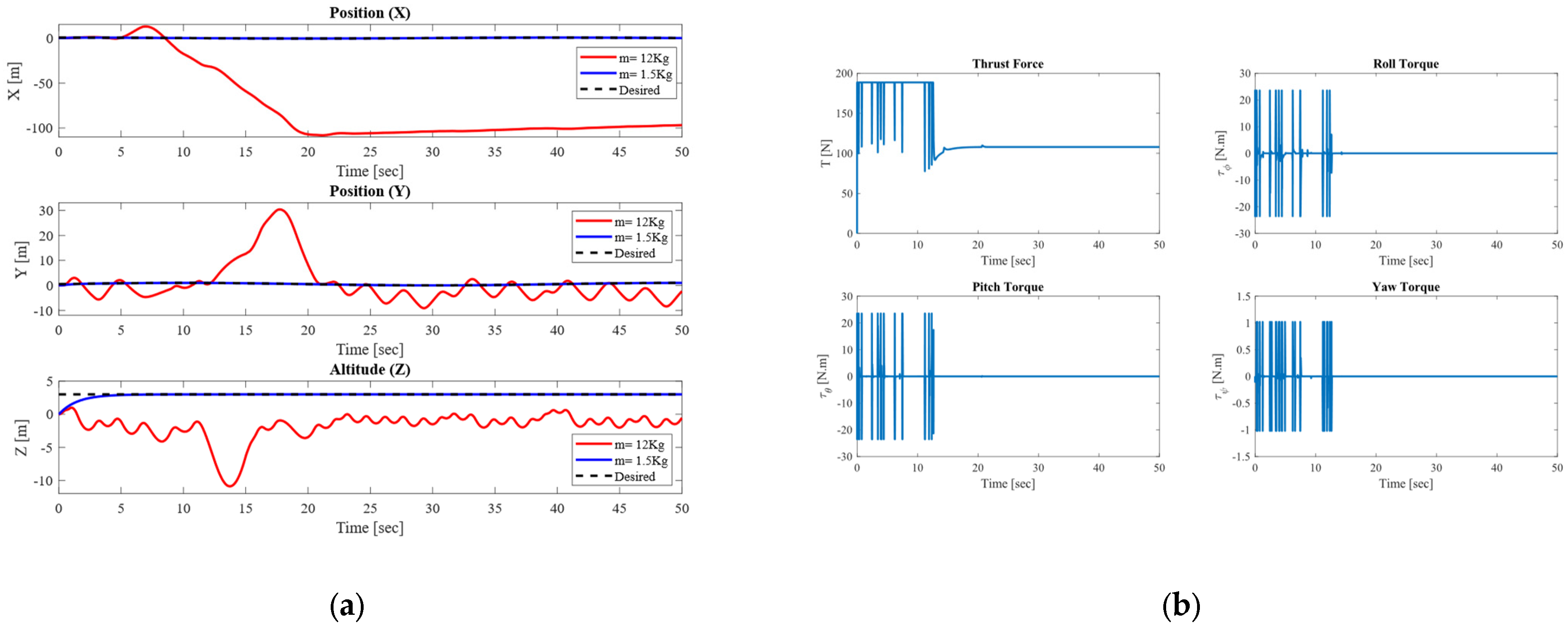
- We consider parameter uncertainty as a mass variation. This variation is 0.5 Kg to 18 Kg without external disturbances and 0.5 Kg to 12 Kg when the system is subjected to a time-varying external disturbance.
- A time-varying disturbance with a maximum magnitude varying from −2 to +2 in position , from −3 to +3 in position , and from −5 to +5 in the direction is added to the system as a wind disturbance [43]. The quadrotor is assumed to be operating under the influence of the time-varying wind depicted in Figure 9.
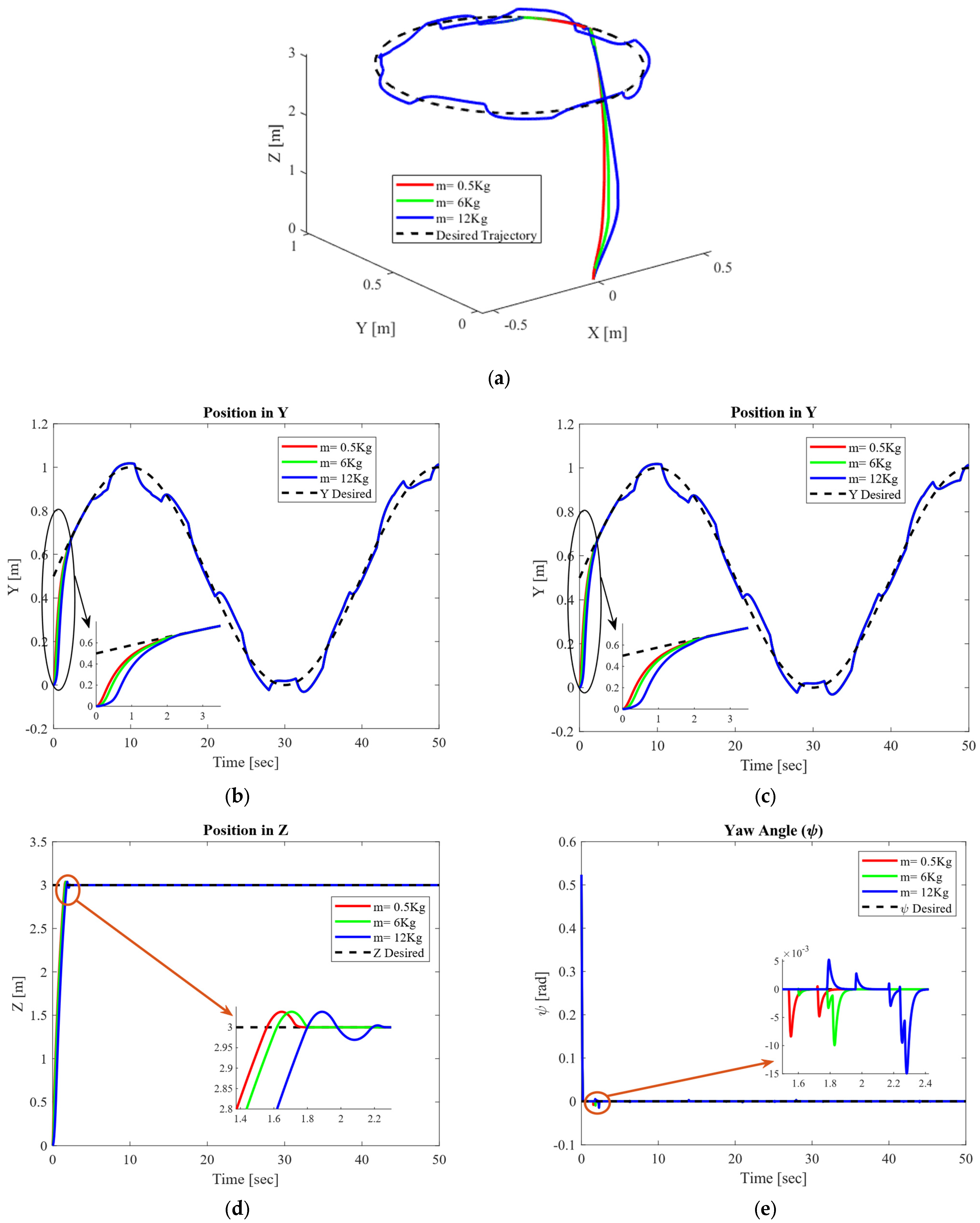
4.2.1. Circular Trajectory Tracking Performance for Masses Varying from 0.5 Kg to 18 Kg
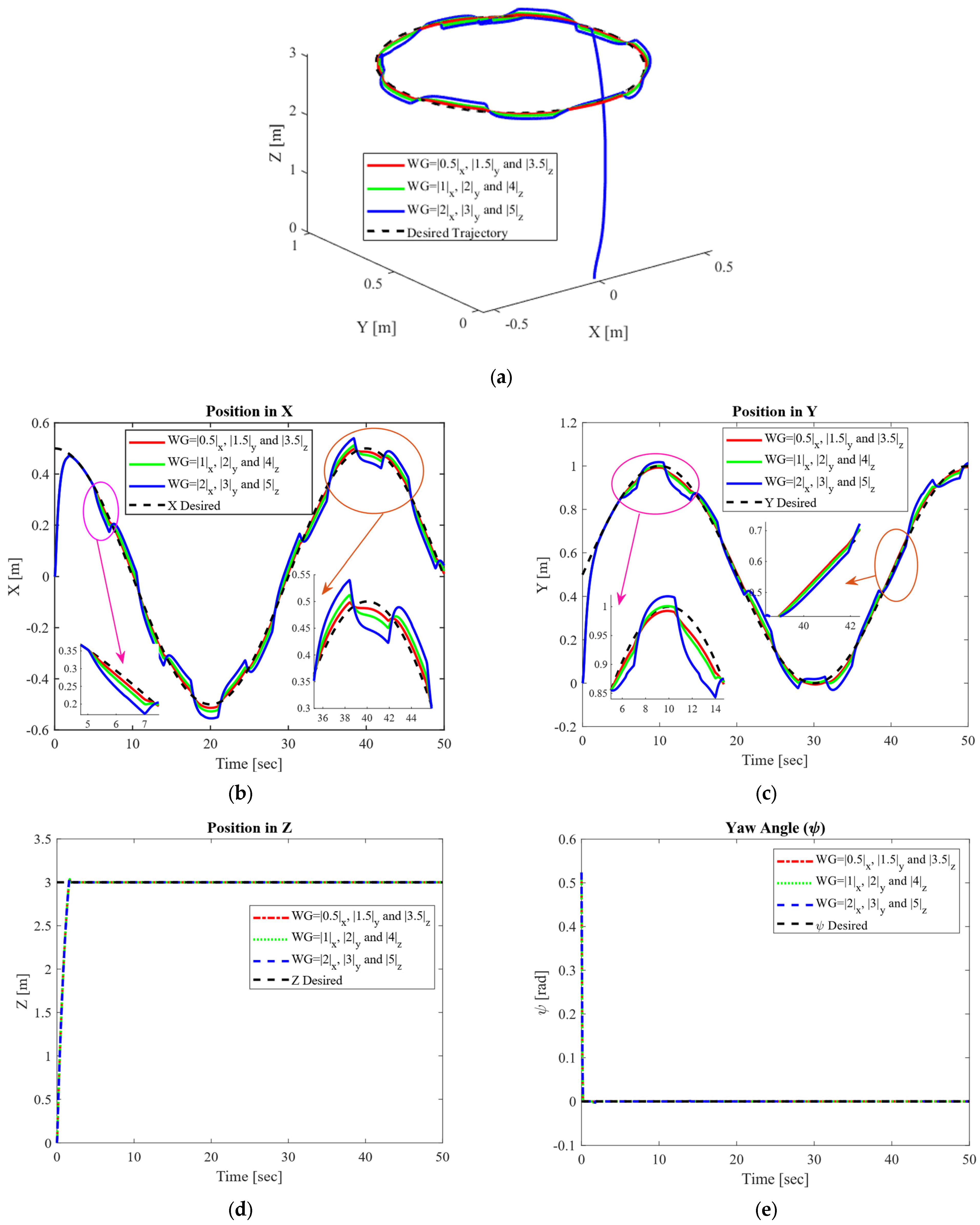
4.2.2. Circular Trajectory Tracking Performance Under Time-Varying External Disturbance With Different Magnitudes
4.2.3. Circular Trajectory Tracking Performance Under Time-Varying External Disturbances and Mass Varying from 0.5 Kg to 12 Kg
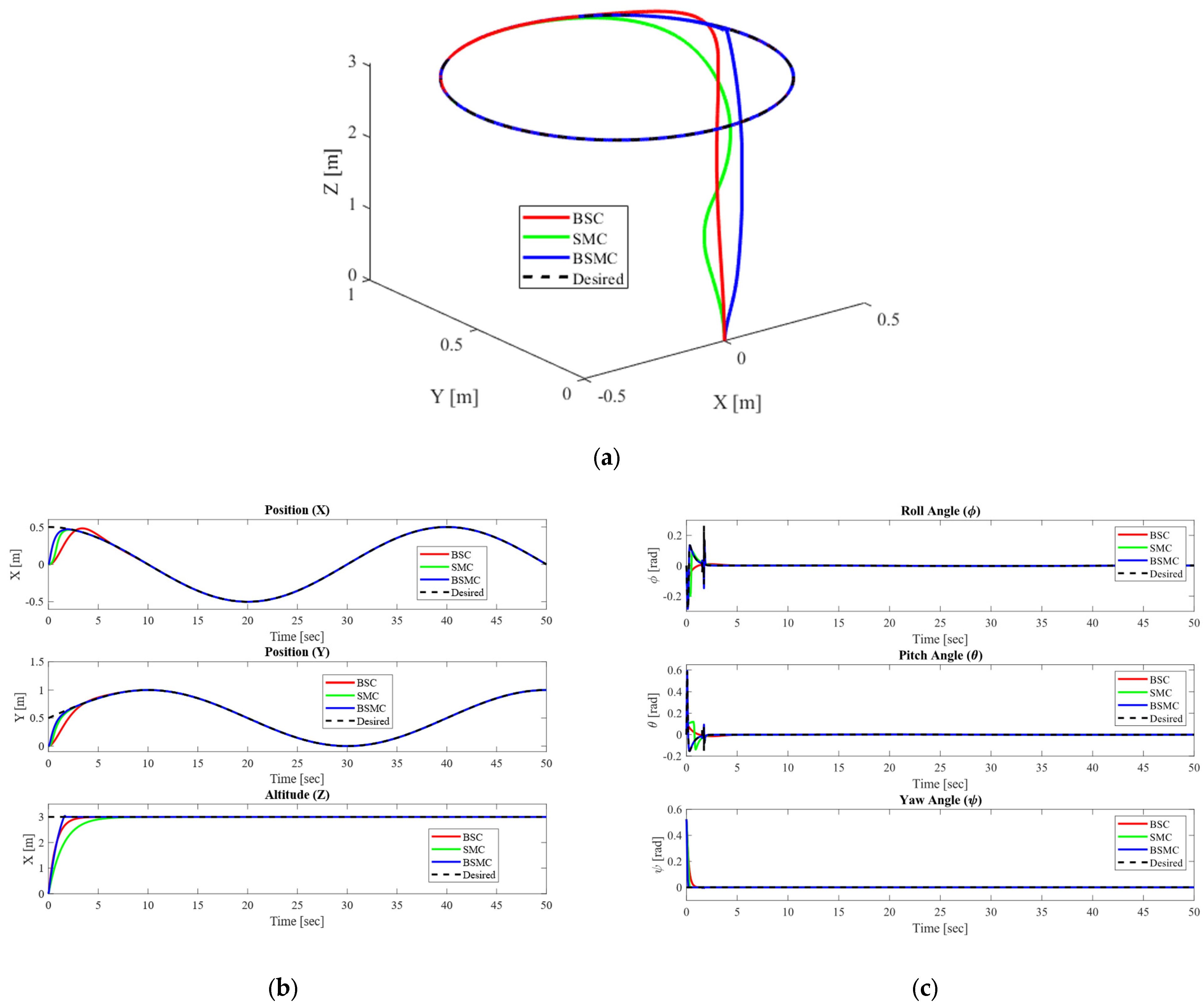
4.3. Comparison of the Proposed Controller with SMC and BSC
4.4. Performance of SMC Under Varying Loads
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSC | Backstepping Control |
| BSMC | Backstepping Sliding Mode Control |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IAE | Integral Absolute Error |
| ISE | Integral Squared Error |
| ITAE | Integral Time Absolute Error |
| ITSE | Integral Time Squared Error |
| LQR | Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| PID | Proportional–Integral–Derivative |
| QUAV | Quadrotor UAV |
| SMC | Sliding Mode Control |
| UAVs | Unmanned Aerial Vehicles |
| VTOL | Vertical Take-Off and Landing |
References
- Anitha, V.R.; Shyni, G.; Mythili, C.; Binoj, J.S. Quadcopter Drone for Surveillance, Monitoring and Emergency Medicine Delivery. Proc. Conf. AIP 2025, 3137, 020044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisankar, R.; Kaushik, A.; Muni, S.S. Path planning for multi-quadrotor 3D boundary surveillance using non-autonomous discrete memristor hyperchaotic system. Frankl. Open 2025, 10, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, H. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Search and Rescue: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shope, J.J. Design and Simulation of an AI-Powered Autonomous Quadrotor Framework for Search and Rescue Operations. Master’s Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, F.; Ceruti, A. Real-Time Search and Rescue with Drones: A Deep Learning Approach for Small-Object Detection Based on YOLO. Drones 2025, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, S. Thermal Image Tracking for Search and Rescue Missions with a Drone. Drones 2024, 8, 20053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALee, J.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Choi, D.; Tirtawardhana, C.; Myung, H. Survey of robotics technologies for civil infrastructure inspection. J. Infrastruct. Intell. Resil. 2023, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, R.H.; Matlekovic, L.; Shi, L.; Malle, N.; Ayoub, N.; Hageman, K.; Hansen, S.; Nyboe, F.F.; Ebeid, E. Design of an Autonomous Cooperative Drone Swarm for Inspections of Safety Critical Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravoory, S.; Eggert, C.A.; Balchanos, M.; Mavris, D. Unmanned aerial system-based tactical operations for supporting emergency response in campus communities. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum, Virtual, 11–15 and 19–21 January 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Li, T. Attitude tracking control of a quadrotor UAV subject to external disturbance with L2 performance. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 10183–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alattas, K.A.; Bouteraa, Y.; Mofid, O.; Mobayen, S. Adaptive finite-time backstepping control tracker for quadrotor UAV with model uncertainty and external disturbance. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 108088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofid, O.; Mobayen, S. Robust fractional-order sliding mode tracker for quad-rotor UAVs: Event-triggered adaptive backstepping approach under disturbance and uncertainty. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tan, X. Adaptability Study of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Actuator Fault Detection Model for Different Task Scenarios. Drones 2025, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, L.B.; Ghosh, A. Quadcopter Trajectory Tracking Control Analysis by Using PID and LQR Controllers. In International Conference on Systems and Technologies for Smart Agriculture. CISCON 2023, Manipal, India, 6–7 October 2023; Springer Proceedings in Information and Communication Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiyama, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Masuda, K. Combined Robust Control for Quadrotor UAV Using Model Predictive Control and Super-Twisting Algorithm. Drones 2025, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihnak, M.S.A.; Edardar, M.M. Comparing LQR and PID Controllers for Quadcopter Control Effectiveness and Cost Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 11th International Conference on Systems and Control, ICSC 2023, Sousse, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2023; pp. 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Alrasheedi, N. Commanded Filter-Based Robust Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadrotor UAV with State Estimation Subject to Disturbances. Drones 2025, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Qi, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Control of quadrotor robot via optimized nonlinear type-2 fuzzy fractional PID with fractional filter: Theory and experiment. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 151, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, A.; Oguntosin, V.; Popoola, O.M.; Idowu, A.A. Modeling and Nonlinear Control of a Quadcopter for Stabilization and Trajectory Tracking. J. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2449901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y. Collision Detection and Recovery Control of Drones Using Onboard Inertial Measurement Unit. Drones 2025, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Wu, L.; Xi, B. A Nonlinear Adaptive Autopilot for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Based on the Extension of Regression Matrix. Drones 2023, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taame, A.; Lachkar, I.; Abouloifa, A.; Mouchrif, I.; El Aroudi, A. Nonlinear Output Feedback Control for Parrot Mambo UAV: Robust Complex Structure Design and Experimental Validation. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2025, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Kang, M. A Synthesized Sliding-Mode Control for Attitude Trajectory Tracking of Quadrotor UAV Systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 28, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, A.W.A.; Gaufan, K.B.; El-Ferik, S.; Al-Dhaifallah, M. Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor Based on Fractional Order Model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 79823–79837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, S.C.; Behera, L.; Nahavandi, S. Adaptive Intelligent Minimum Parameter Singularity Free Sliding Mode Controller Design for Quadrotor. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 1805–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Asadi, D.; Merheb, A.; Nabavi-Chashmi, S.Y.; Tutsoy, O. Active fault-tolerant control of quadrotor UAVs with nonlinear observer-based sliding mode control validated through hardware in the loop experiments. Control Eng. Pr. 2023, 137, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Long, X.; Yuan, Q. Adaptive Terminal Sliding Mode Control for a Quadrotor System with Barrier Function Switching Law. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaruf, M.; Hamanah, W.M.; Abido, M.A. Hybrid Backstepping Control of a Quadrotor Using a Radial Basis Function Neural Network. Mathematics 2023, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbolla-Burillo, P.; Sotelo, D.; Frye, M.; Garza-Castañón, L.E.; Juárez-Moreno, L.; Sotelo, C. Design and Real-Time Implementation of a Cascaded Model Predictive Control Architecture for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Mathematics 2024, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, I.H.; Alyazidi, N.M.; Eltayeb, A.; Ahmed, G. Robust Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Control of Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja-Jaimes, V.; Coronel-Escamilla, A.; Escobar-Jiménez, R.F.; Adam-Medina, M.; Guerrero-Ramírez, G.V.; Sánchez-Coronado, E.M.; García-Morales, J. Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Observer for Actuator Fault Estimation in a Quadrotor UAV. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapnopoulos, A.; Kazakidis, C.; Alexandridis, A. Quadrotor trajectory tracking based on backstepping control and radial basis function neural networks. Results Control Optim. 2024, 14, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettari, Y.; Labbadi, M.; Kurt, S. Adaptive Backstepping Integral Sliding Mode Control Combined with Super-Twisting Algorithm for Nonlinear UAV Quadrotor System. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettari, Y.; Kurt, S.; Labbadi, M. Adaptive Robust Control based on Backstepping Sliding Mode techniques for Quadrotor UAV under external disturbances. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, S. Adaptive Robust Trajectory Tracking Controller for a Quadrotor UAV With Uncertain Environment Parameters Based on Backstepping Sliding Mode Method. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 4446–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaruf, M.; Abubakar, A.N.; Gulzar, M.M. Adaptive backstepping and sliding mode control of a quadrotor. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2024, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Su, B. Backstepping Sliding Mode Trajectory Tracking via Extended State Observer for Quadrotors with Wind Disturbance. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2021, 19, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-H.; Chang, Y.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Chang, L.M. Design and implementation of integral backstepping sliding mode control for quadrotor trajectory tracking. Processes 2021, 9, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsty, D. Particle Swarm Optimization Tuned Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for Altitude Stabilization and Trajectory Tracking of Agricultural Monitoring Quadcopter; Addis Ababa University: Ababa, Ethiopia, 2021; Available online: https://etd.aau.edu.et/items/ea739a2b-2ac2-4753-8fb6-c099fbe4e9cd (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Luukkonen, T. Modelling and Control of Quadcopter; Aalto University Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2014; Available online: https://sal.aalto.fi/publications/pdf-files/eluu11_public.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Alderete, T.S. Simulator Aero Model Implementation; NASA Ames Research Center: Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1995; Available online: https://aethercosmology.com/uploads/short-url/rBEb7fKKTz0TCW5RpEDSOFPmQyl (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Chovancová, A.; Fico, T.; Chovanec, L.; Hubinský, P. Mathematical modelling and parameter identification of quadrotor (a survey). In Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Ji, Y.; Song, Y.; Xu, L.; Niu, W. Fault-Tolerant Control for Quadrotor Based on Fixed-Time ESO. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Arm length | 0.5 | m |
| Moment inertia of the body in the x-axis () | 3.8278 × 10−3 | Nm/(rad/s2) |
| Moment inertia of the body in the y-axis () | 3.8278 × 10−3 | Nm/(rad/s2) |
| Moment inertia of the body in the z-axis () | 7.1345 × 10−4 | Nm/(rad/s2) |
| Moment inertia of the motor () | 2.8385 × 10−5 | Kg/m2 |
| Total mass of the quadrotor () | 0.5 to 18 | Kg |
| Gravitational acceleration () | 9.81 | m/s2 |
| Lift constant () | 2.9842 × 10−5 | N/(rad/s) |
| Drag constant () | 3.232 × 10−7 | Nm/(rad/s) |
| Maximum speed of the motors () | 400 | rad/s |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.6534 | 2.5487 | ||
| 90.3252 | 1.7297 | ||
| 46.0854 | 0.6906 | ||
| 80.9636 | 14.7240 | ||
| 87.8250 | 0.1348 | ||
| 3.7395 | 62.2074 | ||
| 52.8354 | 2.0858 | ||
| 86.9526 | 0 | ||
| 9.6185 | 0.7383 | ||
| 87.0379 | 0 | ||
| 31.0951 | 3.2361 | ||
| 86.7513 | 65.7034 |
| Mass (kg) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (rad) | (rad) | (rad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.2782 | 0.3216 | 1.9333 | 0.0076 | 0.0052 | 0.0387 |
| 10 | 0.3560 | 0.4588 | 2.3905 | 0.0357 | 0.0140 | 0.0401 |
| 15 | 0.4511 | 0.6938 | 3.3416 | 0.0802 | 0.0191 | 0.0789 |
| 18 | 0.5301 | 0.9982 | 6.7203 | 0.0062 | 0.0040 | 0.0390 |
| Bounds of Wind Gusts | (m) | (m) | (m) | (rad) | (rad) | (rad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 3.5 | 0.7737 | 0.8445 | 1.9434 | 0.0113 | 0.0070 | 0.0386 |
| < 4 | 1.2711 | 1.0141 | 1.9435 | 0.0198 | 0.0121 | 0.0387 |
| < 5 | 2.2655 | 1.9306 | 1.9443 | 0.0502 | 0.0283 | 0.0390 |
| Controllers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSC | 0.8836 | 0.8651 | 2.2646 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.1150 |
| SMC | 0.4619 | 0.4508 | 4.3914 | 0.0789 | 0.0783 | 0.0797 |
| BSMC | 0.2785 | 0.3222 | 1.9418 | 0.0078 | 0.0052 | 0.0386 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mulualem, Y.L.; Jin, G.G.; Kwon, J.; Ahn, J. Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor UAV Trajectory. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3205. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193205
Mulualem YL, Jin GG, Kwon J, Ahn J. Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor UAV Trajectory. Mathematics. 2025; 13(19):3205. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193205
Chicago/Turabian StyleMulualem, Yohannes Lisanewerk, Gang Gyoo Jin, Jaesung Kwon, and Jongkap Ahn. 2025. "Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor UAV Trajectory" Mathematics 13, no. 19: 3205. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193205
APA StyleMulualem, Y. L., Jin, G. G., Kwon, J., & Ahn, J. (2025). Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor UAV Trajectory. Mathematics, 13(19), 3205. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193205








