Abstract
Efficient simplification of 3D models is essential for mobile and other resource-constrained application scenarios. Industrial 3D assemblies, typically composed of numerous components and dense triangular meshes, often pose significant challenges in rendering and transmission due to their large scale and high complexity. The Quadric Error Metrics (QEM) algorithm offers a practical balance between simplification accuracy and computational efficiency. However, its application to large-scale industrial models remain limited by performance bottlenecks, especially when combined with curvature-based optimization techniques that improve fidelity at the cost of increased computation. Therefore, this paper presents a parallel implementation of the QEM algorithm and its curvature-optimized variant using the OpenMP framework. By identifying key bottlenecks in the serial workflow, this research parallelizes critical processes such as curvature estimation, error metric computation, and data structure manipulation. Experiments on large industrial assembly models at a simplification ratio of 0.3, 0.5, and 0.7 demonstrate that the proposed parallel algorithms achieve significant speedups, with a maximum observed speedup of 5.5×, while maintaining geometric quality and topological consistency. The proposed approach significantly improves model processing efficiency, particularly for medium- to large-scale industrial models, and provides a scalable and practical solution for real-time loading and interaction in engineering applications.
Keywords:
3D model simplification algorithm; Quadric Error Metrics (QEM); parallel calculation (OpenMP); industrial assembly simplification MSC:
65D18
1. Introduction
Mesh simplification is a critical technique in 3D computer graphics and modeling, designed to reduce the computational overhead and storage demands of complex models while preserving geometric fidelity [1]. As the complexity of 3D meshes continues to grow, particularly in industrial applications, the challenge of simplifying large-scale meshes without compromising essential geometric details have become increasingly prominent. This need is further amplified in domains such as virtual reality, industrial design, and medical imaging, where the need for efficient mesh simplification algorithms has escalated, especially under constrains of limited computational resources and bandwidth [2]. In particular, industrial 3D assemblies, which often involve intricate geometric details and are subject to real-time rendering or mobile platform constraints, pose unique challenges [3,4]. These models require simplification techniques that can reduce size and complexity while maintaining critical attributes such as sharp edges, textures, and overall structural integrity [5].
The research builds on decades of progress in 3D mesh simplification algorithms, particularly focusing on the Quadric Error Metrics (QEM) approach. QEM is recognized for its efficiency in simplifying meshes by minimizing geometric distortion through an error minimization framework. While highly effective, QEM faces challenges when applied to highly detailed models, as it may struggle to preserve local geometric details under significant compression ratios [6]. To address these limitations, this study incorporates OpenMP-based parallel computing to accelerate the simplification process while maintaining geometric fidelity. For industrial-scale 3D assemblies, characterized by their large size and structural complexity, multi-core processing is indispensable to meet the associated computational requirements [7]. Additionally, prior research has explored various optimizations of QEM, including curvature-based refinements and saliency detection methods, which have enhanced the quality of simplification for various mesh types. Nevertheless, substantial challenges remain in efficiently handling large-scale industrial models and the ability to optimize for real-time performance in dynamic applications [7,8].
Over the years, researchers have made considerable progress in the development of 3D mesh simplification algorithms [8]. Foundational works focused on improving the balance between compression ratios and geometric accuracy in mesh simplification [9]. More recent studies have further refined these methods by incorporating geometric detail preservation and saliency-driven mechanisms [10]. The QEM approach remains central to these developments due to its versatility and efficiency [11]. Despite the advancements, several limitations persist. Most existing algorithms are not optimized for large-scale models, particularly those used in industrial-scale 3D assemblies. They often fail to account for the dynamic nature of real-time rendering or the computational constraints of mobile platforms. Moreover, non-uniform simplification remains a challenge, particularly when preserving boundaries and planar surfaces [12,13,14]. These issues highlight the need for a more efficient and scalable simplification algorithm, one that integrates parallel computing strategies to manage the complexity of industrial-scale models effectively.
While many related studies have focused on simplification algorithms for static models, real-time performance and the scalability of these algorithms for industrial applications remain largely unexplored. Existing research has primarily addressed smaller-scale models or focused on preserving broad features, but fine-grained geometric detail preservation under high compression ratios, particularly for complex industrial-scale 3D assemblies, remains a insufficiently addressed [15,16]. Moreover, although parallel computing approaches have been applied to mesh simplification, these methods often lack optimization for large datasets or fail to integrate real-time constraints inherent in mobile and web-based applications. This paper addresses these gaps by applying OpenMP-based parallel computing to the QEM algorithm, which enables real-time simplification of large-scale industrial models. This approach ensures that key geometric details are maintained even under high compression ratios, providing a scalable solution to the challenges of simplifying complex industrial-scale 3D assemblies. The experimental results confirm that the proposed method is not only efficient but also scalable, making it suitable for real-world industrial applications.
Although QEM-based simplification algorithms have been widely studied and applied across different fields, significant research gaps remain in the simplification of industrial-scale models with real-time rendering and mobile compatibility [17,18]. The primary gap in the existing body of research lies in the efficient parallel computing of simplification tasks for large and dynamic 3D assemblies, which often contain intricate geometric details requiring precise preservation. Furthermore, the real-time processing demands of modern applications such as mobile platforms and web-based systems have not been fully addressed by previous research [19]. In recent years, several GPU-accelerated simplification approaches have been proposed to address these performance bottlenecks. Recent studies have proposed various GPU-accelerated approaches to address performance bottlenecks in mesh simplification. For instance, one CUDA-based method employed lock-free priority queues and independent mesh partitioning to enable high-speed edge collapse operations [20]. Similarly, a fully GPU-parallel polygonal mesh generator leveraging half-edge data structures achieved up to 700× speedups in specific scenarios [21]. End-to-end remeshing frameworks using curvature-driven tessellation and Voronoi clustering have also demonstrated notable improvements in both runtime efficiency and output fidelity [22]. However, despite these advances, most GPU solutions remain tailored to static models or narrowly defined remeshing tasks, and they are not readily applicable to large-scale, dynamic assemblies with hierarchical constraints [23]. This limitation underscores the continued need for parallel simplification techniques that are not only computationally efficient but also generalizable and suitable for real-time, interactive environments [24].
While these GPU-accelerated approaches mark notable progress in performance optimization, they often target static models or require highly specialized hardware and data structures, limiting their adaptability in diverse application scenarios [25,26]. In contrast, this study focuses on enhancing real-time performance and scalability by leveraging OpenMP-based parallel computing within the QEM framework. By focusing on real-time performance and scalability through the OpenMP-based parallel computing of QEM, this study introduces a novel contribution to the field. The integration of multi-core processing and curvature-based refinements makes it possible to handle complex meshes efficiently without compromising their visual quality. This study represents a critical step forward in bridging the gap between traditional mesh simplification algorithms and the dynamic, performance-constrained applications of modern industrial-scale 3D assemblies.
Research Work
Aiming at the problems of large-scale 3D mesh data and complex structure in industrial-scale assemblies, this study accelerates and optimizes the key computational modules of the traditional QEM algorithm and its approximate curvature-based refinement strategy through OpenMP-based parallel computing.
Specifically, the QEM algorithm and its key processes are first examined, and the reasons for its tendency to lose local details under high simplification ratios are analyzed. Next, an improved method based on approximate curvature is examined for the additional computational overhead required when it improves geometric fidelity, and the characteristics of the multi-core environment are combined to parallelize the core steps such as multi-part assembly calculation, error calculation, and curvature estimation. Finally, experiments are conducted on assembly model datasets of different scales to compare the similarities and differences between serial and parallel algorithms in terms of running speed, simplification quality, and scalability. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed parallel computing strategy significantly reduces runtime while preserving the key geometric details of the model, thereby providing critical technical support for industrial-scale 3D assemblies in application scenarios such as real-time rendering and mobile deployment.
2. Construction of Quadric Error Metrics Algorithm and Approximate Curvature Algorithm (ACA)
2.1. Construction of Quadric Error Metrics Algorithm
The QEM algorithm introduces a novel framework for estimating edge collapse costs based on simplified linear computations. This approach not only enhances computational efficiency but also improves the geometric fidelity of simplified meshes, laying a solid foundation for many subsequent mesh simplification algorithms.
During the simplification process of the triangular mesh model, the edge collapse operation usually merges a pair of vertices into a new vertex and reconnects the relevant triangular faces. This process removes two to three triangles and alters the geometry of several adjacent triangular faces, as shown in Figure 1. To retain the details of the original mesh as much as possible, the simplification algorithm needs to determine which edge collapse operations cause the least error and prioritize collapsing these edges. In other words, the key issues lie in two aspects: (1) how to measure the error, that is, how to define the optimal pair of collapse vertices; and (2) how to determine the position of the new vertex after collapse in order to minimize the error.
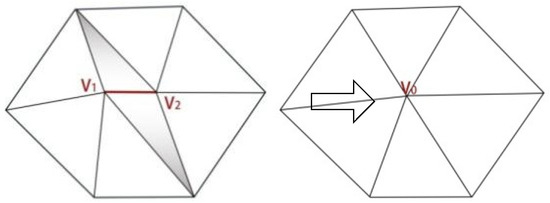
Figure 1.
Diagram of edge collapse simplification algorithm.
The QEM algorithm uses “the sum of the squared distances from the new vertex to the planes of its first-order neighboring triangles” as the measurement standard for collapse cost. Specifically, the error metric is defined as the sum of the squared distances between the collapsed point and the local surface of the original mesh.
For Figure 1, two points are contracted into one point. Then it can be defined in the form of (1).
In the formula, —the first-order neighborhood triangular face of point ; and —the square of the distance from point V to plane P.
In three-dimensional geometric space, a plane can be expressed as , where . Also, can represent the unit normal vector of the plane P. Then, this plane can be written as in terms of the unit normal vector and a point on the plane. The sum of squared distances from any point in three-dimensional space to this plane can be expressed as (2)
The definition of is given in (3).
Then in (2) can be represented by (4).
The quadratic error matrix can be defined by Equation (5). Both and are symmetric matrices, and only 10 elements need to be stored to represent them.
Approximately, it is considered that the sum can be expressed as (6)
Then (4) can be expressed as (7)
The quadratic error matrix of the new vertex can be expressed as (8)
The quadratic error of the new vertex after folding can be expressed as (9)
The error introduced by edge collapse is mainly determined by the position of the new vertex after collapse and the sum of the quadratic error matrices formed by the first-order neighborhood triangular face corresponding to the vertices at both ends of the original edge. In the triangular mesh model, the information of the edge and its associated vertices is known before simplification. Therefore, only by determining the optimal position of the new vertex can the collapse cost of this edge be accurately calculated.
The coordinates of the new point need to minimize the quadratic error of this edge as much as possible. Take the partial derivative of the quadratic error of the new vertex to obtain the value of the new vertex, as shown in (10).
From (10), we can obtain (11).
Therefore, the coordinates of can be directly obtained, and the calculation method is shown in (12):
When the matrix is not invertible, directly select the vertex with the smaller quadratic error among the edges to be folded as the position of the new vertex. If the quadratic errors of the two vertices are the same, select the midpoint of the two points as the position of the new vertex. The specific calculation method is shown in (13).
In the formula, —position of the new point after collapse; —positions of points before collapse; and — respective quadratic error matrices.
Figure 2 illustrates the overall workflow of the QEM simplification algorithm. The process begins with setting simplification parameters such as the target ratio, followed by loading the 3D model in mesh format. Based on the parameters, the target number of faces is computed, and a threshold is established for edge collapse operations. Each edge is then assigned a collapse cost, and those with costs below the threshold are iteratively removed through edge collapse operations. After each collapse, the vertex, edge, and face information of the mesh is updated to ensure geometric consistency. The algorithm continues until the simplification target is reached, after which the final simplified model is output. This flow chart provides a clear procedural overview that complements the mathematical formulations introduced earlier, highlighting the iterative nature of QEM-based mesh simplification. The basic calculation flow chart of the QEM algorithm is as follows:
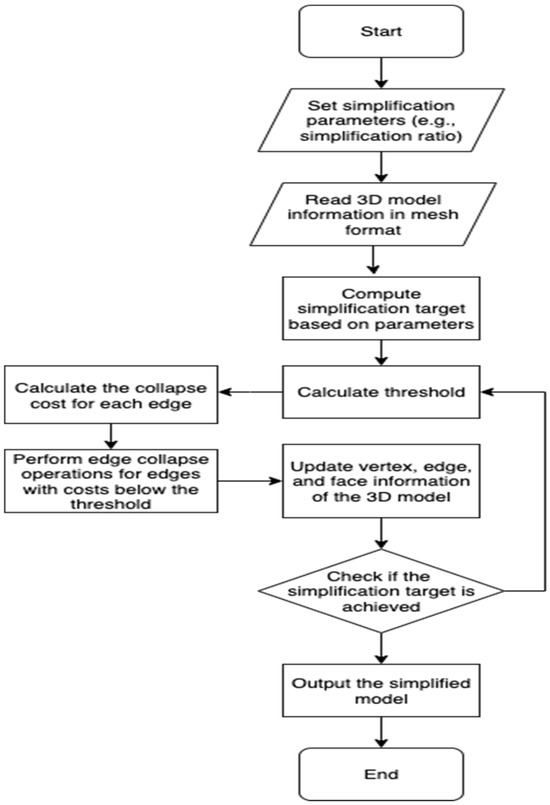
Figure 2.
QEM Calculation Flow Chart of the Algorithm.
2.2. Construction of Approximate Curvature Algorithm
Curvature is used to characterize the degree of bending of a curve. A larger numerical value indicates a more significant bend. Since the surface of the triangular mesh is composed of a series of continuous planes and lacks the smoothness of a real curved surface, approximate curvature is usually used to measure its local geometric variation. Regions with smaller curvature are generally flatter, whereas regions with larger curvature contain more geometric details, reflecting higher geometric complexity. The approximate curvature of the triangular mesh surface can be expressed by Equation (14).
In the formula, —the edge determined by vertices —the approximate curvature of the edge —the vertex normal vector of vertices —the included angle between the normal vector of the two vertices —the length of the edge determined by .
As shown in Equation (14), the calculation of vertex normal vectors directly affects the estimation result of approximate edge curvature. In this process, the algorithm comprehensively considers the area and interior angle information of the first-order neighborhood triangles. That is, triangle-area weighting is applied to reflect the relative influence of different faces on the vertex normal vector, while interior-angle weighting is introduced to correct the deviations caused by differences in triangle shapes. Specifically, triangles with larger areas are assigned higher weights in the normal vector calculation, thus exerting greater influence on the vertex direction estimation. When multiple triangles have similar areas but significantly different shapes, weighting by vertex interior angles more accurately reflects the contributions of different shapes to geometric features, thereby effectively reducing the errors caused by shape differences and improving the accuracy of curvature approximation.
Therefore, the normal vector of vertex is given by Equation (15)
In the equation, —the vertex normal vector of vertex —the interior angle size of a first-order neighborhood triangle corresponding to vertex —the area of this triangle; and —the initial normal vector of this triangle.
A foldable approximate edge curvature can be calculated from (14) and (15).
3. Parallel Processing Algorithm Construction and Experiment
3.1. Overview of Parallel Optimization Strategy
Analysis of the Fast QEM mesh structure reveals a distinct tree-like dependency between triangle-face data and the vertex data. The initialization of base vertices and the computation of the normal vector form the basis for all subsequent edge collapse evaluation and geometric updates. Moreover, the collapse operations on different edges at the same hierarchy level are data-independent, thus demonstrating inherent parallelism. Based on this characteristic, this study proposes a parallel strategy combining multi-level task restructuring with decoupling, which reorganizes the core process of the original serial QEM algorithm in a modular manner and enables thread-based processing, thereby providing structural support for efficient parallelization.
3.1.1. Data Structure Layering Strategy
The mesh-processing workflow of the Fast QEM algorithm can be divided into five stages with clearly defined dependency order: vertex information initialization (designated as the base layer), quadric matrix initialization, triangle referencing and edge error calculation, edge collapse evaluation, and vertex update, as well as topological compression and mesh reconstruction. This hierarchical structure clarifies the computational dependency boundaries, enabling thread-level parallel processing at each stage while fully ensuring data consistency. With this structured parallel design, the proposed method effectively eliminates dependency conflicts among tasks within each stage, significantly improving computational resource utilization.
3.1.2. Concrete Algorithm Implementation
- Step 1. Loading and Preprocessing Stage: All OBJ files of the 3D part models in assembly are loaded simultaneously to construct the 3D mesh data list.
- Step 2. Thread Pool Initialization: A thread pool for parallel simplification is established, followed by the creation of OpenMP parallel tasks to manage simplification states within each thread-private cache.
- Step 3. Parallel Initialization: Triangle references and edge quadric error metrics are initialized in parallel, while new triangle data are constructed concurrently.
- Step 4. Iteration Termination Check: If the number of triangles has not yet reached the target threshold, parallel collapse operations continue.
- Step 5. Compression and Output: Perform the final mesh compression and output the simplified OBJ file.
3.2. Parallel Algorithm Experiment
To evaluate the actual performance of the proposed parallel 3D mesh simplification algorithm (including the traditional QEM algorithm and the ACA) in processing large-scale 3D meshes, three representative industrial models with varying scales and complexities, “Transport Vehicle,” “Robotic Arm,” and “Pipeline”, were selected for experimentation, as illustrated in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. The face counts of these models are 7,892,504, 296,462, and 4,194,970, respectively, with file sizes ranging from 89.9 MB to 2.58 GB, which ensures good representativeness. They collectively comprise 350 individual components, and basic information is summarized in Table 1. All parallel computing experiments were conducted on a high-performance mobile workstation equipped with an Intel i7 hexa-core processor and 64 GB of memory. The operating system was Microsoft Windows 10. All C++ programs were developed and tested using Microsoft Visual Studio 2022 (compiler: MSVC v14.3) and OpenMP 2.0 standard.
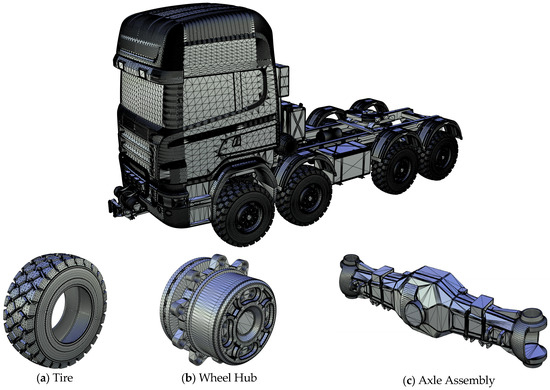
Figure 3.
Transport Vehicle model used in experiments with internal parts (a–c) (source: Open3DModel).
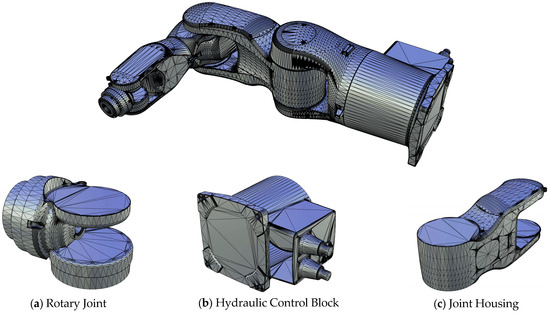
Figure 4.
Manipulator arm model used in experiments with internal parts (a–c) (source: Industry Robot Arm on Free3D).
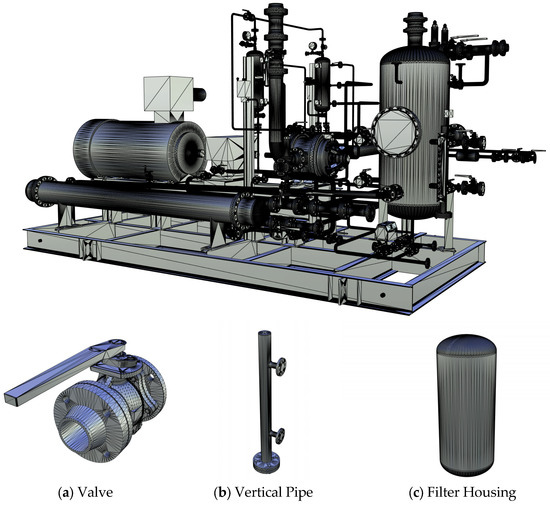
Figure 5.
Pipeline model used in experiments with internal parts (a–c) https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/industrial-units--9-17-026a1fd299ec4e4583422b362c2e7e81 (accessed on 5 September 2025).

Table 1.
Basic information on the 3D model used in parallel computing experiments.
3.3. Analysis of Experimental Results
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed parallel optimization strategy, a comparison was conducted between the traditional QEM algorithm and the approximate curvature-based refinement. Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 illustrate the computation time of the ACA and QEM-based simplification algorithms under different simplification ratios (30%, 50%, and 70%) with varying numbers of threads. A consistent trend is observed across all cases: parallelization significantly reduces computation time compared with the serial baseline, and the benefit becomes more evident as the model size increases. For ACA, which is computationally more intensive, the parallel efficiency improvement is particularly pronounced. At higher simplification ratios (50% and 70%), ACA achieves a substantial reduction in execution time, especially for large-scale meshes (e.g., 500 k–2 M faces), indicating that larger workloads provide more opportunities for parallel exploitation. In contrast, QEM exhibits lower computational demand, resulting in relatively limited speedup; in small-scale meshes (0–10 k faces), the overhead of thread scheduling even dominates, leading to minimal efficiency gain.
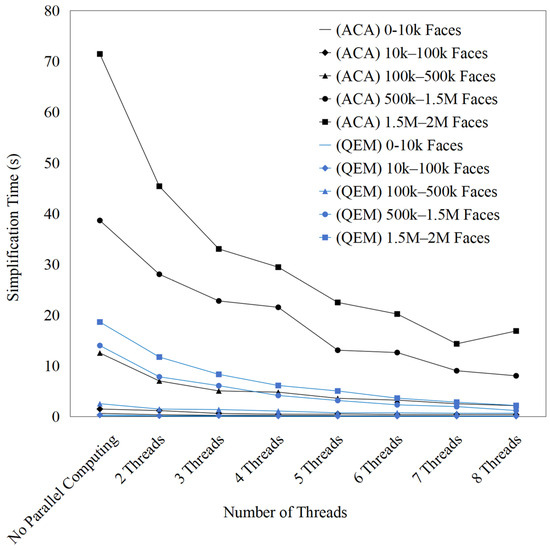
Figure 6.
Computation time with multi-threaded parallelization simplification (simplification ratio: 30%).
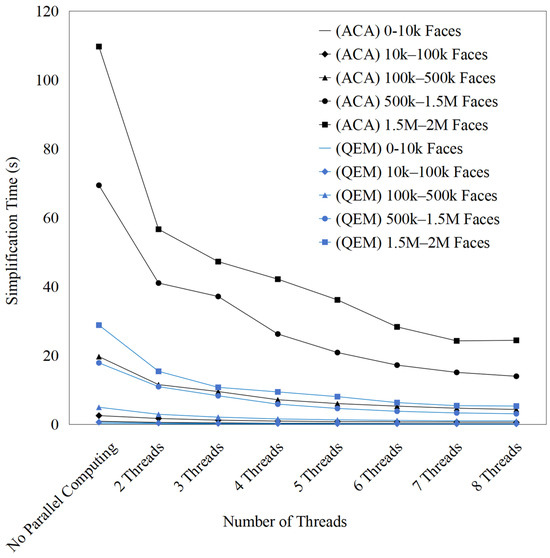
Figure 7.
Computation time with multi-threaded parallelization simplification (simplification ratio: 50%).
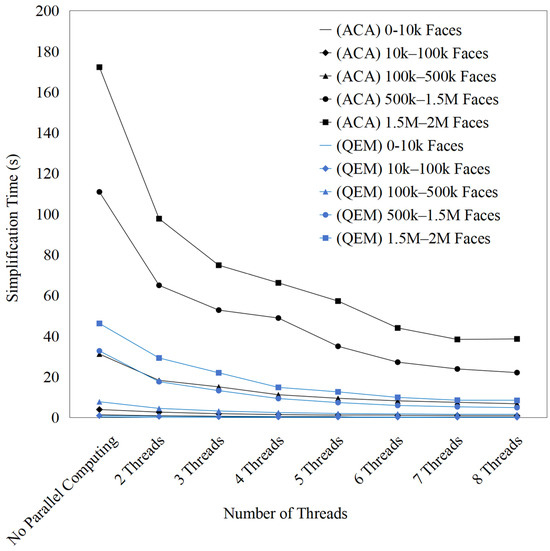
Figure 8.
Computation time with multi-threaded parallelization simplification (simplification ratio: 70%).
To exploit the benefits of multi-thread parallelization, two levels of parallelism were implemented in the simplification framework. First, for large assemblies consisting of multiple parts, simplification was performed independently on each part. Since there is no computational dependency among different parts, the process can be executed concurrently without requiring synchronization. Second, within each part, the calculation of QEM or approximate curvature values for all vertices was parallelized, as the error metric of each vertex is independent of others.
The parallel implementation was realized using OpenMP directives. For vertex-based operations, a static scheduling strategy was adopted to evenly distribute the workload across threads while minimizing scheduling overhead. Shared mesh data, such as vertex and face information, were carefully handled to avoid conflicts: thread-private variables were used for local computations, and updates were aggregated after each parallel section. This design ensures that the majority of computations—particularly part-level simplification and vertex-level error metric evaluation—are executed in a highly parallel manner, while synchronization costs are kept minimal. As a result, the proposed implementation achieves both computational efficiency and reproducibility.
Moreover, the comparison between different simplification ratios highlights that higher ratios enhance the effectiveness of parallelization. At 30% simplification, the total runtime remains relatively short, and the gain from parallel computing is moderate (Table 2). At 50% simplification, the runtime shows a noticeable increase compared with 30%, and parallel computing provides a clear efficiency advantage (Table 3). However, at 70% simplification, the runtime increases significantly in the serial case, and parallel execution yields a much sharper reduction in computation time (Table 4). This finding demonstrates that computational intensity and problem scale are key factors in determining the efficiency of multi-threaded acceleration. Overall, the results confirm that ACA is better suited for parallelization, and higher simplification ratios coupled with large and complex models maximize the benefits of multi-thread computation. Overall, the improved QEM algorithm and approximate curvature-based refinement efficiently utilize multi-core resources, demonstrating strong parallel scalability and stability in simplification tasks for medium-to-large-scale models.

Table 2.
Multi-threaded parallelization calculation of 3D model simplification for computation Time (simplification ratio: 30%).

Table 3.
Multi-threaded parallelization calculation of 3D model simplification for computation time (simplification ratio: 50%).

Table 4.
Multi-threaded parallelization calculation of 3D model simplification for computation time (simplification ratio: 70%).
To substantiate these findings, we conducted experiments comparing the two algorithms on representative industrial meshes under multi-threaded environments. The results show that the ACA achieves a speedup ratio comparable to that of the QEM algorithm across all thread configurations, with performance gains reaching up to 5.5× for large-scale models, thereby confirming the favorable scalability of the proposed approach.
However, the extent of acceleration also varies with the complexity of the models. From the perspective of mesh complexity, experimental results on the three types of models suggest that the speedup ratio increases significantly with the number of triangles. The “Transporter” model, which originally contains more than 7.8 million triangles, can effectively fill the thread task queue, thereby exhibiting superior acceleration potential under multi-threaded computation. In contrast, the “Robotic Arm” model, with fewer triangles, faces limitations in thread scheduling and task partitioning, resulting in relatively lower acceleration performance. Meanwhile, the figure also exhibits the typical characteristic of diminishing marginal acceleration. In general, the acceleration efficiency decreases as the number of threads increases. This phenomenon can be attributed to several factors. First, additional parallel overhead, including thread creation, task scheduling, and synchronization, becomes increasingly significant when more threads are employed, thereby offsetting the benefits of parallelization. Second, according to Amdahl’s law, the inherently sequential portion of the algorithm imposes an upper bound on the achievable speedup, resulting in diminishing returns with larger thread counts. Furthermore, intensive memory access during mesh simplification introduces cache contention and memory bandwidth limitations, which restrict further improvements in execution time. Consequently, while the parallelization strategy effectively reduces the simplification time for large-scale meshes, the efficiency gain tends to saturate as the number of threads increases.
The results presented in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 reveal the impact of multi-thread parallelization on the computational efficiency of both QEM- and ACA-based simplification algorithms under different simplification ratios. Overall, the speedup achieved by parallel computing exhibits a consistent increasing trend with higher thread counts, although the magnitude of improvement strongly depends on the algorithm type, simplification ratio, and model category. Specifically, ACA shows more substantial parallel acceleration than QEM across all tested scenarios, which can be attributed to its higher computational complexity and larger per-thread workload, making it more suitable for parallel exploitation. In contrast, QEM demonstrates only modest speedup gains, especially under lower simplification ratios, where the computational burden is relatively small and parallel overhead offsets much of the benefit (Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4).
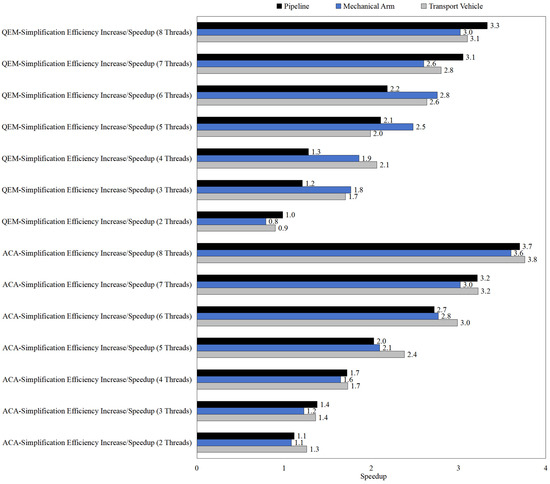
Figure 9.
Multi-thread computational efficiency improvement (simplification ratio: 30%).
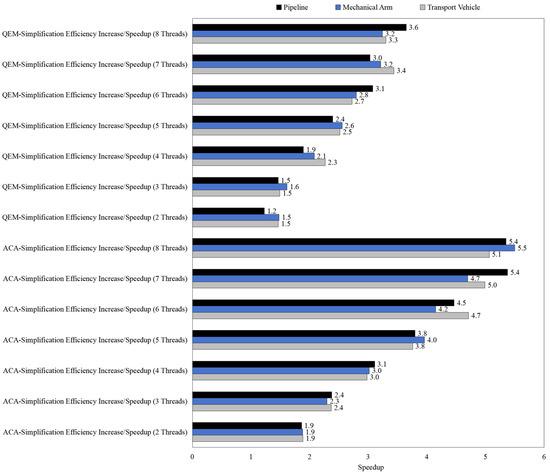
Figure 10.
Multi-thread computational efficiency improvement (simplification ratio: 50%).
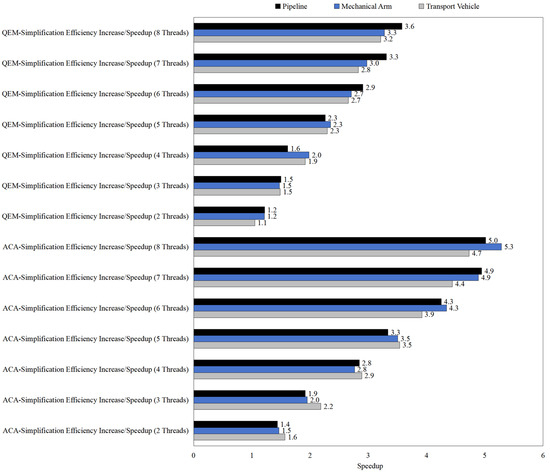
Figure 11.
Multi-thread computational efficiency improvement (simplification ratio: 70%).
Furthermore, increasing the simplification ratio enhances the effectiveness of parallel computing. At 30% simplification, the maximum speedup remains below 4.0 in most cases, whereas at 70% simplification, ACA achieves speedup values exceeding 5.0 for large models such as the transport vehicle. This indicates that larger simplification workloads provide greater parallelism potential, as the overhead of thread management becomes less significant relative to the overall computation. In addition, the performance across different models (pipeline, mechanical arm, and transport vehicle) suggests that geometric complexity and face count distribution also play an important role: more complex models consistently yield higher acceleration efficiency under the same simplification ratio.
In summary, the results highlight that (1) ACA benefits more significantly from multi-thread parallelization than QEM, (2) higher simplification ratios enhance parallel efficiency due to increased computational intensity, and (3) complex models with larger mesh sizes show greater scalability. These findings demonstrate the necessity of tailoring the choice of simplification algorithm and thread configuration to the model size and target simplification ratio in order to achieve optimal computational efficiency.
A comprehensive analysis reveals that the ACA is better suited for executing the mesh simplification task in the multi-threaded parallel environment. The core calculation process of this algorithm features a high degree of task independence and excellent load balancing capability, allowing it to demonstrate greater parallel scalability and execution efficiency on multi-core platforms. In contrast, while the parallel acceleration of the traditional QEM algorithm is less pronounced compared to the ACA, its relatively straightforward overall calculation process and high serial execution efficiency provide it with some parallel potential and practical value in the overall computational environment. For small-scale models or a low thread count, the ACA can more effectively handle the simplification tasks of medium and large 3D meshes while maintaining simplification accuracy and topological consistency. It also boasts stronger engineering adaptability and promising application prospects.
4. Conclusions
To address the increasing demand for efficient and accurate processing of large-scale industrial 3D mesh, this study investigates the parallel optimization of classic simplification algorithms. The QEM algorithm, known for its balanced performance in geometric fidelity and computational efficiency, has laid a solid foundation for 3D mesh simplification in industrial contexts. However, with the growing scale and complexity of industrial assemblies, traditional serial algorithms fall short in meeting real-time and high-throughput requirements.
This research focuses on the parallelization and performance optimization of the QEM algorithm and its enhanced variant based on approximate curvature estimation. To overcome the bottlenecks posed by large and complex assemblies, which introduce an OpenMP-based parallel framework that leverages data hierarchization and task decoupling, key steps—such as multi-component simplification, error metric calculation, and curvature estimation—are optimized through thread-level parallel acceleration. A hierarchical structure is designed to ensure data consistency and task independence during parallel execution, enabling efficient and scalable processing.
The major outcomes of this study are as follows:
- Efficient Parallel Strategy: A hierarchical, decoupled parallel simplification framework was developed, demonstrating reliable performance across diverse industrial-scale models.
- Significant Acceleration: Experimental results on three representative industrial models reveal a maximum speedup of 5.5× over traditional serial approaches, with the improvement being most pronounced for large-scale triangular mesh models.
- Algorithm-Specific Insights: The QEM algorithm shows potential for lightweight optimization due to its low computational density, while the approximate curvature variant benefits more from parallelism under high thread-count environments due to its heavier computation load.
Despite these promising results, some limitations remain. First, the current parallel strategy is primarily CPU-based, which may restrict scalability for ultra-large models. Second, load balancing among threads still poses challenges when processing highly heterogeneous structures. Future work will explore hybrid parallelization schemes, such as GPU acceleration and region-based task scheduling, to further enhance real-time performance and adaptability to larger and more complex assemblies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/math13193183/s1, File S1: Supplementary information’s.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.C., S.W. and Y.F.; software, H.C. and S.W.; validation, S.W.; data curation, J.N.; writing—original draft, S.W., J.N. and Y.F.; writing—review and editing, H.C., S.W. and X.Z.; visualization, X.Z. and Y.X.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, H.C.; funding acquisition, H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported under the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFB3303200) and Korean Government [Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT)]: RS-2024-00344506.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, A.E.; Hebert, M. Control of Polygonal Mesh Resolution for 3-D Computer Vision. Graph. Models Image Process. 1998, 60, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ye, J. A New 3-D Mesh Simplification Algorithm. Rev. Colomb. Comput. 2003, 4, 65–73. Available online: https://doaj.org/article/b28b59d0d56a49b2a18e45ad9a2e1844 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Anjos, R.K.; Roberts, R.; Allen, B.; Jorge, J.; Anjyo, K. Saliency Detection for Large-Scale Mesh Decimation. 2020. Available online: https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/195788/ (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Kwon, S.; Mun, D.; Kim, B.C.; Han, S. Feature shape complexity: A new criterion for the simplification of feature-based 3D CAD models. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Huang, S.; Xu, H.; Li, P. Quadratic Error Metric Mesh Simplification Algorithm Based on Discrete Curvature. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 428917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zhang, D.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Khalil, H.S.U.R.; Wang, X. Two-Round Optimization Algorithm Based on Quadric Error Metrics. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 30021–30035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Peng, Z. Structure-Aware Simplified Algorithm of Mesh Model for Urban Scene. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, X.; Yang, Y.; Lee, I. Review of Three-Dimensional Model Simplification Algorithms Based on Quadric Error Metrics and Bibliometric Analysis by Knowledge Map. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Mesh Simplification for Medical Image Modeling. 2007. Available online: http://dspace.xmu.edu.cn/handle/2288/156695 (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Simplification of 3D Building Models with Texture Features. IEEE Access 2022, 8, 196341–196350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wei, M.; Qin, J.; Wu, J.; Heng, P.-A. Feature-Preserving Mesh Denoising via Normal Guided Quadric Error Metrics. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 62, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, G.; Wolf, C.; Girard, S. Markov Random Fields for Improving 3D Mesh Analysis and Segmentation. 2008. Available online: https://diglib.eg.org/items/9f167637-8adb-4c4c-b838-5ed61f8e3e84 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Tseng, J.-L. Surface Simplification of 3D Animation Models Using Robust Homogeneous Coordinate Transformation. J. Appl. Math. 2014, 2014, 189241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wu, C.; He, F.; Fan, B.; Liang, Y. Delaunay Meshes Simplification with Multi-Objective Optimisation and Fine Tuning. IET Collab. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 5, e12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhou, K.; Shi, J. A New Mesh Simplification Algorithm Based on Triangle Collapses. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2001, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Realtime 3D Reconstruction with Mobile Devices. In International Conference on Applications and Techniques in Cyber Security and Intelligence ATCI 2018; Abawajy, J., Choo, K.K., Islam, R., Xu, Z., Atiquzzaman, M., Eds.; ATCI 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Nan, L. Feature-Preserving 3D Mesh Simplification for Urban Buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Mo, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, T.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, W. An Evolutionary Algorithm with Clustering-Based Selection Strategies for Multi-Objective Optimization. Inf. Sci. Int. J. 2023, 624, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kim, S. Mesh Simplification Algorithms for Rendering Performance. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 13, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.H.; Hussein, M.K. High-performance simplification of triangular surfaces using a GPU. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y. GPU-based mesh reduction strategy utilizing active nodes. Softw. Impacts 2023, 18, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q. GPolylla: Fully GPU-accelerated polygonal mesh generator using half-edge data structures. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.14723. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.14723 (accessed on 2 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Park, M.; Lee, S. End-to-End GPU-Accelerated Low-Poly Remeshing using Curvature Map and Voronoi Tessellation. Comput. Graph. Forum (Eurograph.) 2025, in press. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/370736210_End-to-End_GPU-Accelerated_Low-Poly_Remeshing_using_Curvature_Map_and_Voronoi_Tessellation (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, L. Parallel Topology-Aware Mesh Simplification on Terrain Trees. ACM Trans. Spat. Algorithms Syst. (TSAS) 2024, 10, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Ren, H.; Krishnamurthy, A. Locality-Aware Automatic Differentiation on the GPU for Mesh-Based Computations. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.00406. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.00406 (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Gupta, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. GALE: Leveraging Heterogeneous Systems for Efficient Unstructured Mesh Data Analysis. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.15230. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.15230 (accessed on 7 September 2025). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).