A–ESD: Auxiliary Edge-Server Deployment for Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We formalize the A–ESD problem as a constrained multi-objective optimization model with an emphasis on load balancing, and establish its NP-hardness.
- We propose LBA–GA, an enhanced genetic algorithm, to efficiently identify optimal deployment strategies for auxiliary edge servers.
- We conduct extensive experiments on widely used real-world datasets to evaluate the performance of LBA–GA. Results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods in achieving better load balance, lower latency, and higher cost-effectiveness.
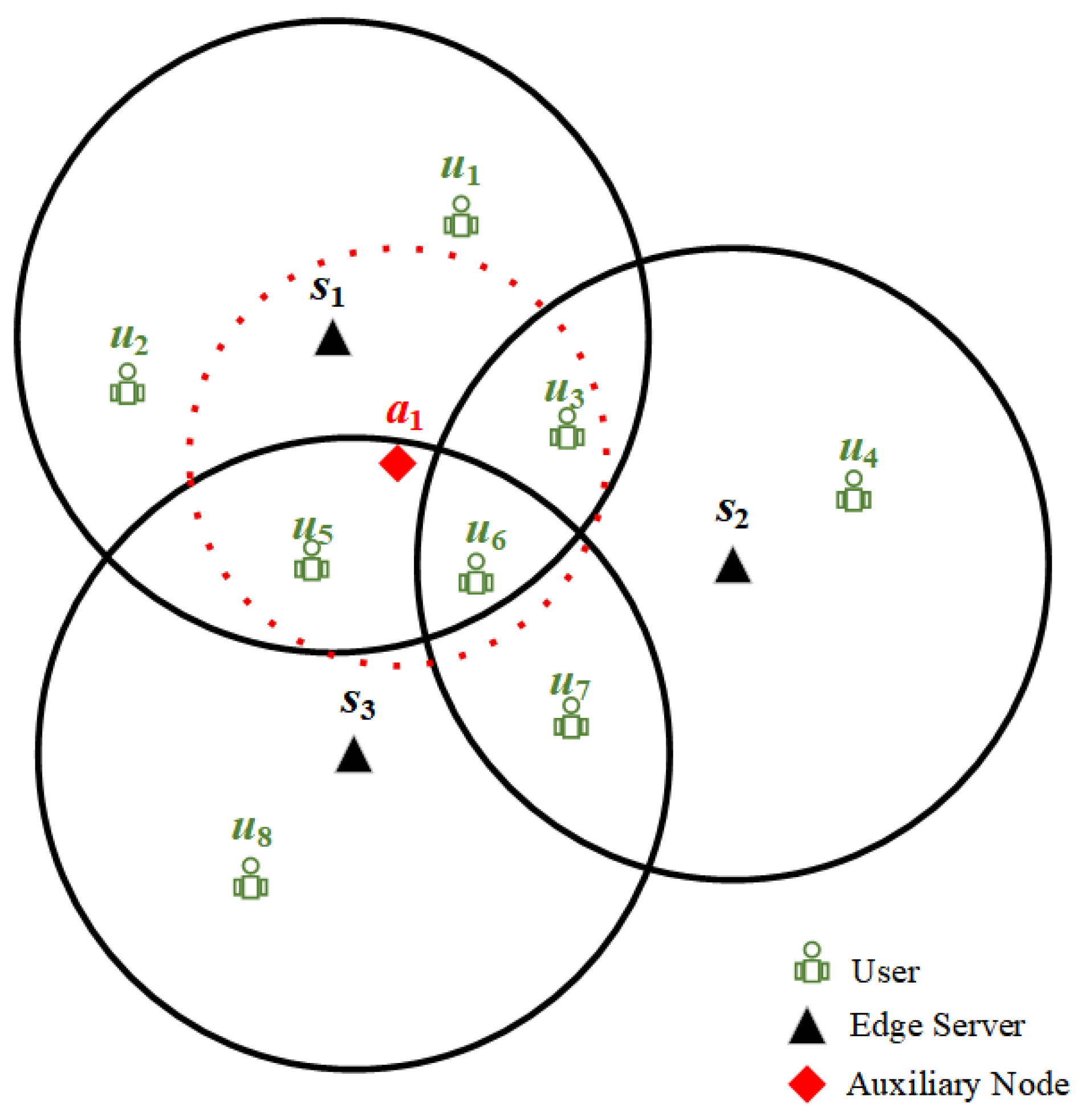
2. Motivating Example
3. System Model
3.1. Edge System
3.2. Load Balancing- and Delay-Aware Model
3.3. A–ESD Problem
4. Approach
4.1. Optimization Model
4.2. A–ESD Problem Hardness
4.3. LBA–GA Method
4.3.1. Overview of LBA–GA Algorithm
4.3.2. Generation Update of LBA–GA
| Algorithm 1: Load balancing-based auxiliary edge-server deployment genetic algorithm (LBA–GA) |
 |
5. Experiments
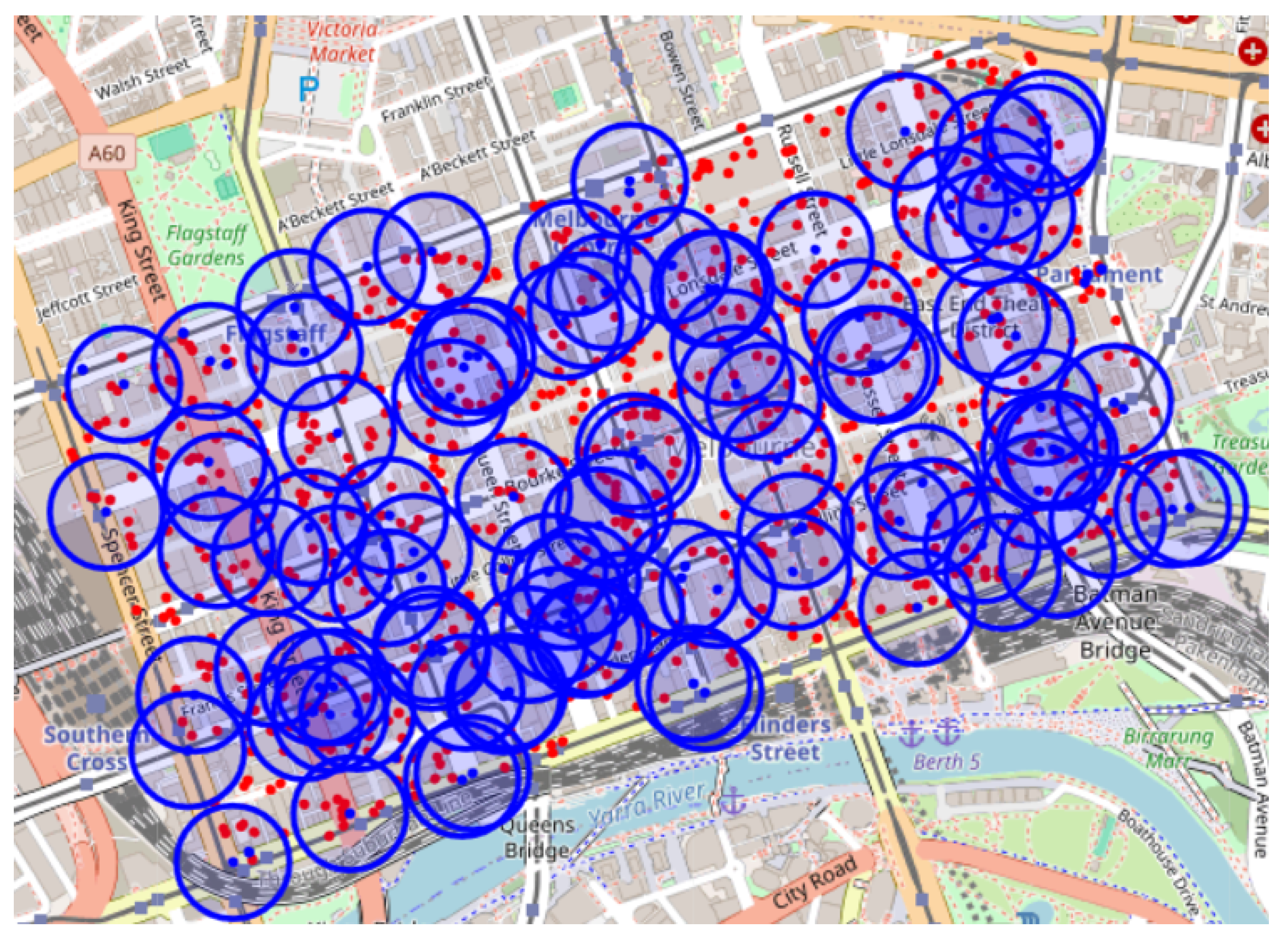
5.1. Experimental Setup and Dataset
5.2. Comparative Methods and Evaluation Metrics
- No-Aux: It does not use additional auxiliary edge servers.
- Random-B: It randomly deploys a number of auxiliary edge servers and selects the servers with optimal performance.
- Trad-GA: It uses traditional genetic algorithms to solve the optimization problem.
- HE-GA [13]: It employs a genetic algorithm to find the optimal solution for the deployment of edge servers by calculating the impact on communication.
- Satisfiability (): It represents a binary indicator used to ascertain whether the task requirements of all users are satisfied.where represents the unprocessed task demand of user .
- Load-Balancing Optimization Rate (): It is measured by the standard deviation reduction ratio to indicate the effectiveness of the method in terms of load balancing.where represents the overall standard deviation of the No-Aux method and represents the overall standard deviation of the current method.
- Delay-Optimization Rate (): It is measured by the reduction ratio of the mean distance to indicate the effectiveness of the method in terms of delay.where represents the overall average distance of the No-Aux method and represents the overall average distance of the current method.
- Load-Balancing Optimization Rate per Node (): It is measured by the reduction ratio of the standard deviation per node to indicate the cost-effectiveness of deploying auxiliary edge servers for load-balancing optimization.
- Delay optimization rate per node (): It is measured by the reduction ratio of the mean distance per node to indicate the cost-effectiveness of deploying auxiliary edge servers for delay optimization.
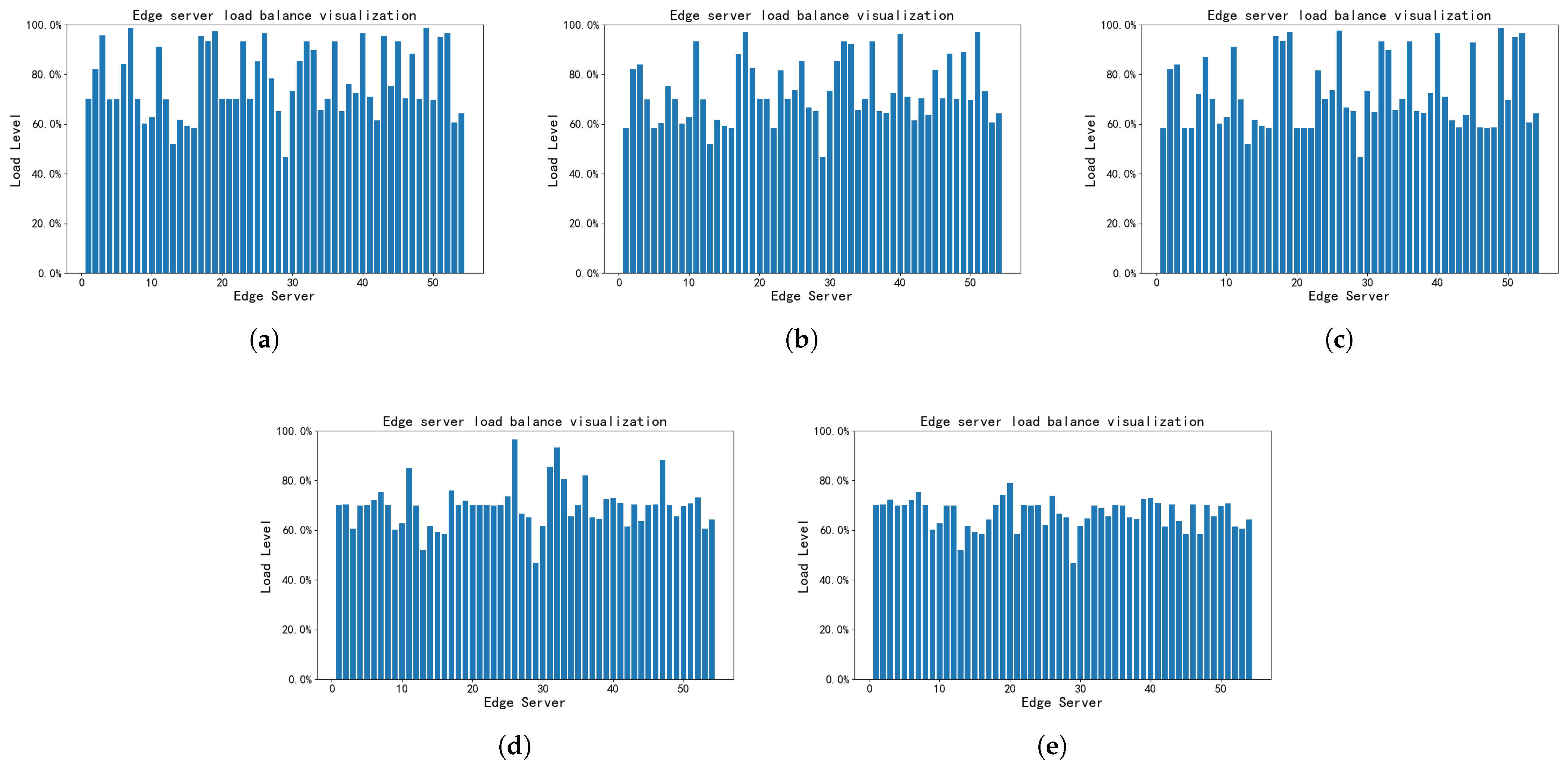
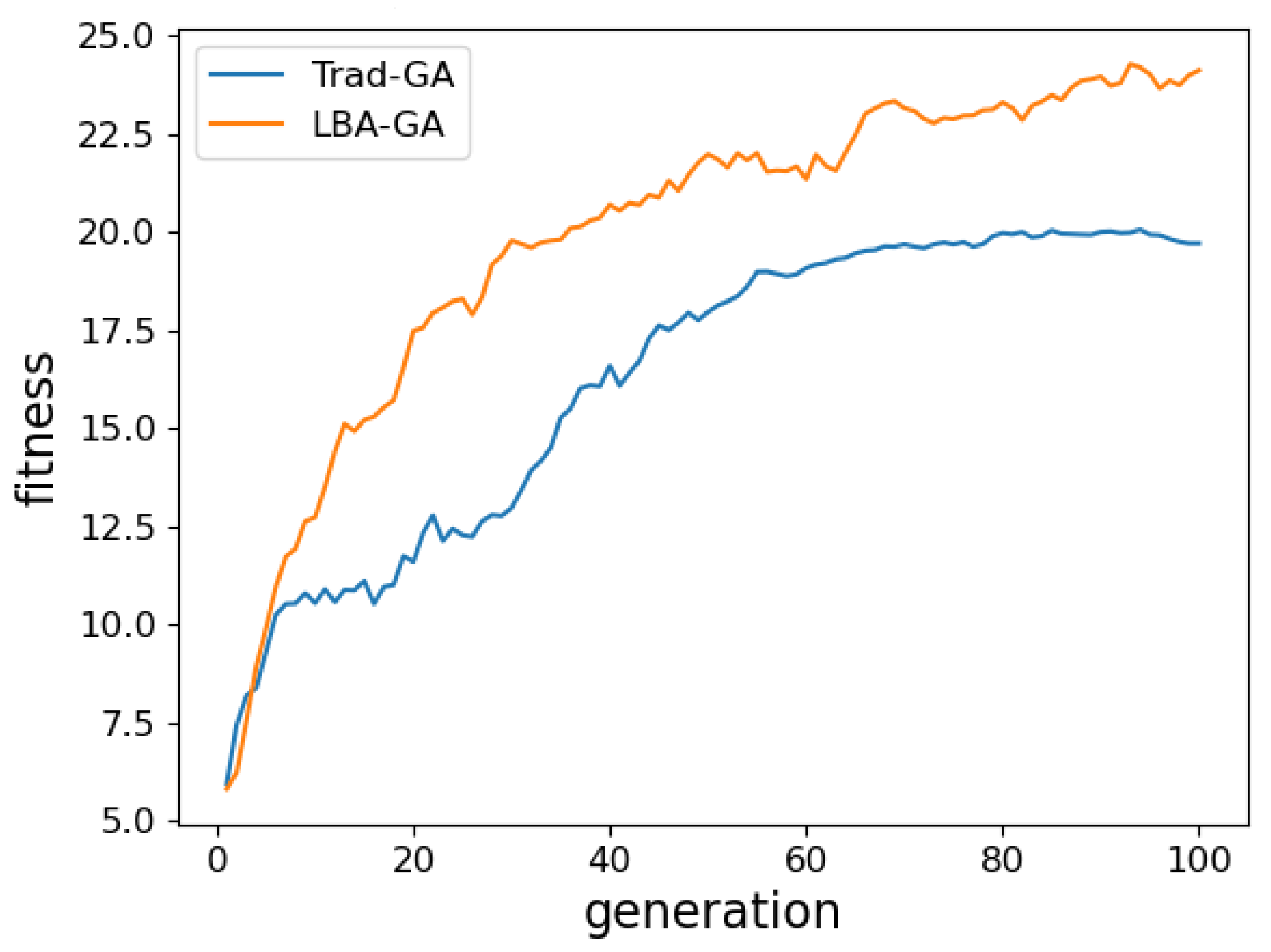
5.3. Experiment Results and Analyses
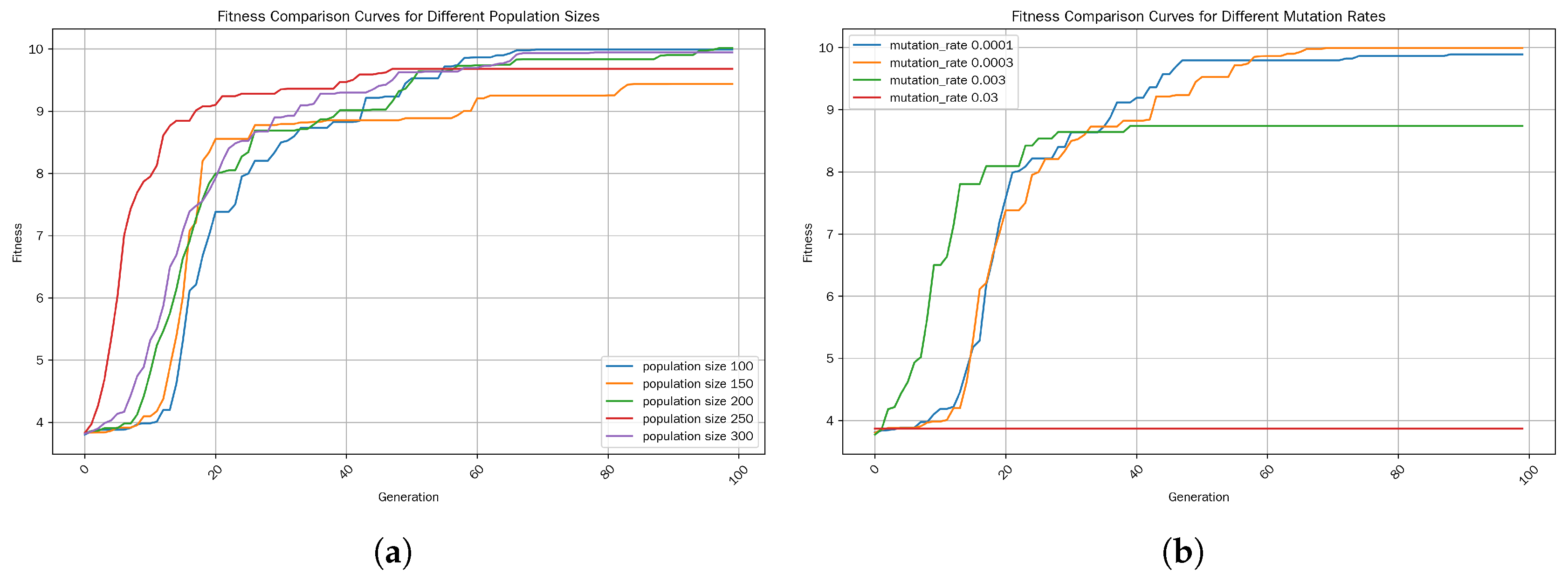
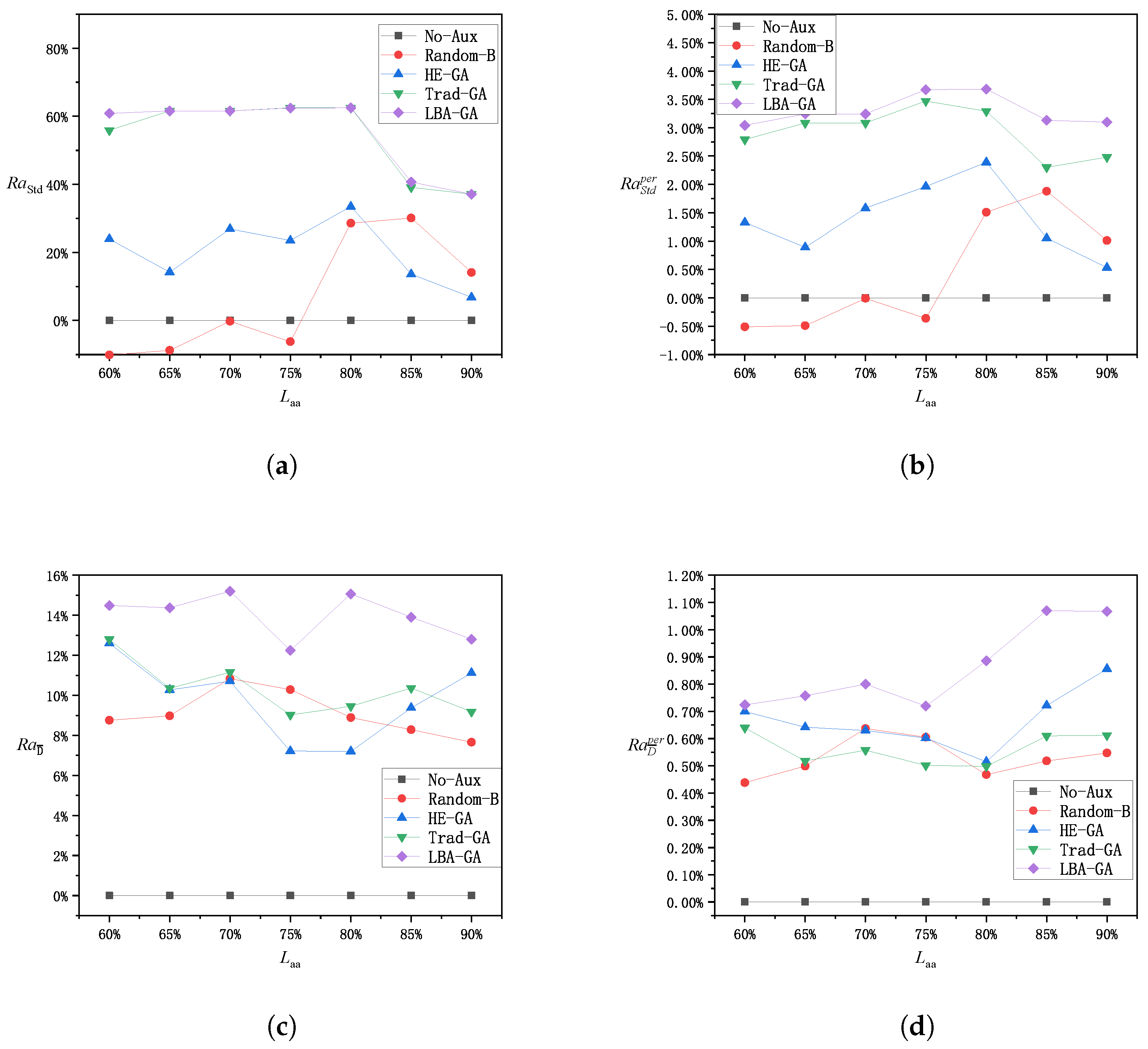
5.4. Performance Impact of Parameters
5.5. Performance Impacts of Parameters
6. Related Work
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinsel, D.; Gantz, J.; Rydning, J. Data Age 2025: The Evolution of Data to Life-Critical. Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.seagate.com/www-content/our-story/trends/files/Seagate-WP-DataAge2025-March-2017.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Shi, W.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Edge computing: Vision and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Tan, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Zeng, P.; Khan, M.; Das, S.K. Edge-computing-driven internet of things: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, P.; Rojaramani, D.; Praveena, V.; Annlin Jeba, S.; Bensujin, B. Data Security and Privacy Requirements in Edge Computing: A Systemic Review. Cases Edge Comput. Anal. 2021, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C. An edge server deployment approach for delay reduction and reliability enhancement in the industrial internet. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 5743–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, A.; Aghdasi, H.S.; Saeedvand, S. Edge server placement and allocation optimization: A tradeoff for enhanced performance. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 5783–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, A.; Ma, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, A.X. QoS driven task offloading with statistical guarantee in mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 21, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ruffini, M. Optical front/mid-haul with open access-edge server deployment framework for sliced O-RAN. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 19, 3202–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, A.M.; Al-Raweshidy, H. Optimal intelligent edge-servers placement in the healthcare field. IET Netw. 2024, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J.; Gu, Z.; Li, K. ECFA: An Efficient Convergent Firefly Algorithm for Solving Task Scheduling Problems in Cloud-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 3280–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, A.; Sayadi, M.; Azgomi, H. Energy-aware edge server placement using the improved butterfly optimization algorithm. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 14954–14980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havas, S.; Azizi, S.; Abdollahpouri, A. A Multistart Power of d Choices Strategy for Edge Server Placement Problem. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Internet of Things and Applications (IoT), Xining, China, 25–27 August 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Cao, B.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Tang, B.; Peng, Z. An edge server deployment method based on optimal benefit and genetic algorithm. J. Cloud Comput. 2023, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; He, Q.; Chen, F.; Jin, H.; Yang, Y. Trading off between user coverage and network robustness for edge server placement. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2020, 10, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Gu, B.; Son, K.; Choi, W. Joint optimization of edge computing server deployment and user offloading associations in wireless edge network via a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2535–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovén, L.; Lähderanta, T.; Ruha, L.; Leppänen, T.; Peltonen, E.; Riekki, J.; Sillanpää, M.J. Scaling up an Edge Server Deployment. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 23–27 March 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Raeisi-Varzaneh, M.; Dakkak, O.; Habbal, A.; Kim, B.S. Resource scheduling in edge computing: Architecture, taxonomy, open issues and future research directions. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 25329–25350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, I.A.; Meshoul, S.; Hammad, M. Joint Task Offloading, Resource Allocation, and Load-Balancing Optimization in Multi-UAV-Aided MEC Systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, G.; Mundada, M.R.; Supreeth, S.; Gardiner, B. Deep learning-based resource prediction and mutated leader algorithm enabled load balancing in fog computing. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2023, 15, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, S.K.; Kasi, M.K.; Ali, K.; Raza, M.; Afzal, H.; Lasebae, A.; Naeem, B.; Ul Islam, S.; Rodrigues, J.J. Heuristic edge server placement in industrial internet of things and cellular networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 10308–10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zheng, S.; Ding, W.; Fuentes, J.; Li, Y. An Edge Server Placement Method Based on Reinforcement Learning. Entropy 2022, 24, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hou, P.; Wu, H.; Hou, F. Optimal edge server deployment and allocation strategy in 5G ultra-dense networking environments. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2021, 72, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, A.; Sohrabi, M.K. Multiobjective edge server placement in mobile-edge computing using a combination of multiagent deep q-network and coral reefs optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 17503–17512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähderanta, T.; Leppänen, T.; Ruha, L.; Lovén, L.; Harjula, E.; Ylianttila, M.; Riekki, J.; Sillanpää, M.J. Edge server placement with capacitated location allocation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.07349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Fan, S.; Zhao, J.; Tian, S.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, Y.; Yang, P. Large-scale many-objective deployment optimization of edge servers. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Deng, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y. Edge server placement for vehicular ad hoc networks in metropolitans. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Lai, C.; Zhang, J. Joint edge server placement and service placement in mobile-edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 11261–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Feng, Z.; Xu, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yadav, R. An edge server placement algorithm based on graph convolution network. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 5224–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; He, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, F.; Jin, H.; Yang, Y. Robustness-oriented k Edge Server Placement. In Proceedings of the 2020 20th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGRID), Melboune, Australia, 11–14 May 2020; pp. 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, P.; Shen, J.; Guo, M. Preference-Aware Edge Server Placement in the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Han, F.; Zhao, Q.; Qi, L.; Dou, W.; Zhou, X. Secure edge server placement with non-cooperative game for internet of vehicles in web 3.0. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 4020–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| Set of edge servers | |
| Maximum values of the system on the X and Y axes | |
| User set | |
| Position of edge server | |
| Set of edge server load levels | |
| Max and current loads of edge server | |
| Communication range of edge server | |
| Position of user | |
| Set of user request demands | |
| Set of auxiliary edge servers | |
| Position of auxiliary edge server | |
| Set of auxiliary edge server load levels | |
| Max and current loads of auxiliary edge server | |
| Communication range of auxiliary edge server | |
| Max number of auxiliary edge servers | |
| Delays between users and their request destinations | |
| Distances between users and their request destinations | |
| Overload critical load level of edge servers |
| Methods | EUA Dataset 1 | EUA Dataset 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Aux | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Random-B | 0 | 29.58% | 6.68% | 1.56% | 0.35% | 0 | 28.59% | 8.89% | 1.51% | 0.47% | |
| HE-GA | 0 | 24.64% | 6.05% | 1.45% | 0.36% | 0 | 33.46% | 7.21% | 2.39% | 0.52% | |
| Trad-GA | 1 | 54.68% | 8.82% | 2.05% | 0.33% | 1 | 62.48% | 9.46% | 3.29% | 0.49% | |
| LBA-GA | 1 | 55.88% | 9.18% | 2.31% | 0.38% | 1 | 62.48% | 15.06% | 3.68% | 0.89% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Liao, K.; Zhang, B.; Zou, G. A–ESD: Auxiliary Edge-Server Deployment for Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193087
Niu S, Zhang X, Wang S, Liao K, Zhang B, Zou G. A–ESD: Auxiliary Edge-Server Deployment for Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics. 2025; 13(19):3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193087
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Sen, Xuewei Zhang, Simin Wang, Kaili Liao, Bofeng Zhang, and Guobing Zou. 2025. "A–ESD: Auxiliary Edge-Server Deployment for Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing" Mathematics 13, no. 19: 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193087
APA StyleNiu, S., Zhang, X., Wang, S., Liao, K., Zhang, B., & Zou, G. (2025). A–ESD: Auxiliary Edge-Server Deployment for Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics, 13(19), 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13193087






