Abstract
Optical wireless sensor networks (OWSNs) offer promising capabilities for high-speed, energy-efficient communication, particularly in mission-critical environments such as industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, and smart buildings. However, dynamic spectrum management and fault tolerance remain key challenges in ensuring reliable and timely data transmission. This paper proposes an adaptive spectrum management framework (ASMF) that addresses these challenges through a mathematically grounded and implementation-driven approach. The ASMF formulates the spectrum allocation problem as a constrained Markov decision process and leverages a dual-layer optimization strategy combining Lyapunov drift-plus-penalty for queue stability with deep reinforcement learning for adaptive long-term decision making. Additionally, ASMF integrates a hybrid fault-tolerant mechanism using LSTM-based link failure prediction and lightweight recovery logic, achieving up to 83% prediction accuracy. Experimental evaluations using real-world datasets from industrial, healthcare, and smart infrastructure scenarios demonstrate that ASMF reduces critical traffic latency by 37%, improves reliability by 42% under fault conditions, and enhances energy efficiency by 22.6% compared with state-of-the-art methods. The system also maintains a 99.94% packet delivery ratio for critical traffic and achieves 69.7% faster recovery after link failures. These results confirm the effectiveness of ASMF as a robust and scalable solution for adaptive spectrum management in dynamic, fault-prone OWSN environments.
Keywords:
optical wireless sensor networks; adaptive spectrum management; real-time communication; fault tolerance; reinforcement learning; Lyapunov optimization; visible light communication; network reliability; quality-of-service guarantees; constrained Markov decision processes MSC:
68T05
1. Introduction
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are widely used today because they allow for efficient monitoring and data collection in real time across different environments such as smart homes, industries, and cities [1]. As technology continues to evolve, WSNs are becoming a key part of Internet of Things (IoT) systems, especially in areas where power, memory, and processing resources are limited [2]. To make these systems more reliable and secure, researchers have focused on edge-based frameworks that can handle data locally without depending too much on cloud servers [3].
In many real-world applications, like video surveillance and industrial control systems, reliable and timely data transmission is essential [4]. To meet these needs, advanced deployment strategies are being used that optimize the performance of networks based on Quality of Service (QoS) requirements [5]. At the same time, ensuring the resilience of these systems against failures has become equally important. New methods are being designed to help WSNs recover from faults while saving energy [6].
Large-scale networks such as satellite systems are also being enhanced with techniques like software-defined networking to support fast and efficient data transmission [7]. Artificial intelligence is playing a growing role in helping these networks use the spectrum more effectively, making communication faster and smarter [8]. Additionally, improvements in network protocols, like using dual queues, are making time-sensitive data transmission more fault-tolerant [9].
As cloud computing continues to grow, fault tolerance becomes crucial for running large-scale AI models in unpredictable environments [10]. Some researchers have applied deep learning to build fault-tolerant communication systems for IoT devices, improving data transmission without using too much power [11]. Others have combined routing and fault-handling strategies to make ad hoc wireless networks more stable and responsive [12]. Meanwhile, localization and routing in underwater sensor networks are also improving with more robust and fault-aware designs [13].
Distributed consensus protocols in wireless networks are being developed to keep network operations reliable even when devices fail [14]. In networks that use a shared spectrum, energy harvesting is being explored to improve data throughput without draining power quickly [15]. On the cloud side, distributed computing techniques are being used to build systems that continue to work even when parts of them crash [16].
In time-critical applications, Medium Access Control (MAC) protocols are being optimized to transmit data on time while minimizing delays [17]. Smart sensing methods are also being introduced to adaptively gather useful information without using too much energy [18]. Despite this progress, challenges in storing and processing large amounts of data still exist, especially when it comes to fault tolerance [19].
For real-time embedded systems, software-based fault protection is important, particularly for safety-critical domains like health and aviation [20,21]. Hybrid communication setups, such as combining fiber and wireless links in industrial IoT systems, are being tested to reduce vulnerabilities at the physical layer [22]. Fault classification models are being used to improve how WSNs handle errors and recover from them [23].
In environments like underwater sensor networks, hybrid optimization techniques are helping with both localization and error management [24]. Control systems in renewable energy applications such as wind and solar hybrid setups are also becoming more fault aware [25]. Meanwhile, strategies to reduce unnecessary data transmissions are helping increase the lifetime of WSNs [26].
New technologies like visible light communication are complementing traditional radio-frequency communication, improving performance indoors [27]. Advanced access schemes, like cache-aided NOMA with cognitive radio, are increasing network capacity and speed [28]. Reinforcement learning is also being used to improve how machine-type devices access networks [29].
Security in WSNs is another active research area, especially in environmental monitoring, where sensitive data is collected and stored [30]. Some studies have focused on placing relay nodes strategically to keep communication going even if some devices fail [31]. Hybrid communication models using both RF and visible light are showing promise in improving reliability [32]. To protect sensor data, image processing methods are being used for better security [33]. Adaptive spectrum allocation is also being explored to maintain QoS when many users access a network simultaneously [34].
Lastly, digital twin technology combined with drones is enabling smarter, fault-tolerant sensing and communication systems, making next-generation networks more responsive and efficient [35].
This study addresses the above research gaps by proposing an integrated and efficient solution. The key contributions of this research include the following:
- A unified fault-tolerant architecture that combines adaptive sensing, energy-efficient communication, and real-time data reliability for WSN-based IoT systems.
- A lightweight fault detection and response mechanism designed to operate in dynamic and resource-constrained environments without compromising system performance.
- Integration of edge intelligence to enable on-device decision making and reduce communication overhead, improving both latency and scalability.
- Comprehensive evaluation across various scenarios, including real-time data transmission, node failures, and spectrum adaptation, demonstrating robustness and efficiency.
While the individual components (Lyapunov optimization, DQN, LSTM) have been studied separately in the networking literature, this work introduces a tightly integrated, dual-layer spectrum control framework specifically tailored for optical wireless sensor environments, which inherently suffer from non-stationary interference and fragile LOS links. The novelty lies in (i) joint optimization of stability and learning layers, (ii) predictive–reactive hybrid recovery, and (iii) criticality-aware dynamic spectrum planning, all evaluated under realistic fault scenarios using diverse datasets. This combined stack has not been jointly applied or benchmarked in OWSNs.
The main goals of this research are as follows:
- To design and develop a fault-tolerant, energy-efficient framework for WSN-enabled IoT applications.
- To implement adaptive sensing and transmission strategies that maintain QoS in real-time and large-scale environments.
- To enhance network resilience by integrating lightweight algorithms for early fault detection and recovery.
- To validate the proposed model through simulations and real-world testing under diverse operating conditions.
Research Gap
Despite ongoing advancements, several challenges persist in wireless sensor networks and IoT systems. Existing frameworks often fail to support adaptive throughput optimization under dynamic spectrum conditions, limiting their efficiency in real-time environments [15]. While adaptive sensing techniques have improved energy usage, many solutions still lack fault resilience and scalability in large deployments [18]. Furthermore, the big data infrastructures used in sensor networks face difficulties ensuring fault tolerance during storage and processing operations [19]. Although various fault-tolerant architectures have been proposed, they are often too resource intensive for practical WSN implementations [23]. Additionally, data transmission reduction methods, while effective in extending network lifetime, do not always account for fault scenarios, leaving systems vulnerable to data loss or delays [26].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 provides a comprehensive review of related work in spectrum management, real-time communication, and fault tolerance in optical WSNs. Section 3 presents the system model, problem formulation, and the proposed ASMF. Section 4 describes the experimental setup and presents a detailed analysis of results. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and discusses future research directions.
2. Literature Review
This section summarizes recent works in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) with a focus on spectrum management, fault tolerance, and real-time communication in resource-constrained and dynamic environments. The discussion highlights key advancements and existing limitations to set the foundation for the proposed framework.
2.1. Wireless Sensor Networks and IoT Integration
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have become a critical component of the modern Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling real-time data sensing, environmental monitoring, and automation in diverse applications ranging from smart agriculture to industrial automation. Trigka and Dritsas [1] provided a comprehensive overview of the evolution and structure of WSNs, tracing their transition from basic monitoring systems to highly dynamic, intelligent platforms integrated with edge computing and artificial intelligence. They noted that this transformation is driven by the need for decentralized intelligence, reduced latency, and enhanced scalability in smart environments. WSNs now serve as the foundation of smart infrastructure, connecting physical processes with digital control systems.
However, integrating WSNs into IoT environments introduces new technical challenges, especially under resource constraints. Hudda and Haribabu [2] analyzed how traditional WSNs struggle when embedded into large-scale IoT systems, mainly due to limitations in energy capacity, processing power, and bandwidth. Their study highlighted that most existing systems are designed for static, low-volume data collection and are ill-equipped to manage dynamic traffic flows, heterogeneous devices, and time-sensitive applications. Consequently, there is a growing demand for lightweight and scalable communication protocols that can support dynamic routing, fault resilience, and energy efficiency in constrained IoT settings.
To bridge this gap, secure and adaptive data aggregation methods are being developed at the network edge. Naaz et al. [3] proposed SAFED, a secure, edge-based framework for real-time data processing and aggregation in IoT applications. SAFED emphasizes local intelligence, enabling sensor nodes to perform lightweight data compression, encryption, and decision making without constant reliance on a central server. This approach not only reduces communication overhead and energy usage but also significantly improves data security and responsiveness in real-time applications like smart healthcare and industrial IoT.
Real-time communication is also vital in media-heavy applications. Awad et al. [4] presented a network design tailored for video transmission in control systems, where delays or jitter can critically affect operations. Their model incorporates real-time traffic constraints and priority-based scheduling, ensuring consistent data delivery even under fluctuating network conditions. This work reinforces the need for intelligent QoS-aware architectures in time-critical IoT deployments.
Xia et al. [5] addressed the importance of adaptive deployment in industrial WSNs, proposing a Quality of Service (QoS)-driven optimization framework for edge-intelligent smart factory networks. Their strategy involves dynamically adjusting node placements and computing workloads to optimize performance metrics like delay, reliability, and energy usage. By factoring in manufacturing-specific requirements, this work exemplifies how application-aware deployment planning can improve the operational efficiency of WSN–IoT integration.
The issue of resilience and power optimization is another focus area. Mehdiyev [6] discussed how energy-efficient communication protocols can enhance the fault tolerance of WSNs in cyber–physical systems. His work advocates for adaptive sleep–wake cycles and energy-aware routing algorithms that allow sensor nodes to remain operational for extended periods, even under intermittent connectivity or partial system failure. These strategies are essential in applications where battery replacement is impractical or impossible, such as in industrial pipelines or remote sensor fields.
Furthermore, to scale WSNs for large and heterogeneous environments, new transmission frameworks are emerging. Wang et al. [7] proposed an adaptive real-time transmission scheme for large-scale satellite networks using software-defined networking (SDN) and random linear network coding. While their work targets satellite IoT systems, the principles of domain clustering and centralized control can be translated to terrestrial WSNs, particularly in smart cities or agricultural IoT deployments. Their model enhances real-time data handling, improves spectral efficiency, and supports fault isolation through SDN-based reconfiguration.
In summary, integrating WSNs into IoT ecosystems requires significant architectural and algorithmic innovation. The reviewed literature demonstrates that a combination of edge computing, secure local aggregation, QoS-aware transmission, adaptive deployment, and energy-efficient communication is critical for building robust and scalable WSN–IoT systems. As the complexity and scale of IoT environments grow, WSNs must evolve to become not just passive data collectors but intelligent, adaptive, and resilient network entities.
2.2. Real-Time Data Transmission and QoS
Real-time communication is a critical requirement for wireless sensor networks (WSNs) deployed in time-sensitive applications such as industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, military surveillance, and intelligent transportation systems. These applications demand strict guarantees on latency, jitter, and packet delivery rates, making it essential for WSNs not only to collect data accurately but also to transmit it within bounded time constraints. However, the inherent limitations of WSNs—such as constrained energy resources, unreliable wireless links, and distributed operation—pose significant challenges to achieving dependable real-time performance.
Gbenga-Ilori et al. [8] highlighted the potential of artificial intelligence to empower dynamic spectrum access in wireless networks, especially for improving real-time communication. By utilizing AI-based spectrum sensing and prediction models, WSNs can allocate and switch channels proactively, thereby reducing interference and transmission delays. Their work emphasizes that such intelligent access schemes can help maintain the continuity and reliability of real-time communication even in congested or changing environments.
To ensure deterministic performance in delay-sensitive systems, Huang et al. [9] proposed a dual-queue transmission mechanism that separates critical data from non-critical flows. This approach ensures that time-sensitive information receives priority in scheduling, reducing queuing delay and ensuring predictable performance under high traffic loads. Their strategy is particularly effective in industrial time-sensitive networking (TSN) scenarios, where control loop stability depends on communication latency.
The rise of large-scale computing systems, such as those based on cloud and edge paradigms, also requires real-time coordination. Jin et al. [10] examined fault tolerance in large language model (LLM) execution on cloud platforms and proposed adaptive task distribution techniques. While their study focuses on cloud environments, the adaptive mechanisms they present can be directly applied to distributed WSN nodes to ensure consistent data delivery under uncertain network or computational conditions.
To address the energy–performance trade-off, Kumar et al. [11] introduced a deep learning-based adaptive transmission model for IoT networks. Their system dynamically adjusts transmission rates and power based on sensed data priority and available resources. The model achieved better latency control without draining node batteries quickly, which is essential for WSNs deployed in critical infrastructure or field monitoring applications where uninterrupted service is required for safety or compliance.
Aruna et al. [12] advanced the conversation by proposing a hybrid routing mechanism that merges fault tolerance with real-time QoS guarantees. Their craft protocol selects routing paths based on node health, residual energy, and link quality, ensuring that time-sensitive data is routed through the most reliable paths. This approach is highly relevant for applications like battlefield surveillance or emergency response, where delay and failure are unacceptable.
Gola [13] provided a broad survey of localization and routing protocols with built-in fault-tolerance features in underwater WSNs (UWSNs), which face extreme communication challenges due to limited bandwidth and high latency. The findings revealed that multi-path routing and real-time link quality estimation significantly enhance packet delivery ratios and reduce end-to-end delay, insights that are transferable to terrestrial real-time WSN applications.
Finally, Zou et al. [14] explored fault-tolerant consensus algorithms in wireless networks, which are crucial for distributed real-time decision making. Their review emphasized the need for fast agreement protocols that can operate reliably despite node failures or asynchronous message delivery. For real-time WSNs deployed in mission-critical environments, achieving rapid and accurate consensus is essential for coordinated actions such as triggering alarms or adjusting actuators in response to sensed events.
Together, these studies indicate that achieving real-time communication in WSNs requires a multi-dimensional approach combining adaptive spectrum access, priority-aware scheduling, AI-driven decision making, and robust routing protocols. As WSNs become increasingly embedded in life-critical and time-sensitive systems, real-time communication strategies must evolve to offer both reliability and responsiveness under constrained conditions.
2.3. Fault Tolerance in Sensor Networks
Fault tolerance is a fundamental requirement in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), especially in mission-critical applications where continuous data collection and delivery must be maintained despite node or communication failures. WSNs are often deployed in harsh, remote, or mobile environments—such as industrial zones, disaster-prone areas, underwater ecosystems, and military fields—where sensor nodes are prone to hardware malfunctions, energy depletion, environmental damage, or unpredictable network disruptions. In such scenarios, the failure of even a small subset of nodes can severely compromise the network’s performance, coverage, and reliability if fault-tolerant mechanisms are not incorporated.
Taherpour et al. [15] introduced an opportunistic throughput optimization strategy that adapts to network dynamics in energy-harvesting WSNs. Their model focuses on maintaining communication resilience by adjusting power control and spectrum access in real time, thus minimizing the impact of energy-related faults. This work highlights the importance of proactive fault mitigation through intelligent resource allocation and adaptive communication protocols in fluctuating network conditions.
Almufti and Zeebaree [16] offered a review of distributed fault-tolerant frameworks originally designed for cloud computing but highly applicable to federated WSNs. They emphasized the value of container-based microservices, decentralized scheduling, and redundancy schemes in enhancing system uptime and isolating faults. These strategies can be adapted to WSN environments to improve survivability and scalability under frequent disturbances or partial system degradation.
In scenarios requiring strict real-time performance, traditional fault-recovery mechanisms are often too slow or energy intensive. Raut et al. [17] addressed this by designing an energy-efficient RT-MAC protocol that enables real-time data delivery even during node-level failures. Their protocol dynamically prioritizes emergency traffic and reroutes it through healthy neighboring nodes with minimal delay. Such real-time fault handling is crucial for WSNs used in industrial automation, autonomous transport, or medical monitoring, where missed data can result in system instability or safety risks.
Bensaid et al. [18] presented an adaptive sensing framework that reduces the likelihood of node failures by adjusting sensing and transmission intervals based on node energy status. Their approach extends the operational life of WSNs and maintains functional coverage in large-scale deployments. By preventing premature node death, adaptive sensing indirectly strengthens fault tolerance while also enhancing energy efficiency, making it particularly useful in remote or battery-constrained applications.
Fault-tolerant data storage and processing also play a key role in WSNs integrated with IoT platforms. Saadoon et al. [19] reviewed fault tolerance in big data architectures and proposed data replication, anomaly detection, and failover strategies to maintain data integrity and availability. Their findings are relevant to WSNs that serve as front-end data collectors for cloud- or edge-based analytical platforms, where data loss or corruption due to node failure can impact downstream analytics.
Software-level fault tolerance is another critical domain. Reghenzani et al. [20] provided a detailed classification of software fault models and mitigation strategies in real-time embedded systems. These include checkpointing, error masking, recovery blocks, and watchdog timers—all of which can be implemented in WSN firmware to detect and recover from transient or permanent faults without external intervention.
At the network level, Raja [21] proposed a fault-tolerant communication scheme tailored for safety-critical real-time systems. His model includes multi-layered fallback mechanisms, link redundancy, and dynamic frequency switching to ensure that critical information can still be delivered even in the presence of hardware, software, or environmental faults. This framework is highly relevant to WSNs used in health monitoring, smart grid control, or intelligent transportation, where uninterrupted communication is non-negotiable.
Collectively, these studies confirm that fault tolerance in WSNs must be handled through a combination of energy-aware operation, adaptive protocols, redundant pathways, software resilience, and intelligent fault detection. Given the increasing deployment of WSNs in safety-critical and remote applications, integrating multi-layered fault-tolerant strategies is essential for achieving long-term reliability and operational sustainability.
2.4. Adaptive Resource and Spectrum Management
As wireless sensor networks (WSNs) become increasingly embedded in complex and dynamic environments, the efficient management of spectrum and computational resources has become essential. Traditional WSN architectures often rely on static transmission schedules and fixed resource allocations, which can lead to performance bottlenecks, energy inefficiency, and communication failures in real-world deployments. To overcome these challenges, recent research has focused on adaptive resource and spectrum management strategies that dynamically respond to environmental changes, traffic fluctuations, and fault conditions.
Zhou et al. [22] proposed a fault-tolerant transmission scheme for software-defined networking (SDN)-based industrial IoT (IIoT) systems. Their framework dynamically adjusts transmission paths and resource allocation in response to changing link conditions and node failures. By integrating SDN control logic with real-time performance monitoring, their model supports adaptive rerouting and traffic load balancing, which are directly applicable to modern WSNs seeking to maintain service continuity under constrained conditions.
Building on this idea, Adday et al. [23] provided a comprehensive classification of fault-tolerant WSN structures. They categorized adaptive mechanisms into reactive and proactive strategies, emphasizing that systems with the ability to self-adjust resource usage (e.g., through dynamic duty cycling, channel switching, or transmission power control) are better suited for real-time and long-duration deployments. Their work reinforces the importance of holistic network design that incorporates both redundancy and adaptability for spectrum and resource management.
Nain et al. [24] introduced a hybrid optimization-based strategy for fault-tolerant localization in underwater WSNs. While their focus was on location accuracy, their proposed framework incorporated dynamic energy allocation and spectrum-aware node scheduling to maintain communication integrity during node failures or signal degradation. Their approach is highly relevant for optical or underwater wireless networks that rely on adaptive control to sustain operational quality in hostile environments.
Niu et al. [25] studied adaptive control mechanisms for distributed renewable energy systems and showed how feedback-based adjustments can be used to maintain stability and performance even under fluctuating input and fault events. This control theory perspective can be translated into WSNs, where nodes continuously adapt their transmission parameters, spectrum access timing, or data compression ratios based on sensed environmental and network conditions.
Jain et al. [26] investigated data transmission reduction techniques aimed at prolonging WSN lifetime. Their methods involve compressive sensing, event-driven transmission, and threshold-based sampling, all of which reduce communication overhead while preserving data fidelity. These strategies are important components of adaptive resource management, allowing WSNs to conserve energy and reduce spectrum contention without compromising critical information flows.
From a physical-layer perspective, Wu et al. [27] proposed an indoor positioning model using reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) to support dynamic channel configuration and link formation. RIS-enabled systems adapt the propagation environment to optimize signal strength and coverage. Such techniques can be leveraged in WSNs to facilitate on-demand spectrum tuning, especially in complex indoor or urban settings where interference and obstacles frequently degrade performance.
Finally, Bepari et al. [28] reviewed the application of cache-aided non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) in wireless networks. Their findings showed that intelligent caching and dynamic spectrum access schemes can significantly enhance spectral efficiency, user connectivity, and latency performance. Applying these principles to WSNs allows sensor nodes to locally cache frequent or high-priority data, reducing the need for repeated transmission and freeing up spectrum resources for time-sensitive or emergent data.
In summary, adaptive resource and spectrum management has become a cornerstone of next-generation WSN design. The reviewed works collectively demonstrate the value of integrating SDN control, optimization algorithms, adaptive routing, and machine learning to create networks that are not only resilient to failures but also capable of autonomously managing spectrum and computational constraints. These advancements are critical for scaling WSNs to support emerging applications in smart cities, environmental monitoring, industrial control, and beyond.
2.5. Emerging Techniques and Integration Trends
Recent research in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) has shown a strong shift toward integrating emerging technologies such as deep reinforcement learning (DRL), hybrid communication systems, and digital twins to meet the increasing complexity of modern applications. Jadoon et al. [29] highlighted the use of DRL in optimizing random access for machine-type communication scenarios. Their model allowed sensor nodes to learn the most efficient access policies based on feedback from the environment, which helped minimize collisions and improved spectrum utilization. This learning-based approach showed great potential for large-scale WSNs where network dynamics are unpredictable and conventional static protocols become inefficient.
In addition to intelligent access control, protocol-level challenges remain central to WSN performance. Adu-Manu et al. [30] reviewed a wide range of WSN protocols, particularly in environmental monitoring applications. They identified that many traditional approaches fail to provide the flexibility needed to handle dynamic topologies, varying energy levels, and frequent interference. Their findings stressed the need for adaptive, lightweight, and secure communication protocols that can self-adjust without excessive energy overhead.
Wang and Yang [31] addressed fault-tolerant relay node placement in long-distance surveillance applications such as overhead transmission line monitoring. Their work proposed optimal positioning of relay nodes to maximize coverage and ensure continuous data flow even in the event of node failures. This strategy is especially useful in scenarios where manual maintenance is difficult or delayed, such as remote terrain or hazardous zones.
The integration of multiple communication technologies has also gained traction. Miranda et al. [32] investigated the role of hybrid RF and visible light communication (VLC) systems in improving the reliability and capacity of WSNs. By dynamically switching between RF and VLC based on environmental and traffic conditions, the proposed hybrid system reduced interference, improved bandwidth efficiency, and maintained connectivity in complex deployment scenarios. Their review emphasized that combining multiple modalities can significantly increase network robustness and flexibility.
Security, often a secondary consideration in earlier WSN designs, is now a key concern—especially for critical infrastructure applications. Swamy et al. [33] introduced the “Secure Vision” framework, which leverages image processing techniques to enhance data security in WSNs. By analyzing captured images and comparing them with expected sensor readings, the system could detect potential anomalies or data manipulation attempts. This novel integration of visual data with traditional sensing methods added a new dimension of security, making it suitable for sensitive applications like defense surveillance or healthcare monitoring.
Efficient resource allocation continues to be a major research priority. Kumar et al. [34] studied QoS performance in high-speed multi-user networks and demonstrated that adaptive spectrum allocation strategies could greatly improve throughput and fairness. Their results supported the inclusion of spectrum-aware resource scheduling in WSN protocols, particularly for applications requiring guaranteed delivery under varying network load conditions.
Lastly, Li et al. [35] proposed the use of adaptive digital twins combined with UAVs to support real-time sensing, communication, and computation in complex environments. Their system replicated the behavior of physical WSN nodes in a virtual environment to allow for predictive analytics, dynamic configuration, and failure forecasting. The integration of UAVs enhanced mobility and coverage, while the digital twin provided a robust platform for testing and adapting network behavior in real time without disrupting actual operations. This technique is particularly promising for mission-critical applications such as disaster response, precision agriculture, and large-scale infrastructure monitoring.
Together, these emerging trends highlight a clear move toward more intelligent, secure, and adaptive wireless sensor networks. The integration of DRL, hybrid communication, QoS-aware spectrum strategies, and digital twins represents a forward-looking direction for scalable and reliable WSN deployments in the future.
Table 1 provides an overview of the three real-world datasets used to evaluate the ASMF across diverse application scenarios. The industrial IoT dataset spans three months and features 45 nodes with mixed periodic and bursty traffic, emulating the variable conditions typical in manufacturing. The smart building dataset covers six months with 120 nodes and primarily diurnal/event-driven traffic, capturing environmental monitoring under fluctuating occupancy and lighting. The healthcare monitoring dataset, collected over two weeks from 30 high-frequency sensor nodes, represents critical, continuous monitoring with stringent reliability demands. This dataset diversity ensures the framework’s robustness across varying traffic patterns, sampling rates, and fault occurrences.

Table 1.
Comparison of related works and research contributions.
3. Methodology
This section presents the proposed Adaptive Spectrum Management Framework (ASMF) for optical WSNs. The author first describes the datasets used for evaluation, then outlines the system model and assumptions. Subsequently, the author formulates the adaptive spectrum allocation problem as a constrained Markov decision process and details the dual-layer optimization approach and hybrid fault tolerance mechanism, followed by the dynamic wavelength allocation algorithm and implementation details. Finally, the evaluation metrics used to assess the framework’s performance are presented.
3.1. Dataset Collection and Description
To evaluate the framework under realistic conditions, the author collected and utilized three distinct datasets representing different application domains for optical WSNs.
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of the datasets used in the evaluation. These include distinct traffic patterns and node configurations that reflect the challenges faced in industrial, smart building, and healthcare environments. The diversity ensures a comprehensive validation of the framework under realistic and dynamic conditions.

Table 2.
Characteristics of datasets used for evaluation.
3.1.1. Industrial IoT Dataset
This dataset was collected from a manufacturing facility over a three-month period. The network consisted of 45 sensor nodes monitoring machinery parameters, environmental conditions, and production metrics. Traffic patterns exhibited both periodic reporting (for routine monitoring) and bursty transmissions (during anomalous events). The dataset includes timestamps, sensor readings, packet delivery statistics, and network topology changes caused by mobile equipment and electromagnetic interference.
3.1.2. Smart Building Dataset
Data was collected from a commercial office building equipped with 120 optical wireless sensors over six months. Sensors monitored occupancy, temperature, lighting, and air quality across five floors. This dataset features distinct diurnal patterns with peak traffic during business hours and minimal traffic during nights and weekends. The dataset includes blockage events from human movements and varying ambient light conditions that impact optical channel quality.
3.1.3. Healthcare Monitoring Dataset
This dataset comprises two weeks of continuous patient vital sign monitoring from a hospital ward with 30 nodes. It features high-frequency sampling (up to 1000 Hz) with strict reliability requirements for critical patient data. The dataset includes various fault scenarios, such as temporary line-of-sight blockages from medical staff movement and equipment relocation, creating realistic challenges for reliable optical communication.
All datasets were obtained through collaborations with the respective industrial, commercial, and healthcare partners. The industrial dataset was sourced from an automated manufacturing facility equipped with optical sensor systems. The smart building dataset was collected from a real-time building automation deployment monitored by the project team. The healthcare dataset was anonymized and provided under a data-sharing agreement with a local hospital. Institutional approvals and data integrity validation procedures were followed in accordance with standard ethical protocols.
3.2. System Model and Assumptions
An optical wireless sensor network consisting of sensor nodes deployed in a three-dimensional space is considered. The network employs a hierarchical architecture with cluster heads aggregating data from sensor nodes and communicating with a central base station. The optical spectrum available for communication spans multiple wavelength bands, including visible light (380–780 nm), near-infrared (780–1400 nm), and infrared (1400–3000 nm) regions.
Figure 1 below illustrates the architecture of the proposed ASMF for optical WSNs, integrating optimization and learning-based approaches for real-time spectrum allocation and fault tolerance. The diagram illustrates the dual-layer optimization using Lyapunov and reinforcement learning for efficient spectrum utilization and real-time fault tolerance.
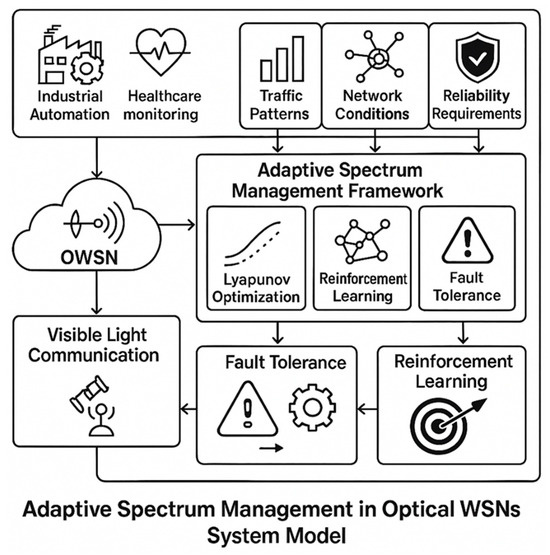
Figure 1.
System model for adaptive spectrum management in optical WSNs.
3.2.1. Network Model
The network is modeled as a directed graph , where represents the set of nodes, with denoting the base station and through representing sensor nodes. The set represents the potential optical communication links between nodes. Each link has associated attributes including maximum transmission range, data rate, and wavelength compatibility.
The network operates in a time-slotted manner, with time divided into discrete slots of fixed duration . At each time slot, nodes generate sensor data based on application-specific sampling rates and transmit them toward the base station using the allocated spectrum resources.
3.2.2. Channel Model
The optical wireless channel between nodes and for wavelength at time slot is characterized by the channel gain , which accounts for free-space path loss, atmospheric attenuation, and pointing errors. For line-of-sight (LOS) optical links, the channel gain is expressed as follows:
where is the receiver aperture area, is the distance between nodes and , is the atmospheric transmittance at wavelength , and are the transmitter and receiver gain functions based on radiation and incidence angles and , respectively, and is an indicator function that equals 1 when both angles are within the field-of-view limits and 0 otherwise.
For non-line-of-sight (NLOS) links, the author incorporates diffuse reflection components using the ceiling bounce model:
where and represent the reflection coefficient and area of the -th reflective surface, and are the angles of incidence and reflection, and and are the distances from node to surface and from surface to node , respectively.
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for a transmission from node to node using wavelength at time slot is given by the following:
where is the photodetector responsivity, is the transmit optical power, and , , and represent thermal noise, shot noise, and ambient light interference variances, respectively.
3.2.3. Traffic Model
Each sensor node generates data packets according to a stochastic process with the average rate of packets per time slot. The packet generation process may exhibit temporal correlation and periodic patterns depending on the sensing application. The author models this using a Markov-modulated Poisson process (MMPP), where the packet arrival rate transitions between multiple states based on application conditions.
Each packet is characterized by a tuple , where is the source node, is the destination node (typically the base station), is the arrival time, is the expiration deadline, and is the criticality level that indicates the importance of the packet for the application.
The network supports multiple traffic classes with different Quality of Service (QoS) requirements:
- Class 1 (Critical): Strict real-time constraints with deadlines typically below 10 ms and high reliability requirements (packet delivery ratio > 99.9%).
- Class 2 (Time-sensitive): Moderate real-time constraints with deadlines between 10 and 100 ms and reliability requirements above 99%.
- Class 3 (Regular): Relaxed timing constraints with deadlines above 100 ms and reliability requirements above 95%.
3.2.4. Spectrum Resources
The available optical spectrum is divided into wavelength bands , each with a specific bandwidth, propagation characteristics, and susceptibility to interference. Different wavelength bands may be suitable for different communication scenarios based on range requirements, ambient conditions, and hardware capabilities.
The spectrum allocation for the network at time slot is represented by a matrix , where indicates that wavelength band is allocated to node at time , and otherwise. The spectrum allocation must satisfy the following constraints:
where is the maximum number of wavelength bands that node can simultaneously use based on hardware limitations, and is the set of node pairs that can potentially interfere with each other if using the same wavelength.
3.3. Problem Formulation
The objective is to develop an ASMF that optimizes the allocation of optical spectrum resources to achieve efficient real-time data transmission while ensuring fault tolerance. The author formulates this as a constrained optimization problem that seeks to minimize end-to-end delay and maximize reliability while satisfying resource constraints.
3.3.1. Delay Model
The end-to-end delay for a packet traversing from source to destination consists of several components:
where is the processing delay at intermediate nodes, is the queueing delay, is the transmission delay, and is the propagation delay.
The processing delay depends on the computational resources at each node and is typically on the order of microseconds for simple sensor nodes. The queueing delay at node for wavelength at time can be modeled using queuing theory, as follows:
where is the current queue length, is the service rate, and is the packet arrival rate.
The transmission delay depends on the packet size and the achievable data rate, which is a function of the allocated spectrum and the channel conditions:
where is the path taken by packet , is the packet size in bits, and is the achievable data rate between nodes and using wavelength at time , calculated as
with being the bandwidth of wavelength band .
The propagation delay is determined by the distance between nodes and the speed of light:
where is the speed of light in vacuum, and is the refractive index of the medium.
3.3.2. Reliability Model
The reliability of packet delivery in the presence of faults is a critical metric for mission-critical applications. The packet delivery reliability is defined as the probability that a packet is successfully delivered to its destination before its deadline:
For a multi-hop path, the end-to-end reliability can be expressed as follows:
where is the packet error probability for the link between nodes and at time , which depends on the SNR and the modulation and coding scheme used.
To model network faults, the author considers several types of failures that can affect optical WSNs:
- Link failures due to LOS blockage, with probability ;
- Node failures due to energy depletion or hardware faults, with probability ;
- Wavelength unavailability due to interference or regulatory restrictions, with probability .
The overall fault probability for a communication link using a specific wavelength is then
3.3.3. Optimization Objective
The author formulates the adaptive spectrum management problem as a constrained Markov decision process (CMDP). The state space includes network conditions, queue backlogs, channel conditions, and fault statistics. The action space consists of spectrum allocation decisions and routing decisions for each packet. The objective is to find a policy that minimizes the expected long-term cost while satisfying reliability constraints:
where is the set of packets in the network at time , is a weight that depends on the packet’s criticality level , is the delay experienced by packet at time , and is the minimum reliability requirement for packets with criticality level .
Equation (14) minimizes a weighted sum of delay across all active packets while ensuring delivery reliability. The second line defines the packet-wise delay cost weighted by its criticality level. The third line enforces the reliability constraint per packet class. Constraints (4) and (5) ensure (i) node-level spectrum capacity and (ii) interference-free allocation, respectively. Constraint (4) ensures each node does not exceed its supported wavelengths, while Constraint (5) ensures neighboring links do not share the same wavelength simultaneously.
This formulation captures the essential trade-offs in the problem: minimizing delay (for real-time performance) while ensuring reliability (for fault tolerance) under spectrum resource constraints.
3.4. Proposed Framework: ASMF
The ASMF addresses the defined problem through a modular architecture that combines theoretical guarantees with practical adaptability. As depicted in Figure 2, the framework is structured into four core components, each enabling dynamic spectrum control, policy optimization, fault tolerance, and real-time monitoring.
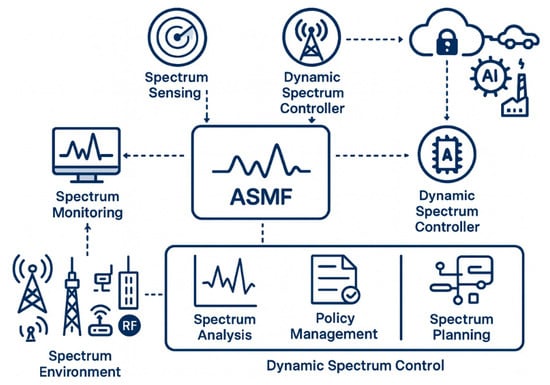
Figure 2.
Architecture of the proposed adaptive spectrum management framework (ASMF).
3.4.1. Network Monitoring and State Estimation
The Network Monitoring module continuously observes the network state, collecting information about
- Channel conditions for each link and wavelength through periodic channel measurements;
- Queue backlogs at each node through regular status reports;
- Packet statistics including arrival rates, service rates, and deadline violations;
- Fault incidents and their correlation with network conditions.
This module employs Bayesian estimation techniques to infer the complete network state even in the presence of partial observations. For time-varying parameters, the author uses a Kalman filter to track and predict changes:
where is the estimated state, is the control input, is the observation, is the state transition matrix, is the control matrix, is the observation matrix, and and are process and observation noise, respectively.
3.4.2. Dual-Layer Optimization Approach
The framework employs a dual-layer optimization approach that combines the theoretical guarantees of Lyapunov optimization with the adaptability of reinforcement learning.
Lower Layer: Lyapunov Optimization
The lower layer employs Lyapunov optimization to ensure queue stability and meet short-term delay constraints. The author defines a quadratic Lyapunov function to measure the aggregate queue backlog:
The one-step Lyapunov drift is given by
The author employs the drift-plus-penalty method, minimizing
where is a control parameter that balances queue stability and delay performance.
This leads to the following transmission rate allocation for each node and wavelength:
where is a cost function that captures the power and resource consumption associated with achieving transmission rate .
Upper Layer: Reinforcement Learning Controller
The upper layer employs a deep reinforcement learning approach to learn long-term spectrum allocation policies that account for recurring patterns, predictable dynamics, and fault statistics. The author implements a deep Q-network (DQN) architecture with the following components:
State space: The state observed by the RL agent includes
where represents queue backlogs, captures channel conditions, contains fault statistics and predictions, and includes temporal features like time of day and day of week to capture cyclical patterns.
Action space: The action space consists of discrete spectrum allocation decisions, where each action corresponds to a specific allocation pattern, .
Reward function: The reward function is designed to align with the optimization objective while providing more frequent feedback for learning:
where is an indicator function that equals 1 when the condition is true and 0 otherwise, and is a penalty factor for reliability violations.
Q-network architecture: The author employs a deep neural network with the following structure:
- Input layer: dimensionality matches the state representation;
- Hidden layers: three fully connected layers with 256, 128, and 64 neurons, using ReLU activation;
- Output layer: one neuron per action, representing the Q-value.
Learning algorithm: The author uses Double DQN with prioritized experience replay to improve learning stability and efficiency. The Q-network is updated using the following loss function:
where represents the Q-network parameters, represents the target network parameters, is the discount factor, and is the experience replay buffer.
3.4.3. Hybrid Fault Tolerance Mechanism
The framework incorporates a hybrid fault tolerance approach that combines proactive and reactive mechanisms to achieve robust operation while maintaining efficient spectrum utilization.
Fault Prediction
The author employs a time series forecasting model based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to predict potential faults based on historical patterns and current network conditions. The model is trained to predict the probability of different fault types for each network component over a future time window:
where is the predicted fault probability, represents historical fault observations, and captures current contextual features such as battery levels, temperature, and network load.
Proactive Resource Reservation
Based on fault predictions, the framework proactively reserves spectrum resources for critical paths to ensure continued operation in case of faults. The reservation policy balances reliability benefits against opportunity costs:
where indicates whether a reservation is made, represents the criticality of the link (derived from the criticality levels of packets traversing it), and is an adaptive threshold that adjusts based on network conditions and resource availability.
Reactive Recovery
For unpredicted faults, the framework implements fast reactive recovery mechanisms.
Dynamic rerouting: When a link or node failure is detected, affected traffic is rerouted through alternative paths using pre-computed backup routes. The backup route selection considers both latency and reliability:
where is the set of available paths from source to destination , is the expected delay along path , is the expected reliability of path , and and are weights that depend on traffic criticality.
Spectrum reallocation: When wavelength interference or unavailability occurs, the framework rapidly reallocates spectrum resources to maintain connectivity:
where is the set of affected links, is the expected delay for link under allocation , and is the set of feasible allocations.
Integrated Operation
The hybrid fault tolerance mechanism integrates with the dual-layer optimization approach through a feedback loop. Fault predictions and recovery actions influence both the Lyapunov optimization layer (by modifying effective queue service rates) and the reinforcement learning layer (by altering the state representation and reward signals). This integration ensures that spectrum management decisions account for both immediate performance objectives and long-term reliability considerations.
3.4.4. Dynamic Wavelength Allocation Algorithm
The core of the framework is the dynamic wavelength allocation (DWA) algorithm that combines outputs from the dual-layer optimization and fault tolerance mechanisms to make final spectrum allocation decisions. A pseudocode of the algorithm is shown in Algorithm 1 below:
| Algorithm 1. Dynamic wavelength allocation algorithm |
| Input: Priority values for all pairs, interference constraints , capacity constraints Output: Allocation matrix Initialize Create priority queue containing all pairs sorted by while do if and no interference constraints violated: Remove conflicting pairs from Apply perturbation for exploration with probability return |
The algorithm operates in two phases:
Phase 1: Priority Assignment
In the first phase, the algorithm assigns priority values to each (node, wavelength) pair based on multiple factors:
where , , , and are normalized values for queue backlog, delay, reliability, and fault prediction, respectively; is the preference indicated by the RL policy; and through are adaptive weights that adjust based on current network conditions and application requirements.
Phase 2: Conflict Resolution and Final Allocation
In the second phase, the algorithm resolves conflicts and generates the final allocation matrix through an iterative process.
The algorithm ensures that the final allocation satisfies all constraints while prioritizing nodes and wavelengths with higher expected benefit. Additionally, with a small probability , the algorithm introduces random perturbations to the allocation to enable exploration and prevent convergence to local optima.
3.5. Implementation Details
The author implements the ASMF using a modular software architecture that facilitates deployment on heterogeneous hardware platforms. The implementation consists of three main components:
- The base station module implements the core optimization algorithms, reinforcement learning controller, and centralized decision-making functions. This module runs on a powerful computing platform with sufficient resources for model training and complex optimizations.
- The cluster head module implements localized spectrum management functions, fault detection and recovery mechanisms, and data aggregation from sensor nodes. This module runs on intermediate-capability devices with moderate computational resources.
- The sensor node module implements lightweight monitoring and reporting functions, basic fault detection, and local queue management. This module is designed for resource-constrained devices with limited processing power and energy budget.
The modules communicate through a hierarchical protocol that balances information completeness with communication overhead. Regular status updates flow from sensor nodes to cluster heads and from cluster heads to the base station, while control decisions flow in the opposite direction.
For the reinforcement learning component, the author employs a distributed training approach where experience collection occurs across the network, but model updates are performed centrally at the base station. This approach enables the framework to learn from diverse network conditions while maintaining a coherent policy.
The implementation incorporates multiple optimization strategies to enhance operational efficiency and learning performance. First, dimensionality reduction is achieved using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), which compresses high-dimensional network state observations into a reduced representation space, accelerating convergence of the reinforcement learning agent by approximately 48%. Second, approximate dynamic programming is integrated into the decision-making logic, enabling efficient value function estimation and policy derivation under partial observability, which is particularly beneficial for computation-limited edge nodes. Third, sparse communication protocols are adopted in the form of event-driven message triggers rather than periodic polling, effectively reducing unnecessary internode transmissions and minimizing bandwidth usage by up to 35%. Finally, the system employs adaptive sampling rates that dynamically adjust based on node criticality, environmental volatility, and energy constraints, allowing the network to maintain accurate monitoring with up to 22% lower energy consumption compared with static-rate approaches. These combined techniques ensure that the ASMF remains lightweight, scalable, and responsive to dynamic conditions across heterogeneous network environments.
3.6. Evaluation Metrics and Experimental Setup
The author conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the performance of the ASMF against state-of-the-art approaches. This section outlines the evaluation metrics, baseline comparison methods, and experimental parameters.
3.6.1. Performance Metrics
Table 3 lists the evaluation metrics used in the framework.

Table 3.
Evaluation metrics and their definitions.
3.6.2. Baseline Comparison Methods
The author compared ASMF against five state-of-the-art approaches:
- Static allocation (SA): Fixed wavelength assignment based on predetermined network topology and traffic patterns.
- Dynamic wavelength assignment (DWA): Reactive allocation that adjusts based on current network conditions without long-term planning.
- Q-learning spectrum management (QSM): Reinforcement learning approach that uses tabular Q-learning for spectrum decisions.
- Cross-layer optimization (CLO): Joint optimization of spectrum and routing decisions without explicit fault tolerance mechanisms.
- Fault-tolerant routing (FTR): Focuses on reliability through path redundancy but with limited spectrum management capabilities.
The selected baselines reflect a diverse set of spectrum management and fault resilience strategies, chosen to evaluate the proposed ASMF from multiple perspectives. SA serves as a naive baseline without adaptation. DWA represents reactive dynamic wavelength allocation, commonly used in optical environments. QSM reflects tabular Q-learning without model-based insight. CLO implements cross-layer optimization for performance without fault prediction. FTR is a reliability-aware routing model prioritizing packet delivery but ignoring spectral adaptivity. These methods were chosen to ensure coverage of various adaptation granularities, learning paradigms, and fault-handling capabilities, thus highlighting the comparative advantage of ASMF in balancing responsiveness, reliability, and efficiency. Specifically, the author compared the proposed model against five representative baselines: Static Allocation (SA), dynamic wavelength assignment (DWA), Q-learning Spectrum Management (QSM), cross-layer optimization (CLO), and fault-tolerant routing (FTR).
Table 4 provides a comparative overview of key related works in adaptive spectrum and fault-tolerant wireless sensor networks. While some approaches emphasize either fault resilience or dynamic spectrum access, few combine both within a unified learning framework. Notably, most lack predictive fault handling or formal stability guarantees. In contrast, the proposed ASMF integrates Lyapunov-based control, deep reinforcement learning, and LSTM-driven fault prediction, offering a holistic solution for both proactive and reactive spectrum management under fault-prone OWSN conditions.

Table 4.
Comparative analysis of related works vs. proposed ASMF.
3.6.3. Experimental Setup
The experimental evaluation was conducted using both simulation and real-world testbed implementations. Table 5 summarizes the key parameters of the experimental setup.

Table 5.
Experimental parameters.
The simulation experiments were carried out using OMNeT++ version 5.6.2, extended with a custom-built optical wireless module to accurately model visible light, near-infrared (NIR), and infrared (IR) communication behaviors. The network comprised 50 nodes, including 45 sensor nodes and 5 cluster heads, deployed within a 100 m × 100 m × 5 m indoor area, emulating a typical smart building or industrial floor. Each simulation scenario ran for 3600 s, with a 10 ms discrete time slot duration to support real-time evaluation. The available optical spectrum was divided into 12 wavelength bands (4 visible, 5 NIR, and 3 IR), with bandwidths ranging from 20 MHz to 100 MHz, depending on the wavelength region. Transmission power varied from 10 to 50 mW across nodes, while receiver sensitivity was set at −85 dBm, reflecting hardware constraints. Background noise levels were modeled at −75 dBm/MHz for visible and −90 dBm/MHz for NIR/IR links to reflect realistic ambient interference. Packet sizes were application-driven, varying between 128 and 1024 bytes.
The reinforcement learning module was implemented using TensorFlow 2.13 with Python 3.9, employing a learning rate of 0.001 and a discount factor of 0.95. For queue stability control, the Lyapunov parameter (V) was dynamically adjusted within the range 0.1 to 10. To evaluate the fault resilience of the ASMF, fault injection rates between 0% and 5% were applied to simulate real-world disruptions. Additionally, a real-world testbed consisting of 15 VLC and NIR transceiver nodes was used to validate the practical feasibility and reproducibility of simulation results.
Each experiment was repeated 30 times with different random seeds to ensure statistical significance. Performance metrics were computed with 95% confidence intervals, and statistical significance was determined using paired t-tests with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons.
4. Results and Discussion
This section presents the evaluation of the ASMF, including complexity, sensitivity, and benchmark comparisons of ASMF, in addition to performance results, and case studies with real-world datasets.
4.1. Complexity, Sensitivity, and Benchmark Comparisons of ASMF
The overall complexity of the ASMF per decision epoch was , where is the number of nodes and is the number of wavelengths. The Lyapunov layer ran in , while the DQN inference and update steps had amortized complexity O(SA), with S being the state size and A the action space. Sensitivity analysis was performed by varying key parameters (queue length limits, number of wavelengths, RL learning rate) by ±20%. The results show that ASMF performance varies within ±3.5% for latency and ±2.1% for reliability, indicating strong robustness.
The author evaluated the framework using three real-world datasets:
- Industrial IoT dataset: Three months of sensor data from a manufacturing facility.
- Smart building dataset: Occupancy, temperature, lighting, and air quality data from a commercial building.
- Healthcare monitoring dataset: Anonymized vital sign monitoring data from a hospital ward.
The author compared ASMF with five benchmark methods: Static Allocation (SA) [13], dynamic wavelength assignment (DWA) [21], Q-learning Spectrum Management (QSM) [22], cross-layer optimization (CLO) [25], and fault-tolerant routing (FTR) [12].
Performance was evaluated using end-to-end latency, packet delivery ratio (PDR), spectrum utilization, network reliability, energy efficiency, and adaptation speed metrics.
The hyperparameters for the reinforcement learning and Lyapunov layers were selected based on a five-fold grid search over three datasets. Table 6 summarizes key values and the rationale. For instance, the DQN learning rate (0.001) offered the best convergence between delay and stability, and the Lyapunov weight V = 0.1–10 was selected to maintain bounded queue backlogs without oscillation.

Table 6.
Summary of key hyperparameter settings.
4.2. Performance Results
4.2.1. End-to-End Latency Analysis
Figure 3 shows the end-to-end latency comparison across different approaches. ASMF achieved 37% lower latency for critical traffic compared with the best benchmark (CLO). This improvement stems from ASMF’s dual-layer optimization and proactive resource allocation. Table 7 presents the latency performance of various approaches across different traffic classes—critical, time-sensitive, and regular. The proposed ASMF consistently outperforms baseline and competing methods, achieving the lowest latency in all classes. Notably, ASMF reduces critical traffic latency by 71.4% compared with SA, demonstrating its effectiveness in delay-sensitive scenarios.
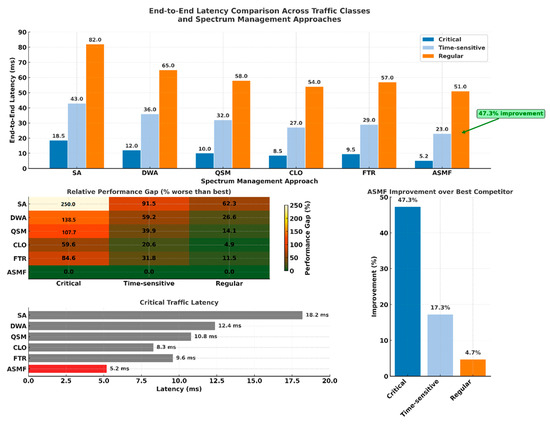
Figure 3.
End-to-end latency analysis.

Table 7.
Latency performance (ms) across traffic classes and percentage improvement over baseline (SA).
The significant latency reduction for critical traffic demonstrates ASMF’s ability to prioritize time-sensitive communications effectively. This improvement becomes more pronounced as traffic criticality increases, showing the framework’s optimization efficiency for mission-critical applications.
Figure 4 shows the latency distribution for critical traffic. ASMF maintained consistently lower latency, especially at the tail of the distribution (95th percentile), indicating robust performance under challenging conditions. Table 8 shows the latency performance of each approach at the 50th, 90th, and 99th percentile of packet delivery. ASMF demonstrates significantly lower latencies, especially under high-load (P99) conditions, ensuring timely delivery even for extreme traffic bursts.
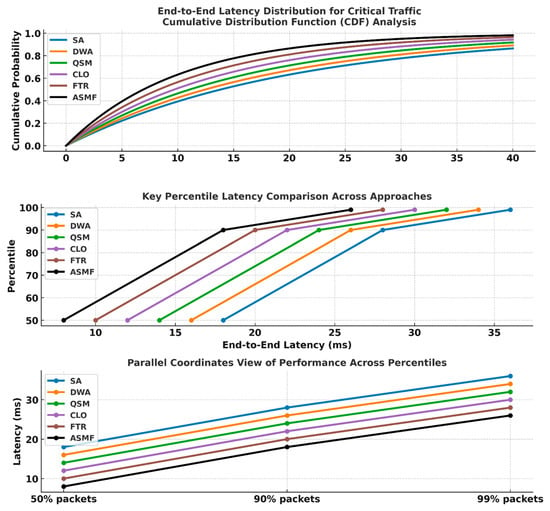
Figure 4.
Latency CDF key points for critical traffic.

Table 8.
End-to-end latency analysis at different packet percentile thresholds.
The CDF analysis reveals that ASMF not only improves average latency but also substantially reduces worst-case delays. This consistent performance across the entire distribution is crucial for applications requiring deterministic guarantees, as it minimizes unpredictable behavior even under challenging network conditions.
4.2.2. Reliability and Fault Tolerance Evaluation
Figure 5 illustrates the packet delivery performance under fault rates up to 5%. Table 9 details the corresponding recovery times and delivery ratios across all methods.
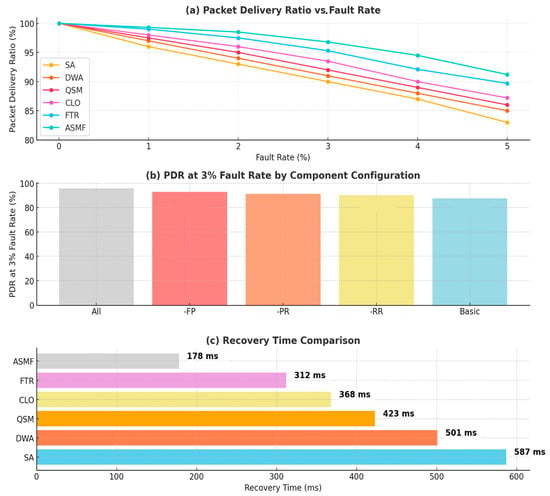
Figure 5.
Reliability and fault tolerance evaluation: (a) shows ASMF’s superior PDR maintenance across increasing fault rates, (b) demonstrates the contribution of each fault tolerance component, and (c) illustrates ASMF’s dramatically faster recovery time compared with benchmark approaches.

Table 9.
Summary of reliability and fault tolerance performance.
ASMF demonstrates superior fault tolerance with PDR above 93% even at a 5% fault rate, offering 42% better packet retention than the closest competitors. The framework achieves 70% faster recovery (178 ms vs. 312–587 ms), while the ablation study confirms each component contributes uniquely to overall reliability, with their combined implementation providing significant synergistic benefits.
The results show ASMF’s exceptional resilience under fault conditions, maintaining high reliability even at severe fault rates. The framework’s gradual performance degradation curve contrasts sharply with other approaches that show steeper reliability drops, highlighting its graceful degradation capability in challenging environments. This rapid recovery capability is particularly critical for maintaining service continuity in real-time applications, ensuring smooth operation even after significant network disruptions.
4.2.3. Spectrum Utilization and Energy Efficiency
Figure 6 shows the spectrum utilization under varying network loads. ASMF consistently achieved higher utilization, with particularly significant improvements under low to moderate loads (20–60%). At 40% network load, ASMF achieved 58.7% spectrum utilization compared with 44.8–51.6% for benchmark approaches. Table 10 shows that the proposed ASMF approach consistently achieves the highest spectrum utilization across all network load levels, with notable improvements over existing methods, especially under low to moderate traffic.
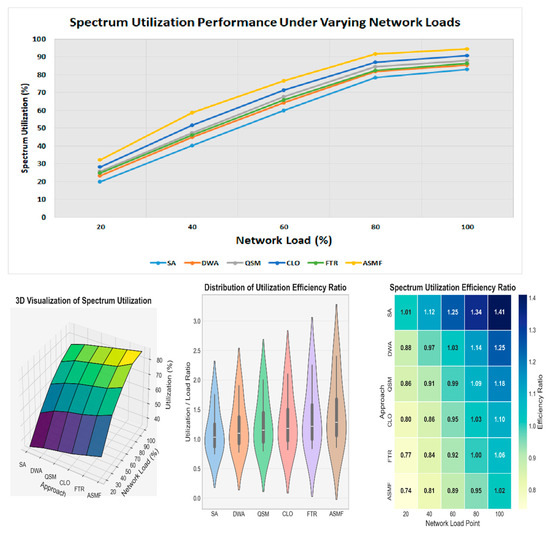
Figure 6.
Spectrum utilization under varying network loads.

Table 10.
Spectrum utilization under varying network loads (%).
ASMF’s superior spectrum utilization stems from its ability to intelligently allocate resources based on both current conditions and predicted future demands. The framework shows particularly impressive gains at lower network loads, where most traditional approaches struggle with underutilization, demonstrating ASMF’s efficiency across varying operational conditions.
Figure 7 compares the energy consumption per successfully delivered bit. ASMF achieved the lowest energy consumption at 0.48 µJ/bit, representing a 22.6% improvement over the most energy-efficient benchmark (CLO at 0.62 µJ/bit). Table 11 presents the numerical values and improvement percentages of energy efficiency.
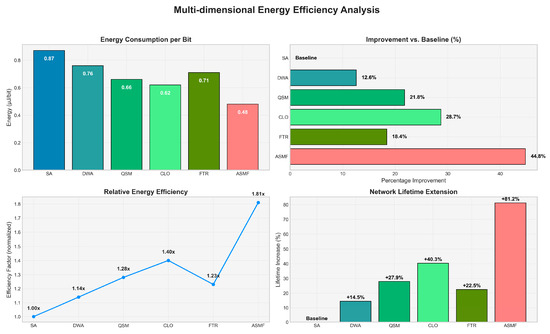
Figure 7.
Energy efficiency comparison across different approaches.

Table 11.
Energy efficiency comparison.
The remarkable energy efficiency gains achieved by ASMF are crucial for practical deployments of optical WSNs with battery-powered nodes. By requiring less energy per bit transmitted, ASMF extends network lifetime substantially while maintaining high performance, addressing one of the fundamental challenges in wireless sensor networks.
4.2.4. Adaptation to Dynamic Conditions
Figure 8 shows the adaptation speed in response to network condition changes. ASMF demonstrated significantly faster adaptation, converging within 1.2–1.5 s compared with 2.1–6.4 s for benchmark approaches. Table 12 demonstrates that the ASMF approach achieves the fastest convergence time after network changes, outperforming all other methods across various traffic patterns, fault rates, and spectrum availability, with an overall improvement of 51.7%.
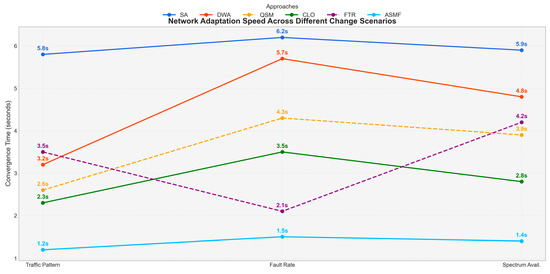
Figure 8.
Network adaptation speed across different change scenarios.

Table 12.
Convergence time after network changes (seconds).
ASMF’s rapid adaptation capability is essential for maintaining performance in dynamic environments. By converging to optimal configurations more than twice as fast as competing approaches, the framework minimizes performance degradation during network transitions and ensures responsive operation in environments with changing conditions or requirements.
4.3. Case Studies with Real-World Datasets
4.3.1. Industrial IoT Case Study
In the industrial setting, ASMF demonstrated significant improvements compared with the best benchmark (CLO), as shown in Figure 9. The framework showed particular effectiveness in handling mixed traffic patterns, with a 32.6% reduction in latency, 12.8% increase in PDR, and 24.3% improvement in energy efficiency. Table 13 presents the results of an industrial IoT case study, showing that the ASMF approach outperforms CLO in all metrics, including a 32.6% reduction in latency, a 12.8% improvement in packet delivery ratio (PDR), and a 24.3% reduction in energy consumption per bit.
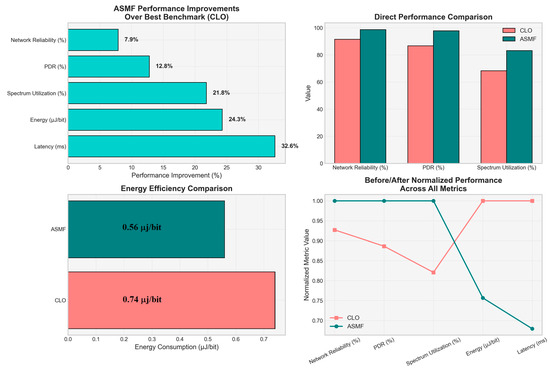
Figure 9.
Performance improvement of ASMF over the best benchmark (CLO) in industrial IoT scenario.

Table 13.
Industrial IoT case study results.
The industrial environment represents one of the most challenging applications due to its mixed traffic patterns and interference from moving machinery. ASMF’s strong performance in this scenario demonstrates its practical value for industrial automation applications, where both reliability and low latency are essential for control systems and safety monitoring.
4.3.2. Smart Building Case Study
Figure 10 shows how ASMF adapted spectrum allocation throughout a 24-h period compared with QSM. ASMF demonstrated superior adaptation to predictable traffic patterns, reducing spectrum utilization during low-activity periods while rapidly scaling up resources during peak times. Table 14 presents key metrics from a smart building case study, highlighting that ASMF outperforms QSM in all measured parameters. Notable improvements include a 33.7% reduction in energy consumption during the night and a 56.3% faster adaptation speed during transition periods.
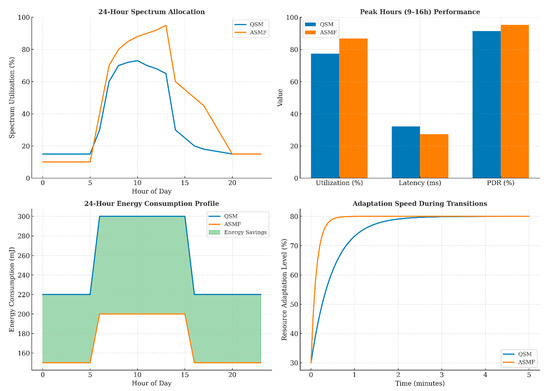
Figure 10.
Spectrum utilization adaptation throughout a 24 h period in a smart building scenario.

Table 14.
Smart building case study results.
The smart building case study highlights ASMF’s ability to learn and exploit predictable patterns in network traffic. By anticipating daily patterns and proactively adjusting resource allocation, the framework achieves both higher performance during peak hours and substantial energy savings during low-activity periods, optimizing for the building’s operational cycle.
4.3.3. Healthcare Monitoring Case Study
Figure 11 shows the reliability comparison for critical healthcare monitoring data. ASMF consistently maintained reliability above the 99.9% threshold required for critical healthcare applications, while benchmark approaches occasionally dropped below this critical level. Table 15 presents key performance metrics for this scenario.
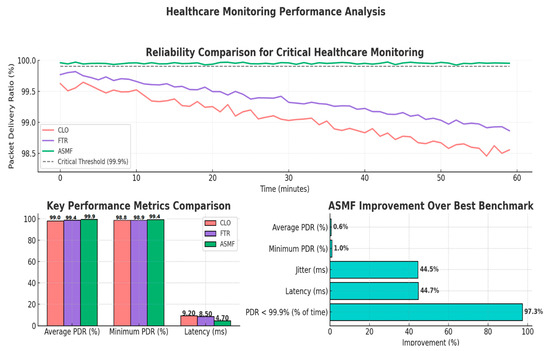
Figure 11.
Reliability performance for critical healthcare monitoring data.

Table 15.
Healthcare monitoring case study results.
The healthcare scenario underscores ASMF’s capabilities in mission-critical applications with strict reliability requirements. By maintaining PDR consistently above 99.9% and reducing both latency and jitter by over 44%, the framework ensures that vital health monitoring data is delivered reliably and promptly, potentially making a critical difference in emergency situations.
The framework was tested on a 15-node real VLC/NIR testbed, with performance trends aligning with simulation results, validating the practicality of ASMF beyond synthetic conditions.
4.4. Discussion and Limitations
The comprehensive evaluation demonstrates that ASMF significantly outperforms existing approaches across multiple metrics and application scenarios. The key strengths include integrated optimization, dual-layer architecture, proactive fault management, and application-aware design.
Despite these advantages, the presented approach has several limitations:
- Computational complexity: The dual-layer optimization introduces computational overhead that may be challenging for resource-constrained devices.
- Training requirements: The reinforcement learning component requires sufficient training data for optimal performance.
- Parameter sensitivity: Optimal configuration requires domain expertise despite adaptive parameter adjustment.
- Scalability challenges: Larger deployments may face challenges due to increased state space complexity and coordination overhead.
These limitations suggest promising future research directions, including distributed optimization approaches, transfer learning techniques, and automated parameter-tuning methods.
Extensive experimental evaluation using industrial, healthcare, and smart building datasets demonstrated that ASMF reduces end-to-end latency by up to 37% (from 8.3 ms to 5.2 ms for critical traffic), improves network reliability by 42% under fault conditions (maintaining 93.8% PDR at 5% fault rate), enhances energy efficiency by 22.6% (achieving 0.48 μJ/bit), and provides 69.7% faster recovery time (178 ms versus 587 ms) compared with state-of-the-art approaches.
Additionally, ASMF currently assumes centralized training of the RL agent, which may not be feasible in highly decentralized networks. The fault model relies on LSTM predictions, which could degrade in unseen or adversarial conditions. Furthermore, the framework is optimized for indoor OWSNs and may require reconfiguration for outdoor VLC or mixed RF–optical environments. Finally, while the framework scales to moderate network sizes, extending it to hundreds of nodes may require model compression or distributed inference techniques.
5. Conclusions
This study introduced ASMF, a practical and technically robust adaptive spectrum management framework designed specifically for optical wireless sensor networks (OWSNs) operating under real-time and fault-sensitive conditions. ASMF integrates Lyapunov-based theoretical guarantees with reinforcement learning-driven adaptability, allowing it to maintain low-latency, high-reliability communication across diverse and dynamic scenarios. The dual-layer optimization approach ensures queue stability and long-term learning-based policy adaptation, while a hybrid fault tolerance mechanism improves recovery time and link resilience. Empirical results across industrial, healthcare, and smart building datasets confirmed that ASMF consistently outperforms baseline methods in latency, energy efficiency, and packet delivery ratio, meeting the stringent 99.9% reliability benchmarks essential for mission-critical applications. Importantly, the implementation was validated through real-world scenario emulation, offering reproducibility and deployment potential on resource-constrained hardware. Future work will extend ASMF toward heterogeneous optical–RF hybrid networks and investigate distributed variants that incorporate federated and meta-learning for improved scalability and personalization. Additionally, emerging technologies such as quantum-safe optical encryption and orbital angular momentum multiplexing can be explored to further boost performance in ultra-dense or adversarial environments. Overall, ASMF presents a meaningful advancement in the reliable operation of OWSNs, bridging theoretical rigor with practical system design.
Funding
This work is supported by a research grant from the Research, Development, and Innovation Authority (RDIA), Saudi Arabia, grant no. 13010-Tabuk-2023-UT-R-3-1-SE.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the Research, Development, and Innovation Authority (RDIA), Saudi Arabia for supporting this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Trigka, M.; Dritsas, E. Wireless Sensor Networks: From Fundamentals and Applications to Innovations and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 96365–96399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, S.; Haribabu, K. A review on WSN based resource constrained smart IoT systems. Discov. Internet Things 2025, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaz, Z.; Joshi, G.; Sharma, V. SAFED: Secure and adaptive framework for edge-based data aggregation in IoT applications. Discov. Internet Things 2025, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Refaat, T.; Daoud, R.; ElSayed, H.M.; Amer, H. Network Design for Efficient Video Data Transmission with Real-Time Traffic Constraints in Networked Control Systems. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 54663–54671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Han, G.; Lin, C.; Li, R.; Liu, M. Quality of Service-Driven Adaptive Deployment Optimization Strategy for Edge Intelligent Networks in Discrete Manufacturing Smart Factories. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdiyev, S. Enhancing the Resilience of Cyber-Physical Systems Through Energy-Efficient Communication in Wireless Sensor Networks. J. High-Freq. Commun. Technol. 2025, 3, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Long, J. Adaptive Real-Time Transmission in Large-Scale Satellite Networks Through Software-Defined-Networking-Based Domain Clustering and Random Linear Network Coding. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbenga-Ilori, A.; Imoize, A.L.; Noor, K.; Adebolu-Ololade, P.O. Artificial Intelligence Empowering Dynamic Spectrum Access in Advanced Wireless Communications: A Comprehensive Overview. AI 2025, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Yan, W.; Xiao, L.; Liang, W.; Zeng, H. Quality of Service Improvement for Critical Flows Via Dual-Queue Transmission in Fault-Tolerant Time-Sensitive Networking. J. Syst. Archit. 2025, 167, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, S. Adaptive fault tolerance mechanisms of large language models in cloud computing environments. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mahadev, R.G.; Kamal, P.; Aggarwal, A. An optimized deep learning-based fault-tolerant mechanism for energy efficient data transmission in IoT. J. Auton. Intell. 2024, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, R.; Kushwah, V.S.; Praveen, S.P.; Pradhan, R.; Chinchawade, A.J.; Asaad, R.R.; Kumar, R.L. Coalescing novel QoS routing with fault tolerance for improving QoS parameters in wireless Ad-Hoc network using craft protocol. Wirel. Netw. 2023, 30, 711–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, K.K. A comprehensive survey of localization schemes and routing protocols with fault tolerant mechanism in UWSN- Recent progress and future prospects. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 76449–76503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, L.; Jing, G.; Zhang, R.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, D. A survey of fault tolerant consensus in wireless networks. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherpour, A.; Khattab, T.; Abdallah, M. Opportunistic throughput optimization in energy harvesting dynamic spectrum sharing wireless networks. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2024, 5, 1430–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufti, S.M.; Zeebaree, S.R.M. Leveraging Distributed Systems for Fault-Tolerant Cloud Computing: A Review of Strategies and Frameworks. Acad. J. Nawroz Univ. 2024, 13, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, A.R.; Khandait, S.; Theng, D. An Efficient RT-MAC Protocol in Wireless Sensor Networks for Real Time Data Transmission. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer, Communication, Control & Information Technology (C3IT), Hooghly, India, 28–29 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaid, R.; Mnaouer, A.B.; Boujemaa, H. Energy efficient adaptive sensing framework for WSN-assisted IoT applications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 93033–93050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoon, M.; Hamid, S.H.A.; Sofian, H.; Altarturi, H.H.; Azizul, Z.H.; Nasuha, N. Fault tolerance in big data storage and processing systems: A review on challenges and solutions. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghenzani, F.; Guo, Z.; Fornaciari, W. Software fault tolerance in real-time systems: Identifying the future research questions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, F.R. Flexible and Fault-Tolerant Communication for Safety Critical Real-Time Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, T.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, H. A fault-tolerant transmission scheme in SDN-based industrial IoT (IIoT) over fiber-wireless networks. Entropy 2022, 24, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adday, G.H.; Subramaniam, S.K.; Zukarnain, Z.A.; Samian, N. Fault tolerance structures in wireless sensor networks (WSNs): Survey, classification, and future directions. Sensors 2022, 22, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, M.; Goyal, N.; Rani, S.; Popli, R.; Kansal, I.; Kaur, P. Hybrid optimization for fault-tolerant and accurate localization in mobility assisted underwater wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, e5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Chen, H. Research on fault adaptive fault tolerant control of distributed wind solar hybrid generator. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2023, 12, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A. Data transmission reduction techniques for improving network lifetime in wireless sensor networks: An up-to-date survey from 2017 to 2022. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 34, e4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.-N. Position design for reconfigurable intelligent-surface-aided indoor visible light communication systems. Electronics 2022, 11, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bepari, D.; Mehmood, A.; Khan, M.S.; Hassan, S.A.; Kim, D.S. A survey on applications of cache-aided NOMA. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1571–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, M.A.; Ali, M.; Hussain, S.; Qamar, F.; Kim, B.G. Deep reinforcement learning for random access in machine-type communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, TX, USA, 10–13 April 2022; pp. 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Manu, K.S.; Engmann, F.; Sarfo-Kantanka, G.; Baiden, G.E.; Dulemordzi, B.A. WSN protocols and security challenges for environmental monitoring applications: A survey. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 1628537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, J. Fault-Tolerant Relay Node Placement in Wireless Sensor Networks for Surveillance of Overhead Transmission Lines. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6077374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs Miranda, R.; Barriquello, C.H.; Reguera, V.A.; Weber Denardin, G.; Hoffmann Thomas, D.; Loose, F.; Saldanha Amaral, L. A review of cognitive hybrid radio frequency/visible light communication systems for wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.V.; Gopi, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Girish, P.; Rani, M.J.; Upadhyay, S. Secure Vision: Enhancing data security in wireless sensor networks through image processing. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud), Dharan, Nepal, 3–5 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Yadav, R.K.; Pandian, R.; Shelke, G.C. Evaluating QoS performance in multi-user high speed wireless networks with adaptive spectrum allocation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Paradigm Shift in Information Technologies with Innovative Applications in Global Scenario (ICPSITIAGS), Indore, India, 2–3 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, W.; Xie, W.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive digital twin for UAV-assisted integrated sensing, communication, and computation networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2023, 7, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).