A Quadratic Programming Model for Fair Resource Allocation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Performance Evaluation and Team Resource Allocation
2.2. Self-Assessment Methods and Risk Mitigation
2.3. Advances in QP Models
2.4. Optimization Techniques for Fair Resource Allocation
2.5. Research Gaps
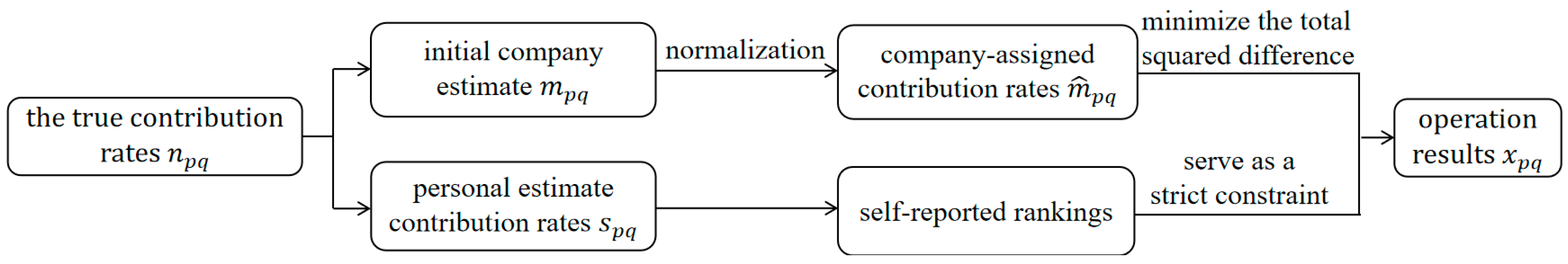
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Mathematical Description
3.2. Model Formulation
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Settings
4.2. Basic Results
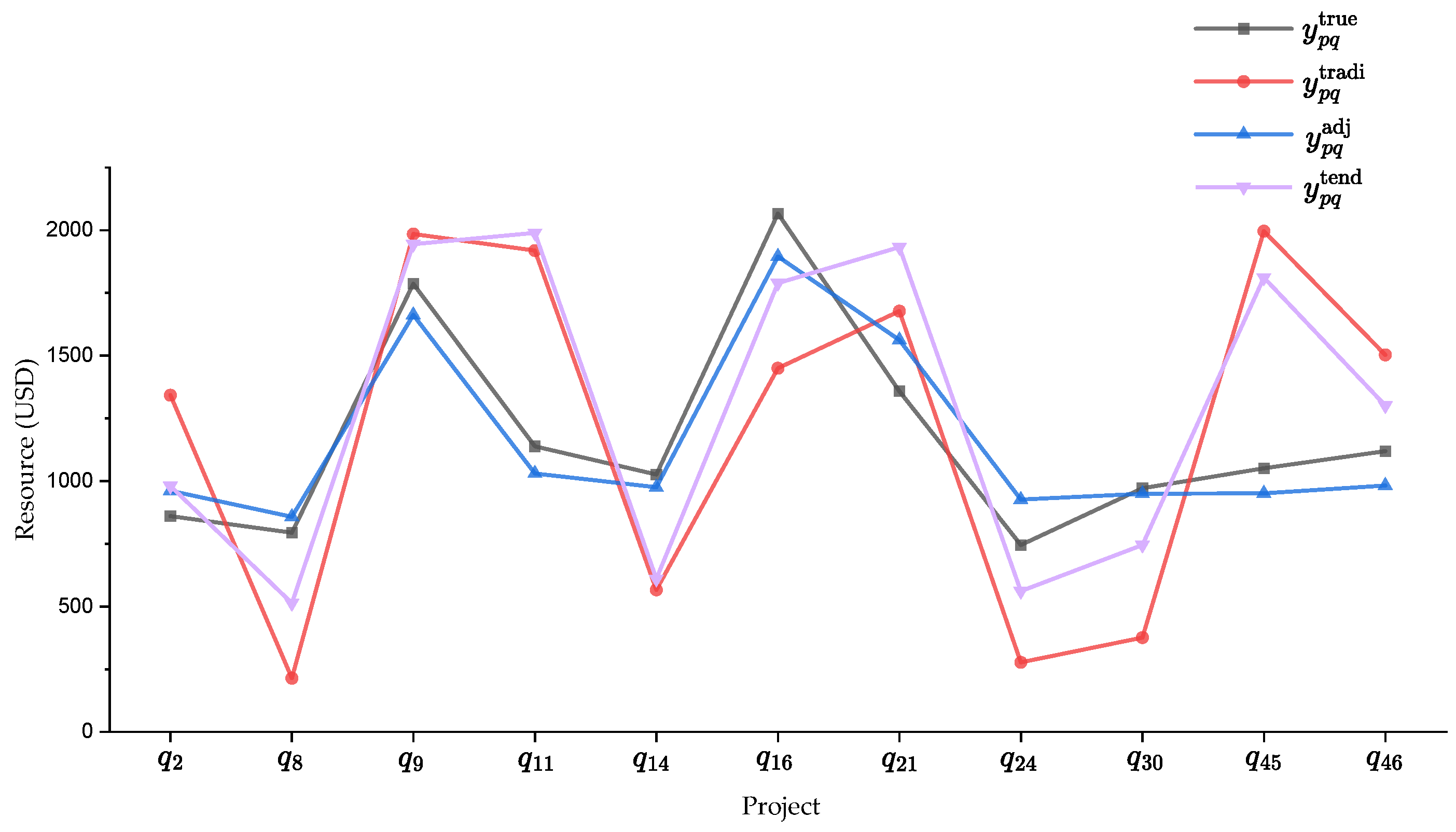
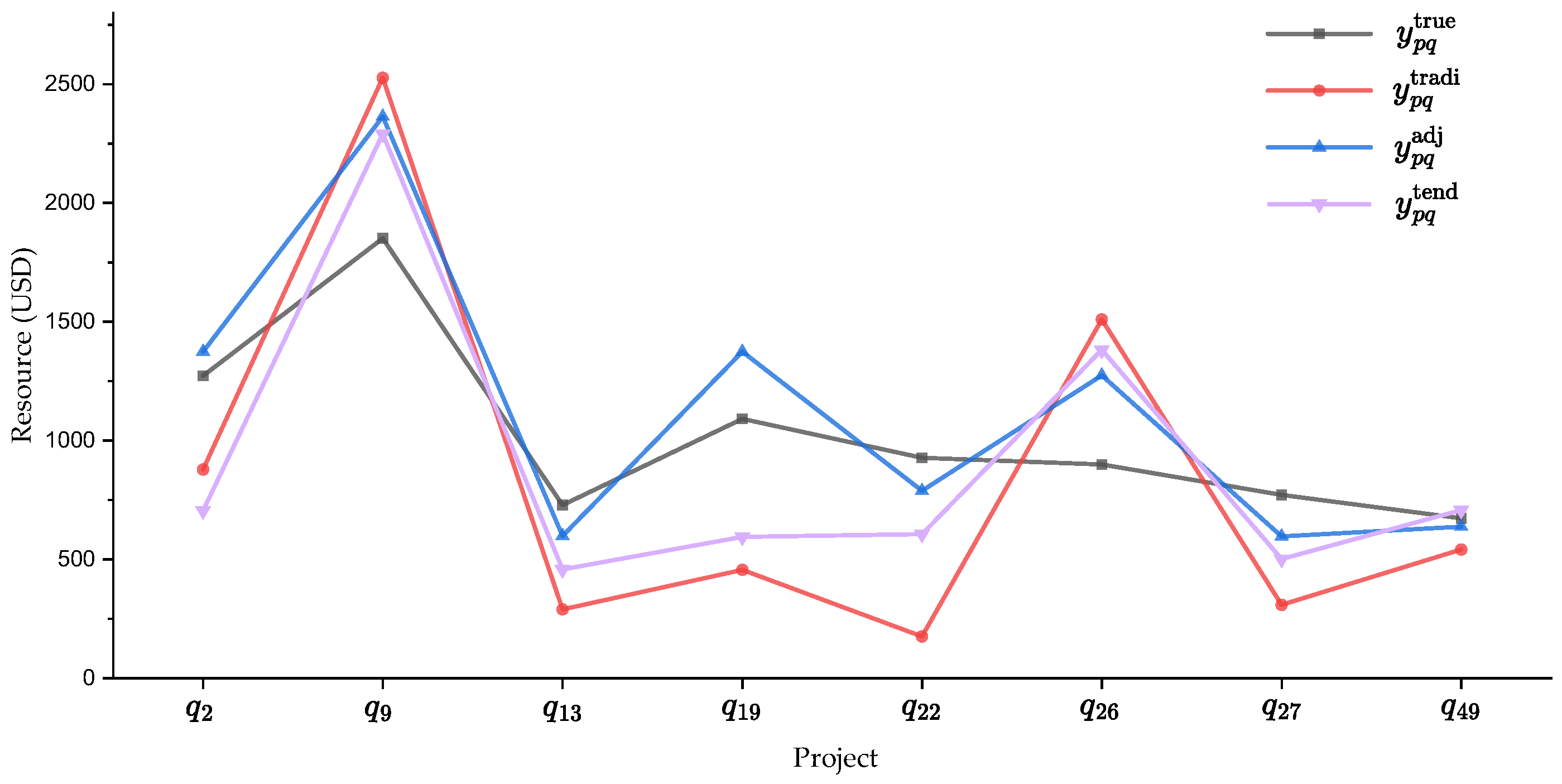
4.2.1. Evaluation of Method Effectiveness
4.2.2. Individual Resource Allocation Analysis
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argyris, N.; Karsu, Ö.; Yavuz, M. Fair resource allocation: Using welfare-based dominance constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 297, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Farias, V.F.; Trichakis, N. On the efficiency-fairness trade-off. Manag. Sci. 2012, 58, 2234–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.O.; Itir Gogus, C.; Yu, R.C.F. When does teamwork translate into improved team performance? A resource allocation perspective. Small Group Res. 2010, 41, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liden, R.C. Making a difference in the teamwork: Linking team prosocial motivation to team processes and effectiveness. Acad. Manag. J. 2015, 58, 1102–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, G.; Díaz-Vicario, A.; Mercader, C. Making steps towards improved fairness in group work assessment: The role of students’ self-and peer-assessment. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2024, 25, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.V.; Hooker, J.N. A guide to formulating fairness in an optimization model. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 326, 581–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpen, S.C. The social psychology of biased self-assessment. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2018, 82, 6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, M.; Smither, J.W. Can multi-source feedback change perceptions of goal accomplishment, self-Evaluations, and performance-related outcomes? Theory-based applications and directions for research. Pers. Psychol. 1995, 48, 803–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsu, Ö.; Morton, A. Inequity averse optimization in operational research. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 245, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejk, M.; Wyvill, M. The effect of the inclusion of self-assessment with peer assessment of contributions to a group project: A quantitative study of secret and agreed assessments. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2001, 26, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.; van der Merwe, N.; Smith, D. Peer assessment: A complementary instrument to recognise individual contributions in IS Student group projects. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Eval. 2005, 8, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ogryczak, W.; Śliwiński, T. On solving linear programs with the ordered weighted averaging objective. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 148, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, S.W.; Ilgen, D.R. Enhancing the effectiveness of work groups and teams. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2006, 7, 77–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luss, H. On equitable resource allocation problems: A lexicographic minimax approach. Oper. Res. 1999, 47, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNisi, A.S.; Murphy, K.R. Performance appraisal and performance management: 100 years of progress? J. Appl. Psychol. 2017, 102, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, P.; Tavis, A. The performance management revolution. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2016, 94, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maley, J.F.; Dabić, M.; Neher, A.; Wuersch, L.; Martin, L.; Kiessling, T. Performance management in a rapidly changing world: Implications for talent management. Manag. Decis. 2024, 62, 3085–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Performance appraisal system and its optimization method for enterprise management employees based on the kpi index. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 1937083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garalde, A.; Solabarrieta, J.; Urquijo, I.; Ortiz de Anda-Martín, I. Assessing peer teamwork competence: Adapting and validating the comprehensive assessment of team member effectiveness–short in university students. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1429485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bah, M.O.P.; Sun, Z.; Hange, U.; Edjoukou, A.J.R. Effectiveness of organizational change through employee involvement: Evidence from telecommunications and refinery companies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, M.N.M.; Sakil, M.B.H.; Al, A. Project management and visualization techniques a details study. Proj. Manag. 2024, 13, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velghe, C.; McIlquham-Schmidt, A.; Celik, P.; Storme, M.; De Spiegelaere, S. Protocol: Employee work motivation, effort, and performance under a merit pay system: A systematic review. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2024, 20, e70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Lai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, L. The optimal strategy of enterprise key resource allocation and utilization in collaborative innovation project based on evolutionary game. Mathematics 2022, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, J.A.; Pearce, M.; Rench, T.A.; Chao, G.T.; Fernandez, R.; Kozlowski, S.W. Going deep: Guidelines for building simulation-based team assessments. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2013, 22, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavoletti, E.; Stephens, R.D.; Taras, V.; Dong, L. Nationality biases in peer evaluations: The country-of-origin effect in global virtual teams. Int. Bus. Rev. 2022, 31, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tian, X.; Pang, K.W.; Cheng, Q.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S. Rightful rewards: Refining equity in team resource allocation through a data-driven optimization approach. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resce, G.; Zinilli, A.; Cerulli, G. Machine learning prediction of academic collaboration networks. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Schee, B.A.; Birrittella, T.D. Hybrid and online peer group grading: Adding assessment efficiency while maintaining perceived fairness. Mark. Educ. Rev. 2021, 31, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ni, W.; Huang, L. Fuzzy assessment of management consulting projects: Model validation and case studies. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L. Peer-and self-assessment: A case study to improve the students’ learning ability. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2016, 7, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, X.; Boud, D.; Lao, H. The effect of self-assessment on academic performance and the role of explicitness: A meta-analysis. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2023, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, L.; Roelle, J. How to support self-assessment through standards in dissimilar-solution-tasks. Learn. Instr. 2024, 94, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, A. Performance evaluation: Subjectivity, bias and judgment style in sport. Group Decis. Negot. 2020, 29, 655–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magpili, N.C.; Pazos, P. Self-managing team performance: A systematic review of multilevel input factors. Small Group Res. 2018, 49, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suls, J.; Wills, T.A. Social Comparison: Contemporary Theory and Research; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barana, A.; Boetti, G.; Marchisio, M. Self-assessment in the development of mathematical problem-solving skills. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, M. Team Metrics: Resources for Measuring and Improving Team Performance; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryczak, W.; Luss, H.; Pióro, M.; Nace, D.; Tomaszewski, A. Fair optimization and networks: A survey. J. Appl. Math. 2014, 2014, 612018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton Bernard, R.; Kermarrec, G. Peer-and self-assessment in collaborative online language-learning tasks: The role of modes and phases of regulation of learning. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2025, 40, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarl, B.A.; Moskowitz, H.; Furtan, H. Quadratic programming applications. Omega 1977, 5, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogklis, K.; Lagaris, I.E. An active-set algorithm for convex quadratic programming subject to box constraints with applications in non-linear optimization and machine learning. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kuhn, D.; Jones, C.N. PIQP: A proximal interior-point quadratic programming solver. In Proceedings of the 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Singapore, 13–15 December 2023; pp. 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shir, O.M.; Emmerich, M. Multi-objective mixed-integer quadratic models: A study on mathematical programming and evolutionary computation. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2024, 29, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, M.; Nazemi, A. Solving general convex quadratic multi-objective optimization problems via a projection neurodynamic model. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2024, 18, 2095–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Proportional-fair resource allocation for coordinated multi-point transmission in LTE-advanced. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 5355–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, J. Profit distribution in IPD projects based on weight fuzzy cooperative games. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2022, 28, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, R.; Safaoui, S.; Di Cairano, S. Real-time mixed-integer quadratic programming for vehicle decision-making and motion planning. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2024, 33, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C. Adaptive virtual team planning and coordination: A mathematical programming approach. J. Model. Manag. 2025, 20, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasescu, L.G.; Vines, A.; Bologa, A.R.; Vîrgolici, O. Data analytics for optimizing and predicting employee performance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, D.; Hssaine, C. Fair incentives for repeated engagement. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2025, 34, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, E.; Margaça, C.; García, J.C.S.; Ribeiro, C. The contribution of reward systems in the work context: A systematic review of the literature and directions for future research. J. Knowl. Econ. 2025, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H.; Akkaya, K.; Ganapati, S. Optimal incentive mechanisms for fair and equitable rewards in PoS blockchains. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Performance, Computing, and Communications Conference, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 7–9 November 2022; pp. 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Tai, W. Optimizing collaborative crowdsensing: A graph theoretical approach to team recruitment and fair incentive distribution. Sensors 2024, 24, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yeoh, W. DECAF: Learning to be fair in multi-agent resource allocation. In Proceedings of the Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, Detroit, MI, USA, 19–23 May 2025; pp. 2591–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Kononenko, I.; Sushko, H. Creation of a software development team in scrum projects. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Science and Information Technologies, Cham, Switzerland, 9–11 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.R. Enhancing Team Effectiveness: A study on the efficacy of servant leadership experiential training as an intervention. Servant Leadersh. Theory Pract. 2025, 12, 4. [Google Scholar]


| Sets, Indices, and List | |
|---|---|
| The set of all participants, | |
| The set of all projects, | |
| The set of projects that participates in, | |
| The index of the project in which participant perceives that he or she has the -th highest contribution rate among all projects in | |
| The ordered list of projects in , representing the perceived ranking by participant , from the highest to lowest contribution rate, | |
| Parameters | |
| The true contribution rate of participant to project , , , for all | |
| The company-assigned contribution rate of participant to project , , , for all | |
| The maximum error allowed in company-assigned contribution rates | |
| The personal estimate of the contribution rate of participant to project , | |
| The total amount of resources available for allocation in one project | |
| The amount of resources that participant should fairly receive from project | |
| The amount of resources allocated to participant in project based on the company-assigned contribution rates in the traditional method | |
| Decision Variables | |
| Continuous variable, indicating the adjusted contribution rate of participant to project , , for all and | |
| (%) | (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320,421 | 192,472 | 160,620 | 49.87 | 16.55 | |
| 155,236 | 121,351 | 104,040 | 32.98 | 14.27 | |
| 224,711 | 92,401 | 53,966 | 75.98 | 41.60 | |
| 328,543 | 182,130 | 104,953 | 68.06 | 42.37 | |
| 212,533 | 204,506 | 70,076 | 67.03 | 65.73 | |
| 239,176 | 175,981 | 107,578 | 55.02 | 38.87 | |
| 191,832 | 112,693 | 94,434 | 50.77 | 16.20 | |
| 390,077 | 289,110 | 220,916 | 43.37 | 23.59 | |
| 190,684 | 122,474 | 68,505 | 64.07 | 44.07 | |
| 203,759 | 144,878 | 82,570 | 59.48 | 43.01 | |
| 189,108 | 123,473 | 68,692 | 63.68 | 44.37 | |
| 267,581 | 174,974 | 85,698 | 67.97 | 51.02 | |
| 258,191 | 133,693 | 100,145 | 61.21 | 25.09 | |
| 258,223 | 185,189 | 36,364 | 85.92 | 80.36 | |
| 229,803 | 124,144 | 97,187 | 57.71 | 21.71 | |
| 272,961 | 179,267 | 162,746 | 40.38 | 9.22 | |
| 372,144 | 249,525 | 169,446 | 54.47 | 32.09 | |
| 229,809 | 208,008 | 113,912 | 50.43 | 45.24 | |
| 317,529 | 252,492 | 212,959 | 32.93 | 15.66 | |
| 210,237 | 137,679 | 76,014 | 63.84 | 44.79 |
| Participant | Project | (USD) | (USD) | (USD) | (USD) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 860 | 1342 | 980 | 961 | 79.05 | 15.83 | ||
| 794 | 214 | 513 | 857 | 89.14 | 77.58 | ||
| 1786 | 1985 | 1944 | 1662 | 37.69 | 21.52 | ||
| 1138 | 1919 | 1989 | 1030 | 86.17 | 87.31 | ||
| 1026 | 566 | 610 | 975 | 88.91 | 87.74 | ||
| 2066 | 1450 | 1789 | 1895 | 72.24 | 38.27 | ||
| 1358 | 1677 | 1932 | 1562 | 36.05 | 64.46 | ||
| 745 | 277 | 561 | 926 | 61.32 | 1.63 | ||
| 971 | 376 | 745 | 949 | 96.30 | 90.27 | ||
| 1051 | 1996 | 1811 | 951 | 89.42 | 86.84 | ||
| 1119 | 1503 | 1301 | 982 | 64.32 | 24.73 | ||
| 1272 | 878 | 705 | 1374 | 74.11 | 82.01 | ||
| 1851 | 2527 | 2291 | 2364 | 24.11 | −16.59 | ||
| 728 | 289 | 457 | 598 | 70.39 | 52.03 | ||
| 1091 | 455 | 594 | 1374 | 55.50 | 43.06 | ||
| 927 | 175 | 606 | 788 | 81.52 | 56.70 | ||
| 899 | 1510 | 1382 | 1274 | 38.63 | 22.36 | ||
| 771 | 308 | 501 | 596 | 62.20 | 35.19 | ||
| 672 | 541 | 707 | 637 | 73.28 | 0.00 |
| GID | EID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G0 | 0–8 | [7, 15, 1] | 5 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.06 |
| G1 | 9–16 | 10 | [1, 8, 1] | 2 | 0.1 | 0.06 | |
| G2 | 17–24 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.06 | |
| G3 | 25–35 | 10 | 5 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.06 | |
| G4 | 36–45 | 10 | 5 | 2 | [0.05, 0.5, 0.05] | 0.06 | |
| G5 | 46–58 | 10 | 5 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.1 | [0.02, 0.5, 0.04] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, S. A Quadratic Programming Model for Fair Resource Allocation. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162635
Tao Y, Jiang B, Cheng Q, Wang S. A Quadratic Programming Model for Fair Resource Allocation. Mathematics. 2025; 13(16):2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162635
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Yanmeng, Bo Jiang, Qixiu Cheng, and Shuaian Wang. 2025. "A Quadratic Programming Model for Fair Resource Allocation" Mathematics 13, no. 16: 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162635
APA StyleTao, Y., Jiang, B., Cheng, Q., & Wang, S. (2025). A Quadratic Programming Model for Fair Resource Allocation. Mathematics, 13(16), 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162635








