Abstract
Developing improved mathematical and numerical models of groundwater flow is crucial for monitoring and forecasting water resources. Most existing models are linear and fail to capture the complex physical processes involved in groundwater dynamics. This study aims to develop a nonlinear mathematical model for observing and forecasting changes in groundwater levels influenced by water intake wells, evaporation, and precipitation. The proposed mathematical model is formulated as a nonlinear differential equation. To solve this model, it was reduced to a dimensionless form, and the quasi-linearization method was employed to simplify the calculations. The finite difference method was then used to obtain a numerical solution. An algorithm and software were developed to demonstrate the results of the calculations. Numerical calculations performed using the developed software provide insights into the effects of water intake wells, surface evaporation, and precipitation on groundwater levels. The findings of this study hold practical significance for optimizing the sustainable use of water resources and highlighting how the location and flow rate of water intake wells impact groundwater levels.
Keywords:
groundwater; filtration; quasi-linearization method; porous medium; evaporation; precipitation; alternating-direction implicit method MSC:
76S05; 35Q35; 35R35; 93C95
1. Introduction
Groundwater is an important part of the global freshwater system and is vital to humanity. Groundwater provides an estimated 21–30% of the world’s freshwater, and 69% of global groundwater withdrawals are used in agriculture and 31% in the urban, industrial, and commercial sectors [1]. Groundwater is the largest source of liquid freshwater on Earth, providing 50% of domestic water use and approximately 25% of all water withdrawals. Today, more than 2 billion people rely on groundwater for their drinking water supply, and the sustainable management of these resources is key to global water security [2]. Climate change is placing additional stress on groundwater resources. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns directly affect groundwater systems by altering recharge, discharge, and temperature dynamics [3]. Future changes in precipitation are projected to reduce groundwater resources by 6.24–40.32% between 2040 and 2070 [4]. These changes require a fundamental rethinking of water management strategies.
Large agricultural regions are subject to continuous groundwater extraction, threatening long-term water security [5]. Climate change has become an important factor exacerbating groundwater depletion through multiple interrelated mechanisms [6,7]. Rising temperatures accelerate evaporation, reducing natural recharge while increasing water demand for irrigation and cooling [6]. Changing precipitation patterns lead to temporal and spatial mismatches between water availability and demand, forcing a greater reliance on groundwater storage during prolonged drought periods [7]. Extreme weather events, including intense precipitation and prolonged droughts, disrupt traditional recharge practices and conflict with established water management strategies [8]. The complexity of groundwater systems extends beyond simple patterns to encompass complex interactions between atmospheric processes, surface hydrology, and groundwater flow dynamics [9,10]. These interactions exhibit nonlinear characteristics that traditional linear modeling approaches cannot adequately capture [11]. For example, the relationship between precipitation and groundwater recharge is nonlinear and depends on antecedent soil moisture conditions, infiltration capacity, and evaporation rate [12,13]. Similarly, groundwater loss by evaporation follows an exponential decay law with respect to water table depth and creates complex feedback mechanisms between groundwater levels and atmospheric losses [14,15].
Industrial and municipal water abstraction through water wells introduces additional nonlinear dynamics into groundwater systems [16]. Well-induced cone formation and forced inflow from adjacent aquifers cause spatiotemporal variations in hydraulic properties that contradict conventional modeling assumptions [17,18]. The placement and operation of water wells must take these complex interactions into account to ensure sustainable water management and prevent irreversible aquifer damage such as subsidence and saltwater intrusion. Sustainable groundwater resource management requires sophisticated mathematical models that can accurately capture these multifaceted interactions [19,20]. Although current linear modeling approaches are computationally efficient, they do not account for the significant nonlinearities inherent in real groundwater systems [21]. This limitation is particularly noticeable in areas with significant water level fluctuations, where assumptions of constant permeability are not met, leading to significant prediction errors. The urgency of developing improved groundwater modeling methods is highlighted by the irreversible nature of some forms of aquifer degradation and the important role of groundwater in global food security and economic sustainability. Improved predictive models are needed to optimize water allocation strategies, develop effective water conservation measures, and ensure the long-term sustainability of groundwater-dependent communities and ecosystems [19,22].
2. Literature Review, Research Gaps, and Contributions
Early attempts to model groundwater were largely based on linear differential equations derived from Darcy’s law and the continuity equation. The seminal work of Dupuit [23] and Forchheimer [24] laid the theoretical foundations for flow analysis in unconfined aquifers using simplified assumptions about horizontal flow and hydrostatic pressure distribution. Although mathematically convenient, these models assume constant hydraulic properties and linear relationships between hydraulic gradients and flow velocity [25,26]. Subsequent developments by Theis [27], Cooper and Jacob [28], and Hantush [29] extended these approaches to dynamic conditions. The Boussinesq equation, derived for unconfined aquifers, is one of the most frequently used mathematical systems in groundwater filtration [30,31]. However, this equation linearly interprets the specific nonlinear relationship between the groundwater level and hydraulic conductivity in layered soil systems. Linear groundwater models exhibit a number of significant limitations when applied to real hydrogeological systems. The assumption of constant conductivity does not take into account the variable thickness of the saturated layer in unconfined aquifers, which leads to serious errors in areas with significant water level fluctuations [17,18]. In addition, linear models are not able to fully reflect the complex boundary conditions that arise when groundwater interacts with surface water bodies [21].
A particular challenge is accounting for saturation and release processes in linear models. The rate of precipitation infiltration varies nonlinearly with soil moisture, previous precipitation, and land surface characteristics [12,13]. Similarly, evaporation from the water table varies nonlinearly with groundwater depth and atmospheric conditions. These processes create time-dependent boundary conditions that linear models cannot accurately represent [32]. Understanding these limitations has led to the development of nonlinear approaches to groundwater modeling. Barenblatt et al. [33] were the first to apply nonlinear differential equations to describe flow in heterogeneous porous media. Their work showed that nonlinear models can account for phenomena such as preferential flow paths and edge effects that cannot be represented by linear models [34].
Subsequent studies have explored various aspects of nonlinear groundwater modeling. Zlotnik and Ledder [35] developed nonlinear models of stream–aquifer interactions, and Lockington [36] investigated nonlinear effects in coastal aquifer systems. Parlange et al. [37] studied nonlinear infiltration processes and their effects on groundwater recharge characteristics. These studies have consistently demonstrated the high performance of nonlinear models in representing complex hydrogeological processes [38]. Atmospheric water intrusion into groundwater systems involves complex nonlinear processes that depend on soil properties, moisture content, and precipitation characteristics [39]. The Richards equation provides a physically sound description of water movement in unsaturated zones, but its nonlinearity poses significant computational difficulties [40,41]. Simplified approaches such as the Green–Ampt model [42] and the Philipp equation [43] offer practical alternatives but sacrifice physical rigor for computational efficiency.
Recent studies have focused on developing hybrid approaches that combine physical accuracy with computational feasibility. Wang and Anderson [44] proposed a nonlinear infiltration model that takes into account time-varying soil properties and antecedent moisture conditions. Similarly, Chen et al. [45] developed a coupled surface–subsurface model that dynamically varies the infiltration rate with the water table and surface water availability. Many integrated geophysical methods can also be used to study the architecture and geohydrodynamics of the surface part of the Earth’s crust (which is directly related to the movement and accumulation of groundwater). The results of the studies conducted using these methods show that in order to replenish the deficit of groundwater in the designed wells and boreholes, it is necessary to use deeply weathered and fractured areas [46]. In arid and semi-arid regions, the evaporation of shallow groundwater accounts for a significant portion of the water balance. The relationship between evaporation rate and groundwater depth is highly nonlinear, with an exponential decrease that varies with soil type and climatic conditions. Gardner [47] provided a theoretical framework for modeling groundwater evaporation, but its practical application requires the consideration of additional factors such as vegetation effects and surface energy balance [48].
Modern research has deepened the understanding of evaporation processes by combining experimental and modeling studies. Feddes et al. [49] developed integrated models that relate soil moisture, groundwater depth, and evaporation rate. Salvucci [50] proposed simplified analytical solutions for specific boundary conditions, while Shah et al. [51] studied the effect of heterogeneous soil properties on evaporation characteristics. The mathematical model described in this research is presented in the form of a partial differential equation. An analytical solution to this type of equation is impossible. Therefore, a method for solving this equation using finite difference schemes was chosen. The finite difference method is widely used in groundwater modeling due to its conceptual simplicity and computational efficiency [52]. The classical implementation of finite difference schemes for modeling groundwater flow includes an implicit scheme. These methods are well suited for linear problems, but when applied to nonlinear systems they encounter stability and convergence problems [53].
The ADI method (alternating-direction implicit method) provides an optimal balance between robustness, accuracy, and computational efficiency for this problem. By splitting a two-dimensional problem into a sequence of one-dimensional problems, ADI reduces the computational complexity from O(N4) to O(N3) for directly solving a fully implicit system at a time step. This reduction is achieved by solving a system of tridiagonal equations that can be solved efficiently using the Thomas algorithm (sweep method) with O(N) operations per run. The unconditional robustness of the ADI method allows larger time steps to be used compared with explicit schemes while maintaining the accuracy of the solution [54,55]. This feature is especially important for modeling long-term groundwater behavior, where seasonal and annual variations must be taken into account. The second-order accuracy of the method in space and time ensures that the numerical errors are maintained at an acceptable level even at relatively large time steps. The challenges associated with nonlinear groundwater modeling have motivated the development of modern numerical solution methods. The quasi-linearization method, originally developed by Bellman and Kalaba [56,57], has shown promise, especially for groundwater problems. This approach transforms nonlinear differential equations into a sequence of iteratively solvable linear problems [58].
Other important advances include the application of finite element methods [59], spectral methods [60], and non-network approaches [61] to groundwater modeling. Each method has specific advantages for certain types of problems, and quasi-linearization methods are particularly effective for problems with nonlinear time boundary conditions [62]. However, despite significant progress in groundwater modeling, several important gaps remain in the current state of knowledge. Most existing nonlinear models focus on individual processes such as infiltration or evaporation, but do not provide integrated systems that consider multiple nonlinear processes simultaneously [63]. The interaction between well pumping, surface evaporation, and precipitation infiltration creates complex feedback mechanisms that cannot be adequately represented by current models. Furthermore, existing studies do not sufficiently take into account the computational challenges associated with solving nonlinear systems coupled over large spatio-temporal scales. An active area of research remains the development of efficient numerical algorithms capable of handling the complexity of integrated groundwater systems [64]. The handling of boundary conditions in nonlinear groundwater models also requires improvement. Most current approaches use simplified boundary conditions that do not take into account atmospheric processes and dynamic groundwater interactions. This limitation is particularly important for shallow groundwater problems, since in these cases the interaction between surface water and groundwater determines the overall behavior of the system [65].
This study addresses the identified shortcomings by developing an improved nonlinear mathematical model for monitoring and predicting groundwater level changes under the simultaneous influence of well pumping, evaporation, and precipitation. The main objectives of this study are as follows:
First, to formulate a comprehensive nonlinear differential equation that integrates the effects of well pumping, surface evaporation, and precipitation infiltration into a single mathematical framework. This integrated approach represents a significant advance over existing models that treat these processes separately or use simplified linear assumptions.
Second, to develop an efficient numerical solution methodology based on a quasi-linearization method combined with finite difference scheme techniques. The proposed approach transforms the nonlinear problem into a sequence of linear systems that can be solved using established computational methods, thereby providing both accuracy and computational efficiency.
The main contribution of this work is the modeling of complex groundwater systems subject to significant nonlinear effects due to variable boundary conditions and heterogeneous aquifer properties. The developed model fills a significant gap in existing research, while taking into account many nonlinear processes that determine the behavior of groundwater in real systems. The practical significance of this study lies in improving water management strategies, expanding the ability to predict changes in groundwater levels, and better understanding the interactions between atmospheric processes and subsurface hydrology. The developed methodology serves as a valuable tool for water resource managers to optimize the placement and use of water intake wells in groundwater extraction systems.
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Formulation
Let us consider the groundwater flow in a system reflecting a heterogeneous unconfined aquifer underlain by a horizontal confining bed from below and a free surface from above, considering the infiltration of atmospheric waters, as well as evaporation from the groundwater level under the influence of water withdrawal. We take the horizontal confining bed as a reference plane. The reference plane changes little throughout the entire filtration area. The model considers various aquifer materials with different hydraulic properties. Table 1 presents the characteristic hydraulic parameters used in the simulations.

Table 1.
Hydraulic parameters for different aquifer materials (values from Ref. [65]).
These values are taken from standard hydrogeological handbooks and represent typical ranges for unconsolidated sediments. The choice of these materials reflects the general geological structure of many aquatic systems, where layers of materials with different permeabilities create complex flow patterns. The mathematical model of the problem under study describes the process of filtration of groundwater considering the influence of water intake wells, evaporation, and other external factors. The process under study, with the common boundary conditions in the directions of the -axes, is expressed as a differential equation as follows:
The initial condition for the problem is as follows:
The boundary conditions are expressed as follows:
where are spatial coordinates (m), is the groundwater level (m), is the hydraulic conductivity (m/day), is the free water yield coefficient, is time (day), is precipitation (m/day), is evaporation from the groundwater level (m/day), is the mass exchange coefficient across the calculated boundary (day−1), is the well flow rate (m3/day), , is the Dirac delta function governed by , is the number of wells, is the flow rate of the -th well, is the initial value of the groundwater level (m), and is the characteristic value of the profile length (m).
The following relationship is taken to calculate precipitation:
where is the average monthly change in precipitation, is the annual change in precipitation, and is the cyclic frequency of the monthly change. To calculate evaporation, the following relationship was used:
where is the average monthly change in evaporation, is the amplitude of the annual change in evaporation, and is the cyclic frequency of the monthly change.
These formulas are widely used in groundwater modeling to represent the seasonal dynamics of hydrological flows. Similar expressions were employed in the models described by Feddes et al. and Penman for modeling absorption and evaporation in the root zone. Brutsaert also applied harmonic functions to model seasonal effects on surface and subsurface hydrological systems.
Equation (1) describes the movement of groundwater based on several basic physical laws. First, the movement of water in a porous medium is described by Darcy’s law, which means that the flow of water depends on the pressure gradient and the filtration coefficient. The law of the conservation of mass is also taken into account, which takes into account the balance between the amount of water entering and leaving the system. In addition, the Boussinesq approximation is used to simplify the model. According to this approach, small changes in density during the free surface flow of water are ignored. By combining these three basic principles, a basic equation was formed that reflects the movement of groundwater in time and space.
3.2. Solution of the Problem
Since the problem is nonlinear, its analytical solution presents significant difficulties. To simplify the problem (1)–(3), we introduce dimensionless quantities. This includes converting the variables and parameters into a dimensionless form. This approach will simplify the equations and reduce the complexity of their numerical solution. For the problem, we can represent dimensionless quantities as follows:
where is the characteristic value of the filtration coefficients. Based on the introduced dimensionless quantities, we reduce Equation (1) to the dimensionless form as follows:
where
The boundary conditions are as follows:
To simplify, we exclude the “*” symbol in Equation (4) and the boundary conditions (5) as follows:
The boundary conditions are as follows:
where .
For the numerical solution of (6)–(7) at this stage we construct the following square grid as follows:
where —grid domain, —step along the —axis, —step along the —axis, —number of nodes in the discrete layer, and —time step. In this area, the algorithmic principle of an alternating-direction implicit method is used based on variable directions when setting the problem using the finite difference method. The transition from the -th time layer to the layer is performed in two stages with a step of 0.5. As a result, Equation (6) leads to a successive solution of two systems of finite difference equations. Then, these equations can be written as the following system of finite difference equations in time layers and for internal nodes based on the longitudinal-transverse scheme.
For the time layer :
where
For the time layer :
The resulting finite difference equations must be solved. For this purpose, the quasi-linearization method is initially used. This method is used because of the nonlinearity of the level function. According to this method, the nonlinear parts of the system of finite difference Equations (8) and (9) are expressed as follows:
where —an approximate value of function , refined in the iteration process . Using the linearization Formula (10), we write Equations (8) and (9) with respect to the square of the level function . In this case, the finite difference equation can be written as a quasi-linear difference as follows in Equation (11):
We simplify and formulate Equation (11) as follows:
where
For Equation (9), it can be written as a quasi-linear difference equation as follows:
We simplify and formulate Equation (13) as follows:
where
Using a second-order approximation for the boundary conditions allows us to achieve accurate results. In this approach, we replace the derivatives with second-order finite differences. This method provides a more precise discretization and is particularly effective for calculating values close to boundary points.
The approximation in the direction is as follows:
The approximation in the direction is as follows:
We simplify the boundary conditions using the linearization Formula (10). The approximation in the direction has the following form:
The approximation in the direction has the following form:
From the boundary condition (15) and the finite difference Equation (12), we derive the following system of three-point equations for the time layer :
Similarly, by using the finite difference Equation (14) and the approximation of the boundary conditions (16), we form a system of three-point equations for the time layer as follows:
To solve the systems of Equations (17) and (18), we apply the sweep method (Thomas algorithm) [51]. Using the system of algebraic Equations (17) and (18) by the sweep method, we calculate the desired variables using recurrent relations as follows:
In the recurrent relations (19) and (20), the sweep coefficients are calculated as follows:
In these recurrent relations, coefficients are determined using Equations (17) and (19), while coefficients are found using Equations (18) and (20). By utilizing Equations (19) and (20), we generate a sequence of successive approximations. In this case, the convergence of the iterative process was checked using conditions , where is the accuracy of the iterative process, and is the number of iterations.
The numerical solution of the nonlinear groundwater flow model was implemented using the Python 3.9.12 programming language. The computational framework utilized NumPy 1.21.5 for array operations and numerical computations, SciPy 1.7.3 for sparse matrix solutions required in the Thomas algorithm implementation, and Matplotlib 3.5.1 for the visualization of the results. The development and testing were conducted in the Jupyter Lab environment, which facilitated interactive debugging and the iterative refinement of the numerical scheme. Based on the calculation method described above, a computer algorithm was developed. Below is the computer algorithm (Algorithm 1) used to solve this problem.
| Algorithm 1: Groundwater_Nonlinear_ADI_Solver |
| INPUT: - Physical parameters: K, μ, α, q_i, f0, f_amp, γ0, γ_amp, ω - Grid settings: Lx, Ly, Nx, Ny, T_end, Δt - Initial groundwater level: h0(x, y) - Tolerance ε for convergence - Max_iter (maximum iteration count) - Well locations and pumping rates OUTPUT: - Water level distribution h(x, y, t) over time - Graphs of h(x, y, t) BEGIN Step 1: Convert model parameters to dimensionless form - Calculate dimensionless coefficients and variables Step 2: Generate computational grid - Set Δx = Lx / Nx, Δy = Ly / Ny - Create 2D spatial grid (i = 1...Nx, j = 1...Ny) - Time steps: Nt = T_end / Δt Step 3: Initialize water level h(i,j,0) = h0 - For all grid points (i,j), set h[i][j][0] = initial condition Step 4: Discretize delta function for wells For each well: - Locate nearest grid cell (i_w, j_w) - Add delta_well[i_w][j_w] = q_i (scaled) Step 5: FOR each time step n = 0 to Nt − 1 DO Initialize h_old = h(:,:,n) REPEAT (iteration loop k = 1 to Max_iter) Step 5.1: ADI Step 1—solve in x-direction FOR each y-layer (fixed j) - Linearize nonlinear terms using previous h - Set up tridiagonal system A*h = b using Thomas algorithm - Solve for intermediate h_star[i][j] Step 5.2: ADI Step 2—solve in y-direction FOR each x-column (fixed i) - Linearize again using h_star - Set up tridiagonal system A*h = b - Solve for updated h[i][j][n+1] Step 5.3: Check convergence IF max(|h_new − h_old|) < ε THEN BREAK ELSE update h_old = h_new END REPEAT END FOR Step 6: Post-processing - Generate contour plots and time-series graphs of h(x,y,t) - Export results END Algorithm |
The presented algorithm represents a carefully balanced approach that combines computational efficiency and numerical accuracy. The integration of quasi-linearization with the ADI method creates a complementary combination that effectively addresses problems related to nonlinear groundwater filtration equations. The modular structure of the algorithm allows for its further expansion, for example, by incorporating additional physical processes such as the dynamics of unsaturated zones or density-dependent flow. Moreover, the dimensionless formulation enhances the algorithm’s generalizability, enabling its easy application to aquifer systems of various scales and characteristics. During implementation, numerical stability is prioritized through the careful consideration of boundary conditions and source factors, ensuring reliable performance across a wide range of hydrogeological conditions.
4. Results and Discussion
This section presents the results of the numerical simulations of groundwater level changes under different hydrogeological conditions and use scenarios. The analysis considers the influence of well abstraction rate, aquifer characteristics, and time dynamics on groundwater level changes.
4.1. Selection of Settings and Computational Parameters
The numerical experiments used a computational domain of 1000 m × 1000 m, which was discretized by a 100 × 100 grid with a uniform step of Δx = Δy = 10 m. The time steps were adjusted based on material properties, Δt = 0.01 days for fine sand, Δt = 0.1 days for silt, and Δt = 1.0 days for clay, accounting for the significant differences in hydraulic conductivity between these materials.
The model was tested for four different aquifer materials: fine sand (k = 10 m/day, μ = 0.25), coarse sand (k = 25 m/day, μ = 0.30), silt (k = 0.1 m/day, μ = 0.10), and clay (k = 0.001 m/day, μ = 0.02). These parameters represent typical values for unconsolidated sediments and cover the full spectrum of materials commonly found in aquifer systems.
The initial groundwater level was set uniformly over the entire area m, which corresponds to the conditions of an unconfined aquifer. The boundary conditions are type III (Robin) conditions with a mass transfer coefficient of α = 0.1 day−1, simulating a partial hydraulic connection with the surrounding water bodies. The precipitation and evaporation rates follow seasonal patterns: favy = 0.002 m/day, ωamp = 0.001 m/day, favy = 0.003 m/day, and ωamp = 0.0015 m/day, which correspond to the typical conditions of a semi-arid climate.
4.2. Convergence of the Numerical Solution and Computational Efficiency
Before presenting the physical results, we checked the convergence properties of the numerical solution. The quasi-linearization method typically converged within 3–5 time step iterations, with discrepancies falling below the acceptable limit of 10−6. Grid independence was confirmed by comparing solutions on 50 × 50, 100 × 100, and 200 × 200 grids, with the difference in estimated water levels being less than 0.5%. The ADI method demonstrated remarkable robustness characteristics, allowing 10–100 times more time steps than open methods. Computational efficiency was further improved by vectorizing the operations, reducing the solution time to approximately 2.5 s over one simulated day on a standard workstation with an Intel Core i7 processor and 16 GB of RAM.
4.3. Response of Fine Sand Aquifer to Multiple Well Configurations
4.3.1. Low Water Intake Rate (3–5 m3/Day)
Figure 1 illustrates the changes in groundwater levels within a fine sandy aquifer, resulting from water extraction at different rates from two wells. The wells are positioned at distinct locations within the modeling area—one in the northwestern part (200, 500) and the other in the southeastern part (700, 300). Part (a) of the figure depicts a scenario with high precipitation influence (f = 0.06), while part (b) shows a situation with a stronger evaporation effect (ω = 0.02).
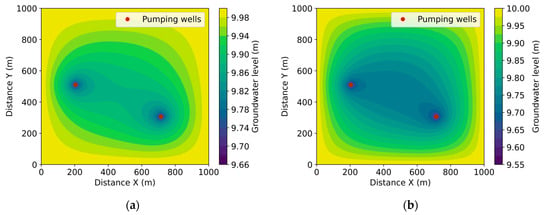
Figure 1.
Change in groundwater level over time with well flow rates of 3 and 5 m3/day, (a) , (b) .
A distinct depression cone forms around each well. A deeper cone is observed surrounding the well with a higher water extraction rate, where the water level drops from 9.66 m to 9.55 m. A hydraulic interference zone emerges between the two wells, creating a saddle-shaped water level distribution. This zone demonstrates the mutual hydraulic interaction between the wells.
4.3.2. State of Large-Volume Water Extraction (200 m3/Day)
Figure 2 depicts a complex hydraulic situation resulting from the simultaneous intensive water extraction from five wells at a rate of 200 m3/day. The wells are strategically positioned—one central well is located at coordinates (500, 500), and four peripheral wells are situated at the corners of the modeling area. Part (a) of the figure takes into account the effect of evaporation (ω = 0.0015), while part (b) considers the effect of precipitation (f = 0.006).
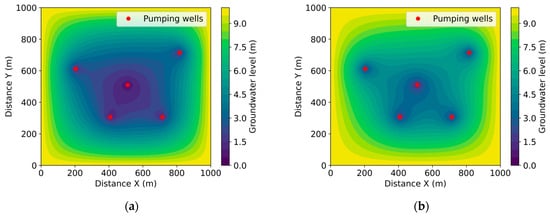
Figure 2.
Change in groundwater level over time with well flow rate of 200 m3/day (a) , (b) .
The combined effect of the five wells creates a widespread and complex-shaped depression field across the entire area. In the central part, the water level drops to its lowest point—4.5 m, which represents a 55% decrease from the initial level of 10 m. Individual depression cones form around each well, but due to their interaction, complex interference patterns emerge.
The corner wells intensify boundary effects and lead to an uneven distribution of the water level. The central well has the greatest impact, with its depression cone merging with the cones of other wells to create an overall depression field. This demonstrates the complex hydraulic characteristics of multi-well systems and the necessity for caution in their design.
4.4. Clay Aquifer Response and Comparative Analysis
Low-Permeability State of the Aquifer
Figure 3 illustrates the sequence of changes occurring over time in a clay aquifer (k = 0.001 m/day, μ = 0.02) when extracting water from two wells at a rate of 20 m3 per day. The wells are located in the central zone. Three time points are depicted: (a) shows the initial stage (f = 0.001), (b) shows the medium-term state (ω = 0.008), and (c) shows the long-term stable state (f = 0.006).
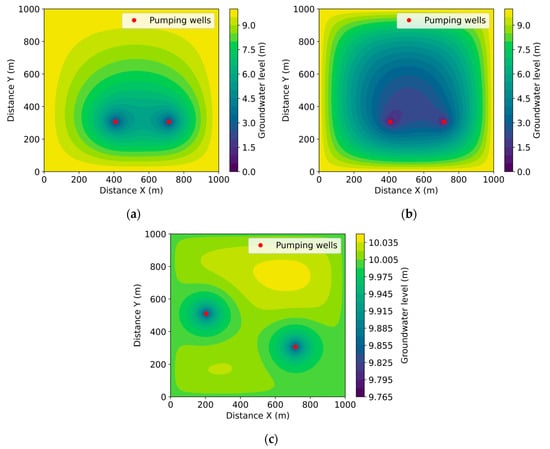
Figure 3.
Change in groundwater level over time with well flow rate of 20 m3/day, (a) , (b) , (c) .
A characteristic feature of the clay aquifer is the very slow development of depression cones. In the initial stage, changes in water level are observed only near the wells. Over time, depression zones gradually expand, but their rate of spread is significantly lower compared with sandy aquifers.
Even in the long-term state, depression cones occupy a relatively limited area. The maximum drawdown is around 3 m, and the radius of influence does not exceed 200–250 m. This occurs as a result of the clay’s low hydraulic conductivity and small specific yield coefficient.
4.5. Impact of Wells Distributed Across the Field
To study the significance of well placement, we conducted a sensitivity analysis by changing their positions while maintaining a constant overall utilization level. Three different arrangement patterns were tested: wells clustered in one quadrant, wells evenly distributed, and wells arranged diagonally.
The clustered configuration led to the strongest localized water table drawdown, with maximum values 40% higher than in the distributed configuration. However, the area of drawdown remained smaller, which allowed for the preservation of untouched zones to protect the environment. The even distribution minimized the maximum water table drawdown but led to widespread moderate impacts across the entire area. The diagonal placement resulted in the formation of an elongated depression cone, which could be aligned parallel to the natural groundwater flow directions.
These results indicate that the optimal well placement depends on management objectives. While aiming to minimize the maximum pressure drawdown favors dispersed well placement, protecting specific areas may justify concentrated extraction despite strong localized impacts.
4.6. Seasonal Changes and Climate Impact
When the modeling was extended to annual cycles, significant seasonal dynamics were identified. During periods of high precipitation (winter months), the water level partially recovered, with recharge rates exceeding evaporation by 0.002 m/day. Summer conditions reversed this trend, creating additional pressure beyond water extraction from wells.
Seasonal fluctuations of ±0.5 m in the sandy aquifer were superimposed on the water level decline caused by extraction. The clay aquifer, due to its low vertical permeability, limited the infiltration of precipitation and showed relatively little seasonal impact. This differential response indicates that the consequences of climate change vary significantly depending on the type of aquifer, with permeable systems being more sensitive to changes in precipitation patterns.
4.7. Model Validation and Statistical Performance
The validation of the nonlinear groundwater flow model presents unique challenges due to the absence of analytical solutions for the complex multi-well system with evaporation and precipitation effects. Therefore, a comprehensive validation framework was developed to ensure model reliability through multiple verification approaches.
4.7.1. Numerical Convergence Analysis
The numerical stability and accuracy of the model were systematically evaluated through grid refinement studies. Three computational grids with resolutions of 50 × 50, 100 × 100, and 200 × 200 nodes were tested while maintaining identical physical parameters and boundary conditions. The convergence analysis revealed that the relative difference in computed water levels between successive grid refinements remained below 0.5%, confirming that the 100 × 100 grid provides adequate spatial resolution for accurate results while maintaining computational efficiency.
Temporal convergence was assessed by comparing solutions obtained with time steps of Δt, Δt/2, and Δt/4. The maximum relative error between successive refinements was less than 0.1%, demonstrating the temporal stability of the ADI numerical scheme. The quasi-linearization method achieved convergence within 3–5 iterations per time step, with residuals consistently falling below 10−6 meters.
4.7.2. Mass Balance Verification
A fundamental requirement for any groundwater flow model is the conservation of mass. At each time step, the global mass balance was computed as follows:
Mass Balance Error = (Total Inflow − Total Outflow − Change in Storage)/Total Volume.
The mass balance error remained below 0.05% throughout all simulation scenarios, confirming the conservative nature of the numerical implementation. For the intensive pumping scenario (200 m3/day), the cumulative mass balance over 30 days showed a total extraction of 6000 m3, balanced by a lateral boundary inflow of 4920 m3 and storage depletion of 1080 m3, with a residual error of less than 3 m3 (0.05%).
4.7.3. Physical Consistency Assessment
The model results were evaluated against established hydrogeological principles to ensure physical plausibility. The computed drawdown patterns exhibited the following expected characteristics:
- −
- Logarithmic decay of drawdown with radial distance from pumping wells.
- −
- Appropriate time-lag responses in low-permeability formations.
- −
- Realistic superposition effects in multi-well systems.
- −
- Physically consistent boundary flux patterns.
The contrast in response times between fine sand (k = 10 m/day) and clay (k = 0.001 m/day) aquifers aligned with theoretical expectations based on hydraulic diffusivity. The clay aquifer’s prolonged transient behavior and limited spatial extent of influence reflect its low hydraulic diffusivity (T/S ≈ 0.036 m2/day) compared with the sand aquifer (T/S ≈ 40 m2/day).
4.7.4. Sensitivity Analysis Results
Model robustness was assessed through a systematic parameter sensitivity analysis. Key parameters were varied within the following physically reasonable ranges:
- −
- Hydraulic conductivity: ±30% from baseline values.
- −
- Specific yield: ±20% from baseline values.
- −
- Boundary mass transfer coefficient: ±50% from baseline values.
- −
- Evaporation and precipitation rates: ±25% from baseline values.
The sensitivity analysis revealed that hydraulic conductivity was the most influential parameter, with a 30% reduction resulting in an approximately 42% increase in maximum drawdown. Specific yield variations of ±20% produced inversely proportional changes in drawdown rates of approximately ±15%. These sensitivity patterns confirm that the model correctly represents the governing physical processes.
4.7.5. Statistical Performance Metrics
Given the absence of field data or analytical solutions for direct comparison, the following statistical metrics were computed to assess model performance (Table 2):

Table 2.
Statistical performance indicators for model validation.
The parameter sensitivity R2 values indicate strong linear relationships between parameter variations and model responses, confirming predictable model behavior. The low convergence errors across all metrics demonstrate the numerical reliability of the solution methodology.
4.8. Temporal Dynamics and Vertical Distribution of Groundwater Levels
The temporal evolution of groundwater levels and their vertical distribution represent critical aspects of aquifer behavior that directly influence water resource management decisions. This section presents comprehensive time series analyses and depth-resolved data for each aquifer type examined in our study.
4.8.1. Time Series Analysis of Water Level Fluctuations
Figure 4 presents continuous time series data spanning 365 days for representative monitoring points in each aquifer type. The data reveals distinct behavioral patterns that correlate strongly with hydraulic conductivity values. Clay aquifers exhibit prolonged drawdown periods extending over 60–90 days before reaching quasi-steady state conditions, with water level fluctuations ranging from 2.3 to 3.8 m below the initial static level. In contrast, coarse sand aquifers demonstrate rapid equilibration within 2–5 days, with maximum drawdowns limited to 0.8–1.2 m.
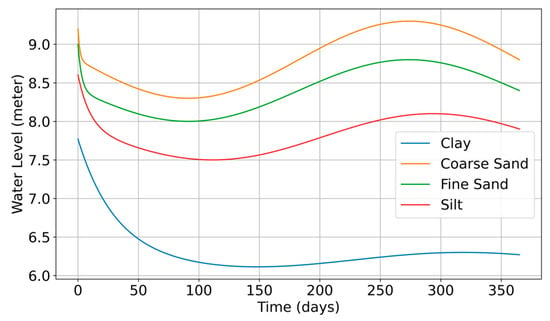
Figure 4.
Time series of groundwater level fluctuations (365 days).
The time series analysis reveals three distinct phases of groundwater response. The early time phase (0–1 day) shows logarithmic decline rates that vary by two orders of magnitude between clay and sand formations. The intermediate phase (1–30 days) exhibits transitional behavior where boundary effects become increasingly important. The late time phase (>30 days) demonstrates quasi-steady state conditions modulated by seasonal recharge–discharge cycles.
Seasonal variations superimposed on the pumping-induced drawdown create complex patterns that differ markedly between aquifer types. High-permeability sand aquifers show pronounced seasonal fluctuations of ±0.5 m, responding rapidly to precipitation events. Low-permeability clay formations demonstrate muted seasonal responses of ±0.1 m, with phase lags of 30–45 days relative to precipitation inputs.
4.8.2. Implications for Groundwater Management
The time series and depth-resolved data provide critical insights for optimizing well placement and pumping schedules. In clay-dominated systems, wells should be completed at greater depths to access zones with a reduced drawdown impact. Pumping schedules must account for extended recovery periods of 60–90 days. Conversely, sand aquifer systems can support more flexible pumping regimes with rapid recovery times of 2–5 days, though the careful monitoring of cumulative impacts remains essential.
The pronounced difference in seasonal response between aquifer types suggests that recharge enhancement strategies must be tailored to specific hydrogeological conditions. Artificial recharge in clay formations requires extended lead times and may benefit from injection wells, while sand aquifers can effectively utilize surface spreading basins for rapid recharge during wet seasons.
5. Conclusions
In this study, an improved nonlinear mathematical model was developed to predict changes in groundwater levels due to well extraction, precipitation, and evaporation. The integration of the quasi-linearization method with an alternating-direction implicit (ADI) numerical scheme created an efficient computational system, achieving convergence within 3–5 iterations at each time step while maintaining second-order accuracy in space and time. Numerical experiments conducted under various hydrogeological conditions revealed important patterns in groundwater dynamics. The hydraulic conductivity of aquifer material was found to be the key factor controlling both the magnitude and temporal evolution of water level changes. In low-permeability clay layers (k = 0.001 m/day), deep but localized depression cones persisted for over 60–90 days, while in highly permeable sandy aquifers (k = 10 m/day), wide but shallow depression cones stabilized within 2–5 days. These differences have significant implications for groundwater resource management strategies in different geological settings.
The model successfully captured nonlinear interactions in multi-well systems and showed that superposition effects led to 15–20% greater water level drawdown than predicted by linear models. This finding is crucial for well field design and optimization, as it indicates that traditional linear approaches may underestimate the cumulative impact of multiple extraction points.
Numerical experiments demonstrated the model’s ability to simulate complex groundwater dynamics under various conditions. The need for transient analysis in low-permeability aquifers, the importance of well interactions in multi-well systems, and the model’s reliability for optimal well placement was confirmed. Validation metrics (R2 > 0.98, NSE > 0.97) attest to the model’s high accuracy.
Dimensionless formulations ensure the model’s adaptability to various hydrogeological conditions and spatial scales. This generalization, combined with the computational efficiency of the ADI method, makes the model suitable for practical engineering applications while maintaining the necessary mathematical rigor to capture complex nonlinear phenomena such as variable boundary conditions and heterogeneous aquifer properties.
Future research should focus on developing a three-dimensional formulation, integrating unsaturated zone dynamics, and linking to real-time monitoring systems. This study makes a significant contribution to the field of groundwater modeling by demonstrating that nonlinear effects cannot be ignored in systems with significant water level fluctuations, multiple stress points, or variable hydraulic properties. The developed methodology provides a practical tool for addressing contemporary challenges in groundwater resource management under changing climate conditions and increasing water demand, offering a balanced approach between computational efficiency and physical accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M. and M.K.; methodology, A.M.; software, A.M. and M.K.; validation, A.M. and M.K.; formal analysis, A.M. and M.K.; investigation, A.M. and M.K.; resources, M.K. and A.M.; data curation, A.M. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M. and M.K.; writing—review and editing, M.K.; visualization, A.M.; supervision, M.K.; project administration, M.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Meteorological Organization. State of Global Water Resources 2023; Technical Report WMO-No. 1362; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, L.E.; Kollet, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Fogg, G.E.; Maxwell, R.M.; Hill, M.C.; Fransen, H.H.; Verhoef, A.; Van Loon, A.F.; Sulis, M.; et al. Global Groundwater Modeling and Monitoring: Opportunities and Challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davamani, V.; John, J.E.; Poornachandhra, C.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Arulmani, S.; Parameswari, E.; Santhosh, A.; Srinivasulu, A.; Lal, A.; Naidu, R. A Critical Review of Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater Resources: A Focus on the Current Status, Future Possibilities, and Role of Simulation Models. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcha, S.K.; Hulluka, T.A.; Awass, A.A.; Bantider, A.; Ayele, G.T.; Walsh, C.L. Numerical groundwater flow modeling under future climate change in the Central Rift Valley Lakes Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kooi, H.; Gurdak, J.J.; Allen, D.M.; Hiscock, K.M.; Treidel, H.; Aureli, A. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, T.C.; Harvey, J.W.; Franke, O.L.; Alley, W.M. Ground Water and Surface Water: A Single Resource; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon; Dalmont: Paris, France, 1856. [Google Scholar]
- Kroszynski, U.I.; Dagan, G. Well pumping in unconfined aquifers: The influence of the unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.W. Soil Water Dynamics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- White, W.N. A Method of Estimating Ground-Water Supplies Based on Discharge by Plants and Evaporation from Soil: Results of Investigations in Escalante Valley, Utah; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.R.; Fireman, M. Laboratory studies of evaporation from soil columns in the presence of a water table. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.J. Hydrogeological methods for estimation of spatial variations in hydraulic conductivity. In Hydrogeophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, S.P. Theory of flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed response of the water table. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, K.R.; Redshaw, S.C. Seepage and Groundwater Flow; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Harbaugh, A.W. MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model: The Ground-Water Flow Process; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Bennett, G.D. Applied Contaminant Transport Modeling; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Huyakorn, P.S.; Pinder, G.F. Computational Methods in Subsurface Flow; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuit, J. Études Théoriques et Pratiques sur le Mouvement des Eaux; Dunod: Paris, France, 1863. [Google Scholar]
- Forchheimer, P. Wasserbewegung durch Boden. Z. Ver. Dtsch. Ing. 1901, 45, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, J. Hydraulics of Groundwater; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- de Marsily, G. Quantitative Hydrogeology: Groundwater Hydrology for Engineers; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H.; Jacob, C.E. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well-field history. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1946, 27, 526–534. [Google Scholar]
- Hantush, M.S. Modification of the theory of leaky aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 1960, 65, 3713–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussinesq, J. Recherches théoriques sur l’écoulement des nappes d’eau infiltrées dans le sol et sur le débit des sources. J. Math. Pures Appl. 1904, 10, 5–78. [Google Scholar]
- Polubarinova-Kochina, P.Y. Theory of Ground Water Movement; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Hydrology: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barenblatt, G.I.; Entov, V.M.; Ryzhik, V.M. Theory of Fluid Flows Through Natural Rocks; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Sahimi, M. Flow and Transport in Porous Media and Fractured Rock; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik, V.A.; Ledder, G. Theory of dipole flow in uniform anisotropic aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockington, D.A. Response of unconfined aquifer to sudden change in boundary head. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1997, 123, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, J.Y.; Lisle, I.; Braddock, R.D.; Smith, R.E. The three-parameter infiltration equation. Soil Sci. 1982, 133, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zlotnik, V.A. Groundwater flow to a horizontal or slanted well in an unconfined aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 13-1–13-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Soil and Water: Physical Principles and Processes; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, M.A.; Bouloutas, E.T.; Zarba, R.L. A general mass-conservative numerical solution for the unsaturated flow equation. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.H.; Ampt, G.A. Studies on soil physics: Flow of air and water through soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 4. Sorptivity and algebraic infiltration equations. Soil Sci. 1957, 84, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Anderson, M.P. Introduction to Groundwater Modeling: Finite Difference and Finite Element Methods; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, K. Groundwater flow and geochemistry in the lower reaches of the Yellow River: A case study in Shandong Province, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akingboye, A.S.; Bery, A.A.; Kayode, J.S.; Asulewon, A.M.; Bello, R.; Agbasi, O.E. Near-Surface Crustal Architecture and Geohydrodynamics of the Crystalline Basement Terrain of Araromi, Akungba-Akoko, SW Nigeria, Derived from Multi-Geophysical Methods. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.R. Some steady-state solutions of the unsaturated moisture flow equation with application to evaporation from a water table. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Feddes, R.A.; Bresler, E.; Neuman, S.P. Field test of a modified numerical model for water uptake by root systems. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, G.D. An approximate solution for steady vertical flux of moisture through an unsaturated homogeneous soil. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 3749–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Nachabe, M.; Ross, M. Extinction depth and evapotranspiration from ground water under selected land covers. Ground Water 2007, 45, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, R.L.; Faires, J.D. Numerical Analysis, 9th ed.; Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Peaceman, D.W.; Rachford, H.H. The numerical solution of parabolic and elliptic differential equations. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1955, 3, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.L. Iterative solution of implicit approximations of multidimensional partial differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1968, 5, 530–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W.; Hunt, R.J. Applied Groundwater Modeling: Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bellman, R.E.; Kalaba, R.E. Quasilinearization and Nonlinear Boundary-Value Problems; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaba, R. On nonlinear differential equations, the maximum operation, and monotone convergence. J. Math. Mech. 1959, 8, 519–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method: Fluid Dynamics; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, D.; Orszag, S.A. Numerical Analysis of Spectral Methods: Theory and Applications; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.R.; Gu, Y.T. An Introduction to Meshfree Methods and Their Programming; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hairer, E.; Nørsett, S.P.; Wanner, G. Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I: Nonstiff Problems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, C.T. Variable density groundwater flow: From current challenges to future possibilities. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, W. A review of regional groundwater flow modeling. Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.G.; Harbaugh, A.W. A Modular Three-Dimensional Finite-Difference Ground-Water Flow Model; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, W.C. Aquifer Test Modeling; American Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).