Optimal Media Control Strategy for Rumor Propagation in a Multilingual Dual Layer Reaction Diffusion Network Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We extend the reaction–diffusion framework to capture the multilingual spatiotemporal diffusion of rumors and the coupling effects of a virtual media layer by proposing a hybrid dual-layer model that integrates an isomorphic media layer with a heterogeneous population layer.
- We formulate the optimal control problem for this hybrid model. By proving the Gâteaux differentiability of the control-to-state mapping, derive the first-order necessary conditions for media-driven spatiotemporal intervention.
- We conduct extensive numerical simulations to demonstrate the adaptability and effectiveness of the proposed media-based spatiotemporal control scheme.
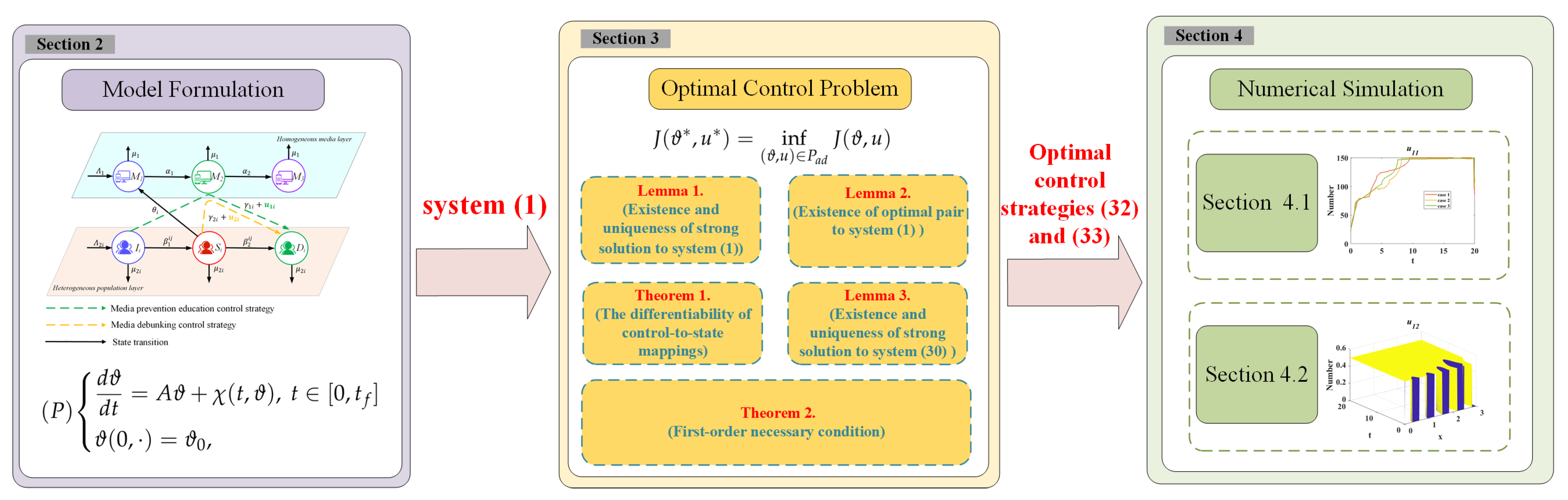
2. Model Formulation
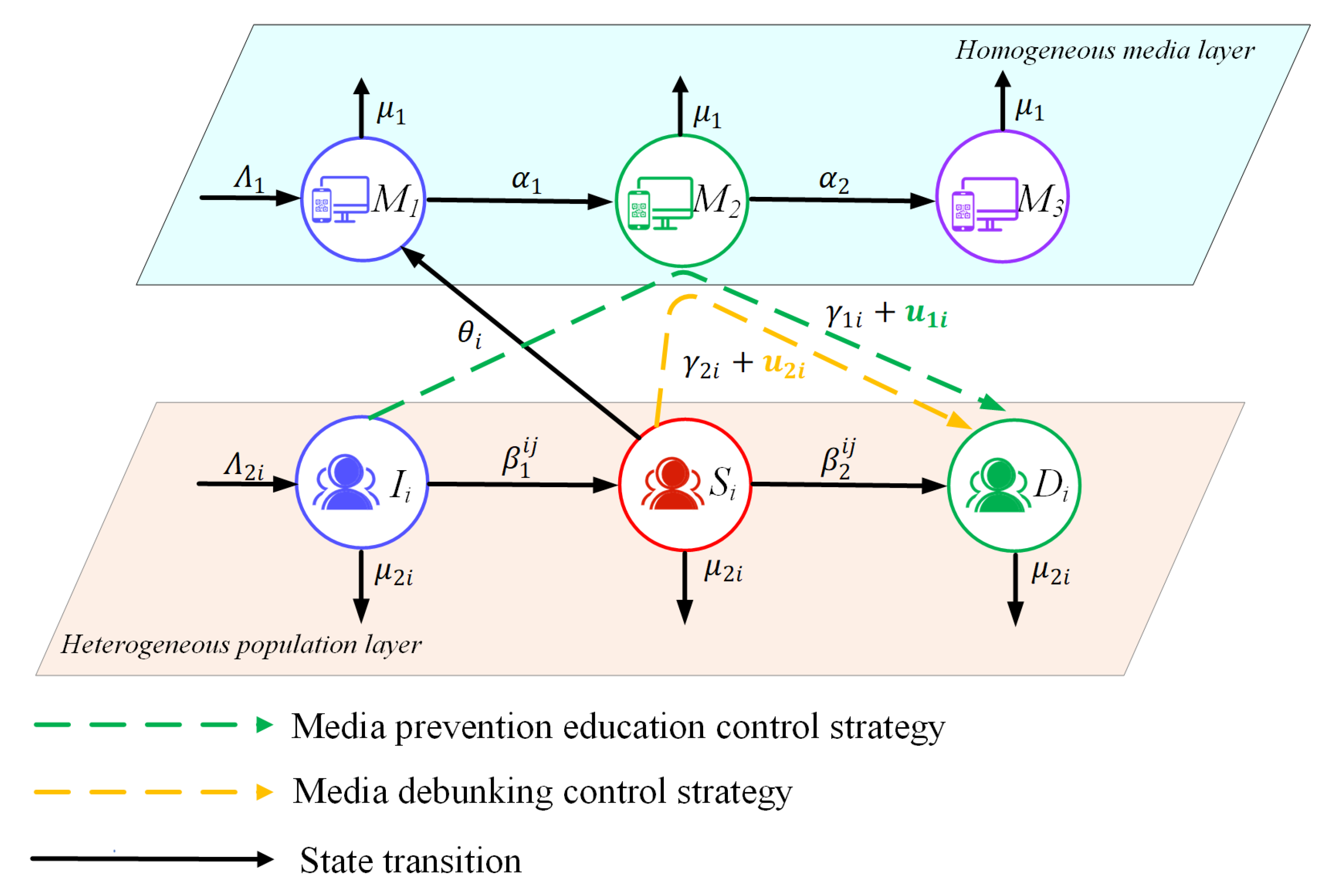
2.1. Model Description
- Media prevention education control strategy: Media platform , for example, official outlets, issues authoritative information and pushes rumor-prevention notices on social networks, thereby increasing the probability that ignoramus encounters truthful information and converts it into active debunkers . This is defined as the continuous control input .
- Media debunking control strategy: Media platform automatically flags misinformation warnings on spreader accounts and sends private messages containing evidential graphics and text, thereby increasing the probability that spreaders recognize the truthful information and convert it into active debunkers . This is defined as the continuous control input .
2.2. Preliminaries
3. Optimal Control Problem
3.1. Preface
3.2. Necessary Optimality Conditions
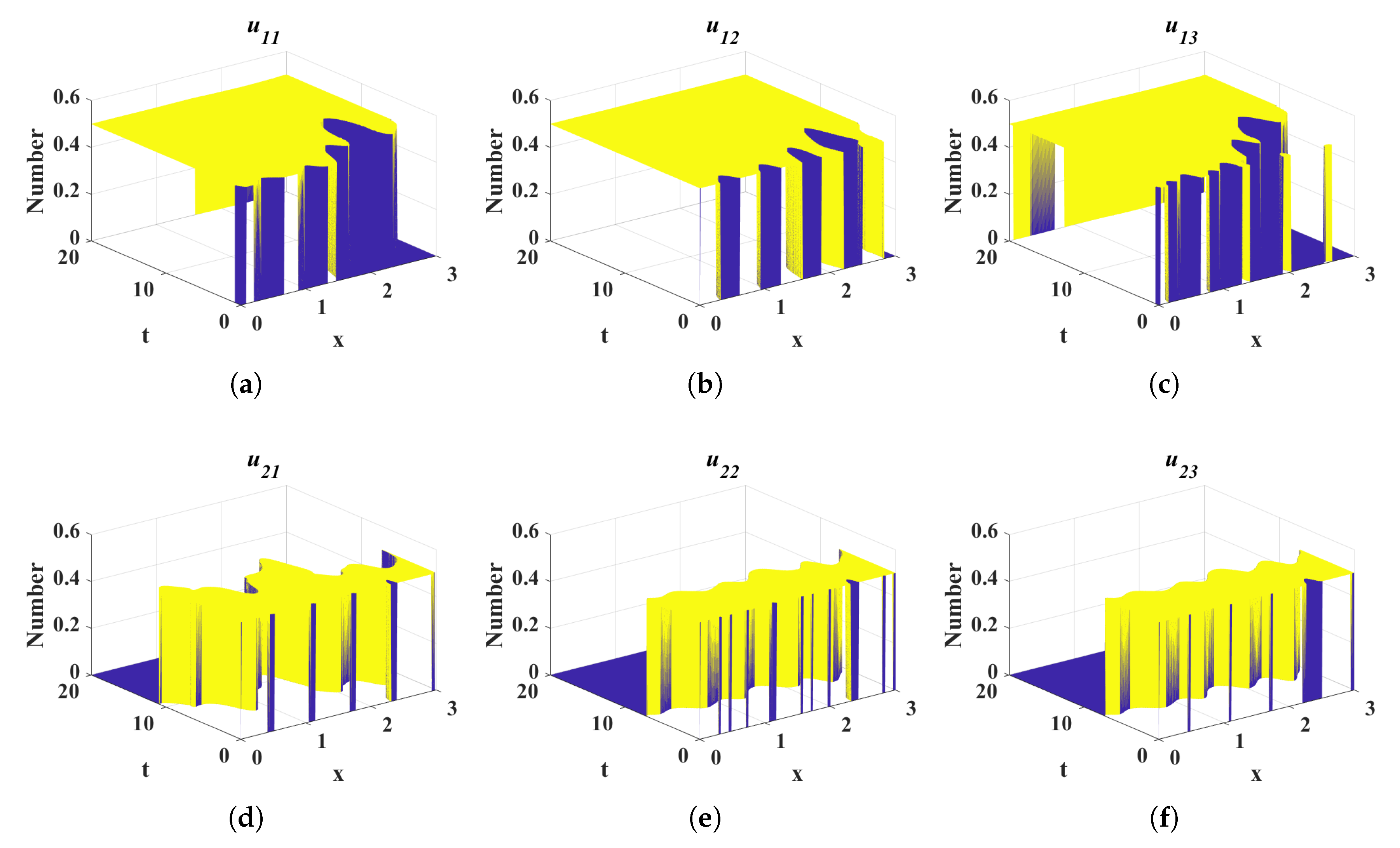
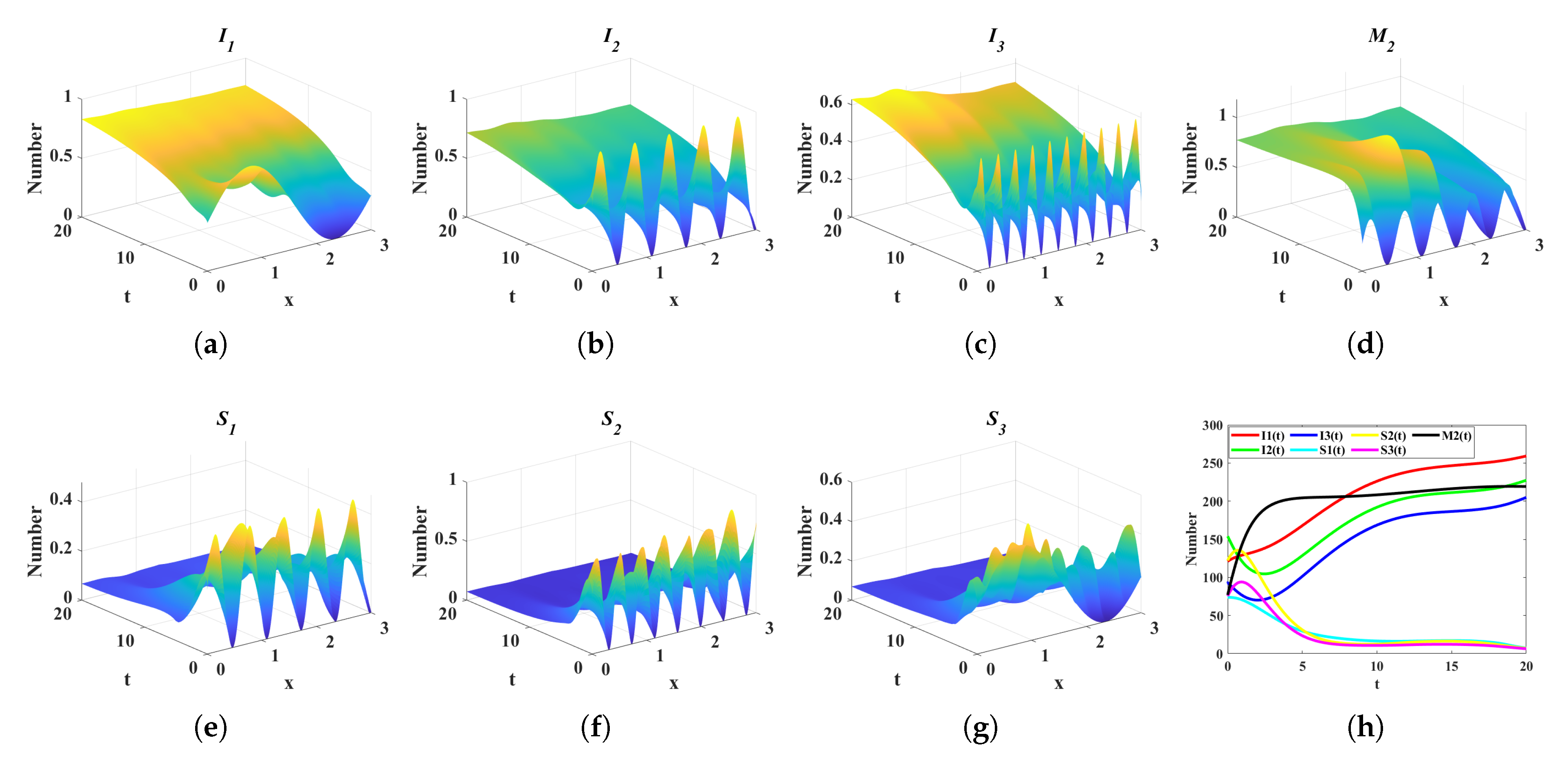
4. Numerical Simulation
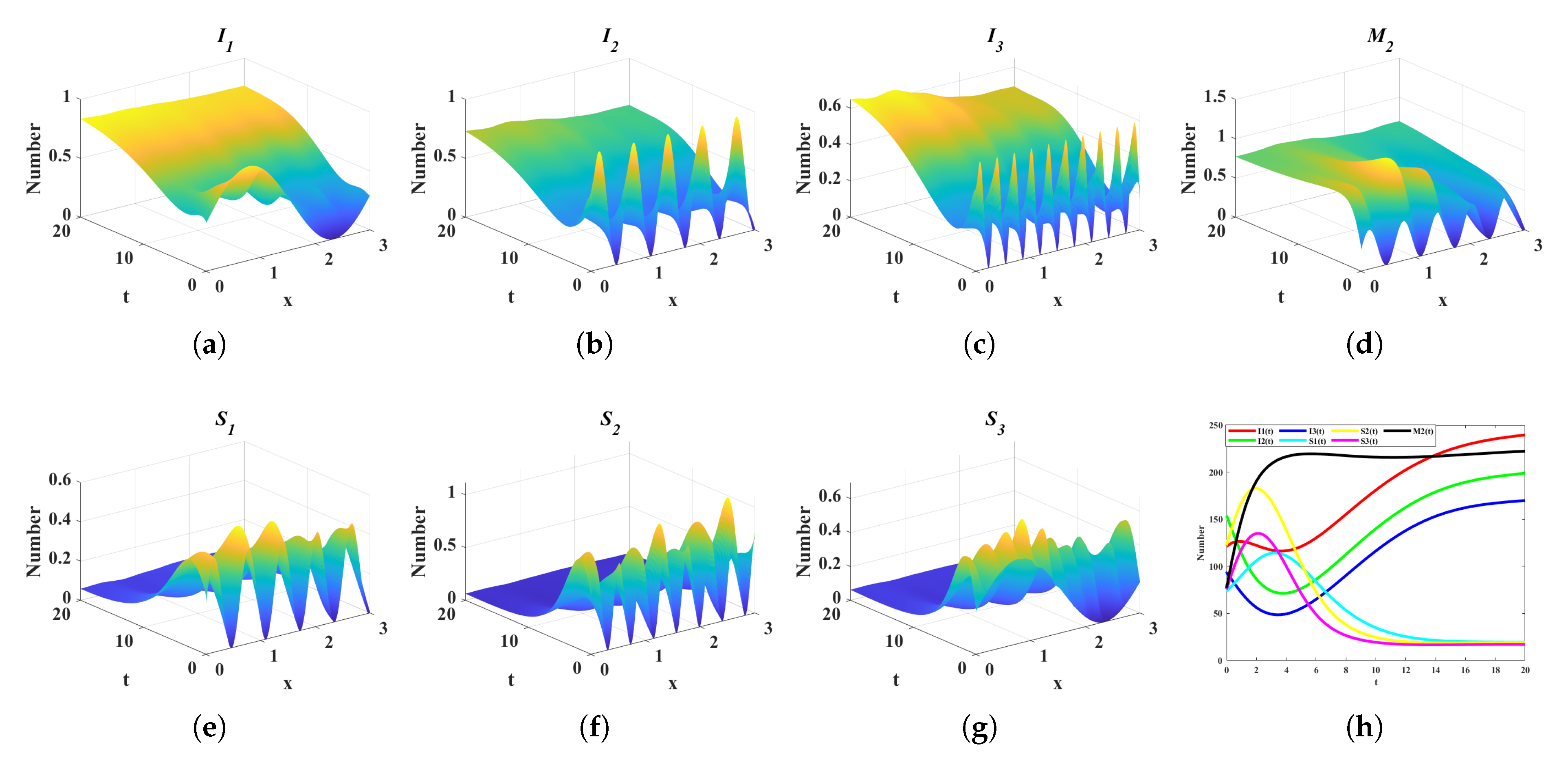
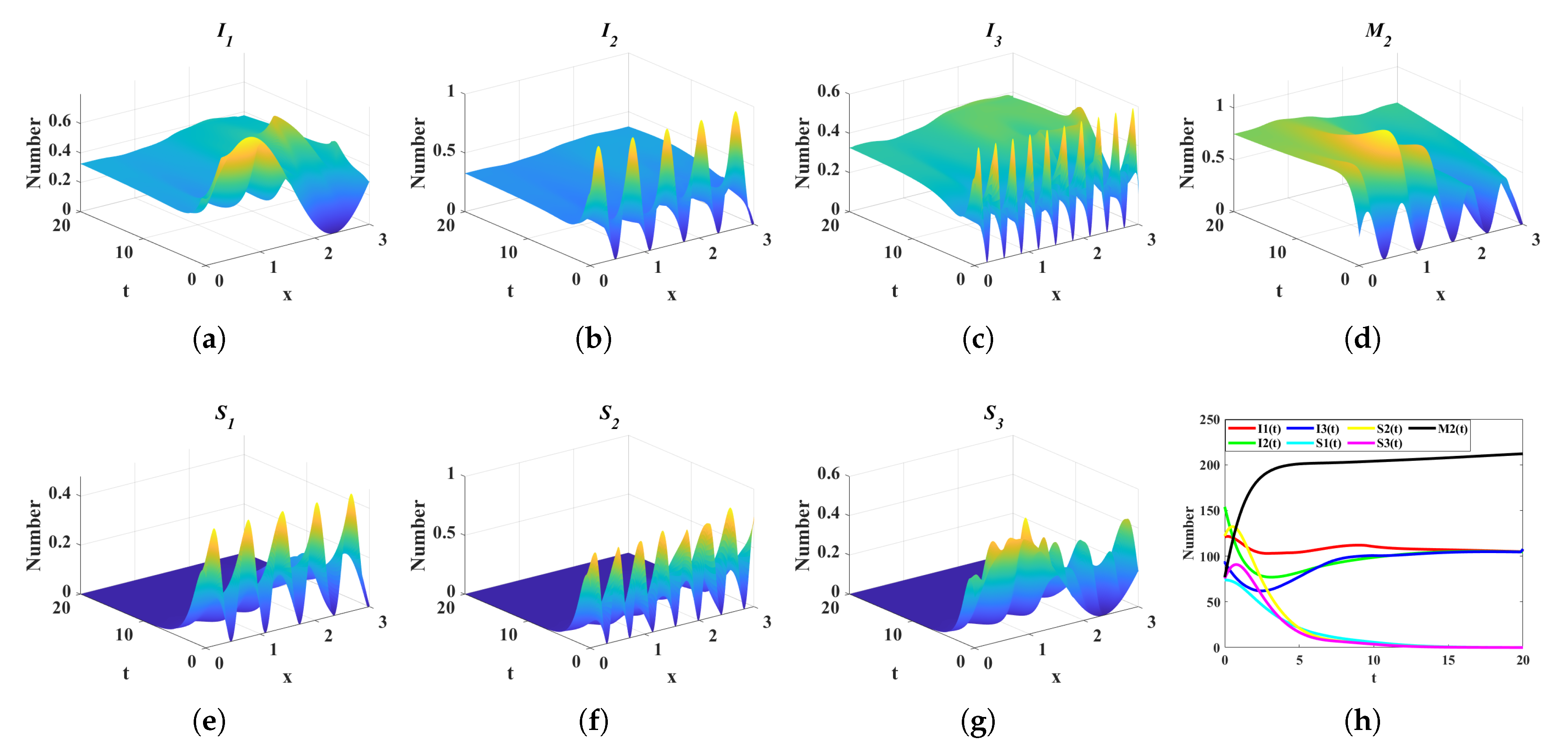
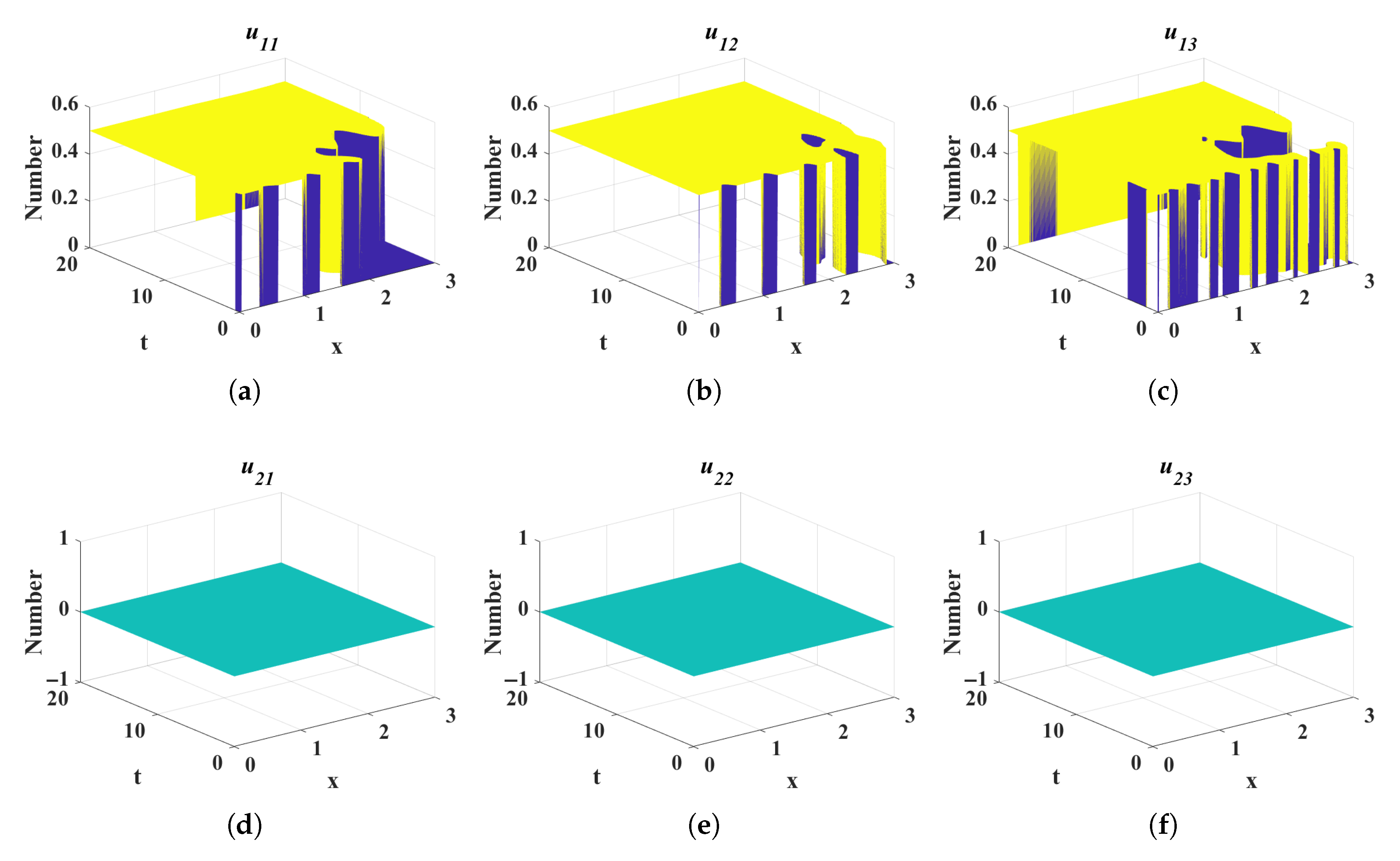
4.1. Impact of Different Diffusion Coefficients on Control Variables
- Case 1:
- Case 2:
- Case 3:
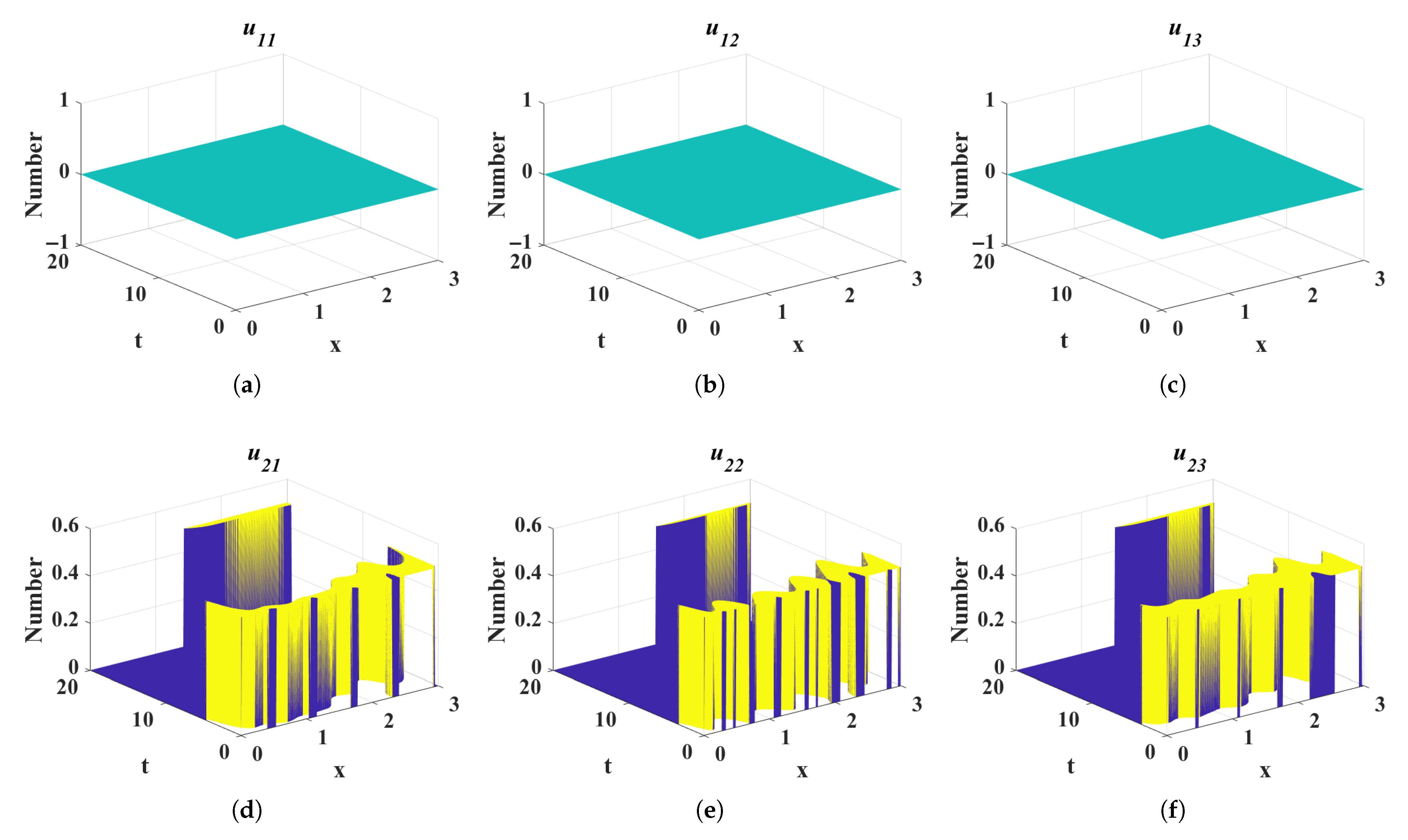
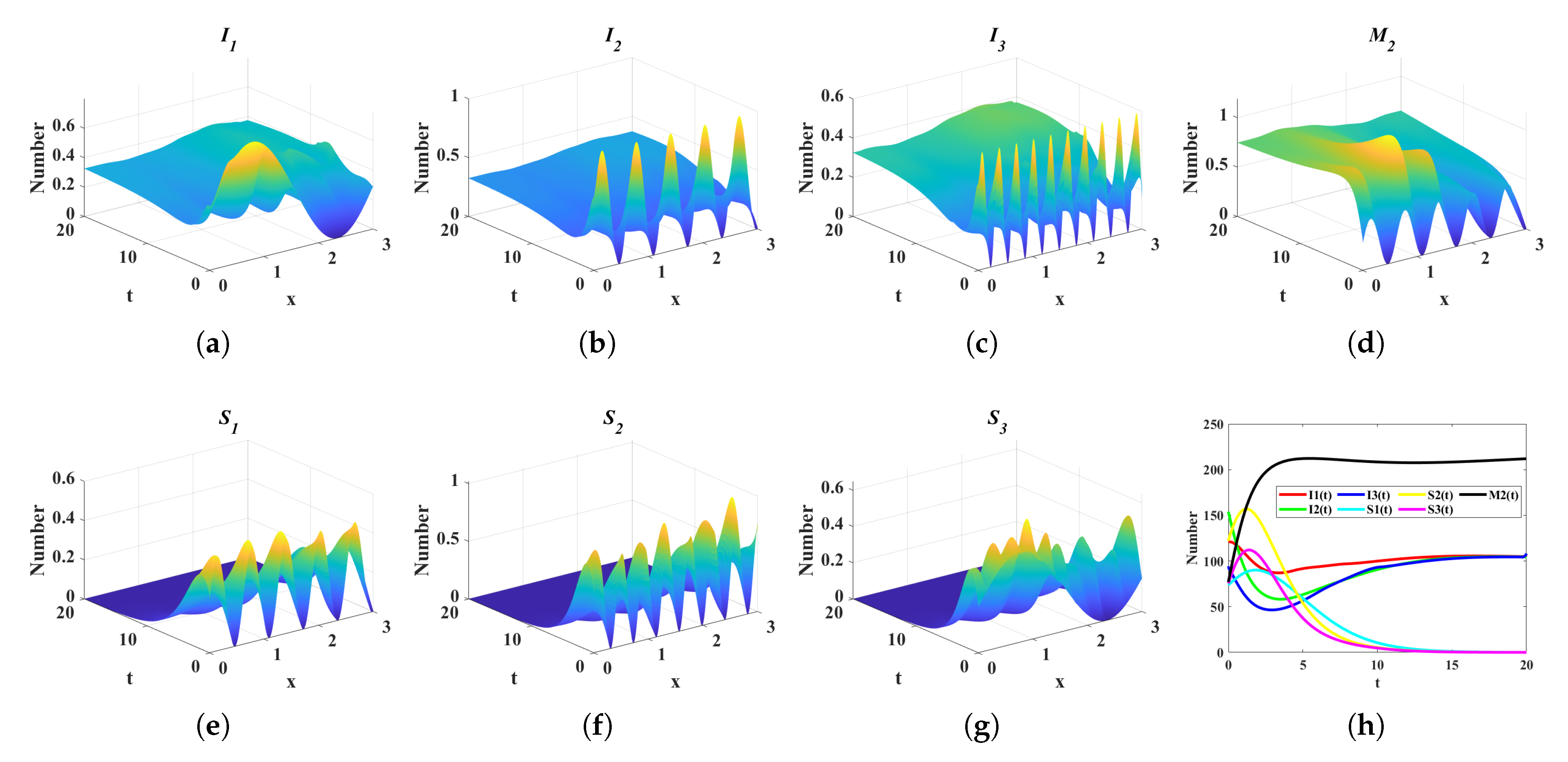
4.2. Comparison of Control Costs in Four Different Scenarios
- scenario 1: Without any control strategy ( and , ).
- scenario 2: Media debunk and prevention education control strategy ( and , ).
- scenario 3: Only media debunking control strategy ( and , ).
- scenario 4: Only media prevention education control strategy ( and , ).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Liao, J.; Lu, J.G.; Li, J.; Liu, M. Dynamic Analysis of the Multi-Lingual S2IR Rumor Propagation Model Under Stochastic Disturbances. Entropy 2025, 27, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Gao, L.; Guo, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Xiao, Y. Information Propagation Dynamic Model Based on Rumors, Antirumors, Prom-Rumors, and the Dynamic Game. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2024, 12, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, C.; Deng, F.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Hu, Z. Model-Based and Data-Driven Stochastic Hybrid Control for Rumor Propagation in Dual-Layer Network. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2024, 12, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, C.; Dong, X.; Bai, D.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Y. Stochastic Stabilization of Dual-Layer Rumor Propagation Model with Multiple Channels and Rumor-Detection Mechanism. Entropy 2023, 25, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, X. The Dynamics and Control of a Multi-Lingual Rumor Propagation Model with Non-Smooth Inhibition Mechanism. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2024, 21, 5068–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Z.; Yu, S.; Luo, X. Dynamic Analysis and Optimal Control of a Reaction-Diffusion Rumor Propagation Model in Multi-Lingual Environments. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2023, 521, 126967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.K.; Ali, S.H.; Ðoàn, L.N.; Yi, S.S.; Trinh-Shevrin, C.; Kwon, S.C. Social Media Use and Misinformation Among Asian Americans During COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 764681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, J.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Y. Multi-Agent Collaborative Rumor-Debunking Strategies on Virtual-Real Network Layer. Mathematics 2024, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, L. Dynamic Analysis of the Rumor Propagation Model with Consideration of the Wise Man and Social Reinforcement. Physica A 2021, 571, 125828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Liu, G.; Deng, F.; Wang, J. Rumor Suppression in a Three-Layer Network: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2025, 12, 2292–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Hu, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, J. Stability and Hopf Bifurcation Analysis of Multi-Lingual Rumor Spreading Model with Nonlinear Inhibition Mechanism. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 153, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Li, M.; Jain, D.K.; Štruc, V.; Huang, D.W. Hybrid Rumor Debunking in Online Social Networks: A Differential Game Approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2025, 55, 2513–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhu, L. Spatio-Temporal Pattern Formation Mechanism of an Epidemic-Like Information Propagation Model with Diffusion Behavior. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2025, 16, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics Analysis and Optimal Control Method for an SI Reaction-Diffusion Propagation Model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2021, 493, 124539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, L. Turing Pattern Analysis of a Reaction-Diffusion Rumor Propagation System with Time Delay in Both Network and Non-Network Environments. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 153, 111542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, P.; Shi, L. Dynamics of a Reaction-Diffusion Rumor Propagation Model with Non-Smooth Control. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 435, 127478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Dong, Y. Dynamics and Near-Optimal Control in a Stochastic Rumor Propagation Model Incorporating Media Coverage and Lévy Noise. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 030202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S.; Chen, S. Dynamic Analysis and Optimal Control of ISCR Rumor Propagation Model with Nonlinear Incidence and Time Delay on Complex Networks. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 3935750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhong, X. Fractional optimal control for malware propagation in Internet of Underwater Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 11632–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, H.; Xiong, L.; Tan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zhong, X. Fractional order optimal control and FIov–MASAC reinforcement learning for combating malware spread in Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 10313–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhong, X. Spatiotemporal Control Optimization of Malware Propagation in Internet of Underwater Things. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 6324–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, K.; Bai, D.; Liang, Z. Spatiotemporal Optimal Control of Reaction-Diffusion Malware Propagation in Multi-AUV Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2025. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, X.; Liang, Z. Spatiotemporal Optimal Control of Malware Propagation in AUV-Assisted UWSNs: A Two-Layer Heterogeneous Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Higher-order rumor and anti-rumor propagation and data-driven optimal control on hypergraphs. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 193, 116082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, X.; Hu, X.; Liang, Z. Hybrid optimal control for malware propagation in UAV–WSN system: A stacking ensemble learning control algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 36549–36568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhong, X. Hybrid control for malware propagation in rechargeable WUSN and WASN: From knowledge-driven to data-driven. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 173, 113703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiang, H.; Li, Z. Optimal control strategies for a reaction–diffusion epidemic system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2019, 46, 446–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Threshold dynamics and regional optimal control of a malaria model with spatial heterogeneity and ivermectin therapy. Appl. Math. Model. 2024, 125, 591–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Liu, B. Optimal control problem for a general reaction-diffusion eco-epidemiological model with disease in prey. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouissa, A.; Tahiri, M.; Tsouli, N.; Ammi, M.R.S. Optimal control of multi-group spatio-temporal SIR model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2025, 542, 128835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiang, H. Optimal control problems of a reaction–diffusion ecological model with a protection zone. J. Process Control 2022, 120, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apreutesei, N.C. An optimal control problem for a pest, predator, and plant system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2012, 13, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| The rate of media-platform creation | ||
| The probability of media-platform deactivation | ||
| The probability that the media platforms propagate | ||
| debunking information issued by the media platforms | ||
| The probability that the media platforms delete their | ||
| debunking information | ||
| The rate at which individuals in the i-th group become | ||
| interested in rumor or truth | ||
| The probability that individuals in the i-th group lose | ||
| interest in both rumor and truth | ||
| The probability that becomes aware of the rumor via spreaders | ||
| of the i-th group () and then issues debunking information | ||
| The probability that the ignoramus from the i-th group accepts the | ||
| truth upon encountering ’s debunking messages without intervention | ||
| The probability that the spreaders from the i-th group accepts the | ||
| truth upon encountering ’s debunking messages without intervention | ||
| The probability that the ignoramus believe the rumor | ||
| by interacting with the spreaders | ||
| The probability that the spreaders believe the truth by | ||
| interacting with debunkers |
| Type | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homogeneous Media Layer | ||||
| Heterogeneous Population Layer | ||||
| Cost Coefficient | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 |
| scenario 1 | 85.8 | 31.82 | 0 | 0 | 41.92 | 6.08 | 0.55 | 2.22 | 168.39 |
| scenario 2 | 59.57 | 10.83 | 23.24 | 39.51 | 3.19 | 2.12 | 138.56 | ||
| scenario 3 | 91.16 | 24.91 | 0 | 41.39 | 6.05 | 0.52 | 2.22 | 166.29 | |
| scenario 4 | 54.65 | 17.93 | 24.04 | 0 | 40.42 | 3.18 | 2.12 | 142.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z. Optimal Media Control Strategy for Rumor Propagation in a Multilingual Dual Layer Reaction Diffusion Network Model. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13142253
Liu G, Xu H, Zhu Y, Ma Y, Chen Z. Optimal Media Control Strategy for Rumor Propagation in a Multilingual Dual Layer Reaction Diffusion Network Model. Mathematics. 2025; 13(14):2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13142253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guiyun, Haozhe Xu, Yu Zhu, Yiyang Ma, and Zhipeng Chen. 2025. "Optimal Media Control Strategy for Rumor Propagation in a Multilingual Dual Layer Reaction Diffusion Network Model" Mathematics 13, no. 14: 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13142253
APA StyleLiu, G., Xu, H., Zhu, Y., Ma, Y., & Chen, Z. (2025). Optimal Media Control Strategy for Rumor Propagation in a Multilingual Dual Layer Reaction Diffusion Network Model. Mathematics, 13(14), 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13142253








