Abstract
In reversible data hiding, prediction error generation plays a crucial role, with pixel value ordering (PVO) standing out as a prediction method that achieves high fidelity. However, conventional PVO approaches select predicted pixels and their predictions independently, failing to fully exploit the inherent redundancy in ordered pixel sequences. This paper proposes a novel PVO-based prediction method that leverages the continuity and spatial correlation of ordering pixels. We first introduce a new prediction technique that exploits the redundancy of consecutive pixels. Our approach selects the most appropriate prediction method from preset prediction errors, considering both pixel position and value characteristics. Furthermore, we implement an adaptive strategy that dynamically selects multiple iteration parameters based on pixel content to obtain more expandable prediction errors and adjusts the modification of prediction errors accordingly. Unlike traditional fixed-parameter methods, our approach better utilizes the inherent structure and redundancy of image pixels, thereby improving data embedding efficiency while minimizing image distortion. We enhance performance by combining pairwise prediction-error expansion with content-based prediction error analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms state-of-the-art solutions in terms of image fidelity while maintaining competitive embedding capacity, confirming the effectiveness of our method for efficient data embedding and image recovery.
MSC:
68U10
1. Introduction
Reversible data hiding (RDH) is a technique that facilitates the embedding of secret information into digital media, such as images and videos, with the capability to perfectly restore the original media after data extraction. This field has garnered significant attention due to its unique advantages over traditional data hiding methods, which often result in irreversible alterations to the carrier medium [1,2,3,4,5]. The industrial relevance of RDH is vast, spanning across diverse sectors including medical imaging, forensics, intellectual property protection, and military communications. In the medical field, RDH is instrumental in embedding patient data into diagnostic images without compromising the integrity of the original images, ensuring accuracy in clinical interpretations. Similarly, in forensics and law enforcement, it plays a crucial role in embedding metadata into digital evidence, preserving the admissibility of the evidence in legal proceedings. The method also aids in safeguarding intellectual property by embedding ownership information into digital products, facilitating tracking and verification while maintaining the original content intact. Furthermore, in military and defense applications, RDH enables the secure transmission of confidential information through media files, with the assurance that the original media can be restored without any loss, which is essential for strategic operations. The importance of RDH lies in its ability to ensure data integrity, enhance security, offer versatility in application, and support compliance with data protection regulations across various industries. As the demand for secure and reliable data embedding solutions grows, the development and application of RDH techniques are becoming increasingly pertinent.
RDH methods are diverse, with some approaches fundamentally rooted in lossless compression techniques. These methods, as referenced in the seminal works [6,7,8,9,10], aim to economize storage space by employing lossless compression algorithms on the feature sets extracted from the cover image. This strategy not only preserves the original image’s quality but also creates a compact space for secret data embedding. Parallel to lossless compression-based methods, histogram shifting (HS) techniques have garnered attention in the RDH domain [11,12,13,14,15]. HS methods ingeniously exploit the statistical properties of images to embed secret data, capitalizing on the distribution of pixel values to create a covert channel for information exchange.
Furthermore, difference expansion (DE) [16,17,18] and derivation prediction error expansion (PEE) [19,20,21,22,23] stand out as innovative approaches within the RDH paradigm. DE operates on the principle of embedding one-bit data into the minute differences between adjacent pixels, a technique that is both simple and effective for certain applications. In PEE-based methods, prediction error which is the difference between the predicted pixel and the one serving as its prediction is expanded to embed data. Because the local correlations are considered in the prediction, PEE can produce prediction error with smaller magnitude, thereby significantly improving the performance. The pixel value ordering (PVO) embedding strategy [24,25,26,27,28] enables the marked image better visual quality with combining the idea of HS and PEE. These methods divide cover image into non-overlapped pixel blocks, pixels are ordered in ascending order to make prediction errors, then data are embedded through prediction error modification.
The principle of the PVO-based data hiding method is to explore the efficient utilization of predicted pixels and their predictions to produce more accurate prediction errors. To gain this advantage, content-based adaptive embedding achieves good performance. Considering the surrounding texture area of the target pixel block, content-based adaptive embedding methods are further studied [27,29,30,31,32,33]. Previous studies only focused on using the smoothness of pixel block selecting embedding method; it is more meaningful to consider the combination of pixel smoothness and prediction error generation to design adaptive prediction errors for the same embedding method. However, existing methods do not fully exploit the redundancy between consecutive pixels or equal pixels.
This paper introduces an innovative data hiding method that leverages the redundancy between consecutive pixels to enhance the efficiency of prediction error generation. Unlike methods that focus solely on pixel smoothness, our work delves into the synergistic effect of pixel continuity and prediction error accuracy. By designing an adaptive strategy that considers both the dynamic prediction error and the noise level of pixel blocks, we aim to minimize image distortion while enlarging the embedding capacity. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows: This paper proposes a novel adaptive reversible data hiding method that can adaptively select multi-pass parameters based on content pixels to obtain more expandable prediction errors, and then adaptively adjust the modification of prediction errors. The ambition of this method is to formulate an optimized embedding strategy for a given cover image and a given secret data, providing new solutions for reversible data hiding. The method introduces a novel approach to adaptively select multi-pass parameters based on the content of pixels to enhance prediction error expansion. It allows for the generation of more expandable prediction errors, which is a departure from traditional fixed-parameter approaches. By dynamically adjusting these parameters, the method can better exploit the inherent structure and redundancy of the image pixel, leading to improved data embedding efficiency and reduced image distortion. A multi-pass PVO-based prediction strategy is proposed to design prediction error modification with less image distortion. It enables a more nuanced and precise control over the prediction error classification and modification, ensuring that the modifications to the prediction errors result in minimal additional distortion to the image. Experimental results show that the proposed scheme outperforms a series of state-of-the-art schemes with moderate capacity in terms of image fidelity.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the related RDH methods are firstly reviewed. In Section 3, the proposed method is introduced in three steps. Section 4 discuss the performance of the proposed method with experimental results. Finally, we summarize our work in the last section.
2. Related Work
In this section, single-pass and multi-pass PVO-based methods are briefly reviewed. Subsequently, we delve into the nuances of pairwise PVO-based prediction error modification. Finally, the motivation of this article is presented.
2.1. Single-Pass PVO-Based Reversible Data Hiding
PVO [24] involves arranging the pixel values within a non-overlapping block in ascending order. Consequently, the largest and smallest pixel are predicted by the second largest and second smallest valued pixels, respectively, with the introduction of a single prediction error. Later, considering the spatial location between the predicted pixel and its prediction, the improved pixel value ordering (IPVO) method proposed in [25] constructed a steeper prediction error histogram (PEH). A steeper PEH facilitates more expandable prediction errors, thereby improving both embedding capacity and accuracy. However, the IPVO method still faces limitations, as each pixel block can carry a maximum of two bits of data. The pixel-based PVO method (PPVO) [34] gains the most significant capacity improvement, where block-by-block prediction is abandoned, and each pixel is predicted and modified according to its sorting context. However, the prediction mechanism limits the performance of embedding, and the embedding capacity still needs to be improved. In [26], PVO is extended to PVO-k by taking the k largest (or smallest) pixels as a prediction unit. However, the fact that embedding one bit of data requires modifying k pixels causes unnecessary pixel distortion. Later, many works focused on embedding k bits data into the largest (or smallest) k pixels, called multi-pass embedding. It is beneficial to raise the utilization rate of pixels after segmenting the image block-by-block and enlarge the embedding capacity.
2.2. Multi-Pass PVO-Based Reversible Data Hiding
Compared to the utilization of a maximum of two pixels in a block, the use of multiple pixels effectively increases the pixel utilization rate. In MIPVO [35], the largest pixel is used as prediction for the remaining pixels, where n is the pixel number of a pixel block. Then, the smallest pixel is used as prediction for the remaining pixels. In addition, [35] also adopts a flexible spatial location method to optimize the location of the pixels participating in the prediction. Thus, MIPVO enlarges the embedding capacity and the fidelity of marked image. However, MIPVO takes the same treatment for all prediction errors and does not deeply discuss the correlation among different prediction errors. The GMP-PVO integrates the PVO framework with a multi-predictor mechanism [32], dynamically adjusting the prediction strategy based on the content of the image blocks. RSP-PVO [36] uses the relationship of the largest three pixels to perform multi-pass embedding, and re-collects the pixels to obtain pixel positions that are more conducive to embedding. However, the predicted pixels and their predictions are fixed, which limits the variety of predictions for the reversibility. Although existing methods have achieved certain effects in utilizing pixel positions, they often neglect the improvement of adaptive prediction mechanisms. We propose a new method that focuses on improving accuracy through adaptive prediction, thereby increasing the utilization rate of pixels while reducing the loss of information. This approach is expected to achieve more efficient data embedding and image recovery in the field of reversible data hiding.
2.3. Pairwise PVO-Based Reversible Data Hiding
Some prominent works have applied the pairwise PEE strategy to the PVO scheme, thereby integrating the advantages of two-dimensional prediction error modification within the PVO framework, which is referred to as pairwise PVO. Some fascinating methods include KPPE [37] which combined K-pass PVO with improved PEE, pairwise MIPVO [35] which combined multi-pass PVO with hybrid PEE, and LPVO [38], which is a self-learning mechanism to select the 2D mapping adaptively according to the image content. Despite these innovations, current methods often generate prediction errors based on static observational laws, which may not fully adapt to the nuances of different images. The EP-PEE [39] proposes an enhanced pairwise PEE, which designs a more efficient 2D mapping by predicting the largest/smallest two pixels depending on the content-selected expansion prediction error. Nevertheless, the discussion of the pixel relationship stops at the complex utilization of the pixel position. However, existing discussions on pixel relationships in these methods tend to focus on the complex utilization of pixel positions, with less emphasis on developing adaptive prediction mechanisms. Future research could benefit from exploring more flexible and adaptive prediction strategies that can better accommodate the diverse characteristics of various images, potentially leading to further advancements in RDH techniques.
3. Proposed Method
In this section, adaptive PVO-based pixel prediction methods along with the corresponding prediction error modification are presented. Next, the pairwise modification and adaptive framework of the proposed method is determined. For the sake of clarity, the detailed embedding and extraction procedure of reversible data hiding is presented. To facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of our approach, Table 1 of important symbols and their definitions is provided below.

Table 1.
Notations and descriptions of key parameters and variables in the proposed embedding method.
3.1. Adaptive k-Pass PVO-Based Prediction
The cover image is first divided into non-overlapped blocks with the size of , where . For each block, pixels are sorted in ascending order as , where denotes the unique one-to-one mapping such that: , if and . As for pixel prediction, is predicted first by to obtain the preset prediction error .
where . Next, () is determined by to predict the . The prediction error is similarly calculated as
In case of or , is predicted by as Equation (2). If or , is predicted by . Then the prediction error is modified as follows.
and are binary secret data. From Equation (7), has been increased by 1 when or . Otherwise, one-bit data are embedded into . Following, is modified according to Equation (8). One bright spot is that distortion occurs in the largest pixel only when secret data are embedded.
The modification on large pixels can be directly applied to small pixels. For the smallest k pixels, adaptive modification is implemented as follows. First, is predicted by to obtain preset prediction error .
where . Based on , the rest prediction error is calculated in two ways as Equation (10).
where and .
In case of or , one-bit data are embedded into . Otherwise, the smallest pixel is decreased by 1 when or .
By modifying only according to the Equation (14), one-bit data can be embedded by referring to .
In the context of extracting embedded data from marked images, it is imperative that the data can be accurately retrieved and that the cover image can be fully restored following the extraction process. Taking the smallest set of k pixels as an example, the prediction errors and for the marked image are computed according to Equations (9) and (10). Conversely, the conduction of prediction errors and the recovery of image pixels diverge from the process of data embedding. Subsequently, the procedures for data extraction and image pixel recovery are delineated as follows.
- If , the embedded data are extracted as as and as and the pixel value is restored as .
- (a)
- If or , there is neither data extraction nor pixel restoration.
- (b)
- If , the embedded data are extracted as and the pixel value is restored as .
- (c)
- If , the embedded bit is extracted as and the pixel value is restored as .
- If , there is no data extraction and the pixel value is restored as .
- (a)
- If , the embedded bit is extracted as and the pixel value is restored as .
- (b)
- If , the embedded bit is extracted as and the pixel value is restored as .
The restoration process for large pixels is analogous to that of small pixels, and thus, it will not be further detailed in this section. Typically, during the data embedding phase, larger pixels are processed prior to smaller ones, whereas the sequence is inverted during the data extraction phase.
Specially, Figure 1 gives an example on the largest three pixels to illustrate the proposed method clearly. For the given pixel block, six pixels are sorted in ascending order to obtain sequences and . Then, we have and . As a result, the one-bit data point is embedded into while another bit data point is embedded into . For the modification on small pixels, the prediction errors are and . Next, the smallest pixel is decreased by 1. The marked pixel sequence is . During extraction, small pixels are restored first and then large pixels. The two prediction errors and are calculated. Following, the smallest pixel is restored as . As for large pixels, and are calculated. Then, is extracted and is restored as , is extracted and is restored as . In general, data embedding follows a position-based strategy that processes pixels sequentially from smaller to larger positions, guided by prediction errors. Data extraction leverages these same positional relationships. This systematic approach mathematically guarantees complete reversibility.
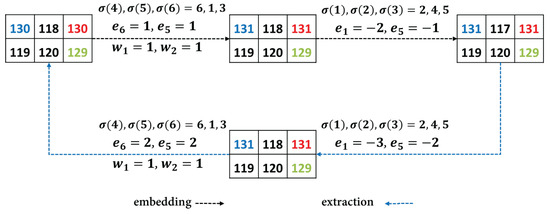
Figure 1.
An example of the largest modification-based data embedding and extraction. The process represented by black solid line is data embedding of TP-IPVO, while the process represented by gray dotted line is data extraction of TP-IPVO.
3.2. Content-Based IPVO-Based Pairwise PEE
In this section, the pairwise PEE is adopted to optimize the use of expandable prediction error. The superiority of pairwise PEE over conventional PVO is attributed to the improved modification of prediction error pairs, each comprising two prediction errors. The PVO-based modification embeds two bits of information into two expandable prediction errors, resulting in a distortion of 2. This approach, while effective, leaves room for improvement in terms of embedding efficiency. To address this, PEE-based modification ingeniously embeds a ternary number ‘0’, ‘1’, or ‘2’ into a single paired prediction error . It reduces the distortion to a minimal value of 1 but also embeds -bits data, thereby enhancing the embedding capacity within the prediction errors.
In the proposed method, the pairwise PEE [22] is adopted to optimize the embedding when and . In this case, the prediction errors are suitable to be combined into prediction error pairs (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0) and (1, 1) for 2D prediction mapping. For a pixel block, when or , k prediction errors can be obtained. When k is an even number, prediction error pairs are formed. When k is odd, prediction error pairs are formed, and the remaining one prediction error is processed in a 1D prediction error modification. For example, when the collected prediction errors are 0, 1, 1. The first two prediction errors form a prediction error pairs (0, 1). The prediction error pairs follow the modification in Figure 2. The final prediction error ’1’ is modified according to the modification of the 1D histogram. In addition, it is not suitable to adapt pairwise PEE embedding as . Pairwise PEE introduces additional computational overhead due to the pairing and 2D mapping of prediction errors, resulting in higher constant factors in both time and space complexity compared to conventional PEE. However, this added complexity significantly improves image quality metrics. Specifically, pairwise PEE achieves higher PSNR values, and larger embedding capacity, due to its ability to reduce overall distortion while embedding more data. This makes pairwise PEE a more effective approach for reversible data hiding, despite its increased computational demands.
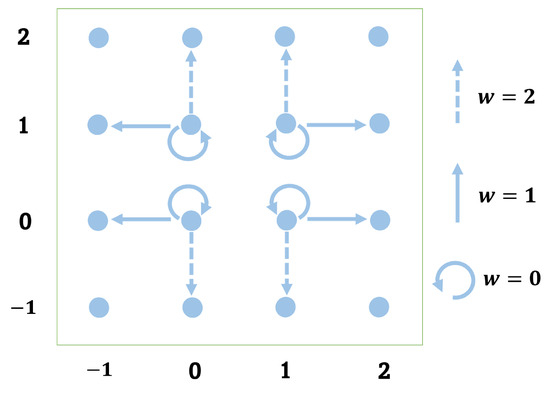
Figure 2.
The modification of prediction pairs in the incorporation of PVO and pairwise PEE, where the horizontal axis represents and the vertical axis represents in 2D-PEH.
Our method balances the embedding quantity for data hiding and the quality of the marked image by adaptively selecting the parameter k, achieving the desired embedding effect. As shown in Figure 3, with an increase of k, there is a corresponding increase in both the total number of prediction errors and the subset of expandable prediction errors. As and , bin 0 and bin 1 represent the primary and secondary peak points, respectively. When , bin 2 emerges as the peak point, yet the counts for bins 0 and 1 continue to rise. However, bin 0 and bin 1 are no longer peak points when . The number of bin 0 and bin 1 is smaller than that under the case . In essence, the challenge is not about changing k, but a way to choose an appropriate k. This selection is contingent upon the characteristics of the given embedding payload and the cover image, which dictate the classification of pixel blocks. The challenge lies not in changing k, but in selecting an appropriate value based on the given embedding payload and cover image characteristics. For a pixel block, the optimal k is set to according to:
In other words, enables the method to embed up to bits of data with larger pixel embedding in a pixel block.
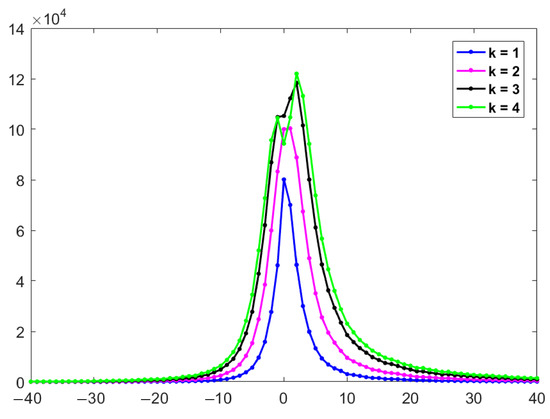
Figure 3.
In Lena, the number of prediction errors for different parameters , , , in KP-IPVO embedding.
To achieve adaptive embedding, we use the complexity of pixel blocks to determine the optimized k. For a block of size , its closed circle pixel blocks form a boundary region. We use the texture of this boundary region to estimate the smoothness of the target pixel block. We define the noise level () as the sum of absolute differences between consecutive pixels in the boundary region, following the approach in [27]. For pixel blocks with the same , we use the most common as parameter k, expressed as .
3.3. Content-Based Adaptive k
For a given cover image and a specified amount of secret data, the parameters k and are adaptively assigned based on the content complexity to achieve adaptive embedding. Using , a threshold T is used to fulfill block classification and embedding. Secret data are embedded into the pixel blocks with complexity less than or equal to the threshold T, where the optimal thresholds is determined by satisfying the embedding capacity and causing minimum image distortion. Thus, embedding in the selected pixel blocks with noise level less than or equal to ensures that the image distortion produced by the given embedding payload is minimized. For pixel blocks with noise levels , they are categorized into distinct classes. Each class of blocks is characterized by its own , which is tailored to the specific blocks. To achieve these settings, the noise level thresholds for pixel blocks are represented as .
where quantifies the distortion introduced by partitioning pixel blocks into distinct sets based on different values. Furthermore, represents the actual embedding payload, while denotes the required embedding capacity. To ensure the image distortion remains below a predetermined threshold while satisfying the required embedding capacity, we precisely calculate the threshold according to Equation (16). This optimization framework effectively balances the trade-off between data hiding security and visual quality preservation, allowing for adaptive parameter selection that maintains the imperceptibility of the marked image while maximizing embedding efficiency.
3.4. Implementation of the Proposed Method
To implement data embedding, auxiliary information are set to embed pure payload. The framework of the proposed embedding method is shown in Figure 4. At first, the cover image is divided into non-overlapped blocks with a size of , where . Subsequently, these pixel blocks are categorized into two distinct sets, referred to as the X-set and the O-set. The secret data are embedded in two stages: first, half of the data are concealed within the X-set, followed by the embedding of the remaining half into the O-set. During the decoding phase, the pixels in the O-set are restored prior to those in the X-set. Given that the embedding technique is uniform across both sets, the X-set is employed as a representative example for illustration purposes. When processing the pixel blocks within the X-set, the adjacent pixel blocks from the O-set serve as the content blocks to calculate noise level.
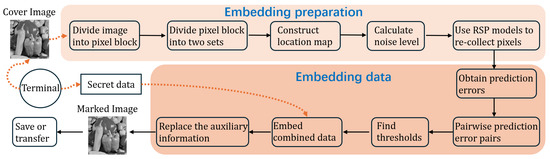
Figure 4.
The flowchart of the proposed embedding method in a cover image.
For eight-bit gray-scale pixels, pixels valued 255 or 0 are susceptible to overflow/underflow when the pixel modification is over 1. To address this, pixels with values of 255 or 0 are adjusted to 254 or 1, respectively, and a location map () is built to record these modifications. A bit 1 in indicates a pixel modification while a bit 0 indicates no pixel modification. By using arithmetic coding, is losslessly compressed into a shorter bit stream. Then, our re-collecting and sorting pixel model [36] is adopted to re-collect pixels in a block. Next, the least significant bits (LSBs) of the first two lines of pixels, the compressed location map and the pure payload (denoted as ) are embedded as a whole. Upon completion of the data embedding process, the auxiliary information is also ascertained. This information comprises six distinct data segments as follows.
- The length of binary auxiliary information (10 bits).
- Block size (4 bits).
- Thresholds ( bits).
- Parameter k ( bits).
- Embedding capacity (16 bits).
- Length of the compressed location map (16 bits).
The length of binary auxiliary information and auxiliary information are recorded as binary data. Finally, the above seven parts of data are embedded into the first two lines of pixels by LSB replacement for blind extraction.
The process of data extraction is briefly described as three steps:
- Auxiliary information extraction The LSBs of the first two lines pixels of the marked image are read to retrieve auxiliary information. First, the length of the binary auxiliary information is obtained according to the first 10 bits of the extracted data. Following, the auxiliary information is extracted.
- Data extraction and image restoration The marked image is divided into non-overlapped blocks with the extracted block size. The noise level of pixel block is calculated. If , extraction is performed with the help of the extracted parameter k and . Otherwise, the block is skipped.
- Restoration of the rest pixels The first two lines of bits data of are used to recover the first two lines of pixels. Then, the location map is restored by decompressing the compressed location map. Finally, pixels valued 0 or 255 are restored according to the location map.
4. Experimental Results
In this section, the performances of the three proposed methods are first compared, then some important parameters are given to verify the embedding. Next, the proposed method is compared with state-of-the-art methods on general images. Finally, the discrimination of the proposed method is proved by t-test.
The indicators for evaluating the performance of similar methods mainly include embedding capacity and visual quality (peak signal-to-noise ratio, also denoted PSNR) of the marked image. Specifically, the embedding payloads were handled from 5000 bits to the EC. General standard images (Airplane, Baboon, Barbara, Boat, Elaine, Lake, Lena, and Peppers in Figure 5) are from the USC-SIPI database http://sipi.usc.edu/database/database.php?volume=misc (accessed on 30 November 2020). Additionally, we also utilized the Kodak dataset https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sherylmehta/kodak-dataset (accessed on 19 May 2025) to validate the performance.

Figure 5.
Eight standard test gray images Boat, Barbara, Lake, Lena, Elaine, Peppers, Airplane and Baboon with a size of .
4.1. Analysis of Three Proposed Methods
When the parameter k is fixed at a stable value of 2, the method described in Section 3.1 is referred to as TP-IPVO. In contrast, when k is dynamically selected, the method is identified as KP-IPVO. Furthermore, the KP-IPVO method, which incorporates pairwise prediction error modifications, is termed PairwiseKP-IPVO. In data embedding, the TP-IPVO (fixed-parameter prediction) and KP-IPVO (dynamic parameter prediction) methods have been proposed to enhance embedding efficiency and image quality. The former achieves rapid embedding through fixed predictive parameters, while the latter optimizes predictive outcomes by dynamically selecting parameters to adapt to different image content. The comparative performance of TP-IPVO, KP-IPVO, and PairwiseKP-IPVO is shown in Figure 6. At low embedding capacities, KP-IPVO exhibits a more pronounced PSNR improvement over TP-IPVO. For example, in reversible data hiding on the Lena image, the PSNR gain is 0.51 dB at an embedding capacity of 10,000, and 0.19 dB at EC of 30,000. This observation indicates that as the embedding capacity increases and smooth pixel blocks are fully exploited, the subsequent utilization of coarser pixel blocks inevitably results in more significant image distortion.
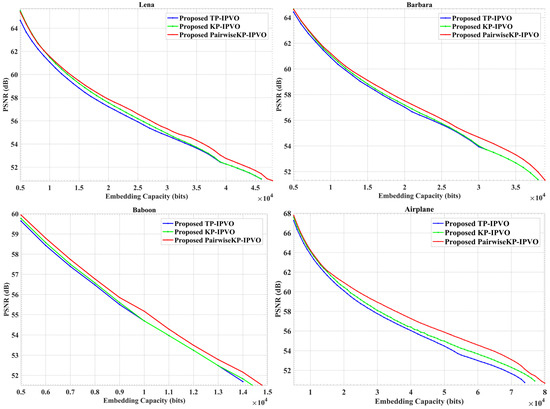
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the fidelity of TP-IPVO, KP-IPVO and PairwiseKP-IPVO, under different embedding payloads. The test images include Lena, Barbara, Baboon and Airplane.
Additionally, the proposed method generates more efficient predictions due to the presence of more consecutive or identical pixels in smooth images. In smooth images, it is easier for adjacent pixel values to be similar. This similarity allows the predictor to produce smaller prediction errors during processing, which is beneficial for obtaining expandable prediction errors rather than shifting errors, thereby increasing the embedding capacity and image quality. This effect is particularly notable for the Airplane image, where a greater number of prediction errors contribute to 2D PEH mapping. This observation demonstrates that the proposed content-based selection can optimize predictions. Since 2D PEH mapping is only applied to part-prediction errors, its main advantage is that it can enhance PSNR under the same embedding capacity. PairwiseKP-IPVO, due to its requirement for multiple pixel block threshold corrections, has a much higher computational load than TP-IPVO, thus taking the longest time under the same conditions. Although this feature reduces processing speed, it effectively improves the PSNR performance of the final image. The results indicate that adaptive prediction not only increases embedding capacity but also enhances PSNR, as content-based optimization prioritizes more accurate predictions.
4.2. Analysis of Parameters
Table 2 delineates the embedding parameters for KP-IPVO and PairwiseKP-IPVO in varying EC in the standard test image, Lena. The embedding parameters for KP-IPVO and PairwiseKP-IPVO are presented in Table 2. It is noteworthy that the parameters vary for pixel blocks of different sizes, reflecting the inherent complexities associated with each block size. In both methods, the complexity threshold tends to increase with the payload. However, the use of pixel blocks with higher complexity introduces additional image distortion, which in turn leads to a rapid decline in the PSNR. Due to the reduced distortion in PairwiseKP-IPVO with 2D prediction error pairs mapping, the advantage in PSNR is more pronounced under larger embedding payloads. Furthermore, the table reveals that PairwiseKP-IPVO benefits from processing more pixels within a block, which enhances the pairing of prediction errors. This is particularly advantageous for larger payloads, where the method’s performance surpasses that of KP-IPVO. Additionally, the relative best PSNR is observed to decrease in smaller pixel blocks under large payloads exceeding 10,000 bits. This decline is attributed to two factors: on one hand, an increase in prediction errors within smaller pixel blocks, and on the other hand, a reduction in pixel continuity that results in lower prediction accuracy. In summary, the directly changes the key indicators. Their appropriate values are obtained after embedding the data.

Table 2.
Embedding parameters for specific capacities on the image Lena, the unit of PSNR is dB.
4.3. Comparison with Advanced Methods
The proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method is compared with the classic PVO-based methods [24,25,26], and competing methods [32,35,38,39] shown in Figure 7. Two comparisons of fidelity are enumerated in Table 3 and Table 4. In general, the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO outperforms other methods in most cases. Unlike PairwiseKP-IPVO, there are at most two prediction errors in a pixel block in PVO [24], IPVO [25] and PVO-K [26]. It limits their embedding capacity. On Lena, 15,000 bits and 10,000 bits improvements of embedding capacity are exited as compared with IPVO and PVO-K, respectively. Different from PVO, IPVO adds the pixel position to optimizes the prediction and make the prediction more accurate. IPVO outperforms PVO under all embedding payloads. The position of the pixels and the self-learning design are combined in the proposed generation of prediction error, greatly improving performance. On Lena, as the payload reaches 10,000 bits, the PSNR advantages of PairwiseKP-IPVO over IPVO and PVO-K are 1.33 dB and 1.19 dB, respectively. Obviously, our method achieves the better performance for most applications.
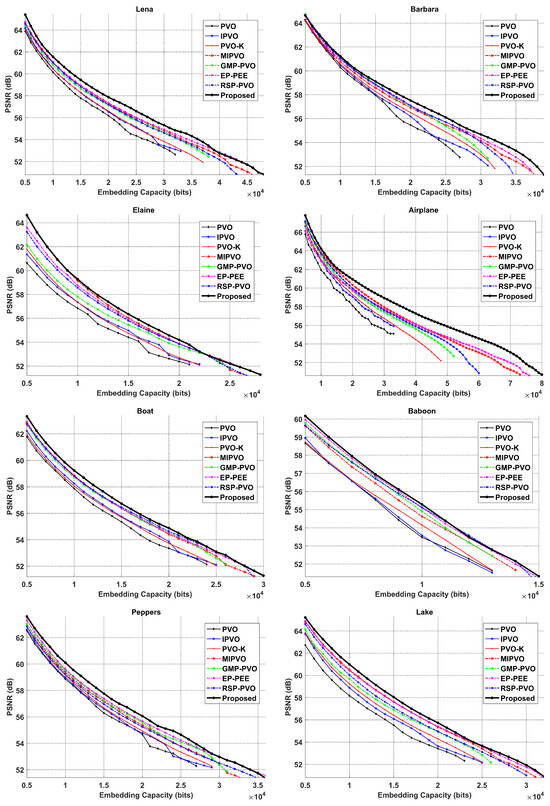
Figure 7.
Evaluation of fidelity of the PVO method [24], IPVO method [25], PVO-K method [26], MIPVO method [35], GMP-PVO method [32], EP-PEE [39], RSP-PVO method [36], and the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method.

Table 3.
PSNR (dB) in the representative methods [25,26], the competing methods [32,35,36,39] and the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method under the embedding payload of 10,000 bits.

Table 4.
PSNR (dB) in the representative methods [25,26], the competing methods [32,35,36,39] and the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method under the embedding payload of 20,000 bits.
MIPVO [35] also generates multiple prediction errors at a time. However, each prediction of MIPVO is independent, while prediction of PairwiseKP-IPVO comes from consecutive or equal pixel values. In theory, the prediction errors produced by consecutive or equal pixels are more correlated, thereby building steeper PEH. The specific data confirm that the proposed scheme achieves 0.20 dB higher PSNR on average in Table 3. The proposed method has image distortion reduced on eight test images and the average PSNR gain of the proposed method is 0.48 dB at 20,000 bits embedding payload. It shows that the advantages of the proposed method are stable for most kinds of applications.
RSP-PVO [36] is a recently proposed method to construct an RSP model to map multiple prediction errors. Since the proposed method improves the prediction of continuous pixels, the PSNR advantage is more significant on smooth images. Likewise, the proposed method performs better on smooth images under all embedding payloads. In addition, embedding capacity is also extended due to the use of error pairs for 2D joint mapping on eight images. As for application, the proposed method has greater advantages in projects with more secret data.
In the GMP-PVO method [32], the generic multiple predictor framework based on content allows predicted pixels to be used as an aid to the PVO-based prediction. In terms of embedding capacity, the proposed method outperforms GMP-PVO on eight test images. Compared to GMP-PVO, the average PSNR values of the proposed method are 0.93 dB and 0.52 dB higher under 10,000 bits and 20,000 bits embedding payloads on eight test images. In Elaine, the PSNR of PairwiseKP-IPVO drops a lot when the actual embedding payload reaches 22,000 bits. At this time, its performance is similar to that of GMP-PVO, because as many pixels as possible are used without prioritizing smooth pixels.
In the EP-PEE method [39], the prediction errors are constructed by the redundancy among the largest three or the smallest three pixels. In order to make better use of the prediction errors, a content selection of expandable bin is proposed to improve the 2D PEH mapping. An adaptive pairwise PEE strategy is adopted in the PairwiseKP-IPVO, combining prediction errors [0,1] into prediction error pairs. On average, the PSNR of PairwiseKP-IPVO is 0.39 dB higher than that of EP-PEE in Table 3 and 0.33 dB in Table 4. In addition, the embedding capacity of PairwiseKP-IPVO is higher than that of [39] on smooth images of Airplane, Lena, Lake, and Barbara. It means that the fidelity advantage is over a wider range of payloads. On the image Lena and Peppers, PairwiseKP-IPVO obtains better PSNR than [39] when the payloads do not exceed 39,000 and 35,000 bits. In the proposed scheme, the prediction errors with low distortion are exhausted at high embedding payloads. Prediction errors in rough pixel blocks introduce more distortion. In this case, the 1D-based modification also introduces more distortion.
To verify the effectiveness of our method, extensive comparisons were conducted on Kodak test images under a 10,000-bit embedding payload, as detailed in Table 5. The Mean Squared Error (MSE) was employed to quantify the average squared difference between the original and marked images, thereby providing a measure of the overall distortion introduced by the embedding process. Compared to PVO [24] and IPVO [25], our method showed significant improvements with average PSNR gains of 11.82 dB and 3.83 dB, respectively, corresponding to substantial MSE reductions from 0.550 to 0.036 and from 0.089 to 0.036. Against PVO-K [26], we achieved consistent advantages of 1.12 dB in PSNR with MSE improvement from 0.049 to 0.036. Our method also outperformed [39] with 0.58 dB higher PSNR and MSE reduction from 0.041 to 0.036. The MSE results further validate less distortion and better image quality preservation of our approach, with our PairwiseKP-IPVO method achieving the lowest average MSE of 0.036 among all compared methods. These dual-metric evaluations confirm that our proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method delivers highly competitive performance with enhanced image quality in reversible data hiding applications.

Table 5.
Comparison of PSNR (dB) and MSE between the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO (Proposed) method and the method of [24,25,26,39], for the embedding capacity of 10,000 bits in 24 other test images.
4.4. t-Test
The paired t-test is suitable for comparing the performance differences between methods. We adopted paired t-tests to determine whether the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method significantly differs from the other four methods in terms of PSNR. For each test image and embedding payload, we paired the PSNR values of our method with each of the other methods to conduct the paired t-tests.
The t-statistics from our paired t-tests are shown in Table 6. A positive t-value indicates that our PairwiseKP-IPVO method achieved higher PSNR values than the compared method. Based on the degrees of freedom in our experiments, t-values greater than 2.78 correspond to p < 0.01, indicating highly significant differences. The results show that our proposed method significantly outperforms the compared methods in most test cases. The only exceptions are with the RSP-PVO method on the Peppers image, where our method performed worse (negative t-value), and with the EP-PEE method on Peppers, where the difference was not statistically significant. Overall, the experimental data demonstrate that the proposed method achieves significant improvement in prediction accuracy by making full use of closely distributed pixels. The superiority is more significant on smoothed images and is prevalent for both digital images.

Table 6.
The t-statistics between the proposed PairwiseKP-IPVO method and methods PVO method [24], RSP-PVO method [36], EP-PEE method [39], and GMP-PVO method [32] in paired t-tests.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented a novel approach of reversible data hiding that leverages the redundancy between consecutive pixels to enhance the efficiency of prediction error generation. Our method introduces an adaptive strategy that dynamically selects multi-pass parameters based on the content of pixels, leading to more expandable prediction errors. This innovative approach departs from traditional fixed-parameter methods, allowing for better exploitation of the inherent structure and redundancy of image pixels. The result is an improved data embedding efficiency with reduced image distortion. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme outperforms a series of state-of-the-art schemes with moderate capacity in terms of image fidelity. This confirms the efficacy of our method in achieving more efficient data embedding and image recovery. As the demand for secure and reliable data embedding solutions grows, our method could service as a promising solution for various applications where data security and image quality are paramount. The proposed method encounters limitations in computational complexity, primarily attributable to the adaptive parameter selection and multi-pass embedding strategy. Future endeavors will concentrate on developing lightweight iterations of the adaptive parameter selection mechanism. Additionally, we will persist in investigating the potential of high-dimensional histogram modification within the realm of RDH.
Author Contributions
X.K. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, software development, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing the original draft and visualization. W.H. contributed to methodology, validation and writing—review and editing. Z.C. contributed to supervision, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and final review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Macau under Grant 0059/2020/A2 and Grant 0052/2020/AFJ, and in part by Guangzhou Development District International Cooperation Project under Grant 2023GH01.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a publicly accessible repository, http://sipi.usc.edu/database/database.php?volume=misc (accessed on 30 November 2020), https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sherylmehta/kodak-dataset (accessed on 19 May 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, M.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Di, F. A Hierarchical Authorization Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted Image Based on Secret Sharing. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, Y.; Chang, C.C.; Horng, J.H. A matrix coding-oriented reversible data hiding scheme using dual digital images. Mathematics 2023, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, J.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, C.C. Embedding Secret Data in a Vector Quantization Codebook Using a Novel Thresholding Scheme. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Dao, T.T. A novel PVO-based RDH scheme utilizes an interleaved data embedding technique using dual-pixels. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2025, 89, 103939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Weng, H.Y.; Huang, C.T. Enhanced reversible data hiding in encrypted images via median preserving pixel value ordering and block-wise difference preservation. Signal Image Video Process. 2025, 19, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M.; Du, R. Lossless data embedding new paradigm in digital watermarking. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2002, 2002, 986842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.U.; Sharma, G.; Tekalp, A.M.; Saber, E. Lossless generalized-LSB data embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.U.; Sharma, G.; Tekalp, A.M. Lossless watermarking for image authentication: A new framework and an implementation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M.; Du, R. Invertible authentication. In Proceedings of the Security and Watermarking of Multimedia contents III. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 20 January 2001; Volume 4314, pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Goljan, M.; Fridrich, J.J.; Du, R. Distortion-free data embedding for images. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Information Hiding, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–27 April 2001; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Shi, Y.Q.; Ansari, N.; Su, W. Reversible data hiding. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2003. ISCAS’03, Bangkok, Thailand, 25–28 May 2003; Volume 2, pp. II–II. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K.; Suh, Y.H.; Ho, Y.S. Reversiblee image authentication based on watermarking. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–12 July2006; pp. 1321–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Gui, X.; Yang, B. A novel reversible data hiding scheme based on two-dimensional difference-histogram modification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2013, 8, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, R.; Shi, Y.Q. Pairwise prediction-error expansion for efficient reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 5010–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Gui, X.; Yang, B. Efficient reversible data hiding based on multiple histograms modification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J. Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2003, 13, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, A.M. Reversible watermark using the difference expansion of a generalized integer transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltuc, D. Low distortion transform for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Yang, B. Efficient reversible image watermarking by using dynamical prediction-error expansion. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 3673–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Coltuc, D. Improved embedding for prediction-based reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 6, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, B.; Zeng, T. Efficient reversible watermarking based on adaptive prediction-error expansion and pixel selection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 3524–3533. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y. Improving Pairwise PEE via Hybrid-Dimensional Histogram Generation and Adaptive Mapping Selection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 2176–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Chang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. High-fidelity reversible data hiding based on enhanced IPPVO and adaptive 2D histogram modification. Signal Process. 2025, 232, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Yang, B. High-fidelity reversible data hiding scheme based on pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, X.; Yang, B. Improved PVO-based reversible data hiding. Digit. Signal Process. 2014, 25, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, R. Reversible data hiding using invariant pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Processing: Image Commun. 2014, 29, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Li, X.; Wang, J. High-fidelity reversible data hiding based on pixel-value-ordering and pairwise prediction-error expansion. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 39, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Shen, Y.; Xu, D.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, C.C. PVO-Based Reversible Data Hiding Using Two-Stage Embedding and FPM Mode Selection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 3512–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Gao, E. Reversible data hiding based on novel embedding structure PVO and adaptive block-merging strategy. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 26047–26071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Pei, Q. A novel reversible image data hiding scheme based on pixel value ordering and dynamic pixel block partition. Inf. Sci. 2015, 310, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Jung, K.H. Enhanced pairwise IPVO-based reversible data hiding scheme using rhombus context. Inf. Sci. 2020, 536, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Pan, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X. A comparative study between PVO-based framework and multi-predictor mechanism in reversible data hiding. J. Vis. Commun. Image R. 2021, 81, 103349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Lu, L.; Song, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, Z. Non-local PPVO-based reversible data hiding using opposite direction pairwise embedding. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2025, 90, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Kim, H.J. Pixel-based pixel value ordering predictor for high-fidelity reversible data hiding. Signal Process. 2015, 111, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Cai, Z. An Insight Into Pixel Value Ordering Prediction-Based Prediction-Error Expansion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Cai, Z. An Information Security Method Based on Optimized High-Fidelity Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8529–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xiong, G.; Weng, S.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y. Reversible data hiding using multi-pass pixel-value-ordering and pairwise prediction-error expansion. Inf. Sci. 2018, 467, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Qi, W.; Guo, Z. Location-Based PVO and Adaptive Pairwise Modification for Efficient Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 2306–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y. High-Fidelity Reversible Image Watermarking Based on Effective Prediction Error-Pairs Modification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).