An Exploratory Assessment of LLMs’ Potential for Flight Trajectory Reconstruction Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A pre-trained LLM (LLaMA 3.1-8B) was fine-tuned on flight trajectory data, and it demonstrated its ability to reconstruct flight trajectories from noisy, missing, and irregular ADS-B inputs. It demonstrated competitive performance compared to the traditional Kalman filter approach and the conventional deep learning approach (sequence to sequence (Seq2Seq) with Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) architecture).
- A novel evaluation metric named containment accuracy to assess trajectory reconstruction quality. This metric reports the smallest allowable error envelope that contains a specified proportion of predictions, providing a more interpretable performance criterion without requiring coordinate transformations.
- Higher accuracy achieved by the LLM model within scenarios with sparse data or abrupt maneuvers underscored the potential of LLMs to augment or surpass traditional methods in this domain. The study also highlighted and discussed the essential limitations observed, such as the LLM’s occasional hallucination of outputs and the constraints imposed by token length (which currently limit the duration of trajectories it can process in one pass).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Flight Trajectory Reconstruction
2.2. LLM on Time Series and Aviation Data
3. Methodology
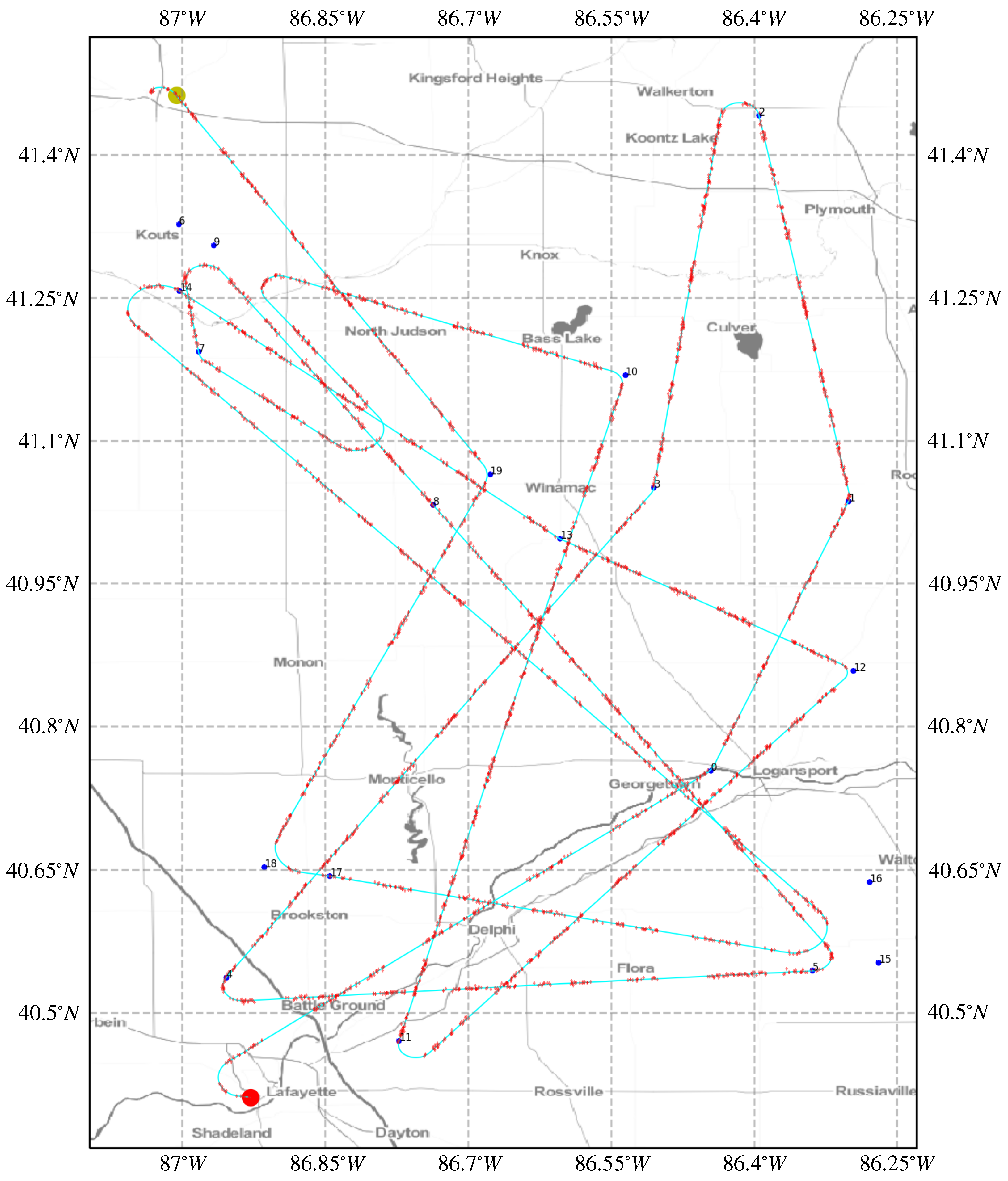
3.1. Flight Data Collection and Generation
3.2. LLM Model Configuration
3.3. Data Preprocessing
3.4. Evaluation Metrics Setup
4. Results
4.1. Base Model Evaluation
4.2. Fine-Tuning Model Evaluation
4.2.1. Linear Flight Trajectories
4.2.2. Curved Flight Trajectories
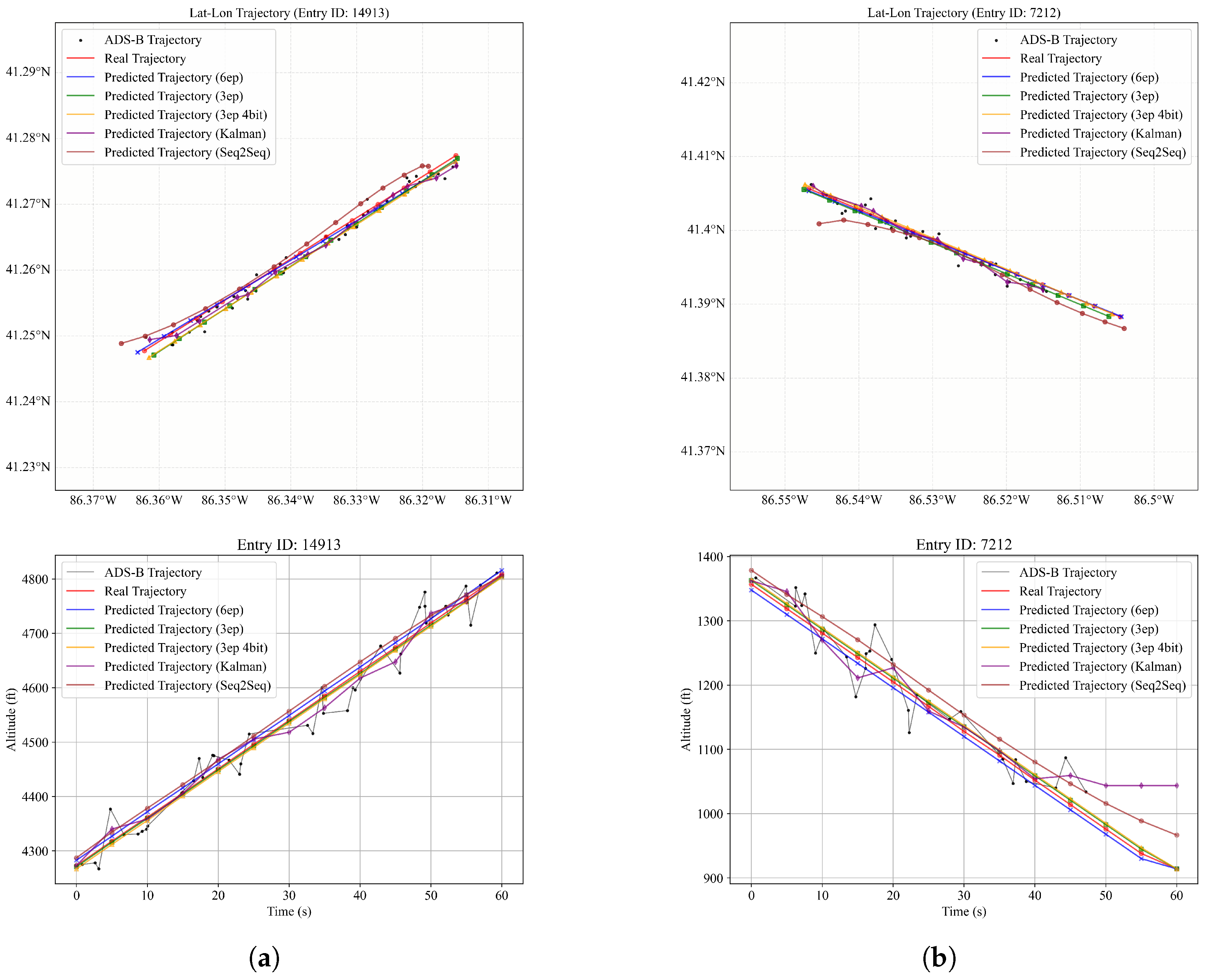
4.2.3. Performance Comparison
4.2.4. Empirical ADS-B Data Evaluation
5. Discussion
5.1. Limitations
5.2. Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xi, Z.; Chen, W.; Guo, X.; He, W.; Ding, Y.; Hong, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Jin, S.; Zhou, E.; et al. The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.07864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mott, J.H.; Johnson, M.E.; Springer, J.A. Development of a Reliable Method for General Aviation Flight Phase Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 11729–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Aviation Administration. ADS-B–Frequently Asked Questions; Federal Aviation Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mott, J.H.; Bullock, D.M. Estimation of aircraft operations at airports using mode-C signal strength information. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 19, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, M.; Pan, Q.; Yan, B.; Zhang, H. LSTM-based flight trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hegselmann, S.; Buendia, A.; Lang, H.; Agrawal, M.; Jiang, X.; Sontag, D. Tabllm: Few-shot classification of tabular data with large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Valencia, Spain, 25–27 April 2023; pp. 5549–5581. [Google Scholar]
- Gruver, N.; Finzi, M.; Qiu, S.; Wilson, A.G. Large Language Models Are Zero-Shot Time Series Forecasters. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Neumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 19622–19635. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Tian, S. A hybrid CNN-LSTM model for aircraft 4D trajectory prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 134668–134680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, J.L.; Hwang, I.; Rotea, M. New algorithms for aircraft intent inference and trajectory prediction. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2007, 30, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porretta, M.; Dupuy, M.D.; Schuster, W.; Majumdar, A.; Ochieng, W. Performance evaluation of a novel 4D trajectory prediction model for civil aircraft. J. Navig. 2008, 61, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipphavong, D.P.; Schultz, C.A.; Lee, A.G.; Chan, S.H. Adaptive algorithm to improve trajectory prediction accuracy of climbing aircraft. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2013, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dy, L.R.I.; Borgen, K.B.; Mott, J.H.; Sharma, C.; Marshall, Z.A.; Kusz, M.S. Validation of ADS-B Aircraft Flight Path Data Using Onboard Digital Avionics Information. In Proceedings of the 2021 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), Virtual, 29–30 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Quan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. A deep learning approach for aircraft trajectory prediction in terminal airspace. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 151250–151266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mott, J.H. Improved Framework for Classification of Flight Phases of General Aviation Aircraft. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2677, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Peng, W.C.; Chen, T.F. Llm4ts: Two-stage fine-tuning for time-series forecasting with pre-trained llms. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.08469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Niu, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. One Fits All: Power General Time Series Analysis by Pretrained LM. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Oh, A., Neumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 36, pp. 43322–43355. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, P.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Pan, S.; et al. Time-LLM: Time Series Forecasting by Reprogramming Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chou, J.; Tien, A.; Zhou, X.; Baumgartner, D. AviationGPT: A Large Language Model for the Aviation Domain. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum and Ascend, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 July–2 August 2024; p. 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.; Clarke, S.S.; Kalyanam, K.M. Towards an aviation large language model by fine-tuning and evaluating transformers. In Proceedings of the 2024 AIAA DATC/IEEE 43rd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 September–3 October 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhak, S.; Hubbard, W.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Li, M.Z. Chatatc: Large language model-driven conversational agents for supporting strategic air traffic flow management. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14850. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y. Integrating spoken instructions into flight trajectory prediction to optimize automation in air traffic control. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q. General Aviation Aircraft Flight Status Identification Framework. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, J.M.; Ellerbroek, J. Bluesky ATC simulator project: An open data and open source approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Research in Air Transportation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 20–24 June 2016; FAA/Eurocontrol USA/Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Volume 131, p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Grattafiori, A.; Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Al-Dahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Vaughan, A.; et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21783. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Luo, Z.; Feng, Z.; Ma, Y. Llamafactory: Unified efficient fine-tuning of 100+ language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.13372. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dettmers, T.; Pagnoni, A.; Holtzman, A.; Zettlemoyer, L. Qlora: Efficient finetuning of quantized llms. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 10088–10115. [Google Scholar]
- Babb, T. How a Kalman Filter Works, in Pictures. 2015. Available online: https://www.bzarg.com/p/how-a-kalman-filter-works-in-pictures/ (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, A.M.; Alias Parth Goyal, A.G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Professor forcing: A new algorithm for training recurrent networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 4601–4609. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Rosasco, L.; Caponnetto, A. On early stopping in gradient descent learning. Constr. Approx. 2007, 26, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, R.; Salem, F.M. Gate-variants of gated recurrent unit (GRU) neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 60th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 August 2017; pp. 1597–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, R.G. Two-sided confidence intervals for the single proportion: Comparison of seven methods. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]




| Determine the curved flight trajectory using |
| these estimated parameters (time, latitude, |
| longitude, altitude, true airspeed, vertical |
| speed, and track angle). Please summarize the |
| precise trajectory considering these inputs: |
| (967, 4140614, 8692362, 4863, 81, 0, 308), |
| (1158, 4140473, 8692565, 4895, 81, 0, 308), |
| (1266, 4140443, 8692432, 4886, 81, 0, 308), |
| … continue with other rows … |
| (5747, 4142412, 8696346, 4871, 81, 0, 271) |
| - - - - - - - |
| Summary: |
| Metric | Kalman Filter | Seq2Seq | 3 Epochs + 4-Bit | 3 Epochs | 6 Epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success rate (%) † | 100.00 | 100.00 | 80.60 | 81.67 | 100.00 |
| RMSE-lat (°) | 0.00419 | 0.00490 | 0.65002 | 0.37361 | 0.00304 |
| RMSE-lon (°) | 0.00721 | 0.00494 | 1.37475 | 0.00514 | 0.00425 |
| RMSE-alt (m) | 52.88 | 32.50 | 24.74 | 23.77 | 18.60 |
| MAE-lat (°) | 0.00204 | 0.00291 | 0.01125 | 0.00425 | 0.00061 |
| MAE-lon (°) | 0.00367 | 0.00337 | 0.02328 | 0.00130 | 0.00081 |
| MAE-alt (m) | 29.49 | 18.67 | 8.03 | 7.34 | 6.06 |
| Acc. in spec. range (%) ‡ | 87.22 | 94.21 | 97.60 | 98.31 | 98.78 |
| 95% CI ‡ | (87.08–87.37) | (94.10–94.31) | (97.53–97.68) | (98.25–98.38) | (98.73–98.83) |
| Lon + lat cont. acc. (°) § | 0.00589 | 0.00616 | 0.00186 | 0.00167 | 0.00098 |
| Alt cont. acc. (m) § | 48.45 | 30.17 | 13.56 | 12.54 | 10.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Mott, J.H. An Exploratory Assessment of LLMs’ Potential for Flight Trajectory Reconstruction Analysis. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111775
Zhang Q, Mott JH. An Exploratory Assessment of LLMs’ Potential for Flight Trajectory Reconstruction Analysis. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111775
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qilei, and John H. Mott. 2025. "An Exploratory Assessment of LLMs’ Potential for Flight Trajectory Reconstruction Analysis" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111775
APA StyleZhang, Q., & Mott, J. H. (2025). An Exploratory Assessment of LLMs’ Potential for Flight Trajectory Reconstruction Analysis. Mathematics, 13(11), 1775. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111775








