Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, so its detection and monitoring are critical. However, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) is particularly vulnerable to complex, unstructured noise, which compromises image quality and diagnostic accuracy. This study proposes the use of NLE-ANSNet, a deep learning-based denoizing framework that integrates multilevel noise level estimators (NLEs) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS) within residual blocks. The model performs progressive, stagewise noise suppression at multiple feature depths, dynamically adjusting normalization based on localized noise estimates. This enables context-aware denoizing, preserving fine anatomical details. To simulate clinically realistic conditions, we developed a hybrid noise simulation framework that combines Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level. This framework aims to approximate a balanced noise distribution for evaluation purposes, with both mean and median noise levels reported to enhance evaluation robustness and prevent bias from extreme cases. NLE-ANSNet achieves a PSNR of 34.01 dB and an SSIM of 0.9393, surpassing those of state-of-the-art models. The method aims to support diagnostic reliability by preserving image structure and intensity fidelity in CE-MRI interpretation. In addition to quantitative analysis, a qualitative assessment was conducted to visually compare denoizing outputs across models, further demonstrating NLE-ANSNet’s superior ability to suppress noise while preserving diagnostically critical information. Unlike previous approaches, this study introduces a denoizing framework that combines multilevel noise estimation and adaptive noise scaling specifically tailored for CE-MRI in HCC under hybrid noise conditions—a clinically relevant and underexplored area. Overall, this study supports improved clinical decision making in HCC management.
Keywords:
denoizing; noise reduction; deep learning; medical image noise; image restoration; image quality; MRI; hepatocellular carcinoma; CE-MRI MSC:
92C50; 92C55; 94A08; 68T07; 65D18; 68T05
1. Introduction
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by enabling the accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of various diseases. However, noise introduced during the imaging process significantly degrades image quality, necessitating advanced denoizing techniques to restore clarity while preserving essential anatomical details. Medical images are an essential component of a patient’s electronic health record (EHR) and are traditionally interpreted by radiologists. However, this process is often constrained by factors such as the radiologist’s experience and fatigue and the time-intensive nature of training skilled professionals, leading some healthcare systems to rely on tele-radiology services for cost efficiency [1]. Imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) [2], magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [3], positron emission tomography (PET) [4], ultrasound (US) [5], and X-rays are fundamental tools in clinical diagnosis [6].
High-quality imaging is critical for improving diagnostic accuracy, ensuring better treatment planning and enabling effective patient monitoring [7]. Despite its importance, noise and artifacts introduced during the acquisition process pose significant challenges for medical imaging. These issues can obscure structural details, degrade image clarity, and directly affect clinical outcomes by making tasks such as segmentation, classification, and diagnosis more difficult [8,9]. Noise in medical imaging can manifest in various forms, each with unique characteristics and impacts on image quality. Gaussian noise, characterized by a normal distribution, is a common type of noise introduced by electronic fluctuations in imaging devices, resulting in uniform intensity variations across the image [10]. Poisson noise, also known as shot noise, arises from the discrete nature of photon detection, which is more pronounced in low-intensity regions, particularly in modalities such as X-rays and nuclear imaging [11]. Rician noise, which is specific to MRI, is generated during the magnitude reconstruction of complex signals and becomes more significant in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regions, making denoizing particularly challenging [12]. These noise types not only degrade image clarity but also pose significant challenges to downstream tasks such as segmentation and diagnosis [13,14].
Noise manifests in various forms, including Gaussian noise, motion blur, diffusion noise, and JPEG compression artifacts [10,11,12,13]. Conventional denoizing methods, such as Gaussian filters and wavelet transforms, are often inadequate because they fail to preserve critical anatomical details, which are essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning [14,15].
Machine learning has become a cornerstone in image processing, enabling the automation of complex tasks such as object detection, classification, segmentation, and image enhancement [16,17,18]. By learning directly from data, machine learning models can identify patterns and features that are often challenging to capture using conventional methods [19]. In medical imaging, machine learning has revolutionized how images are analyzed and interpreted, offering powerful tools to assist in diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. Its ability to process large volumes of data and adapt to diverse imaging modalities has made it indispensable in healthcare, where precision and efficiency are critical [20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
Machine learning, particularly deep learning, has emerged as a transformative approach to address these challenges in medical image denoising [27]. It has shown remarkable success in medical imaging tasks such as classification, segmentation, image enhancement, and anomaly detection, leveraging its ability to automatically learn complex patterns from large datasets. Unlike conventional methods, deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), residual networks (ResNets), and attention mechanisms can learn complex noise patterns, enabling more effective noise suppression in medical images [28,29,30,31]. These models outperform traditional approaches by adapting to diverse noise types and enhancing image quality, thereby improving the performance of downstream tasks such as segmentation and classification.
Recent advancements in deep learning have led to the development of several high-performance denoizing models. SwinIR, which leverages a Swin transformer for efficient restoration, has demonstrated strong performance in natural image denoizing [32]. Similarly, Restormer, an efficient transformer-based model, optimizes spatial and channel attention mechanisms for high-quality image reconstruction [33]. Among CNN-based approaches, DRUNet employs a U-Net-based residual learning framework to enhance image quality while preserving fine details [34]. DnCNN, a widely used deep convolutional denoizing model, applies residual learning and batch normalization to effectively remove Gaussian noise [35].
Attention-based architectures such as RNAN and NLRN incorporate nonlocal mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies, effectively suppressing noise [36,37]. Furthermore, N3Net uses nonlocal neural blocks to improve self-similarity learning, which is beneficial in structured noise removal [38]. FFDNet, on the other hand, is a computationally efficient model that allows for adaptive noise level adjustments, making it versatile for different noise intensities [39].
While these models have demonstrated strong performance across various image restoration tasks, their effectiveness in contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI), particularly in the presence of hybrid noise, remains an area requiring further investigation. This study aims to address this gap by evaluating deep learning-based denoizing techniques tailored for CE-MRI applications.
An important application of these advancements is in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally [40]. Accurate imaging is vital for effective HCC diagnosis and treatment, with CE-MRI being the preferred modality due to its ability to depict liver anatomy and tumor characteristics in detail [41]. Although CE-MRI is known for its high-quality imaging and detailed visualization of HCC, the potential presence of noise, even at minimal levels, can subtly affect the delineation of critical tumor boundaries and vascular features. Addressing these challenges through effective denoising techniques can further optimize the accuracy of segmentation and diagnosis, enhancing the reliability and utility of CE-MRI in both clinical and research applications.
By addressing these challenges, advanced denoizing solutions can improve segmentation accuracy, enhance diagnostic reliability, and ultimately contribute to better clinical outcomes. This study aims to leverage deep learning techniques to develop robust denoising solutions that can significantly enhance CE-MRI image quality while preserving critical anatomical details, offering a pathway for improved diagnostic and therapeutic applications in HCC management.
CE-MRI is a widely used imaging technique that enhances the visualization of anatomical structures and tissue abnormalities by utilizing contrast agents. Among its specialized applications, dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) can quantify critical microvascular parameters, such as the forward volumetric transfer constant (Ktrans), plasma volume (vp), and extravascular extracellular space (ve), which are essential for characterizing tumor physiology and supporting treatment planning. However, conventional quantitative analysis methods in DCE-MRI are highly sensitive to factors such as noise, the sampling interval, and the acquisition duration, often leading to inaccuracies in parameter estimation. The referenced study demonstrates that knowledge-based adaptive models can enhance robustness by learning directly from imaging data, reducing dependency on arterial input functions, and mitigating the impact of noise and temporal limitations [42].
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a powerful technique for assessing tissue microvascular properties and relies on the diffusion of contrast agents such as gadolinium diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid (Gd-DTPA) into the extravascular–extracellular space, which is governed by factors such as vessel permeability, surface area, and blood flow. However, the accuracy of DCE-MRI is highly sensitive to noise, including Gaussian noise, motion artifacts, and variability in precontrast T1 mapping, which can significantly distort pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters such as Ktrans and ve, potentially leading to the misclassification of tissues. As highlighted by Fennessy et al. [43], even minor inaccuracies in precontrast T1 values (±20%) can significantly alter PK results, emphasizing the critical need for effective denoizing methods. Denoizing mitigates these artifacts by enhancing spatial and temporal resolution, preserving signal fidelity, and ensuring accurate and reproducible measurements. While DCE-MRI is not the primary focus of this study, its sensitivity to noise underscores the broader importance of developing robust denoising techniques to improve the reliability of CE-MRI data in quantitative imaging applications. Although DCE-MRI is not directly addressed in this study, the proposed denoising method is potentially applicable to DCE-MRI as well, given the similar noise characteristics and their impact on pharmacokinetic modeling and diagnostic accuracy. This potential will be explored in future work.
CE-MRI is widely recognized for its ability to achieve high-resolution anatomical visualization, particularly in research environments that utilize advanced high-field MRI systems, where resolutions can reach 100–200 µm. However, in routine clinical practice, the achievable resolution is typically lower, often exceeding 300 µm. This reduced resolution, combined with standard imaging protocols, increases susceptibility to noise and can lead to the loss of fine anatomical details [44,45], which is especially critical in applications such as liver lesion detection and monitoring. These challenges underscore the importance of advanced denoizing techniques to ensure diagnostic fidelity in CE-MRI workflows.
The quantitative assessment of signal intensity changes in CE-MRI has demonstrated high sensitivity to alterations in tissue permeability. In preclinical studies, even localized changes in barrier integrity resulted in significant differences in postcontrast MRI signal intensity, with PS-exposed subjects showing markedly elevated values compared with controls (399.7 ± 68.7 vs. 39.2 ± 12.2, p < 0.0001) [46]. These findings underscore the importance of preserving signal fidelity in contrast-enhanced imaging, particularly in hepatic applications such as HCC assessment, where subtle changes in vascular permeability and lesion enhancement are diagnostic. Thus, minimizing noise and artifacts is essential to ensure accurate and reproducible quantitative measurements in liver CE-MRI workflows.
The quality of arterial phase imaging in CE-MRI after gadoxetic acid injection has been shown to improve with a lower injection rate of 1 mL/s compared with the standard 2–3 mL/s used for nonspecific extracellular gadolinium chelates [47,48,49]. One proposed explanation for the improved MRI quality is that a lower injection rate allows more time for gadoxetic acid to bind with proteins, particularly when the bolus is less compact, thereby facilitating the establishment of valences. Additionally, slower circulation of the contrast material ensures that more contrast remains in the arterial vasculature during arterial phase acquisition [47,50]. Importantly, a lower injection rate also reduces the number of truncation artifacts in the k-space, which are known to degrade image quality [49]. These findings highlight the sensitivity of CE-MRI to both acquisition parameters and artifacts, underscoring the critical need for effective denoising strategies to further optimize image quality in CE-MRI.
During CE-MRI with gadoxetic acid, hemangiomas may appear hypointense relative to the liver parenchyma during the equilibrium and delayed phases owing to substantial parenchymal uptake of the contrast agent as early as 3–5 min postinjection. This uptake can create the so-called pseudowashout sign, mimicking hypervascular tumors and leading to potential diagnostic errors [51,52]. These challenges highlight the importance of improving image quality, particularly through advanced denoizing techniques, to reduce noise and enhance the accuracy of tissue contrast interpretation, ultimately minimizing misdiagnoses.
While prior denoizing methods such as FFDNet, DRUNet, and SwinIR demonstrate strong performance on natural images or single noise types, they do not explicitly address the challenges of denoizing CE-MRI for HCC in complex, hybrid noise environments. Moreover, most existing models rely on fixed noise maps or synthetic augmentation, limiting their adaptability. To address these gaps, we propose a framework that (1) integrates multilevel noise estimation modules at increasing feature depths, (2) employs adaptive noise scaling within residual blocks to avoid oversmoothing and preserve anatomical detail, and (3) simulates realistic hybrid noise (Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician) at the pixel level. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the few studies dedicated to CE-MRI denoizing in HCC, which underscores both its clinical relevance and technical novelty.
2. Related Work
Denoizing is one of the fundamental challenges in digital and medical image processing. Noise significantly degrades image quality, impairing its ability to convey accurate and reliable information, which is especially critical in sensitive applications such as medical diagnosis and treatment. The increasing complexity of modern datasets, particularly in medical imaging, has further elevated the need for advanced techniques capable of effectively addressing diverse noise conditions. Conventional denoizing methods often struggle to preserve fine details while removing noise, particularly in complex scenarios. Consequently, recent advancements have focused on leveraging deep learning, attention mechanisms, residual learning, and strategies designed to handle hybrid noise. This section provides an overview of these key developments in image denoizing.
Conventional denoizing methods rely on statistical and mathematical techniques designed to reduce noise while preserving the structural integrity of the image. These approaches typically include transform-based methods, such as wavelet transforms [53], and optimization-based techniques, such as total variation (TV) minimization [54], that aim to enhance the image by suppressing noise without compromising its essential features. While these methods have demonstrated effectiveness in certain scenarios, they often struggle when applied to images with highly intricate details or in the presence of complex, multitype noise. Their inability to adequately distinguish between noise and fine image structures frequently results in the loss of critical details, thereby limiting their utility in more demanding applications.
Deep learning has revolutionized image processing, including the image denoizing task. These models leverage automatic feature learning from the data themselves, enabling them to adapt effectively to various types of noise. Modern deep learning-based approaches, such as CNNs [55] and autoencoders [56], are widely used for denoizing tasks and have remarkable capabilities in restoring fine image details while reducing noise. These methods excel in handling structured and unstructured noise by learning hierarchical feature representations. However, most existing deep learning models are primarily designed to address single-type noise scenarios, which limit their performance when encountering more complex and hybrid noise conditions.
Various deep learning models have been proposed for image denoizing, with significant improvements in handling noise artifacts across different modalities. Among the most effective CNN-based approaches is DRUNet, which uses a residual U-Net architecture to capture multiscale features while preserving fine details [34]. FFDNet [39] provides a computationally efficient framework by introducing noise level maps as external inputs, allowing it to adapt to varying noise intensities. While noise level maps have been explored in models such as FFDNet to improve denoizing flexibility, our contribution lies in extending this concept by integrating noise level estimation directly within the residual blocks as learnable hierarchical estimators across multiple depth stages (32, 64, 128, and 256).
Attention-based models have further improved denoizing performance. RNAN and NLRN incorporate nonlocal attention mechanisms to enhance long-range feature dependencies, effectively suppressing noise [36,37]. N3Net extends this concept by leveraging self-similarity learning through nonlocal operations, achieving strong noise suppression [38]. More recently, transformer-based architectures have gained traction, with SwinIR employing a hierarchical self-attention mechanism for effective restoration [32], whereas Restormer introduces efficient spatial and channel attention to enhance performance with structured noise patterns [33].
To enhance clarity and facilitate direct comparison, Table 1 summarizes key deep learning-based denoizing methods in terms of model architecture, supported noise types, primary strengths and limitations, and their relevance to CE-MRI applications.

Table 1.
A comparative summary of representative deep learning-based denoizing methods and their relevance to CE-MRI applications.
Table 1.
A comparative summary of representative deep learning-based denoizing methods and their relevance to CE-MRI applications.
| Study/Model | Model Type | Noise Type(s) | Strengths | Limitations | Application to CE-MRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFDNet [39] | CNN with a tunable noise map | Gaussian, spatially variant | Fast and flexible; capable of handling spatially varying noise levels | Relies on external noise level map input; not tailored for hybrid or structured medical noise | Not evaluated |
| DRUNet [34] | Residual U-Net architecture | Gaussian | Strong multiscale representation; preserves fine details | Limited to additive Gaussian noise; lacks adaptive noise modeling | Not evaluated |
| NLRN [37] | Recurrent network with nonlocal blocks | Gaussian | Exploits nonlocal self-similarity; efficient parameter sharing | No explicit adaptation to noise types; not validated on hybrid or medical datasets | Not evaluated |
| N3Net [38] | CNN with neural nearest-neighbor blocks | Gaussian | Differentiable KNN relaxation for self-similarity; improves over classical matching | Complex implementation | Not evaluated |
| RNAN [36] | Residual network with nonlocal attention | Gaussian | Long-range attention; adaptive spatial and channel rescaling | Fixed attention scope; lacks noise-specific learning | Not evaluated |
| Restormer [33] | Transformer with efficient attention blocks | Gaussian, structured | Efficient processing of high-resolution images; strong global context modeling | Tends to oversmooth outputs; lacks targeted training for hybrid noise | Not evaluated |
| SwinIR [32] | Swin Transformer with shifted windows | Gaussian | Captures both local and global dependencies effectively | High memory requirements; not optimized for multi-noise environments | Not evaluated |
| Ours (NLE-ANSNet) | CNN with multilevel noise estimation and adaptive noise scaling | Gaussian, Poisson, Rician (Hybrid) | Directly models hybrid noise; adaptive scaling enhances robustness in CE-MRI | Training complexity is higher; not combined with data augmentation pipelines | Evaluated |
While these models have demonstrated promising results on natural image datasets, their performance in medical imaging, particularly CE-MRI, remains underexplored. The high sensitivity of CE-MRI to noise artifacts necessitates further investigation into the robustness of these models, particularly when handling hybrid noise conditions. This study aims to bridge this gap by evaluating and improving deep learning-based denoizing techniques tailored for CE-MRI applications.
Attention mechanisms have emerged as cutting-edge techniques to increase the performance of deep learning models by focusing on the most salient features within an image [57,58]. These mechanisms enable models to prioritize high-importance regions, leading to improved restoration of fine details and more effective noise reduction in critical areas. Channel and spatial attention mechanisms have been successfully applied to various image-related tasks, including denoizing, by dynamically emphasizing relevant features while suppressing irrelevant or noisy information. However, further exploration of attention mechanisms is needed to optimize their performance, particularly in complex and hybrid noise scenarios.
Residual learning is a highly effective approach utilized in deep models to address challenges associated with information loss during training [35,59]. This technique involves integrating the original signal with the reconstructed signal, which helps preserve fine image details and improves the overall reconstruction quality. Residual learning has been widely adopted in various image enhancement applications, including denoizing, where it has demonstrated significant success in reducing noise while maintaining image fidelity. However, its application to complex and hybrid noise scenarios remains limited and requires further research to enhance its efficacy in handling such challenging cases.
Medical images, such as MR images, demand highly precise denoizing techniques to preserve critical details that are essential for accurate diagnosis [60,61,62]. Enhancing the quality of medical images not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also expedites the diagnostic process. While numerous models have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing noise in medical images, challenges associated with complex noise patterns in these images persist. Addressing these challenges requires the development of advanced techniques that can improve denoizing performance without compromising the integrity of diagnostically significant features.
Furthermore, the application of denoizing techniques in CE-MRI studies remains underexplored, particularly in the context of HCC. Despite the crucial role of CE-MRI in diagnosing and monitoring HCC, prior research has revealed a noticeable scarcity of studies focused on denoizing methodologies tailored specifically to this imaging modality. This highlights the urgent need for targeted research aimed at addressing the unique challenges associated with denoizing CE-MRI scans in HCC diagnosis to ensure both enhanced image quality and diagnostic reliability.
Denoizing in the presence of complex, mixed noise types is one of the most intricate challenges in image processing. The interaction and overlap of different noise patterns make it exceedingly difficult to accurately recover the original image. Effectively addressing this problem requires models that can generalize to highly diverse and complex datasets. While many studies have achieved success in addressing individual noise types, few have examined the simultaneous interaction of multiple noise forms, a challenge that remains relevant for developing robust denoizing models in real-world scenarios.
While significant advancements have been made in developing denoizing techniques, most studies focus primarily on image enhancement methods rather than on simulating or introducing complex noise patterns in input images. For example, a study by Gu et al. [63] effectively addressed a wide variety of individual noise types using the TID2013 database, which included 24 distinct distortion types. Such diversity represents a notable advantage in capturing various image degradation scenarios. However, this study did not explore hybrid noise patterns, where multiple noise types coexist in a single image. This represents a limitation when addressing real-world scenarios that often involve overlapping noise sources.
In a published study, a degradation simulator [64] was utilized to simulate multiple types of degradation in fundus images. This simulator systematically applies sequential degradations, including uneven illumination, noise addition, and blurring. While this approach effectively addresses multiple types of degradation, it does not explicitly focus on hybrid noise patterns.
In medical imaging, certain types of noise pose significant challenges due to their impact on image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Gaussian noise commonly occurs because of thermal and electronic fluctuations in imaging sensors, making it a frequent issue. Poisson noise, resulting from the statistical nature of photon detection, is also prevalent, particularly in low-light and low-signal scenarios. Rician noise is particularly notable in MR images due to the nature of the signal processing involved. These noise types are particularly significant in the context of CE-MRI, where they can substantially affect image quality and diagnostic reliability. Addressing these noise types is crucial for improving the accuracy and clarity of CE-MRI images [10,31,60,65,66,67,68].
Building on this, our study adopts a four-stage noise simulation pipeline that incorporates the most common types of noise encountered in medical imaging. The pipeline simulates Gaussian noise, Poisson noise, Rician noise, and a hybrid noise pattern. The hybrid noise combines Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level to reflect complex noise interactions that can occur in real-world scenarios. This approach not only captures the individual effects of each noise type but also models their combined impact, offering a comprehensive simulation framework. By focusing on the most prevalent noise types and extending them to a hybrid level, our study provides a robust foundation for evaluating denoizing techniques under realistic and diverse noise conditions.
Our study advances image denoizing by addressing the often overlooked challenge of hybrid noise patterns, which involve complex combinations of degradation types. Unlike previous studies, such as [69], which focused primarily on either single-source noise or predefined degradation categories, our methodology systematically simulates hybrid noise scenarios that closely resemble the complex imaging conditions encountered in CE-MRI used for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), including scanner variability, contrast agent effects, and overlapping noise sources. This approach not only exposes denoizing models to more challenging and realistic conditions but also ensures robustness and generalizability across diverse types of degradation.
While [70] effectively addresses multidegradation tasks using learnable PCA to unify task-specific priors, our work differs in that it systematically simulates hybrid noise patterns that capture complex, overlapping noise types. This approach aims to enhance robustness and generalizability in CE-MRI scenarios where noise is not easily categorized.
While prior studies, such as [71], focused on multidistortion scenarios addressing sequential and spatial degradation through supervised recognition and conditional inputs on a tailored dataset (HMDD), our study differs in that it systematically simulates hybrid noise patterns specifically combining Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level to enhance generalizability and robustness, particularly in preserving fine details in critical applications such as medical imaging.
Although [72] introduced an effective task-grouping mechanism and adaptive model selection to manage various degradation types, our study takes a different approach by proposing a unified model designed to handle overlapping and complex noise patterns. This design aims to enhance robustness and adaptability in real-world scenarios, especially in critical applications such as medical imaging, by simulating realistic hybrid types of degradation based on known noise types rather than addressing distortions individually or relying on task-specific prior conditioning.
While both our study and prior work [73] share the goal of enhancing medical image quality, they differ significantly in terms of methodology. The referenced approach focuses on specific degradations such as denoizing and deblurring through a multistage framework that incorporates attention mechanisms and relies on predefined degradation-specific networks. In contrast, our method addresses hybrid noise by modeling complex, overlapping distortions without requiring prior classification or separation. This unified design enables robust and generalizable performance across diverse noise patterns, particularly in real-world medical imaging scenarios.
The majority of research aims to improve the quality of degraded images but does not adequately explore the controlled addition or modeling of complex noise types to better reflect real-world scenarios. This lack of focus on input data and noise simulation creates a gap in the field, as robust denoizing models require diverse and realistic training datasets to be generalized effectively. Furthermore, most existing approaches are tailored to handle a single type of noise, thereby leaving a critical gap in effectively addressing scenarios involving complex or hybrid noise conditions.
Our study emphasizes a systematic simulation of hybrid noise patterns to capture the complexity and overlapping nature of real-world types of degradation, providing a more challenging and realistic set of training data for denoizing models. By systematically simulating hybrid noise patterns and incorporating them into the training process, our approach aims to improve robustness under diverse noise conditions, enabling denoizing models to perform effectively in highly complex and realistic scenarios.
2.1. Problem Statement
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains one of the most prevalent and fatal liver malignancies, with early detection playing a crucial role in improving patient survival rates. CE-MRI is a widely adopted imaging modality for HCC diagnosis due to its ability to capture liver tissue characteristics with high contrast resolution [74]. However, CE-MRI is highly sensitive to noise artifacts, which can significantly degrade image quality, obscure fine anatomical structures, and negatively impact diagnostic accuracy [43,44,45,46]. These artifacts compromise critical pharmacokinetic measurements such as Ktrans and Ve, potentially leading to tissue misclassification and reduced clinical reliability [43,44]. The challenge is further amplified in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI, where pseudowashout effects may mimic hypervascular tumors, increasing the risk of misdiagnosis and lesion misinterpretation [51,52]. Additionally, DWI, when combined with CE-MRI, enhances lesion detection, yet high noise levels in DWI hinder its diagnostic utility. Denoizing is therefore essential for improving feature differentiation and ensuring accurate metastasis detection [75].
Despite the importance of CE-MRI in liver cancer imaging, research on noise reduction in CE-MRI remains limited, leaving a significant gap in the field. Clinical applications demand a denoizing approach that preserves fine anatomical details, enhances quantitative accuracy, and maintains diagnostic integrity. While high-field MRI systems in research achieve resolutions of 100–200 µm, clinical CE-MRI often operates at lower resolutions (>300 µm), making images more prone to noise and loss of detail [44,45].
2.1.1. Limitations of Existing Denoizing Approaches
Conventional denoizing techniques, such as Gaussian filtering, wavelet transforms, and total variation minimization, have been widely used in medical imaging but often fail to preserve the fine anatomical details essential for accurate diagnosis, particularly in low-contrast regions of CE-MRI images [76,77,78,79]. Deep learning-based denoizing has garnered considerable attention, with models such as DnCNN, DRUNet, SwinIR, and Restormer demonstrating superior performance compared to conventional methods [32,33,34,35]. CNN-based models such as DRUNet and DnCNN utilize residual learning and convolutional filters to remove noise; however, they struggle with hybrid noise patterns and complex distortions that frequently occur in CE-MRI [34,35]. Transformer-based approaches such as SwinIR and Restormer introduce attention mechanisms that enhance feature learning, but they have been primarily trained on natural image datasets, making their adaptation to medical imaging noise characteristics inadequate [32,33]. Additionally, most deep learning-based denoizing models depend on data augmentation to artificially expand their training sets and do not necessarily generalize well to real-world clinical noise distributions, especially in CE-MRI for HCC diagnosis. While data augmentation techniques are widely used in medical imaging, they often fail to introduce sufficient variation, leading to limited dataset diversity. Furthermore, the effectiveness of these methods varies depending on the specific image modality, disease characteristics, and network architecture, making it challenging to determine an optimal augmentation strategy for medical applications [79,80]. Given the limited availability of annotated CE-MRI datasets, there is an urgent need for a denoizing framework that does not rely on augmentation but generalizes effectively to real clinical conditions.
Building on prior research on noise characteristics in CE-MRI and its diagnostic impact [43,44,45,46,47,49,50,51,52,75], this study develops a hybrid noise simulation framework that generates pixel-level noise contamination. While some previous approaches apply different noise types to separate image regions, our method introduces a pixel-wise mixture to better simulate complex real-world noise patterns encountered in clinical settings.
While the study by Zhang et al. [81], titled “Practical Blind Image Denoising via Swin-Conv-UNet and Data Synthesis”, explored hybrid noise, it did not focus on CE-MRI for liver cancer, which is a medically relevant domain where hybrid noise suppression remains insufficiently explored. Additionally, their noise simulation was applied to generic images rather than real, clinically relevant MRI data, which limits the medical applicability of their findings. While their method contributed to hybrid noise simulation, it did not explicitly enforce a per-pixel noise balance, which may allow certain noise types to dominate and influence the final results. In contrast, our study not only ensures equal pixel-level contributions from multiple noise types but also uniquely evaluates the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM) both before and after denoizing, providing a more transparent and clinically meaningful assessment of model performance.
Although data augmentation is commonly used in medical imaging to increase dataset variability, we intentionally omitted it in our study to ensure that the model learns directly from real, unaltered CE-MRI data. This decision was made to prevent the introduction of synthetic artifacts and to promote better generalization to true clinical noise distributions, which is critical for accurate HCC diagnosis.
By exposing denoizing models to this challenging hybrid noise environment, our approach enhances robustness, generalizability, and real-world applicability. This method aims to address an important gap identified in the literature by providing a comparative evaluation framework for CE-MRI denoizing under complex noise conditions. Additionally, we conducted quantitative noise characterization using PSNR and SSIM to rigorously assess the impact of noise before and after denoising.
2.1.2. Advancing Deep Learning-Based Denoizing for CE-MRI
One of the major weaknesses of existing deep learning models is their inability to adapt dynamically to varying noise intensities across different regions of an image. Most conventional methods employ static denoising operations, which often lead to oversmoothing in low-noise areas and inadequate noise removal in high-noise regions. To overcome these limitations, we introduced noise level estimators (NLEs) at different depths within our network, enabling progressive adaptation to varying noise intensities. Unlike conventional models that apply uniform filtering, our multistage adaptation approach refines denoising predictions based on local noise intensity variations, making the process more adaptive and effective.
Additionally, we incorporated adaptive noise scaling (ANS) within the residual blocks, enabling the model to dynamically modulate feature transformations based on the estimated noise intensity. This design allows each residual block to process features in a noise-adaptive manner, thereby enhancing the model’s generalization ability across varying noise conditions.
2.2. Key Contributions
This study presents significant contributions in terms of both clinical impact and methodological advancements. From a clinical perspective, our approach addresses long-standing challenges in CE-MRI interpretation by enhancing image quality and diagnostic confidence, particularly in liver imaging for HCC. From a technical standpoint, this study proposes simulation and denoizing strategies tailored for CE-MRI applications, contributing to the development of adaptive denoizing models designed for medical imaging scenarios.
This study introduces NLE-ANSNet, a novel denoizing framework for contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with the following key novel contributions:
- Context-Aware Denoizing via Multilevel Estimation:A hierarchical noise estimation strategy is applied at four levels (32, 64, 128, and 256) and embedded within residual blocks to enable real-time, localized adaptation to noise intensity.
- Adaptive Noise Scaling Mechanism:Unlike traditional normalization layers, the proposed adaptive noise scaling (ANS) adjusts feature transformation based on local noise levels, reducing oversmoothing and preserving anatomical details.
- Clinically Oriented Hybrid Noise Simulation:A hybrid simulation method blends Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level to realistically mimic CE-MRI acquisition conditions, enhancing robustness in evaluation.
- Targeted Application to CE-MRI in HCC:One of the few studies dedicated to CE-MRI denoizing in liver cancer, it addresses a clinically important yet underexplored imaging scenario.
- Avoiding Synthetic Noise Maps to Improve Generalization:The model learns from realistic and variable noise distributions rather than relying on fixed or synthetic noise maps, enhancing its adaptability to unseen clinical data.
- Validated Performance under Complex Noise:Quantitative and qualitative benchmarks demonstrate that NLE-ANSNet achieves superior noise suppression while maintaining high structural fidelity, supporting real-world clinical utility in HCC assessment.
2.2.1. Clinical Impact and Diagnostic Improvements
By effectively mitigating noise artifacts in CE-MRI, our approach enhances diagnostic reliability and clinical confidence in liver imaging, particularly in the following aspects:
- Preserving quantitative signal integrity: Previous studies [46] have highlighted the importance of accurate and reproducible signal intensity measurements in CE-MRI. Our denoizing model enhances signal fidelity by effectively suppressing noise without distorting diagnostically relevant contrast, supporting reliable assessment in the pre- and postcontrast imaging phases.
- Enhancing CE-MRI image quality: Previous studies [47,49,50] have demonstrated that denoizing techniques can effectively reduce truncation artifacts and increase signal-to-noise ratios, thereby improving the visualization of vascular structures via CE-MRI. While our study does not directly evaluate arterial phase images, the proposed denoizing method has a strong ability to preserve vascular and anatomical details under simulated hybrid noise conditions, suggesting potential applicability in diagnostically sensitive phases such as the arterial phase.
- Potentially reducing errors in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: Previous studies [52,75] have reported that pseudowashout effects in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI can lead to diagnostic confusion between benign and malignant liver lesions. While our study does not directly evaluate this phenomenon, the proposed denoizing method improves image clarity and contrast preservation under simulated hybrid noise conditions, which may support more accurate interpretations in future clinical evaluations.
- Addressing resolution challenges in clinical CE-MRI: Prior studies [44,45] have noted that clinical CE-MRI, unlike high-field MRI, which achieves resolutions of 100–200 µm, typically operates at lower resolutions (>300 µm), increasing susceptibility to noise and the loss of fine anatomical detail. Our denoizing approach compensates for these resolution limitations, enhancing image clarity and supporting greater diagnostic confidence in clinical practice.
2.2.2. Technical Contributions and Methodological Developments
- Clinically accurate and statistically robust hybrid noise simulation:Our study developed a hybrid noise simulation framework that blends Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level, ensuring a clinically accurate and statistically balanced noise distribution. Unlike conventional methods that model independent noise types separately, our approach guarantees an equitable noise distribution across all pixels, preventing any single noise type from dominating. Moreover, we quantified noise impact using both mean and median values, ensuring a statistically robust representation that enhances the reliability of our evaluation and provides an unbiased assessment of denoizing performance in CE-MRI for HCC.
- Dynamic and multiscale noise estimation for real-time adaptation:We introduced a hierarchical noise level estimation (NLE) framework that operates at multiple feature depths (32, 64, 128, and 256 channels), enabling real-time adaptive denoizing. Unlike conventional models with fixed noise level maps, our method continuously estimates and adjusts noise suppression based on localized intensities, making it more resilient to varying noise distributions in CE-MRI for HCC, where noise artifacts can obscure critical tumor boundaries and vascular features.
- Alternative method for adapting feature transformations to noise intensity variations:Our study incorporates adaptive noise scaling (ANS), a technique that dynamically adjusts feature representations based on localized noise intensities. Unlike traditional normalization methods that apply uniform transformations, ANS intelligently differentiates between noisy and noise-free regions, preventing oversmoothing while preserving the fine anatomical structures essential for precise tumor delineation in HCC-focused CE-MRI.
- Benchmarking a higher standard for CE-MRI denoizing in HCC diagnosis:Our study contributes to ongoing efforts to improve noise mitigation in CE-MRI for imaging HCC by combining clinically relevant hybrid noise simulation with adaptive denoizing mechanisms. This approach ensures that denoizing is evaluated not only by numerical metrics (PSNR and SSIM) but also through structural fidelity, guaranteeing a balance between effective noise reduction and the preservation of diagnostically relevant liver tumor features.
- Noise-aware residual learning for enhanced structural preservation:By embedding noise level estimators (NLEs) within residual blocks, our method preserves high-frequency anatomical details while effectively suppressing complex noise patterns. This ensures that tumor boundaries, vascular structures, and tissue textures remain intact, aiding in accurate lesion characterization for HCC diagnosis via CE-MRI.
- Our method introduces a comprehensive denoizing strategy that combines hierarchical noise estimation, adaptive feature scaling, and efficient feature fusion. While some existing methods prioritize strong noise suppression that may compromise structural detail, our approach seeks to maintain both structural fidelity and computational efficiency, making it suitable for real-world clinical applications, particularly in CE-MRI for imaging HCC, where the accurate delineation of tumor morphology and vascular structures is essential for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Context-aware adaptive denoising for CE-MRI for imaging HCC:Unlike previous models that apply uniform denoizing across the entire image, our approach dynamically adapts to noise distributions in different anatomical regions. This ensures that tumor boundaries, vascular structures, and microtextures are preserved, enhancing diagnostic confidence. This adaptability bridges the gap between noise suppression and structural integrity, making CE-MRI more reliable for clinical decision making in HCC detection, staging, and treatment evaluation.
By incorporating realistic noise simulation, adaptive denoizing mechanisms, and comprehensive performance evaluation, this study, to our knowledge, is the first to integrate noise level estimation at multiple depth levels (32–256) with adaptive noise scaling modules for CE-MRI denoizing. It builds upon prior research and extends it through a hierarchical and context-aware framework specifically designed to address the complexities of hybrid noise in CE-MRI, particularly for HCC diagnosis.
This study represents a significant contribution to the underexplored domain of noise reduction in CE-MRI, particularly for liver imaging and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) diagnosis. While most existing studies focus on classified noise types or other imaging modalities, this research uniquely addresses the challenges of nonclassified hybrid noise and its impact on CE-MRI, a modality critical for liver cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
By introducing robust architectural improvements and validating the models on realistic hybrid noise scenarios, this work establishes a strong foundation for enhancing the quality of CE-MRI images. This is particularly important given the scarcity of studies focusing on CE-MRI for liver applications, making the contributions of this study highly relevant for both clinical practice and future research.
3. Materials and Methods
The proposed denoizing approach leverages a deep learning model specifically designed to increase the robustness and generalizability of CE-MRI image restoration. Our framework consists of a multistage processing pipeline that incorporates a hybrid noise simulation in the preprocessing phase and an enhanced noise-adaptive deep learning model to effectively reconstruct high-quality images, as illustrated in Figure 1. Unlike traditional methods that apply uniform denoizing operations, our approach dynamically adapts to varying noise levels using learned estimators, ensuring optimal noise suppression while preserving anatomical details crucial for medical diagnosis.
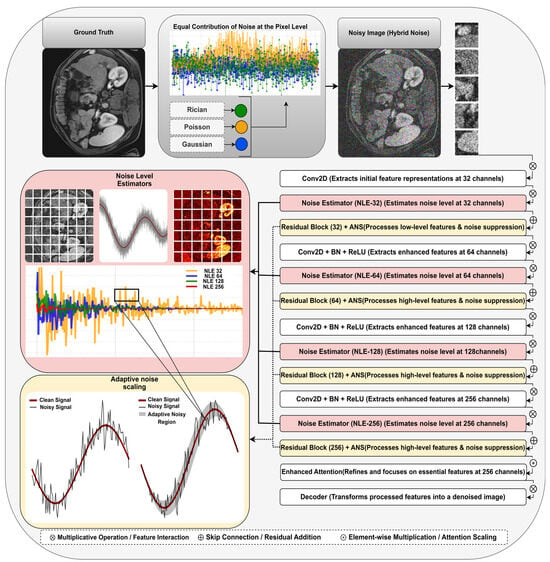
Figure 1.
An overview of the NLE-ANSNet architecture proposed for CE-MRI.
3.1. Data Description
This study utilizes the A Tumor and Liver Automatic Segmentation (ATLAS) dataset [41] that comprises 90 CE-MRI acquisitions from patients diagnosed with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Each scan is accompanied by expert-annotated segmentation masks for the liver and tumors. The data were collected from patients who underwent transarterial radioembolization (TARE) between 2012 and 2023 based on strict clinical criteria and recent T1-weighted CE-MRI scans.
To facilitate noise simulation and downstream analysis, the original 3D scans were converted into 3840 2D slices. All images were acquired using Siemens and GE MRI systems with gadolinium-based contrast agents and are provided in NIfTI (.nii) format. A summary of the dataset’s key specifications is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Dataset specifications.
Given the need for precise noise modeling and localized assessment of denoizing performance, the original 3D CE-MRI volumes were converted into 2D slices. This transformation enables the simulation of pixel-wise hybrid noise that is critical for evaluating localized distortions in CE-MRI and facilitates more granular control of noise level estimation (NLE) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS) mechanisms. Moreover, this setup ensures that the model is exposed to a wide variety of structural and noise contexts, thereby enhancing robustness and generalizability in clinical CE-MRI scenarios.
3.2. Preprocessing: Multistage Simulation for Image Degradation
The preprocessing phase is a critical component of our methodology and is designed to comprehensively evaluate the performance and robustness of the proposed denoizing architectures for liver-focused CE-MRI. To simulate real-world scenarios often encountered in medical imaging, we systematically introduced three types of noise, Gaussian noise, Poisson noise, and Rician noise, followed by the generation of hybrid noise, which combines all three noise types on a per-pixel basis. This rigorous approach ensures a thorough assessment of the denoizing performance for diverse and complex noise distributions, mimicking the challenges faced in clinical imaging environments.
The selection of Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise in our study is based on their well-documented prevalence in medical imaging. Gravel et al. [10] identified these types as the most common noise types encountered in medical images, each originating from distinct acquisition processes. Given our focus on CE-MRI for liver imaging, incorporating these noise models ensures a realistic and comprehensive evaluation of denoizing performance. Additionally, the introduction of hybrid noise, which combines all three types at the pixel level, enhances the robustness of our assessment by simulating complex noise distributions reflective of real-world clinical scenarios.
Three clinically relevant noise types were introduced to simulate realistic CE-MRI degradation. Gaussian noise (Figure 2) reflects uniform distortions from electronic fluctuations, Poisson noise (Figure 3) models signal-dependent variations prominent in low-intensity regions, and Rician noise (Figure 4) represents MRI-specific artifacts from magnitude reconstruction. These noise types were added independently to evaluate the model’s robustness under diverse noise conditions.
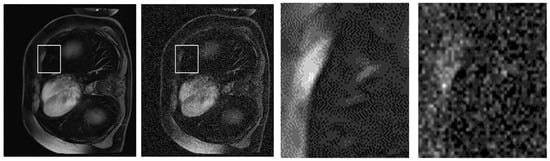
Figure 2.
A sample of Gaussian noise.
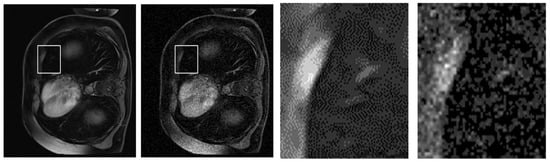
Figure 3.
A sample of Poisson noise.
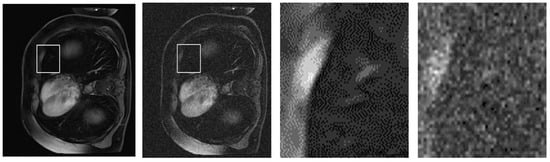
Figure 4.
A sample of Rician noise.
To evaluate robustness under complex conditions, we introduced hybrid noise by blending Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level. This method simulates challenging, real-world-like degradations more effectively than region-based noise applications. This emphasizes the generalization strength of our model. Figure 5 shows a sample of hybrid noise.
Figure 5.
A sample of hybrid noise.
To ensure a balanced distribution of hybrid noise at the pixel level, we carefully adjusted the intensities of Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise across the entire image. Unlike traditional methods that apply different noise types to separate regions, our approach guarantees that each pixel receives an equal contribution from all three noise types, preventing any single noise type from dominating the degradation pattern.
Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 illustrate the independent contributions of Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise, respectively. These plots demonstrate that each noise type is evenly distributed across the pixel columns without significant variation in dominance. Figure 9 presents the final balanced noise contribution per pixel column plot, where the cumulative effects of all three noise types are shown. The balanced spread of noise confirms that our hybrid noise model provides an unbiased evaluation framework for denoizing algorithms under complex and mixed noise conditions.
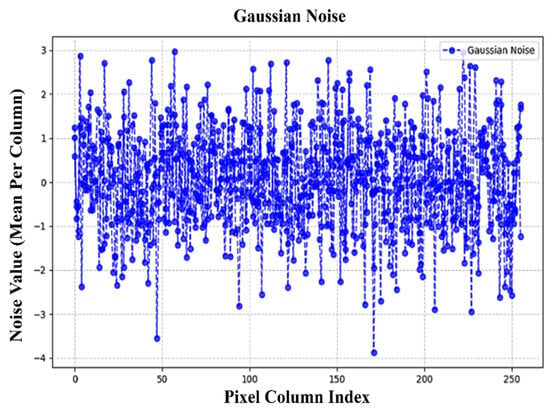
Figure 6.
Independent contributions of Gaussian noise.
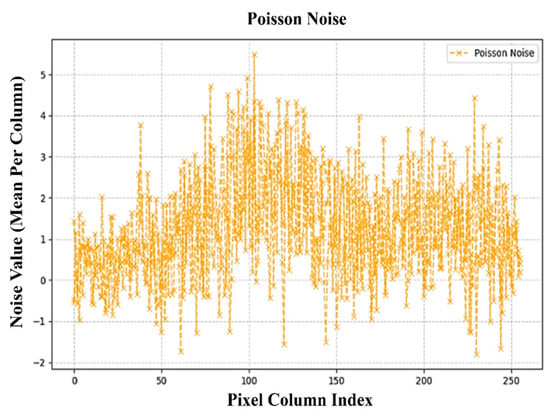
Figure 7.
Independent contributions of Poisson noise.
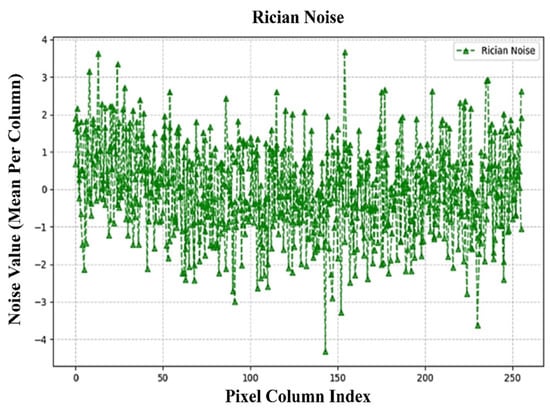
Figure 8.
Independent contributions of Rician noise.
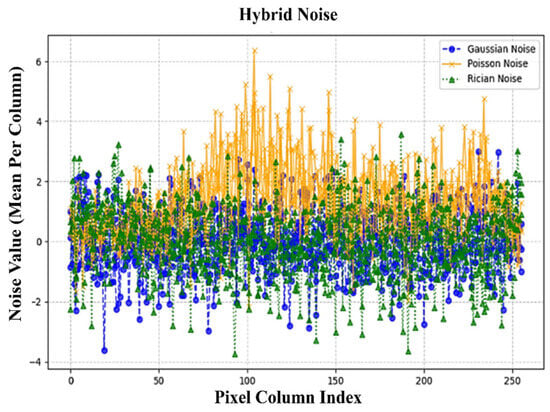
Figure 9.
Balanced noise contribution per pixel.
To systematically evaluate the impact of different noise types on CE-MRI images, we conducted a quantitative analysis of the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM). This analysis serves as a baseline assessment before any denoizing algorithms are applied to ensure a well-defined noise augmentation process.
Each noisy image was compared to its corresponding ground truth image, and the PSNR and SSIM were computed individually per image. Given the inherent variability in medical images, we reported both the mean and median values across the dataset to achieve a statistically robust representation of the noise contribution.
The mean was selected because it provides a global measure of the noise effect across all images:
where represents the metric (PSNR or SSIM) for each image, and N is the total number of images.
The median was included to mitigate the influence of extreme outliers and ensure that the evaluation remained robust:
The two evaluation metrics were computed using the following standard formulations:
The PSNR quantifies the intensity of noise-induced distortion:
where MAX is the maximum pixel intensity (255 for 8-bit images), and the MSE (mean squared error) is given by
where I(i,j) and K(i,j) denote the pixel intensities of the ground truth and noisy image, respectively.
The SSIM measures perceptual similarity to ensure that structural information is preserved:
where are the mean intensities, and are variances, and is the covariance between the images.
The PSNR and SSIM values computed for each noise type are summarized in Table 3. The results indicate that Poisson noise and Rician noise result in higher PSNR and SSIM values than Gaussian noise, suggesting that they introduce relatively less distortion to the image structure. Conversely, hybrid noise results in the most severe degradation, as reflected by its significantly lower PSNR and SSIM values.

Table 3.
The quantitative evaluation of the impact of noise on CE-MRI images.
This preprocessing noise characterization provides an objective basis for evaluating the impact of noise augmentation in medical imaging, ensuring that subsequent denoizing methods are tested under well-defined and realistic degradation conditions. By reporting both the mean and median values, we enhance the statistical robustness of our analysis and ensure that the evaluation is not skewed by extreme cases. This methodological approach strengthens the validity of our noise augmentation process and ensures a fair and unbiased assessment of future denoising techniques.
3.3. Noise Level Estimators and Adaptive Noise Scaling
The core of our denoizing model is a convolutional neural network that incorporates residual learning and hierarchical noise estimation to enhance feature extraction and adaptive noise suppression. A key innovation in our approach is the integration of noise level estimators (NLEs) at multiple depths in the network, which enables the model to adapt to varying noise intensities across different spatial scales. Unlike existing methods such as DnCNN and SwinIR, which apply uniform filtering [32,35], our method explicitly estimates and adjusts to the noise level at different stages of processing. Four estimators, , , , and , process noise representations at different channel dimensions (32, 64, 128, and 256, respectively), allowing the network to progressively refine its denoizing predictions in a hierarchical manner.
The noise estimations from guide the early feature extraction layers, ensuring initial noise suppression at a low feature complexity. further enhances noise adaptation in the intermediate residual blocks, refining feature representation while maintaining structural integrity. is applied in the deeper layers, where more abstract features are learned, enabling high-level noise refinement. Finally, is incorporated in the deepest layers to capture highly abstract noise patterns and aims to balance noise suppression with the preservation of fine anatomical details. This hierarchical noise estimation enables multiscale adaptation to ensure that noise suppression is progressively refined across different network depths.
To accurately estimate the noise characteristics in CE-MRI scans, our model integrates noise level estimators () at multiple depths, providing hierarchical noise adaptation. The , , , and components estimate the noise level at different channel dimensions, allowing the model to refine noise suppression across different feature scales. Mathematically, the noise estimation function is defined as follows:
where represents the estimated noise level at channel dimension C, denotes the convolutional filters responsible for learning noise-specific features, X is the input noisy image, is the learnable bias, (*) represents the 2D convolution operation, and (⋅) is the activation function. These estimations are then propagated through different layers of the network, guiding the residual learning process. Specifically, is utilized in the early feature extraction layers to suppress low-level noise distortions, is applied in intermediate feature processing layers to enhance noise suppression at a broader scale, and is used in deeper layers to refine high-level noise representations while preserving fine anatomical structures. Finally, is incorporated in the deepest layers of the network, allowing the model to capture highly abstract noise representations and ensure optimal suppression while maintaining clinically relevant information. By leveraging this hierarchical noise estimation strategy, our approach dynamically adjusts to varying noise levels in CE-MRI images, ensuring adaptive and context-aware denoizing, as illustrated in Figure 10.
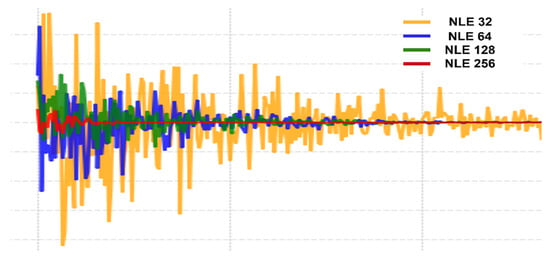
Figure 10.
Noise level estimators at multiple depths.
Figure 10 illustrates the estimated noise outputs from four noise level estimators (NLEs) placed at increasing network depths: NLE 32, NLE 64, NLE 128, and NLE 256. Each curve represents the spatial distribution of estimated noise across feature maps at different levels of feature abstraction. The yellow curve (NLE 32) shows large and highly fluctuating noise estimates, indicating that the shallowest layer captures coarse and high-intensity noise components. As the network progresses deeper, the noise estimation becomes smoother and more stable, as reflected in the blue (NLE 64), green (NLE 128), and red (NLE 256) curves. This progressive refinement suggests that the deepest NLE (256) focuses more on fine-tuning and structural preservation than aggressive noise suppression, highlighting the effectiveness of multiscale noise adaptation in achieving both denoizing and anatomical fidelity.
3.4. Adaptive Noise Scaling in Residual Learning
A major limitation of existing deep learning-based denoizing models is their reliance on static normalization techniques, which do not account for variations in noise levels across images. To address this, our model incorporates adaptive noise scaling (ANS) within residual blocks, ensuring that feature transformations are dynamically adjusted based on the estimated noise intensity. This mechanism introduces learnable parameters, γ and β, that adaptively influence feature processing, making each residual block noise aware and more flexible in handling diverse noise levels.
Mathematically, this is formulated as follows:
where denotes batch normalization, represents the noise level estimated by the network, and and are trainable parameters that control the influence of noise on feature normalization. Instead of applying BatchNorm uniformly across all the features, our method integrates adaptive noise scaling (ANS) into the residual blocks, where BatchNorm is dynamically conditioned on the estimated noise level. This allows the normalization process to adapt to varying noise intensities, making each residual block noise-aware and context-sensitive.
The final feature transformation within the residual block is represented as follows:
where W is the convolutional layers, and is a nonlinear activation function. This formulation ensures that each residual block maintains a noise-adaptive structure, significantly improving the network’s generalization capability. Figure 11 illustrates the adaptive noise scaling (ANS) mechanism.
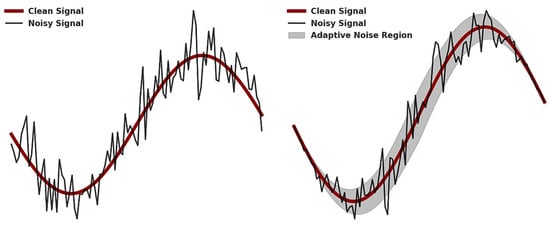
Figure 11.
Adaptive noise scaling.
The proposed model integrates hierarchical noise level estimators (NLEs) at multiple depths, enabling adaptive noise suppression while preserving fine anatomical details. Each NLE stage is coupled with adaptive noise scaling (ANS) to dynamically regulate the denoising strength. In the early NLE 32 stage, where noise is highly unstructured, ANS applies strong suppression to eliminate large distortions while retaining essential edges. As the network progresses to NLE 64, noise adaptation becomes more selective, balancing noise removal with the preservation of tissue structures. In NLE 128, the model refines high-level features, mitigating subtle noise while maintaining essential anatomical structures. Finally, NLE 256 ensures minimal yet precise noise attenuation, preserving fine details relevant for medical imaging. Unlike conventional denoizing methods that apply uniform filtering, this multiscale approach allows for context-aware noise adaptation, ensuring that suppression is dynamically adjusted across different feature representations. The effectiveness of this progressive denoizing process is illustrated in Figure 12, where the transition from high-noise suppression at NLE 32 to refined feature preservation at NLE 256 is demonstrated.
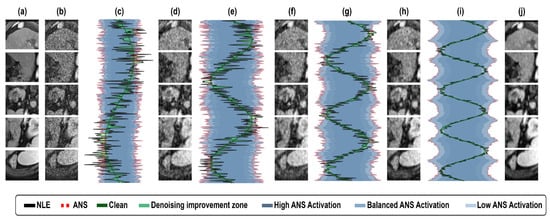
Figure 12.
A comparative visual analysis of denoizing stages. (a) Ground truth, (b) noisy image, (c) NLE 32 + ANS, (d) output of NLE 32 + ANS, (e) NLE 64 + ANS, (f) output of NLE 64 + ANS, (g) NLE 128 + ANS, (h) output of NLE 128 + ANS, (i) NLE 256 + ANS, and (j) output of NLE 256 + ANS.
3.5. Training and Evaluation Protocol
For a fair comparison, all baseline models, including DRUNet, FFDNet, N3Net, the NLRN, Restormer, the RNAN, and SwinIR, were trained under identical conditions, maintaining a consistent learning rate, loss function, and number of epochs. Our training pipeline employs a hybrid loss function that combines the mean squared error (MSE), structural similarity index (SSIM), and L1 loss to balance pixel-wise fidelity with perceptual image quality:
where minimizes intensity-based errors, preserves structural integrity, and enforces sparsity in error distributions. The model was trained for 100 epochs using the AdamW optimizer with a learning rate of , incorporating weight decay and AMSGrad stabilization.
The integration of hybrid noise simulation, hierarchical noise estimation, and adaptive noise scaling redefines the approach to CE-MRI denoizing. Unlike prior methods that rely on uniform filtering or static normalization, our model dynamically adapts to local noise variations, preserving diagnostic features while suppressing complex artifacts. This makes it especially suitable for liver imaging in HCC diagnosis. These findings underscore the importance of noise-aware architectures in real-world medical imaging and open new avenues for future research in robust diagnostic systems.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, we compared it with several state-of-the-art denoizing models, highlighting the key advancements introduced by our noise level estimators (NLEs) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS) mechanisms. Unlike DRUNet [34], which uses predefined noise level maps that remain constant throughout the inference process, our method generates dynamic noise level estimations at multiple depths. These estimations enable the network to adapt to spatially varying noise levels in real time, ensuring more flexible and context-aware denoizing. Additionally, DRUNet applies static feature processing, whereas our ANS mechanism adjusts feature transformations per region, effectively preventing oversmoothing in low-noise areas and underdenoizing in high-noise regions, making our model more effective for CE-MRI by preserving fine anatomical structures while achieving superior denoizing performance. Similarly, FFDNet [39] utilizes predefined noise level maps, whereas our approach estimates noise dynamically at multiple scales. This enables more adaptive denoizing while preserving fine anatomical structures. In contrast, our study preserves spatial resolution while leveraging ANS to dynamically adjust feature scaling and ensure a more adaptive denoising process that prevents unnecessary blurring or incomplete noise suppression, making it more robust for CE-MRI applications.
Compared with the RNAN [36], which employs fixed residual attention mechanisms without explicit noise estimation, our NLEs dynamically estimate noise variations, ensuring targeted noise suppression without compromising structural integrity. Moreover, while the NLRN [37] relies on a fixed recurrent network (RNN) structure, our approach avoids error accumulation over recurrent stages by incorporating ANS, which adjusts feature scaling adaptively per region. This results in improved noise robustness and higher precision in CE-MRI denoizing. Furthermore, N3Net [38] relies on fixed nonlocal feature matching for denoizing but does not explicitly address spatially varying noise levels. In contrast, our NLEs and ANS mechanisms provide localized feature modulation, ensuring that each region receives appropriate noise suppression while maintaining fine anatomical details.
Transformer-based models such as Restormer [33] and SwinIR [32] demonstrate strong global feature extraction through self-attention mechanisms. However, these methods do not include explicit noise estimation or dynamic feature scaling based on local noise variations, which may limit their adaptability in CE-MRI settings. In contrast, our model integrates multilevel noise level estimators (NLEs) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS) to provide region-specific noise adaptation and balance effective suppression with structural preservation in medically critical regions.
Overall, by integrating multiscale noise estimation (NLE) and adaptive feature transformation (ANS) within residual learning, our study presents a more flexible, noise-aware, and clinically reliable denoizing framework. Unlike previous approaches that rely on predefined noise levels, recurrent denoizing, or fixed attention mechanisms, our method dynamically adapts to spatial noise variations, ensuring targeted denoizing while preserving fine medical details and making it particularly effective for enhancing CE-MRI images.
After analyzing the limitations of existing denoizing models, this work introduces significant enhancements specifically tailored for imaging HCC via CE-MRI. The primary innovation lies in the expansion of noise level estimation (NLE) across four progressive stages (32, 64, 128, and 256 channels), enabling the model to adaptively process noise at multiple levels rather than relying on a single-stage estimation, as seen in previous models. This multistage approach enhances the precision of lesion detection in HCC-related CE-MRI by progressively refining noise suppression. Furthermore, the model incorporates adaptive noise scaling (ANS) within each individual layer, dynamically adjusting feature representations based on localized noise levels. This mechanism provides a more precise distribution of noise suppression across feature channels, thereby improving contrast differentiation between cancerous and noncancerous tissues in CE-MRI scans. These advancements enable the model to handle stochastic and nonlinear noise in a more structured and adaptive manner, constituting an architectural variation that builds upon conventional methodologies. Moreover, this work leverages insights from previous models while developing a more adaptive and robust framework for noise suppression, ultimately enhancing diagnostic accuracy and tissue differentiation in CE-MRI for HCC patients.
3.6. Experimental Setup and Fair Comparison
To ensure a fair and unbiased comparison between our proposed method and the existing denoizing architectures (DRUNet, FFDNet, N3Net, the NLRN, Restormer, the RNAN, and SwinIR), all the models were trained and evaluated under the same experimental conditions. This includes maintaining identical learning rates, numbers of epochs, loss functions, and optimizers across all the experiments. Table 4 presents the key hyperparameters and training configuration settings used consistently across all the evaluated methods.

Table 4.
Key hyperparameters and the training configuration.
All the models were trained under standardized conditions using the AdamW optimizer with AMSGrad, a fixed learning rate of 10−4, and weight decay (10−4) for 100 epochs. To ensure a fair comparison, identical preprocessing, noise simulation, and input configurations were applied across the models. Training employed a hybrid loss function that combined the MSE, SSIM, and L1 loss to balance the pixel accuracy, perceptual quality, and error sparsity. This uniform setup isolates the influence of architectural differences, enabling an unbiased evaluation of each model’s denoizing effectiveness.
All the experiments were conducted on a high-performance, deep learning workstation equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Ti SUPER GPU, an Intel Core i9-14900KF processor (3.20 GHz), and 32 GB of DDR5 RAM. The system was run on a 64-bit operating system, utilizing PyTorch (v2.5.1 with CUDA 12.1) to ensure efficient GPU utilization for faster training. The experiments were optimized to balance computational efficiency and training performance.
To evaluate the denoizing performance, the dataset comprising 3840 2D CE-MRI slices was randomly split into training (0.80), validation (0.10), and testing (0.10) subsets. All models were trained using the training set, monitored using the validation set, and evaluated on the unseen testing set to ensure a fair and consistent performance comparison. The proposed model achieved an average training loss of 0.013 and a testing loss of 0.017. In terms of image quality, it reached a PSNR of 34.22 dB and SSIM of 0.9421 on the training set, while attaining a PSNR of 34.01 dB and SSIM of 0.9393 on the testing set.
4. Results
This section presents a quantitative evaluation of our proposed denoizing framework for detecting HCC via CE-MRI. Given the critical role of high-quality CE-MRI in ensuring accurate diagnosis, our model integrates noise level estimators (NLEs) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS) to achieve dynamic noise adaptation. To ensure a fair comparison, all the models were trained under identical conditions, including the same dataset, loss function, optimizer, and training schedule. This standardization guarantees that performance differences are solely attributed to the architectural advancements of each model rather than variations in training configurations.
The evaluation begins by analyzing the impact of NLEs at different levels (32, 64, 128, and 256) with ANS and assessing the effectiveness of our hierarchical noise adaptation strategy, as detailed in Table 5. A comparative analysis is subsequently performed against state-of-the-art denoizing models, including DRUNet [34], FFDNet [39], N3Net [38], the NLRN [37], Restormer [33], the RNAN [36], and SwinIR [32], in terms of the PSNR, SSIM, and computational efficiency.

Table 5.
The performance evaluation of NLE layers with ANS.
To further assess the effectiveness of our proposed NLE-ANSNet method, we compare its performance against that of state-of-the-art denoizing models, including DRUNet, FFDNet, N3Net, the NLRN, Restormer, the RNAN, and SwinIR. The evaluation considers the SSIM, PSNR (dB), and training time (seconds) to ensure a comprehensive analysis of both the restoration quality and computational efficiency. Table 6 presents the results.

Table 6.
A comparison of NLE-ANSNet with existing denoizing methods.
The results provide a balanced evaluation of the performance and computational complexity of the architectures, highlighting the trade-offs involved in selecting effective denoising methods for CE-MRI restoration.
To quantitatively assess the impact of our denoizing strategy on CE-MRI images degraded by clinically realistic noise, we compared the SSIM and PSNR improvements across multiple denoizing models. This evaluation highlights each model’s ability to suppress noise, as shown in Table 6. The noise introduced in the evaluation follows a clinically accurate hybrid noise simulation, which integrates Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level. This method ensures a scientifically validated noise distribution that closely resembles real-world CE-MRI acquisition conditions, where scanner variability, patient motion, and contrast agent effects introduce substantial image degradation.
To provide a comprehensive assessment, the results are reported for both median and mean improvements, allowing for a robust evaluation of the effectiveness of each model in suppressing noise while preserving critical anatomical details. Table 7 presents the median and mean SSIM improvements across various models, establishing a direct comparison under standardized noise conditions and allowing for a direct and fair comparison of their denoizing performance.

Table 7.
SSIM improvement (median and mean) obtained with clinically simulated noise.
To further validate the effectiveness of our proposed denoizing framework, we analyze its impact on PSNR improvements across different models. This evaluation, summarized in Table 6, highlights the ability of each method to enhance signal fidelity while minimizing noise-induced distortions, ensuring the preservation of critical image details.
These results provide a comprehensive assessment of SSIM and PSNR improvements across multiple denoizing architectures. Given the clinical importance of CE-MRI, maintaining high perceptual similarity (as reflected by the SSIM) and accurate reconstruction of intensity variations (as indicated by the PSNR) are critical for maintaining diagnostic fidelity.
Overall, our proposed NLE-ANSNet method demonstrates superior performance in terms of both the SSIM and PSNR metrics while maintaining competitive computational efficiency. These findings reinforce the potential of our adaptive noise scaling strategy in enhancing CE-MRI denoizing, offering a promising direction for improving medical image restoration in clinical settings.
To further substantiate the quantitative improvements achieved by our proposed NLE-ANSNet method, we provide a comparative visual analysis in Figure 13. While the SSIM and PSNR validate the denoizing efficacy numerically, they do not always capture the perceptual quality and diagnostic reliability of the restored images. Excessive smoothing, for example, can artificially inflate these metrics while simultaneously compromising fine anatomical details. Hence, a qualitative assessment is necessary to illustrate the model’s ability to suppress noise while preserving clinically relevant structures.
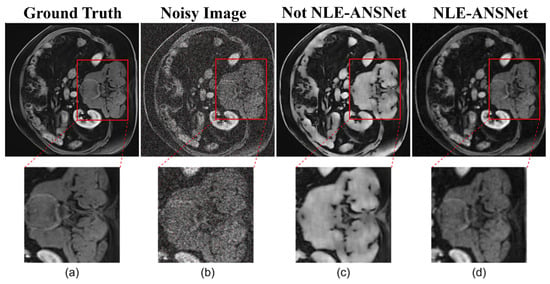
Figure 13.
A qualitative comparison of CE-MRI denoizing results: (a) Ground truth image; (b) Noisy image with significant artifacts; (c) Output from a conventional denoizing method showing oversmoothing; (d) Output from the proposed NLE-ANSNet preserving fine anatomical details.
Figure 13 presents a side-by-side comparison of CE-MRI images processed using different methodologies. Subfigure (a) represents the ground truth image, which serves as the reference for evaluating denoizing fidelity. Subfigure (b) shows the noisy image, which contains significant artifacts that can obscure critical anatomical structures. Subfigure (c) shows the output of a conventional denoizing method, which, despite reducing noise, introduces excessive smoothing that blurs tumor boundaries, vascular structures, and tissue textures, features essential for precise diagnosis. Finally, subfigure (d) shows the denoized image produced by our proposed NLE-ANSNet method, which effectively mitigates noise while maintaining the integrity of the fine structural details. By integrating multilevel noise level estimators (NLEs) at 32, 64, 128, and 256 channels, along with adaptive noise scaling (ANS), our model dynamically adjusts noise suppression to different image regions, ensuring that diagnostically relevant features remain intact.
This qualitative evaluation aligns with the numerical results in Table 6, Table 7 and Table 8, where NLE-ANSNet achieves the highest SSIM and PSNR scores. However, unlike conventional approaches that achieve high scores through excessive smoothing, our method demonstrates that structural preservation and noise suppression can be effectively balanced. Thus, Figure 13 shows that NLE-ANSNet outperforms conventional models, not only in terms of quantitative metrics but also in maintaining diagnostic fidelity, making it a robust solution for CE-MRI denoizing for HCC assessment.

Table 8.
PSNR improvement (median and mean) obtained with clinically simulated noise.
Additionally, Figure 14 compares the outputs from multiple denoizing methods, including DRUNet, FFDNet, N3Net, the NLRN, Restormer, the RNAN, and SwinIR, alongside our proposed NLE-ANSNet method. This figure highlights the differences in noise suppression and structural preservation among these methods, further supporting the robustness of NLE-ANSNet in CE-MRI denoizing.
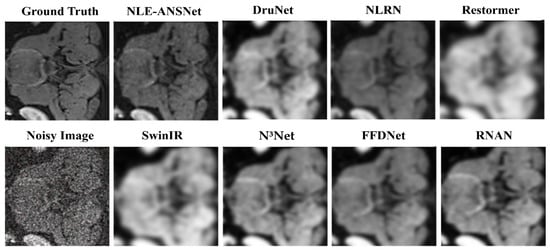
Figure 14.
A comparison of denoizing methods used for CE-MRI images.
5. Discussion
5.1. NLE-ANSNet Design and Noise Modeling Strategy
This study presents an in-depth evaluation of the NLE-ANSNet framework proposed for CE-MRI denoizing for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) diagnosis. Given the diagnostic significance of CE-MRI in liver cancer assessment, effective noise suppression is critical for maintaining the integrity of tumor boundaries, vascular structures, and tissue textures. The findings confirm that NLE-ANSNet outperforms existing denoising methods, demonstrating superior quantitative and qualitative performance under clinically relevant noise conditions. By integrating multilevel noise level estimators (NLEs) and adaptive noise scaling (ANS), NLE-ANSNet dynamically adapts to complex noise distributions without degrading essential anatomical structures.
One of the fundamental advantages of NLE-ANSNet is its ability to handle clinically simulated noise through a per-pixel noise modeling approach. Unlike conventional methods that apply global noise perturbations, this study employs a hybrid noise simulation strategy, where Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise types are applied independently at the pixel level. This methodology closely replicates real-world CE-MRI acquisition noise, where scanner variability, contrast agent dynamics, and patient motion contribute to nonuniform noise distributions. The robustness of NLE-ANSNet under such realistic conditions underscores its potential for clinical applicability, as it generalizes effectively without relying on artificial data augmentation.
The evaluation of multistage noise adaptation performance demonstrated a consistent improvement in denoizing efficacy with increasing NLE levels. The experimental results reveal that NLE-ANSNet with NLEs evaluated at four levels (32, 64, 128, and 256) achieves the highest SSIM (0.9393) and PSNR (34.01 dB), significantly outperforming the other methods. The hierarchical noise estimation mechanism in NLE-ANSNet enables precise noise adaptation, enabling a balance between aggressive noise suppression and structural preservation. However, the increase in computational cost at higher NLE levels highlights the trade-off between denoizing accuracy and processing efficiency. Despite this, the model maintains a computational burden that remains feasible for clinical deployment.
A comparative analysis with state-of-the-art denoizing models, including DRUNet, FFDNet, N3Net, the NLRN, Restormer, the RNAN, and SwinIR, further validated the efficacy of NLE-ANSNet. The results indicate that NLE-ANSNet consistently outperforms competing architectures in terms of the SSIM and PSNR while ensuring better structural fidelity. Unlike DRUNet and FFDNet, which exhibit residual noise artifacts, or SwinIR and Restormer, which suffer from excessive smoothing due to transformer-based feature extraction, NLE-ANSNet effectively preserves critical anatomical details while mitigating noise-induced distortions. The superiority of NLE-ANSNet is particularly evident compared with transformer-based models such as SwinIR and Restormer, which require significantly larger datasets to generalize effectively. These models rely on extensive self-attention mechanisms that necessitate thousands of training images, whereas the dataset utilized in this study consists of 3840 CE-MRI slices. Additionally, deep learning-based denoizing models often employ data augmentation techniques to artificially expand their training sets. However, in medical imaging applications, especially in CE-MRI for HCC diagnosis, such augmentation techniques may not sufficiently capture the variability of real clinical noise distributions. This study deliberately avoided augmentation to ensure that the evaluation remained unbiased and further emphasize the adaptability of NLE-ANSNet to real-world imaging conditions.
Computational efficiency remains a critical factor in the practical deployment of deep learning-based denoizing frameworks. Among the evaluated models, DRUNet demonstrates the highest computational efficiency, requiring only 4811.82 s for training, making it a viable option for applications where rapid processing is prioritized over absolute denoising performance. However, its lower PSNR (30.33 dB) and SSIM (0.9099) than those of NLE-ANSNet suggest that this efficiency comes at the expense of its structural preservation and noise suppression capability. The training time analysis reveals that while NLE-ANSNet has a greater processing cost than DRUNet and FFDNet, it has a strong balance between computational feasibility and denoizing performance. Notably, the RNAN achieves competitive results, with an SSIM of 0.9305 and PSNR of 32.82 dB, which are close to those of NLE-ANSNet, at 0.9393 and 34.01 dB, respectively. The SSIM difference of 0.0088 and PSNR difference of 1.19 dB indicate that the RNAN is a strong contender in CE-MRI denoizing. However, the PSNR difference of 1.19 dB is significant, particularly in the context of HCC, where preserving fine anatomical structures and contrast details is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Even marginal improvements in the PSNR can enhance the clarity of lesion boundaries and vascular structures, reinforcing the superiority of NLE-ANSNet in restoring CE-MRI images. However, its longer training time of 19,426.83 s compared with that of NLE-ANSNet at 20,112.32 s suggests that the proposed model offers a better trade-off between performance and computational demand, making it the most effective choice for balancing accuracy and efficiency in restoring CE-MRI images. It remains within a practical range compared with models such as Restormer and SwinIR, which exhibit significantly longer training durations without proportional improvements in denoizing quality. Notably, Restormer, despite its extensive computational burden, achieves a substantially lower SSIM score due to oversmoothing, which degrades essential structural details. Conversely, NLE-ANSNet strikes a balance between noise suppression and structural preservation, ensuring that diagnostically relevant information is retained without unnecessary computational overhead.
While quantitative metrics such as the SSIM and PSNR provide objective measures of denoizing efficacy, they do not fully capture the perceptual quality and diagnostic reliability of denoized CE-MRI images. A qualitative analysis of denoized outputs, as illustrated in Figure 13 and Figure 14, highlights the limitations of conventional denoizing models that rely on aggressive smoothing techniques. The results confirm that NLE-ANSNet mitigates noise effectively while maintaining high-frequency anatomical structures, ensuring that critical features required for lesion characterization and tumor detection remain intact. Unlike conventional models that prioritize numerical optimization at the expense of perceptual quality, the adaptive nature of NLE-ANSNet enables it to enhance image clarity while preserving the fine-grained details necessary for clinical diagnosis.
The findings of this study suggest that NLE-ANSNet may serve as a promising denoizing approach for CE-MRI in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma. This research is specifically tailored to CE-MRI, particularly for the liver imaging of HCC, a highly aggressive and fatal malignancy that demands precise imaging for early detection and intervention. By integrating adaptive noise scaling and hierarchical noise estimation, the model successfully addresses the fundamental challenges associated with CE-MRI degradation, ensuring that noise artifacts are effectively suppressed while preserving diagnostic information. The superior performance demonstrated across multiple evaluation metrics underscores its potential for real-world clinical applications. Future research should focus on further optimizing the computational efficiency of the model for real-time deployment and extending its applicability to other medical imaging modalities where complex noise patterns pose significant challenges to image interpretation and diagnosis.
To the best of our knowledge, this study represents one of the few dedicated investigations that specifically address denoizing in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). While extensive research has been conducted on MR denoizing, few studies have explicitly addressed CE-MRI denoizing in the context of HCC, underscoring the relevance and targeted focus of the present work.
5.2. Comparison with Related Studies
The proposed NLE-ANSNet framework was evaluated against several state-of-the-art denoizing models, including DRUNet [34], FFDNet [39], N3Net [38], NLRN [37], RNAN [36], Restormer [33], and SwinIR [32]. These models represent a diverse range of architectures and strategies for image restoration, from convolutional designs to attention-based mechanisms. While each offers valuable capabilities, they exhibit limitations when applied to clinically acquired contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) data, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) diagnosis.
CNN-based methods such as DRUNet [34] and FFDNet [39] achieve notable denoizing performance under Gaussian noise. DRUNet uses a residual U-Net architecture that enables strong multiscale representation and the preservation of fine details. FFDNet incorporates noise level maps to facilitate adaptive filtering, providing flexibility for spatially varying noise. However, both methods are constrained by their reliance on additive Gaussian noise and lack explicit mechanisms for adapting to hybrid or structured noise distributions, which are common in CE-MRI. This is reflected in their performance: DRUNet achieved SSIM = 0.9099 and PSNR = 30.33 dB, while FFDNet reached SSIM = 0.9233 and PSNR = 31.31 dB. Despite FFDNet’s computational efficiency (training time = 16,075.40 s), neither model was explicitly designed for the hybrid clinical noise simulated in this study.
Nonlocal attention-based networks such as NLRN [37] and RNAN [36] aim to capture long-range dependencies through nonlocal operations. NLRN employs recurrent nonlocal modules to enhance parameter efficiency and self-similarity learning but does not include noise-specific adaptation. RNAN enhances spatial and channel representation via attention modules, achieving relatively strong results (SSIM = 0.9305, PSNR = 32.82 dB), yet remains limited by a fixed attention scope and a lack of hybrid noise awareness.
N3Net [38] further develops the self-similarity concept using differentiable K-nearest neighbor blocks to improve structural restoration. While effective on structured noise, its complexity and sensitivity to hyperparameters, along with its lack of validation on CE-MRI data, restrict its clinical applicability. Its SSIM and PSNR were 0.9192 and 30.95 dB, respectively, with a high training cost (14,155.23 s).
Transformer-based models such as SwinIR [32] and Restormer [33] leverage self-attention to model a global context. SwinIR, with its shifted window transformer, captures both local and global dependencies but requires large datasets and exhibits high memory usage. It achieved SSIM = 0.8921 and PSNR = 29.93 dB, with a training time of 112,795.38 s. Restormer introduces efficient channel-spatial attention and excels in high-resolution image processing, but it suffers from oversmoothing artifacts and lacks targeted training for hybrid noise. Its SSIM dropped to 0.8239 and PSNR to 26.10 dB, despite a significant training burden of 172,810.38 s. Additionally, both models, like many deep learning-based denoizing approaches, heavily rely on data augmentation to artificially increase dataset diversity. However, such augmentation strategies often fall short in capturing the complex variability of clinical CE-MRI noise, particularly for HCC diagnosis. Their dependence on augmentation reduces generalization capability under real-world conditions, limiting their effectiveness when exposed to noise distributions not represented in the training data.
In contrast, NLE-ANSNet directly addresses the limitations of these models through a clinically oriented design. It integrates multilevel noise level estimators (at 32, 64, 128, and 256 channels) and an adaptive noise scaling mechanism, enabling localized adaptation to variable noise intensities. Unlike FFDNet, which relies on externally provided noise maps, NLE-ANSNet learns noise patterns endogenously. Unlike Restormer and SwinIR, it does not depend on excessive data or artificial augmentation pipelines.
Quantitatively, NLE-ANSNet achieved superior metrics, SSIM = 0.9393 and PSNR = 34.01 dB, while maintaining reasonable computational requirements (training time = 20,112.32 s). It outperformed RNAN by 0.0088 SSIM and 1.19 dB PSNR, representing a meaningful gain in CE-MRI, where subtle tissue contrasts are crucial. Additionally, NLE-ANSNet preserved anatomical detail better than DRUNet [34] and FFDNet [39]—which exhibited residual noise—and outperformed transformer-based models that tended to oversmooth lesions and vascular structures.
Qualitatively, NLE-ANSNet demonstrated robust structural preservation under hybrid noise thanks to its pixel-level simulation of Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise without augmentation. This design ensured better generalization to clinical CE-MRI data, a key limitation in previous models trained on synthetic or uniform perturbations.
Thus, compared to related studies, NLE-ANSNet presents a well-balanced solution, offering high accuracy, structural fidelity, and clinical robustness, outperforming both CNN and transformer-based architectures in CE-MRI denoizing for HCC applications.
6. Conclusions
This study presents NLE-ANSNet, an advanced denoizing framework designed specifically for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By integrating multilevel noise level estimators (NLEs) with adaptive noise scaling (ANS), the model dynamically adapts to spatially varying noise intensities, enabling progressive and context-aware denoizing without relying on data augmentation. The proposed hybrid noise simulation strategy, blending Gaussian, Poisson, and Rician noise at the pixel level, provides a clinically realistic and statistically robust benchmark for evaluation.
Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that NLE-ANSNet outperforms state-of-the-art models in terms of both the PSNR and SSIM while maintaining a favorable trade-off between image quality and training efficiency. Moreover, the method preserves critical anatomical features essential for diagnostic accuracy, enhancing clinical confidence across multiple CE-MRI applications, including arterial phase visualization and gadoxetic acid-enhanced imaging.
By addressing key limitations in conventional denoizing models, such as uniform noise filtering and oversmoothing, this work establishes a new direction for adaptive and robust denoizing in medical imaging. The methodological innovations and clinical relevance of NLE-ANSNet make it a promising tool for advancing CE-MRI interpretation and supporting accurate, high-fidelity imaging in real-world diagnostic workflows.
Funding
This research was funded by the Taif University, Saudi Arabia. The author would like to acknowledge the Deanship of Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, Taif University, for funding this work.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the results of this study are available from a publicly archived dataset. Specifically, the ATLAS dataset (A Tumor and Liver Automatic Segmentation dataset on contrast-enhanced MRI for hepatocellular carcinoma) was used, as described by Quinton et al. [41]. The dataset is accessible at https://atlas-challenge.u-bourgogne.fr (accessed on 21 January 2025). No new data were generated or collected for this study.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the creators and contributors of the ATLAS dataset for making their data publicly available, which greatly facilitated this research. The author would like to acknowledge the Deanship of Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, Taif University, for funding this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ker, J.; Wang, L.; Rao, J.; Lim, T. Deep learning applications in medical image analysis. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 9375–9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, C.; Frauenfelder, G.; Massaroni, C.; Saccomandi, P.; Giurazza, F.; Pitocco, F.; Marano, R.; Schena, E. Emerging clinical applications of computed tomography. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2015, 8, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.P.; Tognarelli, J.M.; Crossey, M.M.; Cox, I.J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; McPhail, M.J. Magnetic resonance imaging: Principles and techniques: Lessons for clinicians. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Halanaik, D.; Malhotra, A. Clinical applications of positron emission tomography-computed tomography in oncology. Indian J. Cancer 2010, 47, 100–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shung, K.K.; Smith, M.; Tsui, B.M. Principles of Medical Imaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, J.A. X-ray imaging physics for nuclear medicine technologists. Part 1: Basic principles of x-ray production. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2004, 32, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Strzelecki, M.; Piórkowski, A. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence in medical imaging and image processing—A review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Chen, X.; AlQahtani, S.A.; Hossain, M.S. Multi-modality MRI fusion with patch complementary pre-training for internet of medical things-based smart healthcare. Inf. Fusion 2024, 107, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotiri, J.; Elleithy, K.; Elleithy, A. An automated region-of-interest segmentation for optic disc extraction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Long Island Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT), Farmingdale, NY, USA, 4 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, P.; Beaudoin, G.; De Guise, J.A. A method for modeling noise in medical images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makitalo, M.; Foi, A. Optimal inversion of the generalized Anscombe transformation for Poisson-Gaussian noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aja-Fernández, S.; Alberola-López, C.; Westin, C.F. Noise and signal estimation in magnitude MRI and Rician distributed images: A LMMSE approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, B.; Agrawal, S.; Sohi, B.S. Noise issues prevailing in various types of medical images. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018, 11, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.G.; Sánchez, M.G.; Vidal, V.; Verdu, G.; Verdú, G.; Mayo, P.; Rodenas, F. Medical image restoration with different types of noise. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 4382–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, S.; Garg, D.; Singh, P.; Ravi, V. Role and Impact of Method Noise on CT Image Denoising. Open Bioinform. J. 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; Chen, S.; Gong, H.; Yang, X. FCE-Net: A fast image contrast enhancement method based on deep learning for biomedical optical images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 3521–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Udupa, J.K.; Zhao, L.; Tong, Y.; Odhner, D.; Pednekar, G.; Nag, S.; Lewis, S.; Poole, N.; Mannikeri, S.; et al. Object recognition in medical images via anatomy-guided deep learning. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 81, 102527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep learning for image classification: A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Cambridge, UK, 9–10 December 2023; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H. Medical image analysis using deep learning algorithms. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1273253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, P.K.; Singh, P.K.; Srivastav, S.; Narayan, V.; Paprzycki, M.; Jaworska, T.; Ganzha, M. A comprehensive review of deep neural networks for medical image processing: Recent developments and future opportunities. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 4, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Bhushan, M. Machine learning and deep learning approach for medical image analysis: Diagnosis to detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 26731–26769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.J.; Korfiatis, P.; Akkus, Z.; Kline, T.L. Machine learning for medical imaging. Radiographics 2017, 37, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galić, I.; Habijan, M.; Leventić, H.; Romić, K. Machine learning empowering personalized medicine: A comprehensive review of medical image analysis methods. Electronics 2023, 12, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, A. Machine Learning in Medical Imaging and Computer Vision; Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET): Stevenage, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufiene, B.O.; Chakraborty, C. (Eds.) Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Recognition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, G.; Kaur, P. A review of denoising medical images using machine learning approaches. Curr. Med. Imaging 2018, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; El-Khamy, M.; Lee, J. Dn-resnet: Efficient deep residual network for image denoising. In Computer Vision–ACCV 2018, Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018, Revised Selected Papers, Part V 14; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. Convolutional neural networks for image denoising and restoration. In Denoising of Photographic Images and Video: Fundamentals, Open Challenges and New Trends; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Nozaki, H.; Kamagata, K.; Mori, S.; Saito, Y.; Aoki, S. Noise reduction by multiple path neural network using Attention mechanisms with an emphasis on robustness against Errors: A pilot study on brain Diffusion-Weighted images. Phys. Medica 2023, 116, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Blanco, A.; Tejos, C.; Irarrazaval, P.; Cameron, I. Noise in magnitude magnetic resonance images. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part A Educ. J. 2008, 32, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Swinir: Image restoration using swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Plug-and-play image restoration with deep denoiser prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 6360–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Residual non-local attention networks for image restoration. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.10082. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wen, B.; Fan, Y.; Loy, C.C.; Huang, T.S. Non-local recurrent network for image restoration. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Plötz, T.; Roth, S. Neural nearest neighbors networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4608–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, H.; Amiri, H.S.; Zibari, G.B. Addressing the worldwide hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, prevention and management. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12 (Suppl. 2), S361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, F.; Popoff, R.; Presles, B.; Leclerc, S.; Meriaudeau, F.; Nodari, G.; Lopez, O.; Pellegrinelli, J.; Chevallier, O.; Ginhac, D.; et al. A tumour and liver automatic segmentation (atlas) dataset on contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for hepatocellular carcinoma. Data 2023, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagher-Ebadian, H.; Brown, S.L.; Ghassemi, M.M.; Nagaraja, T.N.; Valadie, O.G.; Acharya, P.C.; Cabral, G.; Divine, G.; Knight, R.A.; Lee, I.Y.; et al. Dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI estimation of vascular parameters using knowledge-based adaptive models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennessy, F.M.; Fedorov, A.; Gupta, S.N.; Schmidt, E.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Mulkern, R.V. Practical considerations in T1 mapping of prostate for dynamic contrast enhancement pharmacokinetic analyses. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Han, H.; Duan, C.; Yan, Z.; Lu, H.; Gu, X. Bladder wall thickness mapping for magnetic resonance cystography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Carillo, V.; Cozzarini, C.; Perna, L.; Rancati, T.; Valdagni, R.; Gabriele, P.; Fiorino, C. Impact of the radiotherapy technique on the correlation between dose–volume histograms of the bladder wall defined on MRI imaging and dose–volume/surface histograms in prostate cancer patients. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, N115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, R.A.; Smith, N.; Saunders, D.; Van Gordon, S.B.; Wisniewski, A.B.; Tyler, K.R.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Hurst, R.E. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic tool to assess bladder permeability and associated colon cross talk: Preclinical studies in a rat model. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, C.J.; Vos, B.; Nordell, A.; Urich, M.; Blomqvist, L.; Breuer, J.; Reiser, M.F.; Weinmann, H.J. Vascular enhancement in early dynamic liver MR imaging in an animal model: Comparison of two injection regimen and two different doses Gd-EOB-DTPA (gadoxetic acid) with standard Gd-DTPA. Investig. Radiol. 2009, 44, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Ito, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kanki, A.; Higaki, A.; Tanimoto, D.; Higashi, H. Comparison of three different injection methods for arterial phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MR imaging of the liver. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, e284–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, A.; Higuchi, N.; Ueno, A. Reduction of ringing artifacts in the arterial phase of gadoxetic acid-enhanced dynamic MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2012, 11, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Hong, H.S. Comparison of two different injection rates of gadoxetic acid for arterial phase MRI of the liver. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 31, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doo, K.W.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.A.; Park, C.M. “Pseudo washout” sign in high-flow hepatic hemangioma on gadoxetic acid contrast-enhanced MRI mimicking hypervascular tumor. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, W490–W496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thian, Y.L.; Riddell, A.M.; Koh, D.M. Liver-specific agents for contrast-enhanced MRI: Role in oncological imaging. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovik, A.C. Handbook of Image and Video Processing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Que, D. Medical images denoising based on total variation algorithm. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 8, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Azeemuddin, S.M. Image denoising using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N), Greater Noida, India, 16–17 December 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, K.; Singh, D.K.; Ansari, M.A. Autoencoders based deep learner for image denoising. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Attention Methods for Image Denoising: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Cyber-Physical Social Intelligence (ICCSI), Doha, Qatar, 8–12 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiantian, W.; Hu, Z.; Guan, Y. An efficient lightweight network for image denoising using progressive residual and convolutional attention feature fusion. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Mittal, A.; Aggarwal, N. ResDNN: Deep residual learning for natural image denoising. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, L.; Hossbach, J.; Preuhs, E.; Wagner, F.; Arroyo Camejo, S.; Kannengiesser, S.; Nickel, D.; Wuerfl, T.; Maier, A. Self-supervised MRI denoising: Leveraging Stein’s unbiased risk estimator and spatially resolved noise maps. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awudong, B.; Yakupu, P.; Yan, J.; Li, Q. Research and Implementation of Denoising Algorithm for Brain MRIs via Morphological Component Analysis and Adaptive Threshold Estimation. Mathematics 2024, 12, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, M.; Higashi, M.; Yonezawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Iida, E.; Furukawa, M.; Okada, M.; Shinoda, K.; Ito, K. Feasibility of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the liver using deep learning reconstruction based on the deep learning denoising technique. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 80, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W. Deep learning network for blind image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xu, Y.; Tompkins, A.; Pagnucco, M.; Song, Y. Multi-degradation-adaptation network for fundus image enhancement with degradation representation learning. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, D.; Govind, D.; Narayanankutty, K.A. A novel method for removing Rician noise from MRI based on variational mode decomposition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 69, 102737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjón, J.V.; Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Lull, J.J.; García-Martí, G.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Robles, M. MRI denoising using non-local means. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.V.; Damodare, O.H.; Sapkal, A.M. Poisson noise reducing bilateral filter. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 79, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, S.; Kola, L.; Sushma, P.; Archana, S. Analysis of filtering and novel technique for noise removal in MRI and CT images. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 15–16 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. All-in-one multi-degradation image restoration network via hierarchical degradation representation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 26 October–3 November 2023; pp. 2285–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Yao, M.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, F. Ingredient-oriented multi-degradation learning for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5825–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Ahn, N.; Moon, J.H.; Sohn, K.A. Exploiting distortion information for multi-degraded image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Grids: Grouped multiple-degradation restoration with image degradation similarity. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bronik, K.; Papież, B.W. Learning to restore multiple image degradations simultaneously. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, M.W. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using deep learning classifier: A multi-center retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.M.; Collins, D.J.; Wallace, T.; Chau, I.; Riddell, A.M. Combining diffusion-weighted MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI improves the detection of colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuya, T.K.; Rimiru, R.M.; Okeyo, G.O. An image denoising technique using wavelet-anisotropic gaussian filter-based denoising convolutional neural network for CT images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takam, C.A.; Samba, O.; Kouanou, A.T.; Tchiotsop, D. Spark architecture for deep learning-based dose optimization in medical imaging. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilimek, D.; Kubicek, J.; Golian, M.; Jaros, R.; Kahankova, R.; Hanzlikova, P.; Barvik, D.; Krestanova, A.; Penhaker, M.; Cerny, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of wavelet transform filtering systems for noise reduction in ultrasound images. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goceri, E. Medical image data augmentation: Techniques, comparisons and interpretations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 12561–12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, F.A.; da Costa, C.A.; Zonta, T.; Marques, N.M.; Roehe, A.V.; Moreno, M.; da Rosa Righi, R. Segmentation of masses on mammograms using data augmentation and deep learning. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Fan, D.P.; Timofte, R.; Gool, L.V. Practical blind image denoising via Swin-Conv-UNet and data synthesis. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).