An Incentive Mechanism Based on Lottery for Data Quality in Mobile Crowdsensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Non-Monetary Incentive Mechanism for Data Quality and User Participation
2.2. Monetary Incentive Mechanism for Data Quality and User Participation
3. The Lottery-Based Incentive Mechanism
3.1. Physical Model
3.2. Design of the Lottery-Based Incentive Mechanism
3.2.1. Mapping of the Lottery Model
3.2.2. Bonus Pool and User Utility
3.2.3. Users Data Quality Strategy and Bids
3.2.4. The Effect of Objective Reward Probability on the Lower Bound of Price
3.2.5. Winner Selection
3.2.6. Budget Allocation
4. Simulation Experiments
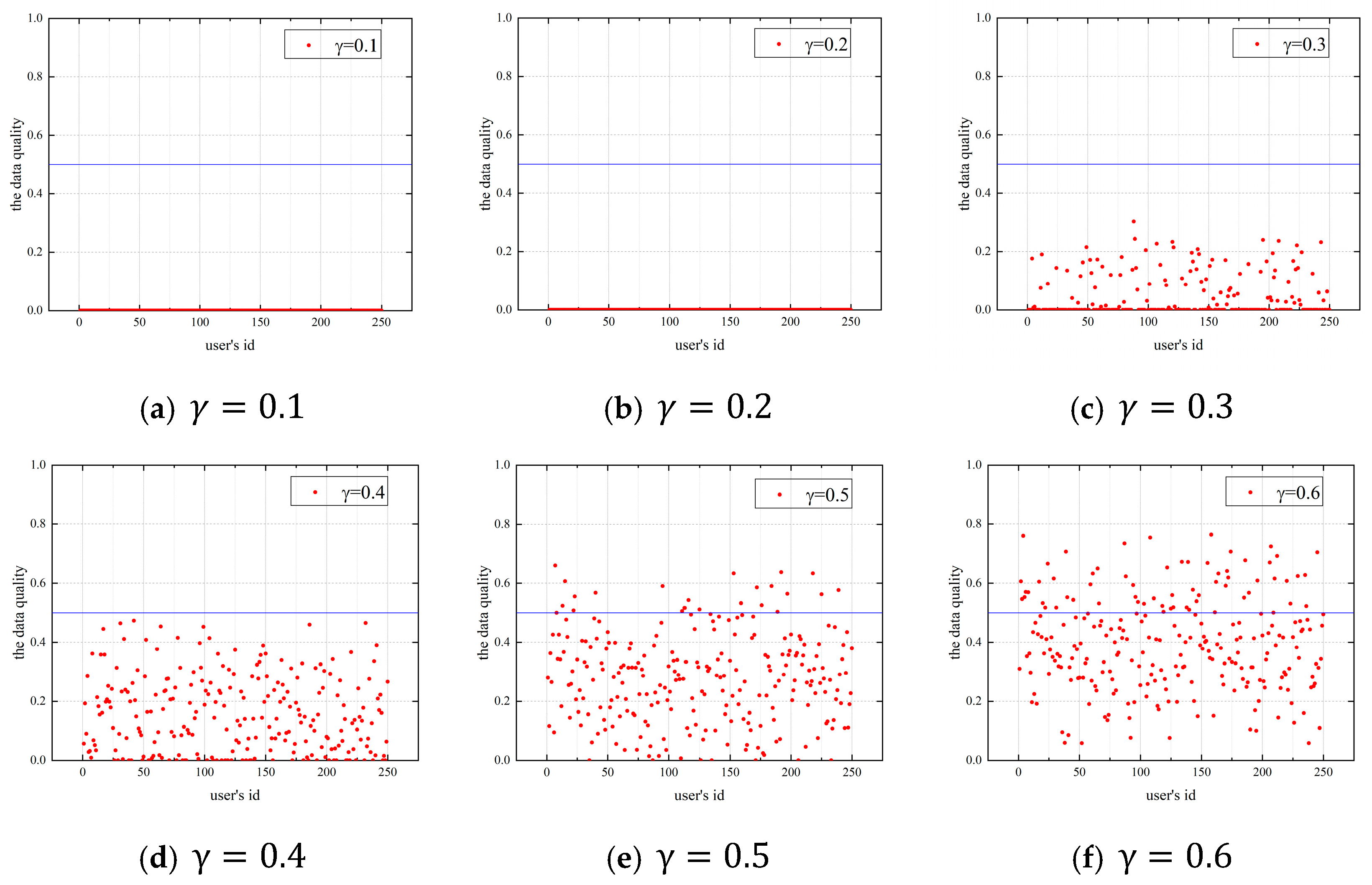
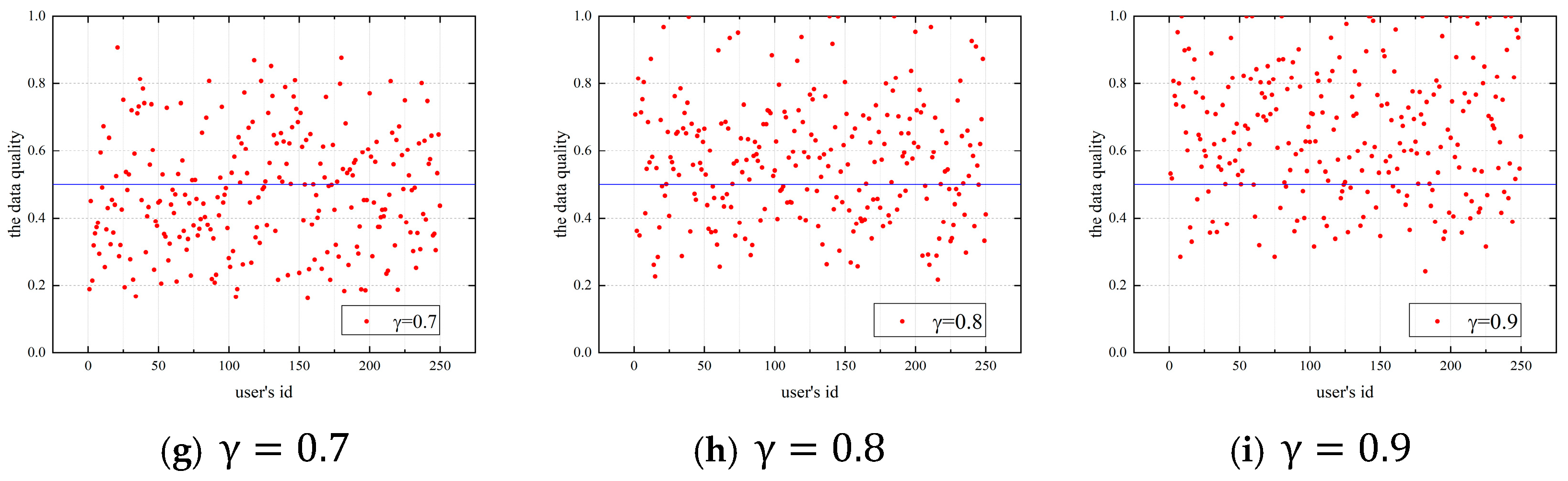
4.1. Discussion of Coefficients
4.1.1. Impact of the Budget Allocation Coefficient on Users’ Data Quality
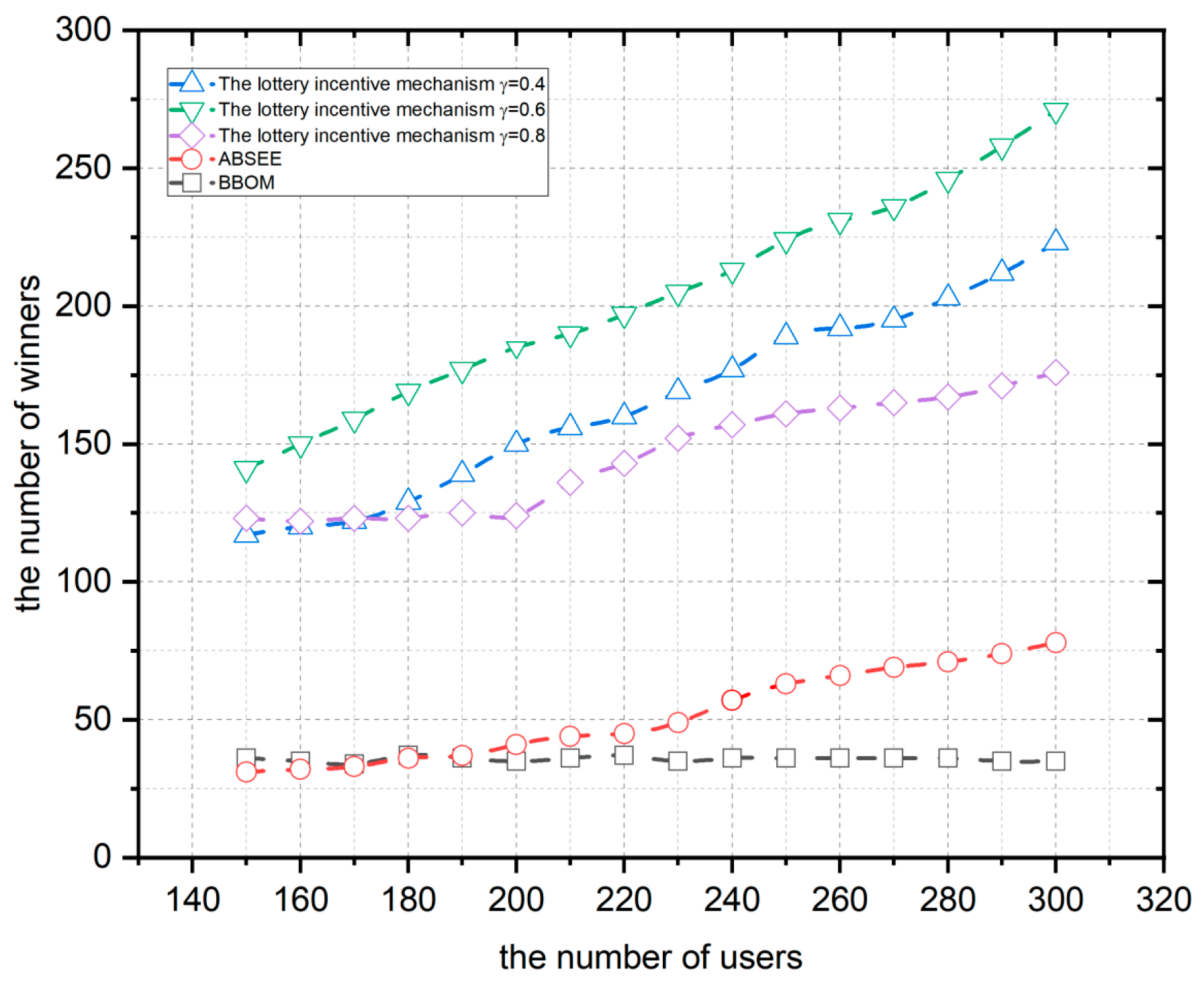
4.1.2. Impact of the Budget Allocation Coefficient on User Participation
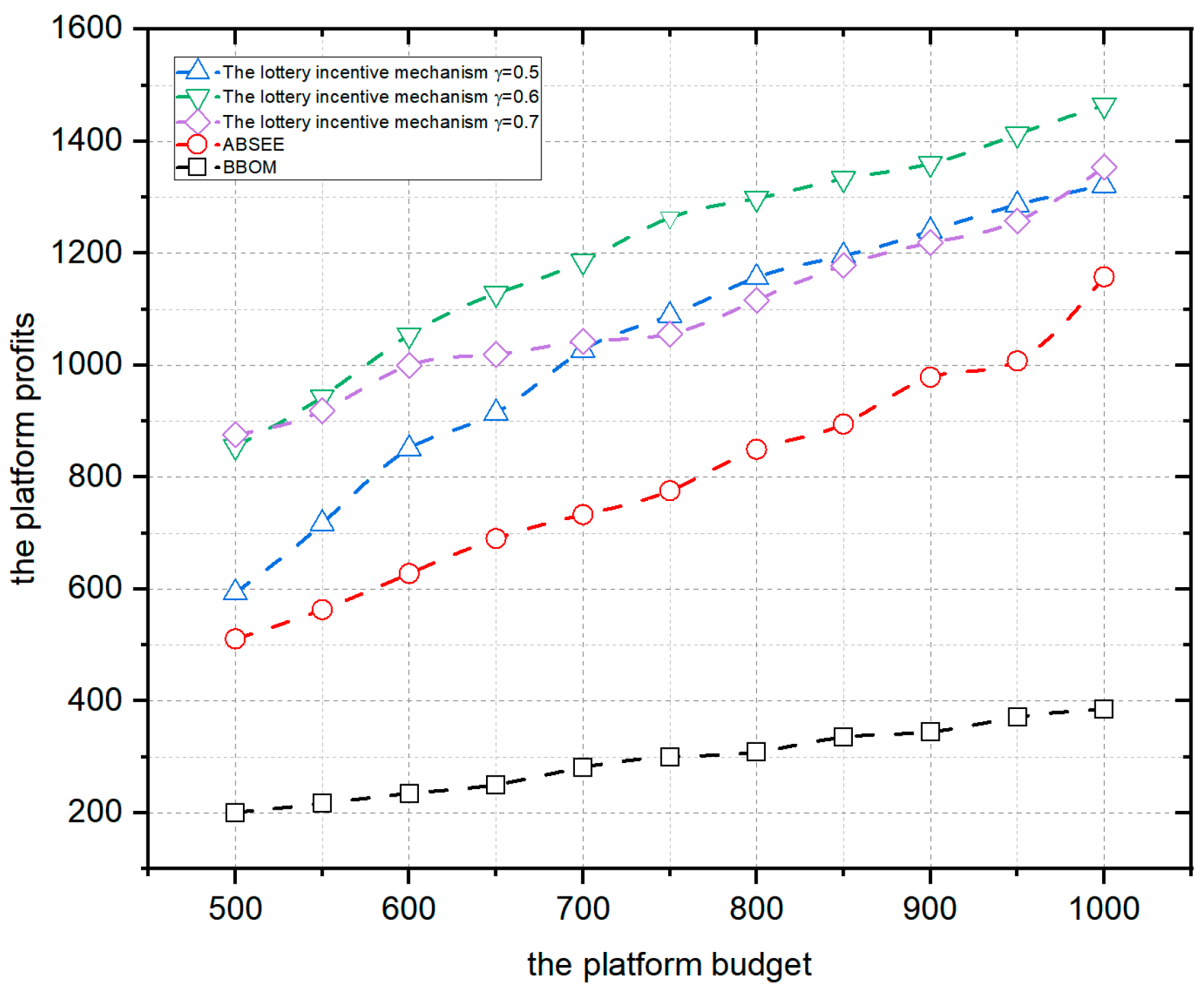
4.1.3. Impact of the Platform Budget and User Number on Platform Profits
4.2. Experimental Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, K.; Cheng, G.; Niu, J.; He, S. A privacy-preserving incentive mechanism for mobile crowdsensing based on blockchain. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2024, 21, 5071–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Chi, D.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zou, D.; Xu, Y. A preference-driven malicious platform detection mechanism for users in mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 2720–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Signoretti, G.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, I.; Costa, D.G. A crowdsensing platform for monitoring of vehicular emissions: A smart city perspective. Future Internet 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zhao, L.; Xie, W. Crowd bus sensing: Resolving conflicts between the ground truth and map apps. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 23, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marche, C.; Perra, L.; Nitti, M. Crowdsensing and Trusted Digital Twins for Environmental Noise Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Mediterranean Conference on Communications and Networking (MeditCom), Madrid, Spain, 8–11 July 2024; pp. 535–540. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ying, C.; Li, L.; Düdder, B.; Wu, H.; Jin, H.; Luo, Y. Incentive Mechanism for Uncertain Tasks under Differential Privacy. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2024, 17, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, J.; Sheng, M.; Xu, Y.; Taleb, T.; Shiratori, N. Mobile crowdsensing ecosystem with combinatorial multi-armed bandit-based dynamic truth discovery. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 13095–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Tu, W.; Xu, X.; Xiong, N.N. IIM-ARE: An Effective Interactive Incentive Mechanism based on Adaptive Reputation Evaluation for Mobile Crowd Sensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, C.; Wu, Q.; Yang, W. Reputation Based Privacy-Preserving in Location-Dependent Crowdsensing for Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Networking and Network Applications (NaNA), Yinchuan, China, 9–12 August 2024; pp. 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cao, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X. A reputation-based multi-user task selection incentive mechanism for crowdsensing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 74887–74900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, C. A reputation-based and privacy-preserving incentive scheme for mobile crowd sensing: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 4685–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Liao, J.; Yu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, B. Trust assessment for mobile crowdsensing via device fingerprinting. ISA Trans. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Tong, F.; Xing, F. IMFGR: Incentive Mechanism With Fine-Grained Reputation for Federated Learning in Mobile Crowdsensing. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence of Things and Systems (AIoTSys), Hangzhou, China, 17–19 October 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Tai, W. Optimizing Collaborative Crowdsensing: A Graph Theoretical Approach to Team Recruitment and Fair Incentive Distribution. Sensors 2024, 24, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, F.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, C.; Yu, F.R. An Incentive Mechanism for Vehicular Crowdsensing with Security Protection and Data Quality Assurance. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, C. Online incentive mechanisms for socially-aware and socially-unaware mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 23, 6227–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Long, S.; Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; Liu, H. Recruitment from social networks for the cold start problem in mobile crowdsourcing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 30536–30550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.; Gao, X.; Chen, G. A dual-embedding based DQN for worker recruitment in spatial crowdsourcing with social network. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1670–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L. Socialrecruiter: Dynamic incentive mechanism for mobile crowdsourcing worker recruitment with social networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 20, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Long, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, K.; Deng, Q.; Li, Z. Propagation verification under social relationship privacy awareness in mobile crowdsourcing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 12461–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilyfard, R.; Moghisi, M. An incentive mechanism design for multitask and multipublisher mobile crowdsensing environment. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 5248–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; An, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, L. Quality-Aware Incentive Mechanism for Social Mobile Crowd Sensing. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 27, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, W.; Min, G. Fairness-aware two-stage hybrid sensing method in vehicular crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 11971–11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Miao, Y.; Luo, B.; Ma, S.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Deng, R.H. Oasis: Online all-phase quality-aware incentive mechanism for MCS. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2024, 17, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montori, F.; Bedogni, L. Privacy preservation for spatio-temporal data in Mobile Crowdsensing scenarios. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2023, 90, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Oguti, A.M.; Ochora, D.R.; Li, S. Towards a privacy-preserving smart contract-based data aggregation and quality-driven incentive mechanism for mobile crowdsensing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 207, 103483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Deep Learning-Enabled Sparse Industrial Crowdsensing and Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 6170–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Peng, J.; Yu, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, W. Adaptive sampling allocation for distributed data storage in compressive CrowdSensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 11, 12022–12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Peng, Z. Research Progress on Incentive Mechanisms in Mobile Crowdsensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 24621–24633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Deng, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. Familiar paths are the best: Incentive mechanism based on path-dependence considering space-time coverage in crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 9304–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Chen, X.; Huang, J. Prospect theoretic analysis of privacy-preserving mechanism. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2019, 28, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhan, W.; Hu, Y.; Tomizuka, M. Interpretable modelling of driving behaviors in interactive driving scenarios based on cumulative prospect theory. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, W.K.; Green, L.; Vuchinich, R.E. Behavioral economics. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1995, 64, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Tversky, A. Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. In Handbook of the Fundamentals of Financial Decision 667 Making: Part I; MacLean, L., Ziemba, W., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013; pp. 99–127. [Google Scholar]
- Prelec, D. The probability weighting function. Econometrica 1998, 66, 497–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Shah-Mansouri, H.; Wong, V.W. Quality of sensing aware budget feasible mechanism for mobile crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 3619–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, F.; He, S. Bi-objective incentive mechanism for mobile crowdsensing with budget/cost constraint. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 23, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Number of rounds | |
| Number of combinations of lottery numbers | |
| The total number of users in t-th round | |
| Number of tasks in t-th round | |
| Total budget for the t-th round | |
| The bonus pool for the t-th round | |
| The budget allocation coefficient in the t-th round | |
| The ability value of in the t-th round | |
| The quality of data provided by in the t-th round | |
| Data quality strategy for in the t-th round | |
| The weight of the task in the t-th round | |
| Objective reward probability | |
| Subjective reward probability | |
| Risk attitude coefficient of |
| The Real-Life Lottery | Lottery Model in Crowdsensing | |
|---|---|---|
| Bonus Pool | 50% of lottery reward | Part of the platform budget |
| Incentive recipients | Buyer | Participants |
| Participation method | The buyer selects m numbers from n numbers to form a set of lottery numbers | After the user performs the task, the platform presents the user with a set of lottery numbers |
| Participation costs | Spend $2 to choose m numbers | Spend the cost to complete the task |
| Additional reward | Place additional bets on the purchased lottery tickets. | Spend more resources to improve data quality and receive greater rewards. |
| Reference points | Lottery reward | Reference Quality |
| Reward | Distribute rewards based on the number of matches between the lottery number and the number chosen by the buyers. | The reward is awarded according to whether the current lottery numbers match the user’s lottery numbers. |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| [50, 300] | |
| [500, 1000] | |
| 600 | |
| (0, 1) | |
| 14,3 | |
| 0.0027 | |
| [0.82, 0.94] | |
| [0.5, 1] | |
| [0.6, 0.8] | |
| 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Sun, S.; Lv, Z.; Liu, J. An Incentive Mechanism Based on Lottery for Data Quality in Mobile Crowdsensing. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101650
Hu X, Sun S, Lv Z, Liu J. An Incentive Mechanism Based on Lottery for Data Quality in Mobile Crowdsensing. Mathematics. 2025; 13(10):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101650
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xinyu, Shengjie Sun, Zhi Lv, and Jiaqi Liu. 2025. "An Incentive Mechanism Based on Lottery for Data Quality in Mobile Crowdsensing" Mathematics 13, no. 10: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101650
APA StyleHu, X., Sun, S., Lv, Z., & Liu, J. (2025). An Incentive Mechanism Based on Lottery for Data Quality in Mobile Crowdsensing. Mathematics, 13(10), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101650





