Global Dynamics of a Predator–Prey System with Variation Multiple Pulse Intervention Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Bifurcation of the Pest-Present Periodic Solution
4. Existence and Global Attractiveness of the Pest-Present Periodic Solution of System (3)
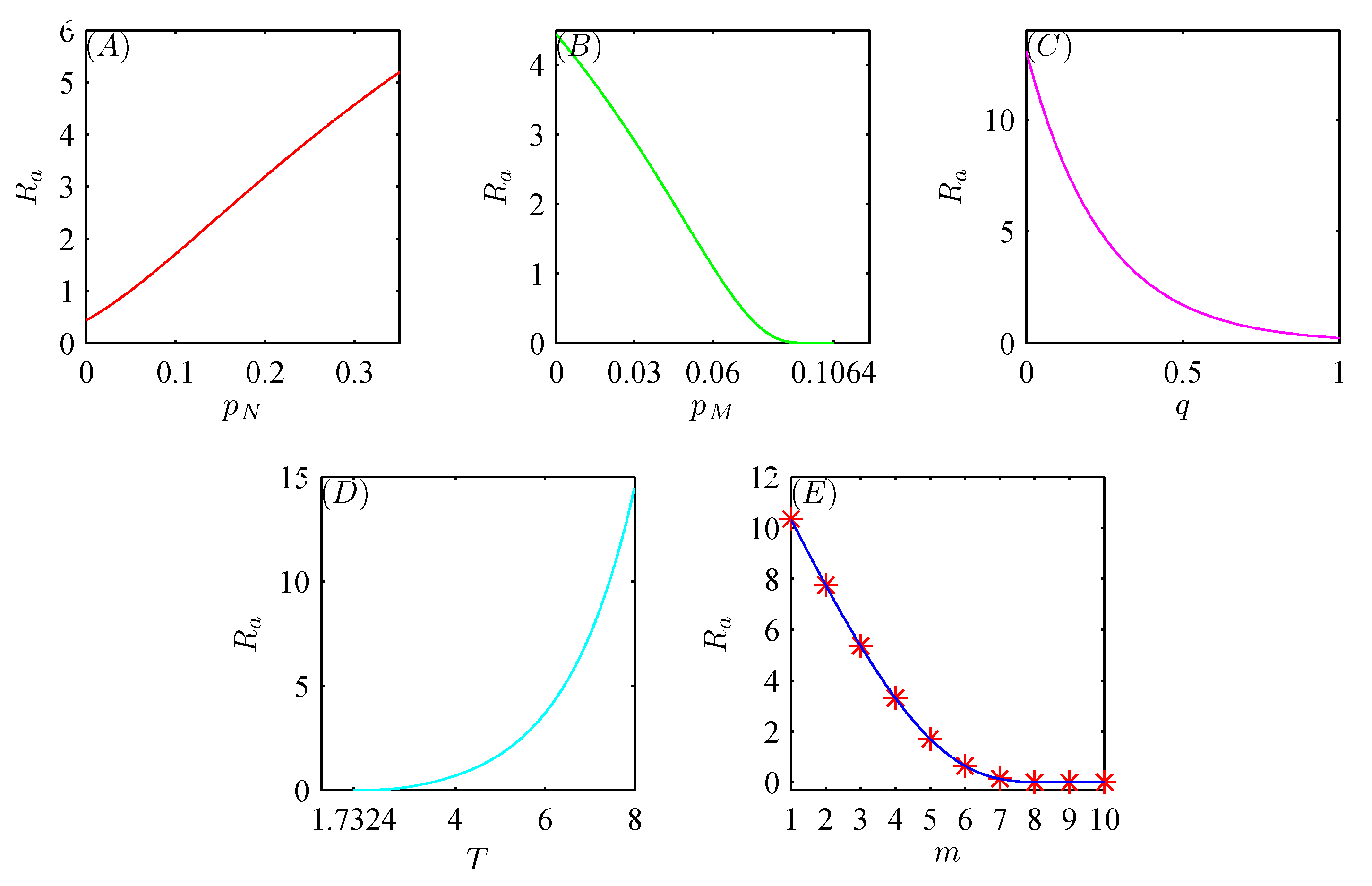
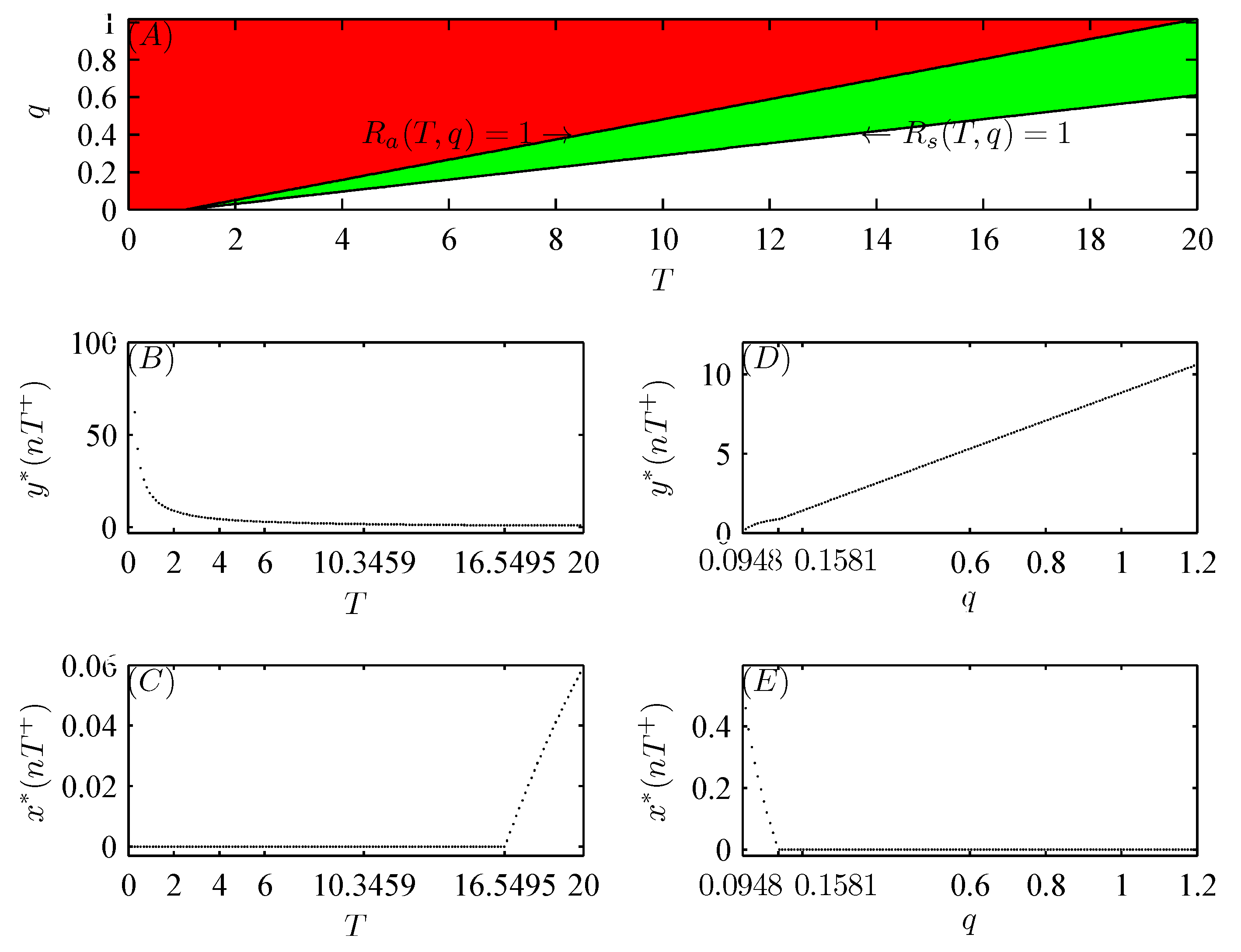
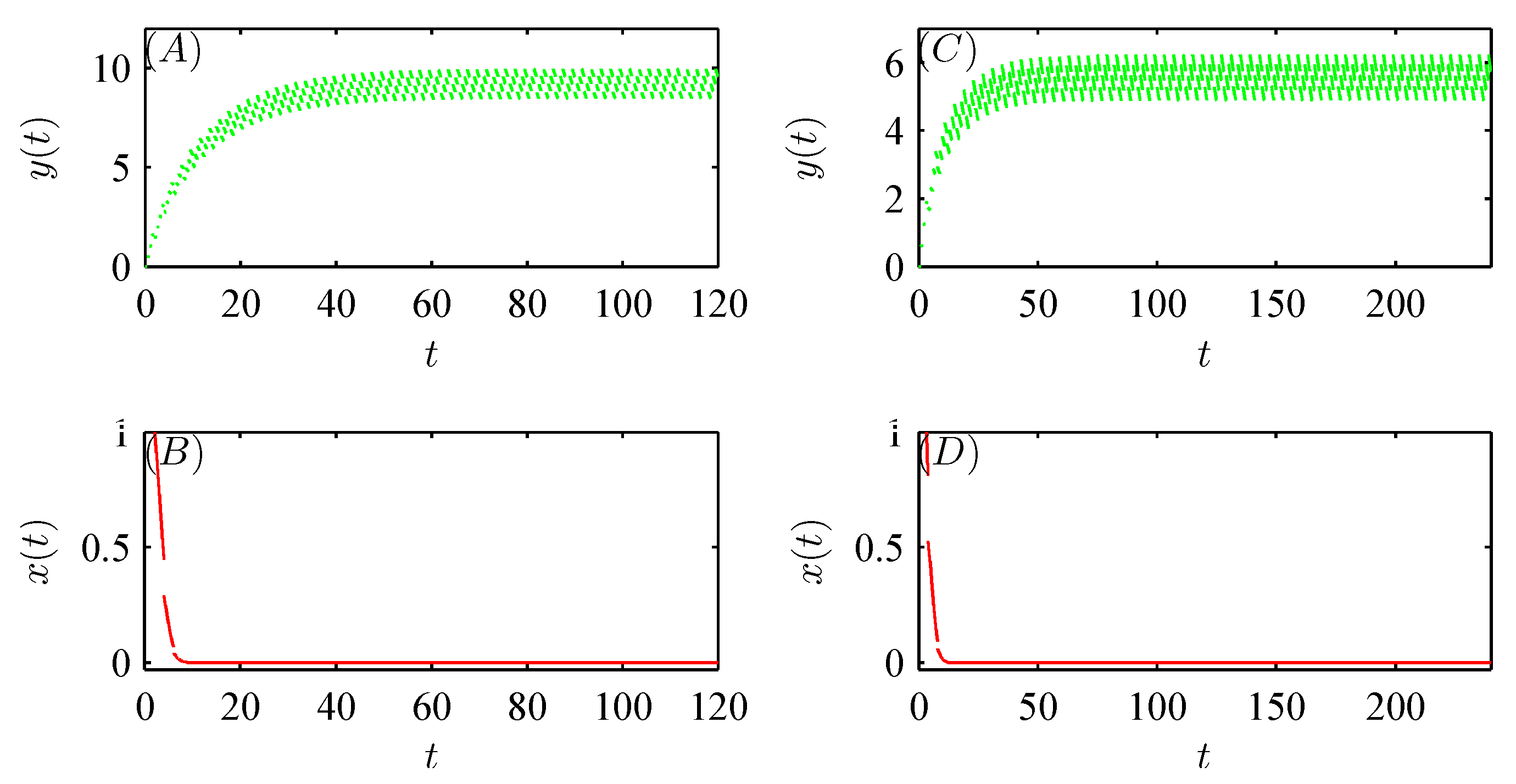
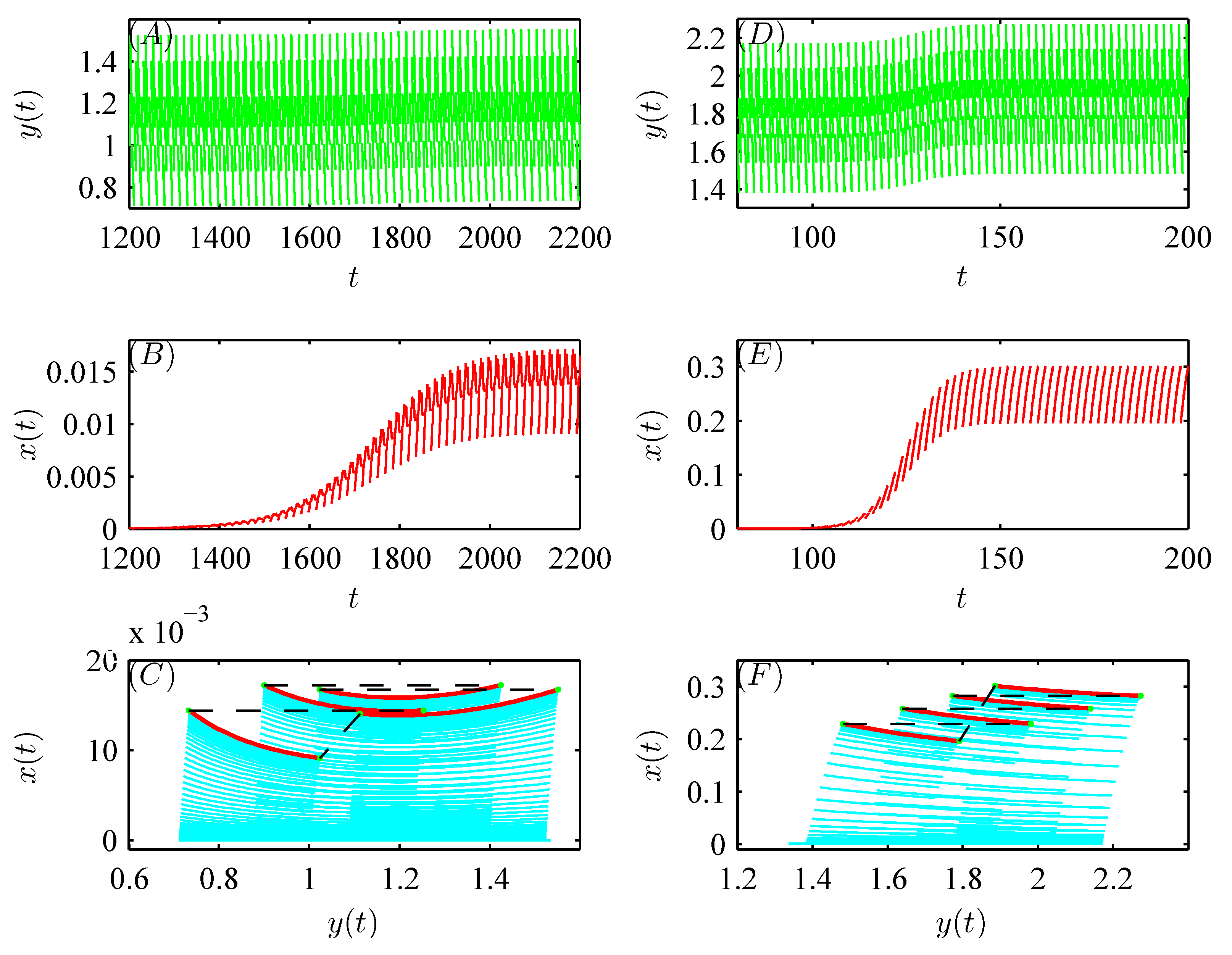
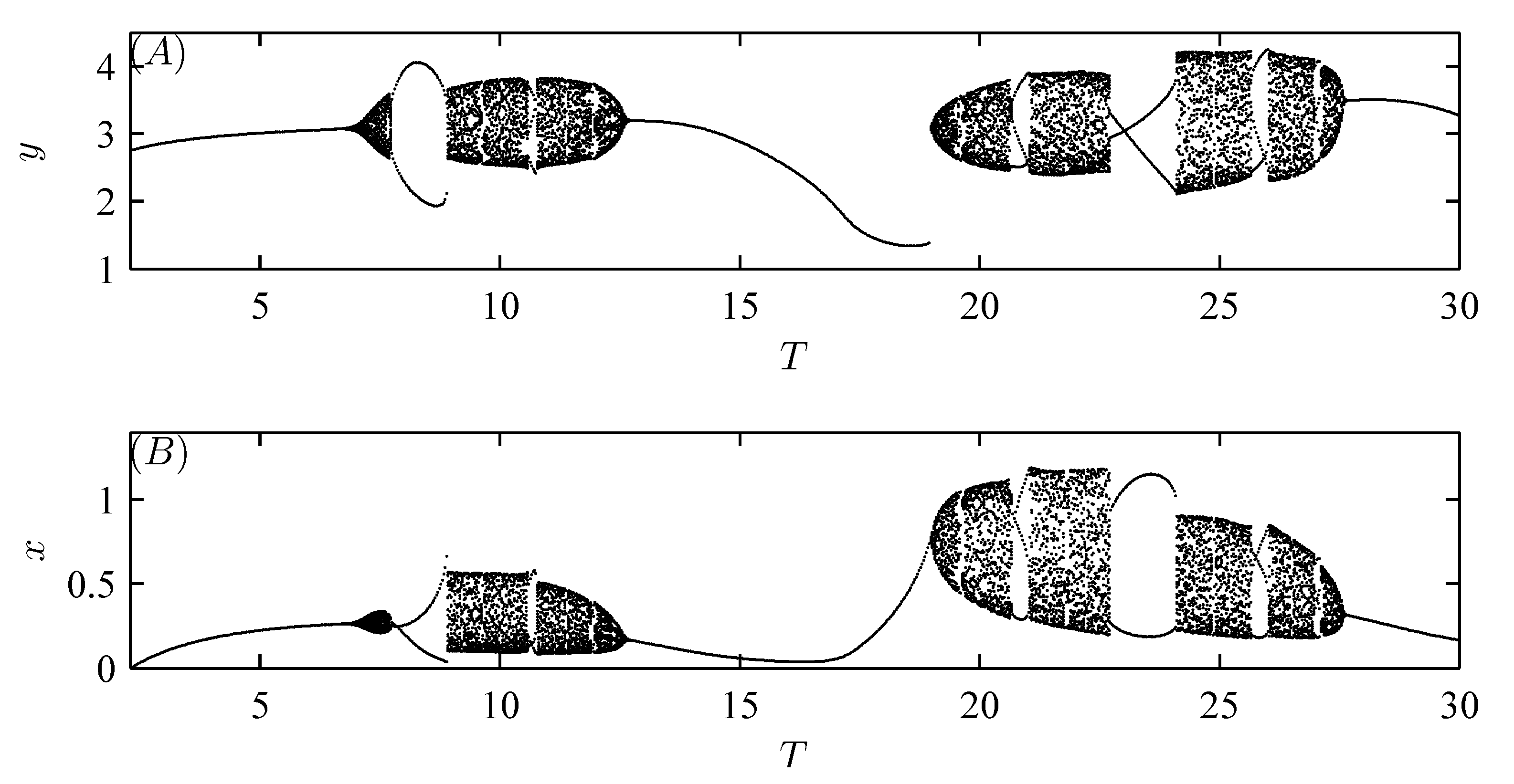
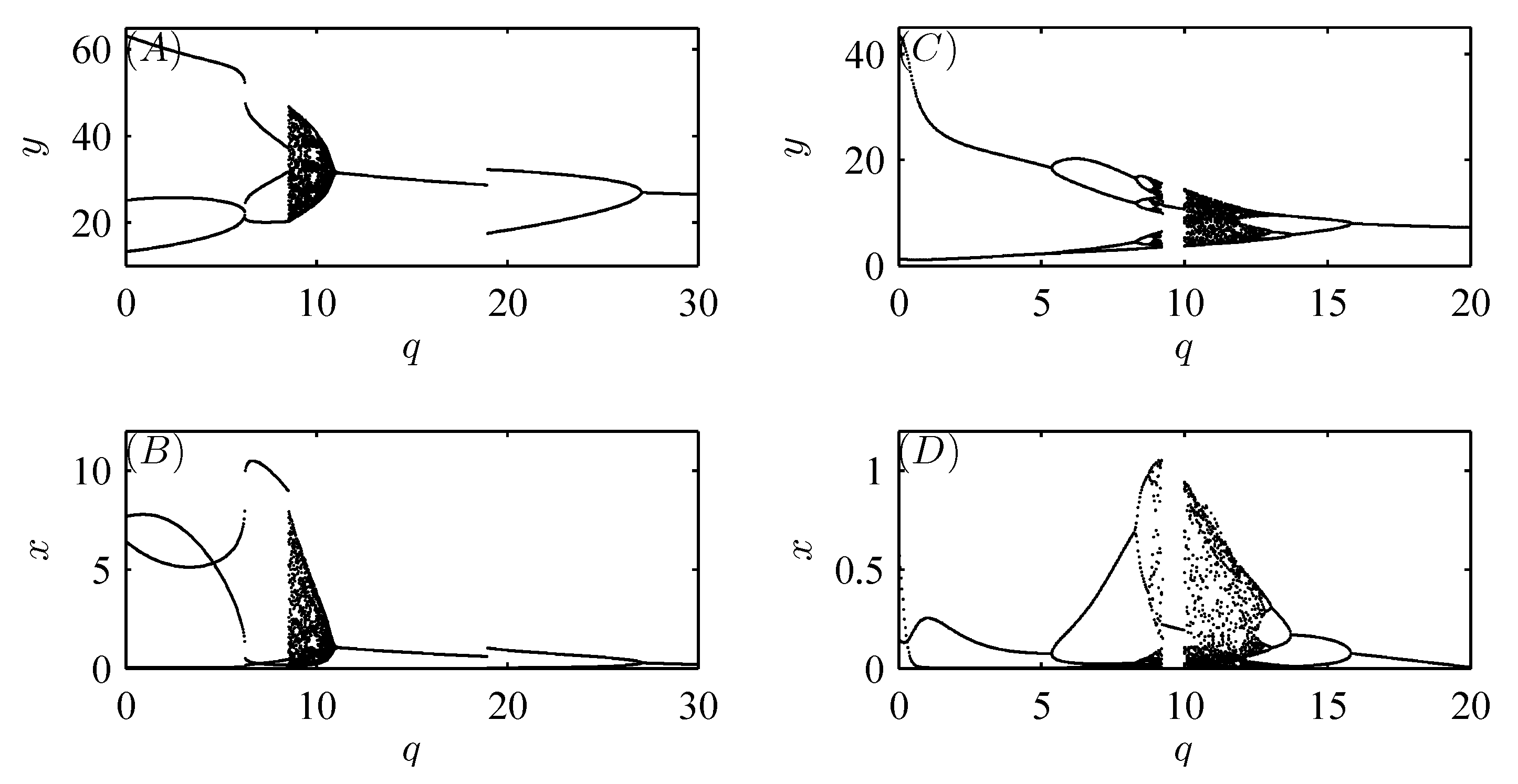
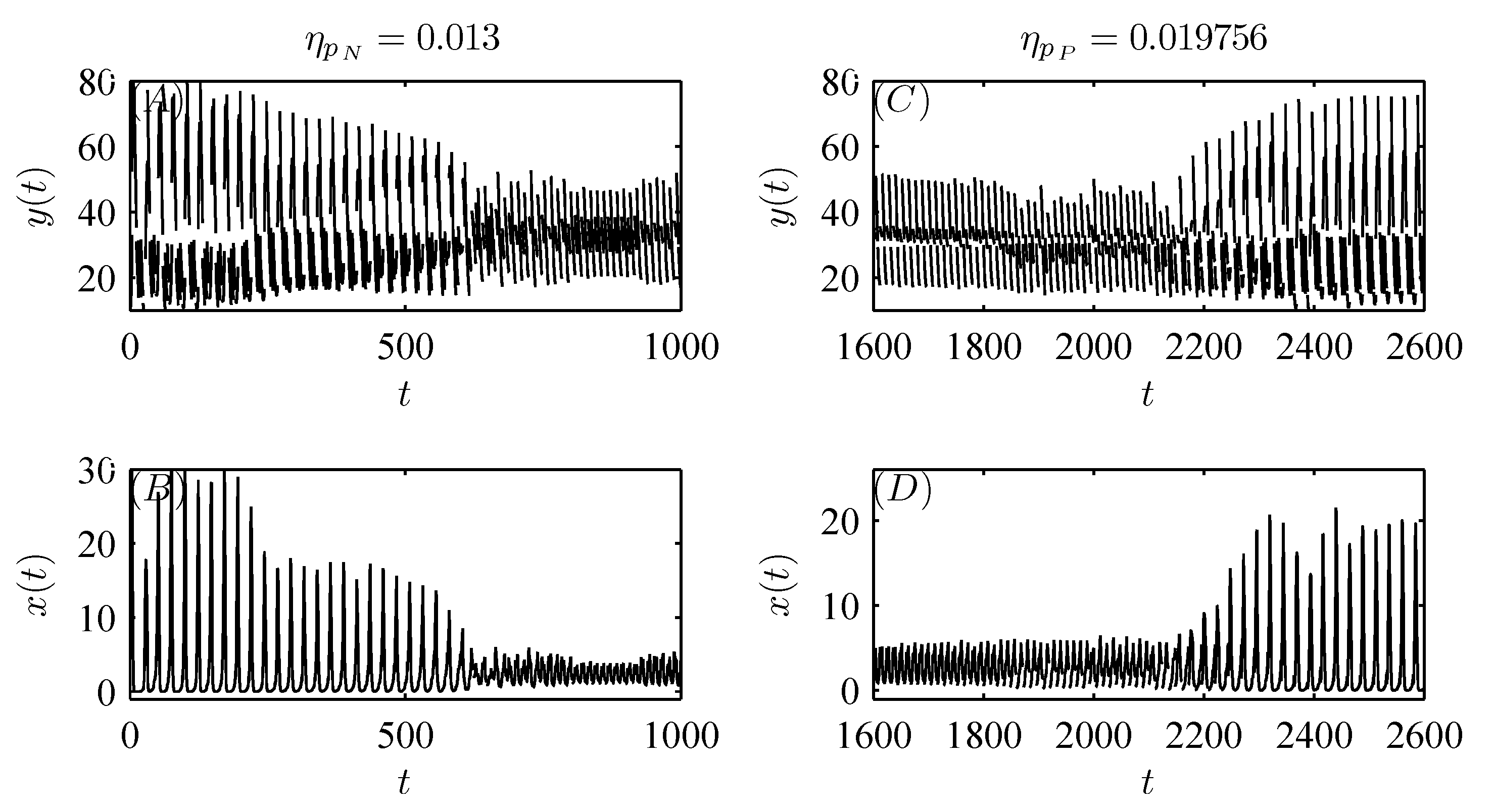
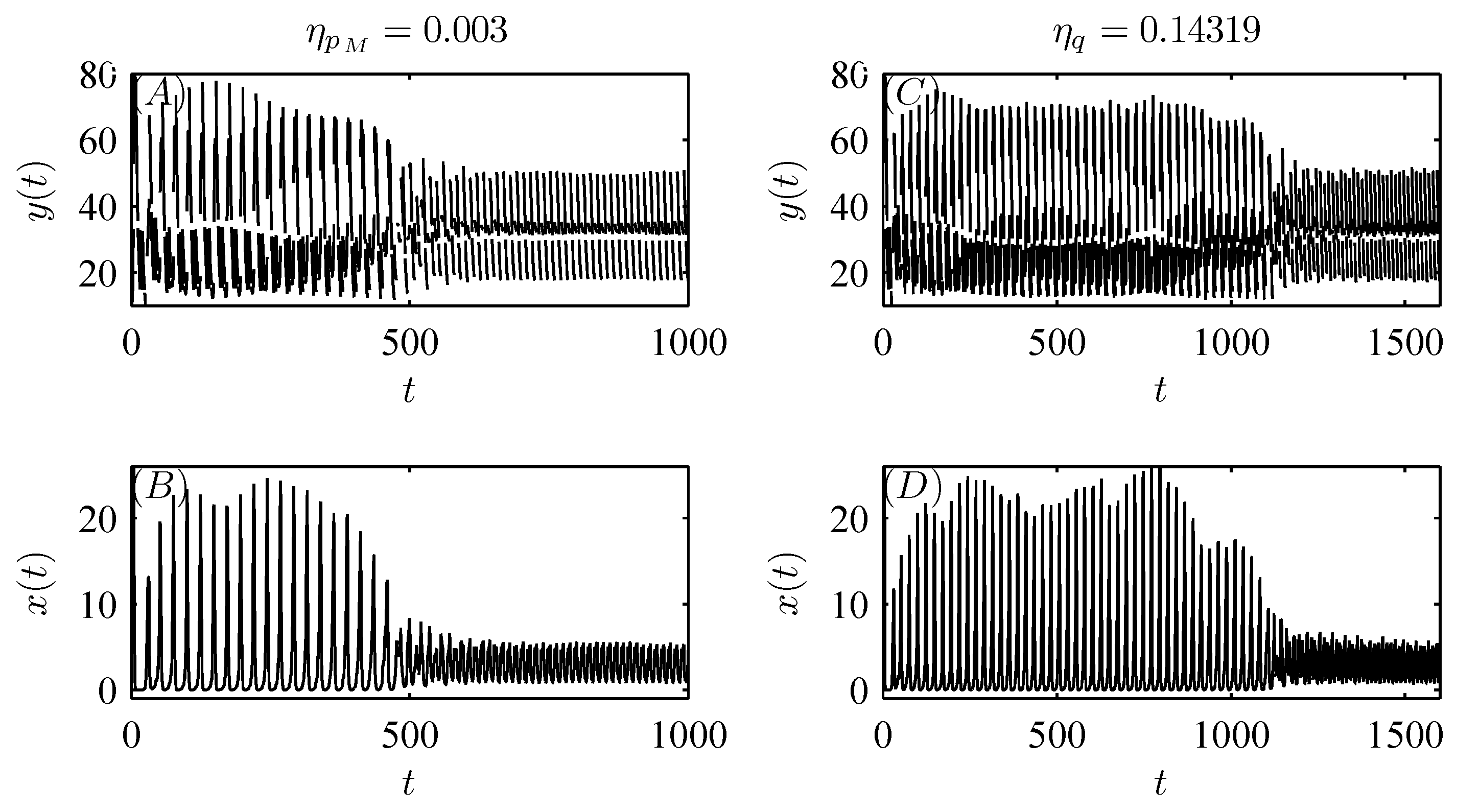
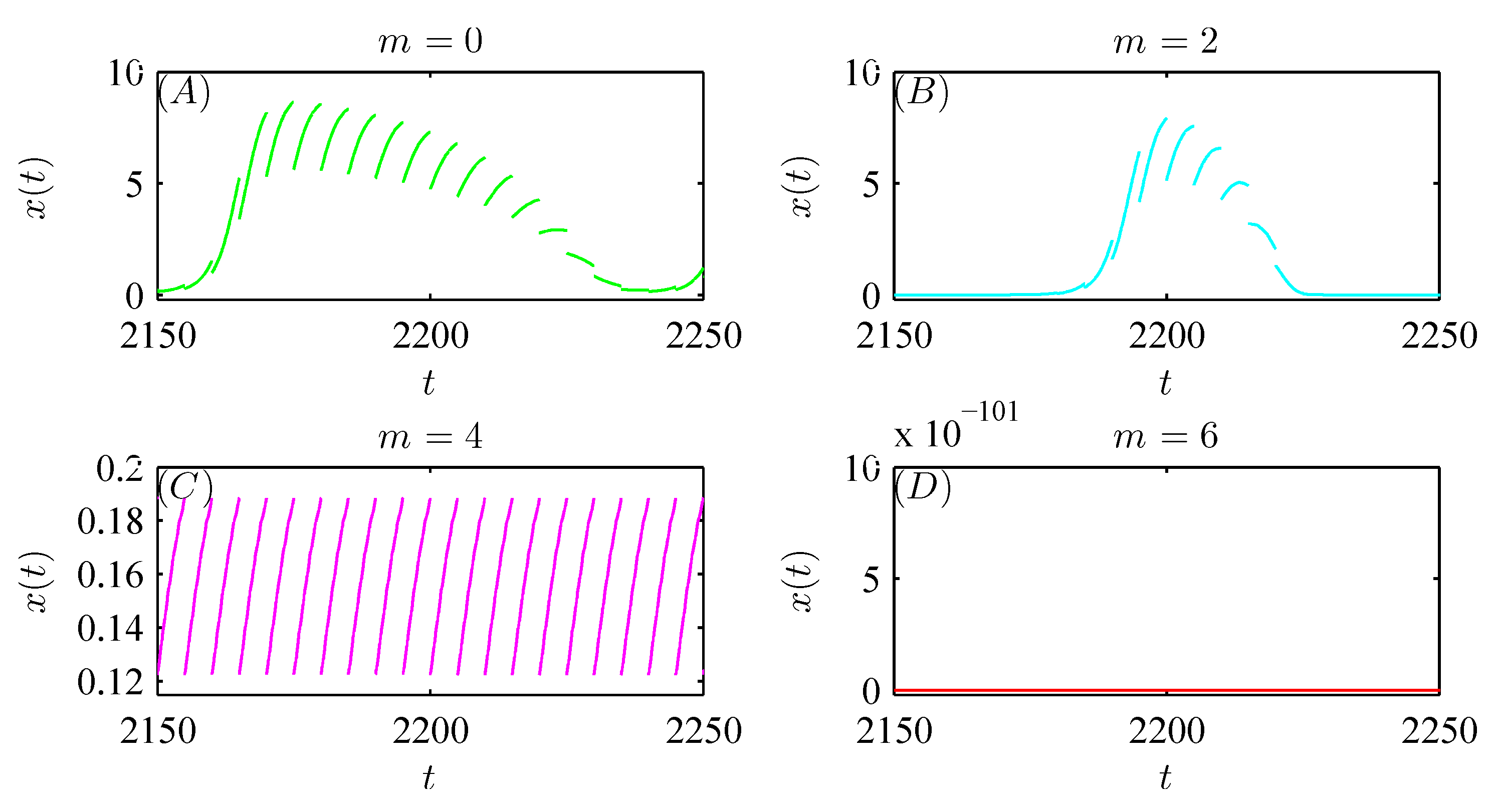
5. Numerical Analysis
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. First-Order Partial Derivatives of y(t) and x(t) with Initial Values
Appendix B. Several Propositions for Determining the Signs of and at Point (Tb, 0)
Appendix C. The Determination of the Sign of at Point (Tb, 0)
Appendix D. Determination of the Sign of at Point (Tb, 0)
References
- Li, Z. A disease-specific screening-level modeling approach for assessing the cancer risks of pesticide mixtures. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josea, S.A.; Raja, R.; Zhu, Q.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V.E. An integrated eco-epidemiological plant pest natural enemy differential equation model with various impulsive strategies. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4780680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Al Basir, F.; Cao, X.; Kumar Roy, P. Integrated pest management for Jatropha Carcus plant: An impulsive control approach. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Fu, J.; Cheng, H. Sensitivity analysis of pesticide dose on predator-prey system with a prey refuge. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2022, 12, 270–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Das, S.; Ray, S. Combined impact of predatory insects and bio-pesticide over pest population: Impulsive model-based study. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2022, 7, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Yuen, P.W.; Li, F.; Deng, L. Modelling of a seasonally perturbed competitive three species impulsive system. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 3223–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseb, S.A.; Ramachandran, R.; Cao, J.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V.E. Stability analysis and comparative study on different eco-epidemiological models: Stage structure for prey and predator concerning impulsive control. Optim. Contr. Appl. Methods 2022, 43, 842–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Yuen, P.; Li, F. A seasonally competitive M-prey and N-predator impulsive system modeled by general functional response for integrated pest management. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C. Dynamic complexity in a prey-predator model with state-dependent impulsive control strategy. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1614894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, S. Dynamics of a density-dependent predator-prey biological system with nonlinear impulsive control. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7318–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, T. Global dynamics of a predator-prey model with fear effect and impulsive state feedback control. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Z. The state-dependent impulsive control for a general predator-prey model. J. Biol. Dynam. 2022, 16, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zhu, C.Z.; Liu, Y.W. Dynamic analysis of a predator-prey model with state-dependent impulsive effects. Chin. Q. J. Math. 2023, 38, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Huang, M. Dynamics of a Gilpin-Ayala predator-prey system with state feedback weighted harvest strategy. AIMS Math. 2023, 8, 26968–26990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiang, Z. Dynamic analysis of a predator-prey impulse model with action threshold depending on the density of the predator and its rate of change. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 10659–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Fu, J. Dynamics analysis of a nonlinear controlled predator-prey model with complex Poincaré map. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2024, 29, 466–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Torres, D.F. Dynamics of a double-impulsive control model of integrated pest management using perturbation methods and Floquet theory. Axioms 2023, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Pita, É.; Otero-Espinar, M.V. Predator-prey models: A review of some recent advances. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, H. Stability and bifurcation analysis of the Bazykins predator-prey ecosystem with Holling type II functional response. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7877–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feketa, P.; Klinshov, V.; Lücken, L. A survey on the modeling of hybrid behaviors: How to account for impulsive jumps properly. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 103, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Yuen, P. Extinction and permanence of the predator-prey system with general functional response and impulsive control. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 88, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Pang, L.; Li, Q. Analysis of a hybrid impulsive tumor-immune model with immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Chaos Solitons Fract. 2021, 144, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L. Global dynamics of the periodic logistic system with periodic impulsive perturbations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2004, 289, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Quan, Q.; Dai, X. Dynamics of a new impulsive predator-prey model with predator population seasonally large-scale migration. Appl. Math. Lett. 2022, 132, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Jiao, H.; Jiao, J.; Quan, Q. Survival analysis of a predator-prey model with seasonal migration of prey populations between breeding and non-breeding regions. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Dai, X.; Jiao, J. Dynamics of a predator-prey model with impulsive diffusion and transient/nontransient impulsive harvesting. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakmeche, A. Birfurcation of non-trivial periodic solutions of impulsive differential equations arising chemotherapeutic treatment. Dynam. Contin. Discret. Impuls. 2000, 7, 265–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bainov, D.; Simeonov, P. Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications; Longman Scientific & Technical Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yi, M.; Tang, S. Dynamics of an antitumour model with pulsed radioimmunotherapy. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 4692772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; She, A.; Xie, Y. The dynamics analysis of Gompertz virus disease model under impulsive control. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zou, X. Qualitative analysis of critical transitions in complex disease propagation from a dynamical systems perspective. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2016, 26, 1650239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, P. Dynamic analysis of impulsive differential chaotic system and its application in image encryption. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Liu, Z.; Cheke, R.A. Periodicity and stability in a single-species model governed by impulsive differential equation. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bohner, M.; Wang, C.K. Impulsive differential equations: Periodic solutions and applications. Automatica 2015, 52, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamen, A.T.; Dumont, Y.; Tewa, J.J.; Bowong, S.; Couteron, P. A minimalistic model of tree-grass interactions using impulsive differential equations and non-linear feedback functions of grass biomass onto fire-induced tree mortality. Math. Comput. Simul. 2017, 133, 265–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Xie, X.; Chen, F.; Lin, Q. Dynamical analysis of a logistic model with impulsive Holling type-II harvesting. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Y. Impulsive control for persistence and periodicity of logistic systems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2020, 171, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoui, A.; Mebarki, K.; Shatanawi, W.; Abodayeh, K. Solution of some impulsive differential equations via coupled fixed point. Symmetry 2021, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Uzcátegui, J.; Ruiz, B.; Pérez, M. Attractive periodic solutions of a discrete Holling-Tanner predator-prey model with impulsive effect. Bull. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 8, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, K.; Gui, Z. Periodic solution of impulsive predator-prey model with stage structure for the prey undercrowding effect. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1903, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Diestra, J.L.H. Positive periodic solutions of a discrete ratio-dependent predator-prey model with impulsive effects. Rev. Union Math. Argent. 2022, 63, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Vijayakumar, V.; Nisar, K.S.; Singh, A.K.; Udhayakumar, R.; Botmart, T.; Albalawi, W.; Mahmoud, M. An analysis on approximate controllability of semilinear control systems with impulsive effects. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12293–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Complex dynamics of Beddington-DeAngelis-Type predator-prey model with nonlinear impulsive control. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8829235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisubtawee, S.; Khansai, N.; Charoenloedmongkhon, A. Investigation on dynamics of an impulsive predator-prey system with generalized Holling type IV functional response and anti-predator behavior. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 2021, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Xie, Y.X.; Deng, Q.C. The dynamic behaviors of a new impulsive predator prey model with impulsive control at different fixed moments. Kybernetika 2018, 54, 522–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, S. Analyzing a generalized pest-natural enemy model with nonlinear impulsive control. Open Math. 2018, 16, 1390–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, S.; Cheke, R.A. Complex dynamics and coexistence of period-doubling and period-halving bifurcations in an integrated pest management model with nonlinear impulsive control. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Fu, S. Dynamical behavior of a predator-prey system incorporating a prey refuge with impulse effect. Complexity 2022, 2022, 2422923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathumwan, D.; Trachoo, K.; Maiaugree, W.; Chaiya, I. Preventing extinction in Rastrelliger brachysoma using an impulsive mathematical model. AIMS Math. 2022, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Yi, M.; Zhang, Z. Global Dynamics of a Predator–Prey System with Variation Multiple Pulse Intervention Effects. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101597
Wang G, Yi M, Zhang Z. Global Dynamics of a Predator–Prey System with Variation Multiple Pulse Intervention Effects. Mathematics. 2025; 13(10):1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101597
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Gang, Ming Yi, and Zaiyun Zhang. 2025. "Global Dynamics of a Predator–Prey System with Variation Multiple Pulse Intervention Effects" Mathematics 13, no. 10: 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101597
APA StyleWang, G., Yi, M., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Global Dynamics of a Predator–Prey System with Variation Multiple Pulse Intervention Effects. Mathematics, 13(10), 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101597





