FMA-Net: Fusion of Multi-Scale Attention for Grading Cervical Precancerous Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose the Fusion of Multi-scale Attention Networks (FMA-Net) for cervical precancerous lesion detection, utilizing colposcopy images from the acetic acid test as the basis for classifying lesions of different degrees.
- Based on the positional characteristics of the lesions, a heterogeneous receptive field convolutional module (HRFC) is proposed to extract features at multiple scales, effectively utilizing spatial information.
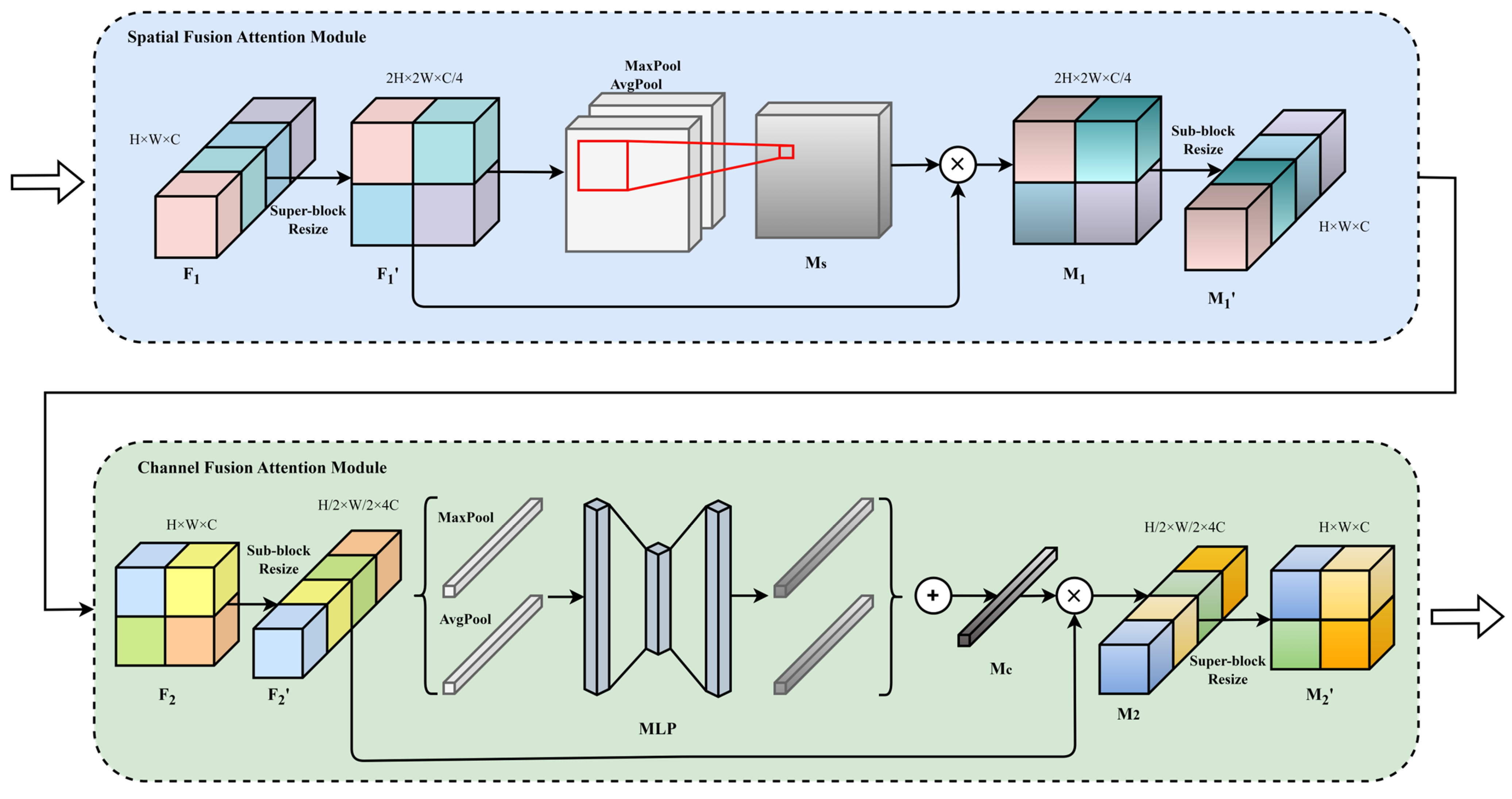
- We propose an Information Fusion Attention Module (IFAM) that combines spatial and channel information through block-based hyper/subscale transformations, enhancing the efficiency of feature communication.
- We design a dual-threshold loss function for our dataset with positive and negative probability thresholds (, ), addressing the issue of sample imbalance and improving the classification performance of the network.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
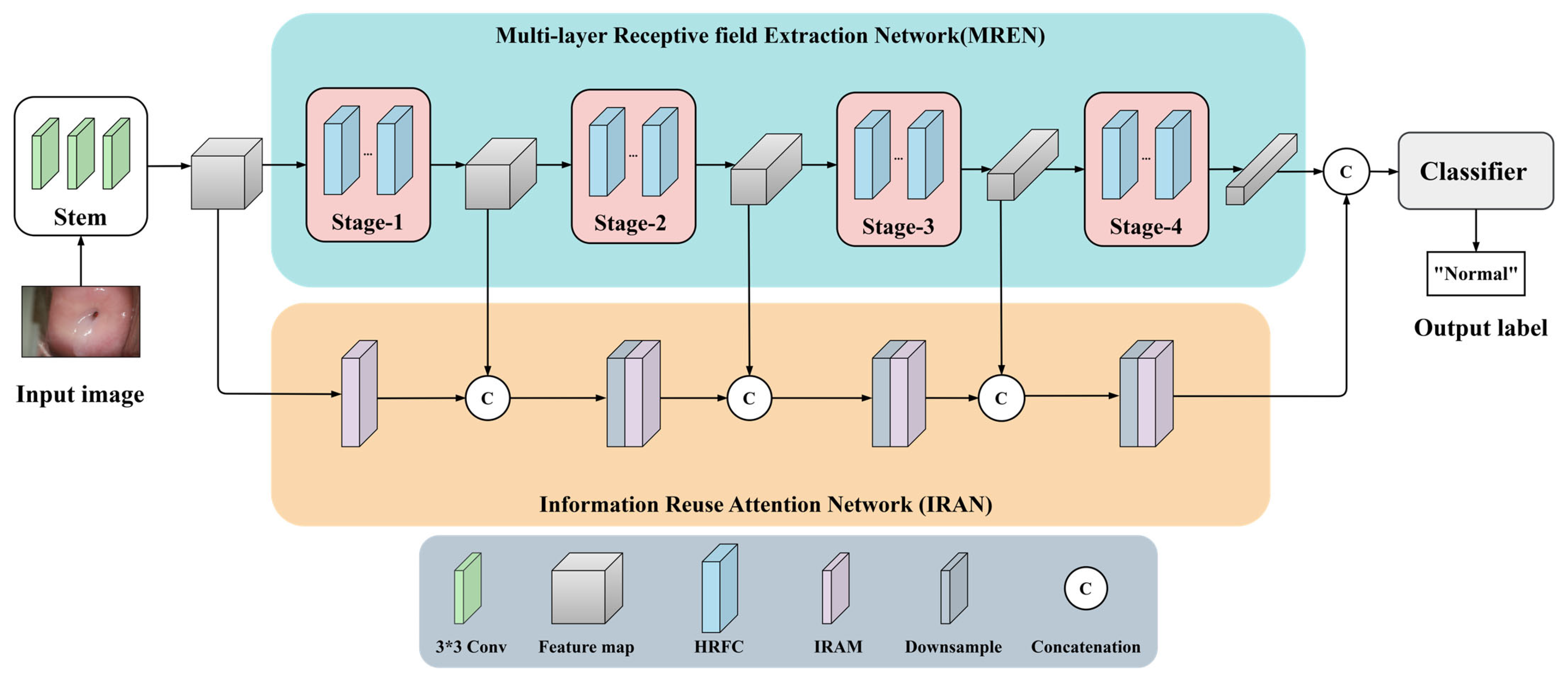
3.1. Network Structure
3.2. Multi-Layer Receptive Filed Extraction Network
3.3. Information Fusion Attention Network
3.4. Optimization of the Loss Function
3.5. Data Source and Processing
- (1)
- Resizing the image to 256 × 256;
- (2)
- Randomly cropping the image to 224 × 224;
- (3)
- Randomly rotating the image within a range of [−10, 10] degrees;
- (4)
- Randomly flipping the image with a probability of 50%;
- (5)
- To tensor and normalization.
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Conditions
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Results and Analyis
4.4. Ablation Experimental Results and Analysis
4.4.1. Module Validation and Analysis
4.4.2. Hyperparametric Experimental Analysis
4.5. Visualization of Experimental Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Cervical Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cervical-cancer#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Kornovski, Y.; Slavchev, S.; Kostov, S.; Ivanova, Y.; Yordanov, A. Precancerous lesions of the cervix—Aetiology, classification, diagnosis, prevention. Oncol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 17, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, K.A.A.; Saad, A.S.; Murad, A.W.A.; Altraigy, A. Visual inspection after acetic acid (via) as an alternative screening tool for cancer cervix. Apollo Med. 2016, 13, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotei, E.; Thirunavukarasu, R. Visual attention condenser model for multiple disease detection from heterogeneous medical image modalities. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 10, 30563–30585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahou, A.; Aseeri, A.O.; Mabrouk, A.; Ibranhim, R.A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Elaziz, M.A. Optimal Skin Cancer Detection Model Using Transfer Learning and Dynamic-Opposite Hunger Games Search. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayya, M.; Arasi, M.A.; Almalki, N.S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Al Sadig, M.; Sayed, A. Internet of Things-Assisted Smart Skin Cancer Detection Using Metaheuristics with Deep Learning Model. Cancers 2023, 15, 5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs. JAMA 2016, 316, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, H.R.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.M.; Yao, J.H.; Seff, A.; Cherry, K.; Kim, L.; Summers, R.M. Improving Computer-Aided Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Random View Aggregation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Chen, H.; Yu, L.Q.; Zhao, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, D.F.; Mok, V.C.T.; Shi, L.; Heng, P.A. Automatic Detection of Cerebral Microbleeds From MR Images via 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-rays with Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yu, S.; Dong, H.; Greg, S.; Pier, L.; Ye, X.; Liu, F.; Simon, A.; Jennifer, K.; Guo, Y.; et al. DAGAN: Deep De-Aliasing Generative Adversarial Networks for Fast Compressed Sensing MRI Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Tang, H.; Gong, G.Z.; Yin, Y.; Huang, C.; Fan, W. CorGAN: Context aware Recurrent Generative Adversarial Network for Medical Image Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (IEEE BIBM), Online, 16–19 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sholik, M.; Fatichah, C.; Amaliah, B. Classification of Cervical Cell Images into Healthy or Cancer Using Convolution Neural Network and Linear Discriminant Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, and Communications Technology (IAICT), Bali, Indonesia, 13–15 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.M.; Ding, L.Y.; Ma, M.Y.; Huang, A.H.; Gan, Y.; Sheng, D.L.; Jiang, Z.N.; Zhang, X. Deep Learning-Based Recognition of Cervical Squamous Interepithelial Lesions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Z.; Huang, X. High Precision Cervical Precancerous Lesion Classification Method Based on ConvNeXt. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Luo, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; Du, Y.; Sun, P.; Dong, B.; Xue, H. Cervical precancerous lesions classification using pre-trained densely connected convolutional networks with colposcopy images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 55, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; Sun, P.; Dong, B.; Ruan, G. MDFI: Multi-CNN Decision Feature Integration for Diagnosis of Cervical Precancerous Lesions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29616–29626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E.H. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, S. An Improved Image Classification Method for Cervical Precancerous Lesions Based on ShuffleNet. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 9675628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.Q.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Loffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Loffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Loffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.Z.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S.N. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B.N. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Online, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Liu, Z.H.; Xue, P.; Chen, J.W.; Ma, K.; Qian, T.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Qiao, Y.L. GRAND: A large-scale dataset and benchmark for cervical intraepithelial Neoplasia grading with fine-grained lesion description. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Module | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet34 | 0.887 | 0.893 | 0.931 | 0.928 |
| GoogleNet | 0.898 | 0.813 | 0.931 | 0.929 |
| Inception-v3 | 0.908 | 0.841 | 0.932 | 0.935 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.901 | 0.895 | 0.920 | 0.931 |
| ViT-B/16 | 0.915 | 0.904 | 0.944 | 0.943 |
| ConvNeXt-T | 0.912 | 0.881 | 0.941 | 0.939 |
| Zhang et al. [17] | 0.901 | 0.895 | 0.920 | 0.931 |
| Luo et al. [18] | 0.916 | 0.897 | 0.947 | 0.941 |
| Li et al. [35] | 0.914 | 0.896 | 0.946 | 0.939 |
| Fang et al. [22] | 0.910 | 0.891 | 0.937 | 0.942 |
| Ours | 0.922 | 0.887 | 0.954 | 0.947 |
| Module | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet34 | 0.914 | 0.946 | 0.936 | 0.906 |
| GoogleNet | 0.914 | 0.813 | 0.931 | 0.929 |
| Inception-v3 | 0.923 | 0.935 | 0.918 | 0.914 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.928 | 0.937 | 0.922 | 0.919 |
| ViT-B/16 | 0.943 | 0.950 | 0.937 | 0.936 |
| ConvNeXt-T | 0.927 | 0.939 | 0.923 | 0.918 |
| Zhang et al. [17] | 0.934 | 0.948 | 0.935 | 0.927 |
| Luo et al. [18] | 0.944 | 0.849 | 0.936 | 0.937 |
| Li et al. [35] | 0.940 | 0.949 | 0.936 | 0.932 |
| Fang et al. [22] | 0.939 | 0.961 | 0.953 | 0.932 |
| Ours | 0.947 | 0.954 | 0.942 | 0.940 |
| Method | AUC (Triple Classification) | AUC (Binary Classification) |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet34 | 0.9064 | 0.9227 |
| GoogleNet | 0.9152 | 0.9240 |
| Inception-v3 | 0.9376 | 0.9532 |
| DenseNet121 | 0.9206 | 0.9443 |
| ViT-B/16 | 0.9394 | 0.9598 |
| ConvNeXt-T | 0.9375 | 0.9521 |
| Zhang et al. [17] | 0.9253 | 0.9542 |
| Luo et al. [18] | 0.9672 | 0.9726 |
| Li et al. [35] | 0.9558 | 0.9674 |
| Fang et al. [22] | 0.9394 | 0.9542 |
| Ours | 0.9862 | 0.9878 |
| Module | Triple Classification | Binary Classification | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC | |
| Base Network | 0.910 | 0.893 | 0.934 | 0.932 | 0.953 | 0.932 | 0.941 | 0.938 | 0.921 | 0.954 |
| HRFC | 0.916 | 0.897 | 0.947 | 0.941 | 0.973 | 0.937 | 0.954 | 0.944 | 0.930 | 0.967 |
| IRAM | 0.915 | 0.904 | 0.944 | 0.943 | 0.969 | 0.934 | 0.949 | 0.936 | 0.927 | 0.961 |
| HRFC + IRAM | 0.921 | 0.894 | 0.950 | 0.943 | 0.981 | 0.944 | 0.943 | 0.927 | 0.936 | 0.979 |
| Total | 0.922 | 0.887 | 0.954 | 0.947 | 0.986 | 0.947 | 0.954 | 0.942 | 0.940 | 0.988 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, B.; Nie, C. FMA-Net: Fusion of Multi-Scale Attention for Grading Cervical Precancerous Lesions. Mathematics 2024, 12, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12070958
Duan Z, Xu C, Li Z, Feng B, Nie C. FMA-Net: Fusion of Multi-Scale Attention for Grading Cervical Precancerous Lesions. Mathematics. 2024; 12(7):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12070958
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Zhuoran, Chao Xu, Zhengping Li, Bo Feng, and Chao Nie. 2024. "FMA-Net: Fusion of Multi-Scale Attention for Grading Cervical Precancerous Lesions" Mathematics 12, no. 7: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12070958
APA StyleDuan, Z., Xu, C., Li, Z., Feng, B., & Nie, C. (2024). FMA-Net: Fusion of Multi-Scale Attention for Grading Cervical Precancerous Lesions. Mathematics, 12(7), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12070958





