Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A chaotic map based on the Courbage–Nekorkin neuron model is applied to the path-planning task for rover-type robots.
- A novel path-planning algorithm with a special parameter for coverage control is implemented.
- The evaluation of the proposed P-RBMCA method (random bit notion command algorithm) shows that it is more efficient in terms of coverage and revisiting rate than existing chaos-based path-planning algorithms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chaotic Map Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Neuron Model
2.2. Pseudorandom Bit Generator Design
- The initial value of the discrete map (4) is chosen, along with the parameters a, b, c, d, and e. These parameters constitute the key of the algorithm.
- At each iteration,is calculated and compared with a threshold value equal to 0.5. Depending on the result of this comparison, “0” or “1” is output and saved.
- The resulting bit sequences are composed into a single bitstream.
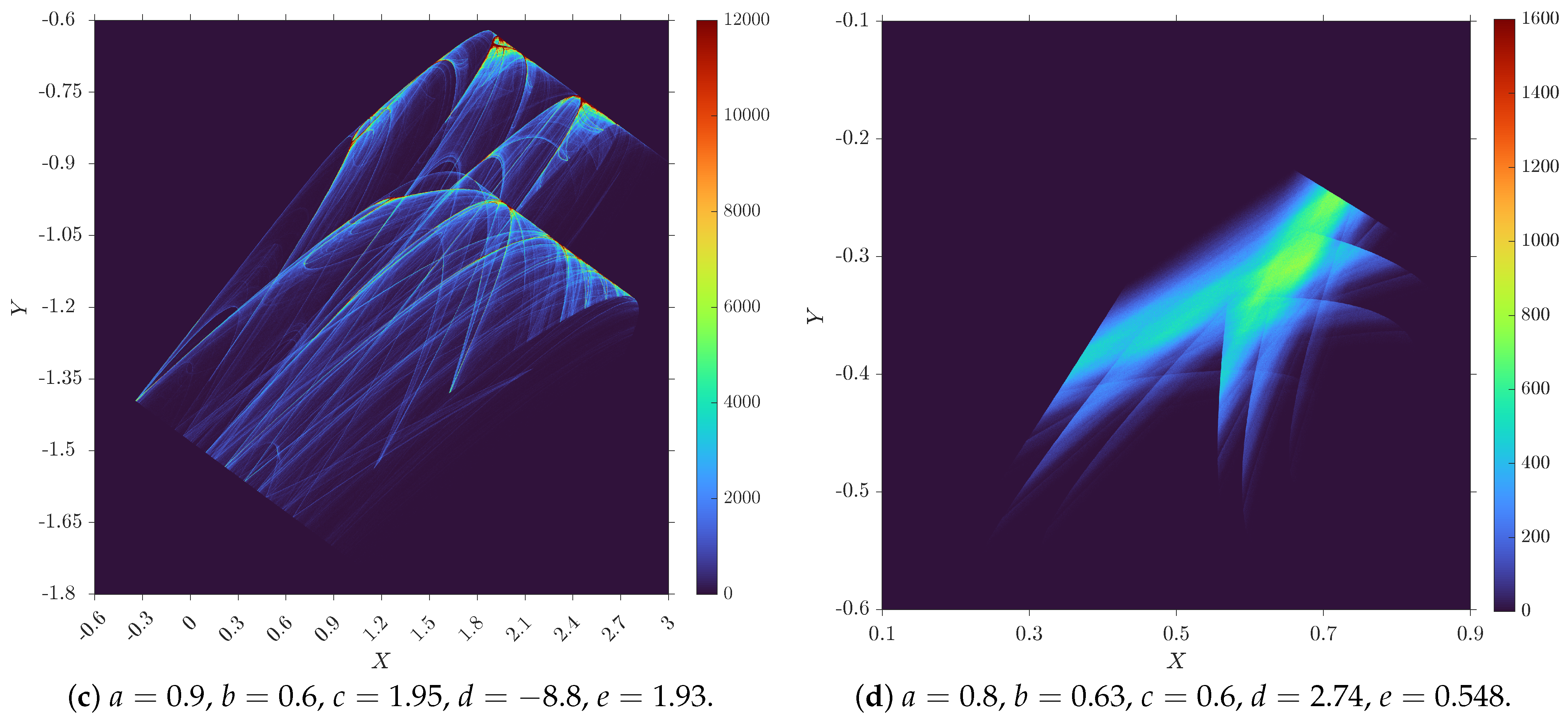
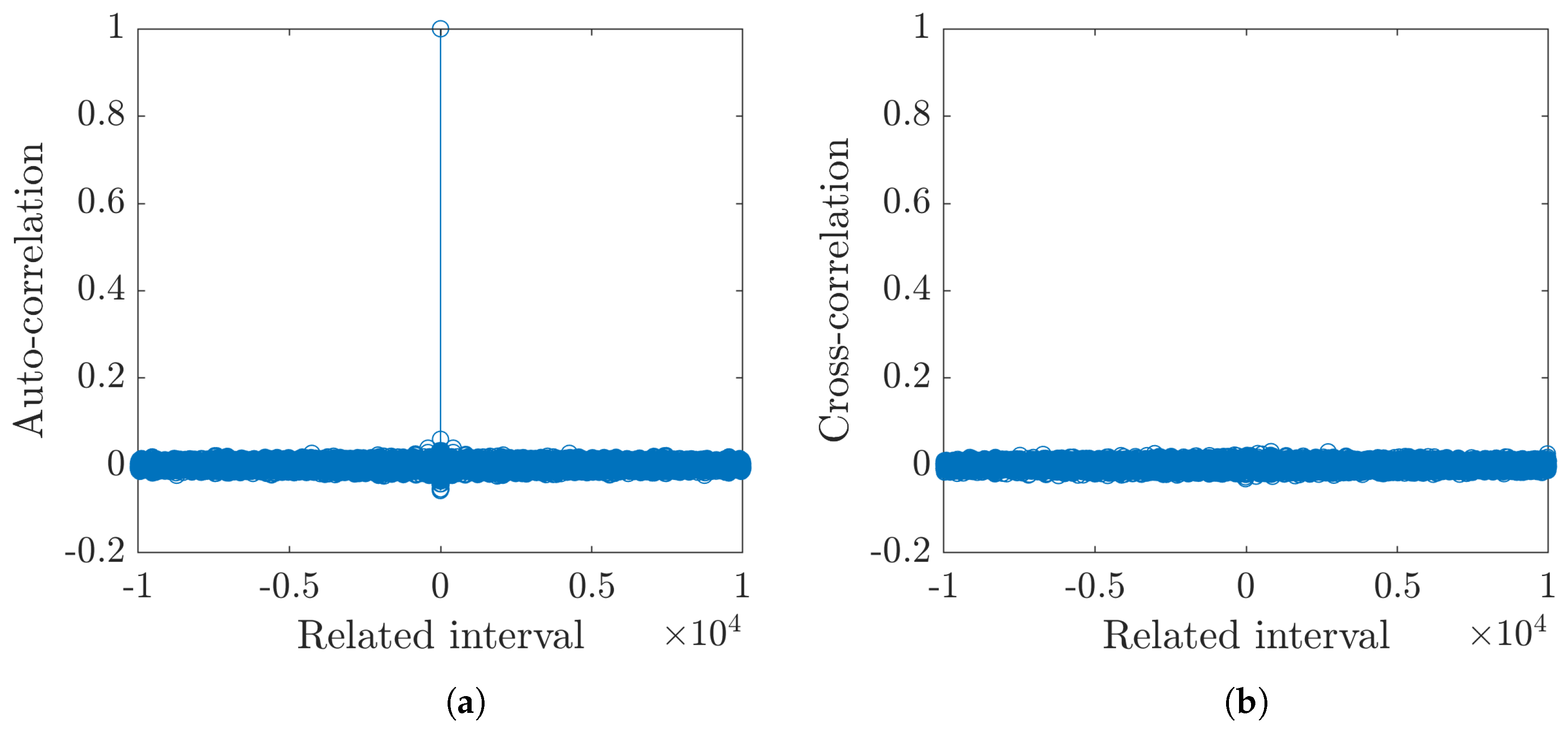
Evaluating the Properties of the Designed PRBG
3. Path-Planning Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Parametric RBMCA algorithm |
|
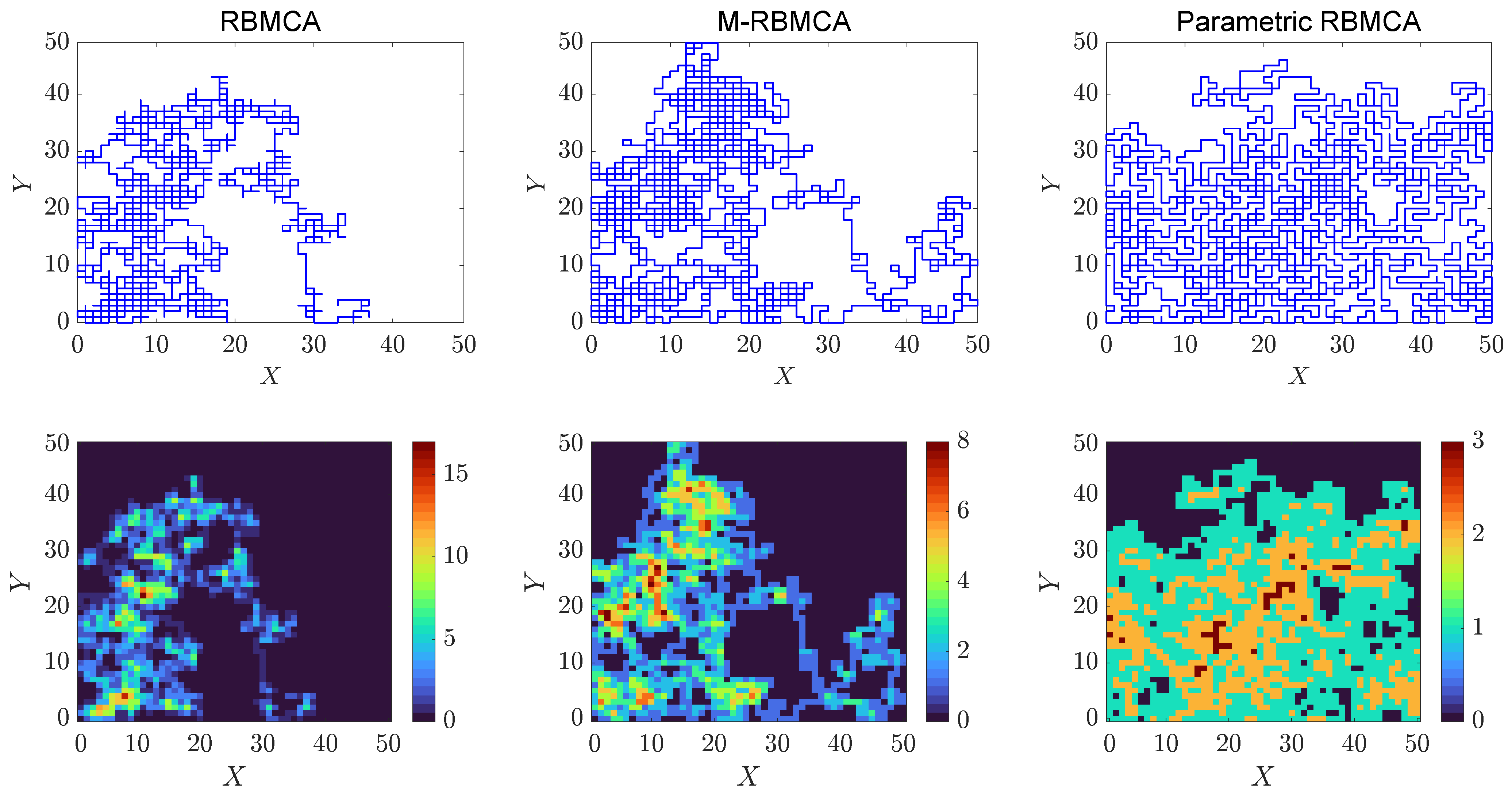
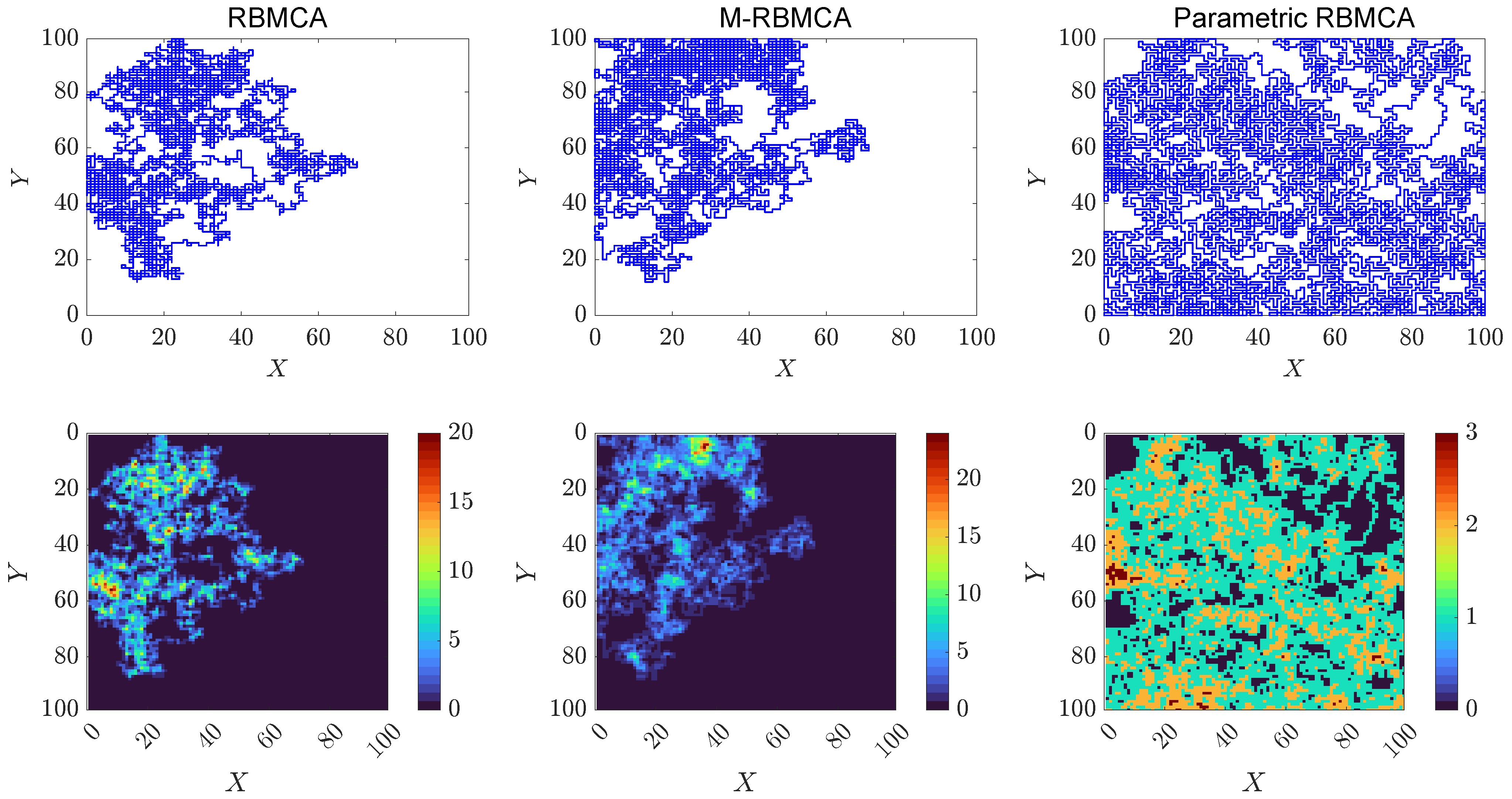
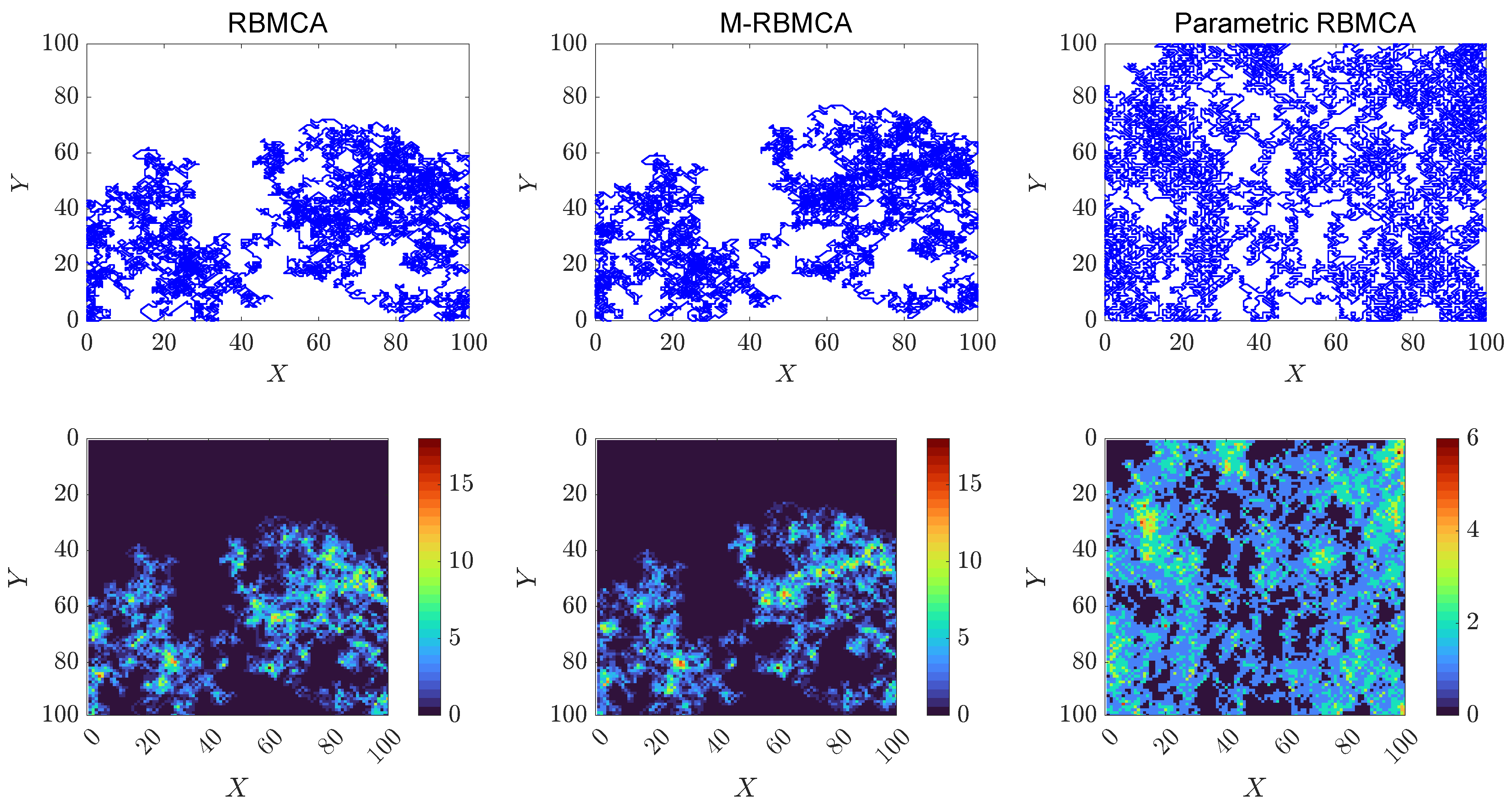
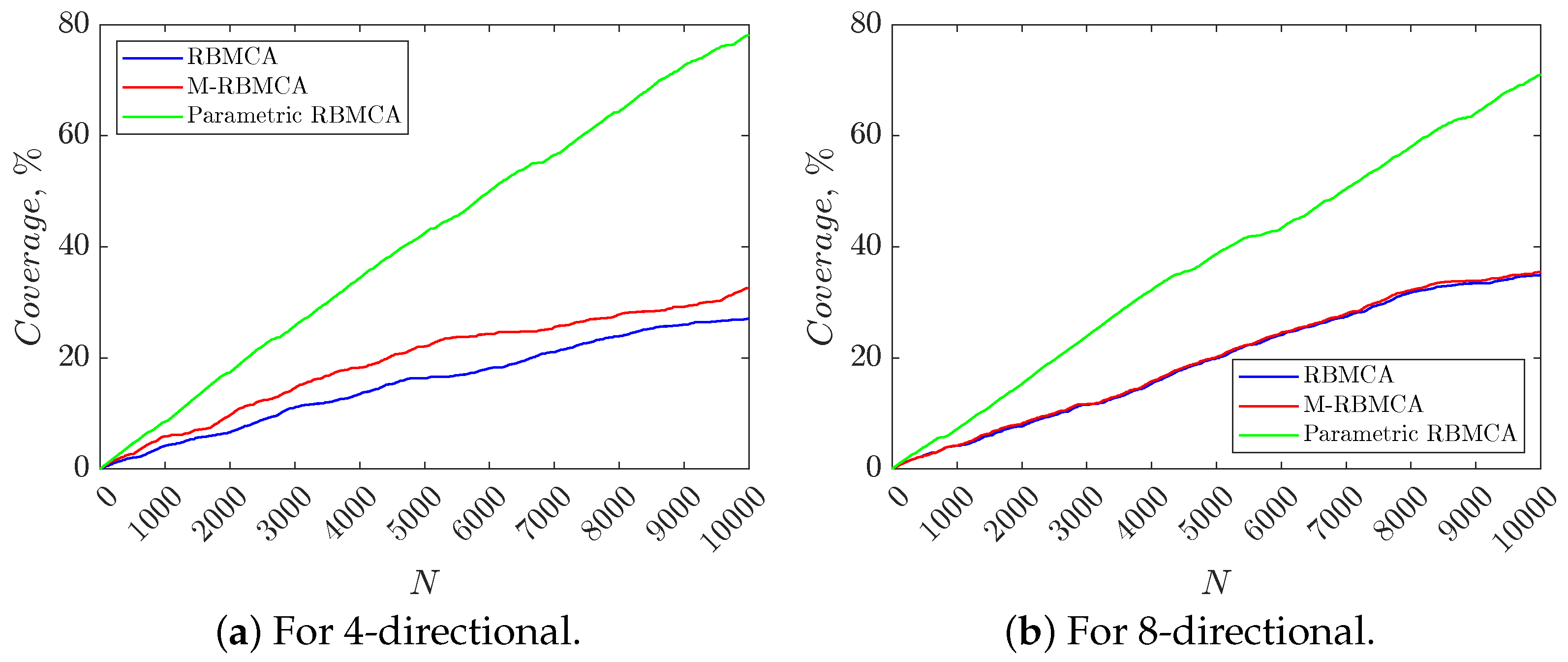
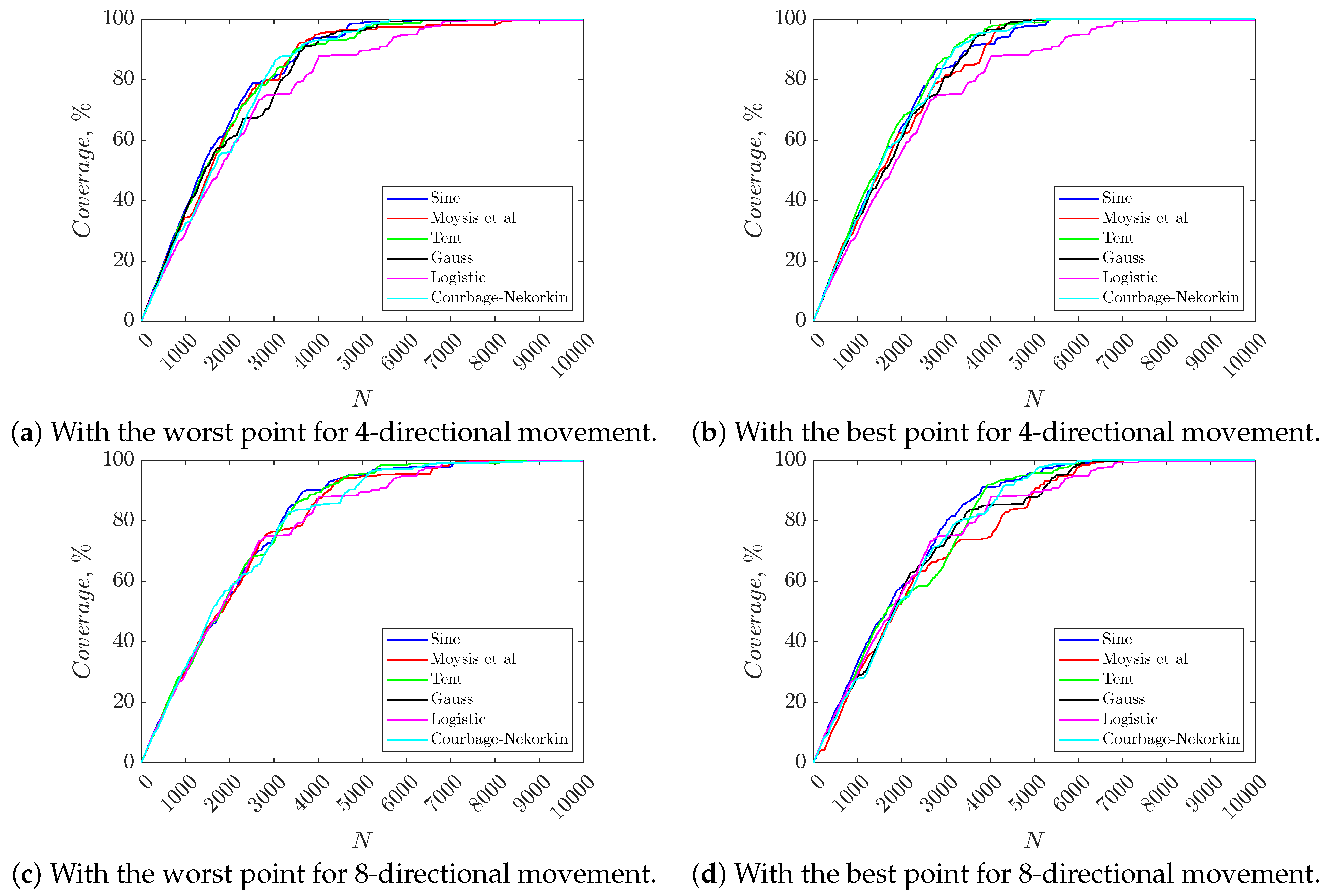
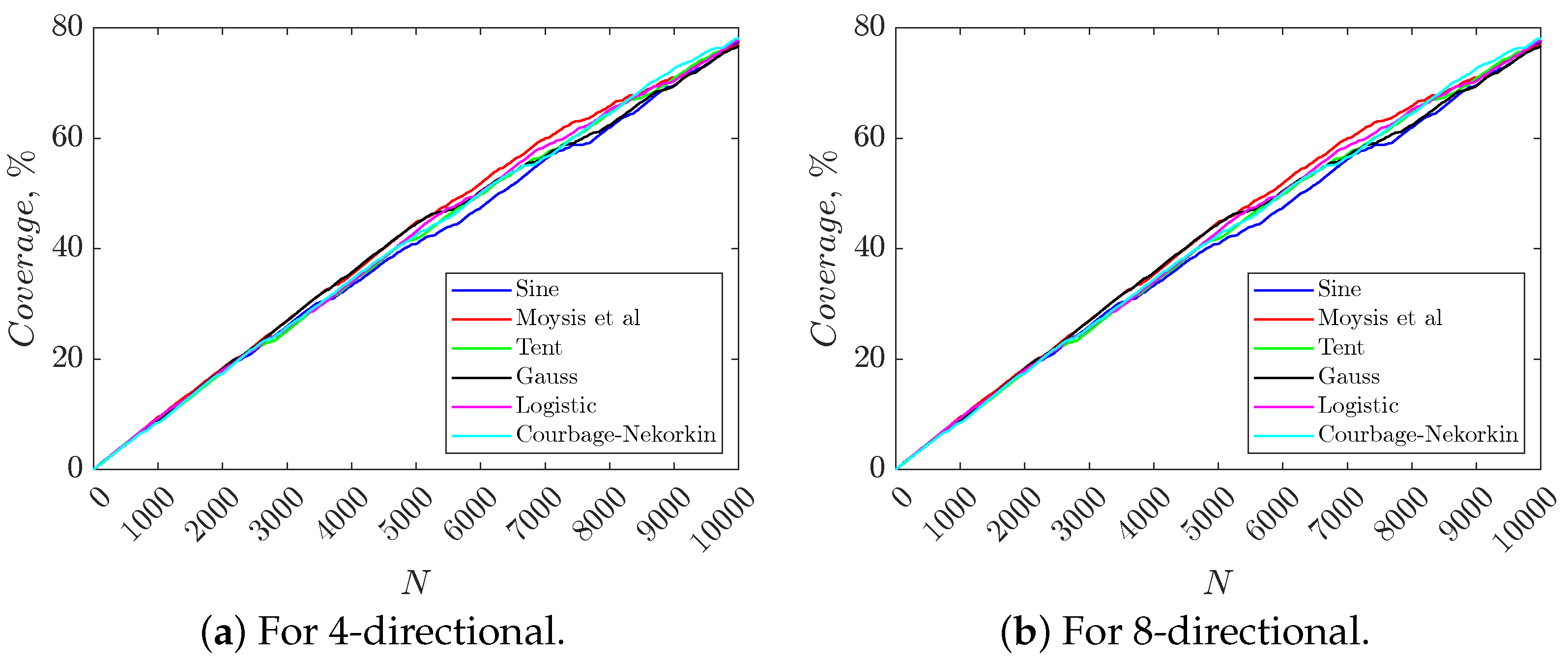
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Block Diagram of Algorithms

References
- Al-Raeei, M. Applying fractional quantum mechanics to systems with electrical screening effects. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 150, 111209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seadawy, A.R.; Ali, S.; Rizvi, S.T. On modulation instability analysis and rogue waves in the presence of external potential: The (n + 1)-dimensional nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 161, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, V.; Butusov, D.; Babkin, I.; Pesterev, D.; Arlyapov, V. Some Properties of a Discrete Lorenz System Obtained by Variable Midpoint Method and Its Application to Chaotic Signal Modulation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2024, 34, 2450009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirjulina, D.; Babajans, R.; Capligins, F.; Kolosovs, D.; Litvinenko, A. Experimental Study on Colpitts Chaotic Oscillator-Based Communication System Application for the Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P. Poincaré, celestial mechanics, dynamical-systems theory and “chaos”. Phys. Rep. 1990, 193, 137–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, D.T.; Mimić, G.; Arsenić, I. Climate predictions: The chaos and complexity in climate models. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 878249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, G.S.; Tribbia, J.J. Synchronized chaos in geophysical fluid dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.J.; Györgyi, L. Chaos in Chemistry and Biochemistry; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, L.F.; Degn, H. Chaos in biological systems. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1985, 18, 165–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovskii, S.V.; Malchow, H. Wave of chaos: New mechanism of pattern formation in spatio-temporal population dynamics. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2001, 59, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karur, K.; Sharma, N.; Dharmatti, C.; Siegel, J.E. A survey of path planning algorithms for mobile robots. Vehicles 2021, 3, 448–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.; Mekki, H.; Bouallegue, K. A multi-scroll chaotic system for a higher coverage path planning of a mobile robot using flatness controller. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 118, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchoň, F.; Babinec, A.; Kajan, M.; Beňo, P.; Florek, M.; Fico, T.; Jurišica, L. Path planning with modified a star algorithm for a mobile robot. Procedia Eng. 2014, 96, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, Q. Application of Dijkstra algorithm in robot path-planning. In Proceedings of the 2011 Second International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, Hohhot, China, 15–17 July 2011; pp. 1067–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.; Iqbal, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J. Applications of chaotic dynamics in robotics. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.; Shim, D.H.; Kim, S.Y. Coverage path planning for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles in maritime search and rescue operations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 161, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.S.; Cheng, M.Y.; Hsieh, Y.M.; Yang, I.T.; Hsu, H.T. Optimal path planning in real time for dynamic building fire rescue operations using wireless sensors and visual guidance. Autom. Constr. 2019, 99, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paucar, C.; Morales, L.; Pinto, K.; Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez, R.; Gutierrez, M.; Palacios, L. Use of drones for surveillance and reconnaissance of military areas. In Developments and Advances in Defense and Security, Proceedings of the Multidisciplinary International Conference of Research Applied to Defense and Security (MICRADS 2018), Salinas, Ecuador, 18–20 April 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Yang, E.; Corney, J.; Chen, Y. Semantic path planning for indoor navigation and household tasks. In Proceedings of the Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems: 20th Annual Conference, TAROS 2019, London, UK, 3–5 July 2019; Proceedings, Part II 20. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparetto, A.; Boscariol, P.; Lanzutti, A.; Vidoni, R. Path planning and trajectory planning algorithms: A general overview. In Motion and Operation Planning of Robotic Systems: Background and Practical Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, H. Occlusion-aware UAV path planning for reconnaissance and surveillance. Drones 2021, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, S.Y.; Peralta, F.; Córdoba, A.T.; del Nozal, Á.R.; Marín, S.T.; Reina, D.G. An evolutionary multi-objective path planning of a fleet of ASVs for patrolling water resources. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 112, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysis, L.; Petavratzis, E.; Volos, C.; Nistazakis, H.; Stouboulos, I. A chaotic path planning generator based on logistic map and modulo tactics. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 124, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Yu, W.; Xiao, K.; Liu, W. Cubic spline interpolation-based robot path planning using a chaotic adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1849240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Peng, Y.; He, C.; Du, Y. Efficient path planning for UAV formation via comprehensively improved particle swarm optimization. ISA Trans. 2020, 97, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiou, P.; Moysis, L.; Kafetzis, I.; Bardis, N.G.; Lawnik, M.; Volos, C. Chaotic Agent Navigation: Achieving Uniform Exploration Through Area Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), Athens, Greece, 9–11 December 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Moysis, L.; Volos, C.; Pham, V.T.; El-Latif, A.A.A.; Nistazakis, H.; Stouboulos, I. Analysis of a Hyperchaotic System with a Hyperbolic Sinusoidal Nonlinearity and Its Application to Area Exploration Using Multiple Autonomous Robots. In New Perspectives on Nonlinear Dynamics and Complexity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gohari, P.S.; Mohammadi, H.; Taghvaei, S. Using chaotic maps for 3D boundary surveillance by quadrotor robot. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2019, 76, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, S.; Inoue, H. Pseudo-random number generators and chaos. IEICE Trans. 1982, 65, 534–541. [Google Scholar]
- Andrecut, M. Logistic map as a random number generator. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 1998, 12, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.A.; Pino, R. A random number generator based on unpredictable chaotic functions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1999, 120, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, V.; Pareek, N.; Sud, K. A new substitution–diffusion based image cipher using chaotic standard and logistic maps. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 3056–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, S. Cryptographic pseudo-random sequence from the spatial chaotic map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 41, 2216–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liao, X.; Xiao, D.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Duan, S. True random number generation from mobile telephone photo based on chaotic cryptography. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawida, M.; Samsudin, A.; Teh, J.S. Enhanced digital chaotic maps based on bit reversal with applications in random bit generators. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, T.; Jiang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Zhao, X. Safety helmet wearing detection based on image processing and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Doha, Qatar, 4–6 February 2017; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, A.; Wang, X. A novel one-dimensional sine powered chaotic map and its application in a new image encryption scheme. Inf. Sci. 2020, 520, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysis, L.; Tutueva, A.; Christos, K.; Butusov, D. A chaos based pseudo-random bit generator using multiple digits comparison. Chaos Theory Appl. 2020, 2, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lambić, D.; Nikolić, M. Pseudo-random number generator based on discrete-space chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 90, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bosque, M.; Pérez-Resa, A.; Sánchez-Azqueta, C.; Aldea, C.; Celma, S. Chaos-based bitwise dynamical pseudorandom number generator on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. A novel hyperchaotic system with fast and slow attractors. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petavratzis, E.; Moysis, L.; Volos, C.; Stouboulos, I.; Nistazakis, H.; Valavanis, K. A chaotic path planning generator enhanced by a memory technique. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 143, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysis, L.; Rajagopal, K.; Tutueva, A.V.; Volos, C.; Teka, B.; Butusov, D.N. Chaotic path planning for 3D area coverage using a pseudo-random bit generator from a 1D chaotic map. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbage, M.; Nekorkin, V.I.; Vdovin, L.V. Chaotic oscillations in a map-based model of neural activity. Chaos 2007, 17, 043109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrichev, A.; Kasatkin, D.; Klinshov, V.V.; Kirillov, S.Y.; Maslennikov, O.V.; Shapin, D.; Nekorkin, V.I. Nonlinear dynamical models of neurons. Izv. VUZ Appl. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 26, 5–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; US Department of Commerce, Technology Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001; Volume 22.
- Crampin, M.; Heal, B. On the chaotic behaviour of the tent map. Teach. Math. Its Appl. 1994, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belazi, A.; Abd El-Latif, A.A. A simple yet efficient S-box method based on chaotic sine map. Optik 2017, 130, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R.C. Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]









| No | Test | p-Value | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Frequency | 0.249704 | Success |
| 2 | Frequency block | 0.296013 | Success |
| 3 | Sequence of identical bits | 0.338489 | Success |
| 4 | The longest sequence of ones in a block | 0.577056 | Success |
| 5 | Ranks of binary matrices | 0.999951 | Success |
| 6 | Spectral | 0.353091 | Success |
| 7 | Nonoverlapping pattern matching | 0.45979 | Success |
| 8 | Overlapping pattern matching | 0.015642 | Success |
| 9 | Maurer’s general | 0.867123 | Success |
| 10 | Linear complexity | 0.124902 | Success |
| 11 | Periodicity | 0.429502 | Success |
| 12 | Approximate entropy | 0.936101 | Success |
| 13 | Cumulative sums | 0.360115 | Success |
| 14 | Randomness | 0.376372 | Success |
| 15 | Other random deviations | 0.541292 | Success |
| Bit Set | Direction |
|---|---|
| 000 | Right |
| 001 | Left up |
| 010 | Down |
| 011 | Left down |
| 100 | Up |
| 101 | Right up |
| 110 | Left |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RBMCA | M-RBMCA | P-RBMCA | |
| 1000 | 14.68 | 20.64 | 33.96 |
| 2500 | 31.2 | 44.04 | 72.44 |
| 5050 | 53 | 72.6 | 100 |
| 7500 | 68.52 | 84.4 | 100 |
| 10,000 | 72.88 | 88.36 | 100 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RBMCA | M-RBMCA | P-RBMCA | |
| 1000 | 17.68 | 16.48 | 27.8 |
| 2500 | 33.68 | 31.64 | 66.32 |
| 5000 | 59.4 | 57.64 | 96 |
| 6330 | 71.8 | 71.96 | 100 |
| 10,000 | 80.28 | 77.52 | 100 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RBMCA | M-RBMCA | P-RBMCA | |
| 1000 | 4.16 | 5.87 | 8.49 |
| 2500 | 8.83 | 12.32 | 22.09 |
| 5000 | 16.33 | 22.05 | 42.48 |
| 7500 | 22.66 | 26.75 | 60.58 |
| 10,000 | 27.04 | 32.55 | 78.16 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RBMCA | M-RBMCA | P-RBMCA | |
| 1000 | 4.16 | 4.18 | 7.16 |
| 2500 | 9.67 | 10 | 19.6 |
| 5000 | 19.93 | 20.13 | 38.67 |
| 7500 | 29.54 | 30.07 | 54.09 |
| 10,000 | 35.01 | 35.46 | 71.03 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sine | Moysisetal. [43] | Tent | Gauss Iterated | Logistic | Courbage–Nekorkin | |
| 1000 | 34.44 | 33.12 | 37.28 | 34.72 | 29.44 | 33.96 |
| 2500 | 77.68 | 71.44 | 76.04 | 71.68 | 68.44 | 72.44 |
| 5000 | 97.8 | 99.76 | 98.96 | 99.68 | 89.56 | 99.96 |
| 7500 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 10,000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sine | Moysisetal. [43] | Tent | Gauss Iterated | Logistic | Courbage–Nekorkin | |
| 1000 | 33.08 | 29.24 | 31.12 | 28.28 | 29.44 | 27.8 |
| 2500 | 66.2 | 63.52 | 58.4 | 65.44 | 68.44 | 66.32 |
| 5000 | 95.84 | 90.04 | 95.88 | 87.8 | 89.56 | 96 |
| 7500 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 10,000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sine | Moysisetal. [43] | Tent | Gauss Iterated | Logistic | Courbage–Nekorkin | |
| 1000 | 8.37 | 8.75 | 8.4 | 8.38 | 8.64 | 7.96 |
| 2500 | 21.54 | 22.47 | 22.2 | 22.26 | 21.8 | 22.09 |
| 5000 | 40.88 | 44.81 | 41.77 | 44.5 | 43.12 | 42.48 |
| 7500 | 58.81 | 63.1 | 60.48 | 59.53 | 61.62 | 60.58 |
| 10,000 | 77.6 | 77.01 | 78.04 | 76.74 | 77.77 | 78.16 |
| Number of Iterations | Coverage, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sine | Moysisetal. [43] | Tent | Gauss Iterated | Logistic | Courbage–Nekorkin | |
| 1000 | 7.43 | 7.8 | 8.01 | 8.12 | 8.15 | 7.16 |
| 2500 | 19.26 | 20.28 | 19.59 | 20.28 | 17.76 | 19.6 |
| 5000 | 35.62 | 39.26 | 38.5 | 37.67 | 36.89 | 38.67 |
| 7500 | 54.33 | 57.45 | 55.48 | 54.4 | 52.17 | 54.09 |
| 10,000 | 71.18 | 69.14 | 70.17 | 70.53 | 69.58 | 71.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kvitko, D.; Rybin, V.; Bayazitov, O.; Karimov, A.; Karimov, T.; Butusov, D. Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model. Mathematics 2024, 12, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12060892
Kvitko D, Rybin V, Bayazitov O, Karimov A, Karimov T, Butusov D. Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model. Mathematics. 2024; 12(6):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12060892
Chicago/Turabian StyleKvitko, Dmitriy, Vyacheslav Rybin, Oleg Bayazitov, Artur Karimov, Timur Karimov, and Denis Butusov. 2024. "Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model" Mathematics 12, no. 6: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12060892
APA StyleKvitko, D., Rybin, V., Bayazitov, O., Karimov, A., Karimov, T., & Butusov, D. (2024). Chaotic Path-Planning Algorithm Based on Courbage–Nekorkin Artificial Neuron Model. Mathematics, 12(6), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12060892







