Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks
1. Introduction
2. Brief Overview of the Contributions to the Special Issue
Conflicts of Interest
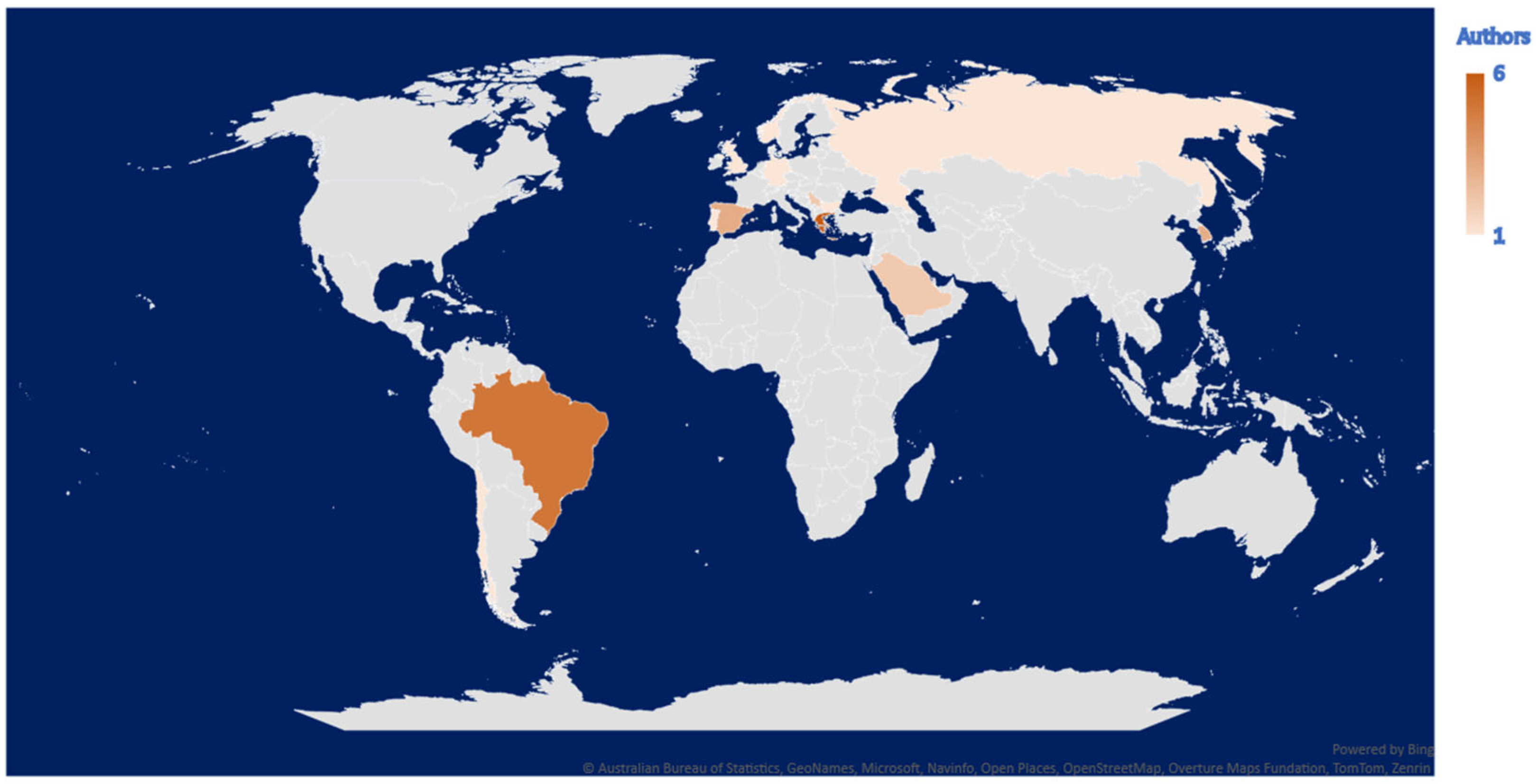
| Country | Count |
|---|---|
| Greece | 6 |
| Brazil | 5 |
| Spain | 3 |
| The Republic of Korea | 3 |
| The Czech Republic | 3 |
| Serbia | 2 |
| Pakistan | 2 |
| Saudi Arabia | 2 |
| Portugal | 1 |
| Russia | 1 |
| Norway | 1 |
| Bulgaria | 1 |
| Israel | 1 |
| Chile | 1 |
| Germany | 1 |
| The United Kingdom | 1 |
| Total | 34 |
List of Contributions
- 1.
- Díaz, G.M.; Medina, R.G.; Jiménez, J.A.A. Integrating fuzzy C-means clustering and explainable AI for robust galaxy classification. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12182797.
- 2.
- Stanimirović, P.S.; Ćirić, M.; Mourtas, S.D.; Brzaković, P.; Karabašević, D. Simulations and bisimulations between weighted finite automata based on time-varying models over real numbers. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12132110.
- 3.
- Hašková, S.; Šuleř, P.; Kuchár, R. A fuzzy multi-criteria evaluation system for share price prediction: A Tesla case study. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11133033.
- 4.
- Bobel, V.A.d.O.; Sigahi, T.F.A.C.; Rampasso, I.S.; Marcondes de Moraes, G.H.S.; Ávila, L.V.; Filho, W.L.; Anholon, R. Analysis of the level of adoption of business continuity practices by Brazilian industries: An exploratory study using fuzzy TOPSIS. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4041. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10214041.
- 5.
- Lima-Junior, F.R.; de Oliveira, M.E.B.; Resende, C.H.L. An overview of applications of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets in supply chain management: The state of the art and future directions. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132814.
- 6.
- Hinov, N.; Gilev, B. Neural network-based design of a buck zero-voltage-switching quasi-resonant DC–DC converter. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12213305.
- 7.
- Ivanova, M.; Durcheva, M. M-polar fuzzy graphs and deep learning for the design of analog amplifiers. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11041001.
- 8.
- Toki, E.I.; Tatsis, G.; Tatsis, V.A.; Plachouras, K.; Pange, J.; Tsoulos, I.G. Applying neural networks on biometric datasets for screening speech and language deficiencies in child communication. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071643.
- 9.
- Abdullah, S.; Almagrabi, A.O.; Ali, N. A new method for commercial-scale water purification selection using linguistic neural networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132972.
- 10.
- Hijji, M.; Yar, H.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Alwakeel, M.M.; Harrabi, R.; Aradah, F.; Cheikh, F.A.; Muhammad, K.; Sajjad, M. FADS: An intelligent fatigue and age detection system. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051174.
Short Biography of Author
 | Francisco Rodrigues Lima Junior is a professor in the Department of Management and Economics and the Graduate Program in Administration at the Federal University of Technology—Paraná (UTFPR). He is also a research productivity fellow with the National Council for Technological Development (CNPq), Brazil. He has authored numerous works on fuzzy logic and neural networks, published in high-impact journals, with over 2900 citations on Google Scholar and 1200 on the Web of Science. He serves as a guest editor for the journals Mathematics and Symmetry (MDPI) and a reviewer for journals from prominent publishing groups such as Elsevier, Springer, IEEE, and Taylor & Francis. He coordinates the research group “Decision Making in Operations Management” at UTFPR and is a member of the “Production Performance Management” research group at the University of São Paulo (USP). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima-Junior, F.R. Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12243949
Lima-Junior FR. Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks. Mathematics. 2024; 12(24):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12243949
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima-Junior, Francisco Rodrigues. 2024. "Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks" Mathematics 12, no. 24: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12243949
APA StyleLima-Junior, F. R. (2024). Advances in Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks. Mathematics, 12(24), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12243949





