Modeling the Transmission Dynamics and Optimal Control Strategy for Huanglongbing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Formulation
3. Some Useful Results
3.1. Positivity and Boundedness of Solutions
3.2. The Basic Reproductive Number
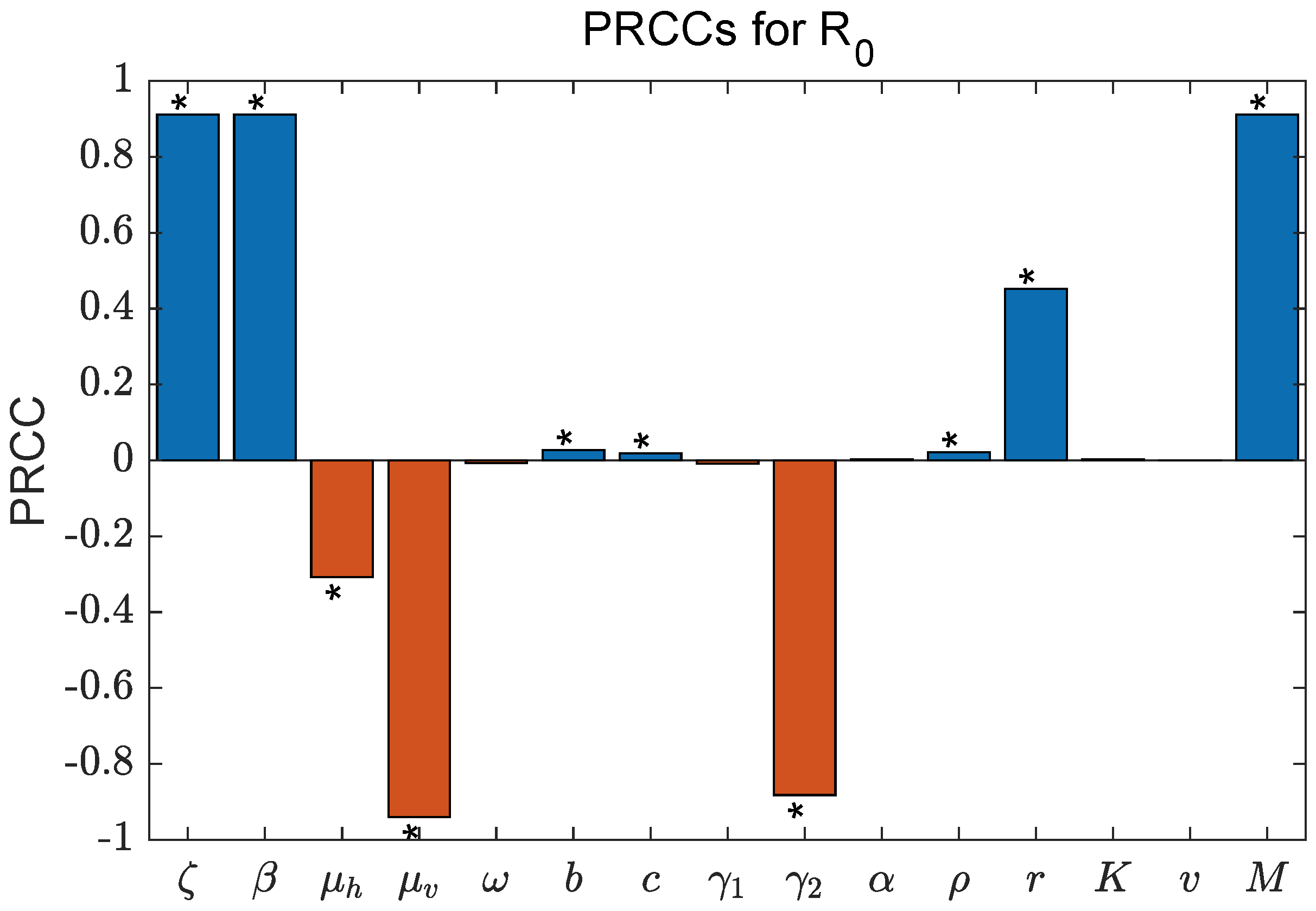
4. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Optimal Control
5.1. Existence of the Control Problem
5.2. Optimal Control Solution
6. Numerical Simulation
6.1. Strategy S1: Cultivating Disease-Free Seedlings Only ()
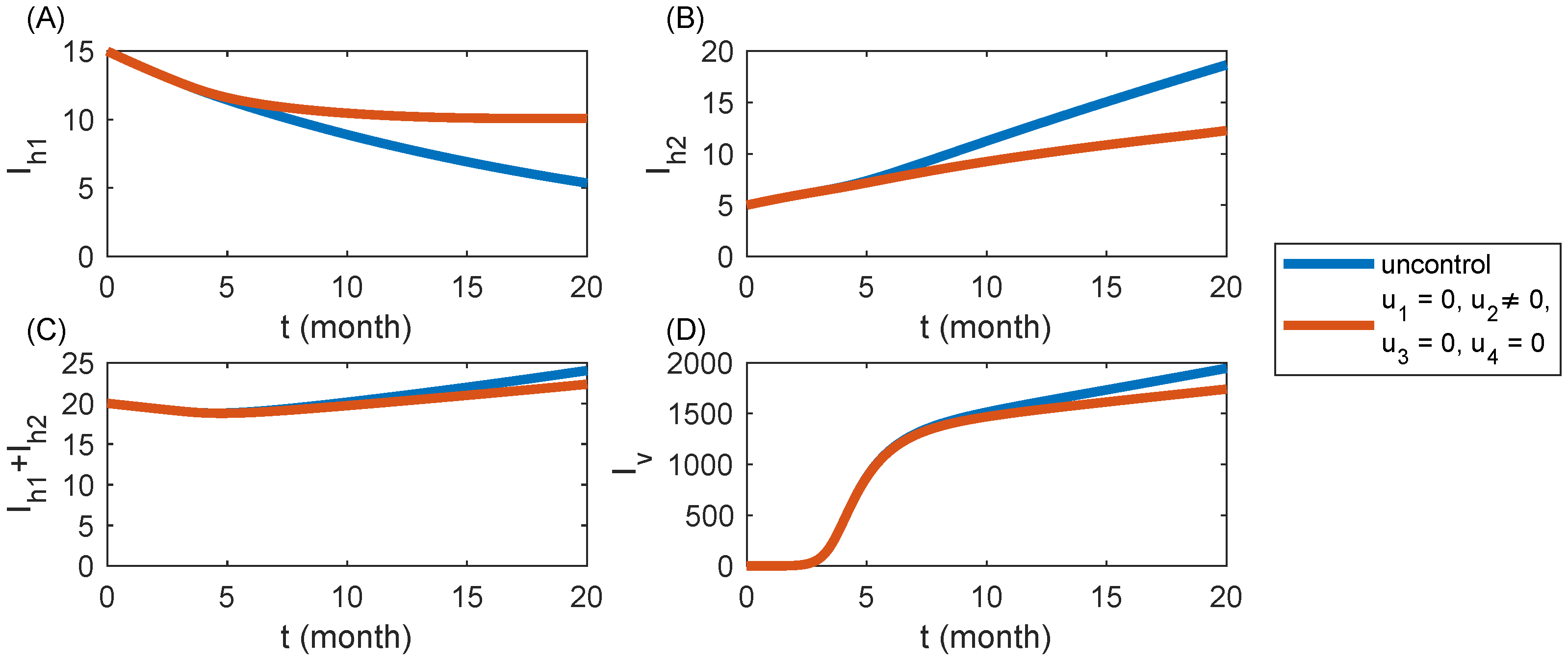
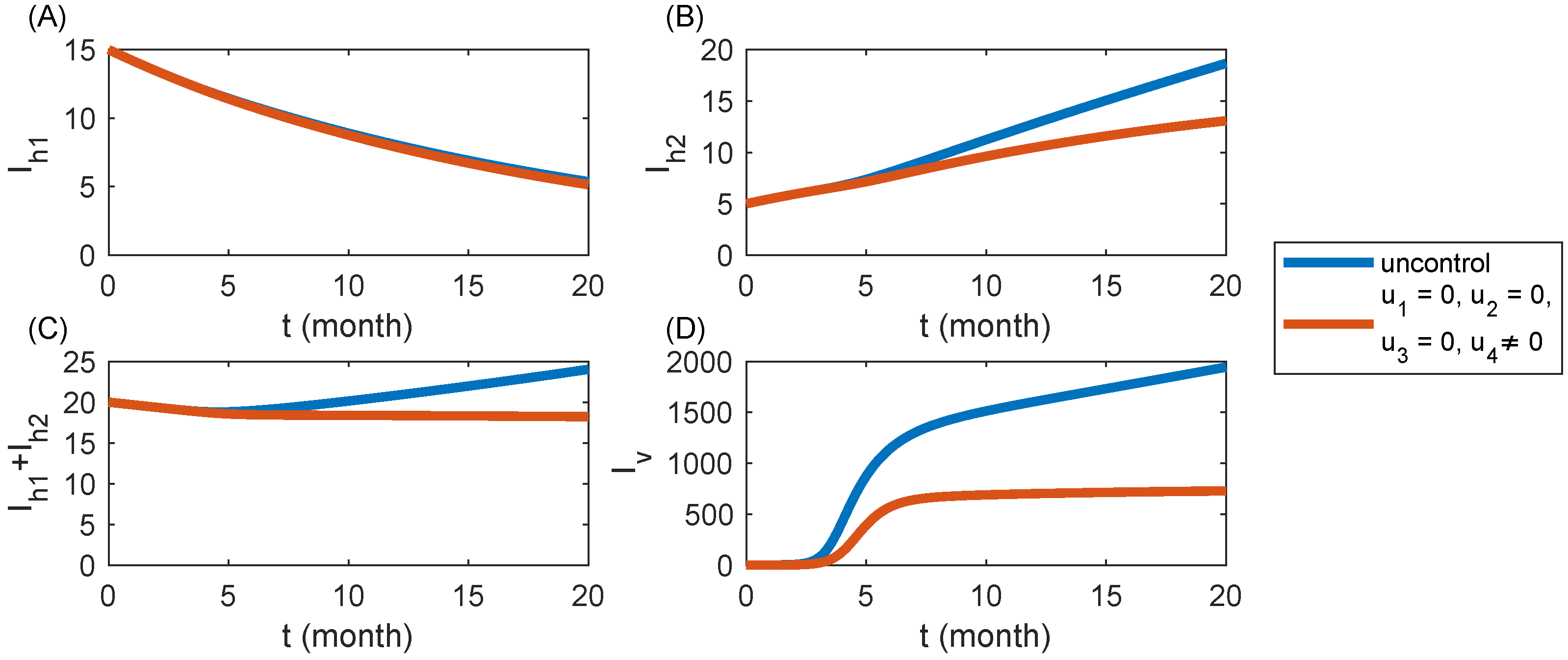
6.2. Strategy S2: Injecting Nutrient Solution Only ()
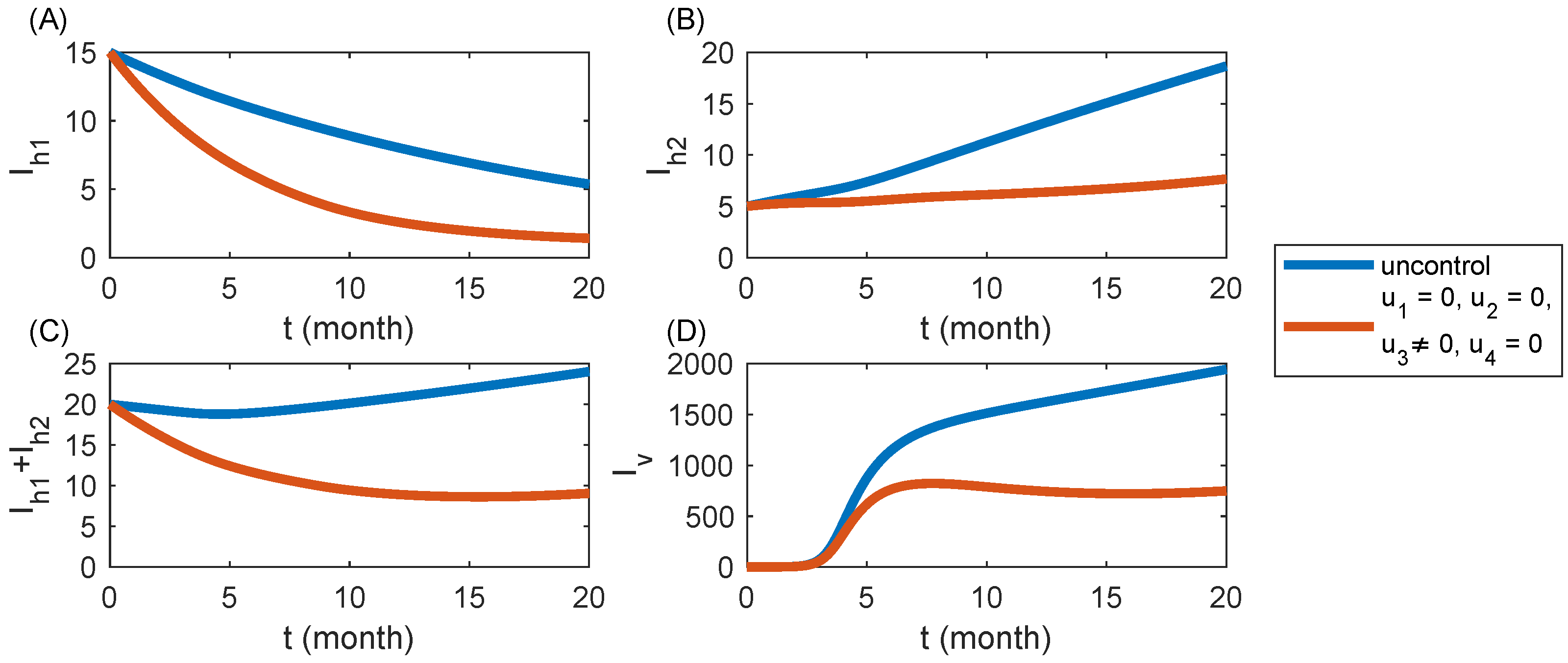
6.3. Strategy S3: Removal of Infected Trees Only ()
6.4. Strategy S4: Spraying Insecticides Only ()
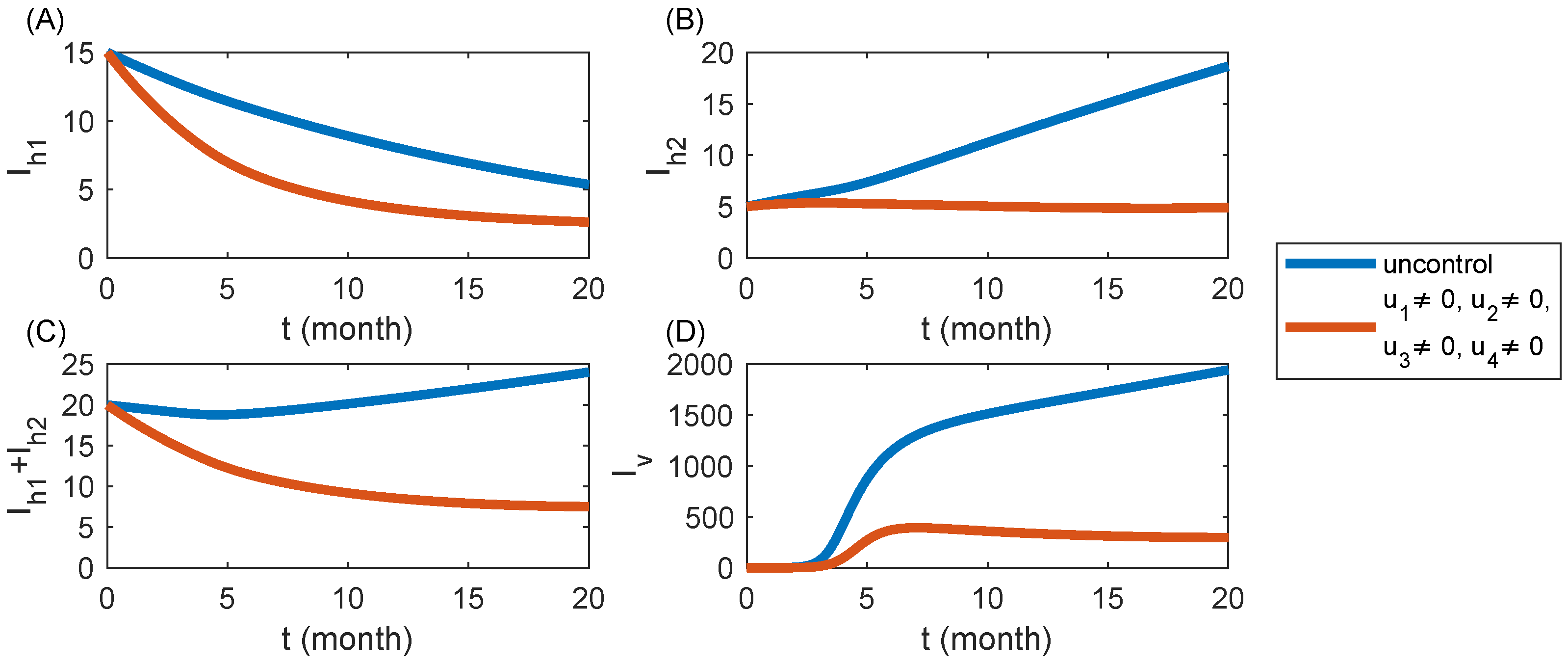
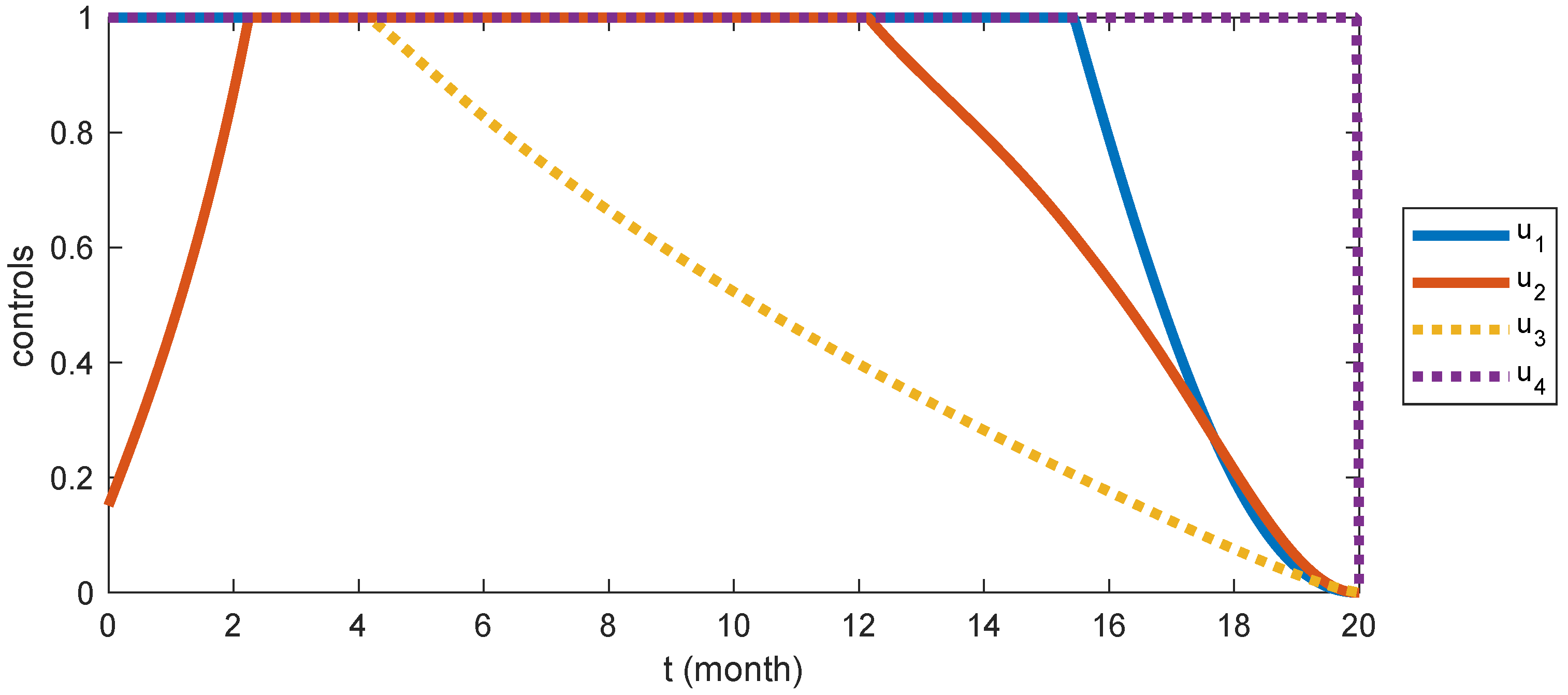
6.5. Strategy S5: Integrated Control ( and )
7. Conclusions
- (i)
- Upon eliminating the sensitivity analysis, it becomes evident that the primary parameters influencing the basic reproduction number () are the infection rates of citrus trees () and citrus psyllids (), the natural death rate of citrus psyllids (), the disease-induced mortality of citrus trees without nutrient solution treatment () and the maximum abundance of ACPs per tree (M);
- (ii)
- When compared to the production of disease-free budwood and nursery trees, as well as the application of nutrient solutions, the removal of HLB-infected trees and insecticide spraying prove to be more effective in minimizing the spread of HLB;
- (iii)
- Among the various strategies, the integrated control strategy, Strategy , emerges as the most effective.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bové, J.M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C. The status of citrus Huanglongbing in China. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2020, 45, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K. Citrus Likubing (pre-report). Taiwan Agric. Rep. 1913, 83, 903–914. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Reinking, O.A. Diseases of economic plants in southern China. Philipp. Agric. 1919, 8, 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.G.; Gottwald, T.R. Pest management practices aimed at curtailing citrus huanglongbing disease. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2011, 22, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.; Stupiansky, J.; Pilyugin, S.S. Mathematical modeling of citrus groves infected by huanglongbing. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2013, 10, 705–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton-Cardwell, E.E.; Stelinski, L.L.; Stansly, P.A. Biology and management of Asian citrus psyllid, vector of the huanglongbing pathogens. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Rohrig, E.; Solís, D.; Thomas, M.H. Citrus greening disease (Huanglongbing) in Florida: Economic impact, management and the potential for biological control. Agric. Res. 2016, 5, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, P.S.; Stockwell, V.O.; Sundin, G.W.; Jones, A.L. Antibiotic use in plant agriculture. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, G.A.; Ternes, G.; Uilamiu, R.G.D.; Castro, A.; Silva, M.V.; Laranjeira, F.F. Modelagem Mathemática da Dinâmica Temporal do HLB em Citros? In Proceedings of the VIII Congresso Brasileiro de Agroinformática, Bento Goncalves, Brazil, 17 October 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chiyaka, C.; Singer, B.H.; Halbert, S.E.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; van Bruggen, A.H. Modeling huanglongbing transmission within a citrus tree. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12213–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.; Mordecai, E.A.; Gilligan, C.A.; Rohr, J.R.; Johnson, L.R. Mathematical models are a powerful method to understand and control the spread of Huanglongbing. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Gao, S.; Yan, S.; Liao, Z. Bifurcation and optimal control analysis of delayed models for huanglongbing. Int. J. Biomath. 2022, 15, 2250049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Gao, S.; Yan, S.; Zhou, G. Transmission dynamics and optimal control of a Huanglongbing model with time delay. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 4162–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, A.; Zhao, X. Optimal control and cost-effectiveness analysis of a Huanglongbing model with comprehensive interventions. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 90, 719–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odionyenma, U.B.; Omame, A.; Ukanwoke, N.O.; Nometa, I. Optimal control of Chlamydia model with vaccination. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2022, 10, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.N.; Zaman, G.; Ali, N.; Ahmad, I.; Shah, Z. Optimal control application to the epidemiology of HBV and HCV co-infection. Int. J. Biomath. 2022, 15, 2150101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, A.; Dubey, U.S.; Dubey, B. Stability and bifurcation analysis of an infectious disease model with different optimal control strategies. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 213, 78–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, J.K.K.; Safianu, B.; Afrifa, E.; Obeng, B.; Seidu, B.; Wireko, F.A.; Sun, G.Q. Optimal control dynamics of Gonorrhea in a structured population. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y. Transmission dynamics and optimal control of stage-structured HLB model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 5180–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qi, G. Population dynamics of Diaphorina citri Kuwayama in different types of citrus orchards in Fogang County, Guangdong Province. J. Biosaf. 2019, 28, 249–253. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M. Forming process and basis and technological points of the theory emphasis on control citrus psylla for integrated control Huanglongbing. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2009, 25, 358–363. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Merwe, C. The Citrus Psylla (Trioza merwei, Pettey). J. Dept. Agric. 1923, 7, 135–141. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10520/AJA0000020_1462 (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Zhang, M.; Powell, C.A.; Zhou, L.; He, Z.; Stover, E.; Duan, Y. Chemical compounds effective against the citrus Huanglongbing bacterium ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ in planta. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Tsai, J.H. Effects of temperature on biology and life table parameters of the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Homoptera: Psyllidae). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2000, 137, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Doud, M.S.; Yang, C.; Duan, Y. Effective antibiotics against ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ in HLB-affected citrus plants identified via the graft-based evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Driessche, P.; Watmough, J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, H.R. Convergence results and a Poincaré-Bendixson trichotomy for asymptotically autonomous differential equations. J. Math. Biol. 1992, 30, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, X.Q. Dynamics in a periodic competitive model with stage structure. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2005, 311, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q. Dynamical Systems in Population Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, N.; Hyman, J.M.; Cushing, J.M. Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bull. Math. Biol. 2008, 70, 1272–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusto, F.B.; Khan, M. Optimal control strategies for dengue transmission in Pakistan. Math. Biosci. 2018, 305, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ren, X.; Magpantay, F.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H. Optimal control of mitigation strategies for dengue virus transmission. Bull. Math. Biol. 2021, 83, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.A.; Blower, S.M. Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive rate: Tuberculosis as an example. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.; Hogue, I.B.; Ray, C.J.; Kirschner, D.E. A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 254, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helton, J.C.; Johnson, J.D.; Sallaberry, C.J.; Storlie, C.B. Survey of sampling-based methods for uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 1175–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.K.; Batabyal, A. Stability analysis and optimal control of an SIR epidemic model with vaccination. Biosystems 2011, 104, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X. Transmission dynamics and optimal control of measles epidemics. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 256, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, W.H.; Rishel, R.W. Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhart, S.; Workman, J.T. Optimal Control Applied to Biological Models; Mathematical and Computational Biology Series; Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
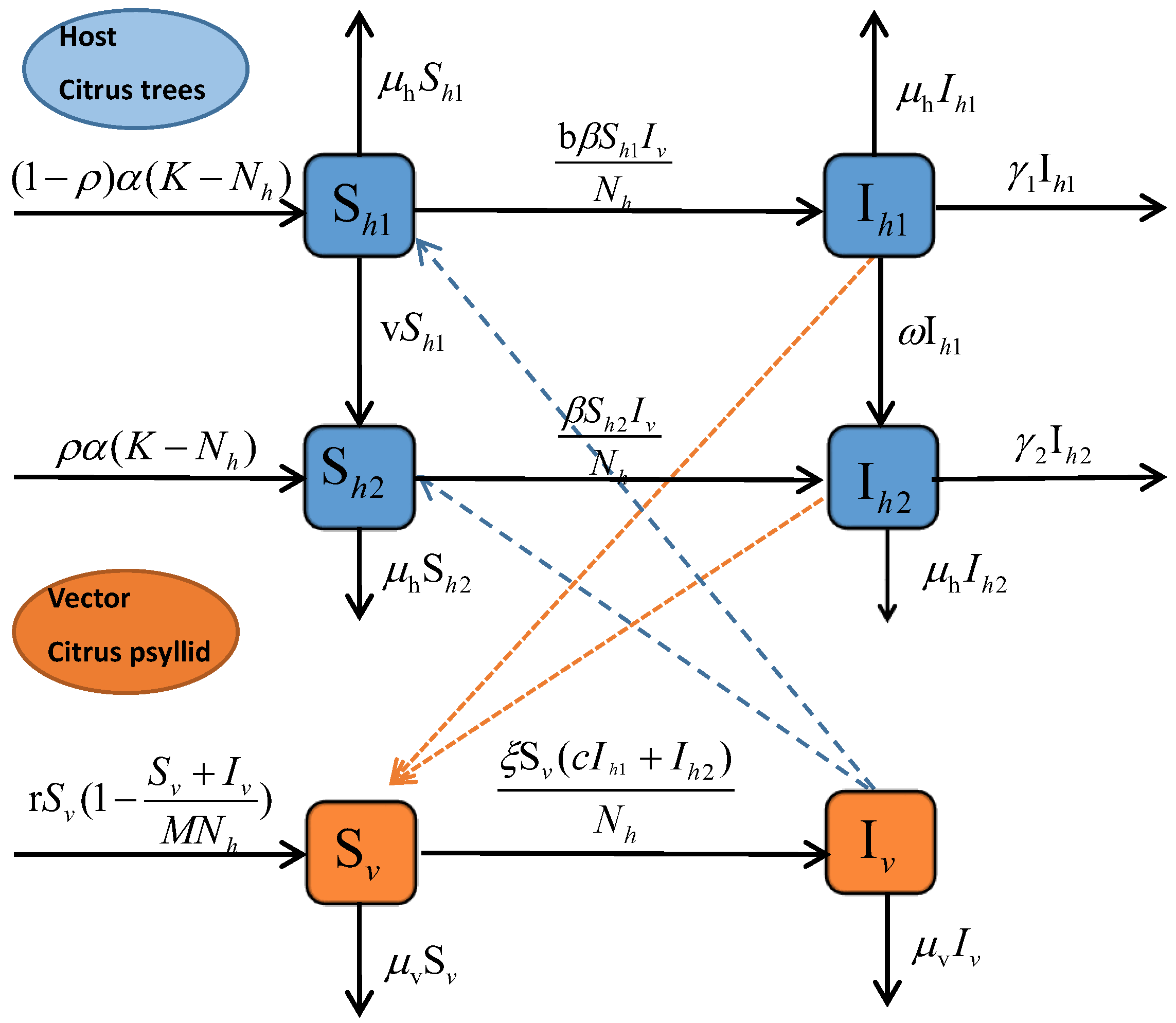

| Parameter | Baseline Value | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | Assume | ||
| 0.0791 | [20] | ||
| 0.000494 | [20] | ||
| 0.0197 | [20] | ||
| K | 2000 | - | Assume |
| M | 3850 | - | [21] |
| 0.0034 | [22] | ||
| 0.7 | [23] | ||
| v | 0.0533 | [24] | |
| 0.05 | Assume | ||
| 0.0417 | [1] | ||
| r | 3.714 | [25] | |
| 0.01 | Assume | ||
| 0.02 | [1] | ||
| b | 0.8 | - | [26] |
| c | 0.8 | - | [26] |
| 0.5 | Assume | ||
| 0.5 | Assume | ||
| 0.1 | Assume |
| Parameter | Description | Sensitivity Index |
|---|---|---|
| Infection rate from infected trees with nutrient solution treatment to susceptible ACPs | 0.5 | |
| Infection rate from infected ACPs to susceptible trees without nutrient solution treatment | 0.5 | |
| M | Maximum abundance of ACPs per tree | 0.5 |
| Replanted rate of citrus tree | 0 | |
| Percentage of susceptible trees without nutrient solution treatment | 0.002215 | |
| r | Oviposition rate of susceptible ACPs | 0.1161 |
| K | Maximum number of citrus trees that can be planted in the grove | 0 |
| Natural death rate of citrus tree | −0.07421 | |
| Natural death rate of ACPs | −0.6161 | |
| b | Decreased probability of being infected of with respect to | 0.01055 |
| c | Decreased probability of infection of with respect to | 0.003269 |
| Disease-induced mortality of citrus trees with nutrient solution treatment | −0.001915 | |
| Disease-induced mortality of citrus trees without nutrient solution treatment | −0.4246 | |
| v | Conversion rate from to | 0.001388 |
| Conversion rate from to | −0.0007031 |
| Strategy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no control | 5.3640 | 18.6695 | 1944.6712 | 357,680 |
| S1 | 6.8321 | 16.6514 | 1877.4227 | 347,445 |
| S2 | 10.0822 | 12.2697 | 1740.0477 | 329,633 |
| S3 | 1.4065 | 7.6593 | 749.2521 | 217,770 |
| S4 | 5.1447 | 13.0783 | 728.6598 | 199,738 |
| S5 | 2.6188 | 4.9042 | 298.0053 | 132,131 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, B. Modeling the Transmission Dynamics and Optimal Control Strategy for Huanglongbing. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172648
Liu Y, Gao S, Chen D, Liu B. Modeling the Transmission Dynamics and Optimal Control Strategy for Huanglongbing. Mathematics. 2024; 12(17):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172648
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yujiang, Shujing Gao, Di Chen, and Bing Liu. 2024. "Modeling the Transmission Dynamics and Optimal Control Strategy for Huanglongbing" Mathematics 12, no. 17: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172648
APA StyleLiu, Y., Gao, S., Chen, D., & Liu, B. (2024). Modeling the Transmission Dynamics and Optimal Control Strategy for Huanglongbing. Mathematics, 12(17), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172648






