Abstract
Human gait recognition (HGR) leverages unique gait patterns to identify individuals, but the effectiveness of this technique can be hindered due to various factors such as carrying conditions, foot shadows, clothing variations, and changes in viewing angles. Traditional silhouette-based systems often neglect the critical role of instantaneous gait motion, which is essential for distinguishing individuals with similar features. We introduce the ”Enhanced Gait Feature Extraction Framework (GaitSTAR)”, a novel method that incorporates dynamic feature weighting through the discriminant analysis of temporal and spatial features within a channel-wise architecture. Key innovations in GaitSTAR include dynamic stride flow representation (DSFR) to address silhouette distortion, a transformer-based feature set transformation (FST) for integrating image-level features into set-level features, and dynamic feature reweighting (DFR) for capturing long-range interactions. DFR enhances contextual understanding and improves detection accuracy by computing attention distributions across channel dimensions. Empirical evaluations show that GaitSTAR achieves impressive accuracies of 98.5%, 98.0%, and 92.7% under NM, BG, and CL conditions, respectively, with the CASIA-B dataset; 67.3% with the CASIA-C dataset; and 54.21% with the Gait3D dataset. Despite its complexity, GaitSTAR demonstrates a favorable balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, making it a powerful tool for biometric identification based on gait patterns.
Keywords:
computer vision; human gait recognition; feature aggregation; feature set transformation; feature fusion; dynamic feature reweighting; deep learning MSC:
68T01
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a shift towards implementing automated monitoring systems to augment human identification efforts and mitigate criminal activity [1]. Biometric-based techniques have emerged as prominent methods for identification and authentication, broadly categorized into behavioral and physical domains [2]. Physical biometrics utilize bodily attributes such as the face, ears, palm, fingerprint, retina, and iris, while behavioral biometrics encompass one’s voice, signature, handwriting, keystrokes, and stride patterns [3]. Human gait recognition (HGR) stands out as a reliable biometric technique, reflecting distinctive walking patterns without requiring explicit consent from a subject [4,5]. The appeal of HGR lies in its ability to capture 24 different components of the human gait, including the angular displacement of body parts and joint angles [6]. This method has applications in various domains, including criminal identification and visual surveillance.
Machine learning (ML) and computer vision (CV) techniques play a crucial role in leveraging HGR for identification purposes [7]. HGR methods are generally classified as model-free or model-based approaches [8]. While model-based methods rely on static gait data and create high-level human models [1], model-free techniques extract features based on shifting body contours [2], offering computational efficiency and adaptability to covariants like shadows and clothing changes [3].
To address the challenge of high-dimensional feature sets, various dimensionality reduction techniques such as entropy-based analysis and principle component analysis are employed [9]. Additionally, classifiers like decision trees (DTs) [10], support vector machines (SVMs) [11], and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are utilized for gait classification tasks [11]. Despite challenges such as time-consuming silhouette-based feature extraction and problem-specific traditional feature extraction techniques, HGR continues to evolve with the integration of deep learning and classical methods, offering a diverse range of approaches for accurate individual identification [12].
In CNN models, features are typically extracted from either the fully connected layer or the average pooling layer [13]. Since many models are trained on raw images, retrieving some noisy or irrelevant features is possible. Upon examining this process, a small group of researchers has concluded that feature extraction occurs significantly later than model training [14]. Traditionally, static hyperparameters such as the learning rate, epochs, and momentum govern the training of CNN models. Additionally, several studies have employed feature selection techniques, including entropy-based selection [11], distance-based selection [15], and evolutionary algorithm-based selection [10], in an attempt to mitigate this issue. However, recent research has highlighted the potential elimination of certain significant traits during the selection process [16].
The aforementioned studies relied on silhouettes and utilized data-driven networks to extract motion characteristics from silhouette sequences [17]. However, these approaches often overlook instantaneous motion properties or short-term motion aspects [18]. To tackle this issue, this study introduces dynamic stride flow representation (DSFR), which incorporates the original gait silhouettes with motion intensity and actual instantaneous motion direction [19]. Additionally, DSFR leverages spatial and temporal contextual cues. While spatial conditions like clothing may alter the body’s form [20], their instantaneous motion remains consistent with that of the body. The DSFR method improves the frame quality by applying histogram equalization before optical flow estimation using the Lucas–Kanade algorithm [8]. The method aims to enhance motion clarity by enhancing the contrast, leading to improved motion estimation accuracy. This technique, beneficial for applications like human gait recognition [21], enhances frame clarity through histogram equalization, aiding in accurate motion estimation, which is crucial for various applications [8], including human gait recognition. The method assumes a constant pixel brightness over time, approximating motion as translational within local neighborhoods between consecutive frames [6]. Utilizing Taylor series expansion, the brightness constancy equation is linearized to estimate optical flow. This process involves solving an overdetermined linear system using least squares optimization, in which spatial and temporal gradients are utilized to compute motion vectors accurately.
An innovative approach in gait recognition is channel-wise attention and keypoint-based embedding. This method incorporates spatial dynamic features to enhance silhouette embeddings alongside comprehensive considerations of spatial–temporal dynamic appearance features using transformer-based attention [22,23,24,25]. By integrating spatial features with temporal data and a channel-wise attention mechanism, GaitSTAR effectively addresses the limitations associated with temporal pooling. Furthermore, to tackle challenging scenarios such as individuals wearing coats that obscure much of the leg region, GaitSTAR leverages model-based techniques utilizing human pose information. This integration enhances the fusion of spatial and temporal features. GaitSTAR harnesses the power of global and local convolutional neural networks [26,27] alongside human position data and temporal attention mechanisms [28,29,30], to generate embeddings across multiple frames.
For example, walking speed is a temporal condition that affects the gait cycle and phase while maintaining the same instantaneous motion direction. The optical-flow images and actual silhouette sequence are cropped and merged along with outlines of corresponding silhouettes in a specific ratio to generate DSFRs. Furthermore, this study proposes Spatial–Temporal Attention-Based Feature Reweighting (GaitSTAR) comprising DSFRs to mitigate the effects of silhouette distortion commonly observed in gait sequences; the feature set transformation (FST) module plays a pivotal role in the integration of image-level features into set-level representations derived from DSFRs. By facilitating the capture of long-range interactions, it serves as a potent mechanism for acquiring contextual information, which is particularly beneficial for enriching the representation of distant objects and bolstering confidence in discerning false negatives. Moreover, the dynamic feature reweighting (DFR) module offers a sophisticated approach to scaling the decoding space of features. The computation of attention distributions across the key embedding of each channel-wise dimension substantially augments the interaction and the decoding of query and key elements across both temporal and spatial domains. According to our experimental results, GaitSTAR demonstrates superior performance compared to the two established benchmarks in gait recognition, namely the CASIA-B [31], CASIA-C [32], and Gait3D [33] gait datasets. The following are this work’s main contributions:
- We propose Spatial–Temporal Attention-Based Feature Reweighting (GaitSTAR) incorporating dynamic-feature weighting via the discriminant analysis of temporal and spatial features by passing them through a channel-wise architecture.
- We introduce DSFRs to enhance the video frame quality, aiding with object feature extraction for improved motion estimation. Our FST architecture integrates image-level features into set-level representations, capturing long-range interactions. DFR further enhances feature decoding by enabling attention computation across key embedding channels, boosting query–key interactions in both temporal and spatial contexts.
- The efficacy of GaitSTAR is substantiated through comprehensive tests and comparisons performed with the CASIA-B, CASIA-C, and GAIT3D gait datasets, unveiling its superior performance over the preceding techniques across both cross-view and identical-view scenarios.
The subsequent sections of this document are structured as follows: Section 2 delves into the interconnected works and fundamental concepts that inform our research. Section 3 offers an in-depth exploration of the DSFR, FST components, and DFW components integral to GaitSTAR. Section 4 delineates the dataset specifics, parameterization, and comprehensive experimental analyses. Finally, Section 5 synthesizes the key findings derived from our research endeavors.
2. Related Works
This section first reviews the current research on using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for human gait identification, and then it concentrates on techniques that are unique to gait feature extraction using enhanced motion estimation and attention-based detections.
Human gait recognition (HGR) has gained significant popularity in the domains of computer vision (CV) and deep learning in recent years [22,24,26,34]. Technological advancements have led to the development of numerous deep learning-based models aimed at mitigating covariate effects [14,33]. Ling et al. [35] presented a unique, scalar, multi-temporal gait identification approach that blends temporal characteristics with different temporal scales, using 3D CNN and a frame pooling approach to handle mismatched inputs between video sequences and 3D networks. Ateep et al. [20] introduced a method for pose estimation that enhances model-based gait recognition by directly estimating optimal skeletal postures from RGB images. They effectively extracted gait characteristics and incorporated spatiotemporal techniques, proposing an improved model-based HGR strategy by combining a gait graph with skeletal poses using graph convolutional networks (GCNs). Zou et al. [36] also targeted human gait angles using MobileNet architectures in real-world scenarios, gathering axisymmetric gait data in unrestricted environments. Empirical evaluations using the CASIA-B dataset demonstrated improved performance compared to SOTA techniques.
Comparing the outcomes of experiments using current approaches with the publicly accessible CASIA-B dataset reveals encouraging results. Hou et al. [37] proposed the Gait Lateral Network (GLN), an HGR approach that focuses on discovering discriminative and compact representations using silhouettes. GLN provides set-level and silhouette-level features by fusing deep CNNs with retrieved attributes. Experiments using the OUMVLP and CASIA-B datasets confirmed that the proposed strategy is effective, demonstrating higher accuracy than other approaches.
To achieve accurate human recognition performance, deep learning methods, particularly hybrid deep CNN models [29,30], are employed. Wen et al. [38] introduced a view-fusion approach and generative adversarial network (GAN) for human gait detection. The GAN is used to transform gait images, while a fusion model combines results from multiple views. Ghosh et al. [39] proposed a faster method based on region convolutional neural networks (R-CNNs) for object extraction and identification from video frames, utilizing walking patterns from gait sequences. Additionally, efficient HGR techniques have been explored using multi-stream approaches, part-fused graph convolutional networks, and graph convolutional networks [3]. Furthermore, Sharif et al. [2] introduced a deep learning-based method for feature extraction and classification that leverages transfer learning and kurtosis-controlled entropy.
While previous approaches have focused on feature reduction, classification, and feature extraction from silhouette photos, preprocessing actions to enhance visual data in video frames were not performed, though they could improve a model’s learning capacity. Thus, this research presents an optimal deep learning-based HGR framework and automated Bayesian optimization to address these limitations.
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
This research article introduces a novel method, termed “GaitSTAR”, which is aimed at enhancing the performance of HGR systems, as shown in Figure 1. The proposed approach employs a sequential enhancement technique that divides video frames into channels and applies contrast enhancement methods to improve frame quality. Subsequently, denoising techniques are utilized to refine the enhanced frames further, enhancing the clarity of motion patterns. This study presents a sophisticated architecture comprising a fusion backbone for spatial and temporal features, coupled with a feature extraction framework for human poses, known as Keypoint-RCNN, which is employed for frame-level feature extraction from gait videos. Subsequently, these extracted frame-level characteristics, encompassing appearance details and human position data, are fed into a channel-wise attention approach. This method computes weights for each frame-level feature, generating sequence-level features for every gait video. The applicability of this method to gait recognition is demonstrated through experiments showcasing its ability to improve the discrimination of gait patterns and enhance the overall performance of gait recognition systems. This method presents a promising avenue for advancing the field of gait recognition by providing enhanced features crucial for accurate analysis and the recognition of human gait patterns, as also described in Algorithm 1.
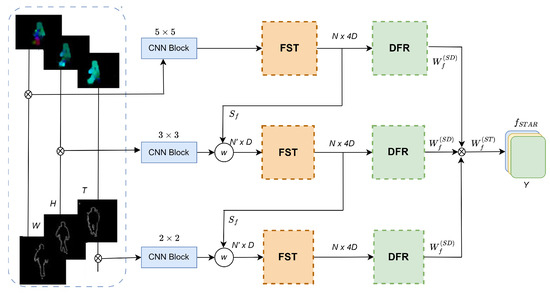
Figure 1.
The pyramid framework of GaitSTAR integrates silhouette edge information and optical flow to capture shape and motion. It uses the Lucas–Kanade algorithm to handle the full dynamic range of pixel values. The framework extracts discriminative features through a scatter matrix and a temporal-attention mechanism, computing a decoding weight vector that enhances the focus on relevant temporal and spatial features. This process generates per-channel decoding weight vectors, leading to a linear projection of reweighted features into a unified channel-wise decoding vector.
3.2. Dynamic Stride Flow Representation
The dynamic stride flow representation method aims to improve the quality of frames in video sequences by enhancing their contrast before applying the Lucas–Kanade algorithm [8] for optical flow estimation. By enhancing the contrast, the method aims to increase the clarity of the frames, which can lead to more accurate motion estimation. Histogram equalization is employed to enhance the image contrast via the redistribution of pixel intensities. This works by stretching the ranges of image intensity, covering the overall dynamic range of the pixel values of images. Our histogram equalization function, , is computed as follows:
where represents the intensity of a pixel at coordinates in the image, is the cumulative distribution function of pixel intensities, is the minimum value of the cumulative distribution function, and L is the maximum intensity level. The enhanced frame, , is obtained by applying histogram equalization to the original frame, :
3.2.1. Motion Estimation Using Optical Flow
The intensity of a pixel remains constant over time, so changes between consecutive frames are due to motion. Motion is approximated as translational within a local neighborhood. Given two consecutive frames, the goal is to estimate the optical flow at each pixel. The brightness-constancy assumption implies that changes in pixel intensity are caused by motion. This relationship can be approximated using the gradients of an image. By applying this approximation to each pixel and combining information from multiple pixels, we obtain a system of linear equations. Under the brightness-constancy assumption, the change in pixel intensity between consecutive frames is solely due to motion. This relationship can be linearized using Taylor series expansion, which involves the gradient of the image. Let , , and represent the spatial and temporal gradients of pixel intensities. To solve this system, we use least squares optimization to estimate the optical flow. This method helps determine the motion between frames by finding the best-fit solution for the horizontal and vertical displacements.
3.2.2. Contrastive Frame Enhancement with a Sequential Approach
Contrast enhancement is a crucial preprocessing step in computer vision, enhancing image clarity and aiding in the extraction of significant object features. In this study, we introduced a novel progressive augmentation incorporating a mean-based contrast enhancement approach, which created multiple channels from an image that is described in Figure 2. Subsequently, we applied a concatenation technique utilized to merge all channels into a unified frame.
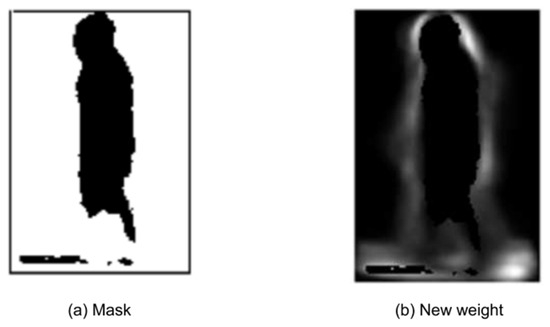
Figure 2.
This figure illustrates feature selection from instances of the CASIA-B. (a) denotes the mask of the targeted area, and the (b) images depict the maximum possible feature area using a discriminative analysis approach.
Specifically, H and W refer to the height and width of the input image, respectively. The temporal dimension, T, represents the sequence of frames. The resultant augmented frame is designated by . The structuring element S is determined through a systematic process. First, a neighborhood is defined around each pixel, typically using a small window, such as 3 × 3 or 5 × 5 pixels, centered on the pixel of interest. Within this neighborhood, local statistics are computed, including measures such as the mean and standard deviation of pixel values. Using these statistics, the structuring element S is constructed. For example, S may be formulated as a matrix in which each element represents either the local mean or a weighted sum of pixel values within the neighborhood. This matrix, S, is then used to adjust pixel values in the local region, thereby enhancing the contrast. Once S is constructed, it is applied to the original image channels to obtain contrast-enhanced channels.
Initially, the primary frame undergoes stratification into three distinct channels via the ensuing algorithmic prescription:
where , , and represent each channel of the input video. The regional contrast of said channels undergoes augmentation via the subsequent formulations:
where , , and denote the resultant locally contrast-augmented images, and S represents the structuring factor to probe the neighboring pixels in a contrasting dilation approach. Next, instead of open-access deep learning-based image-demonizing approaches, we separately incorporated a Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (DnCNN) [40] in a channel-wise manner to refine the frames in the following way:
Finally, the denoised channels are concatenated to form a single frame, yielding the final enhanced frame:
where denotes the first denoised frame, denotes the second denoised frame, and denotes the third denoised frame, respectively.
3.3. Feature-Set Transformation
In pursuit of refining the delineation of data samples across distinct classes, we propose the integration of the Discriminant Common Vector (DCV) methodology. Revered for its prowess in extracting discriminative insights from the intricate fabric of intra-class scatter matrices, DCV concurrently endeavors to encapsulate the inherent intra-class communal attributes shown in Figure 3. Common vectors, epitomizing the cardinal tenets of the null space intrinsic to the within-class scatter matrix , are expressed as follows:
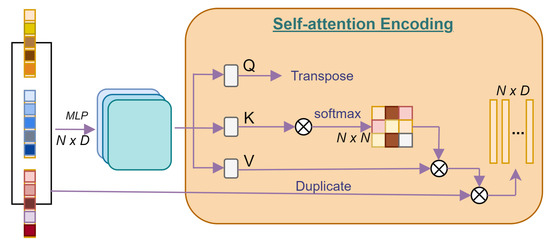
Figure 3.
Illustration of feature set transformation capturing contextual linkages and dependencies. These are processed through a multi-head self-attention mechanism [41] and integrated into an FFN architecture with residual connections for refined feature transformations.
This equation represents the computation of the intraclass variance matrix ; denotes the intraclass variance matrix, which is a crucial statistical measure used to quantify the dispersion or variability of data points within each class, represents the number of samples in the i-th class, denotes the n-th sample in the i-th class, signifies the mean vector of the samples in the ith class, and the expression calculates the outer product of the deviation of each sample from the mean vector within the ith class.
The subspace W is spanned by the eigenvectors of the intra-class scatter matrix , corresponding to non-zero eigenvalues , where k ranges from 1 to r. These eigenvectors capture the directions of maximum variance within the data while being constrained to lie within the subspace defined according to the classes. The subspace is the orthogonal complement of W. It consists of the eigenvectors of , corresponding to zero eigenvalues , where k ranges from to d. These eigenvectors span the subspace orthogonal to W, and they capture the directions of minimum variance within the data, as provided in the following equations:
In practice, directly deriving the common vectors leads to computational complexity due to significant noise within the null space relative to the original signal. However, a more efficient approach involves leveraging the orthogonal complement of the null space of . Let matrix and matrix . Each can be decomposed uniquely as since . Consequently, , where , , and represents the common vector of the ith class. computes the difference between the original data sample and its projection onto the subspace spanned by the principal components. This difference effectively removes the contribution of the principal components from the original data sample, resulting in the centered version, :
We integrated our transformer-based temporal attention mechanism to refine the discriminant features extracted from the data. This attention mechanism enhances the representation of discriminative information by selectively focusing on relevant features across samples and classes.
As shown in Figure 1, the term N denotes the number of feature maps or channels at a particular stage. After it is processed through the CNN block, the dimension of the feature vector is represented by D. The feature set after transformation is indicated by . Additionally, and are the weights applied to spatial-domain features and spatio-temporal features, respectively. These terms are integral to understanding the data flow and operations within the multi-head attention mechanism, and they are clarified in the relevant sections of the manuscript to enhance the comprehension of the diagram.
As shown in Figure 3, our temporal attention-encoding scheme exhibits a structural resemblance to the foundational NLP Transformer encoder, as proposed by Vaswani et al. [42], with the exception of the positional embedding component. This deviation arose due to the inherent inclusion of position information within the point features themselves, thus obviating the need for an additional positional embedding mechanism. Readers can refer to [42,43,44] for more details. represents the computation involved in the temporal-attention mechanism for channel-wise feature extraction.
Here, query, key, and value embeddings Q, K, and V were obtained, respectively, through linear projections , , and , where denotes the D dimensional embedded point features. These embeddings are processed using a multi-head self-attention approach. In a scenario with F attention heads, the query, key, and value are partitioned into F subsets , , and , where , , , , and . Each subset, f, undergoes further computation, as described in the equation, involving element-wise multiplication between the softmax output of scaled according to and , followed by the application of the sigmoid activation function . The softmax function is utilized to compute the attention scores. Subsequently, a feed-forward network (FFN) incorporating two linear layers and a ReLU activation function, denoted by , is applied to further process the attention output.
The resulting feature representation is obtained by passing the output of the FFN ( denoted) through an addition-and-normalization operator, . This operation is iteratively applied three times within our proposed framework, forming a vertical configuration (stack) of three identical self-attention-encoding modules, as was observed to be optimal for our model architecture.
3.4. Dynamic Feature Reweighting
Dynamic feature reweighting is proposed to capture the dynamic variances between classes based on normalized DCVs by FST module. Let n represent the nth element in the column vector, and let denote the mean of all common vectors. This feature weight, denoted as , is sample-independent and normalized to fall within the range of 0 to 1. The formulation of is given by the following:
Here, represents the embedding keys of the f-th head, calculated by projecting the output encoder, and denotes the corresponding embedding query. In the provided equation, represents the reweighted feature for the data point and the channel. This reweighting process involves computing a scaling factor based on the difference between the current feature and its mean , normalized by a factor of 2. This scaled factor is then combined with the query–key interaction term using the element-wise multiplication operation. Finally, the resulting feature reweighting is passed through the sigmoid activation function to ensure non-linearity and boundedness between 0 and 1. This process is applied across all channels to achieve feature reweighting for each temporal attention channel. It is important to note that each value in the vector can be interpreted as the global aggregation for each key embedding. This feature weight highlights both dynamic movement and the body form, as depicted in Figure 3, alongside the feature weight derived from the variance in FST. This process allows the model to focus on different parts of the input sequence for each head, capturing various aspects of the data.
| Algorithm 1 Dynamic stride flow representation |
| Require: Video sequence with frames , where Ensure: Enhanced optical flow estimation
|
3.5. Spatial Dynamic Feature Generation
A more sophisticated method is adopted to further implement the channel-wise information within the key embeddings , as depicted in the attention matrix . This entails computing , resulting in the derivation of D distinct decoding weight vectors. These vectors are subsequently subjected to a linear projection process, culminating in the creation of a unified channel-wise decoding vector [45]. This advanced approach to spatial dynamic re-weighting, illustrated in Figure 4, encapsulates the intricacies of our refined attention mechanism:
Here, represents the reweighted feature vector for the temporal attention head, specifically aimed at capturing spatial information across each channel. This reweighting process involves several steps: Firstly, the query embedding is multiplied by the transpose of the key embeddings , producing a matrix product that iteratively spreads spatial information across each channel. Subsequently, the resulting matrix is multiplied element-wise (⊙) with the transpose of the key embeddings , enhancing the importance of spatial information in the feature reweighting process. The resulting matrix is then scaled by a factor of and normalized by to control the magnitude of the feature reweighting. Finally, the sigmoid activation function is applied to ensure the non-linearity and boundedness of the reweighted features, while represents a scaling factor applied element-wise across the resulting matrix. Overall, this process yields a reweighted feature vector that emphasizes spatial information across each channel, facilitating effective feature extraction and representation in the context of temporal attention mechanisms. The result of the linear transformation is passed through a softmax function to normalize the attention scores. The final output is a weighted sum of the input features, adjusted according to the learned attention weights. Similar to queries and keys, values () are calculated for each head. These values are multiplied by the attention scores and summed up to produce the final output for each head. To amalgamate their attributes, we propose a spatial–temporal re-weighting scheme, as detailed below.
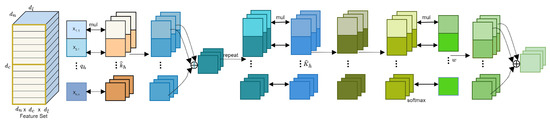
Figure 4.
The figure depicts the data flow through a multi-head attention mechanism in transformer models. It details the steps involved in dynamic feature weighting, which expands the feature decoding space and computes attention distributions across key embeddings for each channel. This process improves query–key interactions, and it enhances expressiveness in both temporal and spatial contexts.
3.6. Spatial–Temporal Feature Reweighting
We began the process by performing a matrix product between the key and query embedding, iteratively spreading the spatial information across each channel. The equation delineates the extended channel-wise re-weighting mechanism, denoted by . It entails a matrix-product operation between the query embedding and key embeddings, fostering the iterative dissemination of spatial insights across individual channels. Following this, the resultant output undergoes element-wise multiplication with the key embeddings to preserve unique channel characteristics. Illustrated in Figure 4, this innovative approach facilitates the generation of decoding weight vectors for all points according to the following expression:
In this context, the function serves as a repeat operator, transitioning from to . This methodology not only upholds global information vis-à-vis conventional channel-wise re-weighting but also amplifies local and nuanced channel interactions relative to standard decoding methods. Furthermore, despite its enhanced functionality, this extended channel-wise re-weighting scheme introduces only a marginal increase in size (approximately 1 KB) compared to alternative approaches. Consequently, the final decoded proposal representation is formulated as follows:
This equation denotes the process of channel-wise feature extraction with temporal attention. Here, represents the output feature vector, which is constructed by concatenating the weighted sums of the transformed key embeddings across all attention heads.
Each denotes a weight vector obtained from the temporal attention mechanism, specifically designed to emphasize the relevance of different channels in the feature extraction process. These weight vectors are computed by applying softmax activation to the scaled dot product between the query and key embeddings, followed by element-wise multiplication with the corresponding value embeddings, . By performing this operation for each attention head, f, and concatenating the resulting weighted sums, the final feature vector encapsulates the temporal dynamics across all channels, enabling effective representation learning for downstream tasks.
3.7. Spatial–Temporal Attention-Based Feature Reweighting
The GaitSTAR framework, as illustrated in Figure 4, integrates optical flow and silhouette-edge data to capture both momentary motion dynamics and shape characteristics comprehensively. Each dynamic stride flow representation (DSFR) undergoes convolutional neural network (CNN) processing, consisting of sequential 5 × 5, 3 × 3, and 2 × 2 layers, to extract image-level features. These features are then aggregated using the aggregate feature representation architecture (AFRA) block, facilitating the transition to set-level representations. Within the dynamic feature weighting (DFW) block, set-level features undergo division and combination to ensure an optimal balance between global and local feature contributions. The resulting feature representations from the DFW block serve as the basis for computing similarities between different gait patterns. Training the GaitSTAR involves leveraging gait features, each associated with unique identifiers are supervised with the application of an overall loss function.
4. Experiments and Results
This section presents the performance evaluation of the Spatial–Temporal Attention-Based Feature Reweighting conducted using the CASIA-B [31], CASIA-C [32], and Gait3D [33] gait datasets, which are publicly accessible datasets. Detailed descriptions of these datasets, including their composition and an overview of the datasets, training, and testing sets, as well as gallery and probe subsets, are initially provided in this section. Subsequently, a comparative analysis is performed between the outcomes of GaitSTAR and alternative techniques. Finally, the effectiveness of each component of GaitSTAR is verified through the results obtained from ablation studies. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the experiments conducted, covering details related to the dataset, experimental conditions, and obtained results.
4.1. Dataset
The CASIA-B dataset encompasses 124 instances featuring 11 viewpoints spanning from 0° to 180°, categorized into three unique walking scenarios: normal (NM), bag (BG), and coat-carrying (CL), as depicted in Figure 5. Out of these, 62 subjects are designated for testing, while the initial 62 subjects constitute the training set. Specifically, the first four sequences of regular walking for each participant are earmarked as the gallery set, while the remaining sequences are designated for the probe set. Similarly, the CASIA-C dataset [32], illustrated in Figure 5, comprises data from 153 individuals engaging in various walking scenarios [46], including normal walking (NW), fast walking (FW), slow walking (SW), and walking with a bag (BW), as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Each subject contributes four NW sequences, two FW sequences, two SW sequences, and two BW sequences. The training set comprises the initial 26, 64, and 100 subjects, while the testing set encompasses the remaining 52 subjects. NW sequences serve as the gallery set for each subject, with the remaining sequences allocated to the probing set.
Figure 5.
This figure illustrates appearance-feature selection from instances of CASIA-B with different angles of a person carrying a bag.

Figure 6.
This figure illustrates the Gait Energy Images (GEIs), presented in sequence from left to right.
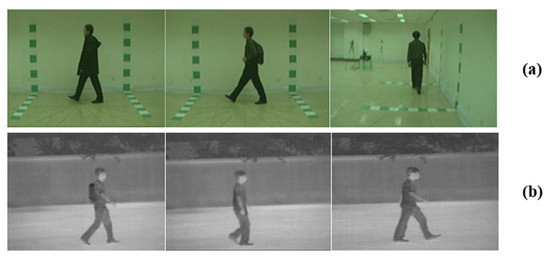
Figure 7.
This figure illustrates instances from the CASIA-B (a) and CASIA-C (b) datasets. In panel (a), the images depict the BG, NM, and CL conditions, arranged from left to right across different perspectives. Panel (b) showcases images depicting the FW, SW, and BW conditions, presented in sequence from left to right.
A substantial gait dataset dubbed Gait3D was amassed within the confines of a supermarket. Here, with a frame rate of 25 FPS and boasting a resolution of 1080 by 1920 pixels, it encompasses a staggering 1090 h of footage. The delineation between gallery and probe sets, along with the training and testing methodologies, strictly adhered to standardized protocols meticulously executed by our team. The principal evaluative metric utilized was the rank-1 accuracy.
4.2. Network Configuration
In our proposed work, we present the configuration of a deep-learning system network tailored for GaitSTAR, a human gait recognition network. The final diagram should begin with the input layer, which consists of image sequences. These sequences are processed through multiple convolutional layers represented by CNN blocks with various filter sizes, such as 5 × 5, 3 × 3, and 2 × 2. Following each convolutional layer, activation functions like ReLU should be indicated if they are used, connecting the CNN blocks to the next stage. If pooling layers are utilized, they should be depicted between the convolutional layers and the subsequent blocks. After the convolutional layers (and any activation or pooling layers), the features proceed to the feature selection/transformation (FST) blocks. These blocks are responsible for selecting or transforming the features extracted via the convolutional layers. Following the FST blocks, the features go through dimensionality reduction (DFR) blocks, which further process the features by reducing their dimensionality.
If the network includes fully connected layers towards the end, these should be shown before the final output. The diagram should culminate with the output layer, which represents the final result Y of the CNN’s processing. Consistent color coding and clear labels should be used throughout the diagram to enhance clarity and the understanding of each component’s role in the network. Training the network involves 100 epochs with a learning rate set to 0.0001 and utilizing the Adam optimizer for an efficient gradient descent. Each training batch consists of 32 samples, and we employ the categorical cross-entropy loss function to measure the disparity between predicted and actual gait classes. Rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation functions are applied to the hidden layers, and they involve transformer channels, , while softmax activation is employed in the output layer to compute class probabilities. To prevent overfitting, we incorporate dropout regularization with a rate of 0.5. Our network expects input images of the size 128 × 128 pixels, and it is designed to classify gait into three distinct classes. For optimal performance, the training process requires access to a high-performance computing environment equipped with a GPU (graphics processing unit) with at least 8 GB of VRAM, 16 GB of RAM, and a multicore CPU. Additionally, efficient data handling and processing capabilities are necessary to manage the large volume of image data required for training. This configuration is crafted to manage the balance between computational efficiency and model complexity, ensuring robust performance in gait recognition tasks.
4.3. GaitSTAR Performance Comparison
Table 1 presents a performance comparison of the CASIA-B dataset across various gait recognition models, Gaitset [47], MT3D [35], GaitGL [27], GaitPart [48], and MSGG [49], in three different sizes of training data under different walking scenarios: normal walking (NM#5-6), bag-carrying (BG#1-2), and coat-wearing (CL#1-2). The models include SPAE, MGAN, Gaitset, Gait-D, GaitPart, GaitGL, GaitNet, GaitGraph, and GaitSTAR. GaitSTAR consistently outperformed other models across all scenarios, achieving the highest accuracy scores in NM, BG, and CL conditions. Specifically, GaitSTAR achieved an accuracy of 97.4% in NM#5-6, 86.7% in BG#1-2, and 68.3% in the CL#1-2 scenarios. In comparison, other models exhibited varying degrees of performance, with GaitPart and GaitGL showing competitive results, particularly in the NM and BG scenarios. However, GaitSTAR maintained a significant performance advantage across all scenarios, demonstrating its robustness and effectiveness in gait recognition tasks.

Table 1.
Comparison of gait recognition model accuracies using the NM#5-6, BG#1-2, and CL#1-2 datasets, with average accuracy using the CASIA-B DATASET. GaitSTAR outperformed other models with an average accuracy of 84.13%.
Table 2 illustrates that GaitSTAR demonstrated the potential to achieve the highest rank-1 accuracy across a wide range of viewing angles. Initially, an analysis of various scenarios, detailed in Table 2, revealed that the progression from normal (NM) to background (BG) and clothing (CL) situations escalated the complexity of gait recognition. The presence of bags or coats led to a gradual degradation in the accuracy performance of all techniques. Specifically, under the NM, BG, and CL conditions, the cutting-edge GaitGL approach achieved recognition accuracy of 97.2%, 94.5%, and 83.6% (utilizing the LT setting).

Table 2.
Performance comparison of gait recognition models with the CASIA-B dataset across different view angles and walking conditions (probe, model, forward walking (FW), sideward walking (SW), backward walking (BW), and average accuracy).
Correspondingly, our findings for GaitSTAR exhibited a parallel trend, with identification accuracies in these scenarios reaching 98.5%, 98.0%, and 92.7%, respectively. Scrutinizing the testing outcomes under the LT setting revealed that GaitSTAR outperformed GaitGL by approximately 1.1% and 3.5% in NM and BG and by approximately 9.1% in CL. This underscores the superior performance of GaitSTAR, particularly in the BG and CL scenarios, underscoring its more discriminative representation compared to other state-of-the-art techniques, as shown in Figure 8. Given that the primary objective of GaitSTAR is to integrate the human posture feature, which offers a more informative gait description, particularly under the BG and CL circumstances, these results were anticipated. Regardless of the type of attire or bag worn by an individual, their skeletal structure remains discernible. Even in single-view (ST) and multi-view (MT) scenarios, GaitSTAR’s rank-1 accuracy yields comparable results. Furthermore, considering that gait data may be captured from various viewing angles and environmental conditions, our performance demonstrates reliability across a spectrum of external factors.
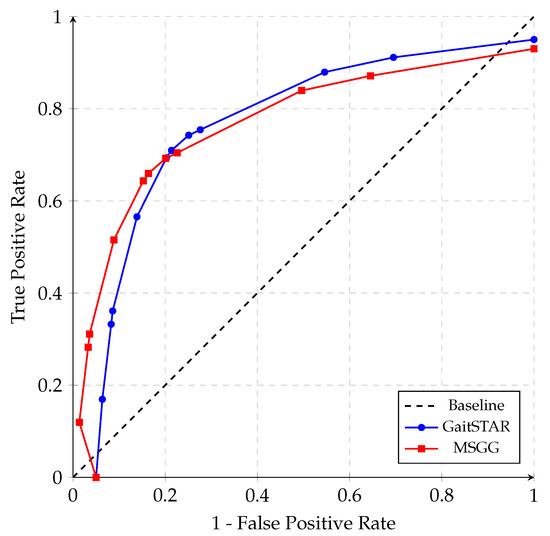
Figure 8.
ROC curves for two models. The black dashed line represents the baseline performance of a random classifier. The blue curve represents the ROC curve for Model 1 (GaitSTAR), and the red curve represents the ROC curve for Model 2 (MSGG).
In the LT scenario, the average rank-1 accuracy of GaitSTAR stands at 96.4%, surpassing MT3D and GaitGL by 6.0% and 4.6%, respectively. An examination of experimental findings using different dataset sizes (e.g., ST, MT, and LT with the CASIA-B dataset) reveals that, under NM conditions, MT3D achieved recognition accuracies of 82.8%, 94.4%, and 96.7%, respectively. Conversely, the proposed GaitSTAR approach achieved comparable identification accuracies of 87.0%, 96.7%, and 98.5%, representing increments of 4.2%, 2.3%, and 2.3%, respectively. Thus, GaitSTAR exhibited greater advancements in the context of small-scale datasets. Additionally, a comparison with another multi-modality approach, MSGG [49], which incorporates posture characteristics in its framework, revealed that GaitSTAR consistently achieved the highest rank-1 accuracy for the BG and CL scenarios across almost all angles.
Moreover, the efficacy of GaitSTAR was evaluated using various training sets with the CASIA-C dataset. As depicted in Table 3, GaitSTAR achieved an average accuracy of 54.1% when trained on a cohort of 24 participants, escalating to 58.4% and 67.3% with training sets comprising 62 and 100 subjects, respectively. This underscores the positive correlation between the size of the training set and the accuracy of recognition, as larger sets facilitated a better delineation of boundary features and mitigated overfitting tendencies.

Table 3.
Performance comparison with CASIA-C dataset with different training sets.
Additionally, the subpar quality of gait sequences in CASIA-C introduced outlier data during optical flow extraction, resulting in overall performance inferior to that observed in CASIA-B. Nonetheless, GaitSTAR exhibited an average accuracy improvement of approximately 1.8% and a notable 5% enhancement under forward walking (FW) conditions compared to the PSN method proposed by [54]. This advancement could be attributed to the spatial information provided by the silhouette’s edge in GaitSTAR, which proves instrumental in refining recognition accuracy, particularly in FW scenarios where motion information may be susceptible to outliers, thereby yielding superior outcomes.
On average, GaitSTAR enhances accuracy by approximately 2.2%(CH), with an increase of roughly 6%(CH) under fast-walking (FW) conditions compared to the PSN method proposed by [35]. This improvement may be attributed to the silhouette edge in the DSFR, which furnishes valuable spatial information to enhance recognition accuracy, particularly under FW conditions where motion information may include outliers.
4.4. Evaluation on Gait3D
Table 4 displays the outcomes of model-free methodologies, model-based approaches, and our proposed GaitSTAR. A conspicuous disparity between laboratory-centric research and real-world deployment is evident, notably observed in the inferior overall performance of model-free techniques with the real-world GREW [33] dataset compared to controlled laboratory datasets like CASIA-B. Notably, model-free methodologies treating frames as an unordered ensemble, exemplified by GaitSet [47], exhibited superior performance compared to those considering the sequential arrangement of frames, such as GaitPart [48], GLN [37], GaitGL [27], and CSTL [55]. This discrepancy likely stemmed from the inherent difficulty in capturing temporal dynamics in unbounded environments, where individuals may interrupt and resume walking along diverse trajectories and at varying velocities.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of gait recognition models with the public dataset Giat3D (probe, model, rank-1 accuracy (R-1), rank-5 accuracy (R-5), mean average precision (mAP), and mean intrapersonal normalized precision (mINP)).
Of particular note is the subpar performance demonstrated for the GEI-based approaches, including GEINet [56], indicating that GEIs overlook crucial gait cues. Conversely, model-based techniques surpassed model-free methods with the Gait3D dataset, a finding that can potentially be attributed to the sparsity of input provided via human-body joints, which lack essential gait characteristics such as body morphology and appearance. Additionally, the unpredictability of the walking pace and trajectory in real-world contexts poses challenges for temporal dynamics’ modeling. Moreover, in terms of rank-1 accuracy, GaitSTAR marginally outperformed the cutting-edge SMPLGait [33] with the Gait3D dataset by a negligible margin of 10.1%. However, for metrics such as mean average precision (mAP) and rank-5 accuracy, GaitSTAR demonstrated superior performance, indicating its potential for gait-recognition applications in practical scenarios.
4.5. Ablation Studies
The outcomes of ablation experiments carried out on the CASIA-B dataset are shown in Table 5, evaluating the effectiveness of various GaitSTAR components. The baseline method, which directly utilizes GEI [56] for classification, is presented in the first row. The second row shows the results obtained by incorporating FST (feature set transformation) and DFR (dynamic feature reweighting) with GEI as an input. Notably, there was an improvement of approximately 21% in the BG and NM conditions, and in CL conditions, the improvement reached approximately 37%. The third row demonstrates the utility of DFSR compared to GEI, with DFSR yielding an increase in accuracy of 3.1% in NM, 0.7% in BG, and 4.1% in CL conditions. It also depicts the outcome of various GaitSTAR modules, emphasizing the effectiveness of FST and DFR. It has been established that utilizing FST as the permutation-invariant function results in a comparison to other popular functions such as the mean, max, median, and attention, with the best accuracy. Ablation studies further indicated that DFR contributes significantly to accuracy, with an increase of approximately 2–3% observed in all conditions with DFR.

Table 5.
Ablation experiments for GaitSTAR and permutation-invariant functions under various walking conditions (NM, BG, and CL) and their impact on various modules using the CASIA-B dataset.
We explored the efficacy of the spatial–temporal attention mechanism in Table 6. Our experimentation leveraged the CASIA-B dataset, employing the LT parameters. Table 6 elucidates that employing average pooling in the spatial dynamic (SD) layer yielded accuracies of 96.9%, 92.2%, and 83.5%, while utilizing the spatial–temporal (ST) layer resulted in accuracies of 98.7%, 97.1%, and 83.8%, respectively. Hence, integrating the ST operation, rather than solely relying on SD, can enhance performance. Moreover, it is evident that attention reweighting (AR) with ST + AR significantly boosts accuracy in the CL scenario by 8.5% compared to ST alone. This substantial improvement is attributed to ST + AR’s ability to extract both human positional and temporal information from gait sequences, thereby enhancing adaptability to changes in the external environment. Consequently, we opted for the ”ST + AR” combination as the ultimate representation for multi-view gait recognition.

Table 6.
Ablation experiments for GaitSTAR with the CASIA-B dataset.
5. Analysis and Discussion
The GaitSTAR framework advances human gait recognition through its innovative architecture and effective handling of key challenges in the field. The framework’s design integrates three core components: dynamic stride flow representation (DSFR), feature set transformation (FST), and dynamic feature reweighting (DFR), each addressing critical issues in gait analysis.
DSFR enhances the video frame quality by combining silhouette-edge information with motion intensity and direction, mitigating silhouette distortion due to factors such as carrying conditions and clothing variations. This module captures both shape and motion characteristics, improving feature extraction accuracy. FST transforms image-level features into set-level representations using the Discriminant Common Vector (DCV) methodology and temporal attention mechanisms. This approach enhances feature richness by capturing contextual linkages and adapting to various viewing angles. DFR dynamically reweights features based on their discriminative power, refining feature interactions and improving recognition accuracy across diverse conditions.
Gait recognition faces challenges, including silhouette distortion, the need to capture short-term motion properties, cross-view recognition difficulties, and real-world deployment complexities. GaitSTAR addresses these challenges effectively. DSFR reduces silhouette distortion, enhancing frame clarity. FST and DFR capture and adapt to both instantaneous and dynamic gait features, improving recognition robustness across different viewing angles and conditions. The integration of advanced methodologies, such as histogram equalization for contrast enhancement and the Lucas–Kanade algorithm for motion estimation, supports GaitSTAR’s ability to handle real-world variations in walking conditions and environments.
GaitSTAR’s effectiveness was quantitatively validated through several performance metrics. With the CASIA-B dataset, GaitSTAR achieved an average accuracy of 84.13%, outperforming other models such as SPAE (40.2%) and MGAN (51.4%). It also compared favorably with advanced models like GaitPart (89.1%) and GaitGL (88.7%), demonstrating its competitive edge. In evaluations using the Gait3D dataset, GaitSTAR achieved rank-1 accuracy of 54.21%, rank-5 accuracy of 72.76%, a mean average precision (mAP) of 44.15%, and mean intrapersonal normalized precision (mINP) of 27.07%. These results surpass those of models like GEINet (rank-1: 7.00%; mAP: 6.05%) and Gaitset (rank-1: 42.60%; mAP: 33.69%) and exceed those of GaitPart (rank-1: 29.90%; mAP: 23.34%) while approaching GaitGL (rank-1: 23.50%; mAP: 16.40%).
Overall, GaitSTAR’s architecture, which combines DSFR, FST, and DFR, offers a robust solution to gait-recognition challenges. The superior performance metrics affirm its effectiveness in practical scenarios, marking it as a leading framework in the field.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
The Enhanced Gait Feature Extraction Framework (GaitSTAR) represents a significant advancement in human gait recognition (HGR). It integrates dynamic feature weighting through discriminant analysis and employs a channel-wise architecture to overcome the limitations of traditional silhouette-based systems. The framework’s innovations—dynamic stride flow representation (DSFR) for silhouette distortion, transformer-based feature set transformation (FST) for feature integration, and dynamic feature reweighting (DFR) for an enhanced contextual understanding—collectively enhance gait recognition accuracy and robustness. Empirical results highlight GaitSTAR’s high performance across various datasets and conditions, demonstrating its effectiveness in challenging scenarios. The framework’s advanced features and deep-learning components entail substantial computational resources, particularly during the model training and inference stages. While GaitSTAR achieves high accuracy, its implementation requires careful consideration of computational costs and efficiency. Optimizing model parameters and leveraging hardware acceleration can mitigate these demands, ensuring that GaitSTAR remains practical for real-world applications. Overall, GaitSTAR’s balance of high accuracy and computational feasibility underscores its potential as a valuable tool for biometric gait recognition. Looking forward, future research could explore dynamic feature-fusion techniques within GaitSTAR. By dynamically integrating and adapting features from different scales and modalities, such as temporal dynamics and spatial structure, we aim to further enhance the robustness and discriminative power of gait analysis. This approach could involve advanced fusion strategies that adaptively weigh and combine features based on their relevance and discriminative potential, potentially leading to even higher accuracy and reliability in human-gait identification tasks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B., H.J., H.M., M.A., G.A. and M.E.; data curation, H.M. and M.E.; formal analysis, M.B.; funding acquisition, M.E.; investigation, H.M., G.A. and M.E.; methodology, M.B., H.J., H.M., M.A., G.A. and M.E.; resources, H.J. and M.A.; software, M.B.; supervision, H.J. and M.A.; validation, M.B., H.J., M.A. and G.A.; visualization, G.A.; writing—original draft, M.B.; writing—review and editing, H.J., H.M., M.A., G.A. and M.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by EIAS Data Science and Blockchain Lab, CCIS, Prince Sultan University. Also, the authors would like to thank Prince Sultan University for paying the article-processing fees for this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available on request from the corresponding authors, and the datasets CASIA-B and CASIA-C are publicly available at http://www.cbsr.ia.ac.cn/english/Gait%20Databases.asp.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prince Sultan University for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Khan, M.A.; Arshad, H.; Damaševičius, R.; Alqahtani, A.; Alsubai, S.; Binbusayyis, A.; Nam, Y.; Kang, B.G. Human gait analysis: A sequential framework of lightweight deep learning and improved moth-flame optimization algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8238375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, M.I.; Khan, M.A.; Alqahtani, A.; Nazir, M.; Alsubai, S.; Binbusayyis, A.; Damaševičius, R. Deep learning and kurtosis-controlled, entropy-based framework for human gait recognition using video sequences. Electronics 2022, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teepe, T.; Gilg, J.; Herzog, F.; Hörmann, S.; Rigoll, G. Towards a deeper understanding of skeleton-based gait recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1569–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, H.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.I.; Yasmin, M.; Tavares, J.M.R.; Zhang, Y.D.; Satapathy, S.C. A multilevel paradigm for deep convolutional neural network features selection with an application to human gait recognition. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.K.; Schunck, B.G. Determining optical flow. Artif. Intell. 1981, 17, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Arshad, H.; Khan, W.Z.; Alhaisoni, M.; Tariq, U.; Hussein, H.S.; Alshazly, H.; Osman, L.; Elashry, A. HGRBOL2: Human gait recognition for biometric application using Bayesian optimization and extreme learning machine. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Blachut, K.; Kryjak, T. Real-time efficient fpga implementation of the multi-scale lucas-kanade and horn-schunck optical flow algorithms for a 4k video stream. Sensors 2022, 22, 5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Trajcevski, G.; Bonsangue, M. Multi-view learning with distinguishable feature fusion for rumor detection. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 240, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.f.; Gong, D.w. A return-cost-based binary firefly algorithm for feature selection. Inf. Sci. 2017, 418, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jia, H.; Abualigah, L.; Xing, Z.; Zheng, R.; Wang, H.; Altalhi, M. Enhance teaching-learning-based optimization for tsallis-entropy-based feature selection classification approach. Processes 2022, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W.Q. Gait recognition using multichannel convolution neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 14275–14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipi Gonçalves dos Santos, C.; Oliveira, D.d.S.; Passos, L.A.; Gonçalves Pires, R.; Felipe Silva Santos, D.; Pascotti Valem, L.; Moreira, T.P.; Cleison, S.; Santana, M.; Roder, M.; et al. Gait recognition based on deep learning: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhan, J.; Chen, R.; Wei, T.; Huang, Z. GaitSlice: A gait recognition model based on spatio-temporal slice features. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 124, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahee, S.A.; Ananthakumar, U. An effective distance based feature selection approach for imbalanced data. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 717–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.F.G.d.; Oliveira, D.D.S.; Passos, L.A.; Pires, R.G.; Santos, D.F.S.; Valem, L.P.; Moreira, T.P.; Santana, M.C.S.; Roder, M.; Papa, J.P.; et al. Gait recognition based on deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.03323. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, A.; Makihara, Y.; Yagi, Y. Silhouette transformation based on walking speed for gait identification. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Farnebäck, G. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In Image Analysis, Proceedings of the 13th Scandinavian Conference, SCIA 2003, Halmstad, Sweden, 29 June–2 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Nevatia, R. Gait recognition using 3-d human body shape inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 909–918. [Google Scholar]
- Teepe, T.; Khan, A.; Gilg, J.; Herzog, F.; Hörmann, S.; Rigoll, G. Gaitgraph: Graph convolutional network for skeleton-based gait recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 2314–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakunniran, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Gait recognition under various viewing angles based on correlated motion regression. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2012, 22, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.U.; Nasralla, M.M.; Aslam, F.; Ali, S.S.; Khattak, S.B.A. A Novel Approach based on Multi-level Bottleneck Attention Modules using Self-guided Dropblock for Person Re-identification. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 123160–123176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Peng, J.; Wu, Y.; Gupta, B.B.; Abd El-Latif, A.A. Real-Time Traffic Speed Estimation for Smart Cities with Spatial Temporal Data: A Gated Graph Attention Network Approach. Big Data Res. 2022, 28, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahevar, M.; Ganatra, A.; Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Bahaj, S.A. Spatial–Temporal Dynamic Graph Attention Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 21546–21553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, H.; Deng, X.; Ullah, I.; Ali, M.; Hayat, B. O2SAT: Object-Oriented-Segmentation-Guided Spatial-Attention Network for 3D Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicles. Information 2024, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, Q.; Yao, R.; Zhu, D.; Chen, H. Adversarial learning-based skeleton synthesis with spatial-channel attention for robust gait recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X. Gait Recognition via Effective Global-Local Feature Representation and Local Temporal Aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 14628–14636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulila, W. An approach based on performer-attention-guided few-shot learning model for plant disease classification. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Boulila, W.; Ghandorh, H.; Masood, S.; Alzahem, A.; Koubaa, A.; Ahmed, F.; Ahmad, J.; Khan, Z. A transformer-based approach empowered by a self-attention technique for semantic segmentation in remote sensing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, S.; Yaseen, M.U.; Ali, S.S.; Nasralla, M.M.; Khattak, S.B.A. PAN-DeSpeck: A Lightweight Pyramid and Attention-Based Network for SAR Image Despeckling. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 76, e041195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tan, D.; Tan, T. A Framework for Evaluating the Effect of View Angle, Clothing and Carrying Condition on Gait Recognition. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 4, pp. 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Huang, K.; Yu, S.; Tan, T. Efficient Night Gait Recognition Based on Template Matching. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 3, pp. 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; He, L.; Yan, C.; Mei, T. Gait recognition in the wild with dense 3d representations and a benchmark. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 20228–20237. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Wang, W.; Dong, J.; Tan, T. Temporal sparse adversarial attack on sequence-based gait recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 133, 109028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, S.; Bao, F. Gait recognition with multiple-temporal-scale 3d convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 3054–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Deep learning-based gait recognition using smartphones in the wild. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3197–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y. Gait lateral network: Learning discriminative and compact representations for gait recognition. In Computer Vision, Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 382–398. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J. Multi-view gait recognition based on generative adversarial network. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 54, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R. A Faster R-CNN and recurrent neural network based approach of gait recognition with and without carried objects. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 205, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. Trans. Img. Proc. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenga, H.; Cai, S.; Liu, Y.; Deng, B.; Huang, J.; Hua, X.S.; Zhao, M.J. Improving 3D Object Detection with Channel-wise Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, NY, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Zhao, G.; Li, P.; Yu, Y. BOAT: Bilateral Local Attention Vision Transformer. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 21–24 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Liu, C.; Guo, G. Dynamic Group Transformer: A General Vision Transformer Backbone with Dynamic Group Attention. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03937. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, H.; Deng, X.; Ali, M.; Hayat, B.; Raza Sherazi, H.H. DFA-SAT: Dynamic Feature Abstraction with Self-Attention-Based 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güner Şahan, P.; Şahin, S.; Kaya Gülağız, F. A survey of appearance-based approaches for human gait recognition: Techniques, challenges, and future directions. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 18392–18429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Gaitset: Regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8126–8133. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Peng, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Hou, S.; Chi, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; He, Z. Gaitpart: Temporal part-based model for gait recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14225–14233. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z. Learning rich features for gait recognition by integrating skeletons and silhouettes. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 7273–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Huang, Y. Invariant feature extraction for gait recognition using only one uniform model. Neurocomputing 2017, 239, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shan, H.; Wang, L. Multi-task GANs for view-specific feature learning in gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L. Gait-D: Skeleton-based gait feature decomposition for gait recognition. IET Comput. Vis. 2022, 16, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Makihara, Y.; Xu, C.; Yagi, Y.; Ren, M. Gait recognition via semi-supervised disentangled representation learning to identity and covariate features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13309–13319. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; Sun, T. Gait Recognition Based on Local Graphical Skeleton Descriptor With Pairwise Similarity Network. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; He, B.; Liu, W.; Feng, B. Context-sensitive temporal feature learning for gait recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12909–12918. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraga, K.; Makihara, Y.; Muramatsu, D.; Echigo, T.; Yagi, Y. GEINet: View-invariant gait recognition using a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Halmstad, Sweden, 13–16 June 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Makihara, Y.; Xu, C.; Yagi, Y.; Yu, S.; Ren, M. End-to-end model-based gait recognition. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).