On Neural Observer in Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Wind Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Configuration and Structure of Turbine
2.1. The Aerodynamic Part
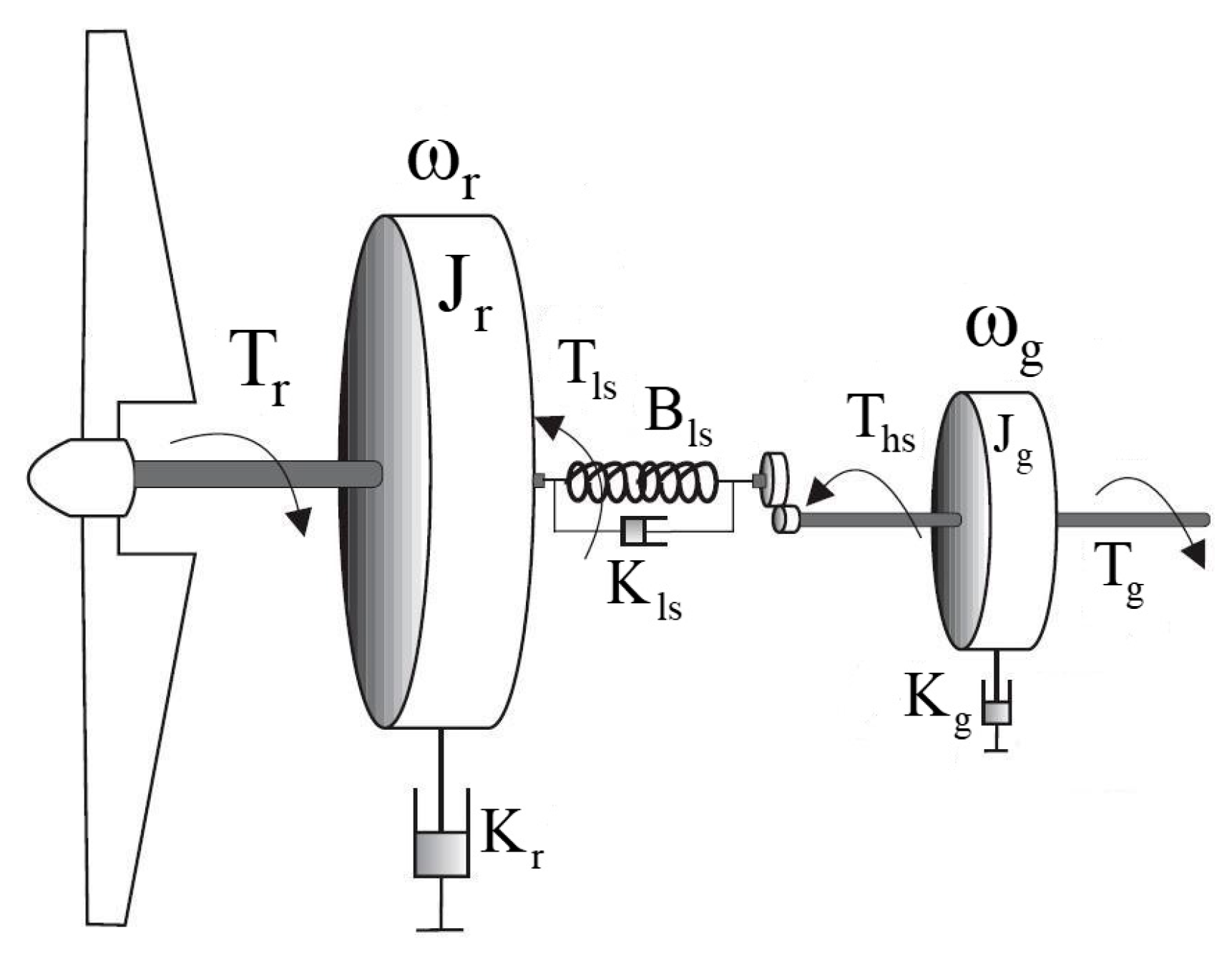
2.2. The Drivetrain Part
2.3. The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator (PMSG) Part
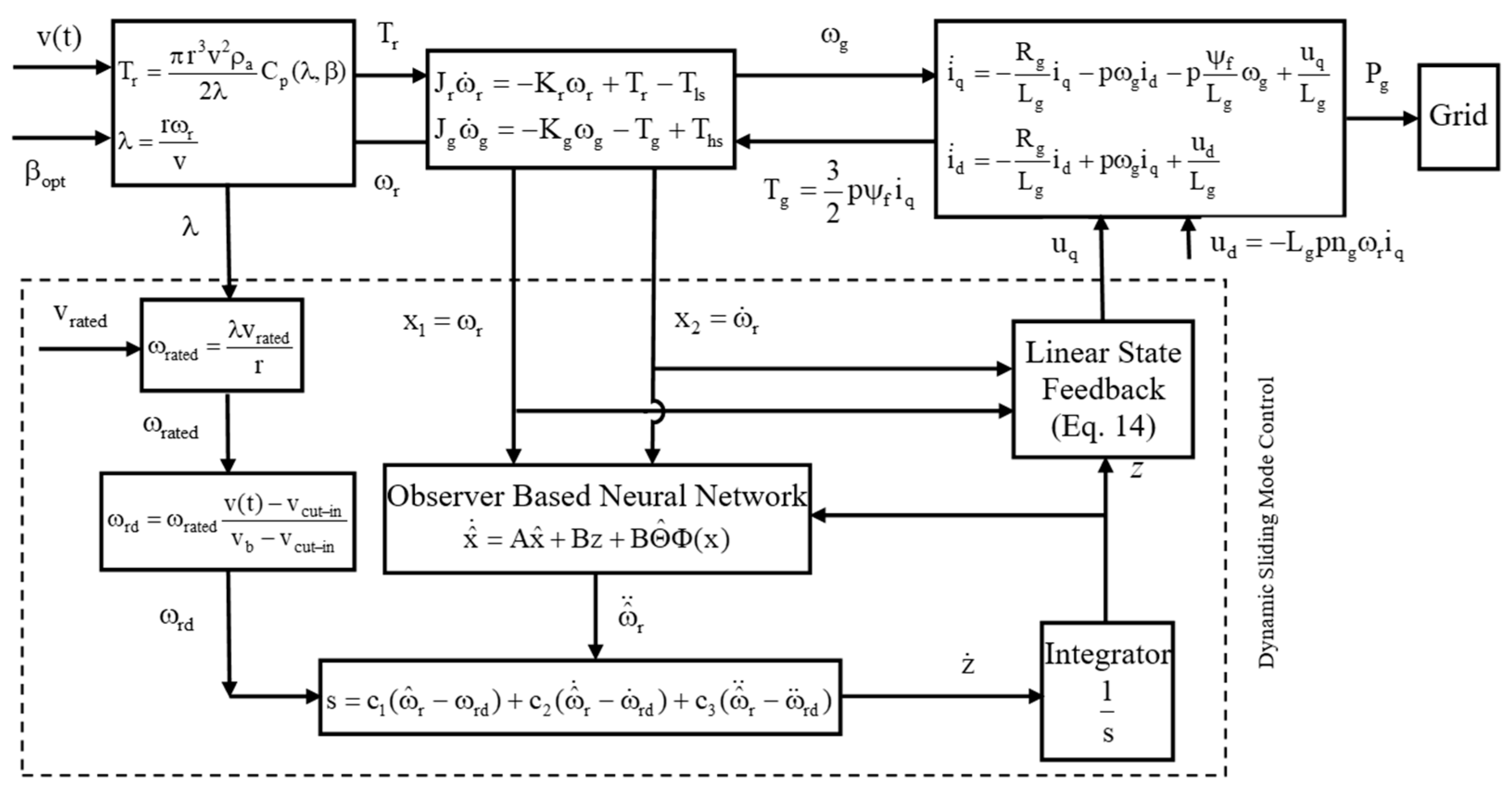
3. The Observer-Based Neural Network (ONN) Proposed Approach
4. Sliding Mode Controller (SMC) Design
4.1. The Proposed D-SMC Approach
4.2. The Proposed T-SMC Approach
4.3. The Reference of Rotor Angular Velocity
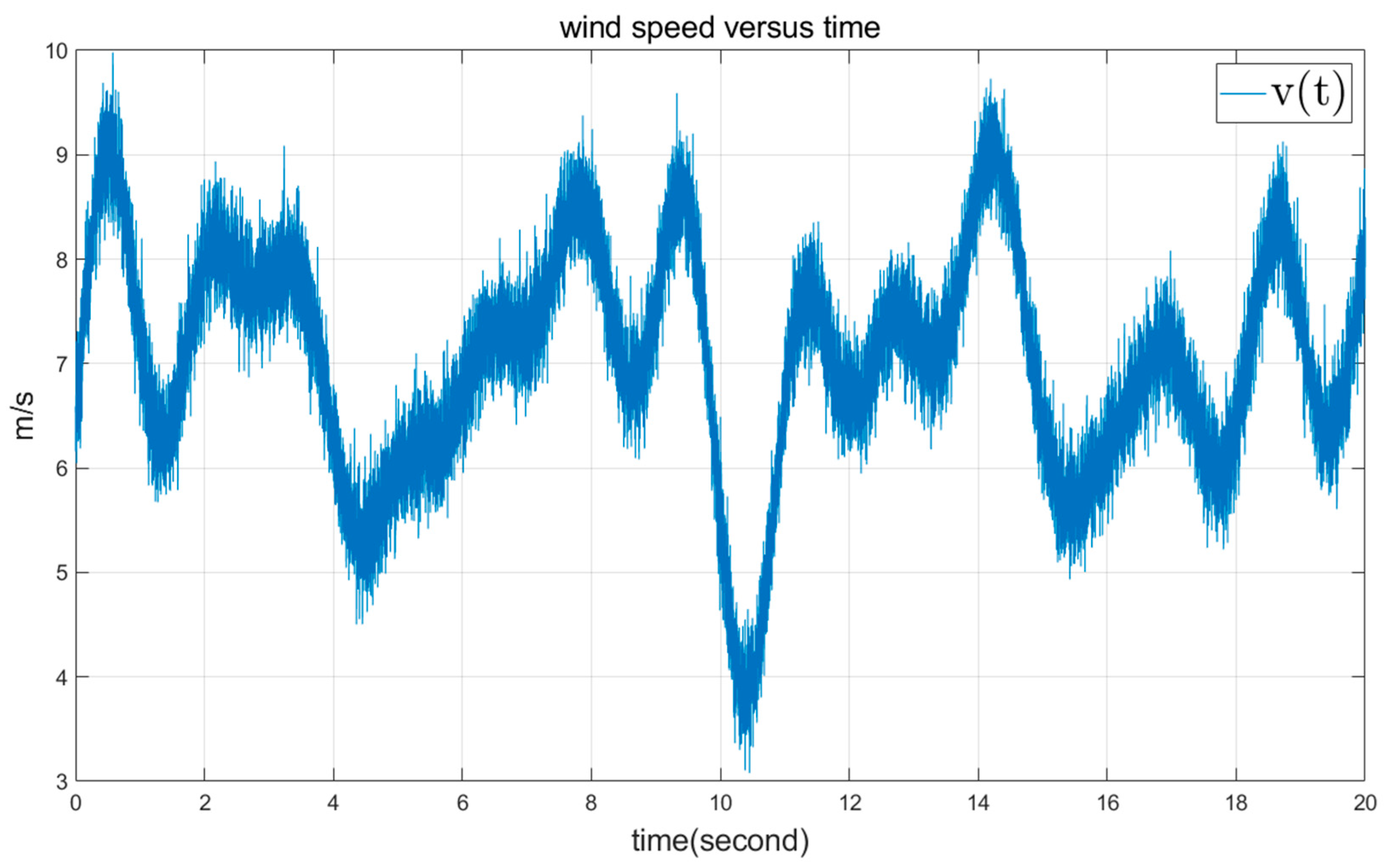
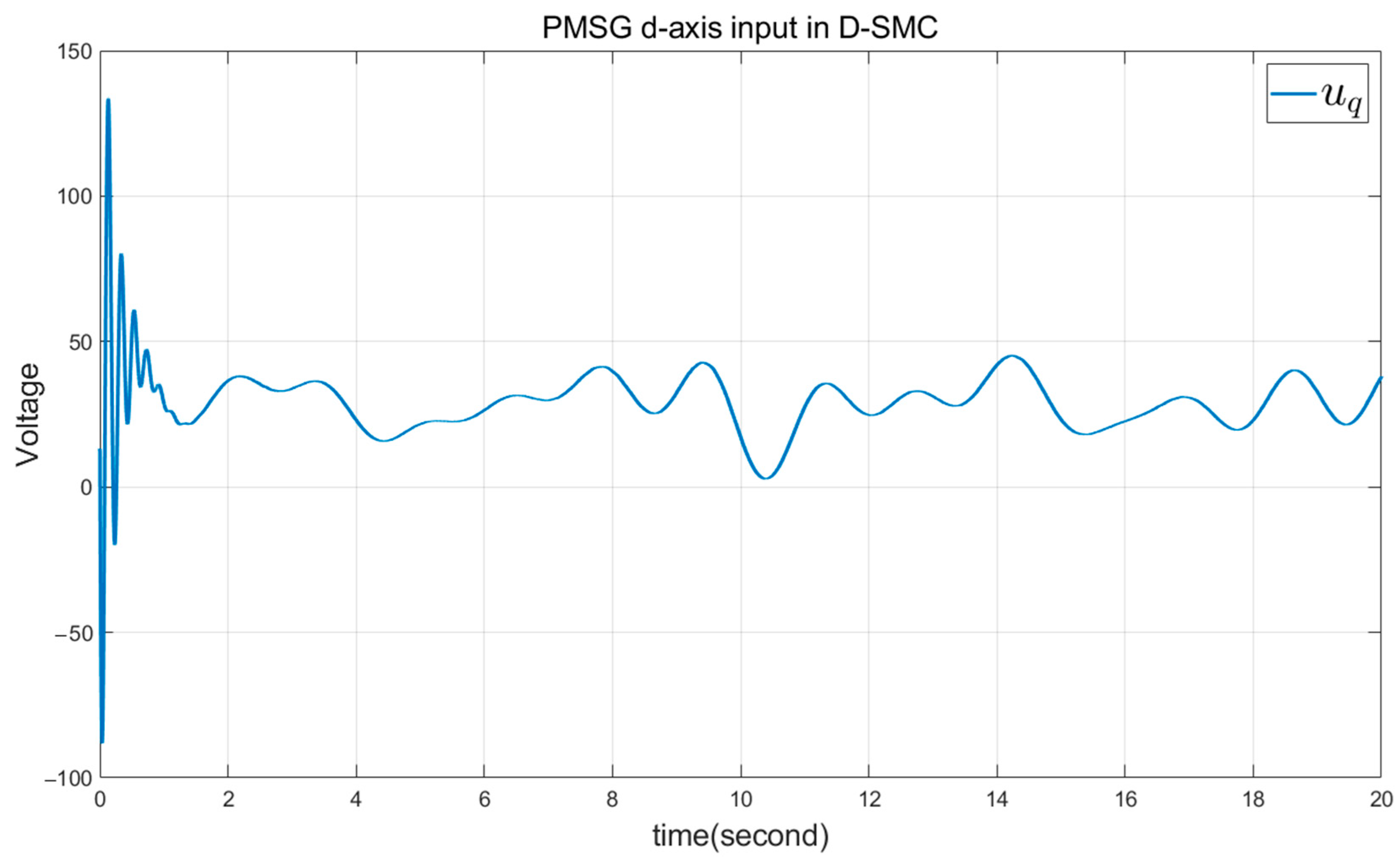
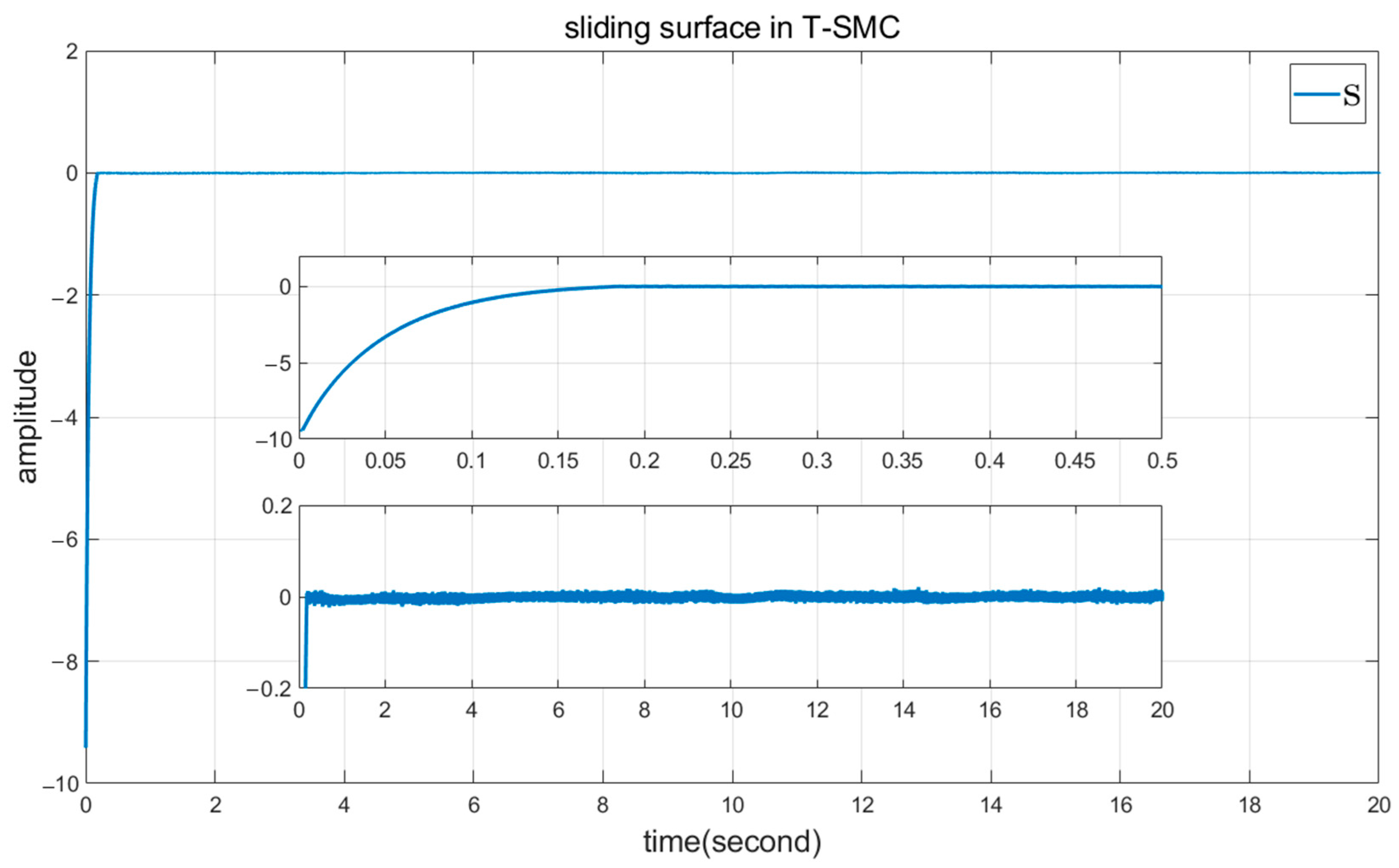
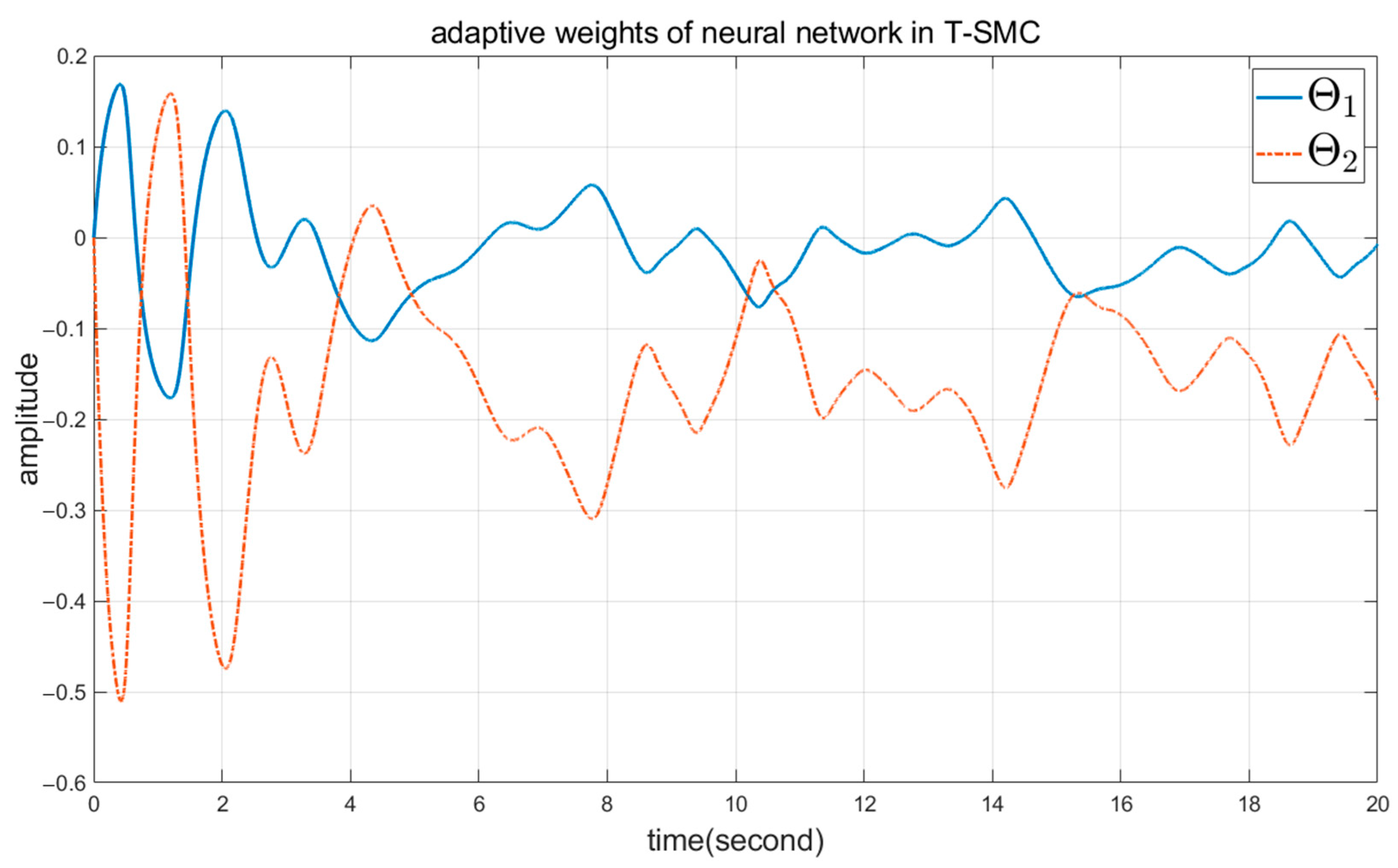
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burton, T.; Sharpe, D.; Jenkins, N.; Bossanyi, E. Wind Energy Handbook; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Manwell, J.F.; McGowan, J.; Rogers, A. Wind Energy Explained: Theory, Design and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Carlin, P.W.; Laxson, A.S.; Muljadi, E.B. The history and state of the art of variable-speed wind turbine technology. Wind Energy Int. J. Prog. Appl. Wind. Power Convers. Technol. 2003, 6, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.D.; Dhinakaran, B.; Bao, X.Y. Variable speed control of wind turbines using nonlinear and adaptive algorithms. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2000, 85, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Dou, B.; Qu, T.; Zeng, P.; Lei, L. Experimental investigation of a novel vertical axis wind turbine with pitching and self-starting function. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 217, 113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Parniani, M. Dynamic behavior and transient stability analysis of fixed speed wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumper, A.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Sudri-Andreu, A.; Villafafila-Robles, R.; Rull-Duran, J. Response of fixed speed wind turbines to system frequency disturbances. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poultangari, I.; Shahnazi, R.; Sheikhan, M. RBF Neural network based PI pitch controller for a class of 5-MW wind turbines using particle swarm optimization algorithm. ISA Trans. 2012, 51, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barambones, O.; Cortajarena, J.A.; Calvo, I.; Gonzalez de Durana, J.M.; Alkorta, P.; Karami-Mollaee, A. Variable speed wind turbine control scheme using a robust wind torque estimation. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.D.; de Battista, H.; Mantz, R.J. Wind Turbine Control Systems: Principles, Modelling and Gain Scheduling Design; Springer Science and Business Media: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Camblong, H. Digital robust control of a variable speed pitch regulated wind turbine for above rated wind speeds. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharniaa, A.; Shahnazi, R.; Jamali, A. Performance and robustness of optimal fractional fuzzy PID controllers for pitch control of a wind turbine using chaotic optimization algorithms. ISA Trans. 2018, 79, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J. Implementation of a torque and a collective pitch controller in a wind turbine simulator to characterize the dynamics at three control regions. Renew. Energy 2015, 79, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolvafaei, M.; Ganjefar, S. Maximum power extraction from a wind turbine using second-order fast terminal sliding mode control. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, M.; Zergeroglu, E.; Tatlicioglu, E. Non-linear control of variable-speed wind turbines with permanent magnet synchronous generators: A robust backstepping approach. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hand, M.M. Variable-Speed Wind Turbine Controller Systematic Design Methodology: A Comparison of Nonlinear and Linear Model-Based Designs; NREL report TP-500-25540; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund, T. Speed control of wind turbines in the stall region. In Proceedings of the 1994 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Control and Applications (CCA), Glasgow, UK, 24–26 August 1994; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, P.; Ekelund, T.; Jovik, Y.; Schmidtbauer, B. Modeling and control of variable-speed wind-turbine drive system dynamics. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1995, 15, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Stol, K.A.; Fingersh, L.J. Wind Turbine Field of State-Space Control Designs; NREL/SR-500-35061; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bossoufi, B.; Karim, M.; Lagrioui, A.; Taoussi, M.; Derouich, A. Observer backstepping control of DFIG-generators for wind turbines variable-speed: FPGA based implementation. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsisi, M. New design of adaptive model predictive control for energy conversion system with wind torque effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolvafaei, M.; Ganjefar, S. Adaptive second-order terminal PID sliding mode control design for integer-order approximation of wind turbine system for maximum power extraction. IET Control Theory Appl. 2021, 15, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyam, R.; Joo, Y.H. Memory-based ISMC design of DFIG-based wind turbine model via T-S fuzzy approach. IET Control Theory Appl. 2021, 15, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotine, J.J.E.; Li, W. Applied Nonlinear Control; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Perruquetti, W.; Barbot, J.P. Sliding Mode Control in Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Mollaee, A.; Pariz, N.; Shanechi, H.M. Position control of servomotors using neural dynamic sliding mode. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2011, 133, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Mollaee, A.; Tirandaz, H.; Barambones, O. Dynamic sliding mode position control of induction motors based load torque compensation using adaptive state observer. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 37, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenov, K.; Sarsembayev, B.; Hong Phuc, B.D.; Do, T.D. Disturbance observer-based integral sliding mode control for wind energy conversion systems. Wind Energy 2020, 23, 1026–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, F.E.; Yasami, A.; Alsubaie, H.; Alotaibi, A.; Jahanshahi, H. Control of a hydraulic generator regulating system using Chebyshev-neural-network-based non-singular fast terminal sliding mode method. Mathematics 2023, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Utkin, V.I. Chattering suppression methods in sliding mode control systems. Annu. Rev. Control 2007, 31, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, C.-C. Variable-thickness boundary layers for sliding mode control. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2008, 16, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Renn, J.-C.; Su, J.-P. Sliding mode control with varying boundary layers for an electro-hydraulic position servo system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 26, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Sliding mode-like fuzzy logic control with adaptive boundary layer for multiple-variable discrete. J. Intell. Syst. 2016, 25, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandikota, G.; Das, D.K. Disturbance observer–based adaptive boundary layer sliding mode controller for a type of nonlinear multiple-input multiple-output system. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2019, 29, 5886–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucuzzella, M.; Incremona, G.P.; Ferrara, A. Design of robust higher order sliding mode control for microgrids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2015, 5, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, R.; Yamashita, Y.; Tsubakino, D. General scheme for design of higher-order sliding-mode controller. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), Chicago, IL, USA, 1–3 July 2015; pp. 5176–5181. [Google Scholar]
- Levant, A. Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control. Int. J. Control 1993, 58, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Homogeneity approach to high-order sliding mode design. Automatica 2005, 41, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plestan, F.; Glumineau, A.; Laghrouche, S. A new algorithm for high-order sliding mode control. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2008, 18, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output-feedback control. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2010, 76, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, S.; Jiang, P. A modified super-twisting sliding mode control with inner feedback and adaptive gain schedule. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2017, 31, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, Q.R.; Bhatti, A.I.; Mufti, M.R.; Rizvi, M.A.; Awan, I. Modeling and online parameter estimation of intake manifold in gasoline engines using sliding mode observer. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2013, 32, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Second-order sliding mode observer for mechanical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.B.; Joo, Y.H. Disturbance observer-based integral fuzzy sliding-mode control and its application to wind turbine system. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fei, J.; Yang, X. Adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy neural network sliding mode control of nonlinear systems using improved extended state observer. Mathematics 2023, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Mollaee, A.; Barambones, O. Sliding observer in sliding mode control of multi-inputs fractional order chaotic systems. Pramana–J. Phys. 2022, 96, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Kung, T.-T.; Chang, K.-M.; Chen, S.-Y. Observer-based adaptive sliding mode control for pneumatic servo system. Precis. Eng. 2013, 37, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, M. Back-stepping sliding mode control for missile systems based on an extended state observer. IET Control Theory Appl. 2011, 5, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Saif, M. Sliding mode observer for nonlinear uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2001, 46, 2012–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mseddi, A.; Naifar, O.; Rhaima, M.; Mchiri, L.; Ben Makhlouf, A. Robust control for torque minimization in wind hybrid generators: An H-Infinity approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchaib, A.; Rachid, A.; Audrezet, E.; Tadjine, M. Real-time sliding-mode observer and control of an induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1999, 46, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhezzar, B.; Siguerdidjane, H. Nonlinear control of a variable-speed wind turbine using a two-mass model. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 26, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y. Dynamic response regulation of non-linear feedback linearised wind turbine using a two-mass. IET Control Theory Appl. 2017, 11, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Plestan, F. Adaptive sliding mode control of floating offshore wind turbine equipped by permanent magnet synchronous generator. Wind Energy 2021, 24, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tao, L.; Xu, B. Linear parameter varying observer-based adaptive dynamic surface sliding mode control for PMSM. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossanyi, E.A.; Wright, A.D.; Fleming, P.A. Controller Field Tests on the NREL CART2 Turbine; No. NREL/TP-5000-49085; National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Notation | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Notation | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karami-Mollaee, A.; Barambones, O. On Neural Observer in Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Wind Generator. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12142246
Karami-Mollaee A, Barambones O. On Neural Observer in Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Wind Generator. Mathematics. 2024; 12(14):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12142246
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarami-Mollaee, Ali, and Oscar Barambones. 2024. "On Neural Observer in Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Wind Generator" Mathematics 12, no. 14: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12142246
APA StyleKarami-Mollaee, A., & Barambones, O. (2024). On Neural Observer in Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Wind Generator. Mathematics, 12(14), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12142246









