PSSegNet: Segmenting the P- and S-Phases in Microseismic Signals through Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
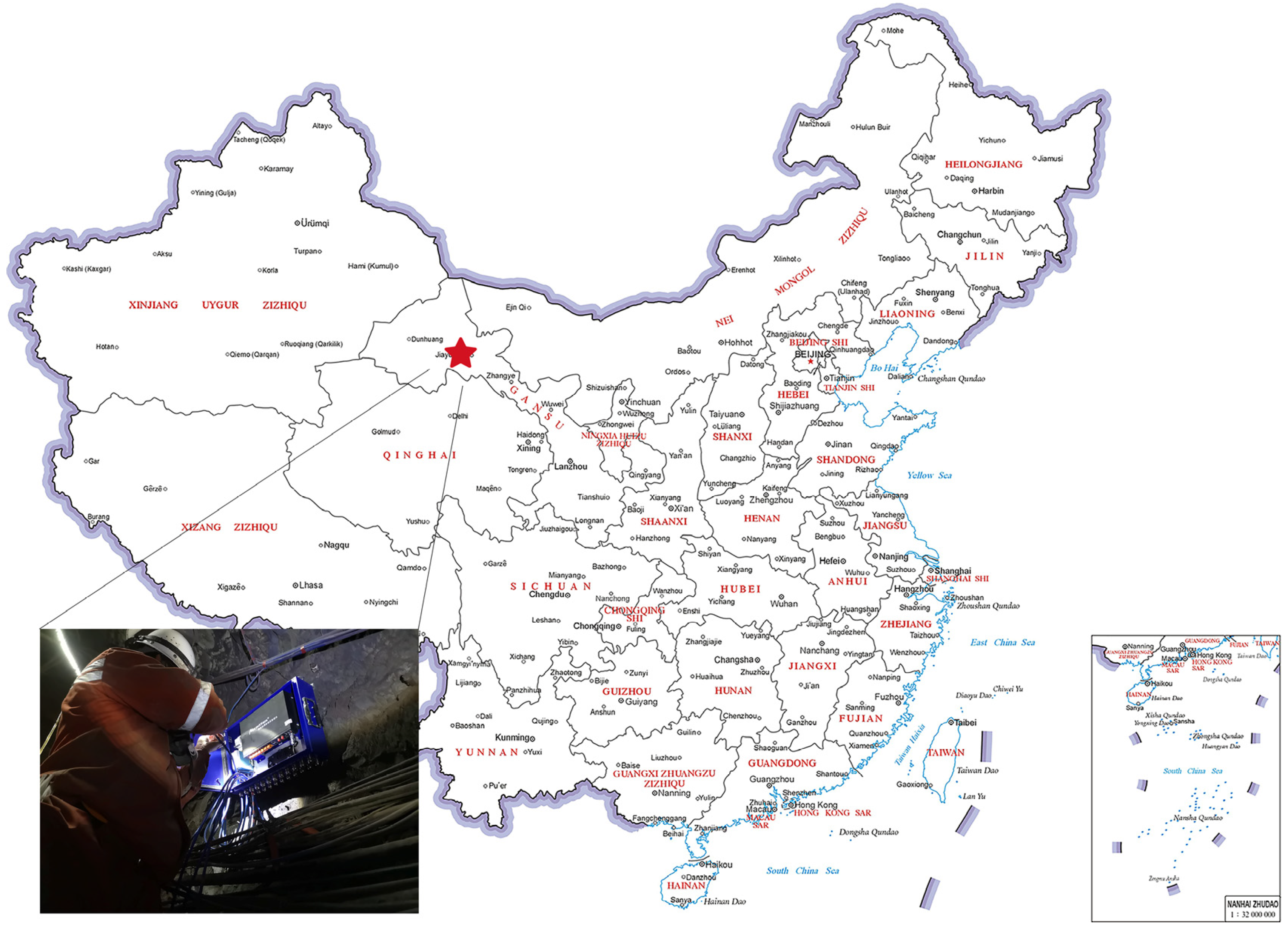
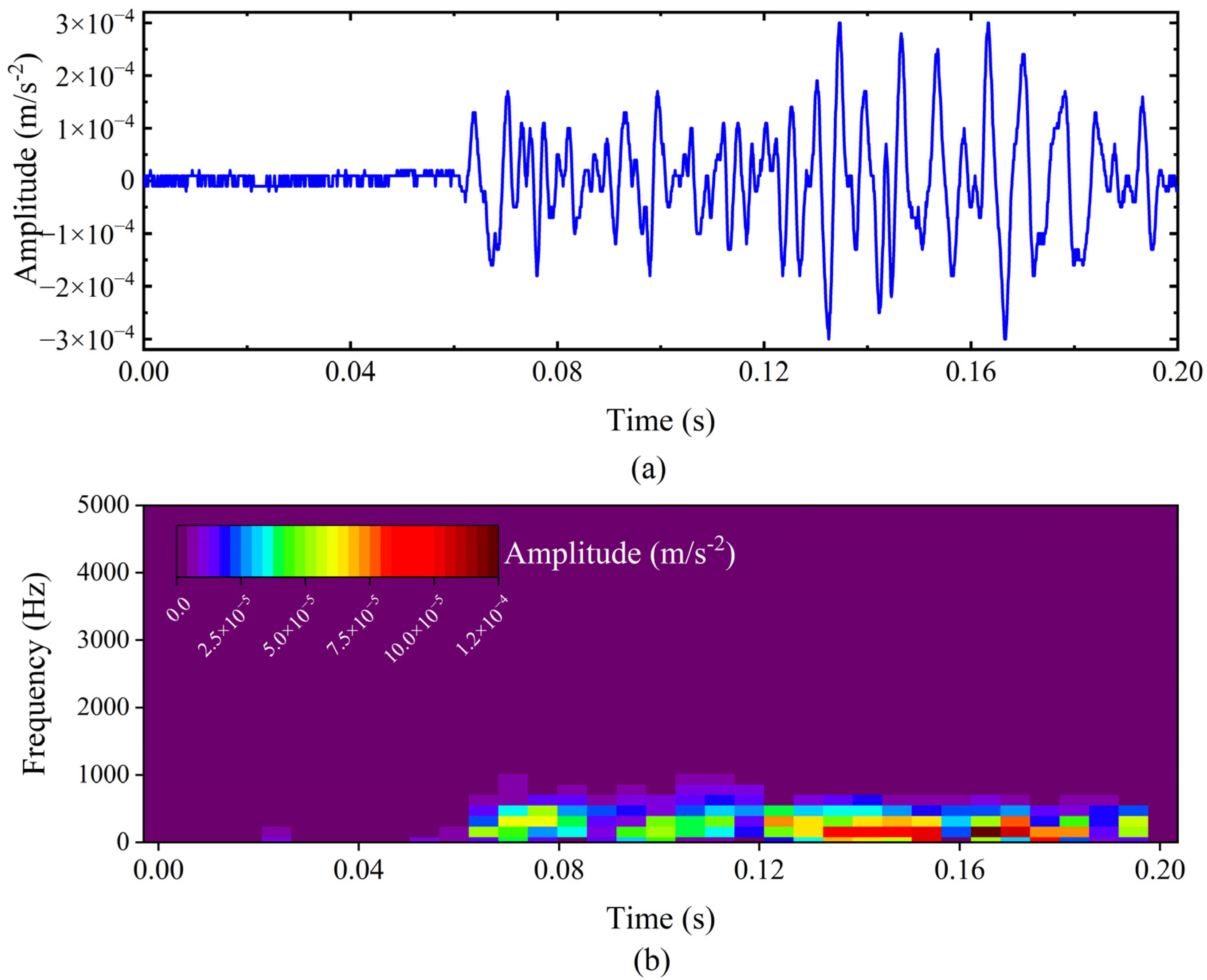
2.1. Dataset
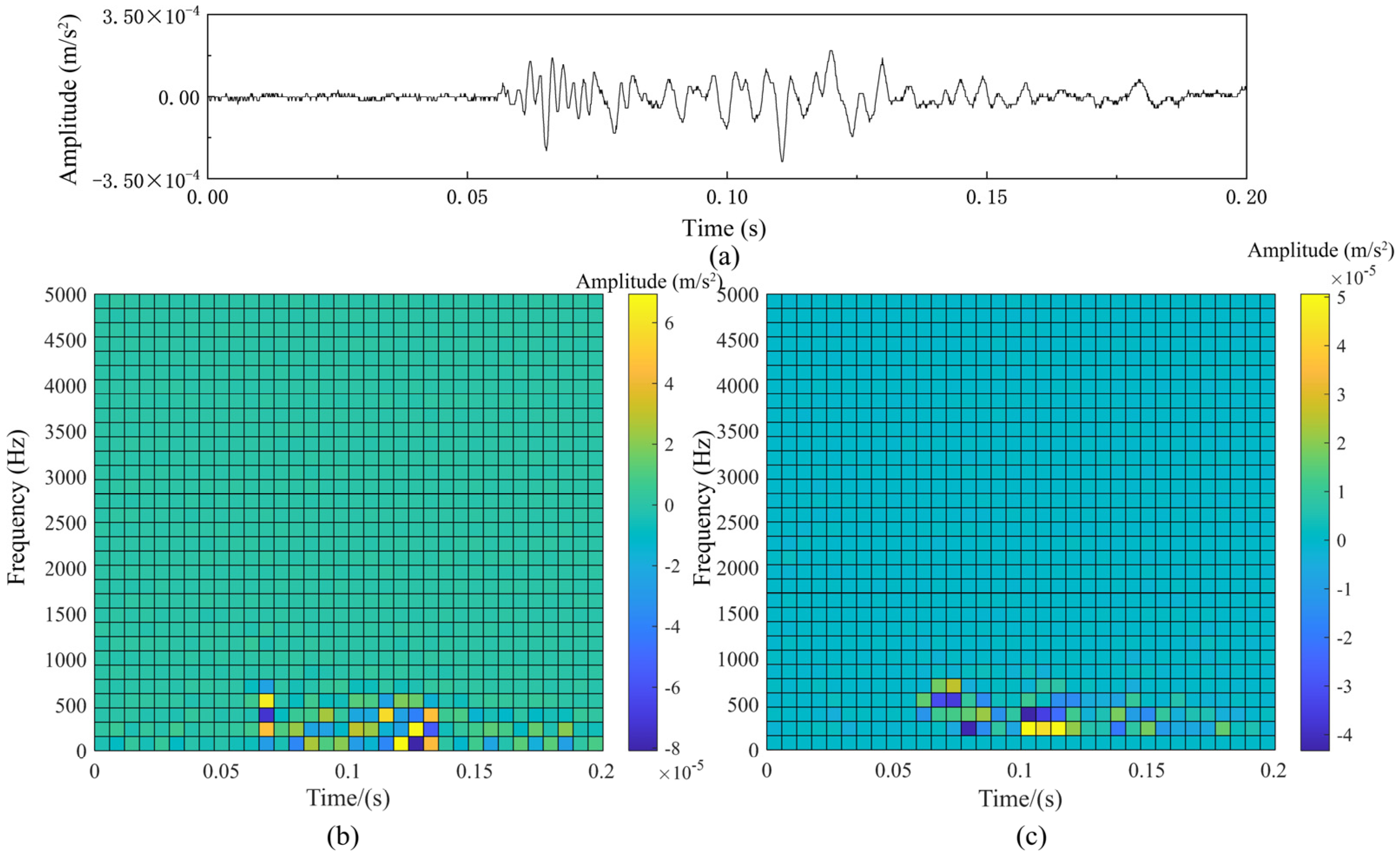
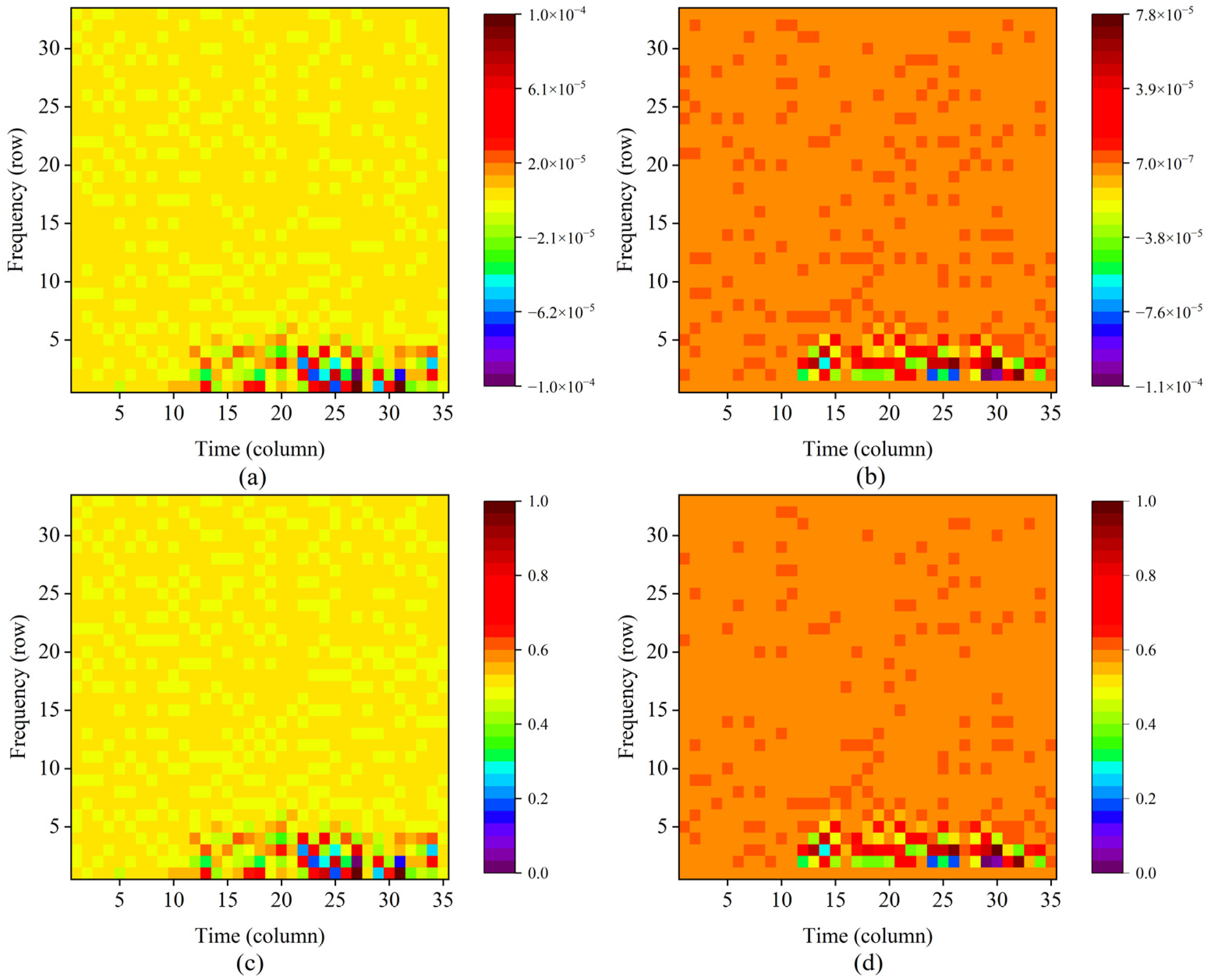
2.2. Mask Design
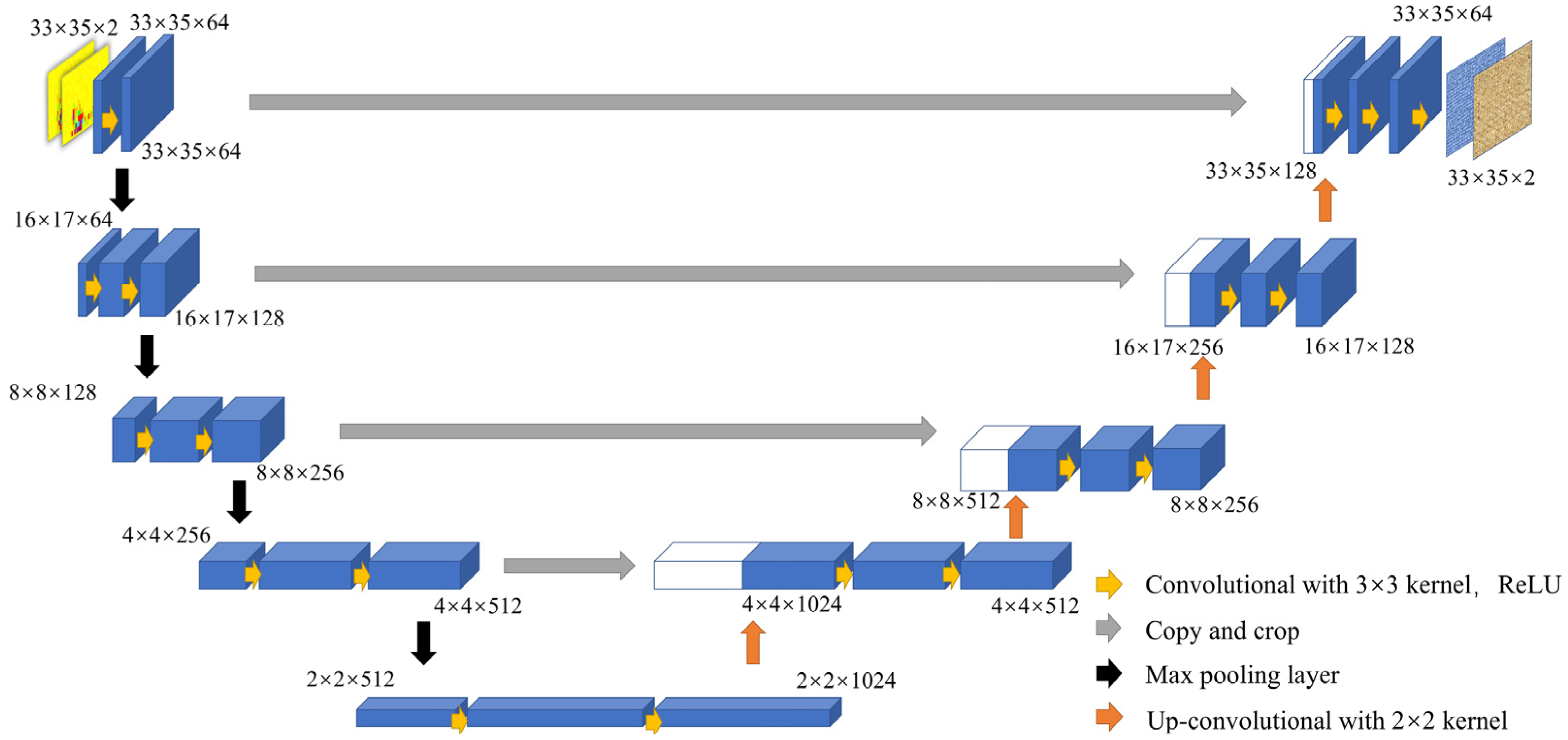
2.3. PSSegNet
3. Results
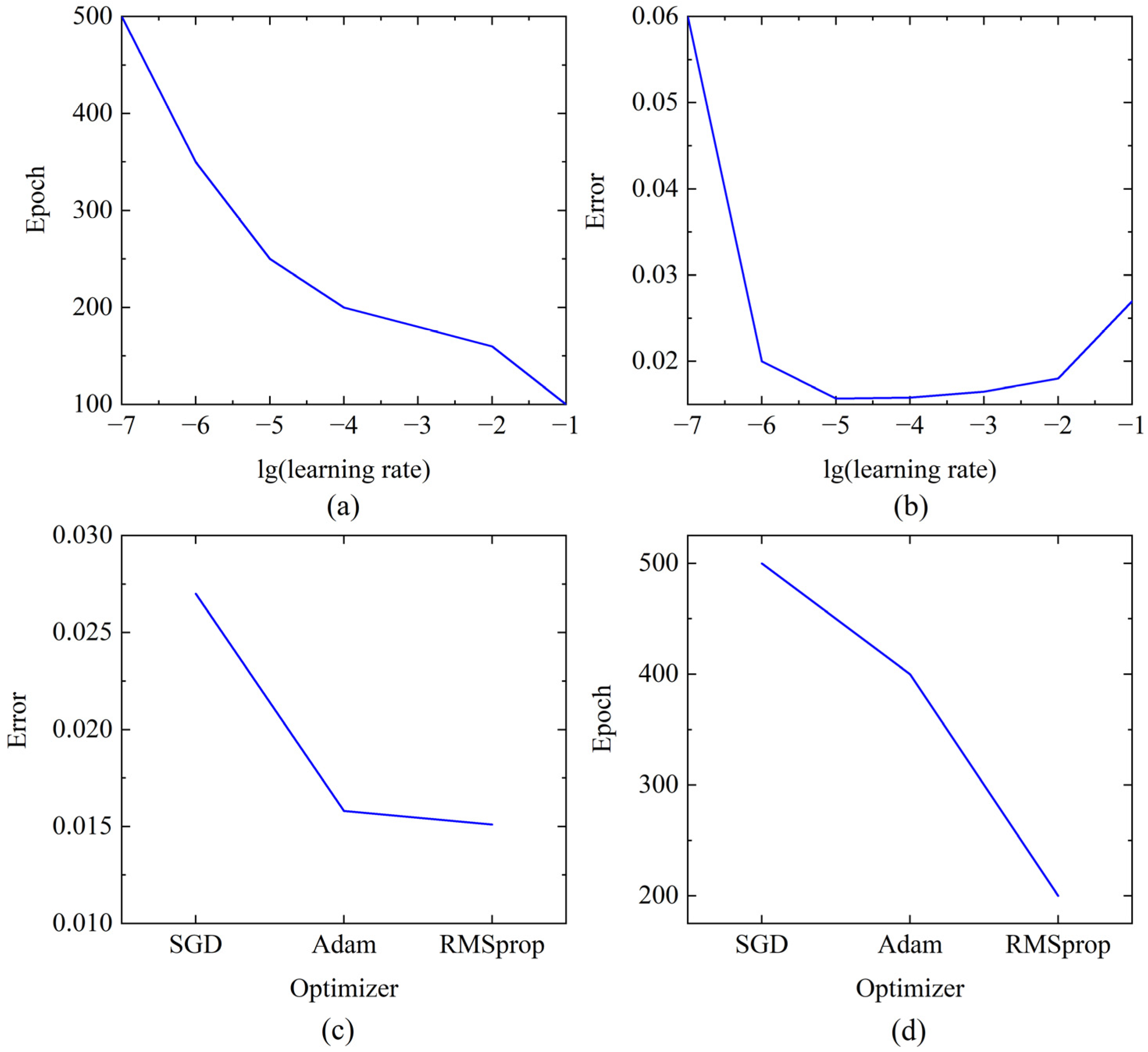
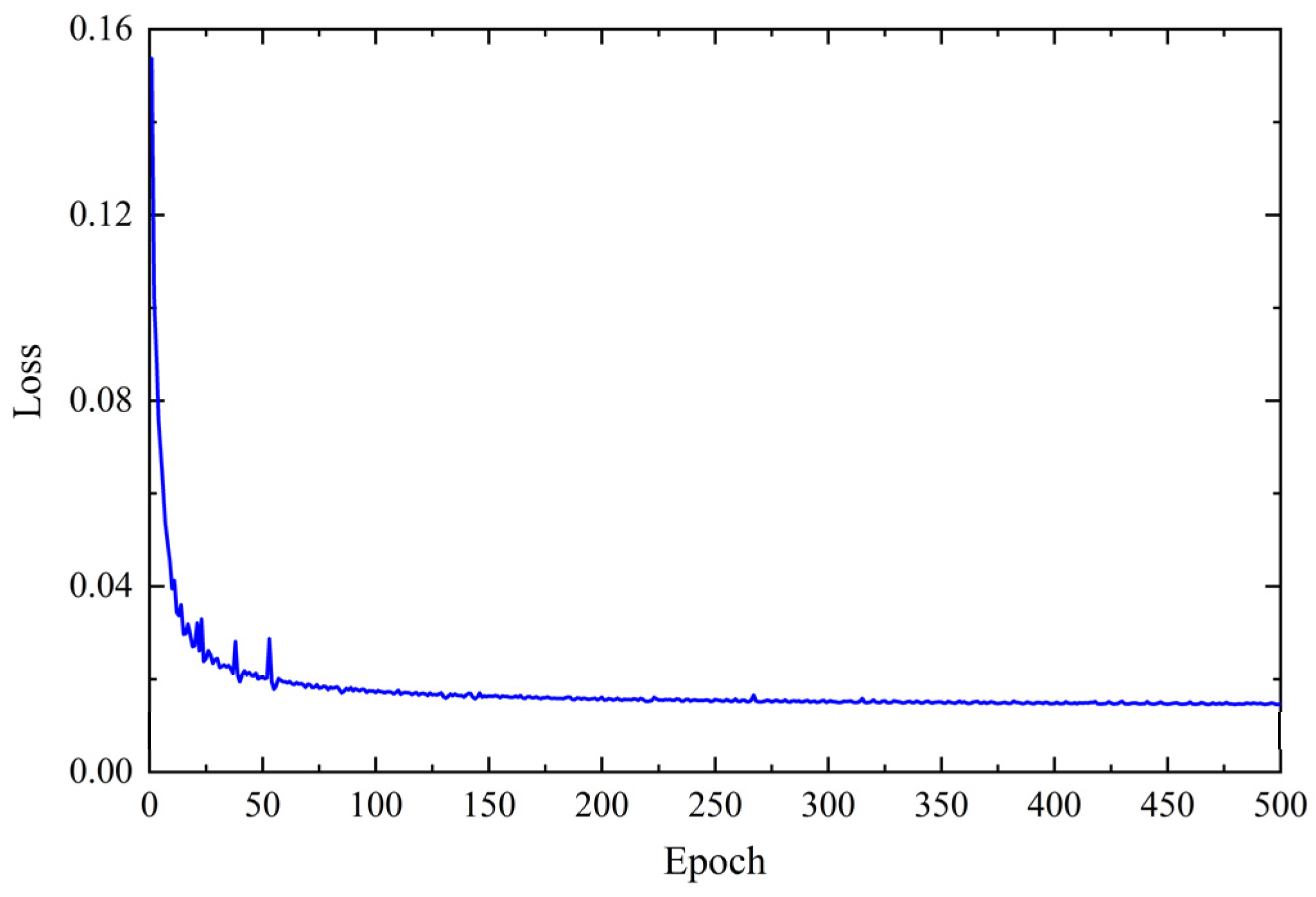
3.1. PSSegNet Traning
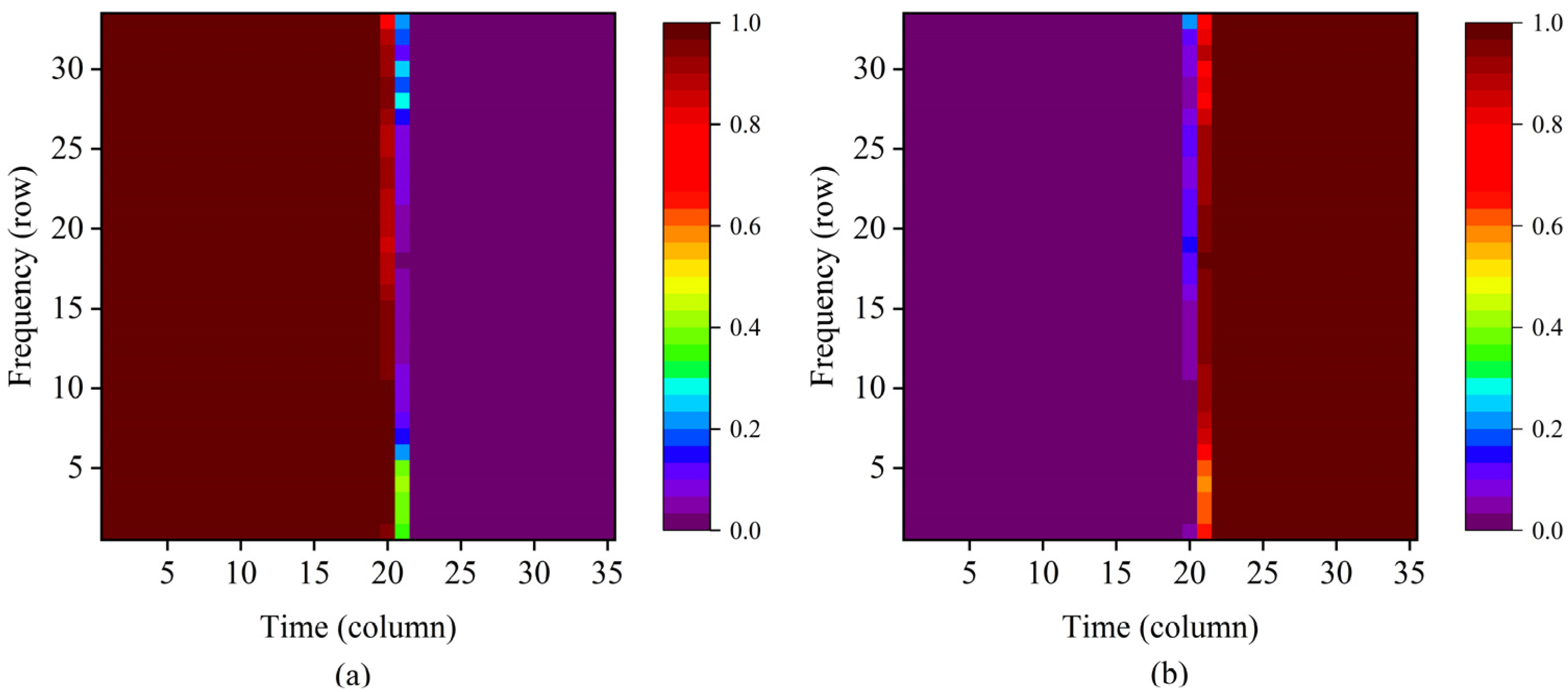
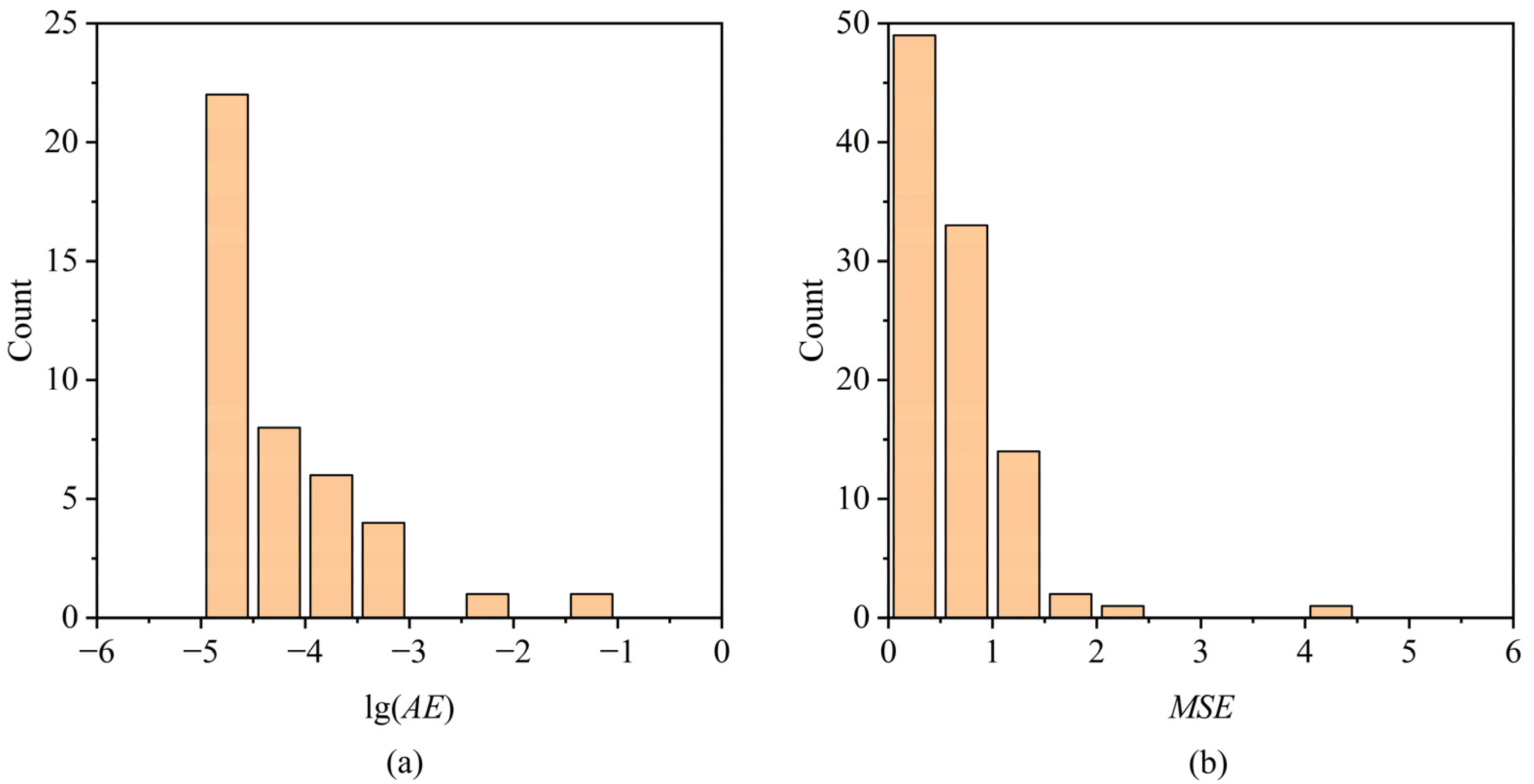
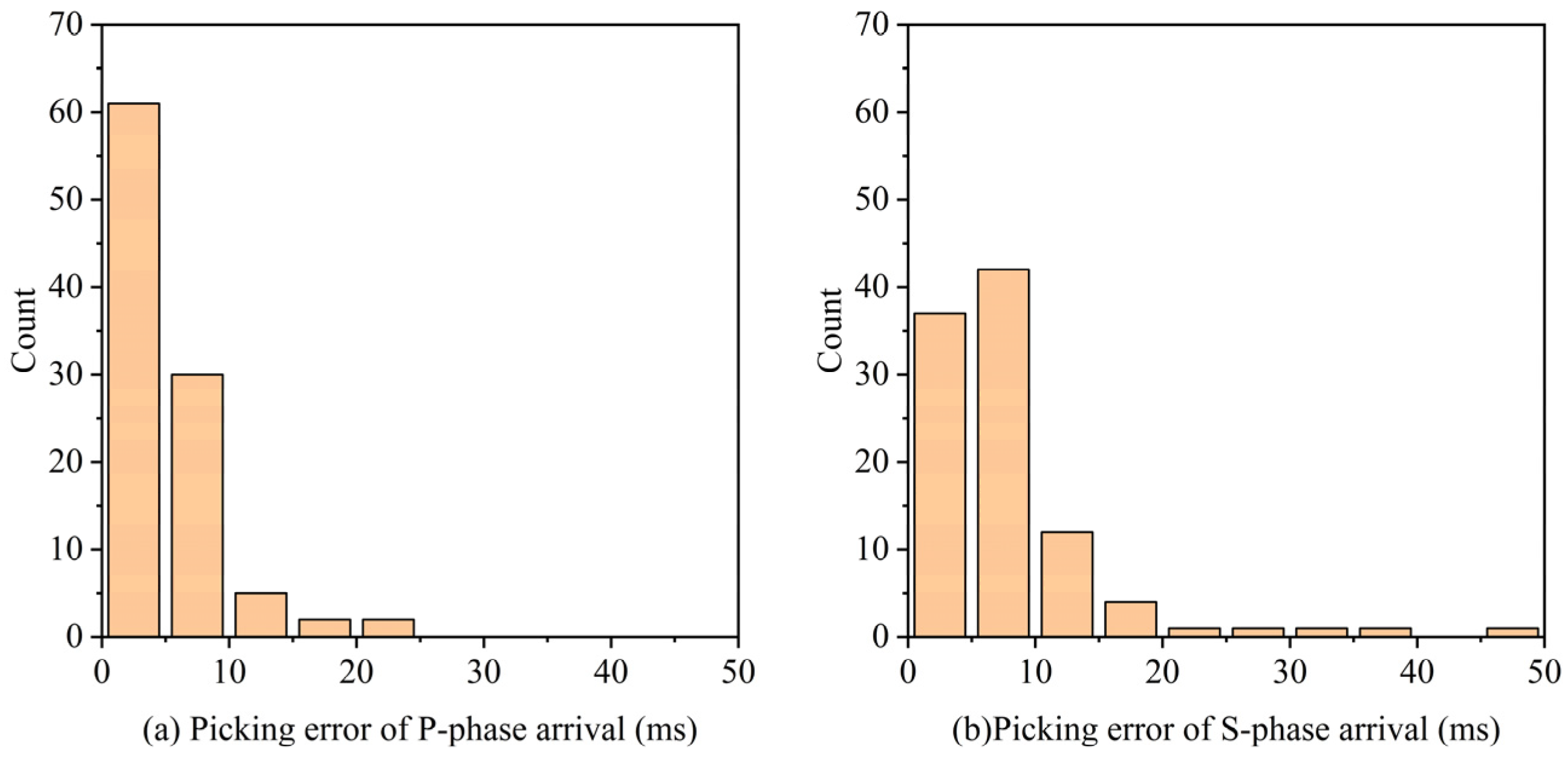
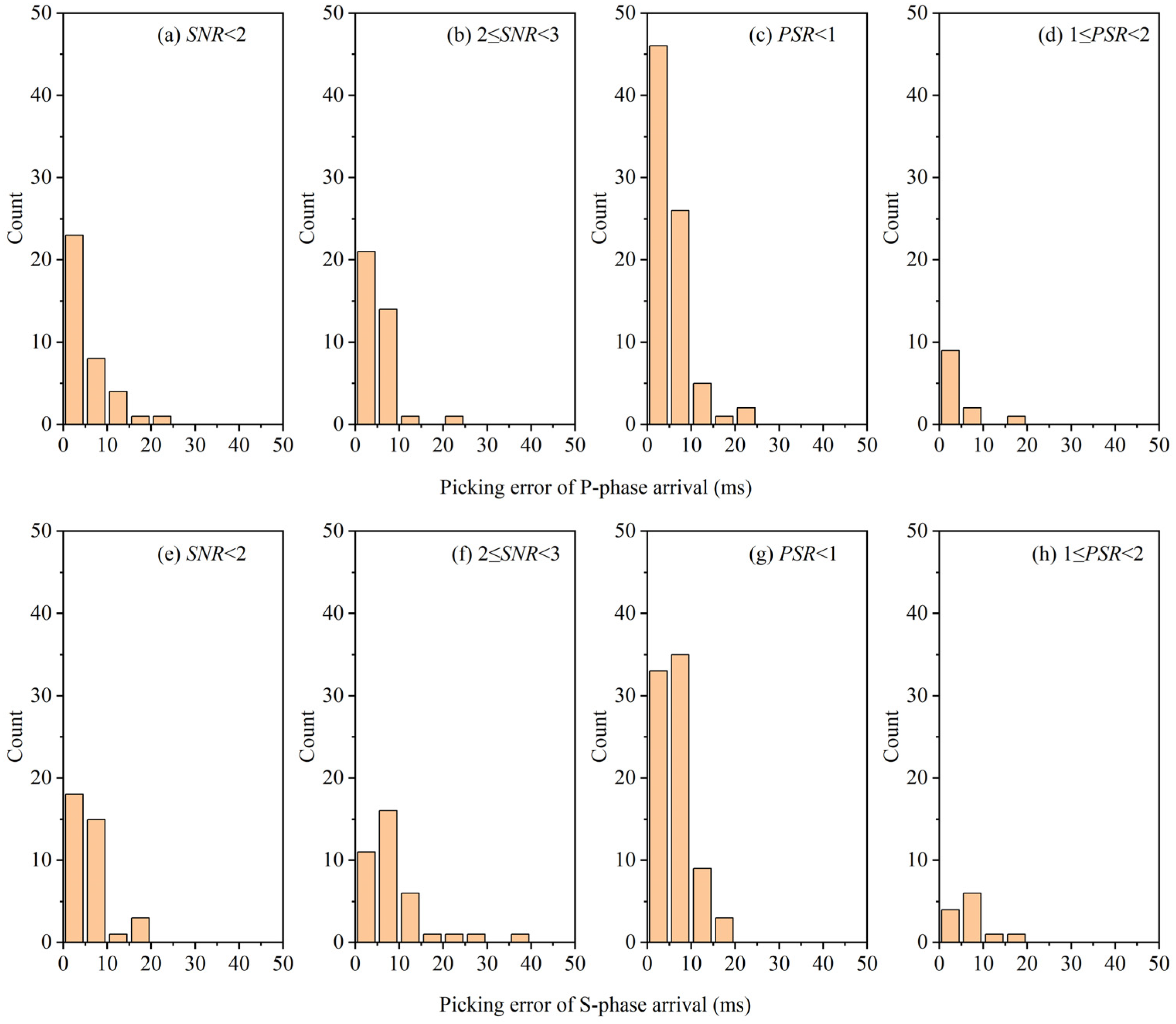
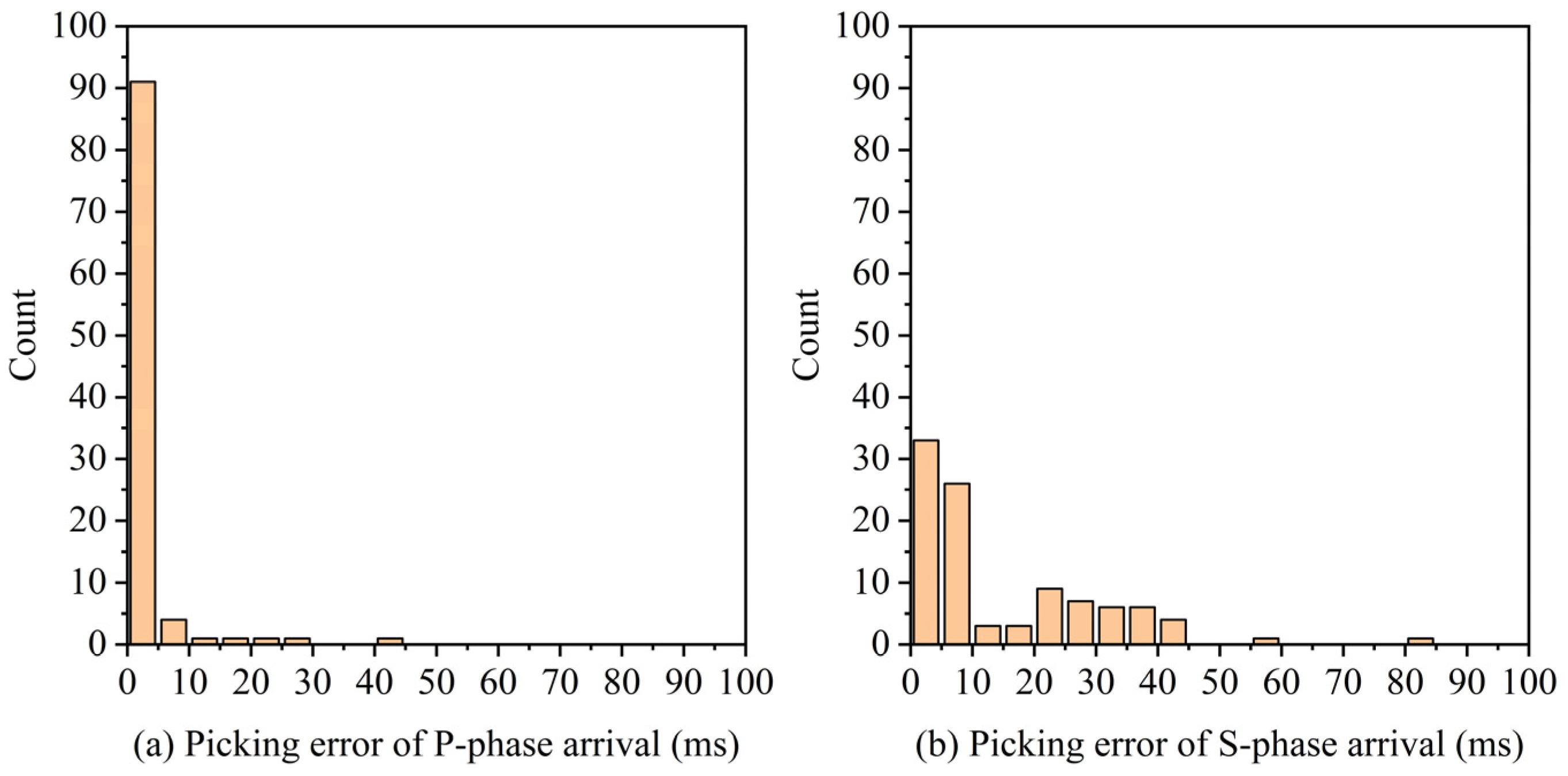
3.2. Testing Results
3.3. Generalization
3.4. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shi, D. Diffusion Characteristics of Airflow and CO in the Dead-End Tunnel with Different Ventilation Parameters after Tunneling Blasting. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36269–36283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralston, J.; Reid, D.; Hargrave, C.; Hainsworth, D. Sensing for Advancing Mining Automation Capability: A Review of Underground Automation Technology Development. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Peng, P.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. Efficient and Accurate Mapping Method of Underground Metal Mines Using Mobile Mining Equipment and Solid-State Lidar. Measurement 2023, 221, 113581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xie, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Ruan, S.; Yang, P.; Fang, Z. Strengthening Mechanism of Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag on the Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Modified Magnesium Slag-Based Cemented Backfilling Material. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 174, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.V. Automatic Earthquake Recognition and Timing from Single Traces. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1978, 68, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Li, Z.; Qin, N.; Jin, W. Adaptive Picking of Microseismic Event Arrival Using a Power Spectrum Envelope. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Arrowsmith, S.J.; Anderson, D.N. Detection of Short Time Transients from Spectrograms Using Scan Statistics. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2010, 100, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaci, S. The Use of Wavelet-Based Denoising Techniques to Enhance the First-Arrival Picking on Seismic Traces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4558–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikesell, T.D.; Van Wijk, K.; Ruigrok, E.; Lamb, A.; Blum, T.E. A Modified Delay-Time Method for Statics Estimation with the Virtual Refraction. GEOPHYSICS 2012, 77, A29–A33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, F. FIRST ARRIVAL PICKING ON COMMON-OFFSET TRACE COLLECTIONS FOR AUTOMATIC ESTIMATION OF STATIC CORRECTIONS*. Geophys. Prospect. 1985, 33, 1212–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbione, J.I.; Velis, D. Automatic First-Breaks Picking: New Strategies and Algorithms. Geophysics 2010, 75, V67–V76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küperkoch, L.; Meier, T.; Lee, J.; Friederich, W.; Group, E.W. Automated Determination of P-Phase Arrival Times at Regional and Local Distances Using Higher Order Statistics. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragiotis, C.D.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J.; Panas, S.M. PAI-S/K: A Robust Automatic Seismic P Phase Arrival Identification Scheme. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragiotis, C.D.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J.; Rekanos, I.T.; Panas, S.M. Automatic P Phase Picking Using Maximum Kurtosis and kappa-Statistics Criteria. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N. A Method for Reading and Checking Phase Time in Auto-Processing System of Seismic Wave Data. Zisin1 1985, 38, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, M. Comparison of Manual and Automatic Onset Time Picking. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2000, 90, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, R.; Van Eck, T. Robust Automatic P-Phase Picking: An on-Line Implementation in the Analysis of Broadband Seismogram Recordings. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1999, 113, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronicke, J. The Influence of High Frequency Uncorrelated Noise on First-Break Arrival Times and Crosshole Traveltime Tomography. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. JEEG 2007, 12, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meersman, K.; Kendall, J.-M.; Van Der Baan, M. The 1998 Valhall Microseismic Data Set: An Integrated Study of Relocated Sources, Seismic Multiplets, and S-Wave Splitting. GEOPHYSICS 2009, 74, B183–B195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanidis, V.; Papadimitriou, P. Estimation of Arrival-Times in Intense Seismic Sequences Using a Master-Events Methodology Based on Waveform Similarity: Master-Events Method Using Waveform Similarity. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 187, 889–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bose, S.; Valero, H.-P.; Shenoy, R.G.; Ounadjela, A. Detecting Small Amplitude Signal and Transit Times in High Noise: Application to Hydraulic Fracture Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; pp. IV-530–IV-533. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, X.; Van Der Lee, S.; Lloyd, S. AIMBAT: A Python/Matplotlib Tool for Measuring Teleseismic Arrival Times. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2013, 84, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Azuma, T.; Imoto, H.; Raufy, R.; Lin, H.; Nakamura, H.; Tamano, S.; Takagi, S.; Umemura, S.; Sakuma, I.; et al. Novel Automatic First-Arrival Picking Method for Ultrasound Sound-Speed Tomography. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 07HF10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criss, C.J.; Kappius, R.; Cunningham, D. First Arrival Picking Using Image Processing Methods. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2003; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Denver, CO, USA, 2003; pp. 1984–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mousa, W.A.; Al-Shuhail, A.A.; Al-Lehyani, A. A New Technique for First-Arrival Picking of Refracted Seismic Data Based on Digital Image Segmentation. GEOPHYSICS 2011, 76, V79–V89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrot, S. Optimal Measurement of Relative and Absolute Delay Times by Simulated Annealing. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 151, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rawlinson, N.; Kennett, B.L.N. Rapid Estimation of Relative and Absolute Delay Times across a Network by Adaptive Stacking. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiana-Merino, J.J.; Rosa-Herranz, J.L.; Parolai, S. Seismic P Phase Picking Using a Kurtosis-Based Criterion in the Stationary Wavelet Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3815–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Automatic P-Wave Arrival Detection and Picking with Multiscale Wavelet Analysis for Single-Component Recordings. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2003, 93, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, J.; Eaton, D.W. A Review and Appraisal of Arrival-Time Picking Methods for Downhole Microseismic Data. Geophysics 2016, 81, KS71–KS91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, J.; Eaton, D.; Onge, A.S. Automatic Event-Detection and Time-Picking Algorithms for Downhole Microseismic Data Processing. In Proceedings of the 4th EAGE Passive Seismic Workshop, European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17–20 March 2013; p. cp-337. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; He, C.; Yu, J.; Feng, G. A Combined Method for Automatic Microseismic Event Detection and Arrival Picking. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2014; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Denver, CO, USA, 2014; pp. 2335–2340. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shang, X.; Morales-Esteban, A.; Wang, Z. Identifying P Phase Arrival of Weak Events: The Akaike Information Criterion Picking Application Based on the Empirical Mode Decomposition. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 100, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Automatic Microseismic Event Picking via Unsupervised Machine Learning. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 222, 1750–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Peng, S.; Jiang, T. An Automatic Microseismic or Acoustic Emission Arrival Identification Scheme with Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 212, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, S.; Hu, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Van Nguyen, H. A Robust First-Arrival Picking Workflow Using Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. GEOPHYSICS 2020, 85, U109–U119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, Z.E.; Meier, M.-A.; Hauksson, E. P Wave Arrival Picking and First-Motion Polarity Determination with Deep Learning. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 5120–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhu, T.; Gao, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, J. AEnet: Automatic Picking of P-Wave First Arrivals Using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5293–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xu, X.; PAn, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. The CGAS Deep Learning Algorithm for P-Wave Arrival Time Picking of Mining Microseismic Events. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 102961–102970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Peng, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y. PickCapsNet: Capsule Network for Automatic P-Wave Arrival Picking. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, O.M.; Chen, Y. Earthquake Detection and P-Wave Arrival Time Picking Using Capsule Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6234–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Peng, P. Accurate Identification of Microseismic P- and S-Phase Arrivals Using the Multi-Step AIC Algorithm. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 150, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, T.; Deichmann, N.; Kissling, E.; Husen, S. Automatic S-Wave Picker for Local Earthquake Tomography. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1906–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küperkoch, L.; Meier, T.; Brüstle, A.; Lee, J.; Friederich, W.; EGELADOS working group. Automated Determination of S-Phase Arrival Times Using Autoregressive Prediction: Application to Local and Regional Distances: Automatic S-Phase Picking. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 188, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, A.; Sokos, E.; Martakis, N.; Paraskevopoulos, P.; Tselentis, G.-A. A New Automatic S-Onset Detection Technique: Application in Local Earthquake Data. GEOPHYSICS 2013, 78, KS1–KS11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Beroza, G.C. PhaseNet: A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Seismic Arrival-Time Picking Method. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 216, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yue, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, S. Hybrid Event Detection and Phase-Picking Algorithm Using Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2019, 90, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Ellsworth, W.L.; Zhu, W.; Chuang, L.Y.; Beroza, G.C. Earthquake Transformer—An Attentive Deep-Learning Model for Simultaneous Earthquake Detection and Phase Picking. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, H.; Schurr, B. DeepPhasePick: A Method for Detecting and Picking Seismic Phases from Local Earthquakes Based on Highly Optimized Convolutional and Recurrent Deep Neural Networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 227, 1268–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Tai, K.S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Bailis, P.; Beroza, G.C. An End-To-End Earthquake Detection Method for Joint Phase Picking and Association Using Deep Learning. JGR Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Mousavi, S.M.; Beroza, G.C. Seismic Signal Denoising and Decomposition Using Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9476–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

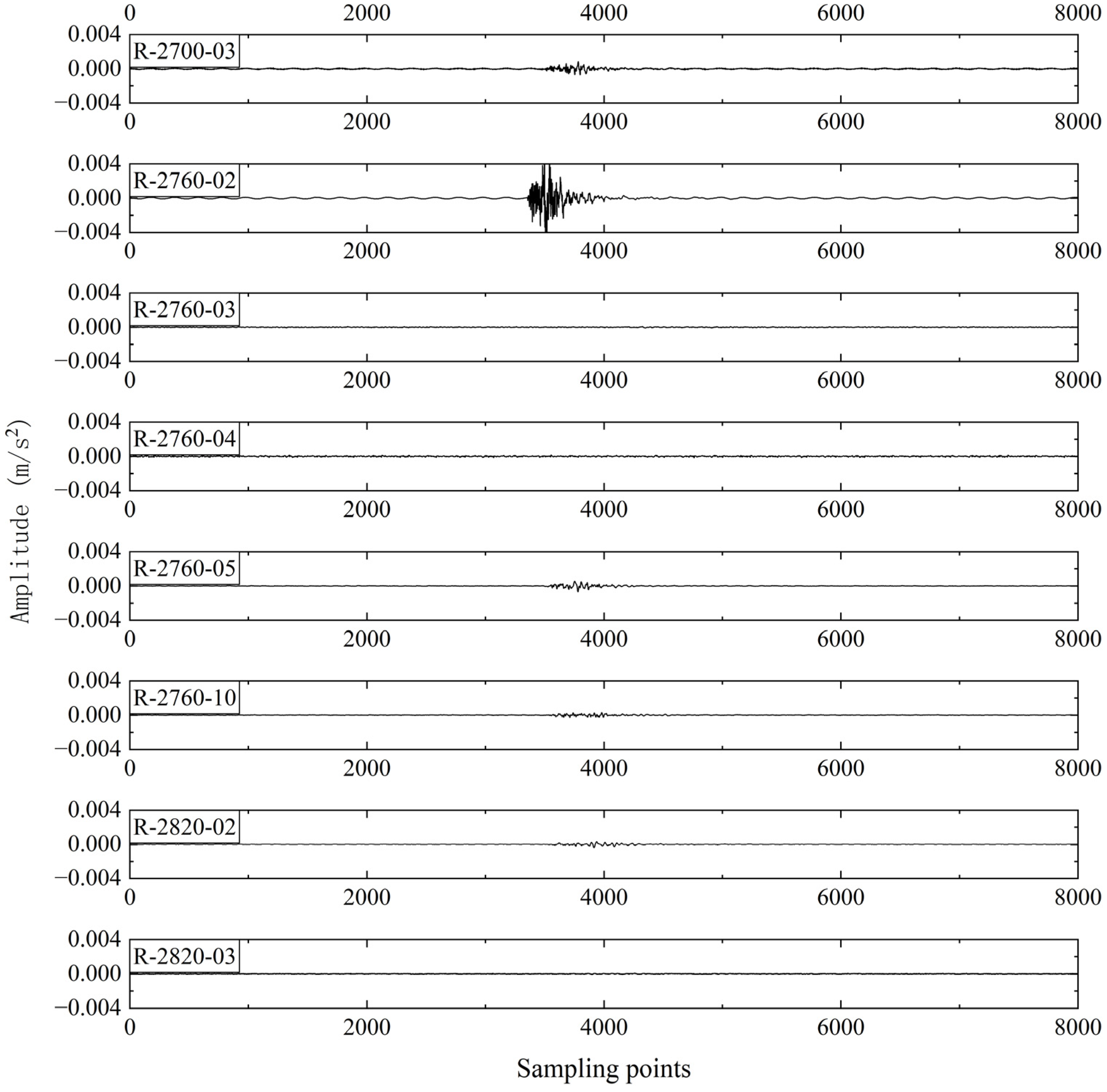



| Sensor | X | Y | Z | Sensor | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-2820-01 | 12,110.576 | 8615.488 | 2821.972 | R-2700-01 | 12,236.783 | 8583.922 | 2702.058 |
| R-2820-02 | 12,000.213 | 8670.474 | 2822.144 | R-2700-02 | 12,241.372 | 8629.458 | 2701.662 |
| R-2820-03 | 11,958.893 | 8761.138 | 2818.54 | R-2700-03 | 12,191.075 | 8622.778 | 2702.345 |
| R-2820-04 | 12,018.628 | 8843.893 | 2821.774 | R-2700-04 | 12,164.519 | 8675.117 | 2702.125 |
| R-2820-05 | 12,051.731 | 8804.489 | 2822.346 | R-2700-05 | 12,108.346 | 8685.187 | 2702.04 |
| R-2820-06 | 12,090.328 | 8744.155 | 2822.469 | R-2700-06 | 12,085.612 | 8726.988 | 2702.401 |
| R-2760-01 | 12,181.087 | 8573.237 | 2759.917 | R-2700-07 | 12,138.957 | 8759.831 | 2702.275 |
| R-2760-02 | 12,094.117 | 8619.037 | 2759.961 | R-2700-08 | 12,047.007 | 8741.941 | 2702.096 |
| R-2760-03 | 12,039.003 | 8679.226 | 2758.961 | R-2700-09 | 12,025.402 | 8792.233 | 2702.281 |
| R-2760-04 | 11,990.874 | 8733.964 | 2759.257 | R-2700-10 | 11,966.233 | 8887.393 | 2702.286 |
| R-2760-05 | 11,931.208 | 8875.974 | 2758.237 | R-2700-11 | 11,921.350 | 8964.683 | 2702.219 |
| R-2760-06 | 11,880.954 | 8917.851 | 2757.815 | R-2700-12 | 11,842.552 | 9050.731 | 2701.619 |
| R-2760-07 | 11,968.433 | 8859.945 | 2758.346 | R-2700-13 | 11,833.117 | 9118.063 | 2702.046 |
| R-2760-08 | 12,039.310 | 8810.887 | 2758.791 | R-2640-14 | 12,150.326 | 8702.537 | 2647.752 |
| R-2760-09 | 12,096.173 | 8750.540 | 2759.295 | R-2640-15 | 12,085.930 | 8660.176 | 2648.047 |
| R-2760-10 | 12,142.769 | 8704.456 | 2758.919 | R-2640-16 | 12,185.542 | 8661.853 | 2647.841 |
| Number | Layer | Output | Kernel/Stride | Copy and Crop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv 1 | 33 × 35 × 64 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 2 | Conv 2 | 33 × 35 × 64 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 3 | Max pooling 1 | 16 × 17 × 64 | 2 × 2/2 | |
| 4 | Conv 3 | 16 × 17 × 128 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 5 | Conv 4 | 16 × 17 × 128 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 6 | Max pooling 2 | 8 × 8 × 128 | 2 × 2/2 | |
| 7 | Conv 5 | 8 × 8 × 256 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 8 | Conv 6 | 8 × 8 × 256 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 9 | Max pooling 3 | 4 × 4 × 256 | 2 × 2/2 | |
| 10 | Conv 7 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 11 | Conv 8 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 12 | Max pooling 4 | 2 × 2 × 512 | 2 × 2/2 | |
| 13 | Conv 9 | 2 × 2 × 1024 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 14 | Conv 10 | 2 × 2 × 1024 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 15 | Up-Conv 1 | 4 × 4 × 1024 | 2 × 2/1 | Conv 8 |
| 16 | Conv 11 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 17 | Conv 12 | 4 × 4 × 512 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 18 | Up-Conv 2 | 8 × 8 × 512 | 2 × 2/1 | Conv 6 |
| 19 | Conv 13 | 8 × 8 × 256 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 20 | Conv 14 | 8 × 8 × 256 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 21 | Up-Conv 3 | 16 × 17 × 256 | 2 × 2/1 | Conv 4 |
| 22 | Conv 15 | 16 × 17 × 128 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 23 | Conv 16 | 16 × 17 × 128 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 24 | Up-Conv 4 | 33 × 35 × 128 | 2 × 2/1 | Conv 2 |
| 25 | Conv 17 | 33 × 35 × 64 | 3 × 3/1 | |
| 26 | Conv 18 | 33 × 35 × 64 | 3 × 3/1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Xu, X.; Rao, D.; Peng, P.; Wang, J.; Tian, S. PSSegNet: Segmenting the P- and S-Phases in Microseismic Signals through Deep Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12010130
He Z, Xu X, Rao D, Peng P, Wang J, Tian S. PSSegNet: Segmenting the P- and S-Phases in Microseismic Signals through Deep Learning. Mathematics. 2024; 12(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhengxiang, Xingliang Xu, Dijun Rao, Pingan Peng, Jiaheng Wang, and Suchuan Tian. 2024. "PSSegNet: Segmenting the P- and S-Phases in Microseismic Signals through Deep Learning" Mathematics 12, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12010130
APA StyleHe, Z., Xu, X., Rao, D., Peng, P., Wang, J., & Tian, S. (2024). PSSegNet: Segmenting the P- and S-Phases in Microseismic Signals through Deep Learning. Mathematics, 12(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12010130










