Assisting the Human Embryo Viability Assessment by Deep Learning for In Vitro Fertilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We developed a novel architecture, a feature supplementation-based blastocyst segmentation network (FSBS-Net), for the multiclass segmentation of blastocyst images to confirm blastocyst viability for successful IVF.
- FSBS-Net uses effective feature supplementation (FS) mechanisms at different scales and stages of the network to enhance the blastocyst segmentation performance. In addition, FSBS-Net uses an ascending channel convolutional block (ACCB), which applies ascending channels to the convolved initial potential spatial information and transfers them to the deep stage of the network to reduce spatial loss.
- The proposed method (FSBS-Net) was evaluated using a publicly available blastocyst segmentation database. FSBS-Net exhibited promising performance, requiring a small number of parameters (2.01 million).
2. Material and Methods
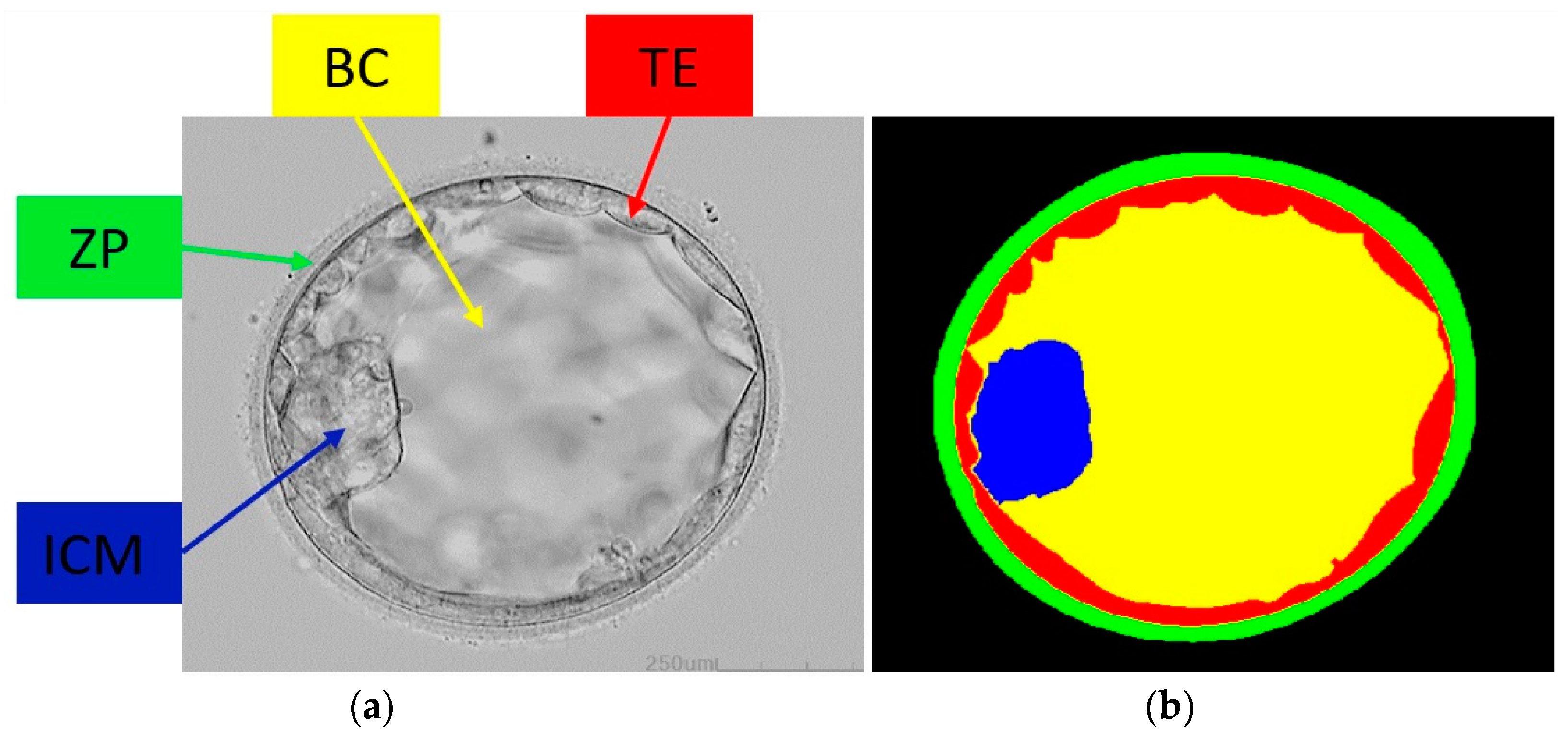
2.1. Database
2.2. Method
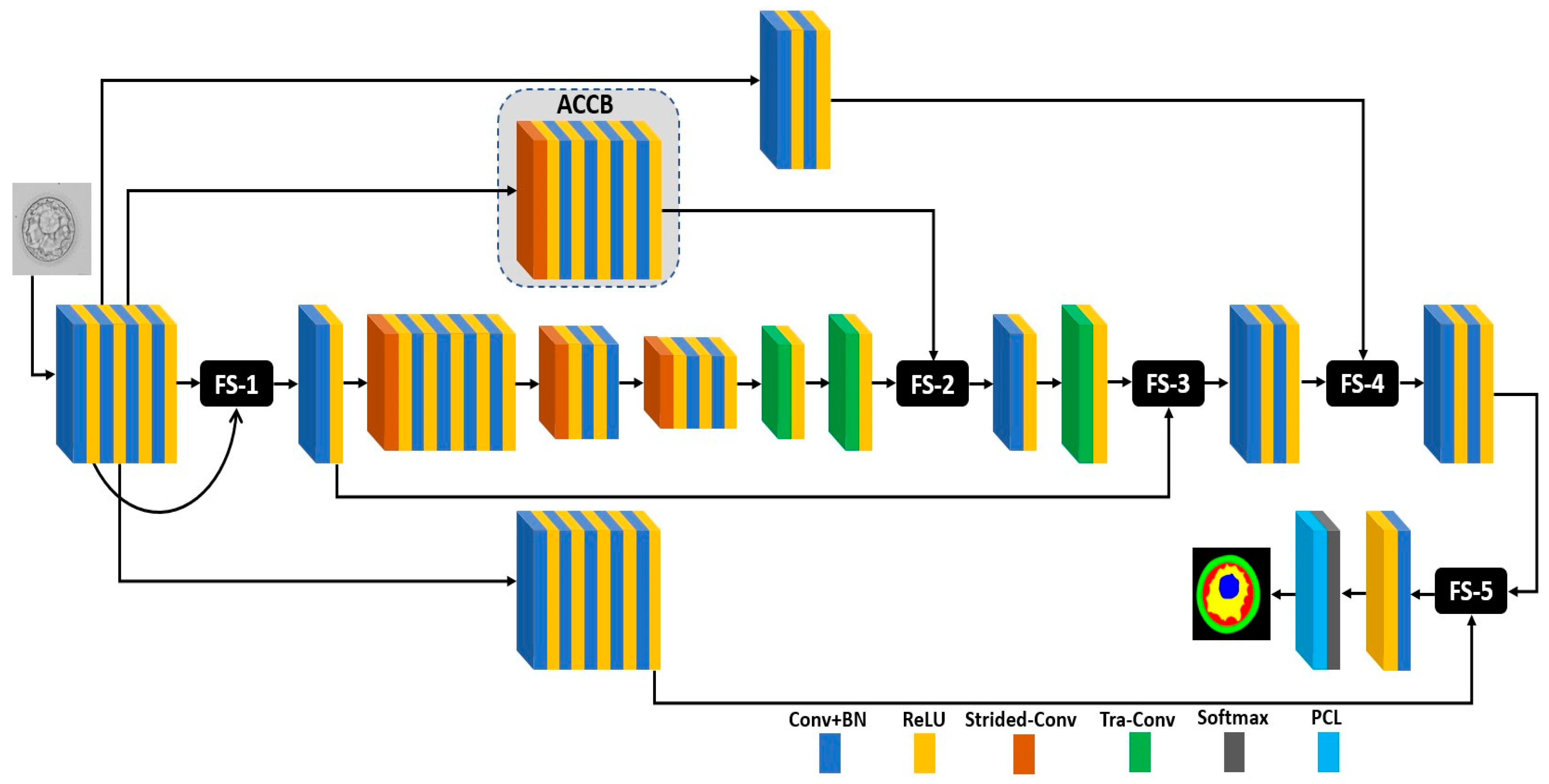
2.2.1. Summary of Proposed Method
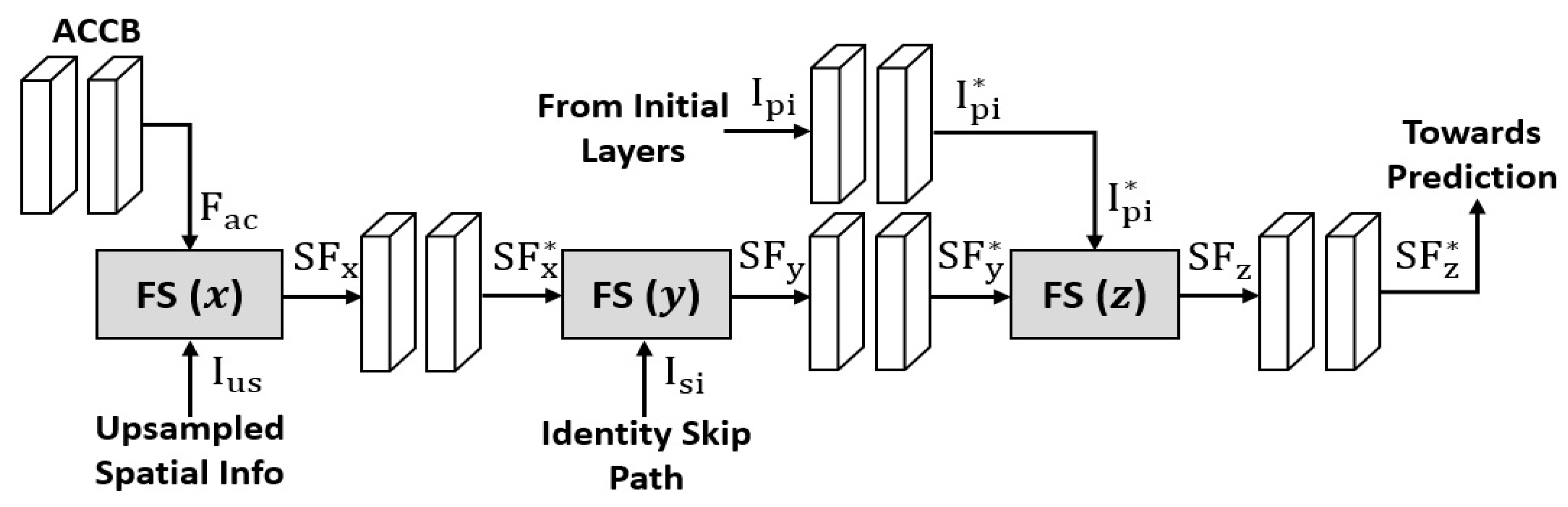
2.2.2. FSBS-Net Architecture and Working
2.2.3. Experimental Details and Data Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation Measure
3.2. Comparing FSBS-Net with Those of the State-of-the-Art Methods
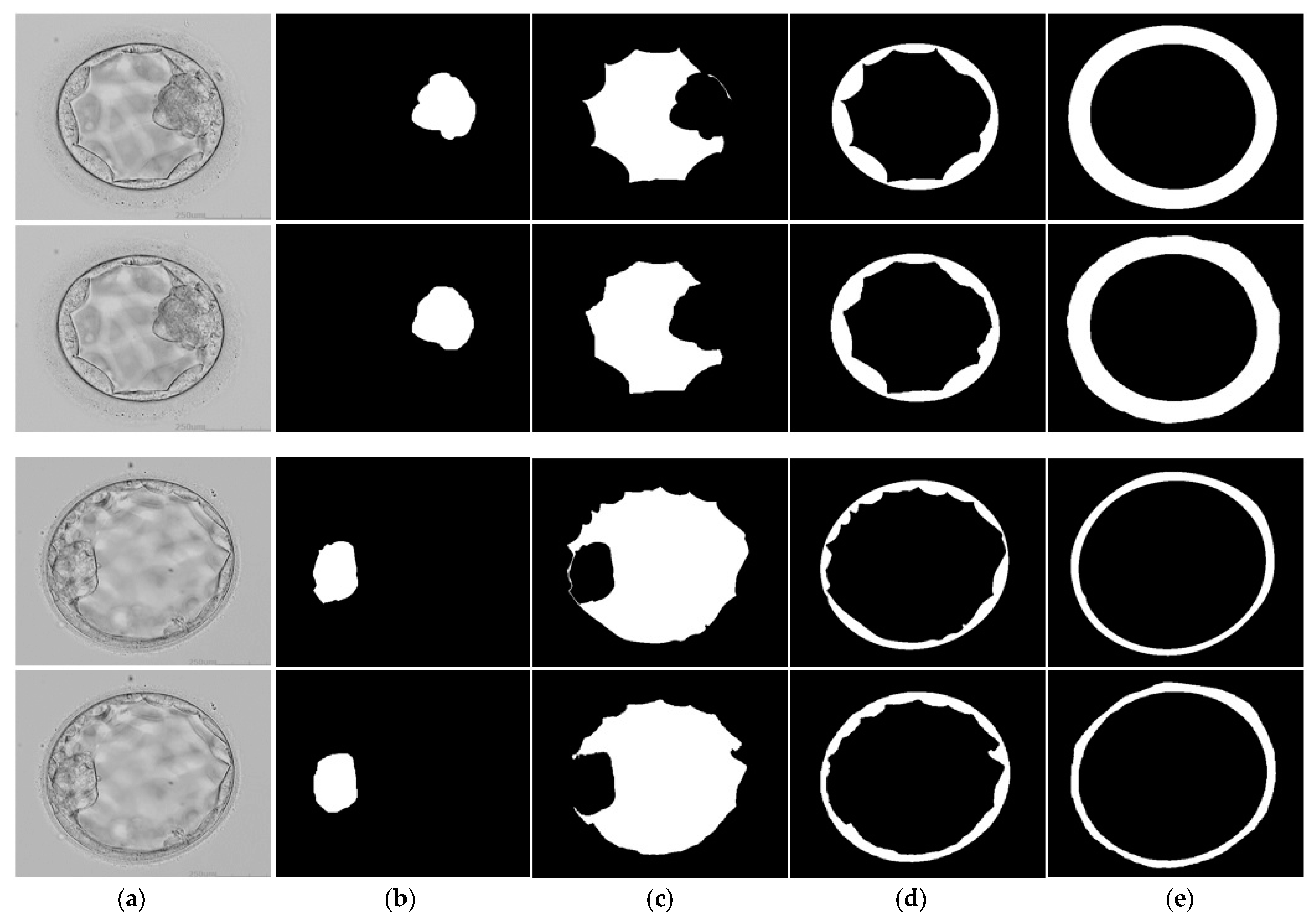
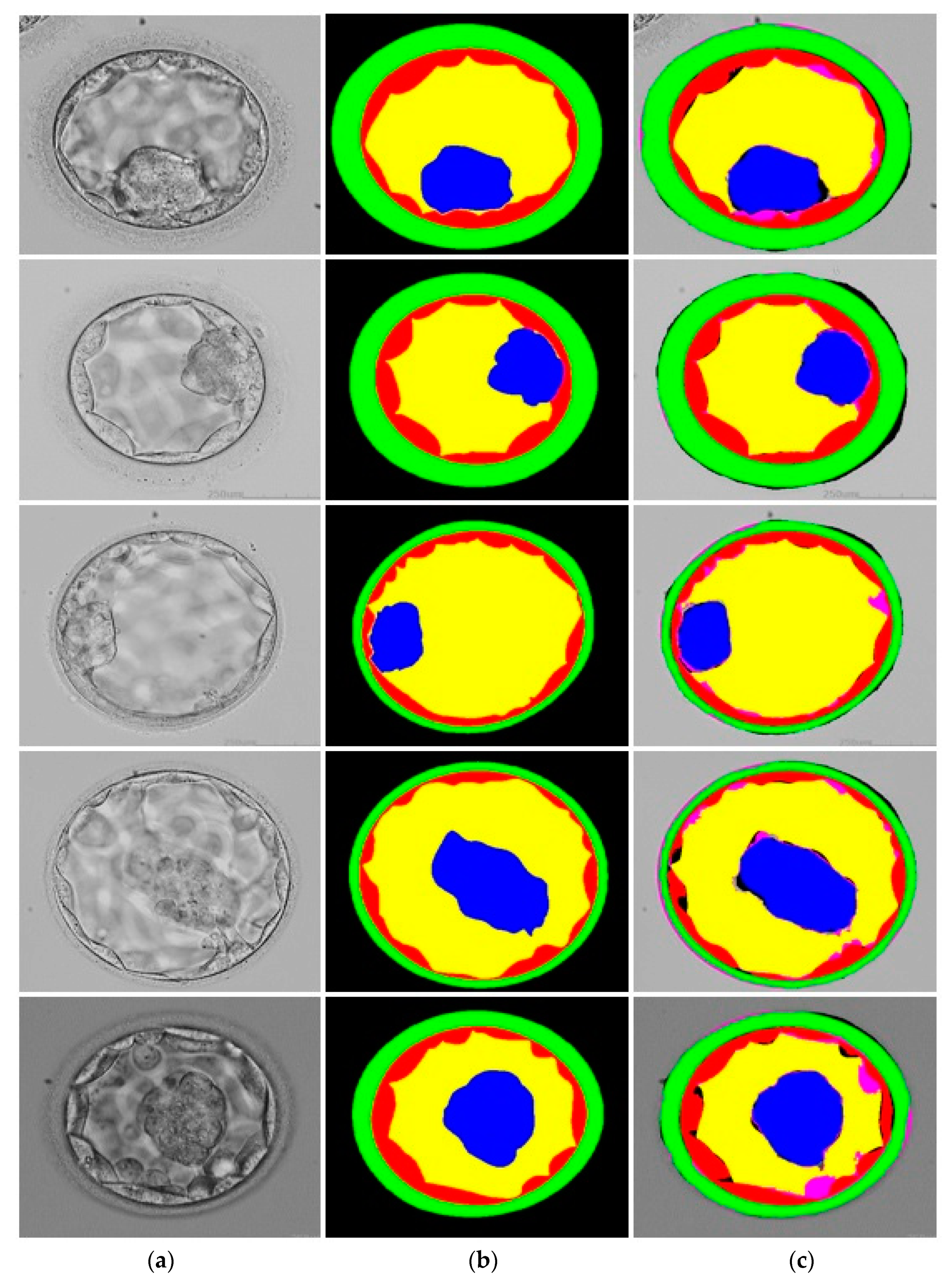
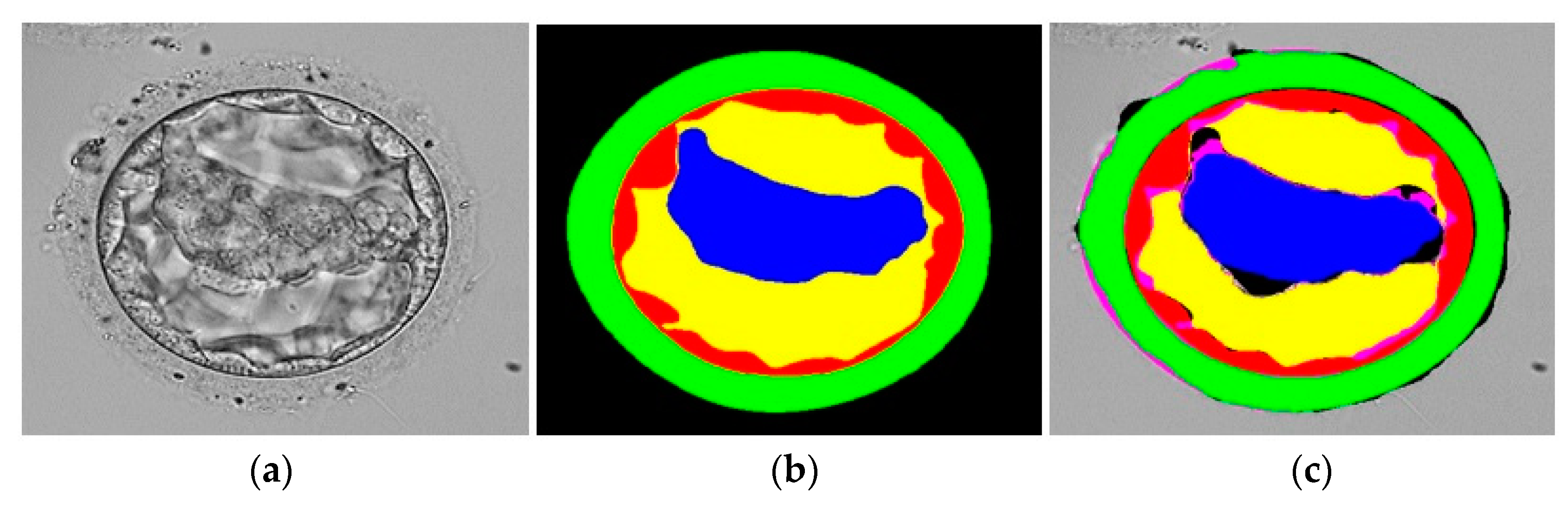
3.3. Qualitative Results Produced by FSBS-Net for Blastocyst Components Segmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purkayastha, N.; Sharma, H. Prevalence and Potential Determinants of Primary Infertility in India: Evidence from Indian Demographic Health Survey. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 9, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, M.; Petruzziello, A. A Situation-Aware DSS to Support Assisted Reproductive Technology Outcome Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Cognitive and Computational Aspects of Situation Management, Tallin, Estonia, 14–21 May 2021; pp. 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, A.; Mumtaz, M.; Raza, A.; Salem, N.; Yasir, M.N. Artificial Intelligence-Based Detection of Human Embryo Components for Assisted Reproduction by In Vitro Fertilization. Sensors 2022, 22, 7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulou, M.; Sfakianoudis, K.; Maziotis, E.; Antoniou, N.; Rapani, A.; Anifandis, G.; Bakas, P.; Bolaris, S.; Pantou, A.; Pantos, K.; et al. Are Computational Applications the “Crystal Ball” in the IVF Laboratory? The Evolution from Mathematics to Artificial Intelligence. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.S.; Noble, J.A.; Wells, D. A Review on Automatic Analysis of Human Embryo Microscope Images. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, R.M.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. BLAST-NET: Semantic Segmentation of Human Blastocyst Components via Cas-caded Atrous Pyramid and Dense Progressive Upsampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1865–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Magurany, K.A.; Chang, X.; Clewell, R.; Coecke, S.; Haugabrooks, E.; Marty, S. A Pragmatic Framework for the Application of New Approach Methodologies in One Health Toxicological Risk Assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 192, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Haider, A.; Koo, J.H.; Park, K.R. Segmenting Retinal Vessels Using a Shallow Segmentation Network to Aid Ophthalmic Analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Arsalan, M.; Lee, Y.W.; Park, K.R. Deep Features Aggregation-Based Joint Segmentation of Cytoplasm and Nuclei in White Blood Cells. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 3685–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Arsalan, M.; Park, C.; Sultan, H.; Park, K.R. Exploring Deep Feature-Blending Capabilities to Assist Glaucoma Screening. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 133, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Baek, N.R.; Owais, M.; Mahmood, T.; Park, K.R. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Pigment Signs for Analysis and Diagnosis of Retinitis Pigmentosa. Sensors 2020, 20, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisto, F.M.; Santiago, C.; Nunes, N.; Nascimento, J.C. Introduction of Human-Centric AI Assistant to Aid Radiologists for Multimodal Breast Image Classification. Int. J. Hum. -Comput. Stud. 2021, 150, 102607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisto, F.M.; Nunes, N.; Nascimento, J.C. Modeling Adoption of Intelligent Agents in Medical Imaging. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2022, 168, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamir, S. Artificial Intelligence in Human Reproduction: Charting the Ethical Debate over AI in IVF. AI Ethics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.C.; Siristatidis, C.S. Automation, Artificial Intelligence and Innovations in the Future of IVF. In In Vitro Fertilization: A Textbook of Current and Emerging Methods and Devices; Nagy, Z.P., Varghese, A.C., Agarwal, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 847–860. ISBN 978-3-319-43011-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zaninovic, N.; Elemento, O.; Rosenwaks, Z. Artificial Intelligence: Its Applications in Reproductive Medicine and the Assisted Reproductive Technologies. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, R.A.; Arsalan, M.; Qaiser, T.; Khan, T.M.; Razzak, I. Sensor Data Fusion Based on Deep Learning for Computer Vision Applications and Medical Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewski, R.; Kuczyńska, A.; Stankiewicz, B.; Kuczyński, W. How Much Information about Embryo Implantation Potential Is Included in Morphokinetic Data? A Prediction Model Based on Artificial Neural Networks and Principal Component Analysis. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, K.; Berkkanoglu, M.; Bulut, H.; Donmez, L.; Isikli, A.; Coetzee, K. Blastocyst Age, Expansion, Trophectoderm Morphology, and Number Cryopreserved Are Variables Predicting Clinical Implantation in Single Blastocyst Frozen Embryo Transfers in Freeze-Only-IVF. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, R.; Palini, S.; Vento, M.E.; La Ferlita, A.; Lo Faro, M.J.; Caroppo, E.; Borzì, P.; Falzone, L.; Barbagallo, D.; Ragusa, M.; et al. Identification of Extracellular Vesicles and Characterization of MiRNA Expression Profiles in Human Blastocoel Fluid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, H. Effects of Abnormal Zona Pellucida on Fertilization and Pregnancy in IVF/ICSI-ET. J. Reprod. Contracept. 2015, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.-W. Overall Blastocyst Quality, Trophectoderm Grade, and Inner Cell Mass Grade Predict Pregnancy Outcome in Euploid Blastocyst Transfer Cycles. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribenszky, C.; Nilselid, A.-M.; Montag, M. Time-Lapse Culture with Morphokinetic Embryo Selection Improves Pregnancy and Live Birth Chances and Reduces Early Pregnancy Loss: A Meta-Analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2017, 35, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Yee, D.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Automatic Identification of Human Blastocyst Components via Texture. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2968–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.C.; Loewke, K.E.; Bossert, N.L.; Behr, B.; De Jonge, C.J.; Baer, T.M.; Pera, R.A.R. Non-Invasive Imaging of Human Embryos before Embryonic Genome Activation Predicts Development to the Blastocyst Stage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, E.S.; Noble, J.A.; Poli, M.; Griffiths, T.; Emerson, G.; Wells, D. A Method for Semi-Automatic Grading of Human Blastocyst Microscope Images. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Au, J.; Saeedi, P.; Havelock, J. Automatic Segmentation of Trophectoderm in Microscopic Images of Human Blastocysts. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, R.M.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Multi-Resolutional Ensemble of Stacked Dilated U-Net for Inner Cell Mass Seg-mentation in Human Embryonic Images. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 3518–3522. [Google Scholar]
- Bori, L.; Dominguez, F.; Fernandez, E.I.; Del Gallego, R.; Alegre, L.; Hickman, C.; Quiñonero, A.; Nogueira, M.F.G.; Rocha, J.C.; Meseguer, M. An Artificial Intelligence Model Based on the Proteomic Profile of Euploid Embryos and Blastocyst Morphology: A Preliminary Study. Reprod. BioMedicine Online 2021, 42, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.M.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Human Blastocyst’s Zona Pellucida Segmentation via Boosting Ensemble of Complementary Learning. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 13, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, S.; Saeedi, P.; Bajic, I. Human Blastocyst Segmentation Using Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ca-nadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15–19 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.T.F.; Kosasa, T.; Walker, B.; Arnett, C.; Huang, C.T.F.; Yin, C.; Harun, Y.; Ahn, H.J.; Ohta, A. Deep Learning Neural Network Analysis of Human Blastocyst Expansion from Time-Lapse Image Files. Reprod. BioMedicine Online 2021, 42, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, S.; Singh, A.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Inner Cell Mass Segmentation in Human HMC Embryo Images Using Fully Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 1752–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Sun, H. A Deep Learning Framework Design for Automatic Blastocyst Evaluation With Multifocal Images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 18927–18934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.M.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Trophectoderm Segmentation in Human Embryo Images via Inceptioned U-Net. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 62, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Howe, S.; Tizhoosh, H.R. The Effects of Image Pre- and Post-Processing, Wavelet Decomposition, and Local Binary Patterns on U-Nets for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Virtual, 18–22 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks Introduces Release 2021a of MATLAB and Simulink. Available online: https://ch.mathworks.com/company/newsroom/mathworks-introduces-release-2021a-of-matlab-and-simulink.html (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Haider, A.; Arsalan, M.; Lee, M.B.; Owais, M.; Mahmood, T.; Sultan, H.; Park, K.R. Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Glaucoma Using Retinal Fundus Images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Pan, X.; Li, F. DenseU-Net-Based Semantic Segmentation of Small Objects in Urban Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 65347–65356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Rottmann, M.; Hüger, F.; Schlicht, P.; Gottschalk, H. Application of Decision Rules for Handling Class Imbalance in Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.08394. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Family. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/geforce/graphics-cards/30-series/rtx-3080-3080ti/ (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Kragh, M.F.; Karstoft, H. Embryo Selection with Artificial Intelligence: How to Evaluate and Compare Methods? J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Haider, A.; Choi, J.; Park, K.R. Detecting Blastocyst Components by Artificial Intelligence for Human Embryological Analysis to Improve Success Rate of In Vitro Fertilization. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisto, F.M.; Santiago, C.; Nunes, N.; Nascimento, J.C. BreastScreening-AI: Evaluating Medical Intelligent Agents for Human-AI Interactions. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 127, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai , R.; Gunawan , D. Optimizing CNN Hyperparameters for Blastocyst Quality Assessment in Small Datasets. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 88621–88631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 Encoder Pre-Trained on ImageNet for Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05746. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, Y.; Maeda, T.; Fukunaga, E.; Shiba, R.; Okano, S.; Kinutani, M.; Horiuchi, T. Selection of High-Quality and Viable Blastocysts Based on Timing of Morula Compaction and Blastocyst Formation. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2020, 19, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, P.; Kazemi, E.; Zhan, Q.; Malmsten, J.E.; Toschi, M.; Zisimopoulos, P.; Sigaras, A.; Lavery, S.; Cooper, L.A.D.; Hickman, C.; et al. Deep Learning Enables Robust Assessment and Selection of Human Blastocysts after in Vitro Fertilization. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Blastocyst Component | PRE | RC | DSC |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZP | 97.66 | 94.01 | 92.29 |
| TE | 97.50 | 92.21 | 88.90 |
| BC | 97.30 | 91.20 | 94.06 |
| ICM | 98.73 | 92.63 | 92.0 |
| BG | 98.10 | 99.04 | 97.65 |
| Average | 97.85 | 93.81 | 92.98 |
| Method | No. of Parameters | ZP | TE | BC | ICM | BG | Mean JC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet-Baseline [47] | 31.03 M | 79.32 | 75.06 | 79.41 | 79.03 | 94.04 | 81.37 |
| TernausNet U-Net [48] | 10 M | 80.24 | 76.16 | 78.61 | 77.58 | 94.50 | 81.42 |
| PSP-Net [49] | 35 M | 80.57 | 74.83 | 79.26 | 78.28 | 94.60 | 81.51 |
| DeepLab V3 [50] | 40 M | 80.84 | 73.98 | 78.35 | 80.60 | 94.49 | 81.65 |
| Blast-Net [6] | 25 M | 81.15 | 76.52 | 80.79 | 81.07 | 94.74 | 82.85 |
| SSS-Net Residual [44] | 4.04 M | 82.88 | 77.40 | 88.39 | 84.94 | 96.03 | 85.93 |
| SSS-Net Dense [44] | 4.04 M | 84.51 | 78.15 | 88.68 | 84.50 | 95.82 | 86.34 |
| ECS-Net [3] | 2.83 M | 85.34 | 78.43 | 88.41 | 85.26 | 94.87 | 86.46 |
| FSBS-Net (Proposed) | 2.01 M | 85.80 | 80.17 | 89.15 | 85.55 | 95.62 | 87.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishaq, M.; Raza, S.; Rehar, H.; Abadeen, S.e.Z.u.; Hussain, D.; Naqvi, R.A.; Lee, S.-W. Assisting the Human Embryo Viability Assessment by Deep Learning for In Vitro Fertilization. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092023
Ishaq M, Raza S, Rehar H, Abadeen SeZu, Hussain D, Naqvi RA, Lee S-W. Assisting the Human Embryo Viability Assessment by Deep Learning for In Vitro Fertilization. Mathematics. 2023; 11(9):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092023
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshaq, Muhammad, Salman Raza, Hunza Rehar, Shan e Zain ul Abadeen, Dildar Hussain, Rizwan Ali Naqvi, and Seung-Won Lee. 2023. "Assisting the Human Embryo Viability Assessment by Deep Learning for In Vitro Fertilization" Mathematics 11, no. 9: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092023
APA StyleIshaq, M., Raza, S., Rehar, H., Abadeen, S. e. Z. u., Hussain, D., Naqvi, R. A., & Lee, S.-W. (2023). Assisting the Human Embryo Viability Assessment by Deep Learning for In Vitro Fertilization. Mathematics, 11(9), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11092023











