Modification of Learning Ratio and Drop-Out for Stochastic Gradient Descendant Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Learning Ratio and Learning Drop-Out: Issues, Analysis and Possible Solutions
3.1. Dynamic Alpha
3.2. Dynamic Drop-Out
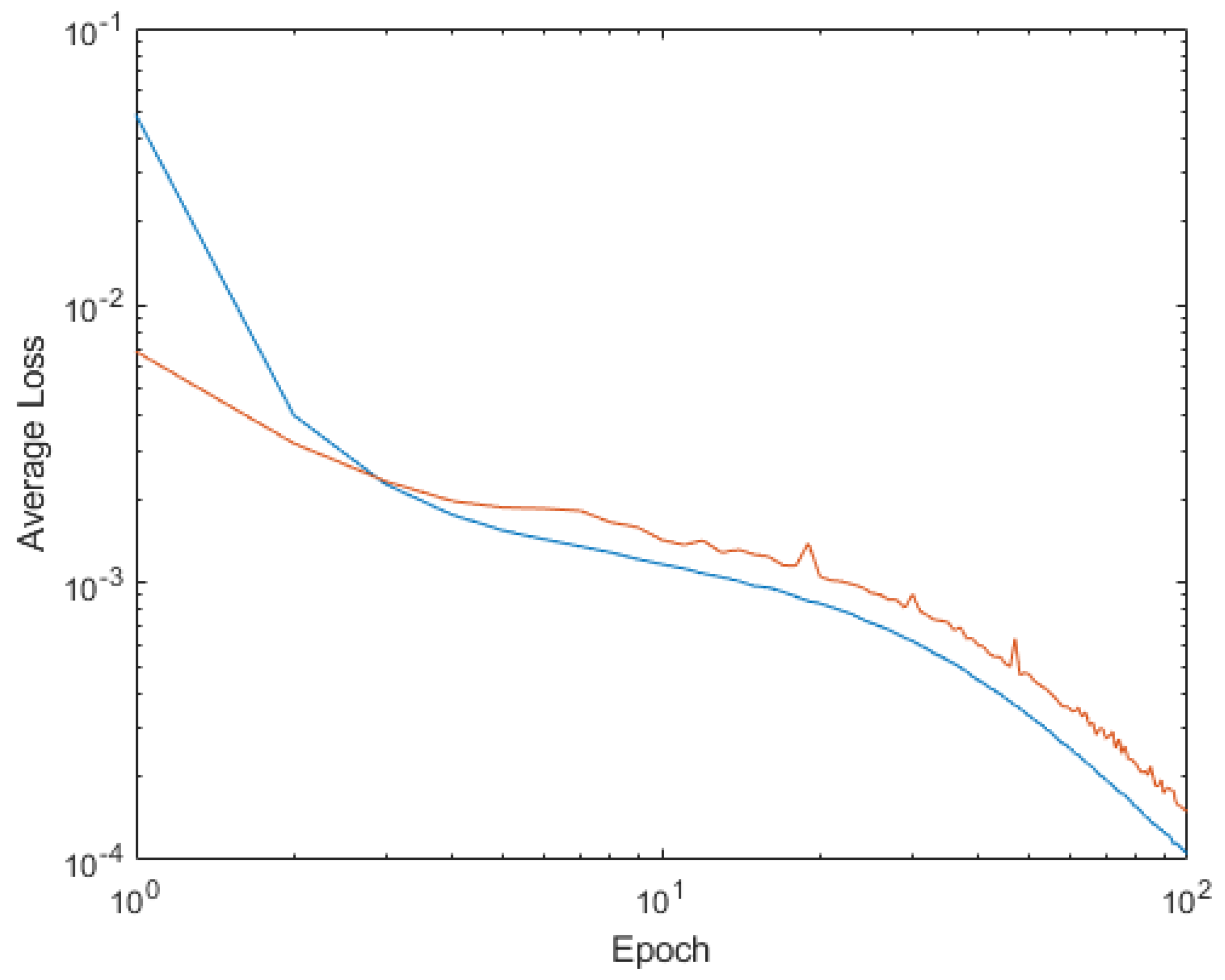
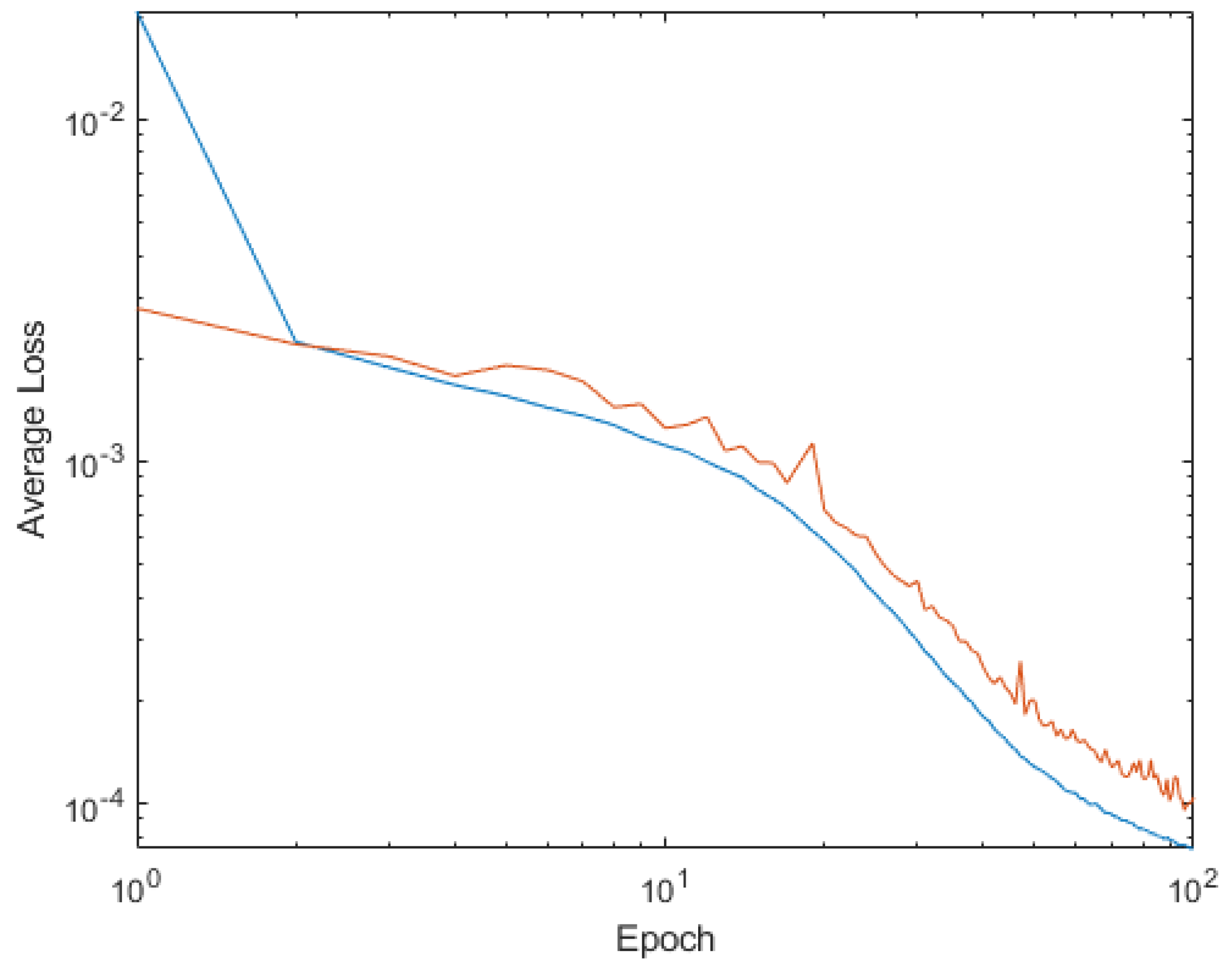
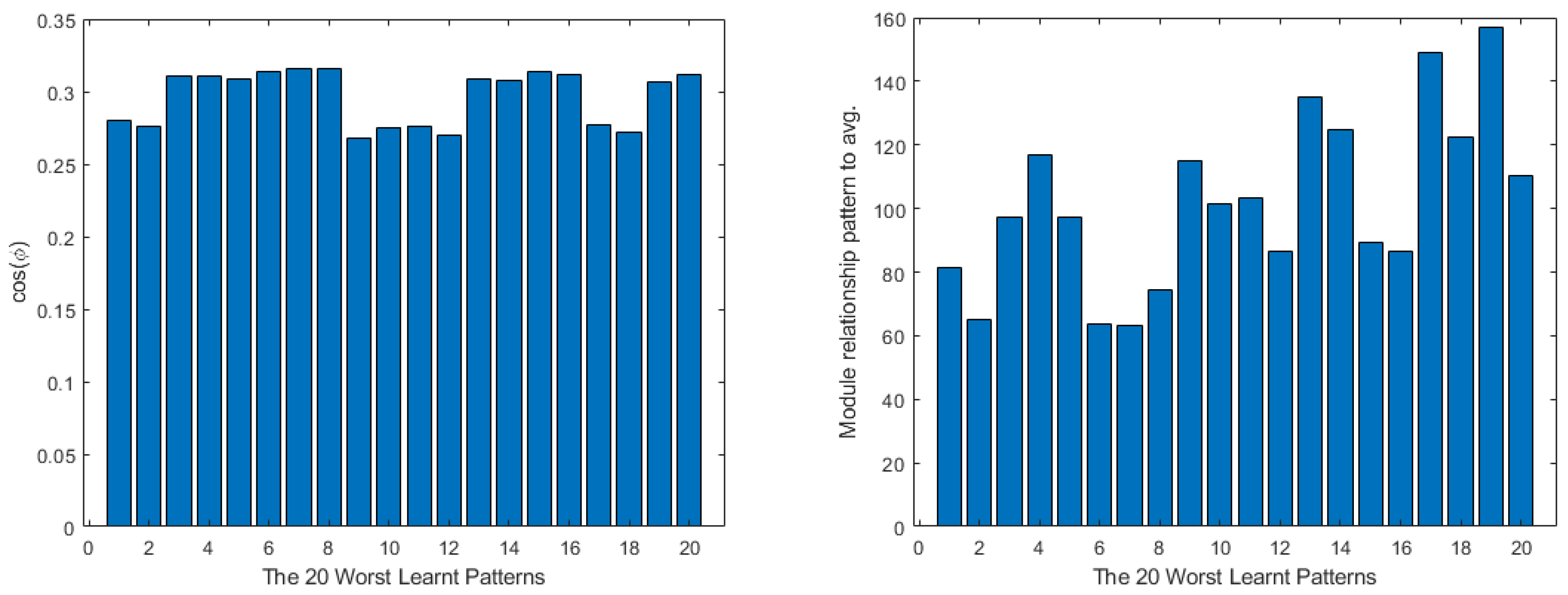
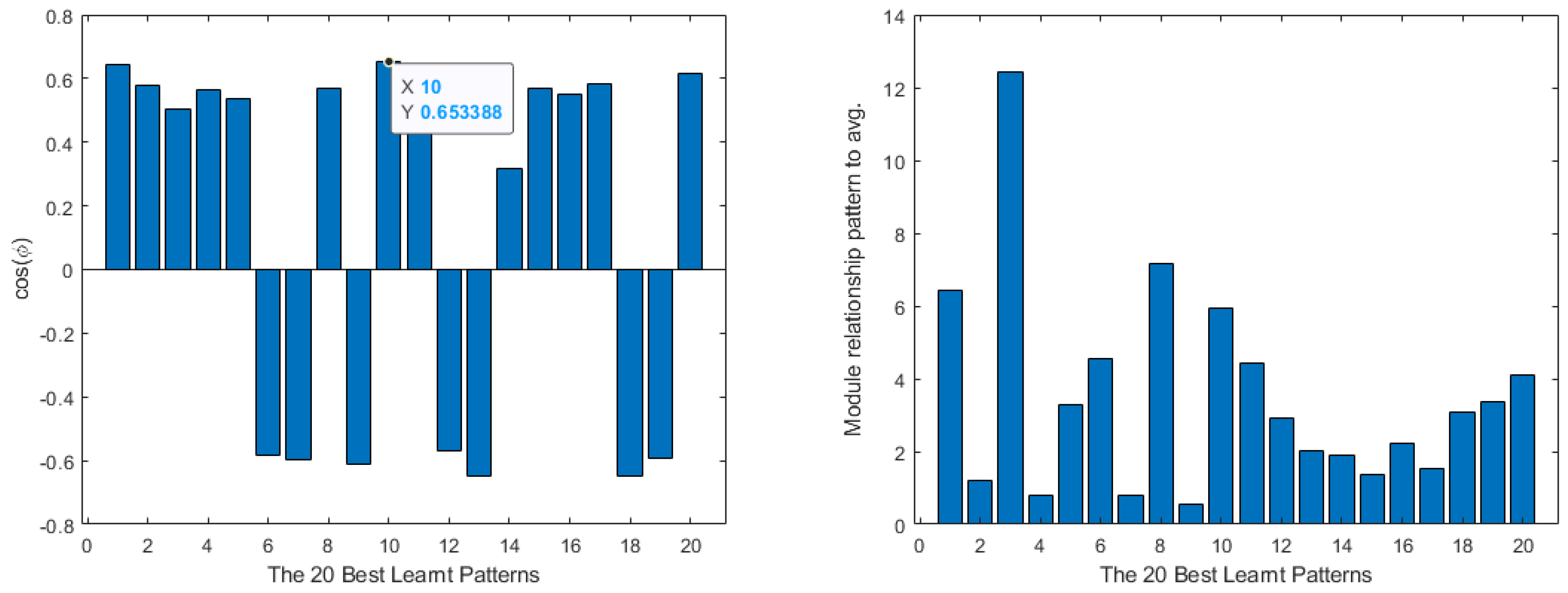
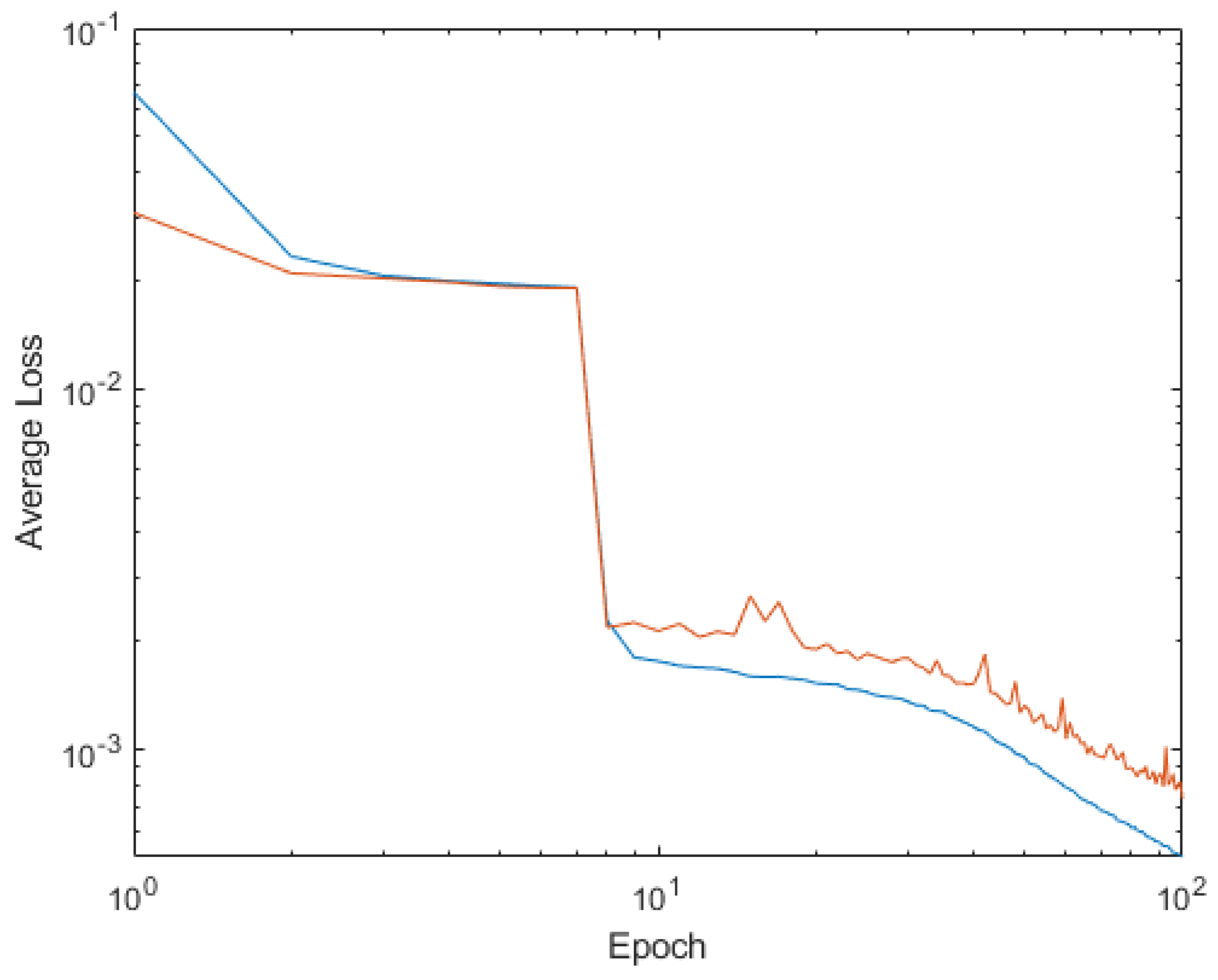
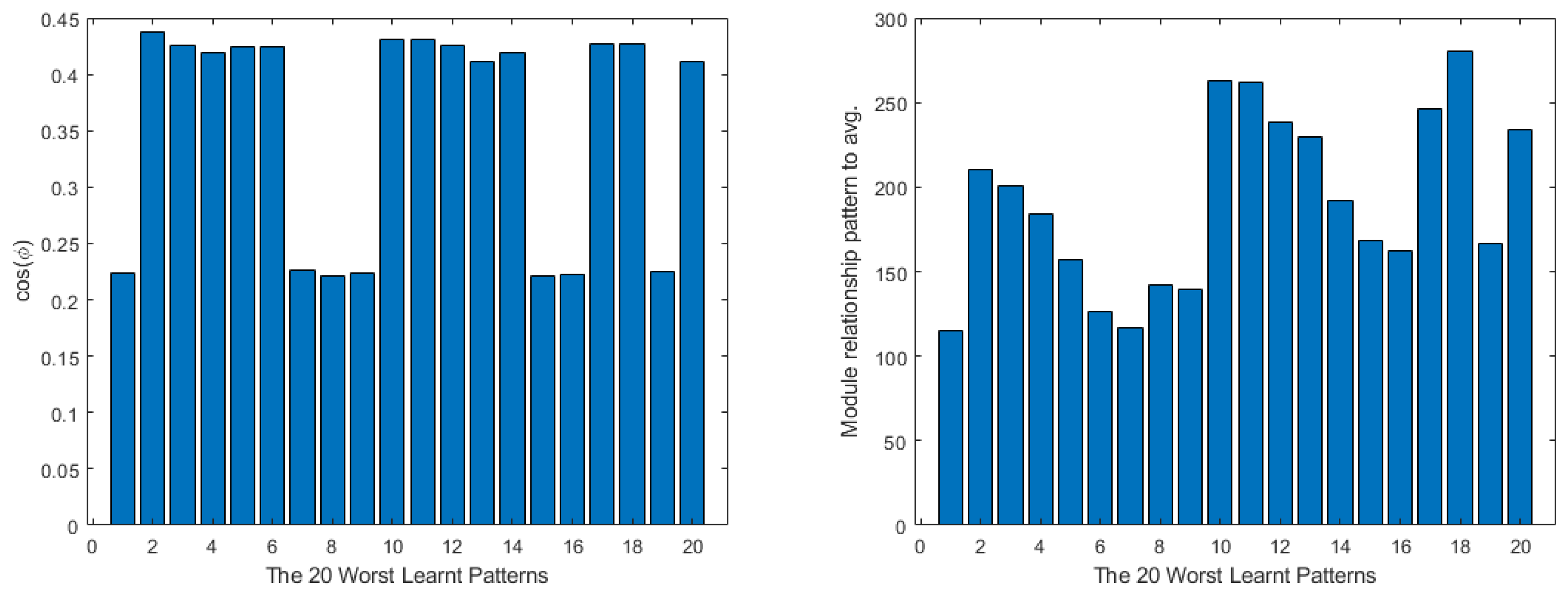
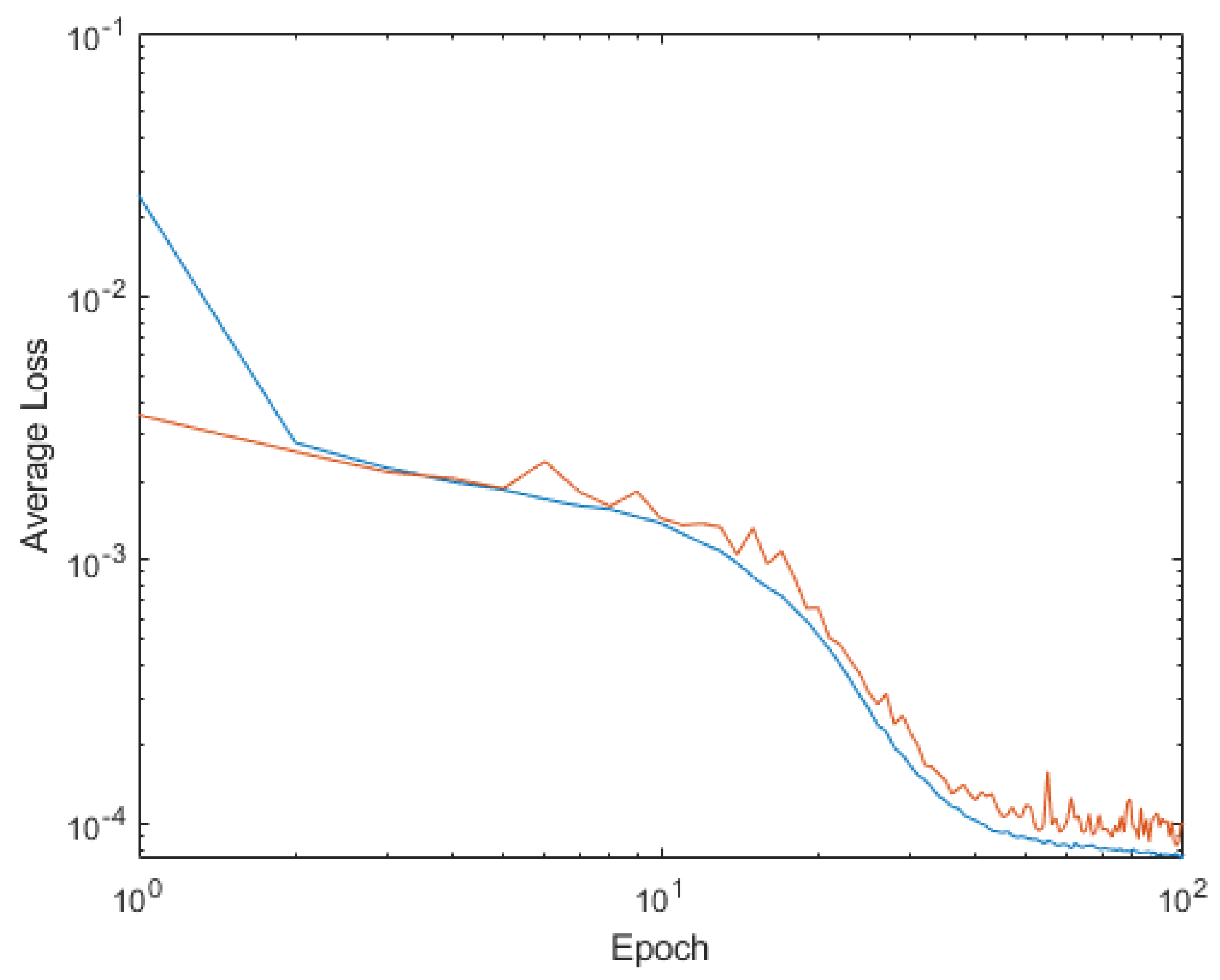
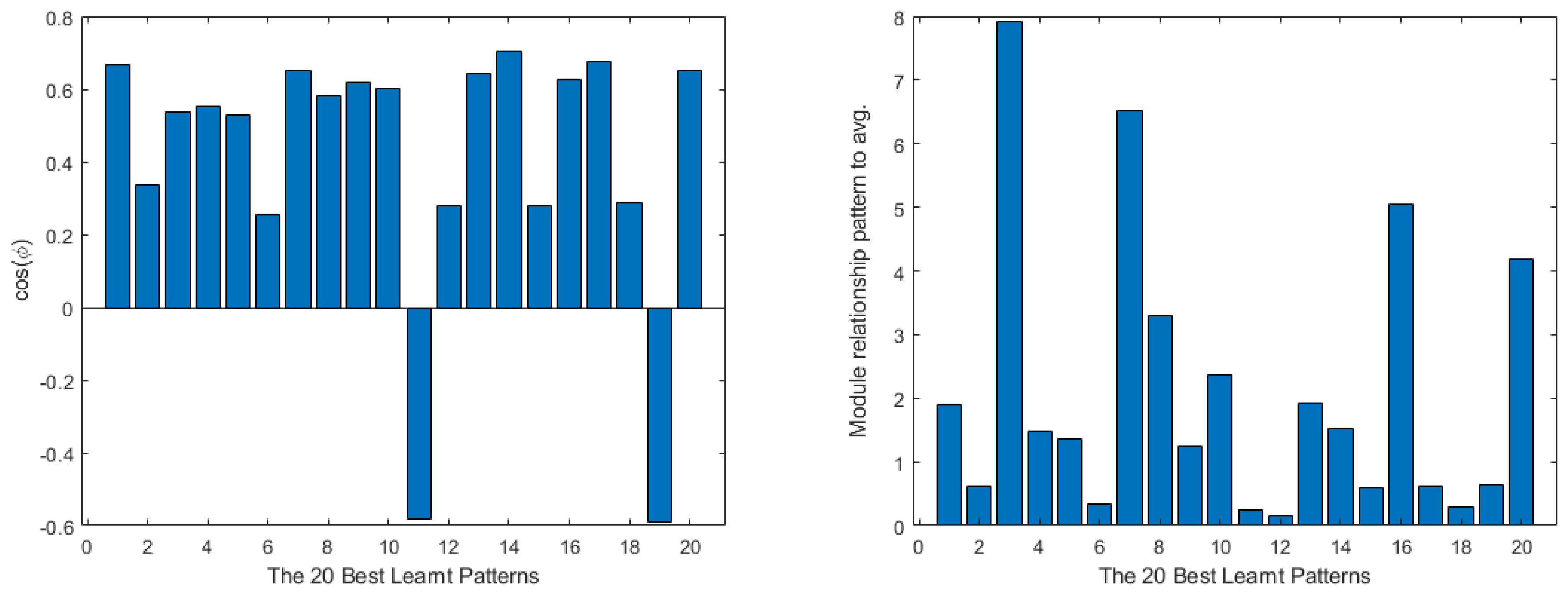
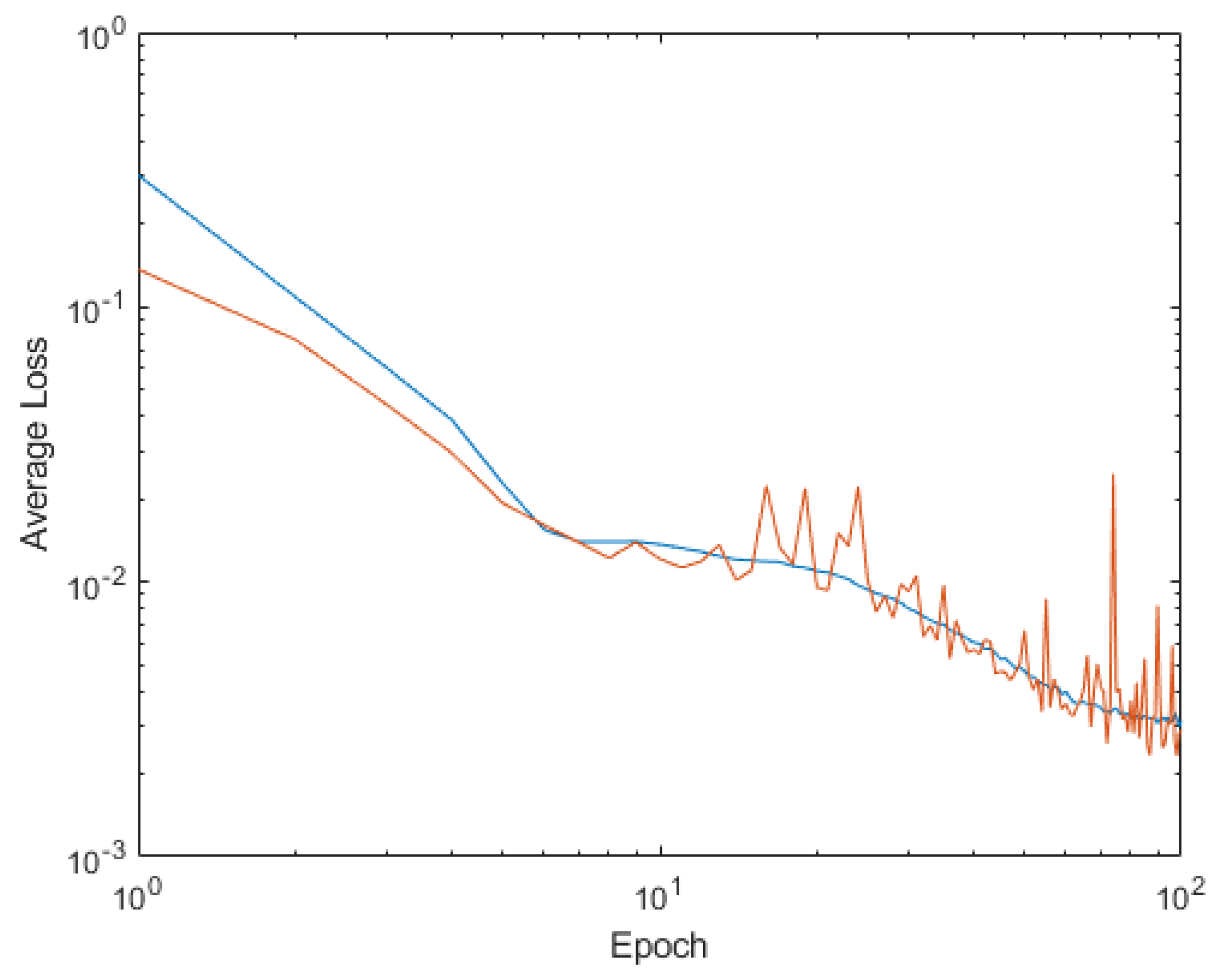
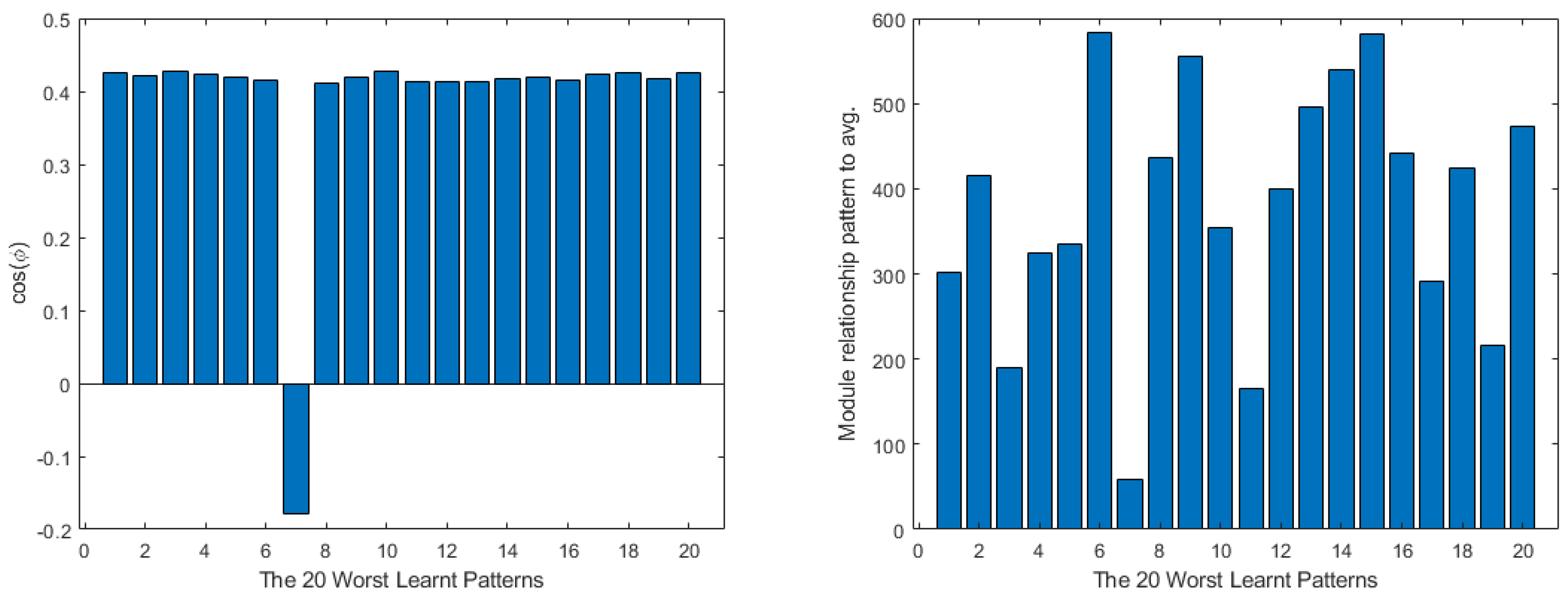
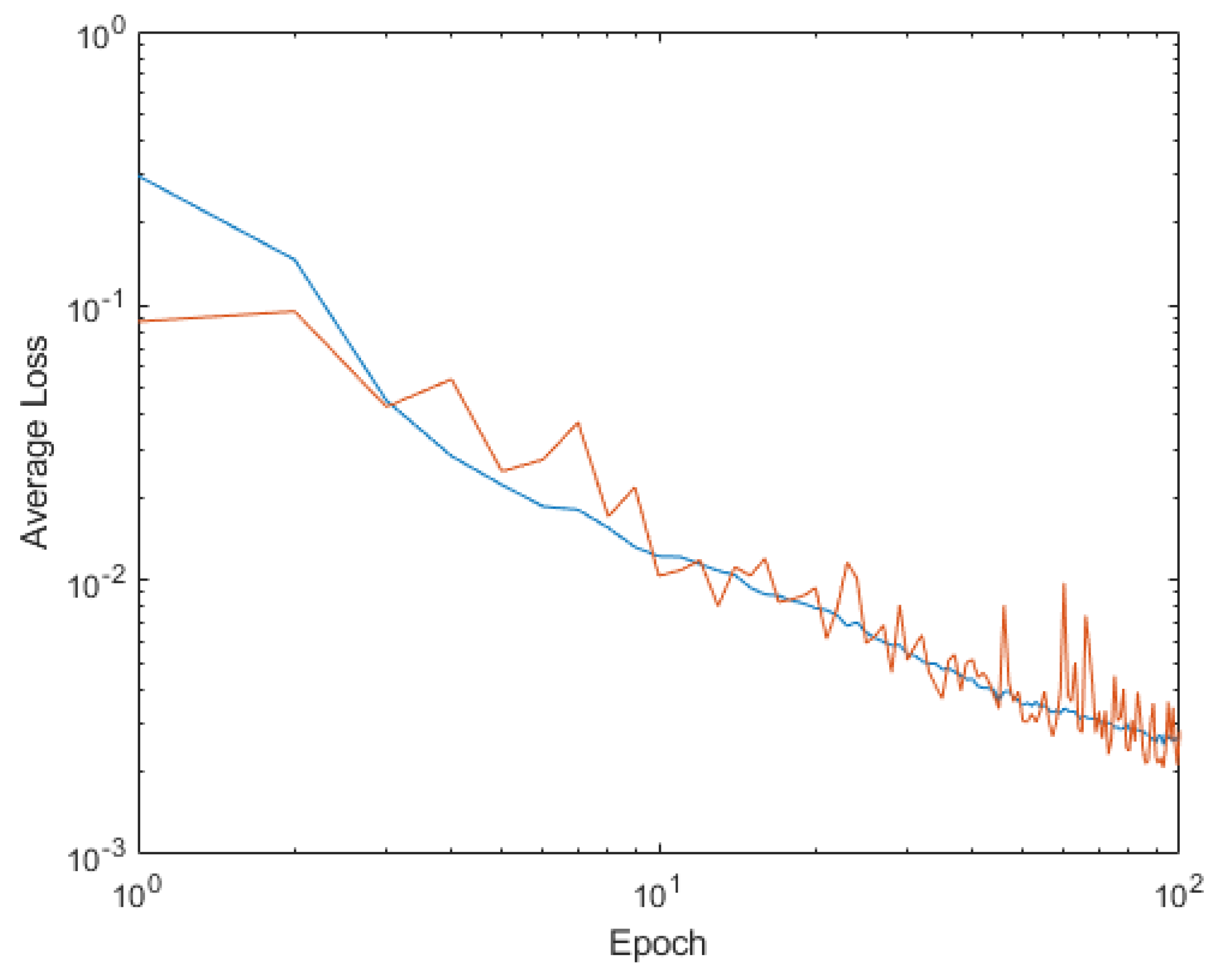
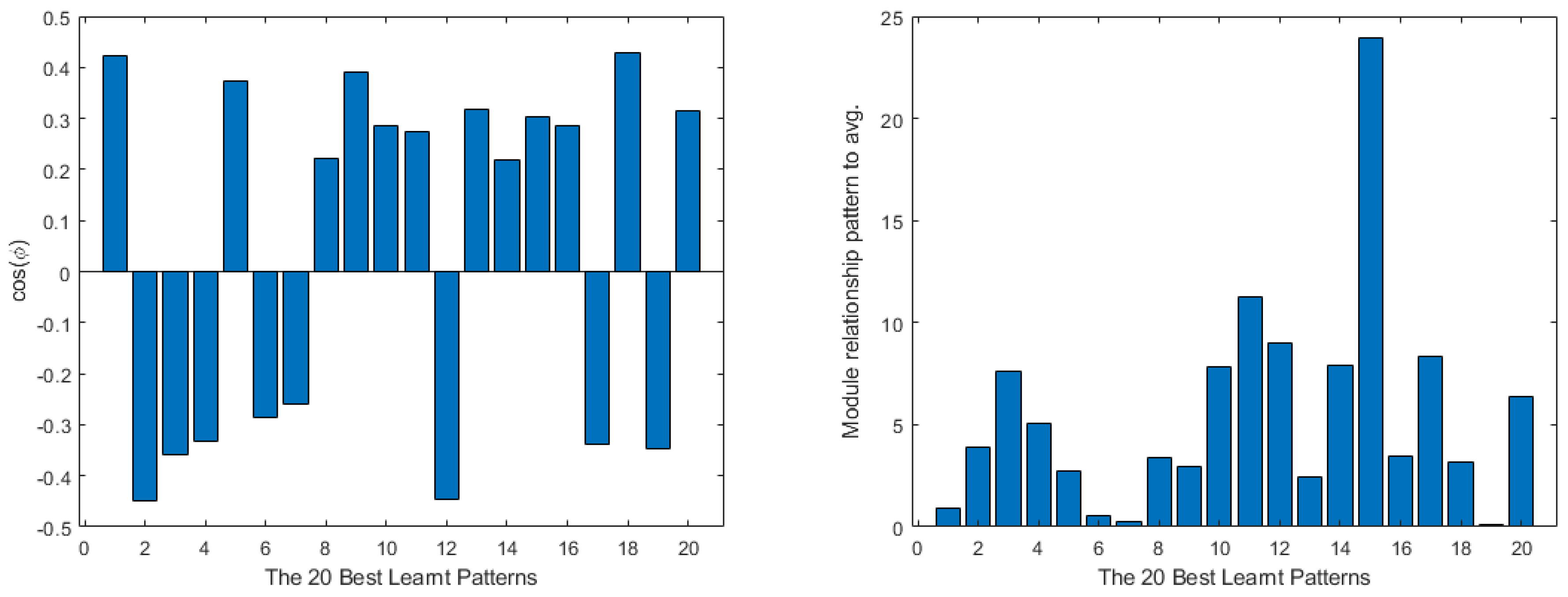
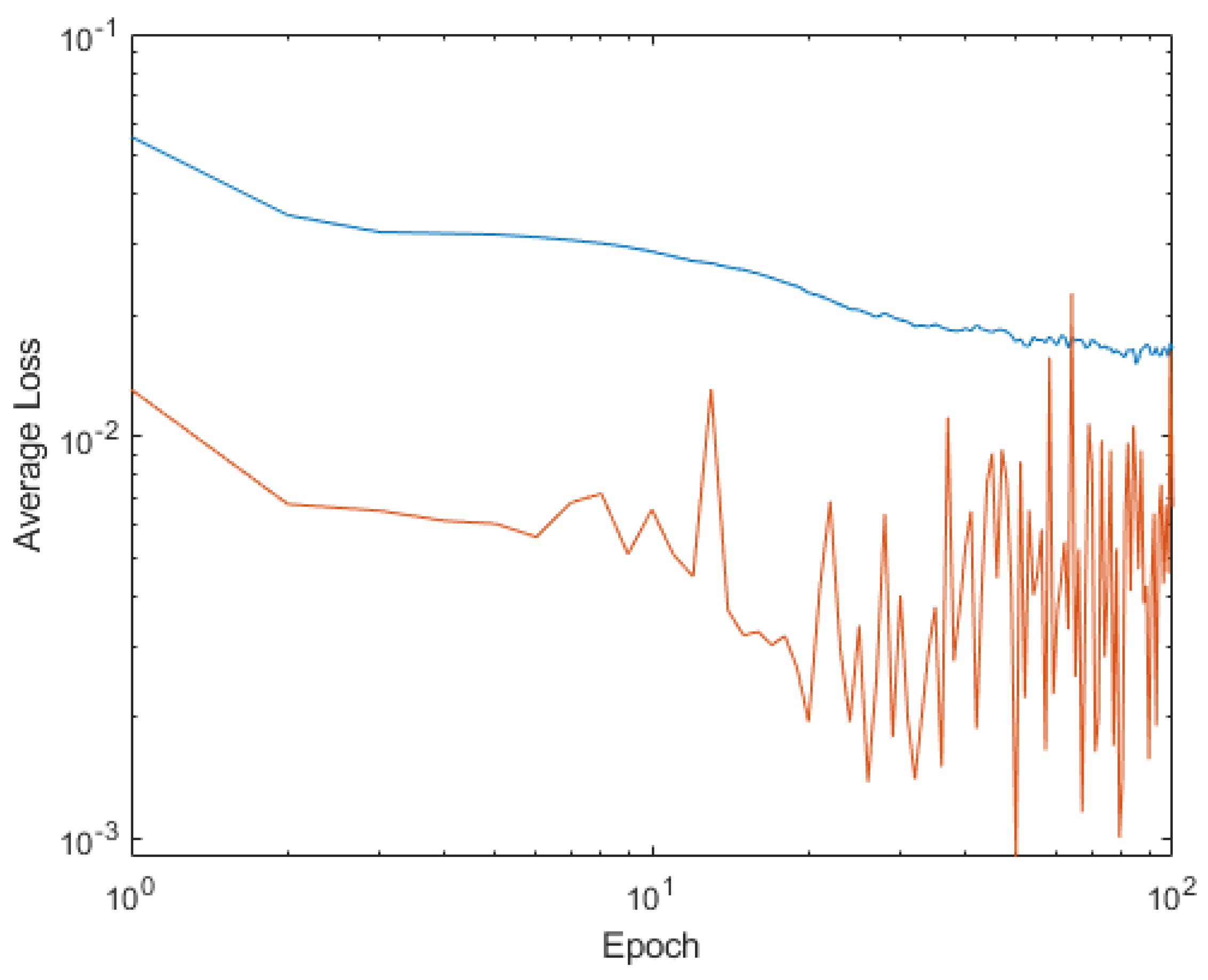
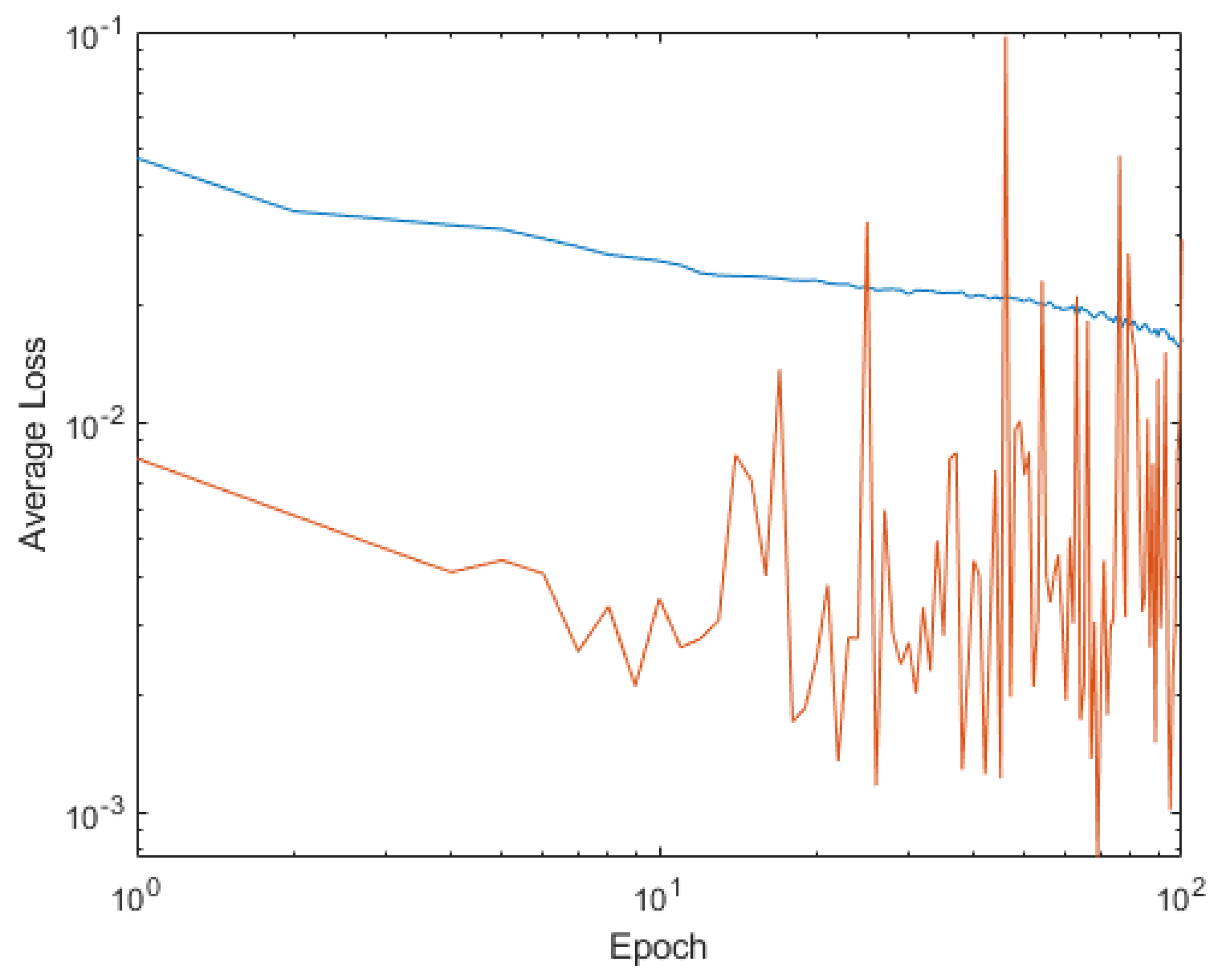
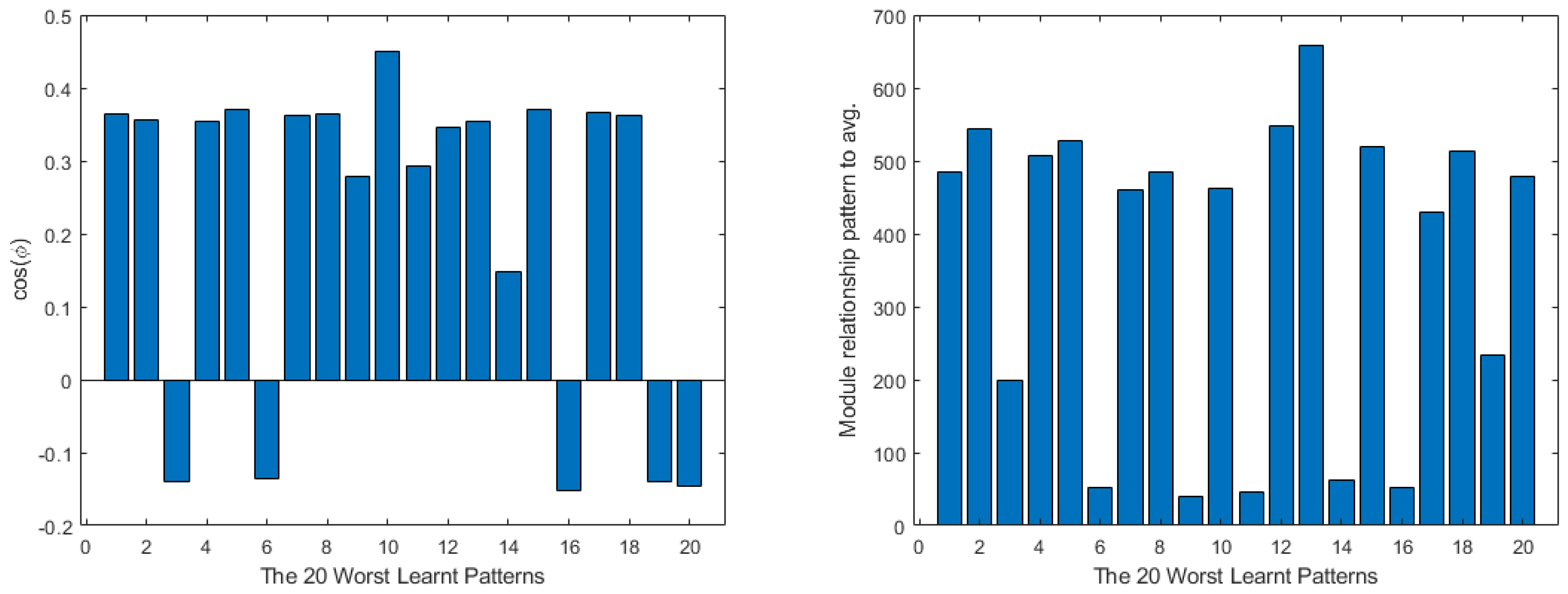
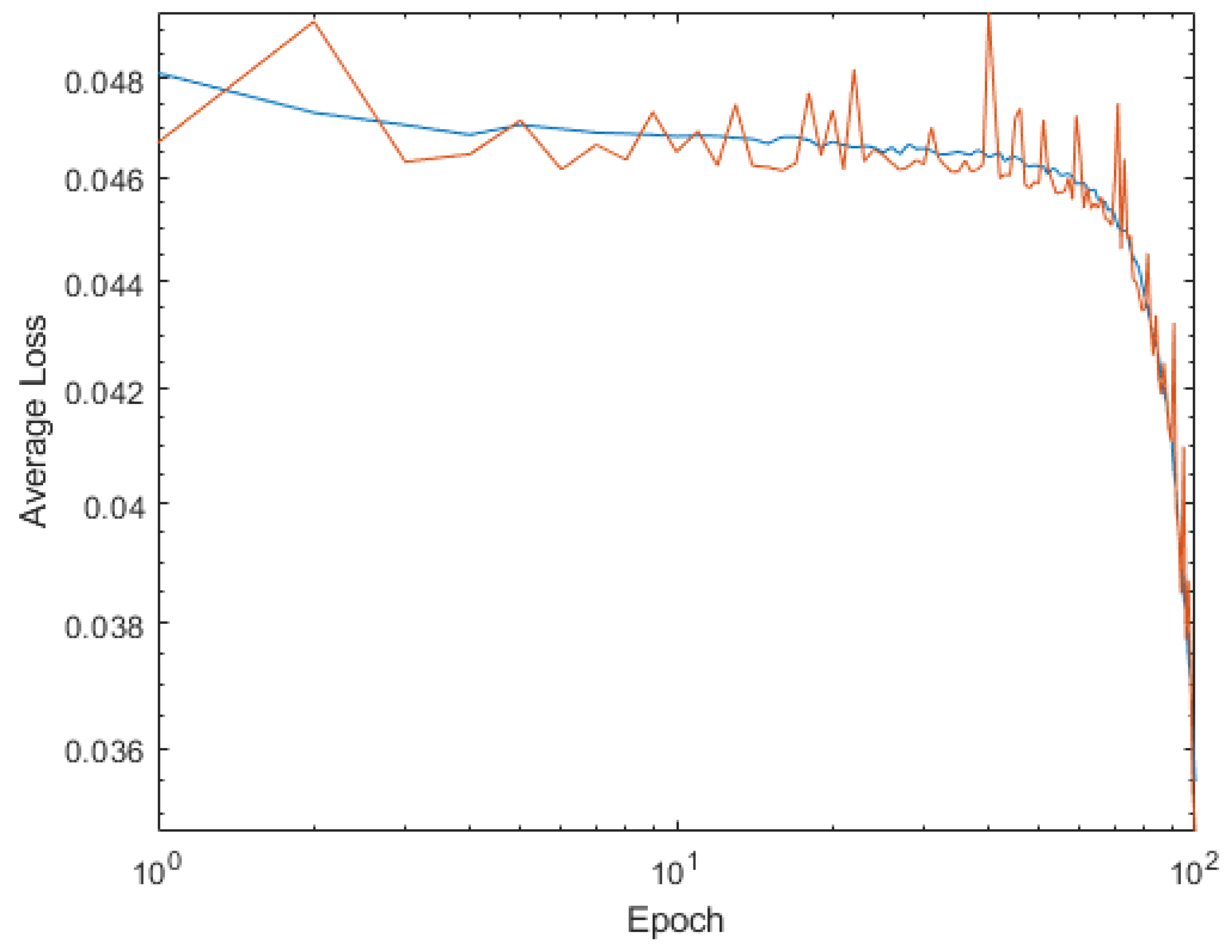
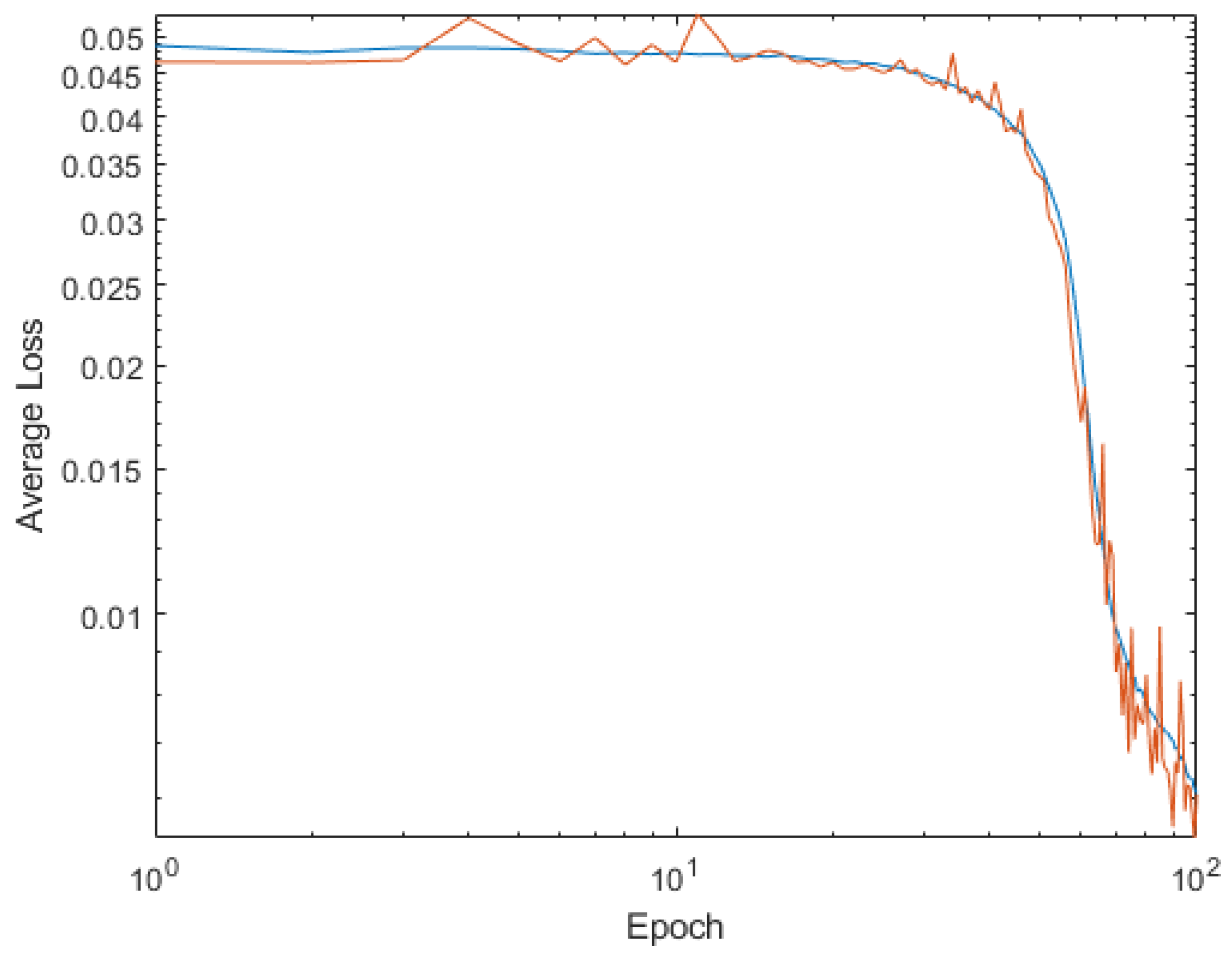
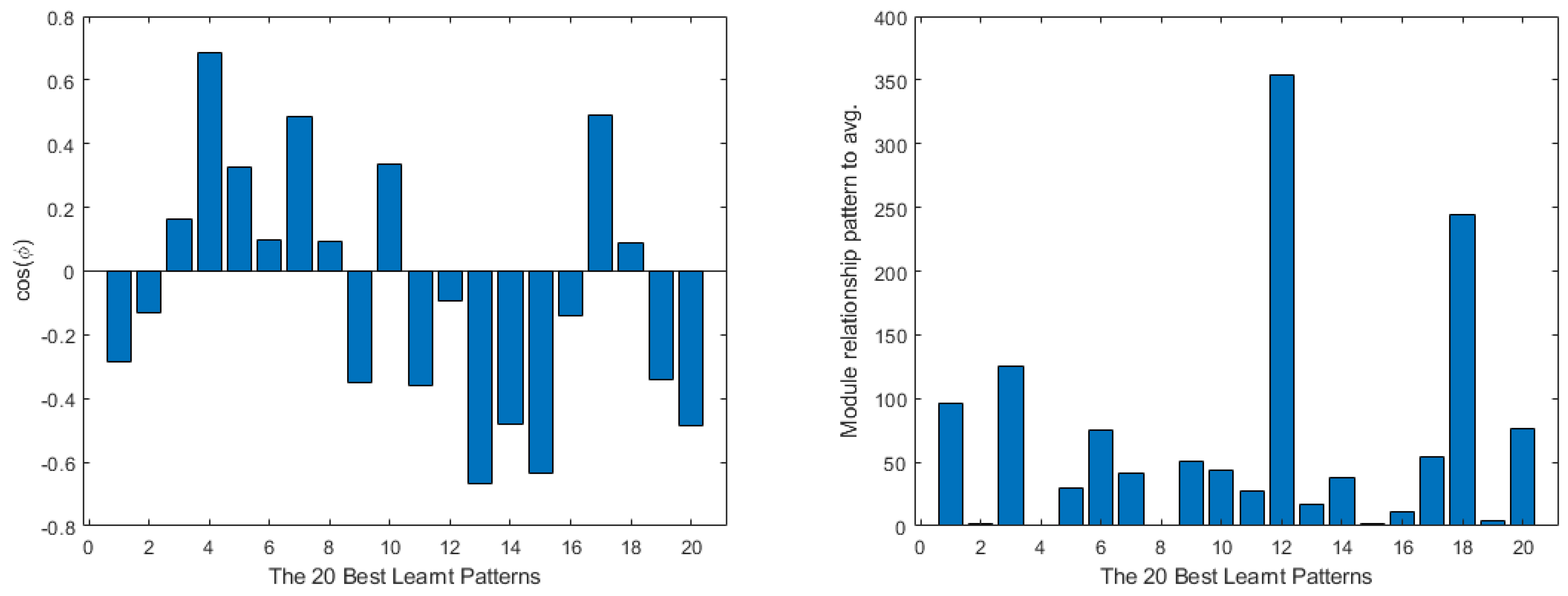
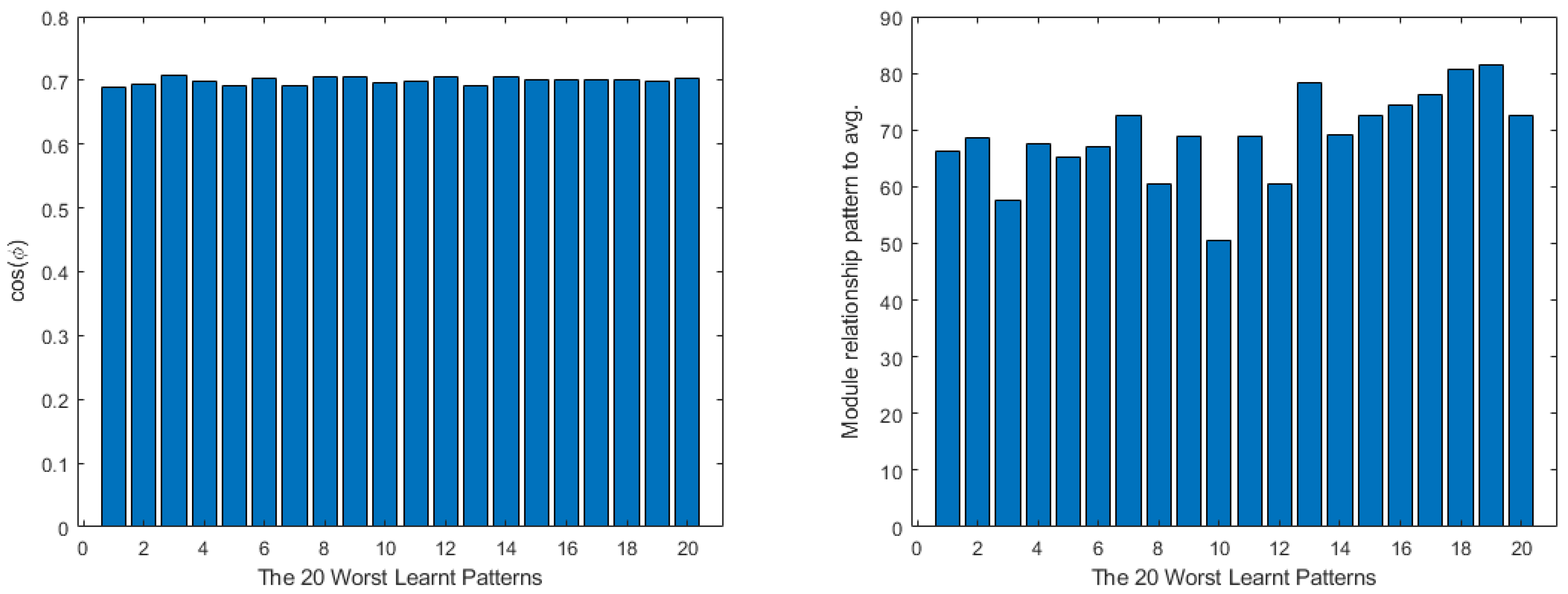
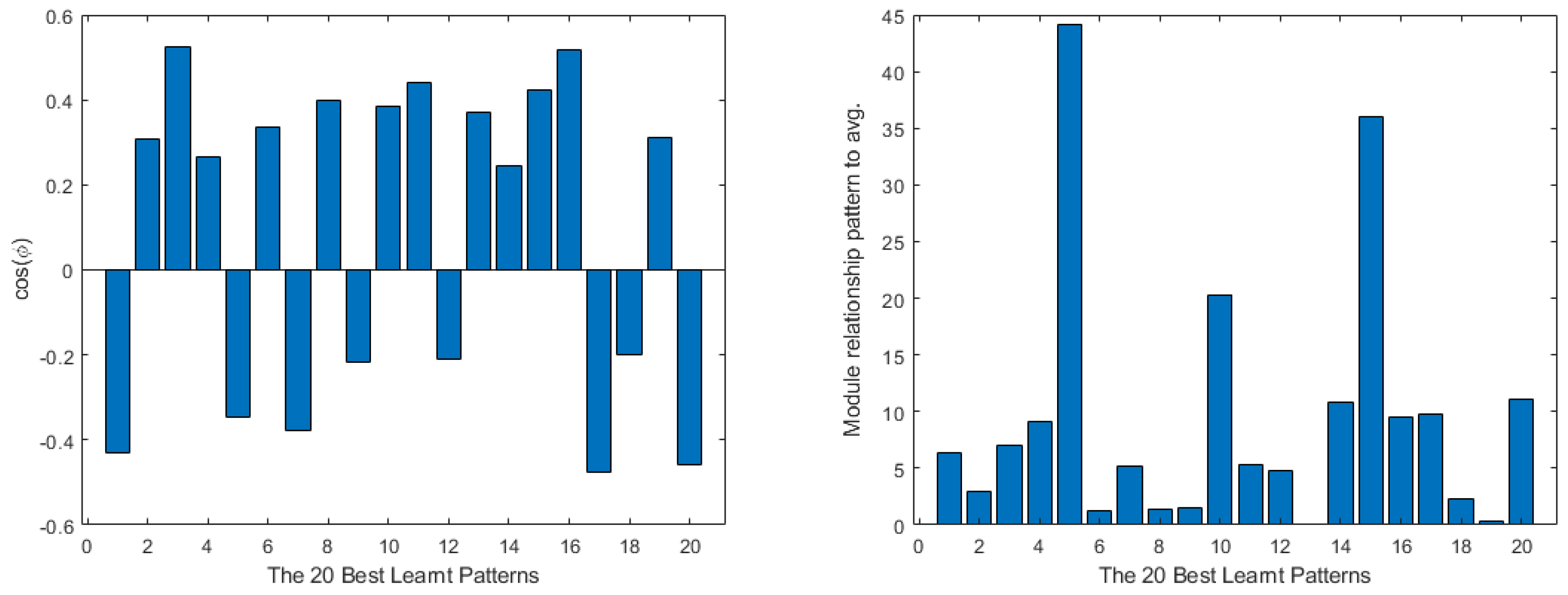
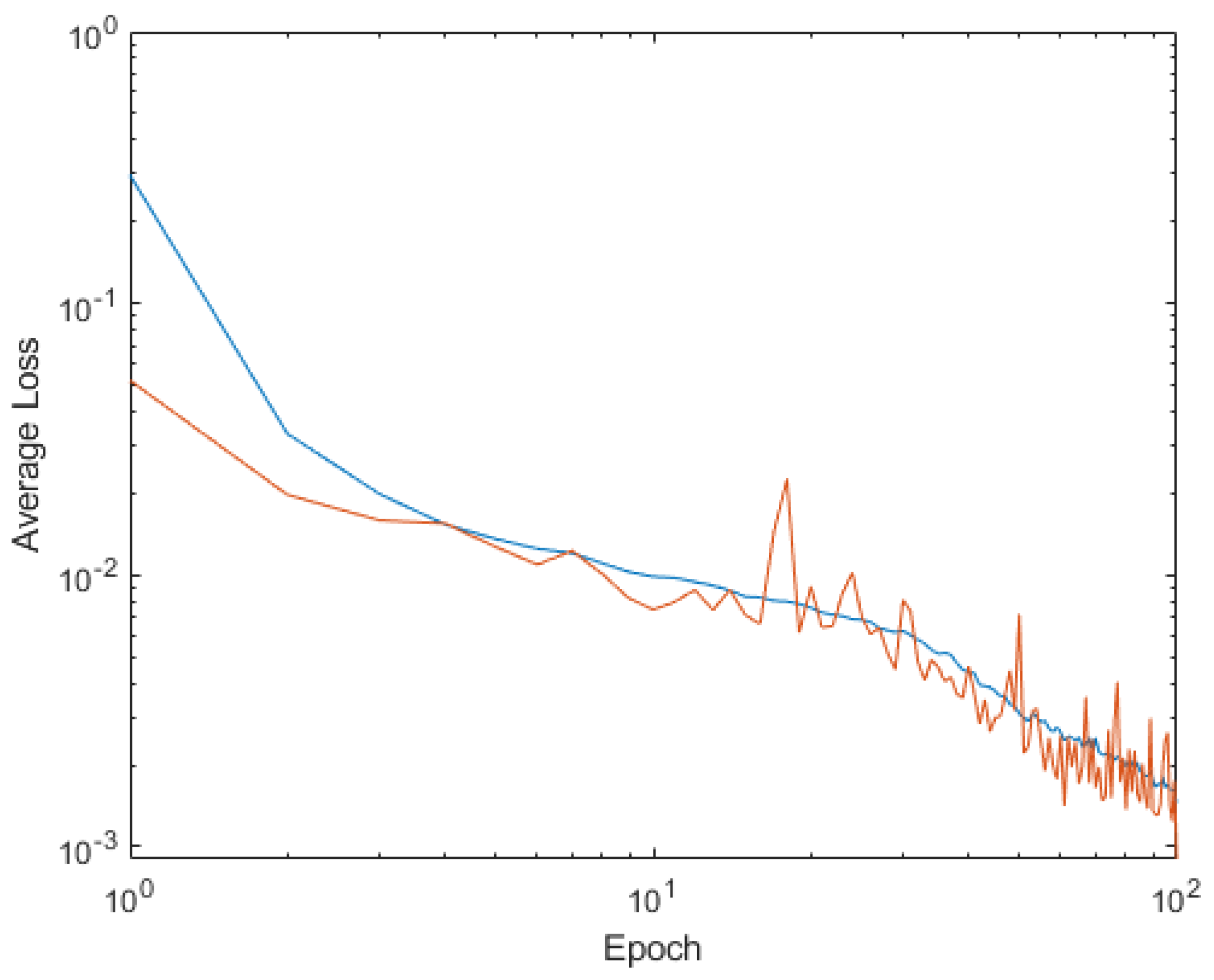
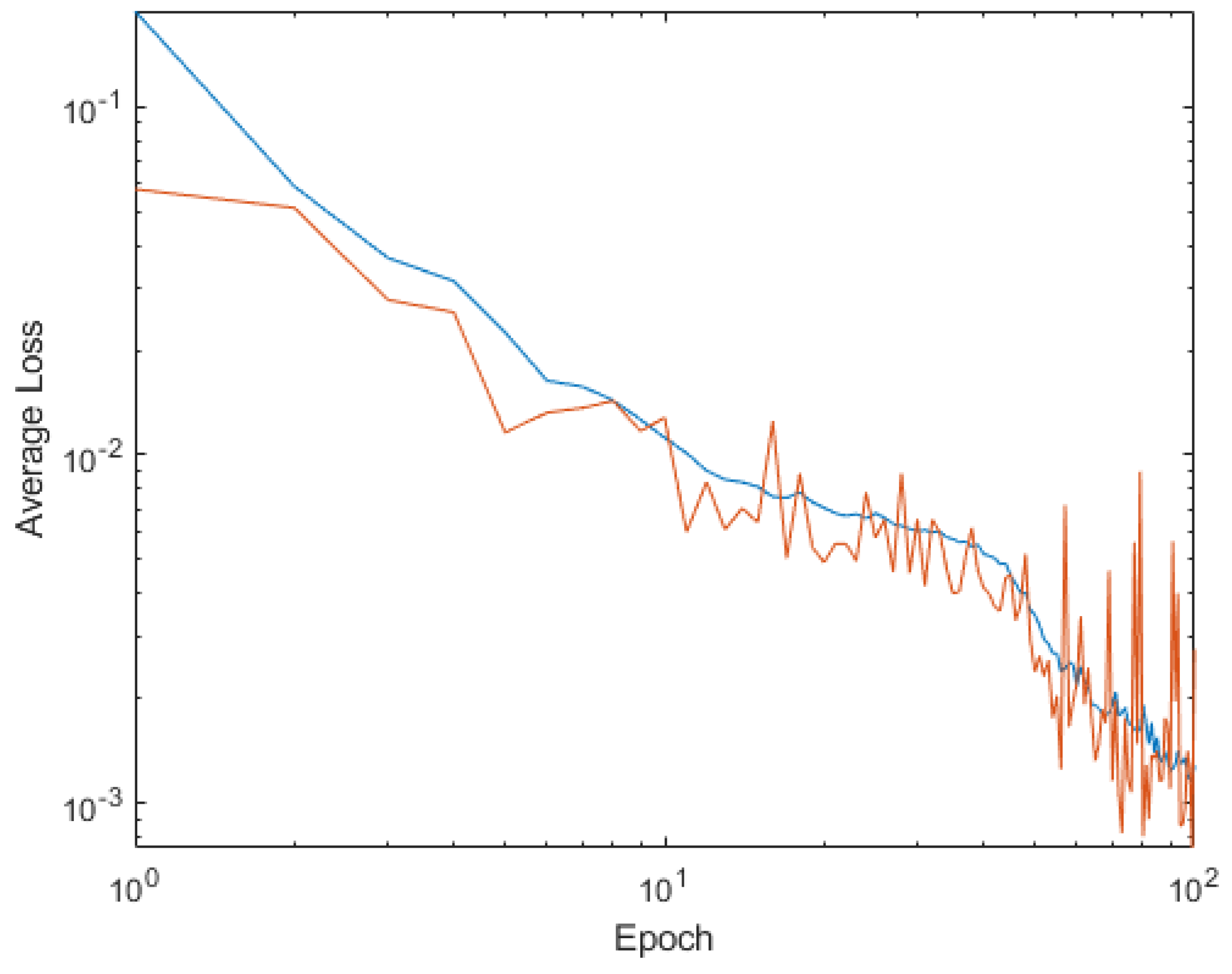
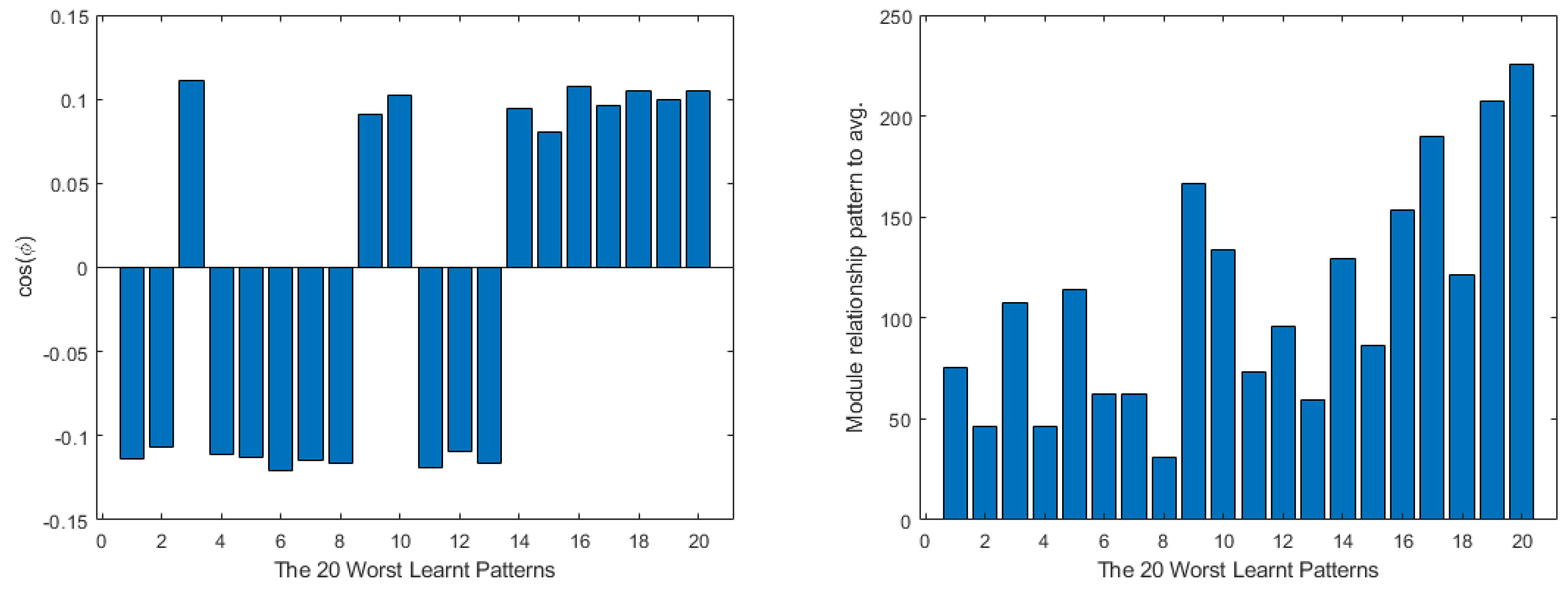
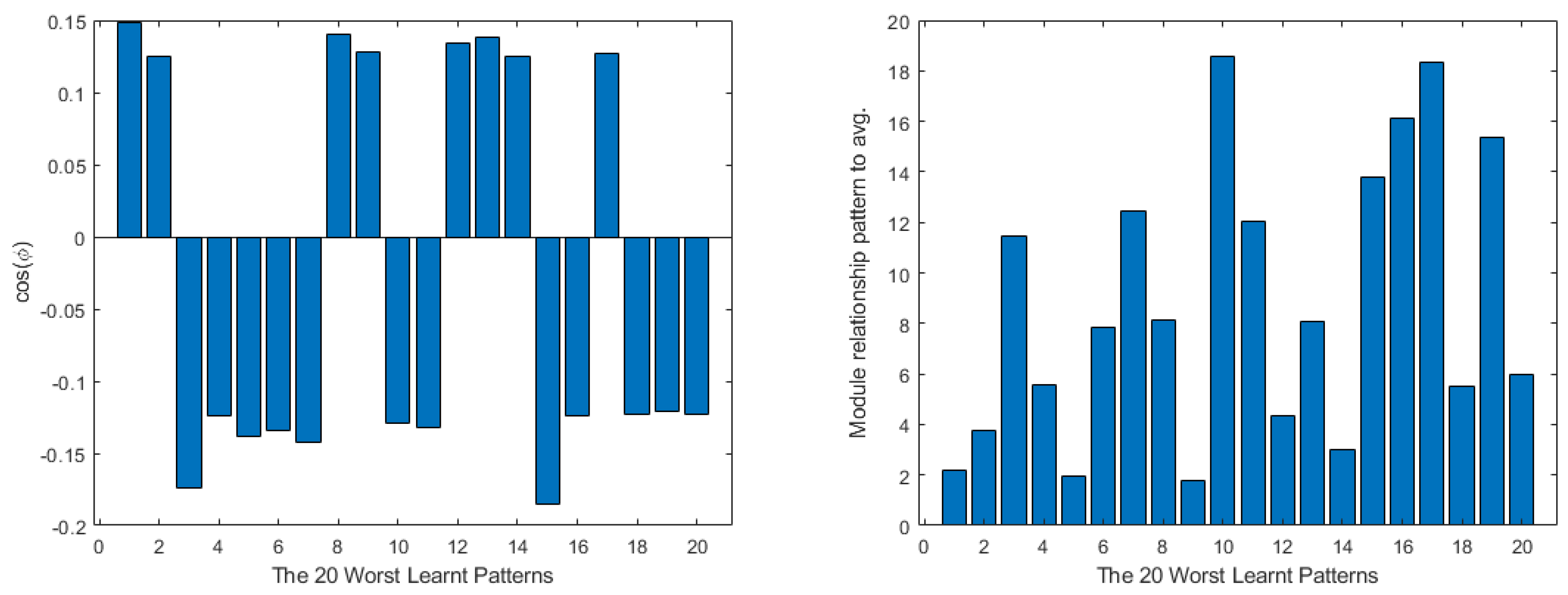
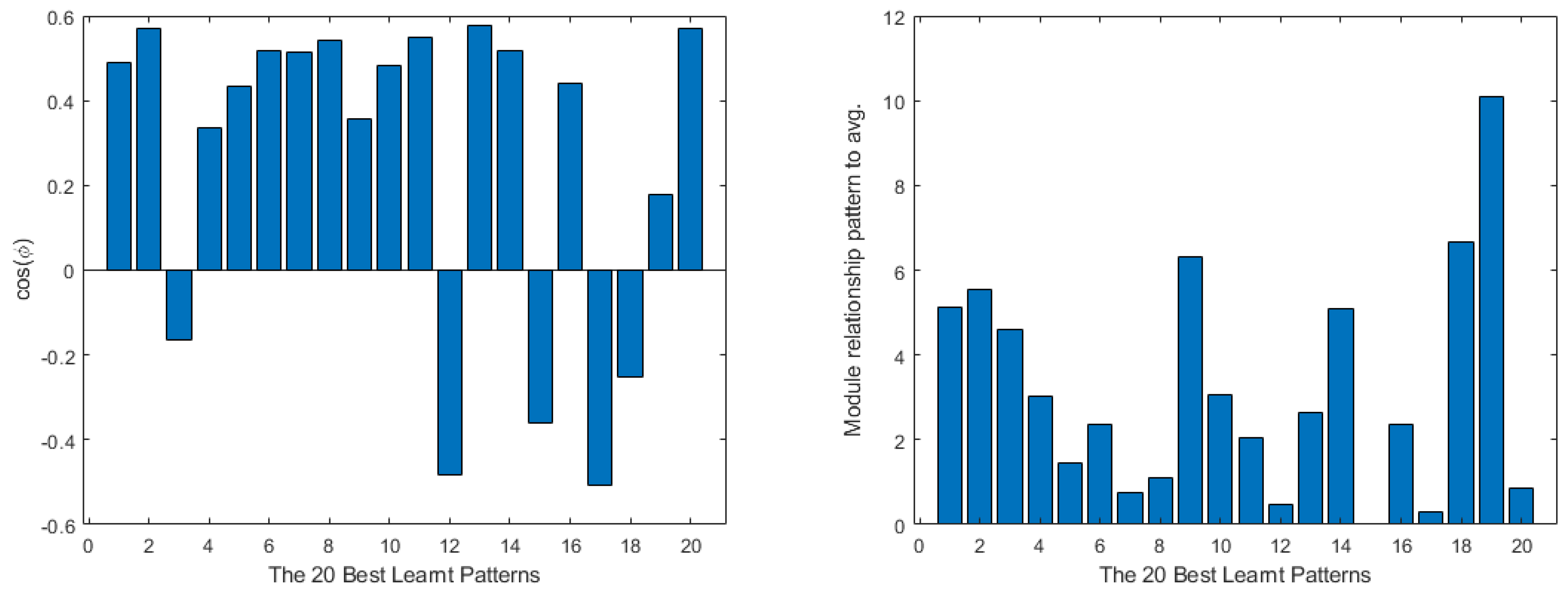
4. Shallow Neural Network Examples and Results
4.1. “Mexican Hat”
4.1.1. Dynamic Alpha
4.1.2. Dynamic Drop-Out
4.1.3. Mixed Together
4.2. Ackley Function
4.3. Cross-in-Tray Function
4.4. Drop-Wave Function
4.5. Goldstein Prize Function
5. Conclusions
6. Future Works
- To analyze the SWARM intelligence as an algorithm, using the example of a shallow network.
- To try to apply recursiveness in the shallow neural network alongside the obtained SGD modifications to try to see if the performance is improved.
- To use pruning algorithms as a basis in order to identify the weakest parts of the network and then reinforce them.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A Stochastic Approximation Method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Jha, N.N.; Lele, M.M. Stochastic gradient descent algorithm for the predictive modelling of grate combustion and boiler dynamics. ISA Trans. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.; Wang, Y.-X.; Azizzadenesheli, K.; Anandkumar, A. signSGD: Compressed Optimisation for Non-Convex Problems. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.04434. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Kamilov, U.S. SignProx: One-bit Proximal Algorithm for Nonconvex Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, D. Sign Stochastic Gradient Descents without bounded gradient assumption for the finite sum minimization. Neural Netw. 2022, 149, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Tang, K.; Li, D. Gradient Descent Learning With Floats. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geron, A. Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems, 2nd ed.; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, J. Python Deep Learning, 1.0; MARCOMBO, S.L.: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P. MATLAB Deep Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, M.A.; Afzal, S. A New Framework for Fine Tuning of Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Srivastava, N.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.0580. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Duchi, J.; Hazan, E.; Singer, Y. Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2121–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakas, F.; Troussas, C.; Voyiatzis, I.; Sgouropoulou, C. A deep learning classification framework for early prediction of team-based academic performance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 106, 107355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-K.; Fong, C.-M.; Yang, P.; Hung, C.-K.; Lu, W.-L.; Chang, C.-W. AdaGrad Gradient Descent Method for AI Image Management. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics—Taiwan (ICCE-Taiwan), Taoyuan, Taiwan, 28–30 September 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Z. An Adaptive Quasi-Hyperbolic Momentum Method Based on AdaGrad+ Strategy. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision and Machine Learning (ICICML), Xi’an, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; Han, F.; Wang, C. Full-waveform inversion with adversarial losses via deep learning. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 205, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, K.; Chopra, N. Generalized AdaGrad (G-AdaGrad) and Adam: A State-Space Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Austin, TX, USA, 13–15 December 2021; pp. 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, C.; Pauwels, E. Sequential convergence of AdaGrad algorithm for smooth convex optimization. Oper. Res. Lett. 2021, 49, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.V.K.; Rao, B.S.; Raju, K.P. Handwritten Hindi Digits Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Network with RMSprop Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniki, M.A.L.; Hadi, M.B.; Manthouri, M. Feedback Error Learning Controller based on RMSprop and Salp Swarm Algorithm for Automatic Voltage Regulator System. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 29–30 October 2020; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mandic, D.P. Convergence of the RMSProp deep learning method with penalty for nonconvex optimization. Neural Netw. 2021, 139, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Qin, Z. Adversarial Samples Generation Based on RMSProp. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Nanjing, China, 9–11 October 2021; pp. 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Shen, L.; Jie, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W. A Sufficient Condition for Convergences of Adam and RMSProp. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11119–11127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, R.; Shaziya, H. A Study of the Optimization Algorithms in Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 Third International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 10–11 January 2019; pp. 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; He, W.; Zhang, C. The research and optimization on levenberg-marquard algorithm in neural net. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 25–26 March 2017; pp. 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangmei, L.; Zhi, Q. The application of Hybrid Neural Network Algorithms in Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on E-Business and E-Government (ICEE), Shanghai, China, 6–8 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KUcak; Oke, G. RBF neural network controller based on OLSSVR. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Singh, A.; Malik, H.; Azeem, A. Cost Analysis of Transformer’s Main Material Weight with Artificial Neural Network (ANN). In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Katra, Jammu, India, 3–5 June 2011; pp. 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Azeem, A.; Singh, A.; Malik, H.; Rahi, O. Application Research Based on Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to Predict No-Load Loss for Transformer’s Design. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Katra, Jammu, India, 3–5 June 2011; pp. 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucak, K.; Oke, G. Adaptive fuzzy PID controller based on online LSSVR. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications, Trabzon, Turkey, 2–4 July 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, M.M.; Alaidarous, E.S.; Maturi, D.A.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shoaib, M. A Levenberg–Marquardt Backpropagation Neural Network for the Numerical Treatment of Squeezing Flow With Heat Transfer Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 227340–227348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teso-Fz-Betoño, A.; Zulueta, E.; Cabezas-Olivenza, M.; Teso-Fz-Betoño, D.; Fernandez-Gamiz, U. A Study of Learning Issues in Feedforward Neural Networks. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, N.L.; Schmidt, M.; Bach, F. A Stochastic Gradient Method with an Exponential Convergence Rate for Finite Training Sets. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1202.6258. [Google Scholar]
- Defazio, A.; Bach, F.; Lacoste-Julien, S. SAGA: A Fast Incremental Gradient Method With Support for Non-Strongly Convex Composite Objectives. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.0202. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P.; Kakade, S.M.; Kidambi, R.; Netrapalli, P.; Sidford, Y.A. Accelerating Stochastic Gradient Descent. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.08227. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z. Adaptive stochastic conjugate gradient for machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 206, 117719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zheng, N. Convergence analysis of asynchronous stochastic recursive gradient algorithms. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 252, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shang, T.; Liu, X.; Qian, P.; Zhang, Y. Advanced multi-feedback stochastic parallel gradient descent wavefront correction in free-space optical communication. Opt. Commun. 2023, 533, 129268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhen, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, G. Adaptive stochastic parallel gradient descent approach for efficient fiber coupling. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13141–13154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phong, L.T.; Phuong, T.T. Differentially private stochastic gradient descent via compression and memorization. J. Syst. Arch. 2023, 135, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Smyth, E. A simplified convergence theory for Byzantine resilient stochastic gradient descent. EURO J. Comput. Optim. 2022, 10, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Mhamdi, E.M.E.; Guerraoui, R.; Stainer, J. Machine Learning with Adversaries: Byzantine Tolerant Gradient Descent. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Qu, C.K.; Gong, P. Anomalous diffusion dynamics of learning in deep neural networks. Neural Netw. 2022, 149, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjellström, C.; Nyström, K. Deep learning, stochastic gradient descent and diffusion maps. J. Comput. Math. Data Sci. 2022, 4, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, V.; Nicosia, G. Backpropagation Neural Tree. Neural Netw. 2022, 149, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil, R.; Narayanan, B.; Velmurugan, K. Develop the hybrid Adadelta Stochastic Gradient Classifier with optimized feature selection algorithm to predict the heart disease at earlier stage. Meas. Sens. 2023, 25, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, J.; Frey, B. Adaptive dropout for training deep neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Weng, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Cai, Q.; Gu, W. Adaptive Dropout Method Based on Biological Principles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzadeh, S.I.; Farajtabar, M.; Ghasemzadeh, H. Dropout as an Implicit Gating Mechanism For Continual Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yi, Z. Adaptive sparse dropout: Learning the certainty and uncertainty in deep neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 450, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeJeune, D.; Javadi, H.; Baraniuk, R.G. The Flip Side of the Reweighted Coin: Duality of Adaptive Dropout and Regularization. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.07769. [Google Scholar]
- Surjanovic, S.; Bingham, D. Virtual Library of Simulation Experiments: Test functions and Datasets. 2013. Available online: https://www.sfu.ca/~ssurjano/index.html (accessed on 6 August 2022).










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teso-Fz-Betoño, A.; Zulueta, E.; Cabezas-Olivenza, M.; Fernandez-Gamiz, U.; Botana-M-Ibarreta, C. Modification of Learning Ratio and Drop-Out for Stochastic Gradient Descendant Algorithm. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051183
Teso-Fz-Betoño A, Zulueta E, Cabezas-Olivenza M, Fernandez-Gamiz U, Botana-M-Ibarreta C. Modification of Learning Ratio and Drop-Out for Stochastic Gradient Descendant Algorithm. Mathematics. 2023; 11(5):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051183
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeso-Fz-Betoño, Adrian, Ekaitz Zulueta, Mireya Cabezas-Olivenza, Unai Fernandez-Gamiz, and Carlos Botana-M-Ibarreta. 2023. "Modification of Learning Ratio and Drop-Out for Stochastic Gradient Descendant Algorithm" Mathematics 11, no. 5: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051183
APA StyleTeso-Fz-Betoño, A., Zulueta, E., Cabezas-Olivenza, M., Fernandez-Gamiz, U., & Botana-M-Ibarreta, C. (2023). Modification of Learning Ratio and Drop-Out for Stochastic Gradient Descendant Algorithm. Mathematics, 11(5), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051183






