Abstract
The task of partitioning convex shape objects from images is a hot research topic, since this kind of object can be widely found in natural images. The difficulties in achieving this task lie in the fact that these objects are usually partly interrupted by undesired background scenes. To estimate the whole boundaries of these objects, different neural networks are designed to ensure the convexity of corresponding image segmentation results. To make use of well-trained neural networks to promote the performances of convex shape image segmentation tasks, in this paper a new image segmentation model is proposed in the variational framework. In this model, a fuzzy membership function, instead of a classical binary label function, is employed to indicate image regions. To ensure fuzzy membership functions can approximate to binary label functions well, an edge-preserving smoothness regularizer is constructed from an off-the-shelf plug-and-play network denoiser, since an image denoising process can also be seen as an edge-preserving smoothing process. From the numerical results, our proposed method could generate better segmentation results on real images, and our image segmentation results were less affected by the initialization of our method than the results obtained from classical methods.
Keywords:
image segmentation; fuzzy membership function; convex shape; plug-and-play ADMM; deep convolutional neural network MSC:
65K10; 35Q68
1. Introduction
Convex shape image segmentation, which refers to partitioning convex object regions from images, is a challenging, but important, problem in image processing, since convex objects, such as books, buildings and some human organs, are widely found in many application scenarios [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Mathematically, a convex set means that a line segment linked by any two points in the set also lies in this set. Based on this point, Gorelick in [7] proposed a discrete graph cut-based convex shape image segmentation model, in which all 1-0-1 configurations in the inner region of convex objects in images were penalized. However, as the energy in discrete graph cut-based models is not submodular [8], some zigzag edges can be found in the image segmentation results. To overcome this drawback, continuous convex shape image segmentation methods are proposed. Bae in [9] found that a convex region could be guaranteed its convexity if the curvature of the continuous boundary curves of the region were kept non-negative. Then, by using a signed distance function (SDF), which is also a special level set function, to implicitly represent an estimated object region, Yan, in [10], proposed a level set function-based convex shape image segmentation model, in which a simple linear constraint whereby the Laplacian of the SDF is held non-negative could ensure that this estimated region was convex. However, it is time-consuming to strictly keep the estimated level set function an SDF during the iteration-solving process.
In order to improve the efficiency of convex shape image segmentation, Luo, in [11], proposed employing a classical binary label function (BLF) instead of a level set function, such as the SDF used in [10], to indicate the estimated target region and to construct a quadratic convex shape constraint on the BLF to guarantee the convexity of the estimated region. However, as the non-continuity problem of the BLF is quite similar to the problem of the above graph cut-based image segmentation models, some zigzag edges can also be found in the image segmentation results obtained from the model in [11]. To overcome the zigzag edge problem, the BLF needed to be smoothed. Here, a smoothed BLF is usually called a fuzzy membership function (FMF) [12]. In order to ensure the above quadratic convex shape constraint held for the FMF as well, the FMF needed to approximate to the BLF well. Classically, the convex total variation (TV) regularizer in [13] and some nonconvex regularizers in [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] are used to measure the smoothness of the FMF, while some important geometrical structural details of the FMF are preserved. Here, different regularizers mean different smoothness priors are assumed on the FMF. As image smoothness priors are usually learned from some deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) in [22,23,24,25] in the field of image denoising, in this paper we tried to integrate a well-trained DCNN, named DRUNet in [26], into our convex shape image segmentation task to obtain better smoothing performance on the estimated FMF. In fact, an FMF itself can be seen as an image, and an image denoising process is equivalent to an image smoothing process, while some important image details need to be preserved during the smoothing process. The integration wherein the DRUNet is embedded into convex shape image segmentation tasks can be seen as a plug-and-play (P&P) approach [27,28,29], since the DRUNet to be employed in this paper is pre-trained for image denoising tasks, rather than being directly trained for image segmentation tasks.
The main idea of a deep P&P approach is that, with the aid of the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) [30,31,32] or half-quadratic splitting (HQS) [33,34,35], an image processing problem can be separated into several subproblems, one of which corresponds to a denoising problem that can be solved via well-trained denoisers of DCNNs. Classically, the deep P&P approach is only used to deal with image restoration problems, such as image deblurring [36,37], image inpainting [38,39] and single image super resolution [40,41], etc. In this paper, we propose introducing the P&P approach to deal with the convex shape image segmentation problem.
In this paper we used FMFs to represent the foreground or the background and to develop the convex shape prior. A P&P network denoiser intended to ensure the FMFs approximated typical BLFs well, since an image denoising process can be regarded as an edge-preserving smoothing process. The main contributions involve three aspects. Firstly, we employ continuous FMFs to represent image regions and propose the convex shape prior. Secondly, a denoising neural network is incorporated into our image segmentation method to control the smoothing process of FMFs. Lastly, a corresponding algorithm is constructed to obtain our final solutions. The P&P–ADMM method and two convex set operators constitute the main body of our algorithm.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, two related works are reviewed, including a BLF-based convex shape image segmentation model and a typical P&P–ADMM-based image segmentation framework with a DCNN denoiser. Our proposed P&P network-based convex shape image segmentation model and details of our corresponding algorithm of the proposed model are given in Section 3. Numerical results, as well as their analysis, are provided in Section 4. Section 5 concludes the whole paper.
2. Related Work
2.1. The BLF-Based Convex Shape Image Segmentation Model
Let be an image defined on the image domain , where or mean that I represents a grayscale image or a color image, respectively. A general image segmentation model to partition into the foreground region and the background region to solve the minimization problem with respect to is as follows:
where the function (resp. ) penalizes the dissimilarity between the pixel and other pixels in this region (resp. ), indicates the enclosed boundary curve of , represents the length of , and , and are positive tuning parameters. Usually, , , where can be modeled by a Gaussian mixture model defined as follows:
where are positive weights satisfied such that , and
where the operator maps to be a K dimensional feature image for each pixel , the expectation and the covariance matrix are two key features of a general K dimensional Gaussian distribution. Different features about each pixel are proposed to deal with partitioning different kinds of images. such as images with inhomogeneous lightness and textures.
As the minimization problem in model (1) is hard to directly minimize with respect to a geometrical variable , variable usually needs to be equivalently transferred into a BLF , which is defined by:
Then, model (1) can be converted into the following form,
where , and when , the second term in model (5) equals to in model (1). The first and the second terms of model (5) are called the data fidelity term and the regularization term, respectively. The regularization term is usually specified by some explicit and hand-crafted smoothness priors on . Different choices of function mean that different smooth measurements are given on , and smoothing levels of on pixels should be higher than pixels . Obviously, the performances of model (5) depend largely on different choices of function , since most classical regularization terms are usually hand-crafted.
To make the boundary curves of estimated from model (5) have convex shapes, Luo, in [11], introduced a convex shape inequality constraint on the BLF into model (5), namely,
where ∗ is the classical convolution operator and the neighborhood function satisfies
For computational simplicity, variable r in constraint (6) is usually quantized to .
2.2. A P&P–ADMM Image Segmentation Framework with a DCNN Denoiser
For convenience of discussion, model (5) without the constraint can be rewritten into the following more general form,
This model can be solved by using an ADMM approach which contains the following three main steps.
Firstly, by introducing an auxiliary function , which equals to , model (8) can be converted into the following equivalent constrained form:
This step is also called a variable splitting step.
Secondly, a so-called augmented Lagrange function and a proximal operator need to be, respectively, defined as follows:
and
where is the Lagrange multiplier and denotes a step size to update . In the following, variables in formulae are dropped for conciseness. Then, for a given initialization and , the ADMM approach obtains a sequence from the following iteration system:
Thirdly, as the minimization problem shown in Equation (11) can also be seen as a denoising problem with a noise level parameter , the proximal operator can be correspondingly substituted by a more effective pre-trained DCNN denoising operator , where different indicate different noise levels. More precisely, the first sub-problem shown in the iteration system (12) is changed into the following form:
Note that the above substitution procedure is the so-called P&P approach.
3. Our Proposed Convex Shape Image Segmentation Method
3.1. Our Proposed Model
To overcome the difficulties of minimizing model (5) because of the non-continuity of the BLF , we introduced an FMF into our model as a continuous approximation of the classical BLF . Moreover, to ensure the convexity of the FMF in our model, we followed Equation (6) to use the constraint . However, in order to make and as far as possible, we followed model (8) to introduce the DRUNet [26] as a P&P DCNN into our model. Then, based on model (8), our proposed image segmentation model solves a constrained minimization problem as follows:
Here, the FMF satisfying constraints (I) and (II) can be seen as a loose version of the classical BLF in model (8) together with constraints as well as . The regularization term in our model (14) makes the FMF approximate to the BLF well. More precisely, ensures that some important details of , which can differentiate image foreground and background regions, are preserved well. This is quite similar to the requirements of image denoising on in model (11), namely, noises on need to be removed/smoothed, while some important image details of need to be preserved. Then, it makes sense that the well-trained , mentioned in Section 2.2, can be integrated into our image segmentation task in a P&P way. However, different from the classical unconstrained model (8), our proposed model (14) is a constrained model. Then, some projecting operators needed to be integrated into the original P&P–ADMM algorithm, discussed in Section 2.2, to solve our constrained model (14).
3.2. Algorithm to Our Model
Constraints (I) and (II) on the FMF in model (14) can be respectively achieved by two simple projection operators, as follows:
and
Obviously, and hold for all .
Below, we focus on solving the minimization problem in model (14) without considering constraints (I) and (II):
As the minimization problem (17) is the same as the one shown in model (8), we followed the iteration system (12) to solve the minimization problem (17) and incorporated into the iteration system (12). More precisely, for a given initialization and , a sequence (k is an iteration index) can be obtained by the following iteration system:
Here, is a well-trained denoising operator with the noise level . The solution of the unconstrained minimization problem (17), , can be obtained by setting when in the iteration system (18). Then, the final solution of our constrained model (14), , can be generated by:
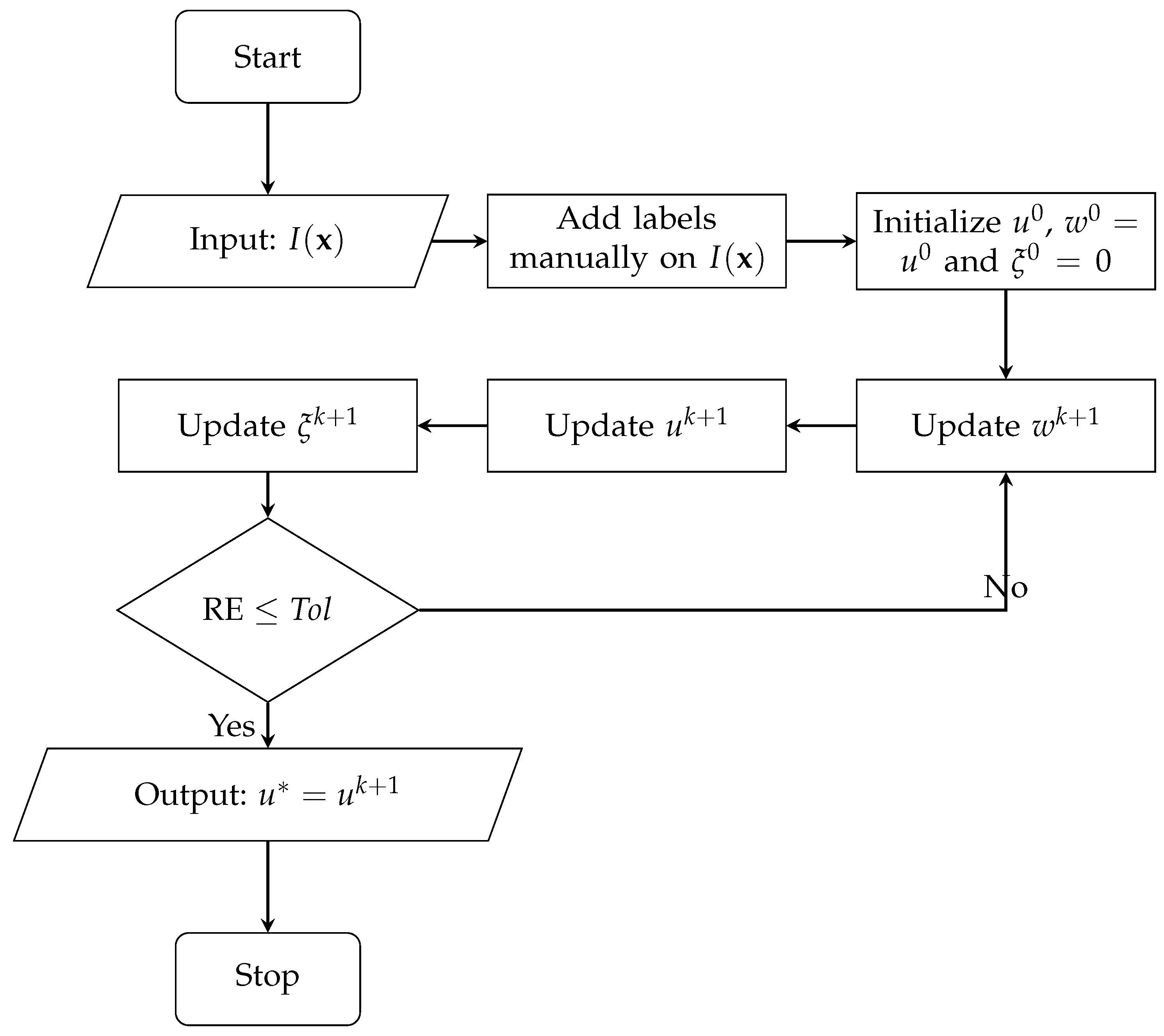
Our complete algorithm is shown in Algorithm 1. For simplicity, we call our plug-and-play neural network-based convex shape image segmentation algorithm the PPA-CS algorithm. In the algorithm, the initial image segmentation result, , is manually obtained. More concretely, a foreground region is roughly marked by several curves, and for each pixel in the region of the convex envelope of the curves, and otherwise, . In addition, we initialized and . The stopping criterion of our PPA–CS algorithm is to reach the maximum iteration number ( in our experiments), or to satisfy the relative error ( in our experiments), where:
and represents the classical norm.
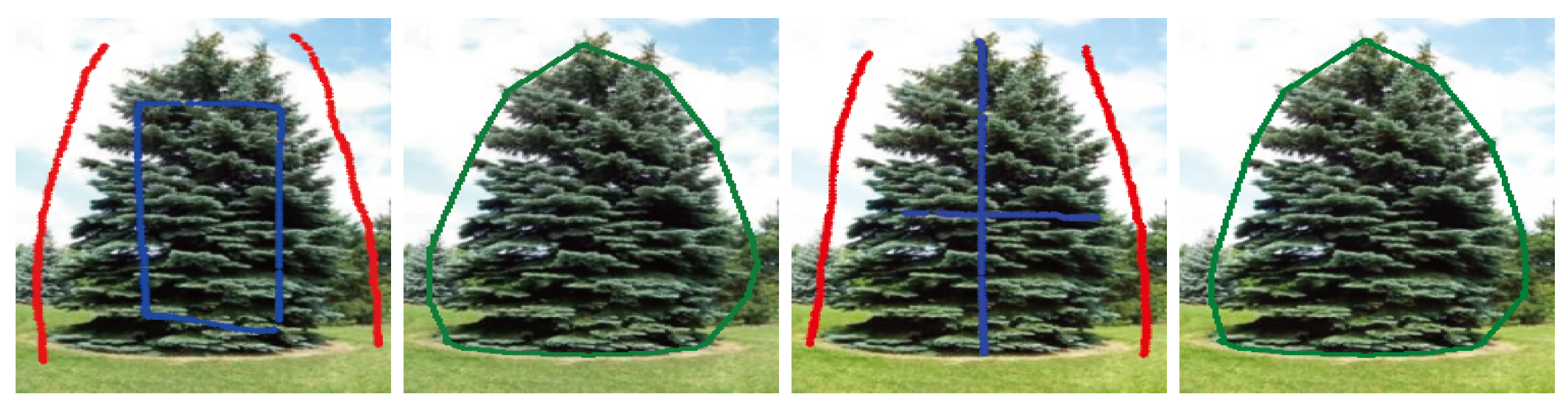
The figure of methodology about our method is shown in Figure 1.
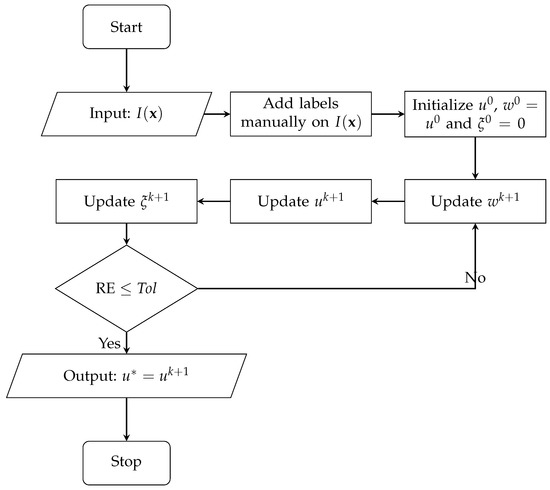
Figure 1.
The figure of methodology of the proposed PPA-CS method.
| Algorithm 1 Our proposed plug-and-play neural network-based convex shape image segmentation algorithm (the PPA–CS algorithm). |
| Initialization: initialize manually, and , give some parameters, including , , , , and , and set the iteration index . |
| Repeat: |
| update in (18); |
| update in (18); |
| update in (18); |
| project ; |
| ; |
| Until a stopping criterion is satisfied |
| Output: our final estimated FMF result . |
4. Numerical Results and Discussion
In this section, several representative convex shape image segmentation results are listed to validate the performance of our proposed PPA–CS method. Here, the images to be tested were chosen from two widely used image datasets, called the Berkeley segmentation dataset and benchmark 500 (BSDS500) and the Weizmann segmentation evaluation database (WSED). During the evaluation process, our results were also compared with those obtained from the BLF and TV regularizer-based convex shape (BLF-TV-CS) image segmentation method in [11] and the FMF and TV regularizer-based convex shape (FMF–TV–CS) image segmentation method. Note that the only difference between the BLF–TV–CS method and the FMF–TV–CS method lies in the fact that the BLF in the former method is changed to become the FMF in the latter method. The FMF–TV–CS method is also a new method constructed in this paper, and this method can be seen as an intermediate method between the classical BLF–TV–CS method and our finial PPA–CS method. The reasons why we chose these methods as comparisons are that all of these methods are discussed in the variational framework. It is convenient to verify the effectiveness of our designed FMF-based convex shape constraint, as well as the superiority of our introduced P&P network regularizer.
4.1. Environmental Setting
The BLF–TV–CS method, the FMF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method were all implemented in the environment of Python 3.10 on an Intel (R) Xeon (R) E-2176M CPU and NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650Ti PC. Some necessary model parameters, like , , , , and , were necessary to start up our PPA–CS method. We simply set (resp. ), which meant that and (resp. and ) in Equation (2) were assigned the same weights in our model. According to the expressions shown in the iteration system (18), parameter was not only used as a step size for updating the Lagrange multiplier , but also played a role in the smoothing process of . By means of testing, we found that we could simply fix . In addition, we set as the default value and searched for the best of each image manually. If the target region was rich in detail or the whole foreground was not convex, the could choose a larger value. We tuned from a 1-step in application since the denoiser in our method used as the argument when . To even things up, all of the parameters in the BLF–TV–CS method and the FMF–TV–CS method were optimized. The parameter optimizing process was similar to that of tuning the parameter in our PPA–CS method.
4.2. Segmentation Results on BSDS500 and WSED
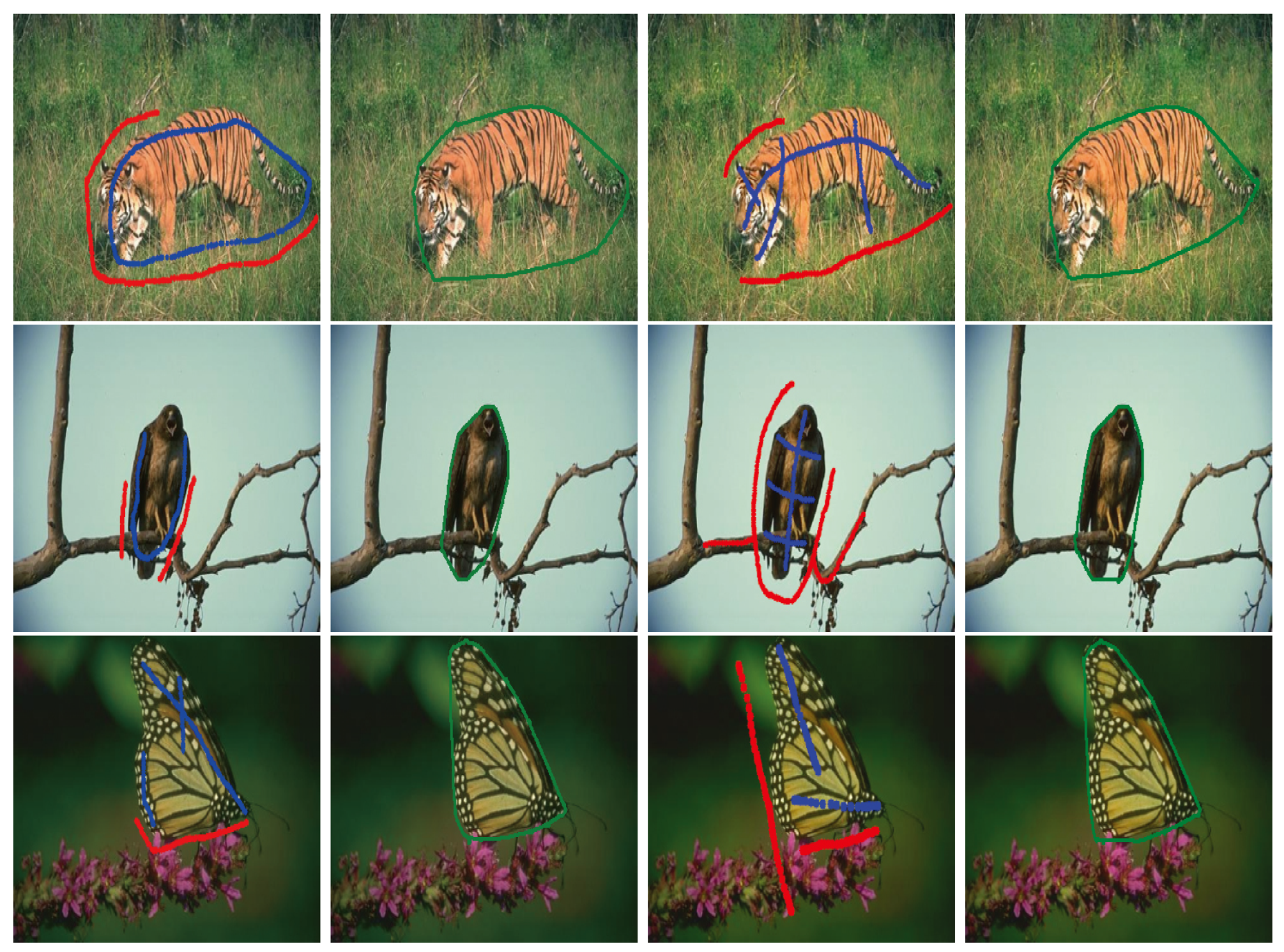
In Figure 2 (resp. Figure 3), we compared our image segmentation results with those obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method by randomly choosing ten test images from BSDS500 (resp. WSED). In both Figure 2 and Figure 3, (a) shows the original test images on which blue and red markers were used to differentiate the foreground region and the background region, respectively. For convenience of discussion, the images shown in Figure 2a (resp. Figure 3a) are numbered Figure 2a (resp. Figure 3a ) from left to right and from top to bottom, where and . Similar notations can also be defined, such as Figure 2b and Figure 3c . We also used the notations , and to represent the set of blue marker points, the convex envelope region of the blue markers and the set of red marker points, respectively. Then, for pixel , the initialization of our image segmentation , and for pixels , , and for the k-th iteration of our PPA–CS method, for , and for .
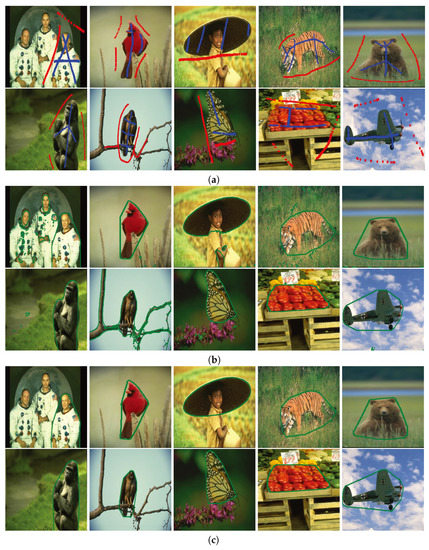

Figure 2.
Different convex shape image segmentation results for images in BSDS500, where (a) shows ten original images on which blue and red markers were used to differentiate the foreground region and the background region, respectively, and (b,c) were corresponding image segmentation results of (a) obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively.
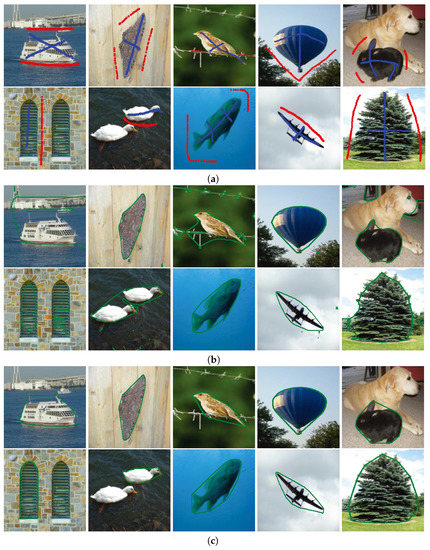

Figure 3.
Different convex shape image segmentation results for images in WSED, where (a) shows ten original images on which blue and red markers were used to differentiate the foreground region and the background region, respectively, and (b,c) are corresponding image segmentation results of (a) obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively.
In Figure 2 and Figure 3, (b) and (c) show image segmentation results obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively. Here, green curves show the estimated boundaries between foreground regions and background regions. In order to make more detailed comparisons on image segmentation results between the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, Table 1 (resp. Table 2) lists the judgments on whether the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method could generate a correct convex shape image segmentation result for each test image shown in (a) of Figure 2 (resp. Figure 3). Table 3 presents the optimal value of for each image in Figure 2 and Figure 3. More precisely, for a given method, if the estimated foreground region from an image was not convex in shape from vision, we marked it with an “F” symbol. If not, we marked it with a “T” symbol.

Table 1.
Comparison of different image segmentation methods as to whether the estimated shape of the foreground region of each image shown in Figure 2a was convex from vision, where the notation corresponds to the image shown in Figure 2a and the notation “T” means the corresponding estimated shape was convex. Otherwise, the notation “F” was given.

Table 2.
Comparison of different image segmentation methods as to whether the estimated shape of the foreground region of each image shown in Figure 3a was convex from vision, where the notation corresponds to the image shown in Figure 3a and the notation “T” means the corresponding estimated shape was convex. Otherwise, the notation “F” was given.

According to the results shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, as well as Table 1 and Table 2, we simply found that our proposed PPA–CS method performed better than the BLF–TV–CS method from vision. In fact, for the twenty images shown in Figure 2a and Figure 3a, our method and the BLF–TV–CS method held 100% and 40% accuracy in extracting the convex shape foreground regions of the images, respectively. Furthermore, considering the undesired image segmentation results marked by “F” in Table 1 and Table 2, we found that the estimated foreground regions from the BLF–TV–CS method tended to be strongly hampered by their corresponding similar background regions. For example, according to the undesired image segmentation results of the BLF–TV–CS method, for the original image shown in Figure 2a , we found that the branch colors in the background region of this image were very close to the feather colors in the foreground eagle region. This proved that the introduction of the DRUNet as a regularizer into our method benefitted our image segmentation performance better than the classical TV regularizer used in the BLF–TV–CS method, since our model inherited the powerful image recognition capabilities of neural networks.
The numbering iterations and CPU time for obtaining the desired image segmentation results of the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method on the original images shown in Figure 2a are compared in Table 4. Here, the desired image segmentation results are those shown in the subfigures , , and of both Figure 2b and Figure 2c. From the results shown in Table 4, we found that, compared with the BLF–TV–CS method, which took about 5.87 s, in our proposed PPA–CS method it took, on average, about 15.00 s for each image to obtain the desired image segmentation result. However, integrating the results listed in both Table 1 and Table 4, we believe that, compared with the effectiveness of our proposed image segmentation method, the CPU time was a secondary consideration.

Table 4.
Iterations and CPU time (in seconds) of the BLF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA-=CS method for the original images shown in Figure 2a , , and .
4.3. Model Sensitivity to Initial Contours
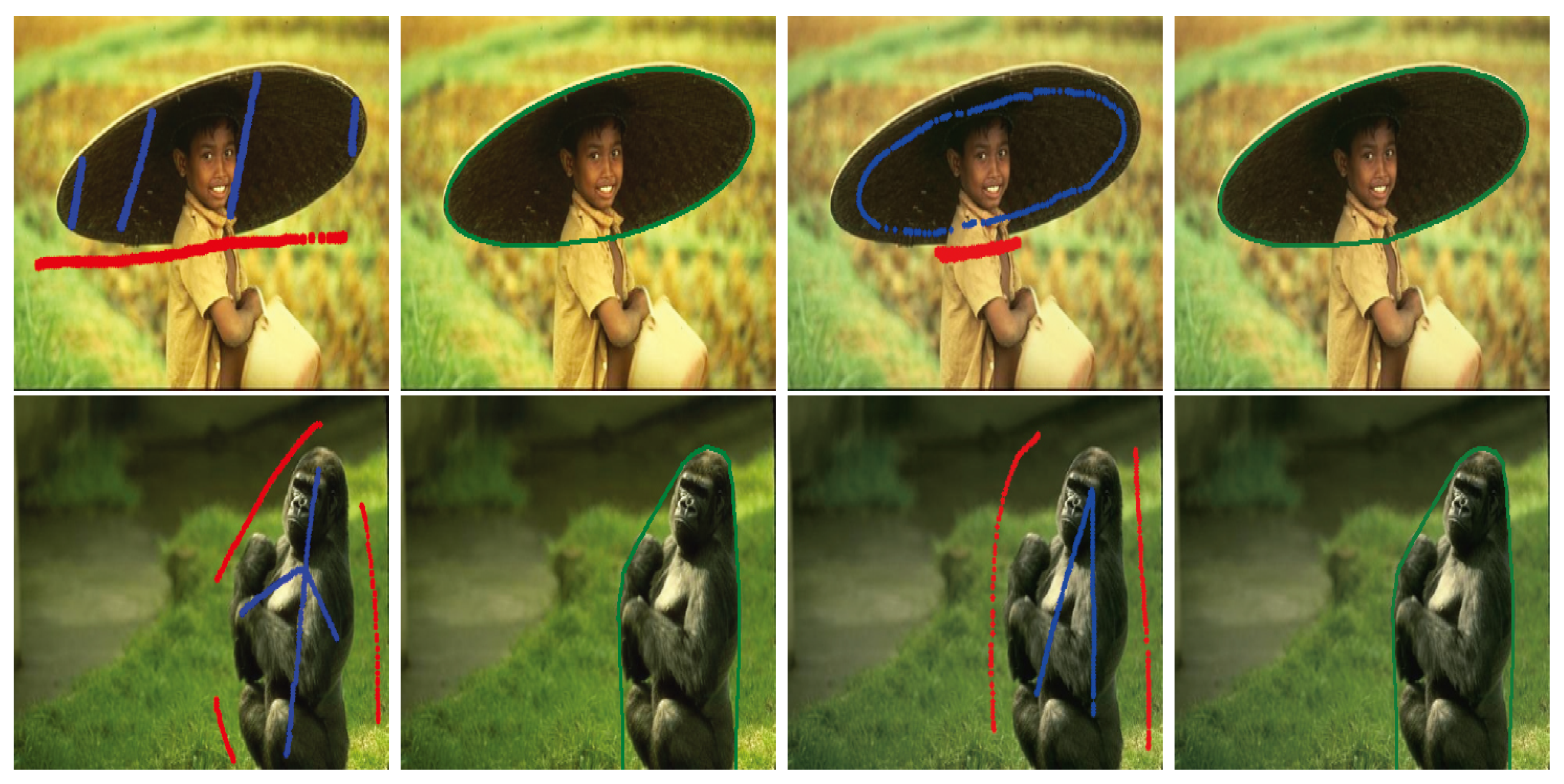
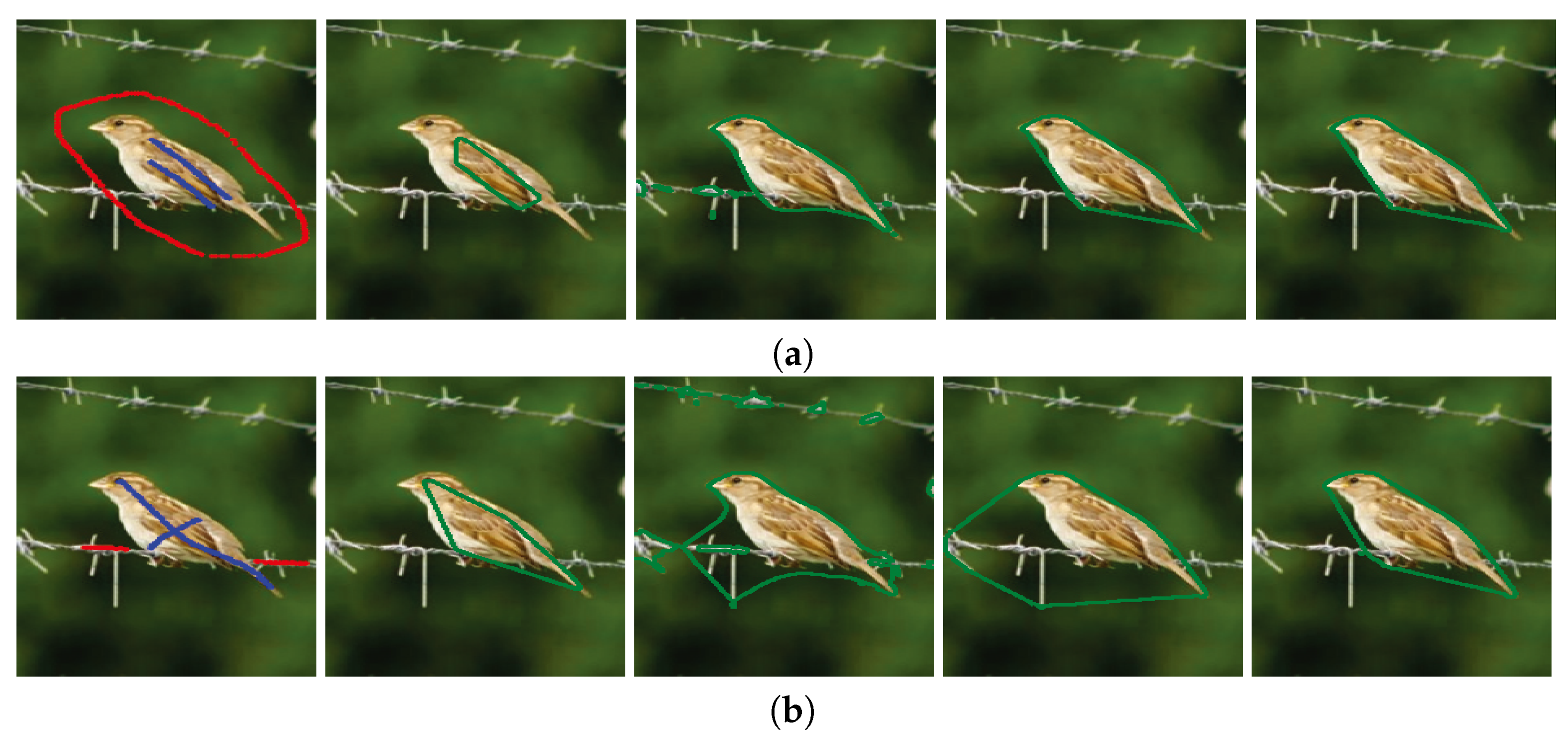
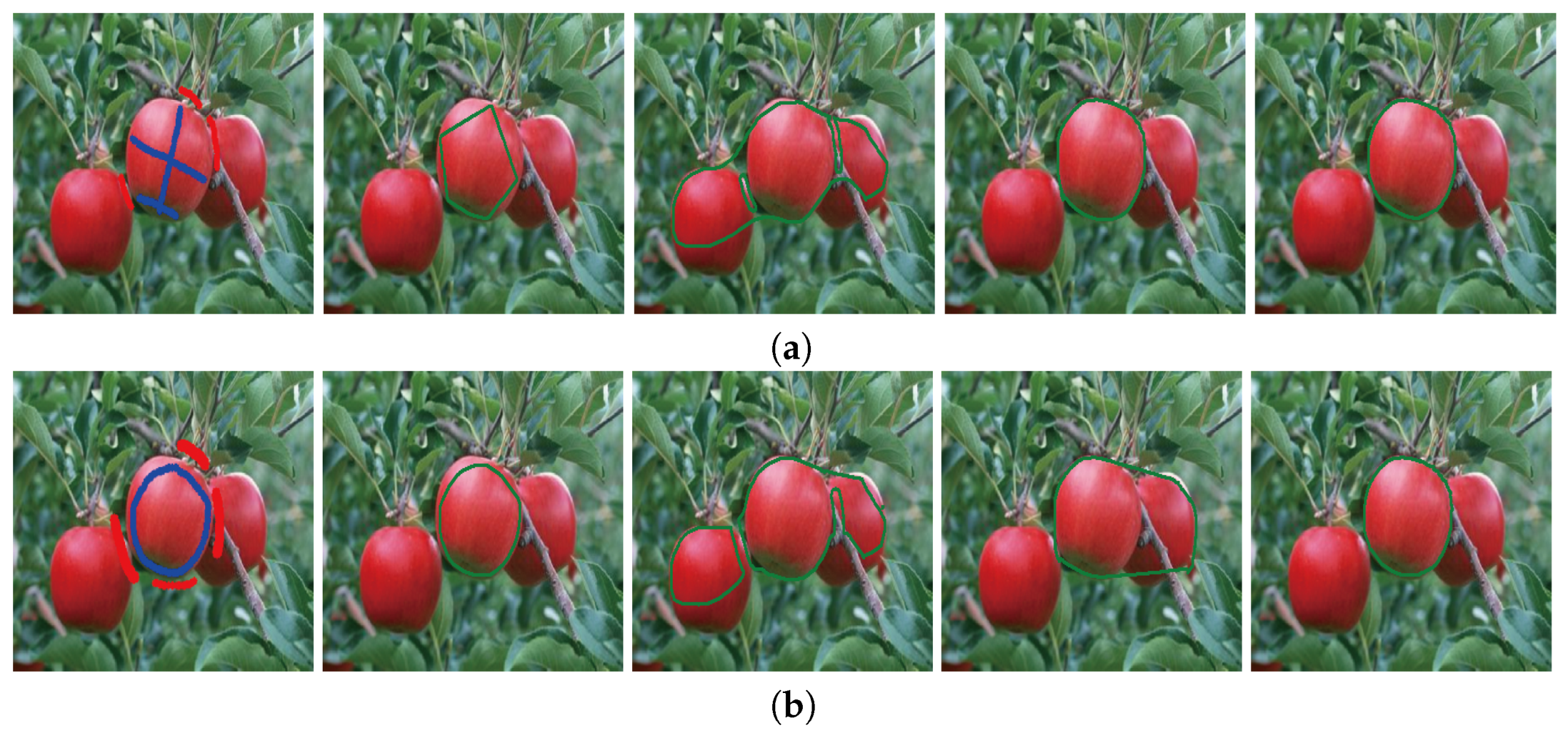
To validate the robustness of our proposed image segmentation method, we compared some image segmentation results generated by different methods with different initial contours in Figure 4 and Figure 5. In these figures, (a) and (b) show two different groups of image segmentation results with different initial given contours. From left to right, the first columns shown in (a) and (b) are the original images on which foreground and background regions are, respectively, marked by blue and red curves, the second columns show the initial contours of foreground regions, and the last three columns are the image segmentation results obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method, the FMF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively.
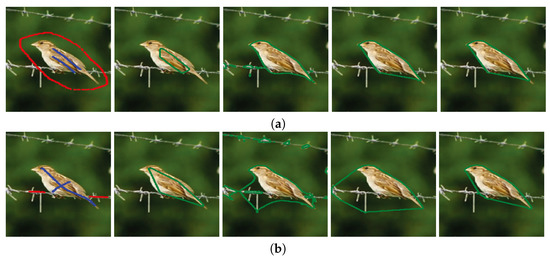
Figure 4.
Comparison of image segmentation results with different initial contours, where the first column and the second column shown in (a,b) show the original images and the initial contours of foreground regions, respectively, and the last three columns in (a,b) are the image segmentation results obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method, the FMF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively.
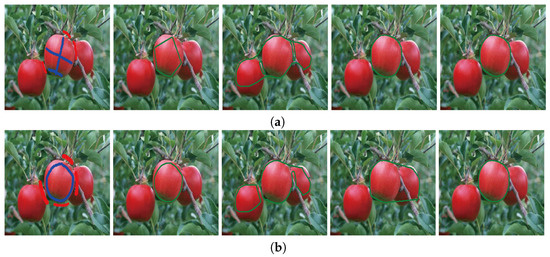
Figure 5.
Comparison of image segmentation results with different initial contours, where the first column and the second column shown in (a,b) show the original images and the initial contours of foreground regions, respectively, and the last three columns in (a,b) are the image segmentation results obtained from the BLF–TV–CS method, the FMF–TV–CS method and our proposed PPA–CS method, respectively.
Comparing the results shown in the last three columns of Figure 4a, we found that all of the three methods generated the desired image segmentation results when the initial contours were given as the forms shown in the first column of Figure 4a. However, when the initial contours changed to the forms shown in the first column of Figure 4b, the results of the BLF–TV–CS method and the FMF–TV–CS method varied significantly, while our results experienced no noticeable change. In order to further validate the robustness of our proposed method to initial contours, we designed a special test image segmentation experiment in Figure 5. Here, the background region of the original image contained similar content to the foreground region. From the results shown in Figure 5a,b, we found that the desired image segmentation results were obtained from our proposed method, given the two different initial contours shown in the first column of (a) and (b), while the other two methods could not generate effective results in the experiment. Based on the results shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, we drew a conclusion that our results were more robust to initial contours than the other two methods.
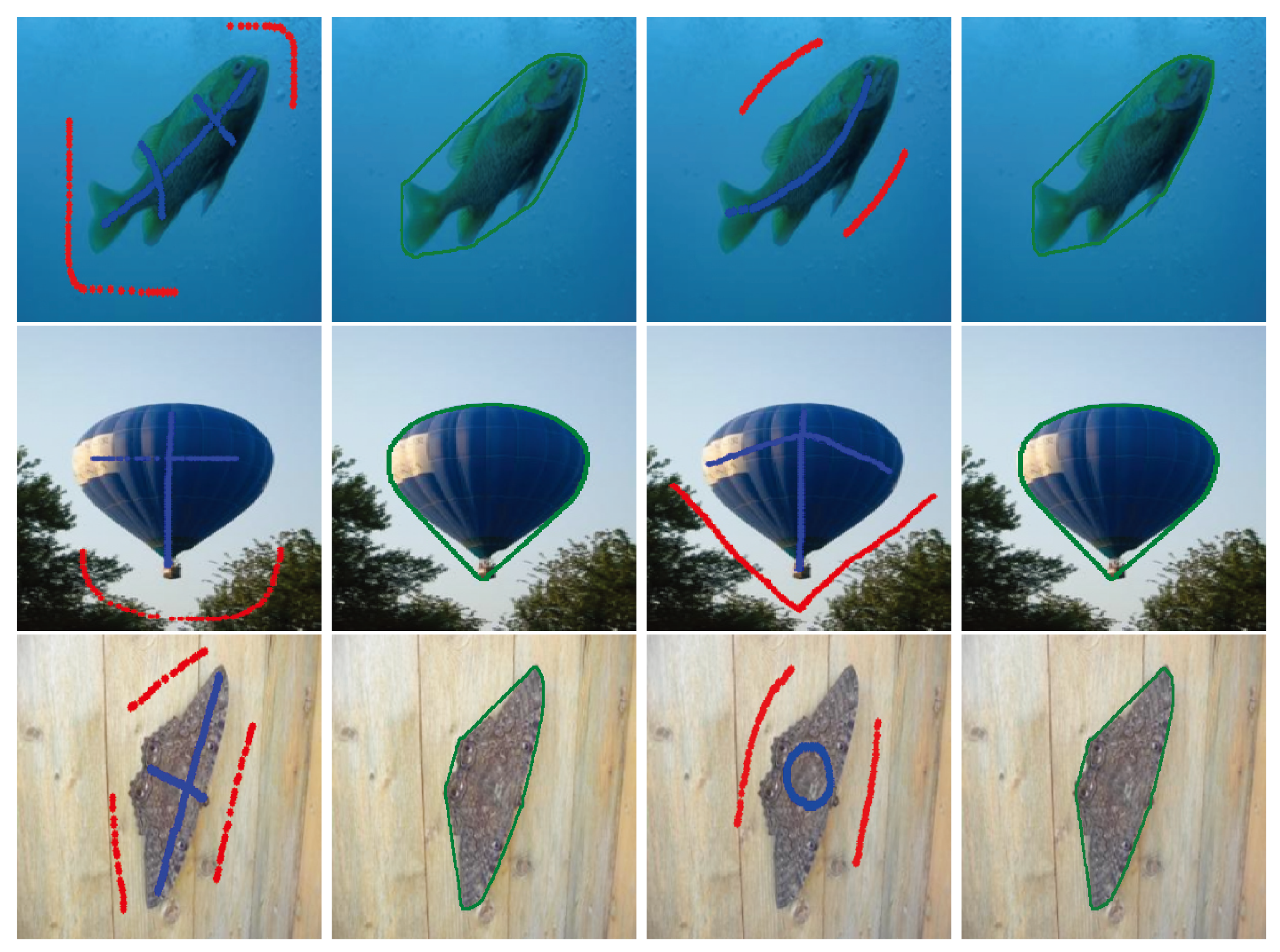
In order to further demonstrate the robustness of our proposed method on different initial contours, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 show some image segmentation results generated by our proposed method with two different initial contours for each original image. Here, the original images in Figure 6 and Figure 7 of the results correspond to the ones shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 and were not properly partitioned by the BLF–TV–CS method, while the original images in Figure 8 are images which could be partitioned by the BLF–TV–CS method in Figure 3. From these results, we found that, for a given original image, our two different image segmentation results had no obvious distinctions from vision. This demonstrated that, even for challenging cases, our proposed method was robust to initial contours. Here, challenging cases meant that proper image segmentation results were hard to obtain from the BLF–TV–CS method in these cases.
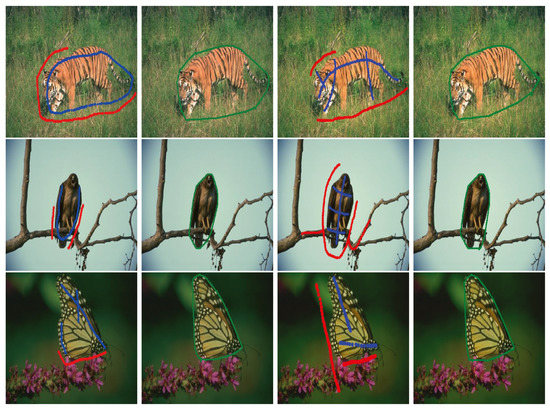


Figure 6.
The robustness tests of different initial contours on our image segmentation methods with some original images shown in Figure 2. In each row of the figure, the first two columns and the last two columns show the original images with given initial contours and our corresponding image segmentation results, respectively.


Figure 7.
The robustness tests of different initial contours on our image segmentation methods with some original images shown in Figure 3. In each row of the figure, the first two columns and the last two columns show the original images with given initial contours and our corresponding image segmentation results, respectively.
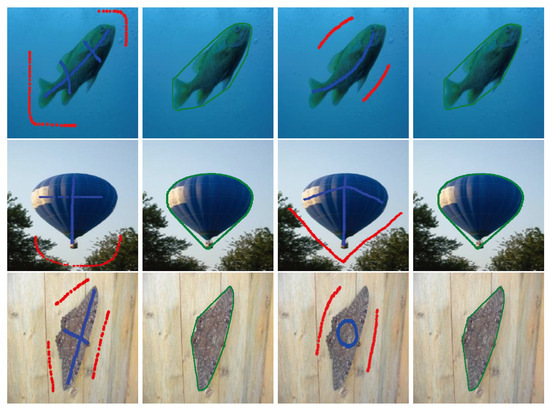
Figure 8.
The robustness tests of different initial contours on our image segmentation methods with some original images shown in Figure 3. In each row of the figure, the first two columns and the last two columns show the original images with given initial contours and our corresponding image segmentation results, respectively.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a novel convex shape image segmentation method called the PPA–CS method. This method is based on a well-trained DRUNet regularizer on a fuzzy membership function. Here, the fuzzy membership function was used to indicate different image regions. The DRUNet regularizer was used to preserve the geometrical structure details of the fuzzy membership function and to make the fuzzy membership function approximate the classical binary label function well. By integrating a P&P–ADMM approach and a projection method, we designed an iteration algorithm to solve our model. Compared with the BLF–TV–CS method and the FMF–TV–CS method, our proposed method not only generated the desired convex shape image segmentation results better by testing the images of the BSDS500 and the WSED, but also showed more robust performance on the choices of initial segmentation contours.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z., Y.H. and C.X.; data curation, X.Z.; formal analysis, X.Z. and Y.H.; investigation, X.Z.; methodology, X.Z. and Y.H.; resources, X.Z. and S.L.; software, X.Z. and S.L.; supervision, Y.H.; validation, X.Z.; visualization, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z. and Y.H.; writing—review and editing, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded, in part, by the National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong under Grant 2023A1515011394, in part, by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62072312 and Grants 61972264, and also, in part, by the HD Video R & D Platform for Intelligent Analysis and Processing in the Guangdong Engineering Technology Research Centre of Colleges and Universities under Grant CZX-A1409. In addition, this work was supported, in part, by the Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen under Grant CYJ20210324094009026.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations were used in this manuscript:
| SDF | Signed distance function |
| BLF | Binary label function |
| FMF | Fuzzy membership function |
| TV | Total variation |
| DCNNs | Deep convolutional neural networks |
| P&P | Plug-and-play |
| ADMM | Alternating direction method of multipliers |
| HQS | Half-quadratic splitting |
| RE | Relative error |
| BSDS500 | The Berkeley segmentation dataset and benchmark 500 |
| WSED | The Weizmann segmentation evaluation database |
References
- Luo, S.S.; Tai, X.C.; Glowinski, R. Convex object(s) characterization and segmentation using level set function. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2022, 64, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, B.Y. Adaptive segmentation model for liver CT images based on neural network and level set method. Neurocomputing 2021, 453, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.P.; Tai, X.C.; Lui, L.M. Topology- and convexity-preserving image segmentation based on image registration. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 100, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.D.; Xing, P.; Zhang, B. Semantic segmentation of breast ultrasound image with fuzzy deep learning network and breast anatomy constraints. Neurocomputing 2021, 450, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q. Deep level set learning for optic disc and cup segmentation. Neurocomputing 2021, 464, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, R.; Jia, W.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Jiang, B. Accurate and automatic tooth image segmentation model with deep convolutional neural networks and level set method. Neurocomputing 2021, 419, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, L.; Veksler, O.; Boykov, Y.; Nieuwenhuis, C. Convexity shape prior for binary segmentation. IEEE T. Pattern Anal. 2017, 39, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savchynskyy, B. Discrete Graphical Models: An Optimization Perspective. Found. Trends Comput. Graph. Vis. 2019, 11, 160–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.; Tai, X.C.; Zhu, W. Augmented Lagrangian method for an Euler’s elastica based segmentation model that promotes convex contours. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2017, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Tai, X.C.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.Y. Convexity shape prior for level set-based image segmentation method. IEEE T. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7141–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.S.; Tai, X.C.; Wang, Y. Convex shape representation with binary labels for image segmentation: Models and fast algorithms. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09600v1. [Google Scholar]
- Mory, B.; Ardon, R. Fuzzy region competition: A convex two-phase segmentation framework. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision, Ischia, Italy, 30 May–2 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lv, X.; Jiang, L.; Sun, X.; Fang, B. Nonconvex regularization for convex image smoothing. Signal Process. 2023, 205, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Tang, L.M. A nonconvex hybrid regularization model for restoring blurred images with mixed noises. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 130, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.G. Feature-preserving Mumford–Shah mesh processing via nonsmooth nonconvex regularization. Comput. Graph. 2022, 106, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, C.; Peng, D.; Chen, W. Large-scale affine matrix rank minimization with a novel nonconvex regularizer. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 4661–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, X.; Ni, G.X.; Zeng, T.Y. Nonconvex regularization for blurred images with Cauchy noise. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2022, 16, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Jiao, Y.; Lu, X.; Zeng, T. A nonconvex model with minimax concave penalty for image restoration. J. Sci. Comput. 2019, 78, 1063–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Wu, C.L.; Duan, Y.P. The TVp regularized Mumford-Shah model for image labeling and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7061–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Mao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, T. Efficient color image segmentation via quaternion-based L1/L2 regularization. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 93, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, M.; Huang, Y. Plug-and-play-based algorithm for mixed noise removal with the logarithm norm approximation model. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, F.; Ohba, H.; Ote, K.; Kakimoto, A.; Tsukada, H.; Ouchi, Y. 4D deep image prior: Dynamic PET image denoising using an unsupervised four-dimensional branch convolutional neural network. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, N.T.; Trinh, D.H.; Trung, N.L.; Luong, M. Low-dose CT image denoising using deep convolutional neural networks with extended receptive fields. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, C. NSTBNet: Toward a nonsubsampled shearlet transform for broad convolutional neural network image denoising. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 123, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Plug-and-Play image restoration with deep denoiser prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6360–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascarano, P.; Piccolomini, E.L.; Morotti, E.; Sebastiani, A. Plug-and-play gradient-based denoisers applied to CT image enhancement. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 422, 126967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurault, S.; Leclaire, A.; Papadakis, N. Proximal denoiser for convergent plug-and-play optimization with nonconvex regularization. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.13256. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R.Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, G.X. Truncated residual based plug-and-play ADMM algorithm for MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2022, 8, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.H.; Liu, X.W. Non-convex fractional-order TV model for impulse noise removal. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 417, 114615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Z.M. An inexact symmetric ADMM algorithm with indefinite proximal term for sparse signal recovery and image restoration problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 417, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X.T.; Guo, G. Learning non-locally regularized compressed sensing network with half-quadratic splitting. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 3236–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti-Meymandi, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Fatemizadeh, E. Plug and play augmented HQS: Convergence analysis and its application in MRI reconstruction. Neurocomputing 2023, 518, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hua, X.; Liu, G.; Fei, J.; Shi, Y. Visual sensitivity filtering based local maximum variation prior for blind image deblurring. Optik 2022, 261, 169118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Young, G.S.; Tie, Y.; Gu, X.; Xu, X. A new framework of designing iterative techniques for image deblurring. Pattern Recogn. 2022, 124, 108463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chang, M.H. An image inpainting method for object removal based on difference degree constraint. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 80, 4607–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.; Reinić, N. Shock filter as the classifier for image inpainting problem using the Cahn-Hilliard equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2022, 123, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.D.; Zhou, D.W. A very lightweight and efficient image super-resolution network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Chen, J.S. Double paths network with residual information distillation for improving lung CT image super resolution. Biomed. Signal Proces. 2022, 73, 103412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).