Abstract
This research is devoted to the determination of hidden dependencies between the flow of particles that come from the Sun and precipitation-induced floods in the United Kingdom (UK). The analysis covers 20 flood events during the period from October 2001 to December 2019. The parameters of solar activity were used as model input data, while precipitations data in the period 10 days before and during each flood event were used as model output. The time lag of 0–9 days was taken into account in the research. Correlation analysis was conducted to determine the degree of randomness for the time series of input and output parameters. For establishing a potential causative link, machine learning classification predictive modeling was applied. Two approaches, the decision tree, and the random forest were used. We analyzed the accuracy of classification models forecast from 0 to 9 days in advance. It was found that the most important factors for flood forecasting are proton density with a time lag of 9, differential proton flux in the range of 310–580 keV, and ion temperature. Research in this paper has shown that the decision tree model is more accurate and adequate in predicting the appearance of precipitation-induced floods up to 9 days ahead with an accuracy of 91%. The results of this study confirmed that by increasing technical capabilities, using improved machine learning techniques and large data sets, it is possible to improve the understanding of the physical link between the solar wind and tropospheric weather and help improve severe weather forecasting.
MSC:
85-10
1. Introduction
The occurrence of extreme weather events, such as heavy precipitation causing floods, represents some of the most significant natural hazards with major social, economic, and environmental impacts [1]. In particular, floods can lead to loss of life, property damage, crop destruction, and livestock loss. Long-term impacts, caused by infrastructure damage, comprise disruptions in the supply of clean water and electricity, damage to the transport, communication, and health infrastructure, as well as deterioration of physical and mental health due to population displacement. Even though our understanding of the processes that lead to heavy precipitation that can cause floods has advanced, due to the large negative impacts, there is a growing need for improved methods of forecasting extreme weather and hydrological events. Although there are many factors affecting weather and climate across a variety of atmospheric scales, the possible influence of external factors has been widely reported.
A possible relationship between solar activity and the Earth’s climate has been examined over the last 200 years [2], while this subject came into the focus of scientific interest at the beginning of the nineties of the 20th century [3]. Various forms of solar activity, such as solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and fast solar wind, cause variability of solar energy reaching the Earth and affect atmospheric parameters directly or indirectly [4,5]. Although the existence of a link between solar activity and climate variables has not been widely accepted, there is a series of papers investigating empirical relationships between them, such as [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], etc. A detailed list of papers demonstrating the connection between solar and atmospheric processes is provided in [14,15]. Numerous hypotheses have tried to explain the mechanism of solar influence on the Earth’s atmosphere. The simplest explored mechanism of the Sun–Earth connection is through direct heating of the Earth by solar radiation, the total solar irradiance. It is claimed that periods with many sunspots are related to higher irradiance, especially in the ultraviolet part (UV) of the spectrum, influencing tropospheric temperature and wind [2,16,17]. Large changes in UV radiation coming from the sun affect the amount of ozone in the stratosphere, warming, atmospheric circulation, and the strength and stability of the polar vortex. These disorders are transmitted to the troposphere and affect mid-latitude storms, often over the north Atlantic and Europe [15,18,19]. Another major possible mechanism includes galactic cosmic rays that are modulated by solar and terrestrial activity. It is indicated that galactic cosmic rays can trigger cloud condensation nuclei formation and enhance cloudiness [15,20,21,22].
It is known that the weather at mid latitudes largely depends on the process of formation, evolution, and movement of cyclones and anticyclones in the atmosphere. Therefore, the study of the influence of solar activity and related interplanetary environment disturbances on the development of extratropical cyclones has prognostic significance. There is a series of papers demonstrating changes in cyclonic activity in response to geomagnetic activity driven by solar activity. Tinsley [23] discussed possible triggering mechanisms for condensation and freezing within convective clouds of the cyclone induced by solar-modulated energetic particles. Veretenenko and Thejll [24,25] revealed that solar proton events, with energies above 90 MeV, may intensify cyclonic activity at middle latitudes in the cold period of the year (October–March). Stozhkov et al. [26] investigated the effect of charged particle fluxes in the atmosphere on the intensity of precipitation in the territory of the former USSR and found an increase in precipitation intensity during solar proton penetration into the Earth’s atmosphere of ~10%. Bhattacharyya and Narasimha [27] analyzed four solar activity indices and seven major Indian monsoon precipitation time series, over two distinct test periods of low and high solar activity, respectively, each comprising three complete solar cycles. They found that the average precipitation is higher in all seven precipitation indices during the periods of greater solar activity, at confidence levels varying from 75% to 99%, being 95% or greater in three of them. Prikryl et al. [28] revealed that arrivals of solar wind high-speed streams from coronal holes can be followed by heavy precipitation causing floods and flash floods.
Exploring the time differences between different solar events and atmospheric responses is also important, but there is no common consent about it in the recent literature. According to Lilensten and Bornarel [29], in conditions where a coronal hole or active region approaches the geo-efficient position, solar wind becomes stronger, while its effects on the Earth can be expected in 2–3 days. Artamonova and Veretenenko [30] analyzed the short-term variation in galactic cosmic rays and found a delay period of 3–4 days for tropospheric pressure field variation in extratropical latitudes of the northern hemisphere after the event onset. Todorović and Vujović [5] studied the impact of coronal holes and active regions on cold fronts, precipitation, and temperature decrease on the surface and higher layers in the Belgrade region (Serbia) and found that the maximum amount of precipitation occurs 14 days after the solar wind is observed. Prikryl et al. [28,31,32,33,34,35] indicated that extratropical cyclones and heavy precipitation causing floods tend to occur within several days of high-speed solar winds coming from the coronal hole.
Despite the advances made in forecasting and improved understanding of complex atmospheric and hydrologic conditions and processes, predictions of extreme precipitation events and floods continue to present difficult challenges. Among the new methods, machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly used in environmental sciences, especially in hydrology.
Machine learning is one of the most famous areas of artificial intelligence that has recently been used in geography, aiming to simulate human intelligence by recognizing patterns in an intelligent way [36]. It presents a set of software applications composed of engineering, mathematics, and statistics that can learn from data and create outputs by using minimal human intervention [37]. There are three areas of ML: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning [38]. Supervised learning uses labeled datasets to train ML algorithms to classify data or predict the outputs accurately. It can be categorized into regression and classification models. While the regression model predicts a continuous output, classification refers to a predictive modeling problem where a class label is predicted for a given example of input data. In other words, classification predictive modeling is based on identifying the patterns in the data that group examples into the category, or class labels.
Different ML techniques are widely used due to the increasing availability of different data sets and the complexity of hydrological processes that are difficult to model with linear or undemanding nonlinear statistical methods. A large number of ML applications have already appeared in the hydrological literature in recent years. A detailed list of papers demonstrating the use of ML in hydrology is provided in [39,40,41,42,43]. ML techniques have already shown superior performance in solving a number of hydrological problems. For example, Schmidt et al. [44] used two popular ML algorithms, artificial neural networks, and random forests, to analyze a large flood data set across Germany and showed that ML can capture basic hydrological principles well and that ML models achieve higher prediction accuracy than linear regression, while Cappelli et al. [45] demonstrated high usability of ML feature importance technique to identify the role of sub-basins in hydrological response. The use of ML techniques in space weather is not new, but it is in expansion in the last several years. Advances in ML techniques have led to a range of new tools to better solve traditional and new challenging problems from a data-driven perspective. Bearing in mind that there are numerous data from satellites and observatories that monitor cosmic weather processes between the Sun and the Earth, the use of ML in determining the impact of solar activity on the Earth’s climate offers a new opportunity to learn from the data. Moreover, the problem of space weather is very complex and our understanding of the basic processes of space weather is still too limited to properly describe the physical and mathematical relationships using traditional methods [46]. In this paper, we focused on establishing hidden dependencies between precipitation-induced floods in the United Kingdom (UK) and the flows of particles from the Sun based on 20 flood events in the UK in the period October 2001–December 2019. To justify and also quantify the relationship we are advocating, we used machine learning classification predictive modeling. As a result of establishing the hidden dependencies between precipitation-induced floods and solar parameters, a forecast model was produced. This “directly from the data” learning approach provided the opportunity to uncover hidden knowledge about relationships within the data and to deepen our understanding of physical processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The territory of the UK has a dense drainage network, with about 200,000 km of watercourses draining around 1500 discrete basins (Figure 1) [47,48]. The numerous watercourses are short, shallow, and prone to significant disturbances caused by anthropogenic influence. The river regime is influenced by climatic conditions (above all precipitation, air temperature, and insolation), geological features of individual catchments (their permeability), terrain morphology, and anthropogenic factor (riverbed changes, water utilization, land-use changes, etc.).
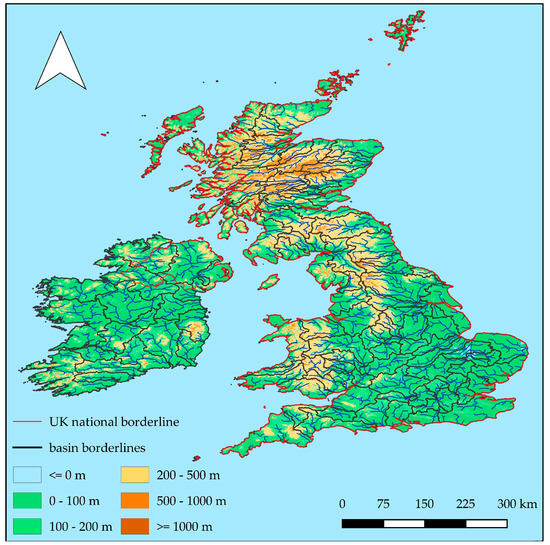
Figure 1.
Physical geographic map of the UK.
Kingston et al. [49] emphasized that winter NAO (North Atlantic Oscillation) influences river flows by controlling moisture and heat advection over the UK. Laizé and Hannah [50] pointed out that a higher NAO index enhances westerly air flows across the UK, leading to higher than average precipitation and temperature and, in turn, higher river flows (and vice versa for a lower NAO index). In contrast to uplands, lowland basins receive less precipitation and therefore the influence of other factors (such as permeability, elevation, and physical basin properties) also has an impact on the flow regime. Due to the wide variety of climate and basin types in the UK, rivers range from mountain torrents draining headwaters receiving up to five meters of precipitation a year to the lowland watercourses being groundwater-fed in southern and eastern England where precipitation is lower [48]. Precipitation in the UK is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, with a modest tendency toward an autumn/winter maximum, especially in the western basins. However, seasonal variations in air temperature and the amount of sunlight cause high evaporation in the summer half of the year (April–September). This conditions the intra-annual distribution of flows in rivers with natural regimes. It is observed that the maximum flows are registered during the winter, and the minimum is in the summer or autumn. It is noteworthy that urban watercourses have been significantly modified and are not always in line with this pattern. For example, low flows can be artificially amplified (by overflowing reservoirs, transfers between basins, etc.). Hannaford and Buys [51] analyzed river flow trends in 89 basins with almost natural flow regimes in the UK for four standard seasons in the period 1969–2008. Their findings are the following: an overall increase in winter river flows (with the largest increases in northern and western upland basins, while low flows decreased in some western basins); a regionally coherent decrease in spring flows; increasing summer flows (in the north and west basins), and primarily weak positive and negative trends (in the English lowlands); an increase in autumn flows (particularly for high flows in northeast, central, and southwest parts of the UK). Observed trends (such as increasing winter flow and decreasing spring flows) may be influential for water management, and the tendency toward higher flows may reflect an increase in flood risk.
2.2. Data Description
In this study, several data sets and data sources were used to test the possible relationship between solar activity and precipitation-induced floods. Data from 20 independent data blocks for different flood events (r) were used for analysis. Each data block consisted of separate data sets (DSs):
- Flood (F): (date, precipitations (mm), days from the beginning of the flood).
- Integral proton flux (IPF, ): .
- Differential electron and proton flux (DF, p/cs2-sec-ster). These blocks contained different sun energy characteristics for different periods during different flood events. The measured ranges for differential electron flux were 38–53 keV and 175–315 keV for all analyzed floods, while the measured ranges for differential proton flux varied depending on the period in which the flood occurred. The differential proton fluxes were measured in the following ranges: 47–65 keV, 47–68 keV, 65–112 keV, 112–187 keV, 115–195 keV, 310–580 keV, 761–1220 keV, 795–1193 keV, 1060–1900 keV, and 1060–1910 keV. However, the only common range for all flood events was 310–580 keV.
- Solar wind (SW): = ( ).
- Radio flux of 10.7 cm (RF, solar flux units): .
The flood data used in this study were taken from the Emergency Events Database Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (EM-DAT database). This database was launched by the Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) in 1988 with the initial support of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Belgian Government [52]. EM-DAT database contains essential core data on the disasters in the world from 1900 to the present day and it is compiled from various sources. Data collection in the EM-DAT database was carried out according to the place of origin, development, and cause of disasters, and the classification was made according to the one proposed by the United Nations. For a disaster to be entered into the EM-DAT database, at least one of the following criteria must be fulfilled: ten or more reported deaths; one hundred or more reported people affected; declaration of a state of emergency; and call for international assistance [52]. In this study, twenty floods in the UK recorded in the EM-DAT database were selected for the period 2001–2019. One flood was registered in 2001, three in 2002, one in 2004, three in 2007, two in 2008, one in 2009, five in 2012, and one in 2014, 2015, 2017, and 2019. Out of twenty selected floods in the EM-DAT database, fourteen were classified as riverine floods, three were flash floods, and the remaining three were not defined in more detail. The geographical locations of the studied flood events are presented in Figure 2. Regarding the regional aspect, out of twenty analyzed floods, eighteen occurred in England, five in Wales, four in Scotland, and two in Northern Ireland. According to the seasons, most of the floods occurred in autumn (eight), followed by summer (seven), winter (three), and spring (two). The duration of the floods ranged from one day (in July 2002, December 2012, and December 2015), to twenty-eight days (November–December 2012). The average duration of the selected floods was 4.6 days. Areas endangered by floods ranged from 60 km2 to 126,150 km2 and occurred in numerous rivers basins, such as Thames, Severn, Stour, Exe, Ouse, Dearne, Aire, Avon, Calder, Don in Yorkshire, etc.
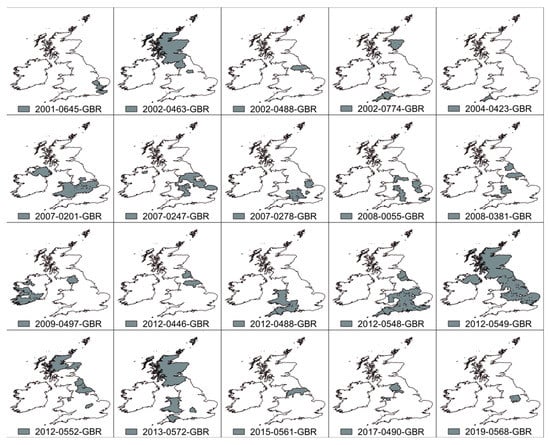
Figure 2.
The geographical position of the studied flood events.
Daily precipitation data for ten days before the flood event and during the flood event were used from the European Climate Assessment and Dataset [53,54]. For each flood event, we collected precipitation data from all the stations located in the flood plain. The data from a total of 123 measuring stations were used. The source for integral proton flux, differential electron and proton flux, proton density, bulk speed, and ion temperature was the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) satellite [55]. This satellite measures the changes in the solar wind parameter that is directed toward the Earth, while its position is always between the Sun and the Earth. Available ranges for differential proton flux varied depending on the period in which the flood occurred.The data source for the 10.7 cm radio flux was The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics [56] at the University of Colorado Boulder (CU) for the period 2001–2004 and Space Weather Canada [57] for the period 2007–2019. The solar radio flux at 10.7 cm (2800 MHz) is an excellent indicator of solar activity. It is also called the F10.7 index. The F10.7 radio emissions originate high in the chromosphere and low in the corona of the solar atmosphere [58]. These parameters represent solar wind and activity variability and are used in previous research. All the parameters used in this study are used in the investigation of dependencies between forest fires and solar activity [59,60], while some of them (IPF > 10 MeV, solar wind, and 10.7 cm radio flux) were used in the research of the relationship between solar activity and hurricanes [10,61]. Since previous research showed that a causal link exists, in this research we attempted to examine if there is a connection between these parameters of solar activity and precipitation-induced floods.
2.3. The impact of Precipitation on the Occurrence of Floods
To determine the influence of precipitation on flood occurrences, the daily precipitation amount was analyzed on the day of each flood event, as well as for each of the 10 days preceding the floods. For this analysis, the design of superposed epochs was used [62]. Furthermore, a one-way analysis of variance was applied to examine if there is a significant influence of precipitation on flood occurrences. It can be concluded that there is a statistically significant difference between the amounts of precipitation during the observed days (Table 1).

Table 1.
Results of the one-way analysis of the variance of the amount of precipitation on the day when the flood occurred and during the ten days preceding it.
For the determination of the day in which the precipitation was significantly different from the precipitation on each of the remaining days, Hochberg and Games–Howell post-hoc tests were applied. These tests were chosen considering the results of Levene’s test, which showed that there is no equality of variances for the analyzed variables [63,64].
The analysis showed that the average amount of precipitation on the day of the flood and the day before the beginning of the flood (14.3 mm and 17.4 mm, respectively) is significantly higher than the amount of precipitation on the other days before the beginning of the flood (1.8–5.9 mm). Based on the data from Table 2, the amount of precipitation on the day of the flood and the day preceding it is significantly higher (significance level of 0.05) than the amount of precipitation in all the remaining days that preceded them (according to the Hochberg test). According to the Games–Howell test, the amount of precipitation on the day of the flood is statistically significantly higher than that which falls 10, 8, 7, 6, and 5 days before the flood. Therefore, it can be concluded that the amount of precipitation on the day of the flood, and the day preceding it, plays a significant role in the occurrence of floods. For the UK area, Cotterill et al. [65] and Kendon [66] reached similar findings.

Table 2.
Results of post-hoc tests of the amount of precipitation on the day when the flood occurred and during the ten days preceding it (statistically significant values are in bold).
2.4. Preliminary Processing of Input Data and Correlation Analysis
The parameters of solar activity were observed for 10 days before and during the flood. Data on solar activity and flood were recorded at different time intervals. In the case of solar parameters, the data are presented by averaged values for a certain time interval (1 and 5 min), or measurements are performed several times per day (for F10.7 cm). The information about time sampling is provided in Table 3. According to their sources, all the data were grouped in corresponding data sets (DSs).

Table 3.
Time intervals of input and output features.
For further analysis, the data sets for each flood event were grouped into separate data sets (), with a maximum interval of 1 day. As a result, 20 separate DSs were received for each flood event:
where r is the river flood event index. To obtain the final data set for each flood event, we did not use the absolute values as input features, but we first performed binary classification on data. The days of precipitation were marked as True (1), while the days without precipitation as False (0). The input feature values are True/False for each field, taking into account the lag, while the target is also a binary field. The positions of the peaks for the solar activity fields were calculated (Figure 3), and the beginning and end of the flood event were recorded. The position of the peaks was determined programmatically with subsequent manual verification. After binarization, a lag transformation of these binary data sets was performed. To achieve this, each input feature was duplicated and shifted vertically by the required number of lags. The forecast model for each flood event can be formalized as follows:
where r is the river flood index, m is the number of input parameters, and n is the maximum lag.
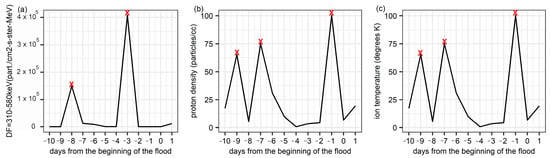
Figure 3.
Example of setting peaks for (a) DF 310–580 keV, (b) proton density, and (c) ion temperature). Read crosses represent peaks.
Since the input data sets for different flood events have different features for differential proton flux, the first attempt was to find independent functional dependencies for each flood event separately. To achieve this, a correlation analysis was performed between input factors and precipitation. The results in Table 4 show that there are no uniform linear relationships between factors for all flood events. Thus, in some flood events, there is a high correlation for one of the factors (e.g., 61–1220 keV, R = 0.68), while it is completely absent for other flood events. This indicates the randomness of this dependence.

Table 4.
Maximum values of correlation coefficients between input factors and precipitations (/ means no peaks, - means no data).
2.5. Machine Learning and Forecast of Precipitation
Classification ML models predict categorical class labels based on specific data sets. The classification algorithms work by using input data sets to create a mapping function. Generally, the input data set is divided into training and testing datasets [67]. The training data set contains observations whose classifications are already known so the algorithm can use them as a guide. This helps determine output variables (or predictions) in the testing data set with varying degrees of accuracy. In other words, the training dataset has an output variable that needs to be predicted or classified in the testing data set.
In ML, there are many different types of algorithms for classification and no strict rules for their selection. In this study, we used the decision tree and ensemble classification to allow a clear understanding and justify the classification decision. The decision tree algorithm is one of the most popular ML algorithms. It uses tree-like structures and their possible combinations to solve a particular problem. The decision tree algorithm should identify the features that contain the most information about the target feature and by using the if–then rules divide the data set into subsets based on that feature, to make the resulting nodes as clean as possible. In the tree-like structure, each internal node presents a test on a characteristic, each branch presents the outcome of the test, each leaf node presents a class label, and the paths from the root node to the leaf node present the classification rules. The rules are learned sequentially using the training data one by one. Each time a rule is learned, the tuples covering the rules are removed. The decision tree algorithm has the goal of creating a model that predicts the target variable by learning simple decision-making rules derived from the characteristics of the previous data. The main advantages of choosing this method are easy interpretation, handling various data types, and the ability to visualize the result. Disadvantages are the tendency to overfit, long duration, and greater complexity than other algorithms. The primary challenge in implementing a decision tree is to identify the attribute of the root node at each level. This process is known as attribute selection. There are different attribute selection measures, and one of them is the Gini index [68]. The Gini index measures how often a randomly chosen element would be incorrectly classified, that is, it calculates the probability of a specific feature that is classified incorrectly when selected randomly. This means that an attribute with a lower Gini index should be preferred. The strategy used to select the split in each node is used to find the best distribution.
Ensemble methods combine the predictions from multiple models to derive better predictive performance than the one that could be obtained from any of the constituent learning algorithms alone. There are three different ways to build model ensembles, including boosting, bagging, and stacking [69,70]. In this study, 3 different ML algorithms (classifiers, Table 5) with different parameters, and 3 ensembles were used [69]. Moreover, we tested ensembles of models based on boosting (AdaBoost classifier and gradient boosting classifier) and bagging (bagging classifier).

Table 5.
List of classifiers and ensembles that were used in calculations.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lag Analysis
According to our hypothesis, the period of delay between the flood and the outbreak of solar activity can be up to 10 days. To test this hypothesis, the following experiment was performed. All classification models were fitted and tested for input data that did not contain a time delay. Next, the data containing a time delay of one day were added to the input parameters. After that, the models were refitted, and the recall metric was calculated. These iterations lasted up to 9 lags due to the fact that we only had data available for 10 days before the flood. Shifting the data by 10 days and deleting the 10 empty records that should appear would result in no flood days remaining in the target field. Accordingly, this would make classification impossible. Formally, the tasks of classification were reduced to the following form:
3.2. Gini Index
The Gini index, also known as the Gini impurity, is very important for this classification. It takes values between 0 and 1, where 0 means absolute equality (all the elements belong to a specified class or only one class exists there), and 1 denotes complete inequality (random distribution of elements across various classes). It is used to select the best feature at each step. The impurity of the feature is the size of the difference between the number of points that the feature has and the number of points that the feature does not have. If the number of points that the feature has is equal to the number of points that the feature does not have, then the feature impurity is zero.
The Gini index can be represented by the following formula:
where c is the number of classes and pi is the probability associated with the i-th class. It means that if we randomly select two features from the dataset, they have to be of the same class and the probability is 1 if the dataset is pure. If the Gini value is higher, the homogeneity of data is higher. The value of 0.5 on the Gini index shows an equal distribution of elements over some classes. While designing the decision tree, the features possessing the least value of the Gini index would be preferred.
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
Classification predictive modeling algorithms are evaluated based on their results. There are four different metrics for estimating the fitted model’s quality: “accuracy”, “precision”, “recall”, and “f1”. In this study, we used the metric called “accuracy” to assess the fitted model’s quality, which is related to the recall metric. In our case, it is important to predict the precipitation. Thus, the mistake of the model, when, according to the forecast, there is no precipitation—but it actually happens—is critical. The “recall” metric is used to assess such situations. This metric assesses the accuracy of positive predictions. Other metrics take into account the forecast of both the onset of the precipitation and its absence. Therefore, these metrics will a priori have higher values of accuracy, but they are not adequate in our case.
The “recall” is the ratio:
where tp is the number of true positives and fn is the number of false negatives. The recall is the ability of the classifier to intuitively find all the positive samples.
recall = tp/(tp + fn),
The accuracy of the model was determined by using a cross-validation that allows the training set to be divided randomly into three parts acting as the test [71]. This means that the classifier fitted three times on three different data sets, while the accuracy of both training and test sets was calculated and averaged. The value analysis of these metrics enables the accessing of accuracy, adequacy, and availability of overfitting. This means that the decision tree algorithm keeps going deeper and deeper to reduce the error of the training set, resulting in the increased test-set error at the same time. As a consequence, it further reduces the accuracy of prediction in the model.
The obtained results are presented in Table 6. The results allow us to analyze the dynamics of metric changes in the consistent addition of new lags to the input parameters. Recall values were compared for test and training sets. The analysis of the adequacy of the models was evaluated on the following grounds:

Table 6.
Accuracy for training and test sets with Gini index criterion at consecutive addition of lags and error variance between test and training data sets.
- If the error of the test and training sets is close (small variance) it indicates that the model is well fitted and predicts unknown values at the same level as the known ones. The absolute value shows how accurate such a model is.
- If the accuracy on the training set reaches 1, and on the test set it is close to 0.5, it indicates overfitting. That is, the known data are perfectly predicted, and the unknown ones are guessed (50:50) and are impossible to predict.
Table 6 shows all the classifiers for small lags have lower accuracy or overfitting. However, when the lag is increased up to 7–9, the accuracy increases significantly, and the models become quite adequate and accurate. This means that there is indeed a significant time lag between a solar flare and precipitation.
3.4. Forecasting Models
According to the previous analysis, there are time delays between solar activity and precipitation. To build a precipitation forecast for n days in advance, it is necessary to extract data with lags (0 − (n − 1)) from the input parameters of all the models:
As can be seen, the number of input features decreases, which leads to the reduction of forecast accuracy. The accuracy of classification models forecast from 0 to 9 days in advance with the Gini index criterion was analyzed (Figure 4). This analysis showed that the accuracy of the decision tree varies by one level within the model error. This approach allows us to build a decision tree for forecasting any lag. Therefore, in this study, the forecast for lags from 0 to 9 requires the construction of 10 different decision trees.
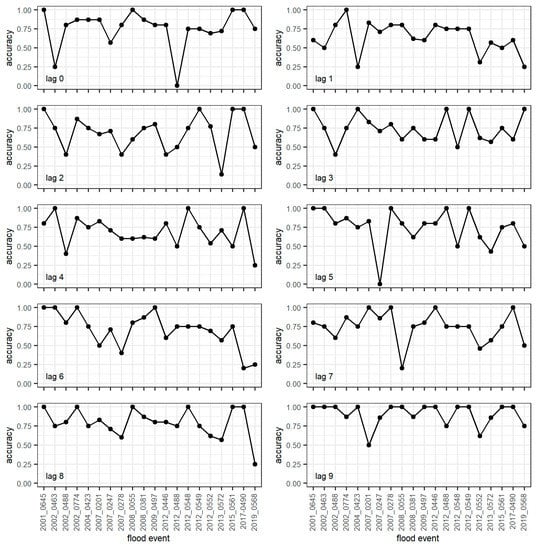
Figure 4.
The accuracy of precipitation models forecast with the Gini index criterion from 0 to 9 days in advance.
The obtained results in Figure 4 are the representation of the accuracy of precipitations models forecast with the Gini index criterion from 0 to 9 days in advance. They show that the model accuracy score with the Gini index criterion is higher than 0.7 in 75%, 80%, and 90% for 7, 8, and 9 days in advance, respectively. Furthermore, the average accuracy of precipitation models forecast for 9 days in advance is about 91% for the given set of data.
This allows us to determine the most important classification features in these cases. According to Figure 5, the most important classification features are proton density, differential proton flux in the range of 310–580 keV, and ion temperature.
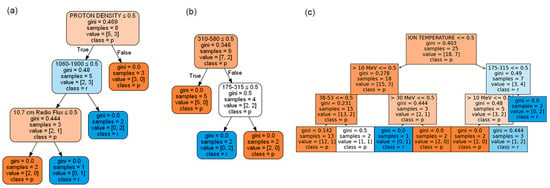
Figure 5.
The most important classification features ((a) proton density, (b) differential proton flux in the range of 310–580 keV, and (c) ion temperature) in the forecasting of precipitation model for 7, 8, and 9 days in advance.
To improve the predictability of the proposed decision tree ML model, we have used the ensemble classification methods by combining multiple ML classification models, specifically random forest and K-nearest neighbors, and testing these models by using the ensembles of models based on boosting (AdaBoost classifier and gradient boosting classifier) and bagging (bagging classifier). For that purpose, we combined all the data into one data set:
We prepared another tree-based algorithm (random forest). We built the model with 10 decision trees and 100 decision trees, but the results were the same. We determined the importance of the factors, as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
The most important factors in the random forest classification.
As can be seen from Table 7, the most important factors are ion temperature (t-4), 10.7 cm radio flux (t-9), and 38-53 (t-5). It is also obvious that different factors affect the onset of precipitations with different time delays. It is also clear that an outbreak of a factor such as ion temperature can lead to precipitation events with various time delays, or it may take a few flashes to cause precipitation. It should be noted from Table 8 that the accuracy of this classifier on the test is 0.81 by using the bagging classifier SVC.

Table 8.
Recall accuracy of forecast models for the cross-validation test.
As can be seen from Table 8, the accuracy of the ensemble models, as well as the decision tree model is smaller when we use the combined data. One of the reasons can be the joining of data sets and different variances of the target data. That is, such an ensemble of models can be used to forecast floods up to 9 days in advance, but the model accuracy will be much smaller than when we use the independent data sets.
3.5. Discussion
Several authors have presented a possible theoretical (physical) explanation of the mechanism that could explain the interaction considered in this paper. Stevančević et al. [72,73] explained that high-energy particles from the Sun directly influence atmospheric processes by capturing air masses with hydrodynamic pressure. If the point of contact becomes saturated with moisture, clouds and precipitation can form. The mechanism of precipitation formation is explained by the principle of electron valence. According to [72,73], electromagnetic characteristics of solar wind, the location of the Sun from which it is emitted, and its chemical structure determine cloud formation and the appearance of precipitation, and the occurrence of heatwaves and dry periods. The abovementioned mechanism is explained by the circulation of vectors of interplanetary magnetic fields. Prikryl et al. [34] discussed two flash floods in Slovakia that followed the arrival of two high-speed solar wind streams from coronal holes and indicated that “vertical coupling in the atmosphere exerts downward control from the solar wind to the lower atmospheric levels influencing tropospheric weather development”. Prikryl et al. [28] indicated that heavy precipitation events leading to floods and flash floods in Japan, Australia, and the continental U.S. tend to follow the arrivals of high-speed solar wind streams from coronal holes. They hypothesize that the formation of a series of convective cells that cause heavy rainfall and flooding may be triggered by downwelling atmospheric gravity waves (AGWs). When descending AGWs are over-reflected in the warm frontal zone of extratropical cyclones, even the small additional lift they would provide to a moist air parcel already rising above the cold air ahead can initiate oblique convection, thus forming a band of precipitation. Hagiwara and Tanaka [74] showed that the waves can propagate downward into the troposphere as damping gravity waves and found that “wave propagation and surface reflections create a geopotential antinode at the bottom of the atmosphere that corresponds to the vertical width of the initial shock state”. They suggested that standing waves in temperature create a knot on the ground surface that changes the stability of the atmosphere and may affect cyclone development. According to [28], major floods in southeastern Australia [75] also appear to show a tendency to occur after the arrival of the high-speed stream from coronal holes.
Other mechanisms influencing cloud formation and precipitation have also been investigated. Dickinson [76] pointed out the processes by which the ionization effects of galactic cosmic rays influence the formation of sulfate aerosol and cloud nucleation near the tropopause. Harrison and Stephenson [77] used 50 years of data from the UK and found that days with high cosmic rays were more likely to be cloudy and coincided. Moreover, the influence of the coronal mass ejection effect on cosmic rays, and consequently on cloud formation was studied in several works [78,79,80].
The statistical results presented in this study confirm the findings of previously published studies that precipitation-induced floods are usually accompanied by the arrival of sudden flows of charged particles from the Sun. The research showed that the applied model is accurate and adequate for predicting the occurrence of precipitation-induced floods 9 days in advance, after the outbreak of charged particles from the Sun. The model shows that in 91% of cases, the outbreak of charged particles influenced the occurrence of precipitation that can cause floods. Due to the nature of the data from the ACE satellite which, after passing through the ordered energy region through the geo-efficient position, no longer detects the flow of high-energy particles, as well as the fact that the interplanetary magnetic field moves in the form of curved lines, we believe that the continuation of the research should aim processing data on the parameters of the solar wind aimed at our planet, which can be measured by other satellites. Additionally, although it is not included in this research, we believe that the continuation of the research should also include the influence of cosmic rays on the occurrence of precipitation caused by floods.
4. Conclusions
The understanding of the complex and dynamic processes between the Sun and the Earth is not complete, so their prediction is also difficult. However, accurate forecasting and early warning systems are urgently needed in today’s society. The large amounts of satellite data that monitor the processes between the Earth and the Sun and the development of new ML techniques that can learn from the data present a chance to discover patterns that are not visible using traditional methods. Even though the connection between solar activity and climate parameters is not widely accepted and there are numerous hypotheses to interpret possible physical mechanisms, the establishment of an appropriate hidden dependence relationship between solar activity and environmental processes, such as precipitation-induced flooding, is a contribution to this field of research. It has been shown that occurrence of the flood in the investigated river basins are highly sensitive to the sudden increase in precipitation amount. Although flood occurrence is a complex issue depending on many factors, the amount of precipitation on the day or the day before plays a major role in a flood occurrence. Using a decision tree modeling approach to ML classification, we have shown that precipitation-induced floods in the UK tend to follow the arrival of high-speed solar wind streams. The results showed that the occurrence of precipitation-induced floods can be expected up to several days after the appearance of sudden flows of charged particles from the Sun. The response to changes in solar emissivity is expected to have a time lag, but there is no consensus on this in the recent literature. The research in this paper has shown that the decision tree model is accurate and adequate and could be used to predict the appearance of precipitation-induced floods up to 9 days ahead. According to the presented results, the decision tree models can explain the occurrence of precipitation-induced floods or their absence in 91% of cases. Proton density, differential proton flux in the 310–580 keV range, and ion temperature were found to be the most important factors for precipitation-induced flood forecasting. On the other hand, the random forest model can define the most important factors of solar activity for the precipitations and flood events. In addition, it has been shown that the independent datasets can provide the models with higher accuracy than the joined data. Our research shows that with increasing technical capabilities, and the use of improved ML techniques and large data sets, the knowledge about observed processes can be expanded. The results of this study confirm that a better understanding of the physical link between solar wind and tropospheric weather is very important because it can help predict severe weather (which is still in its early stages) and enable further assessment of the risk of severe weather. We can assume that the results obtained in this study can be connected with the nature of the data used, so we consider that the continuation of the research should be directed toward (i) obtaining and processing data measured by other satellites, (ii) including the influence of cosmic rays, and (iii) expanding the research to other geographical regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.-M., M.M.R., and Y.V.; Data curation, A.M.P., M.M., and V.P.; Formal analysis, S.M.-M., M.M.R., S.D.R., Y.V., and B.M.; Funding acquisition, M.M.R., and M.P.; Investigation, S.M.-M., M.M.R., B.M., M.M., M.P., P.S., and M.G.; Methodology, S.M.-M., M.M.R., S.D.R., and Y.V.; Project administration, M.M.R.; Resources, S.M.-M., A.M.P., M.M., and V.P.; Software, Y.V.; Supervision, S.M.-M., and M.M.R.; Validation, S.M.-M., M.M.R., S.D.R., Y.V., and B.M.; Visualization, S.M.-M., S.D.R., Y.V., and V.P.; Writing—original draft, S.M.-M., S.D.R., Y.V., B.M., and A.M.P.; Writing—review and editing, S.M.-M., M.M.R., S.D.R., Y.V., B.M., A.M.P., M.P., P.S., and M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Requests for the data used for analysis can be directed to S.M.M.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gaume, E.; Bain, V.; Bernardara, P.; Newinger, O.; Barbuc, M.; Bateman, A.; Blaškovičová, L.; Blöschl, G.; Borga, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; et al. A Compilation of Data on European Flash Floods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitka, W.; Burnecki, K. Impact of Solar Activity on Precipitation in the United States. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 2019, 527, 121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.D. The Sun and the Earth’s Climate. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2007, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, B.; Radovanović, M. Connection between Solar Activity and Atmospheric Circulation in Period 1891-2004. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić. SASA 2009, 59, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorović, N.; Vujović, D. Effect of Solar Activity on the Repetitiveness of Some Meteorological Phenomena. Adv. Sp. Res. 2014, 54, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.M.; Scherrer, P.H.; Svalgaard, L.; Roberts, W.O.; Olson, R.H. Solar Magnetic Sector Structure: Relation to Circulation of the Earth’s Atmosphere. Science 1973, 180, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, J.M.; Scherrer, P.H.; Svalgaard, L.; Roberts, W.O.; Olson, R.H.; Jenne, R.L. Influence of Solar Magnetic Sector Structure on Terrestrial Atmospheric Vorticity. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.H.; Han, Y.B.; Yin, Z.Q. Possible Influence of the 11-Year Solar Cycle on Precipitation in Huashan Mountain of China over the Last 300 Years. Earth. Moon. Planets 2010, 107, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.; Milovanović, B.; Leko, T.; Milenković, M.; Milošević, Z.; Milanović Pešić, A.; Jakovljević, D. Hurricane Genesis Modelling Based on the Relationship between Solar Activity and Hurricanes. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.M.; Stanojević, G.B.; Milovanović, B.; Leko, T.; Milenković, M.; Petrović, M.; Yamashkin, A.A.; Pešić, A.M.; Jakovljević, D.; et al. Hurricane Genesis Modelling Based on the Relationship between Solar Activity and Hurricanes II. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2018, 180, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srećković, V.; Šulić, D.; Vujčić, V.; Jevremović, D.; Vyklyuk, Y. The Effects of Solar Activity: Electrons in the Terrestrial Lower Ionosphere. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić, SASA 2017, 67, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina, A.; Čadež, V.; Bajčetić, J.; Andrić, M.; Jovanović, G. Responses of the Ionospheric D-Region to Periodic and Transient Variations of the Ionizing Solar Lyα Radiation. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2017, 67, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliniemi, V.; Asikainen, T.; Mursula, K. Decadal Variability in the Northern Hemisphere Winter Circulation: Effects of Different Solar and Terrestrial Drivers. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2018, 179, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landscheidt, T. Solar Wind near Earth: Indicator of Variations in Global Temperature. In Proceedings of the 1st Solar and Space Weather Euroconference, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain, 25–29 September 2000; pp. 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, L.J.; Beer, J.; Geller, M.; Haigh, J.D.; Lockwood, M.; Matthes, K.; Cubasch, U.; Fleitmann, D.; Harrison, G.; Hood, L.; et al. Solar Influences on Climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Bell, C.; Woollings, T.; Harrison, R.G.; Gray, L.J.; Haigh, J.D. Top-down Solar Modulation of Climate: Evidence for Centennial-Scale Change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, L. Has Global Warming Modified the Relationship between Sunspot Numbers and Global Temperatures? Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 2017, 468, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.D. The Impact of Solar Variability on Climate. Science 1996, 272, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ineson, S.; Scaife, A.A.; Knight, J.R.; Manners, J.C.; Dunstone, N.J.; Gray, L.J.; Haigh, J.D. Solar Forcing of Winter Climate Variability in the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensmark, H.; Friis-Christensen, E. Variation of Cosmic Ray Flux and Global Cloud Coverage—A Missing Link in Solar-Climate Relationships. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 1997, 59, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, K.S.; Harrison, R.G.; Kirkby, J. Cosmic Rays, Clouds, and Climate. Science 2002, 298, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solheim, J.-E.; Stordahl, K.; Humlum, O. The Long Sunspot Cycle 23 Predicts a Significant Temperature Decrease in Cycle 24. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 80, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, B.A. Influence of Solar Wind on the Global Electric Circuit, and Inferred Effects on Cloud Microphysics, Temperature, and Dynamics in the Troposphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Thejll, P. Effects of Energetic Solar Proton Events on the Cyclone Development in the North Atlantic. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2004, 66, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Thejll, P. Influence of Energetic Solar Proton Events on the Development of Cyclonic Processes at Extratropical Latitudes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 409, 012237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stozhkov, Y.I.; Pokrevskij, P.E.; Okhlopkov, V.P.; Zullo, Z.; Martin, I.M.; Pellegrino, Z.K.; Pinto, K.S.; Bezerra, P.S.; Turnelli, A. Effect of Charged Particle Fluxes on Intensity of Precipitations. Geomagn. I Aehronomiya 1996, 36, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, S. Possible Association between Indian Monsoon Rainfall and Solar Activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L05813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Rušin, V.; Prikryl, E.A.; Šťastný, P.; Turňa, M.; Zeleňáková, M. Heavy Rainfall, Floods, and Flash Floods Influenced by High-Speed Solar Wind Coupling to the Magnetosphere–Ionosphere–Atmosphere System. Ann. Geophys. 2021, 39, 769–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilensten, J.; Bornarel, J. Space Weather, Environment and Societies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; ISBN 978-94-024-0455-5. [Google Scholar]
- Artamonova, I.V.; Veretenenko, S.V. Effect of Solar and Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Duration of Macrosynoptic Processes. Geomagn. Aeron. 2013, 53, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Rušin, V.; Rybanský, M. The Influence of Solar Wind on Extratropical Cyclones—Part 1: Wilcox Effect Revisited. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Muldrew, D.B.; Sofko, G.J. The Influence of Solar Wind on Extratropical Cyclones—Part 2: A Link Mediated by Auroral Atmospheric Gravity Waves? Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Iwao, K.; Muldrew, D.B.; Rušin, V.; Rybanský, M.; Bruntz, R. A Link between High-Speed Solar Wind Streams and Explosive Extratropical Cyclones. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2016, 149, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Bruntz, R.; Tsukijihara, T.; Iwao, K.; Muldrew, D.B.; Rušin, V.; Rybanský, M.; Turňa, M.; Šťastný, P. Tropospheric Weather Influenced by Solar Wind through Atmospheric Vertical Coupling Downward Control. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2018, 171, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Nikitina, L.; Rušin, V. Rapid Intensification of Tropical Cyclones in the Context of the Solar Wind-Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Atmosphere Coupling. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2019, 183, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallin, A.; Downs, J.A. Machine Learning in Geography–Past, Present, and Future. Geogr. Compass 2021, 15, e12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R.; Carbonell, J.; Mitchell, T. Machine Learning: An Artificial Intelligence Approach, 1st ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1984; ISBN 1493303481. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnamgari, S.K. R Machine Learning Projects: Implement Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning Techniques Using R 3.5, 1st ed.; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781789806090. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, A.Y.; Scanlon, B.R. How Can Big Data and Machine Learning Benefit Environment and Water Management: A Survey of Methods, Applications, and Future Directions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Batelaan, O.; Fadaee, M.; Hinkelmann, R. Ensemble Machine Learning Paradigms in Hydrology: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, A.; Davies, E.G.R. A Workflow to Address Pitfalls and Challenges in Applying Machine Learning Models to Hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 152, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaee, T.; Khani, S.; Ravansalar, M. Artificial Intelligence-Based Single and Hybrid Models for Prediction of Water Quality in Rivers: A Review. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 200, 103978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyralis, H.; Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. Super Ensemble Learning for Daily Streamflow Forecasting: Large-Scale Demonstration and Comparison with Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.; Heße, F.; Attinger, S.; Kumar, R. Challenges in Applying Machine Learning Models for Hydrological Inference: A Case Study for Flooding Events Across Germany. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, F.; Tauro, F.; Apollonio, C.; Petroselli, A.; Borgonovo, E.; Grimaldi, S. Feature Importance Measures to Dissect the Role of Sub-Basins in Shaping the Catchment Hydrological Response: A Proof of Concept. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natras, R.; Schmidt, M. Machine Learning Model Development for Space Weather Forecasting in the Ionosphere. In Proceedings of the CEUR Workshop, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, C.; Marsh, T.J. Water Quality in the Environment; Natural Environment Research Council: Swindon, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- UK River and Flow Regimes. Available online: https://nrfa.ceh.ac.uk/uk-river-flow-regimes (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Kingston, D.G.; McGregor, G.R.; Hannah, D.M.; Lawler, D.M. Large-Scale Climatic Controls on New England River Flow. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laizé, C.L.R.; Hannah, D.M. Modification of Climate–River Flow Associations by Basin Properties. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, J.; Buys, G. Trends in Seasonal River Flow Regimes in the UK. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Below, R.; Hoyois, P. EM-DAT: The CRED/OFDA International Disaster Database. Available online: https://www.emdat.be/ (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Wijngaard, J.B.; Können, G.P.; Böhm, R.; Demarée, G.; Gocheva, A.; Mileta, M.; Pashiardis, S.; Hejkrlik, L.; Kern-Hansen, C.; et al. Daily Dataset of 20th-Century Surface Air Temperature and Precipitation Series for the European Climate Assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, E.J.; Klein Tank, A.M.G. Updated and Extended European Dataset of Daily Climate Observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA, Space Environment Center. Available online: https://sohoftp.nascom.nasa.gov/sdb/goes/ace/daily/ (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- LASP Interactive Solar Irradiance Data Center. Available online: https://lasp.colorado.edu/lisird/data/noaa_radio_flux/ (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Daily Flux Values. Available online: http://www.spaceweather.gc.ca/solarflux/sx-5-flux-en.php (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Space Weather Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Available online: https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/phenomena/f107-cm-radio-emissions (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.M.; Stanojević, G.; Petrović, M.D.; Ćurčić, N.B.; Milenković, M.; Malinović-Milićević, S.; Milovanović, B.; Yamashkin, A.A.; Milanović Pešić, A.; et al. Connection of Solar Activities and Forest Fires in 2018: Events in the USA (California), Portugal and Greece. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.; Vyklyuk, Y.; Stevančević, M.; Milenković, M.; Jakovljević, D.; Petrović, M.; Malinović-Milicević, S.; Vuković, N.; Vujko, A.; Yamashkin, A.; et al. Forest Fires in Portugal—Case Study, 18 June 2017. Therm. Sci. 2019, 23, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyklyuk, Y.; Radovanović, M.M.; Milovanović, B.; Milenković, M.; Petrović, M.; Doljak, D.; Malinović-Milićević, S.; Vuković, N.; Vujko, A.; Matsiuk, N.; et al. Space Weather and Hurricanes Irma, Jose and Katia. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.L. Compositing or Superposed Epoch Analysis. ATM 552 Notes. Available online: http://www.atmos.washington.edu/~dennis/552_Notes_2.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Shingala, M.; Rajyaguru, A. Comparison of Post Hoc Tests for Unequal Variance. Int. J. New Technol. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tamhane, A.C. A Comparison of Procedures for Multiple Comparisons of Means with Unequal Variances. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterill, D.; Stott, P.; Christidis, N.; Kendon, E. Increase in the Frequency of Extreme Daily Precipitation in the United Kingdom in Autumn. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 33, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, M. Severe Flooding South Yorkshire, November 2019. Available online: https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/binaries/content/assets/metofficegovuk/pdf/weather/learn-about/uk-past-events/interesting/2019/2019_012_november_rain.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Ramzan, B.; Bajwa, I.S.; Jamil, N.; Amin, R.U.; Ramzan, S.; Mirza, F.; Sarwar, N. An Intelligent Data Analysis for Recommendation Systems Using Machine Learning. Sci. Program. 2019, 2019, 5941096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raileanu, L.E.; Stoffel, K. Theoretical Comparison between the Gini Index and Information Gain Criteria. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 2004, 41, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, M.; Lasota, T.; Trawiński, B.; Trawiński, K. Comparison of Bagging, Boosting and Stacking Ensembles Applied to Real Estate Appraisal. In Intelligent Information and Database Systems. ACIIDS 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Nguyen, N.T., Le, M.T., Świątek, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 340–350. ISBN 978-3-642-12101-2. [Google Scholar]
- Trostianchyn, A.; Duriagina, Z.; Izonin, I.; Tkachenko, R.; Kulyk, V.; Pavliuk, O. Sm-Co ALLOYS COERCIVITY PREDICTION USING STACKING HETEROGENEOUS ENSEMBLE MODEL. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2021, 27, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrar, D. Cross-Validation. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 542–545. [Google Scholar]
- Stevančević, M.; Radovanović, M.; Todorović, N. The Possibility of Application of Electromagnetic Method in Mid Term Weather Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Collection of Papers EkoIst’04 Ecological Truth, Bor, Serbia; 2004; pp. 396–399. [Google Scholar]
- Stevančević, M.; Radovanović, M.; Todorović, N. Analysis of Characteristic Mistakes in the Heliocentric Electromagnetic Long-Term Forecast. In Proceedings of the “Tourist Valorisation of Tara” Theme Collection of the Geographical Institute “Jovan Cvijic” SASA and Sport-Recreative Center Bajina Bašta, Belgrade, Serbia, 12–15 June 2006; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, M.; Tanaka, H.L. A Theoretical Analysis of the Atmospheric Gravity Wave That Connects the Thermosphere and the Troposphere. Tsukuba Geoenvironmental Sci. 2020, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, J.; Power, S. A Vertical Wind Structure That Leads to Extreme Rainfall and Major Flooding in Southeast Australia. J. South. Hemisph. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 66, 380–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E. Solar Variability and the Lower Atmosphere. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1975, 56, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G.; Stephenson, D.B. Empirical Evidence for a Nonlinear Effect of Galactic Cosmic Rays on Clouds. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 462, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogovic, J.; Albert, C.; Arnold, F.; Beer, J.; Desorgher, L.; Flueckiger, E.O. Sudden Cosmic Ray Decreases: No Change of Global Cloud Cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L03802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, J.E.; Stjern, C.W.; Stordal, F.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Myhre, G.; Jónasson, K. Cosmic Rays, Cloud Condensation Nuclei and Clouds—A Reassessment Using MODIS Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 7373–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensmark, H.; Bondo, T.; Svensmark, J. Cosmic Ray Decreases Affect Atmospheric Aerosols and Clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).