REKP: Refined External Knowledge into Prompt-Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We introduce external knowledge to enhance the verbalizer by expanding related words, which improves the granularity of the tag thesaurus and enriches the mapping range of tags.
- We propose three methods to refine the enhanced verbalizer and remove the noise words to optimize the model.
- Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets, namely AG’s News, Yahoo, IMDB, and Amazon, demonstrate the superiority of REKP over the competitive baselines in terms of Micro-F1 on knowledge-enhanced text classification tasks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Few-Shot Text Classification
2.2. Prompt Tuning for Few-Shot Learning
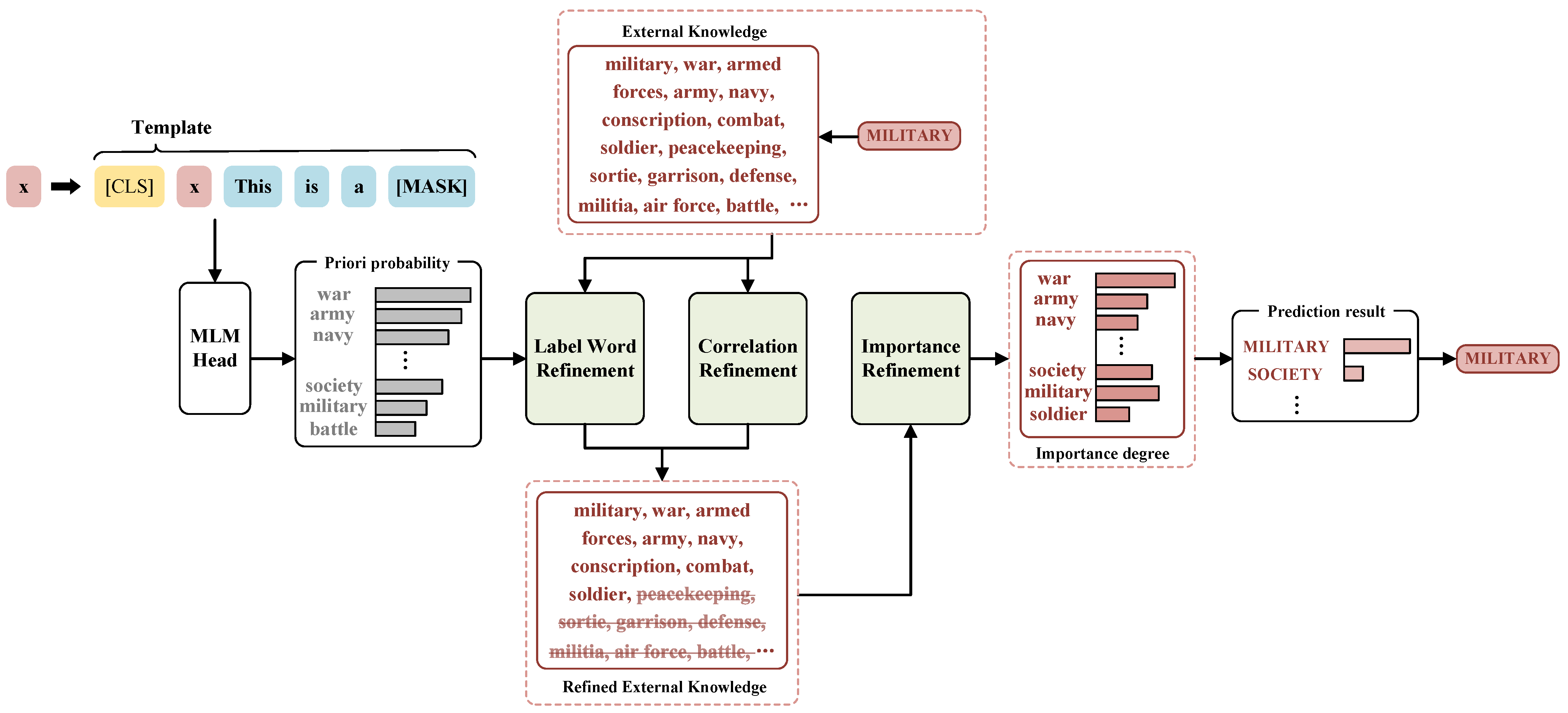
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. Overall Framework
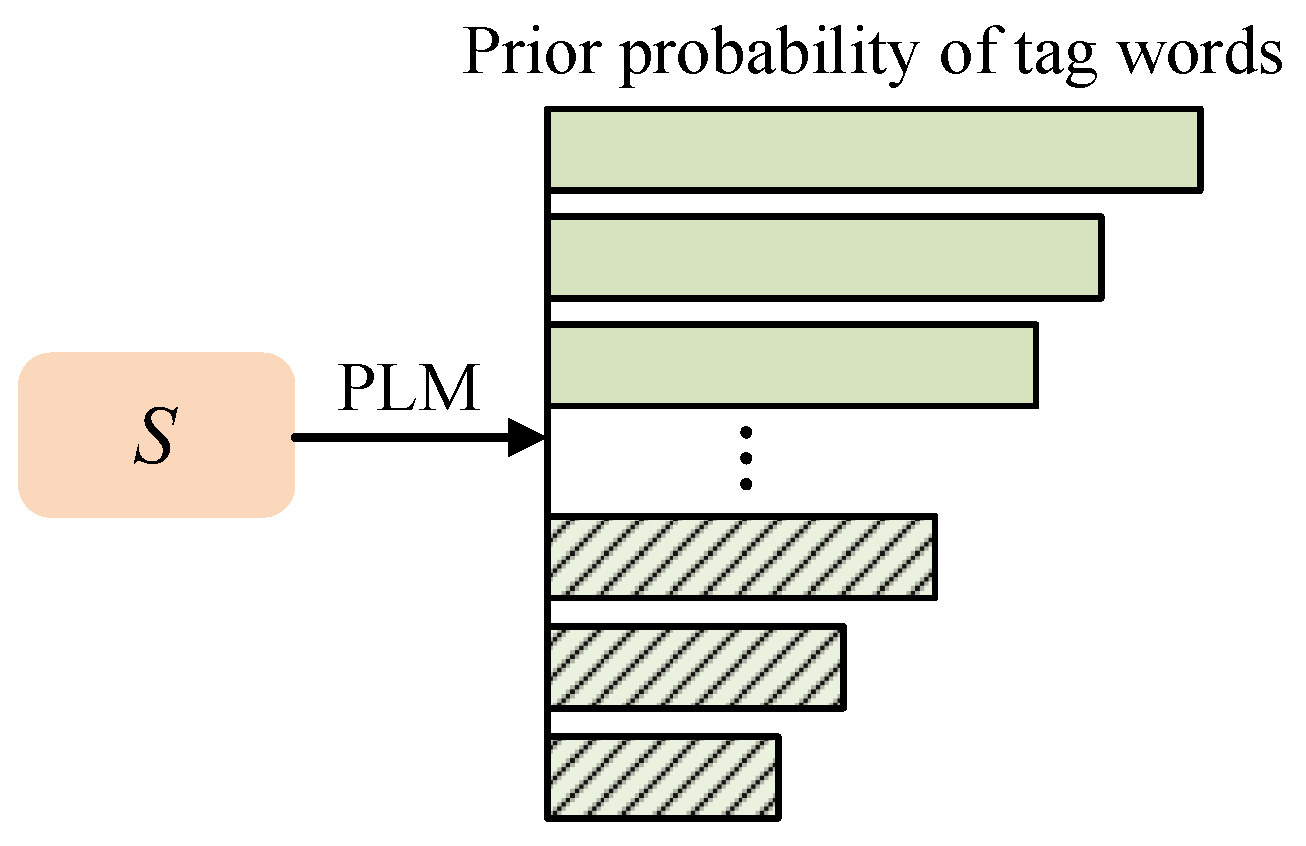
3.2. Template Conversion
3.3. Verbalizer Construction
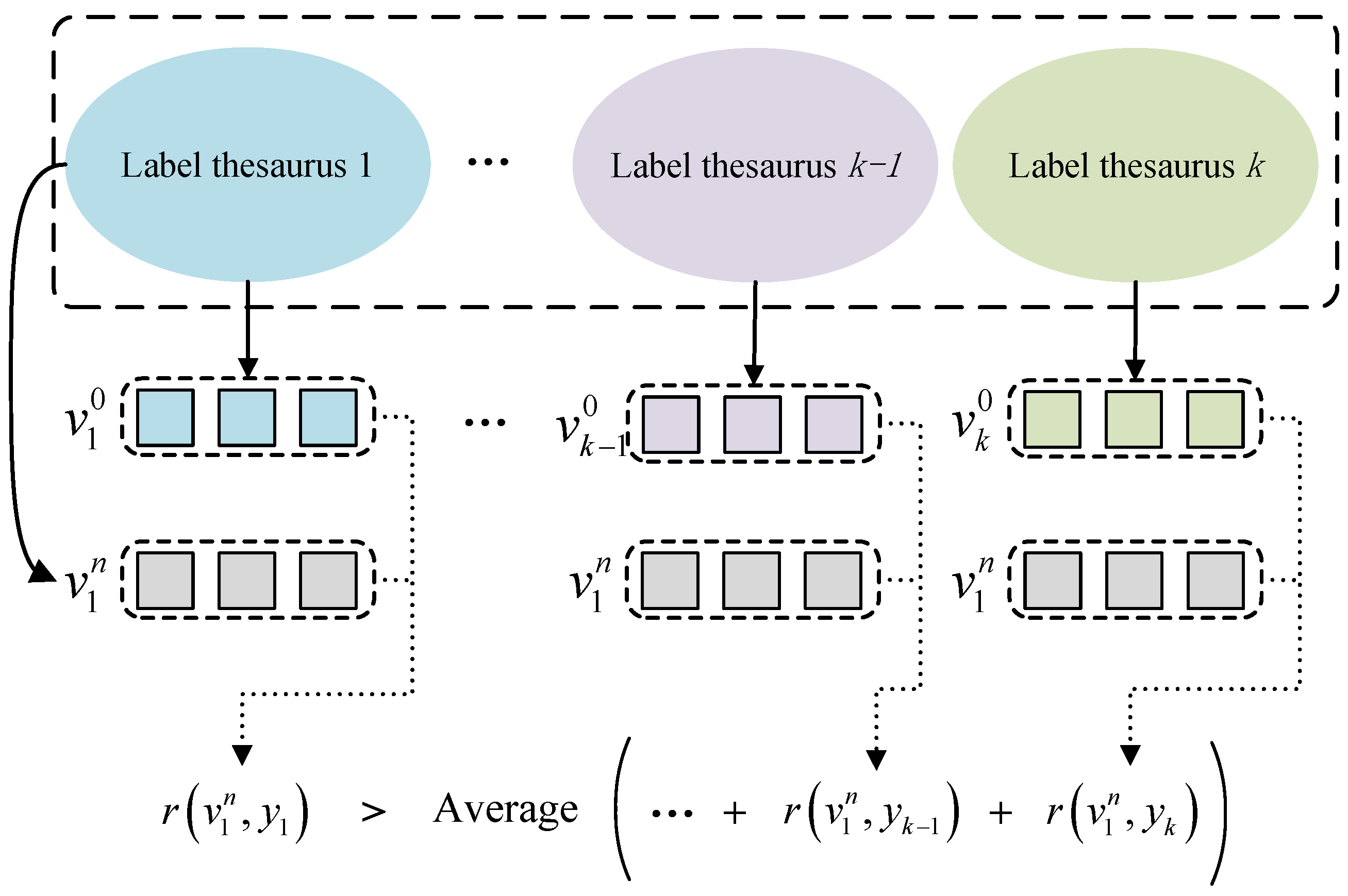
3.3.1. Label Word Refinement (WR)
3.3.2. Correlation Refinement (CR)
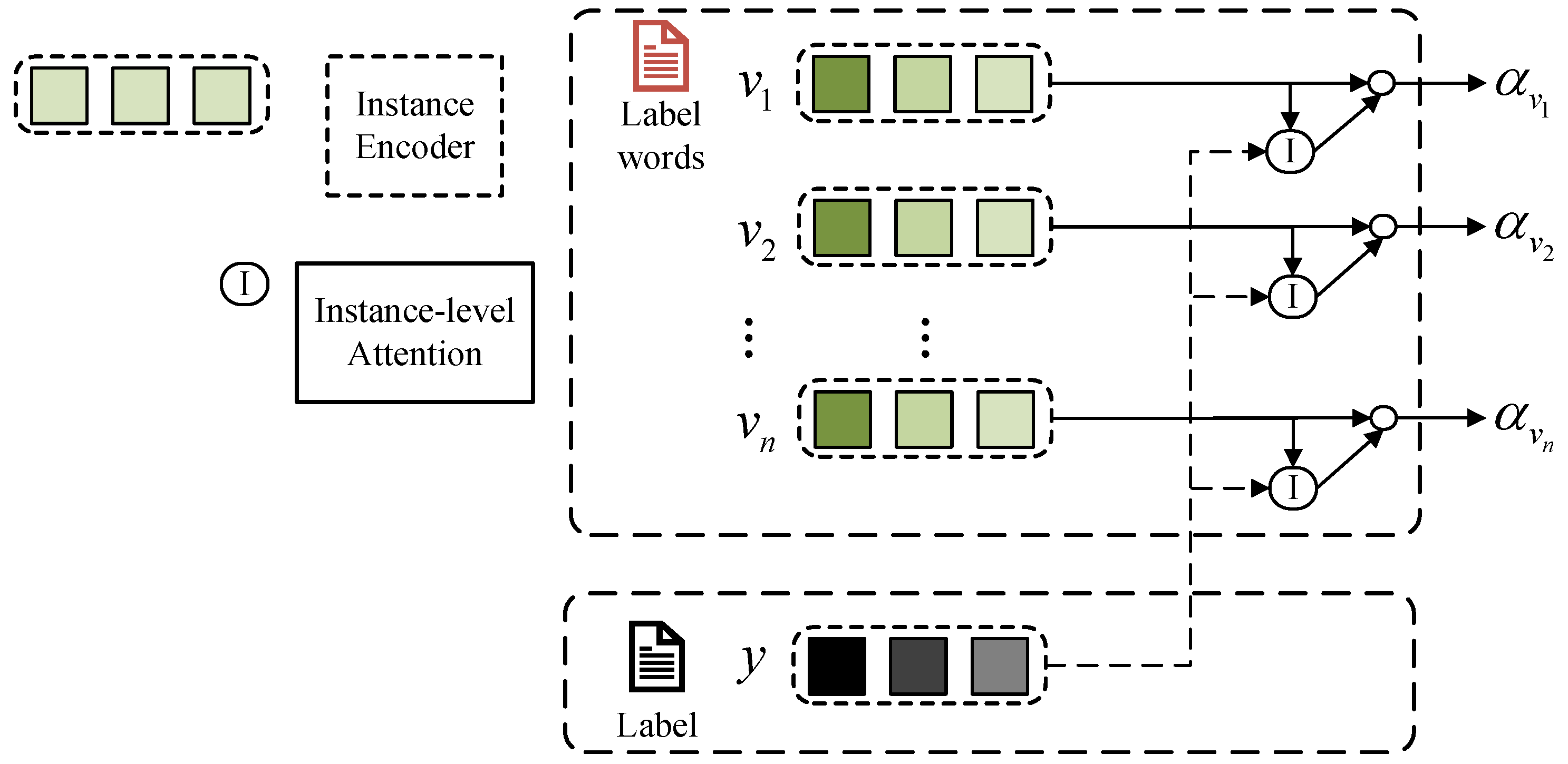
3.3.3. Importance Refinement (IR)
3.4. Verbalizer Utilization
4. Experiments
4.1. Research Questions
- (RQ1)
- Can our proposed REKP outperform the baselines in terms of performance?
- (RQ2)
- How does each refinement in verbalizer contribute to REKP?
- (RQ3)
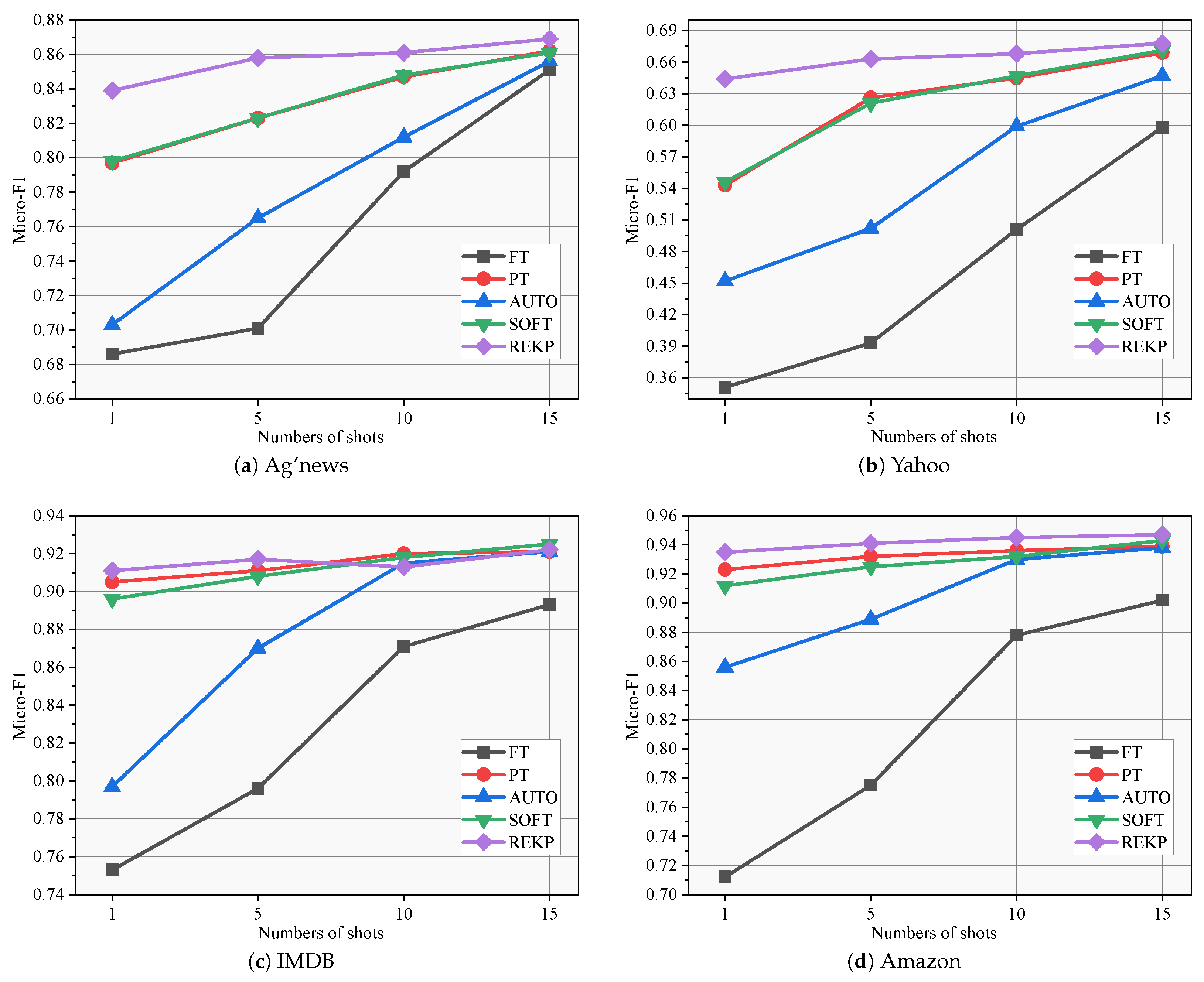
- How our PTEK model and baselines perform in terms of classification accuracy depends on the number of training samples?
- (RQ4)
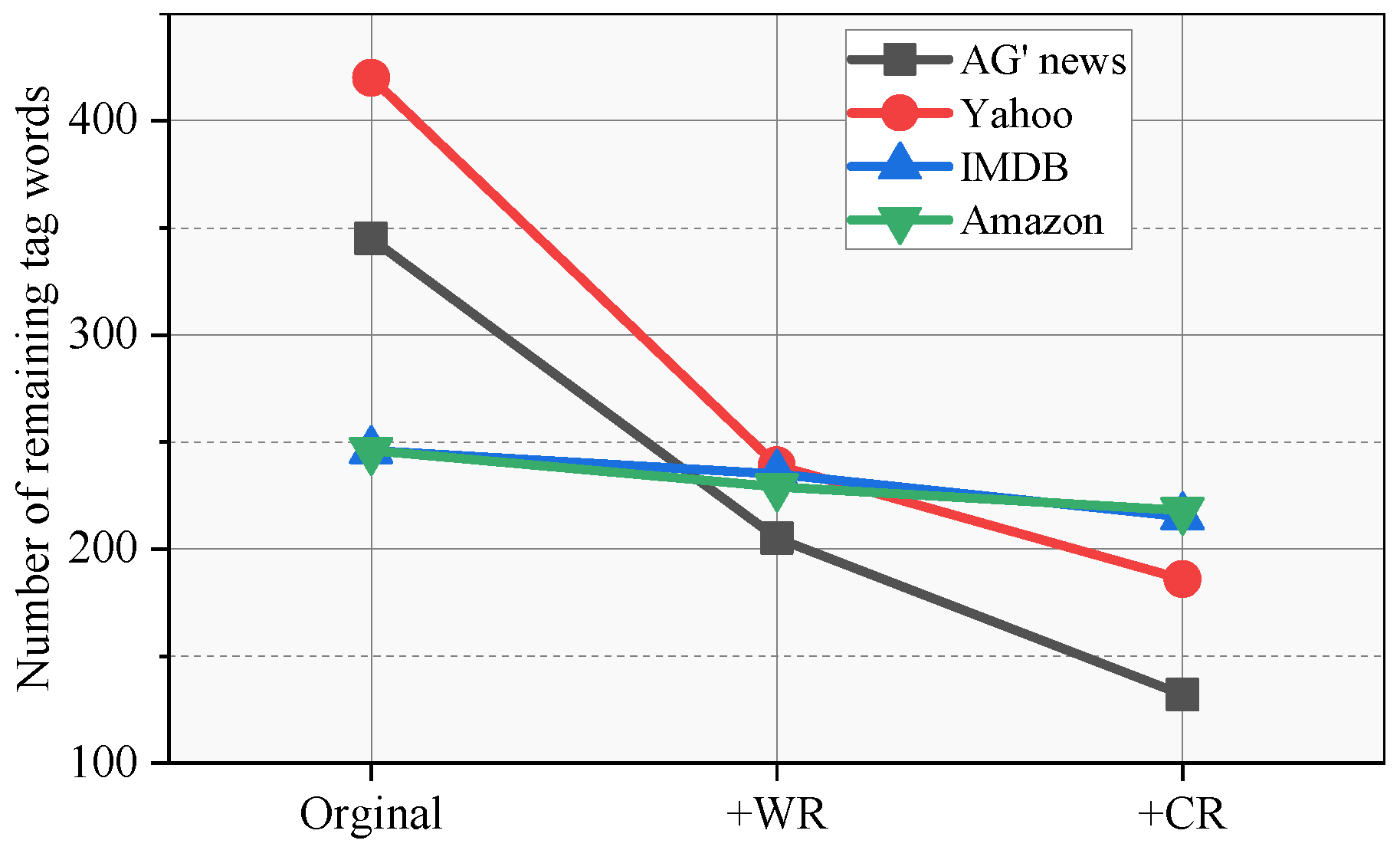
- What is the particular impact of refinement on the number of label thesaurus?
4.2. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Baselines
- FT inputs the [CLS] hidden embedding of the pre-trained model into the classification layer for label prediction.
- PT [8] is a classical model for text classification with few-shot using prompt learning. It inserts a short text template with the [MASK] token, utilizing the name of the category as an unusual label, and predicting the results of the labeled words in direct response to the category results.
- AUTO [9] is a model that automatically chooses the most informative terms from the PLM vocabulary as tag words, eliminating the need for manually established class names.
- SOFT [10] uses consecutive vectors to represent the classes, and the output of the MLM is dot-produced with the class vectors to obtain the predicted probabilities for each class. The method is carried on by REKP, which uses the class vectors that are the word embeddings of the class names.
4.4. Model Configuration
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Overall Performance
5.2. Ablation Study
- w/o WR removes Label Word Refinement from REKP;
- w/o CR removes Correlation Refinement from REKP;
- w/o IR removes Importance Refinement from REKP;
- w/o RRR removes three refinement modules of REKP.
5.3. Impact of Sample Number
5.4. Refinement Visualization
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal language model fine-tuning for text classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.06146. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, A.; Harada, T. Revisiting fine-tuning for few-shot learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.00216. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Qin, J.; Savvides, M.; Cheng, K.-T. Partial is Better Than All: Revisiting Fine-Tuning Strategy for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 9594–9602. [Google Scholar]
- Kowsari, K.; Jafari Meimandi, K.; Heidarysafa, M.; Mendu, S.; Barnes, L.; Brown, D. Text classification algorithms: A survey. Information 2019, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Hierarchical BERT with an adaptive fine-tuning strategy for document classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Van Hee, C.; Hoste, V. Automatic classification of participant roles in cyberbullying: Can we detect victims, bullies, and bystanders in social media text? Nat. Lang. Eng. 2022, 28, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, T.; Schütze, H. Exploiting cloze questions for few shot text classification and natural language inference. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.07676. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, T.; Schmid, H.; Schütze, H. Automatically identifying words that can serve as labels for few-shot text classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.13641. [Google Scholar]
- Hambardzumyan, K.; Khachatrian, H.; May, J. Warp: Word-level adversarial reprogramming. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.00121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; LeCun, Y. Character-level convolutional networks for text classification. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.01626. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, M.; Gao, M.; Zhou, A. Meta-learning adversarial domain adaptation network for few-shot text classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.12262. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, D.; Chen, Y.; Mao, B.; Qiu, D.; Liu, K.; Zhao, J. Knowledge guided metric learning for few-shot text classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.01907. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dai, X. MEDA: Meta-Learning with Data Augmentation for Few-Shot Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 3929–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, M.; Kim, S.; Yang, Y. Transductive propagation network for few-shot learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10002. [Google Scholar]
- Boney, R.; Ilin, A. Semi-Supervised Few-Shot Learning with MAML. 2018. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=r1n5Osurf (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Bayer, M.; Kaufhold, M.-A.; Reuter, C. A Survey on Data Augmentation for Text Classification. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Woo, D.; Oh, S.J.; Cha, J.-W.; Han, Y.-S. ALP: Data Augmentation Using Lexicalized PCFGs for Few-Shot Text Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’2022), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 10894–10902. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Fu, Y. Adversarial Feature Hallucination Networks for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’2020), Virtual, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13470–13479. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, M.; Kwitt, R.; Niethammer, M.; Vasconcelos, N. Aga: Attribute-guided augmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7455–7463. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.; Sha, N.; Qin, S.; Yan, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, R. Advances in neural information processing systems. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. Available online: https://par.nsf.gov/biblio/10195511 (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Mao, Y.; Xu, J. ContrastNet: A Contrastive Learning Framework for Few-Shot Text Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 10492–10500. [Google Scholar]
- Munkhdalai, T.; Yu, H. Meta Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2554–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cheung, N.-M. Attentive Weights Generation for Few Shot Learning via Information Maximization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13499–13508. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.K.; Jang, T.Y. LEA: Meta Knowledge-Driven Self-Attentive Document Embedding for Few-Shot Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 July 2022; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Snell, J.; Swersky, K.; Zemel, R. Prototypical Networks for Few-shot Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Hybrid Attention-Based Prototypical Networks for Noisy Few-Shot Relation Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 6407–6414. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Z.; Ding, M.; Qian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. GPT Understands, Too. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, W.; Ding, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Ptr: Prompt tuning with rules for text classification. AI Open 2022, 3, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, G.; Xie, P.; Zheng, H.-T.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Kim, H.-G. Prompt-learning for fine-grained entity typing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.10604. [Google Scholar]
- Ezepue, E.I.; Nwankwor, P.P.; Chukwuemeka-Nworu, I.J.; Ozioko, A.N.; Egbe, C.O.; Ujah, J.; Nduka, C.; Edikpa, E.C. Evaluating the Local Language Dimensions for Effective Teaching and Learning Sustainability in the Secondary Education System in Southeast Nigeria: Results from a Small-Scale Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Fisch, A.; Chen, D. Making pre-trained language models better few-shot learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15723. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Ding, N.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, M. Knowledgeable prompt-tuning: Incorporating knowledge into prompt verbalizer for text classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.02035. [Google Scholar]
| Category | Method | Introduction |
|---|---|---|
| Discrepancy | Manual Template | Manual template design based on the nature of specific tasks and prior knowledge. |
| Heuristic-based Template | Build templates by heuristic search, etc. | |
| Generation | According to the given training data with few samples, an appropriate template is generated. | |
| Continuity | Word Embedding | Initialize discrete templates and train them by gradient descent method. |
| Pseudo Token | Use the template as a trainable parameter. |
| Ag’news | A [MASK] news : x |
| This topic is about [MASK] . | |
| [Category : [MASK]] | |
| [Topic : [MASK]] | |
| IMDB | A [MASK] question : |
| x This topic is about [MASK] . | |
| [Category : [MASK]] | |
| [Topic : [MASK]] | |
| Yahoo, Amazon | It was [MASK] . |
| Just [mask]! | |
| All in all, it was [MASK] . | |
| In summary, it was [MASK] . |
| Shot | Method | AG’s News | Yahoo | IMDB | Amazon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT | 68.6 ± 8.9 | 35.1 ± 6.5 | 75.3 ± 5.3 | 71.2 ± 4.7 | |
| PT | 79.7 ± 6.3 | 54.3 ± 5.8 | 90.5 ± 4.3 | 92.3 ± 3.4 | |
| 1 | AUTO | 70.3 ± 7.2 | 45.2 ± 6.2 | 79.7 ± 4.9 | 85.6 ± 4.0 |
| SOFT | 79.8 ± 6.1 | 54.6 ± 5.6 | 89.6 ± 4.3 | 91.2 ± 3.5 | |
| REKP | 83.9 ± 4.1 | 64.4 ± 3.5 | 91.1 ± 3.3 | 93.5 ± 3.1 | |
| FT | 70.1 ± 8.2 | 39.3 ± 6.3 | 79.6 ± 4.2 | 77.5 ± 3.1 | |
| PT | 82.3 ± 6.2 | 62.6 ± 4.2 | 91.1 ± 1.6 | 93.2 ± 1.9 | |
| 5 | AUTO | 76.5 ± 7.2 | 50.2 ± 5.9 | 87.0 ± 3.4 | 88.9 ± 2.9 |
| SOFT | 82.3 ± 5.9 | 62.1 ± 4.8 | 90.8 ± 1.8 | 92.5 ± 1.5 | |
| REKP | 85.8 ± 3.8 | 66.3 ± 2.8 | 91.7 ± 2.7 | 94.1 ± 2.5 | |
| FT | 79.2 ± 5.2 | 50.1 ± 5.1 | 87.1 ± 3.8 | 87.8 ± 2.5 | |
| PT | 84.7 ± 3.2 | 64.5 ± 4.5 | 92.0 ± 2.1 | 93.6 ± 2.1 | |
| 10 | AUTO | 81.2 ± 4.1 | 59.9 ± 5.1 | 91.5 ± 2.8 | 93 ± 2.5 |
| SOFT | 84.8 ± 2.9 | 64.7 ± 3.8 | 91.8 ± 2.7 | 93.2 ± 2.6 | |
| REKP | 86.1 ± 2.5 | 66.8 ± 1.9 | 91.3 ± 1.5 | 94.5 ± 1.7 | |
| FT | 85.1 ± 2.5 | 59.8 ± 3.1 | 89.3 ± 2.4 | 90.2 ± 1.8 | |
| PT | 86.2 ± 1.5 | 66.9 ± 2.4 | 92.1 ± 1.9 | 93.9 ± 1.4 | |
| 15 | AUTO | 85.3 ± 2.1 | 64.7 ± 2.6 | 92.1 ± 2.1 | 93.8 ± 1.2 |
| SOFT | 86.1 ± 1.4 | 67.1 ± 0.9 | 92.5 ± 1.0 | 94.3 ± 1.1 | |
| REKP | 86.9 ± 0.8 | 67.8 ± 0.3 | 92.2 ± 0.5 | 94.7 ± 0.6 |
| Dataset | Method | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG’s News | REKP | 83.9 | 85.8 | 86.1 | 86.9 |
| w/o WR | 83.7 ↓ | 85.2 ↓ | 86.1 = | 86.8 ↓ | |
| w/o CR | 83.0 ↓ | 85.6 ↓ | 86.5 ↑ | 86.9 = | |
| w/o IR | 83.9 = | 85.9 = | 86.7 ↑ | 87.4 ↑ | |
| w/o RRR | 82.5 * ↓ | 83.6 * ↓ | 85.6 * ↓ | 86.6 * ↓ | |
| IMDB | REKP | 91.1 | 91.7 | 91.3 | 92.2 |
| w/o WR | 91.0 ↓ | 91.7 = | 91.3 = | 92.2 = | |
| w/o CR | 90.8 ↓ | 91.6 ↓ | 90.5 ↓ | 92.4 = | |
| w/o IR | 90.8 ↓ | 91.8 = | 90.5 ↓ | 92.1 ↓ | |
| w/o RRR | 90.7 ↓ | 91.5 ↓ | 90.2 ↓ | 91.9 ↓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. REKP: Refined External Knowledge into Prompt-Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11234780
Dang Y, Chen W, Zhang X, Chen H. REKP: Refined External Knowledge into Prompt-Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification. Mathematics. 2023; 11(23):4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11234780
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Yuzhuo, Weijie Chen, Xin Zhang, and Honghui Chen. 2023. "REKP: Refined External Knowledge into Prompt-Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification" Mathematics 11, no. 23: 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11234780
APA StyleDang, Y., Chen, W., Zhang, X., & Chen, H. (2023). REKP: Refined External Knowledge into Prompt-Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification. Mathematics, 11(23), 4780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11234780






