Benford’s Law in Electric Distribution Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- determine whether lists of COVID-19 infection numbers, claiming to be measurements of real events or sizes, were manipulated,
- -
- analyze lightning data and assess the negative effects with precise parameters of lightning in kA unit,
- -
- detect image forgery during resizing and compression,
- -
- detect anomalies in the number of publications per researcher and the number of researchers per publication,
- -
- analyze the distribution of starting letters in novels and similar studies,
- -
- evaluate the quality of economic data in companies.
- using BL for electricity theft detection methods,
- verifying the detection sensitivity by affecting different amounts of the original dataset,
- examining the dataset behavior according to BL by applying different kinds of intervention operations.
2. The Theory behind Benford’s Law
- The dataset must not be radically restricted in value range (e.g., the dataset of people’s height or IQ is a radical restriction because of a very small range of possible values).
- The dataset must not be influenced by any kind of artificial effects caused by human actions aiming to change the values intentionally.
- The value range in the dataset must be large enough, e.g., [14]:
- 4.
- The dataset should be large enough.
3. Other Observations Regarding Benford’s Law and Operations Performed on Datasets Following This Law
- Conversion from one numeric system into another (base-invariance) means only changing the base of the logarithm.
- Scale invariance means that the significant digit distribution should be invariant under changes of scale and thus must comply with Benford distribution according to the following definition:
- -
- A probability measure P on (R+, A) with A ⊃ S has scale-invariant significant digits if and only if P(A) = B(A) for every A ∈ S, i.e., if and only if P follows Benford’s law (proof can be found in [17]).
- Furthermore, the sum-invariance term says that the first digit probability distribution has sum-invariant digits if, in a set of numbers with that distribution, the sums of all entries with the first digit 1 has the same value as each other of the sums for all entries with the remaining first digits. For example, the sum of all the entries with the first two significant digits 1 and 3, respectively, has the same value as the sum of all remaining entries with any other combination of the first two significant digits, etc.
4. Benford Law in Electric Power Engineering
- Small data sets—In case we have only small data sets as the input of the comparison, these data sets are not statistically significant,
- Specific data distribution—BL distribution can fail in cases when the first digits of the data are symmetrically distributed around zero, or the first digit probability is distributed evenly by the nature of the data,
- Data manipulation—This manipulation can be considered natural, and usually, it is introduced by companies intentionally in order to fulfill specific production or distribution process requirements,
- Deviations from normal processes—In case of irregular and exceptional situations, e.g., electricity supply dropouts, the dataset is influenced.
5. Dataset for Our Experiments
- The data in the dataset must come from the same situation/effect or should describe the same parameter,
- There should be no limits on minimum and maximum values,
- The dataset should be statistically random; the data must not be generated according to pre-defined rules or equations (serial or telephone number, any identification numbers, etc.),
- The dataset should include smaller than bigger values, the mean value should be smaller than the median, and the dataset should have positive skewness,
- The values in the dataset should be on the same scale,
- The values should have at least two orders.
6. The Methods Used in Our Experiment
- Adding +1 to dataset values,
- Division of the dataset values by 2,
- Multiplication of the dataset value by 2.
- 75% of the overall dataset values were affected (32,757 values were replaced by pseudo-random numbers),
- 50% of the overall dataset values were affected (21,838 values were replaced by pseudo-random numbers),
- 25% of the overall dataset values were affected (10,919 values were replaced by pseudo-random numbers),
- and 10% of the overall dataset values were affected (4367 values were replaced by pseudo-random numbers).
- Environmental and social errors, which means that the dataset can be influenced by seasonal factors, e.g., weather in general, outside temperature, etc., and the social behavior of electricity consumers. All these aspects of course change the original dataset in unnatural way, causing its corruption and deviation from BL distribution. This aspect was significantly canceled by proper selection of data recording interval.
- Data quality includes measurement accuracy and completeness.
- A single recording method can be another source of inaccuracies in data values.
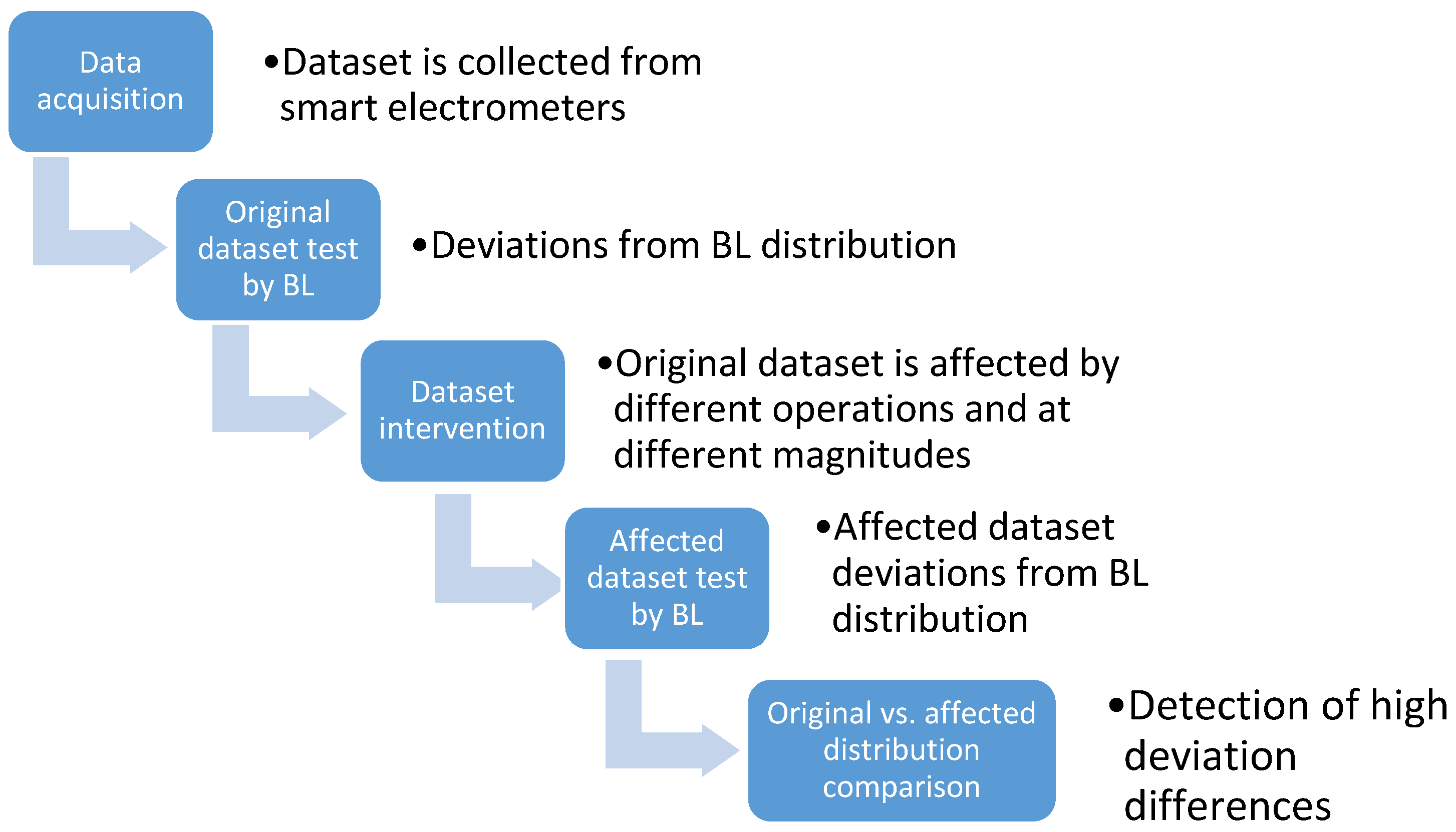
7. The Results of the Experiments
7.1. Violation Operation–Division by Two
7.2. Violation Operation–Adding Integer Number to the Dataset Values
7.3. Violation Operation–Multiplying the Dataset Values by Integer Number
7.4. Violation Operation–Affection 75% of Dataset Values
7.5. Violation Operation–Affection 50% of Dataset Values
7.6. Violation Operation–Affection 25% of Dataset Values
7.7. Violation Operation–Affect Only 10% of Dataset Values
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
- -
- The data examined in this manuscript are unique as they come from an operation distribution system. Because this kind of data is not always freely accessible, they have not been extensively explored in other publications. Therefore, one of the contributions of our study is the validation of Benford’s law in this specific domain. Publication [2] focuses on the analysis of electric meter data, but it uses different methods for detecting electricity theft. However, the model presented in [2] is highly sensitive to changes in input data, whereas our results are more accurate. The accuracy of error detection can be further enhanced by additional conditions defined by the distribution company and by further investigation of the method sensitivity and accurate detection threshold determination.
- -
- Previous research did not focus on the impact of data sensitivity as it is in our paper. We also examined the quantity of pseudo-random numbers within the overall dataset, gradually altering 10%, 25%, 50%, and 75% of the overall dataset values. Our research results demonstrate whether and how the quantity of altered data affects the overall dataset values.
- -
- We also artificially modified the data in several ways, including 1. Adding +1 to dataset values; 2. Division of the dataset values by 2, 3; Multiplication of the dataset value by 2. Such diversity of changes in previous research references in the field of electricity consumption data has not yet been explored nor verified.
- -
- The data in our study did not always have a range of values for orders of magnitude that exceeded three. After studying various publications, the authors recommended an order of magnitude for datasets exceeding 3. In our case, this value was not always higher than three, which is again an area that has not been explored. Our research shows the possibility of using Benford’s law even with a dataset order of magnitude slightly lower than three.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, A. A basic theory of Benford’s Law. Probab. Surv. 2011, 8, 1–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Sundararajan, A.; Sarwat, A.I.; Biswas, S.; Ibrahim, E. A distributed intelligent framework for electricity theft detection using benford’s law and stackelberg game. In Proceedings of the 2017 Resilience Week (RWS), Wilmington, DE, USA, 18–22 September 2017; pp. 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietronero, L.; Tosatti, E.; Tosatti, V.; Vespignani, A. Explaining the uneven distribution of numbers in nature: The laws of Benford and Zipf. Phys. A 2001, 293, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolion, J.-M. Images and Benford’s Law. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2001, 14, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durtschi, C.; Hillison, W.; Pacini, C. The Effective Use of Benford’s Law to Assist in Detecting Fraud in Accounting Data. J. Forensic Acc. 2004, 5, 14–34. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, F.; Gómez-Expósito, A. Detection of Cyber-Attacks of Power Systems through Benford’s Law. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 2741–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cella, R.; Zanolla, E. Benford’s Law and transparency: An analysis of municipal expenditure. Braz. Bus. Rev. 2018, 15, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürlimann, W. Benford’s Law in Scientific Research. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, B. Sensitivity to statistical regularities: People (largely) follow Benford’s law. Proc. Annu. Meet. Cogn. Sci. Soc. 2009, 31, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Evaluation and correction of electricity consumption statistics based on Benford-Zipf. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S. Benford’s Law: Theory and Applications; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 116. ISBN 9781400866595. [Google Scholar]
- Nigrini, M. A taxpayer compliance application of Benford’s Law. J. Am. Tax. Assoc. Sar. 1996, 18, 72. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/taxpayer-compliance-application-benfords-law/docview/211023799/se-2 (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Ley, E. On the Peculiar Distribution of the U.S. Stock Indexes’ Digits. Am. Stat. 1996, 50, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimi, R. The Peculiar Distribution of First Digits. Sci. Am. 1969, 221, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.; Kincanon, E. Benford’s law and physical constants: The distribution of initial digits. Am. J. Phys. 1991, 59, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, A.R. The first digit problem. Am. Math. Mon. 2018, 83, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrini, M.J.; Miller, S. Data Diagnostics Using Second-Order Tests of Benford’s Law. Audit. J. Pract. Theory 2009, 28, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benford, F. The Law of Anomalous Numbers. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1938, 78, 551–572. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C.; Okamura, K. Benford’s Law and COVID-19 Reporting; SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 3586413; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2020; p. 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, N. Can we rely on COVID-19 data? An assessment of data from over 200 countries worldwide. Sage Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211021232, Erratum in: Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211030581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Hill, T.P. Benford’s Law Strikes Back: No Simple Explanation in Sight for Mathematical Gem. Math. Intell. 2011, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, E.; Randi, G. Using the Benford’s Law as a First Step to Assess the Quality of the Cancer Registry Data. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butgereit, L. COVID-19 New Cases Measurements and Benford’s Law with Specific Focus on South Africa. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD), Durban, South Africa, 5–6 August 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoochehrnia, P.; Rachidi, F.; Rubinstein, M.; Schulz, W.; Diendorfer, G. Benford’s Law and Its Application to Lightning Data. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2010, 52, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, E.; Mostajabi, A.; Schulz, W.; Diendorfer, G.; Rubinstein, M.; Rachidi, F. On the Use of Benford’s Law to Assess the Quality of the Data Provided by Lightning Locating Systems. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Li, T.; Su, Q.; Chen, B.; Tang, Y. Detection of content-aware image resizing based on Benford’s law. Soft. Comput. 2017, 21, 5693–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Shi, Y.; Su, W. A generalized Benford’s law for JPEG coefficients and its applications in image forensics. In Proceedings of the SPIE, 9th Conference on Security, Steganigraphy, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 January–1 February 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K.; Chiverton, J.; Partridge, M.; Barry, M.; Kadhem, H.; Ott, B. Quantifying the Partial Volume Effect in PET Using Benford’s Law. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2007, 54, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošić, A.; Vičič, J. Use of Benford’s law on academic publishing networks. J. Informetr. 2021, 15, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, S.G.; Kim, B.J.; Minnhagen, P. Benford’s Law and First Letter of Word. Phys. A 2018, 512, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Yang, C. Testing firm-level data quality in China against Benford’s Law. Econ. Lett. 2020, 192, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnak, A.; Baleghi, Y.; Kazemitabar, J. A Novel Forgery Detection Algorithm Based on Mantissa Distribution in Digital Images. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS), Sadjad University, Mashhad, Iran, 23–24 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.A.; Pereira JL, R.; Alves, G.O.; Oliveira, B.C.; Melo, I.D.; Garcia, P.A.N. Detection and identification of energy theft in advanced metering infrastructures. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 182, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossovsky, A.E. On the Mistaken Use of the Chi-Square Test in Benford’s Law. Stats 2021, 4, 419–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepolesa, L.J.; Achari, S.; Cheng, L. Electricity Theft Detection in Smart Grids Based on Deep Neural Network. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 39638–39655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, E.; Qi, R.; Zheng, J. Feature Engineering for Semi-supervised Electricity Theft Detection in AMI. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Denver, CO, USA, 19–21 April 2023; pp. 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
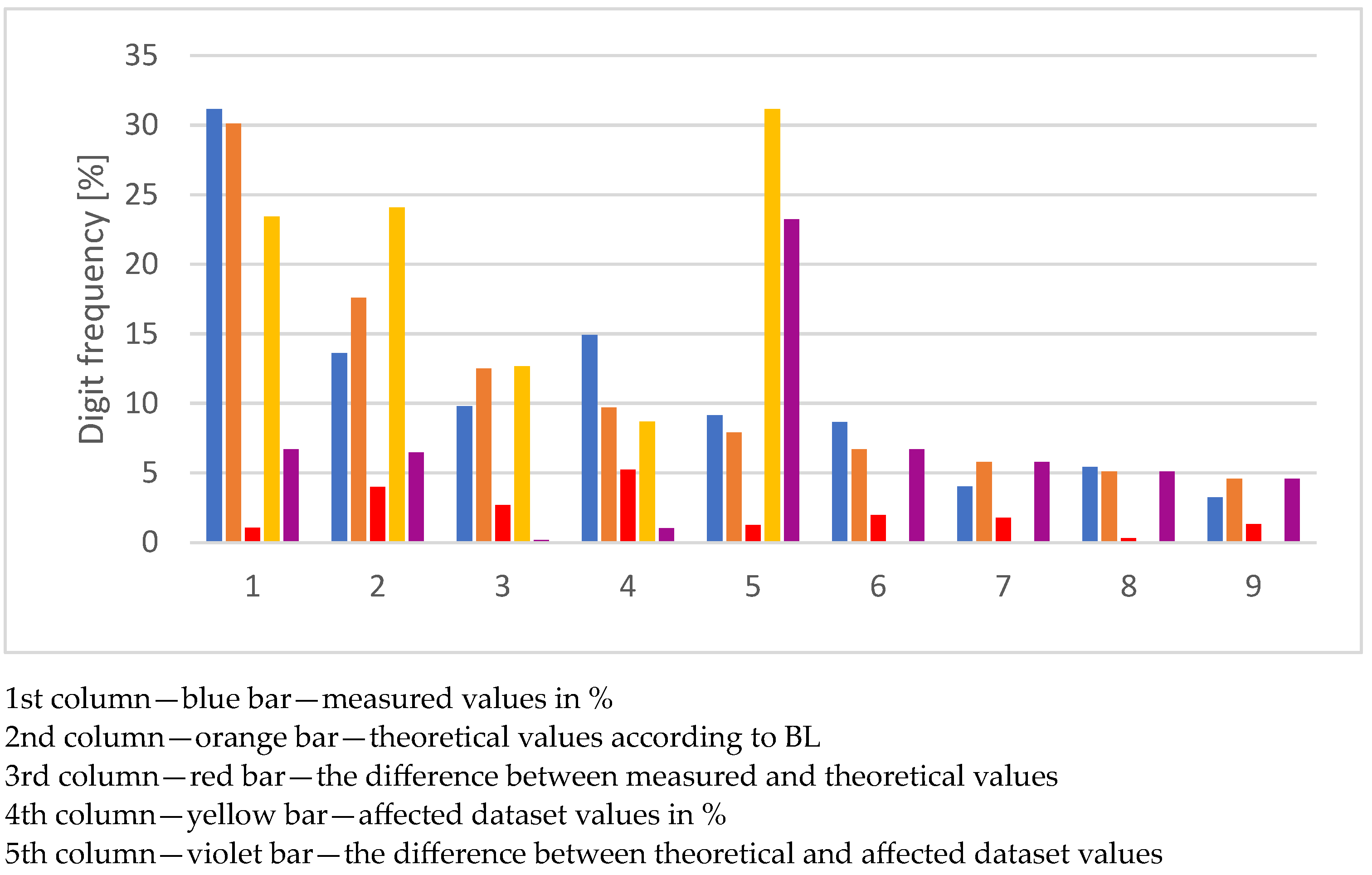
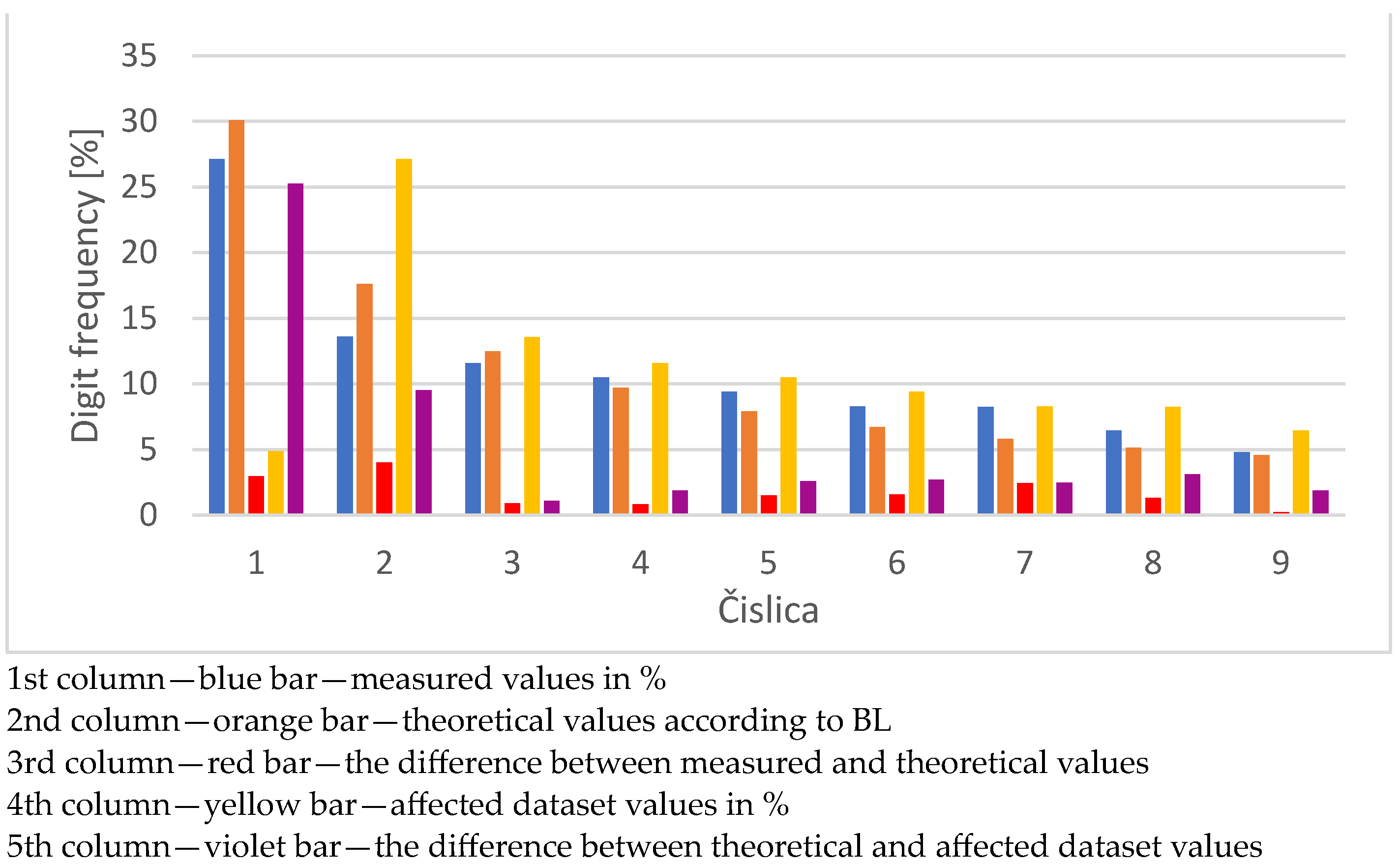
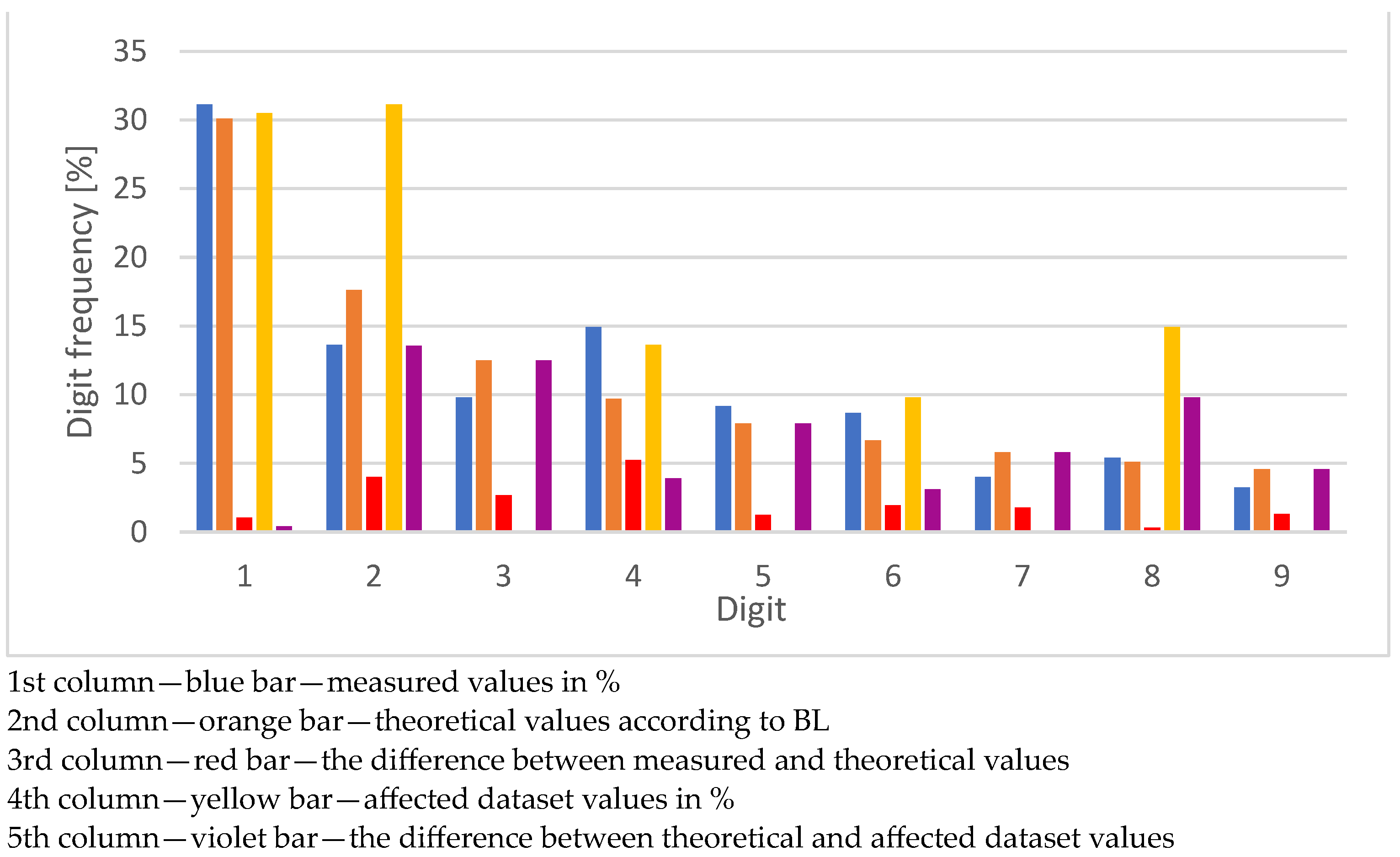
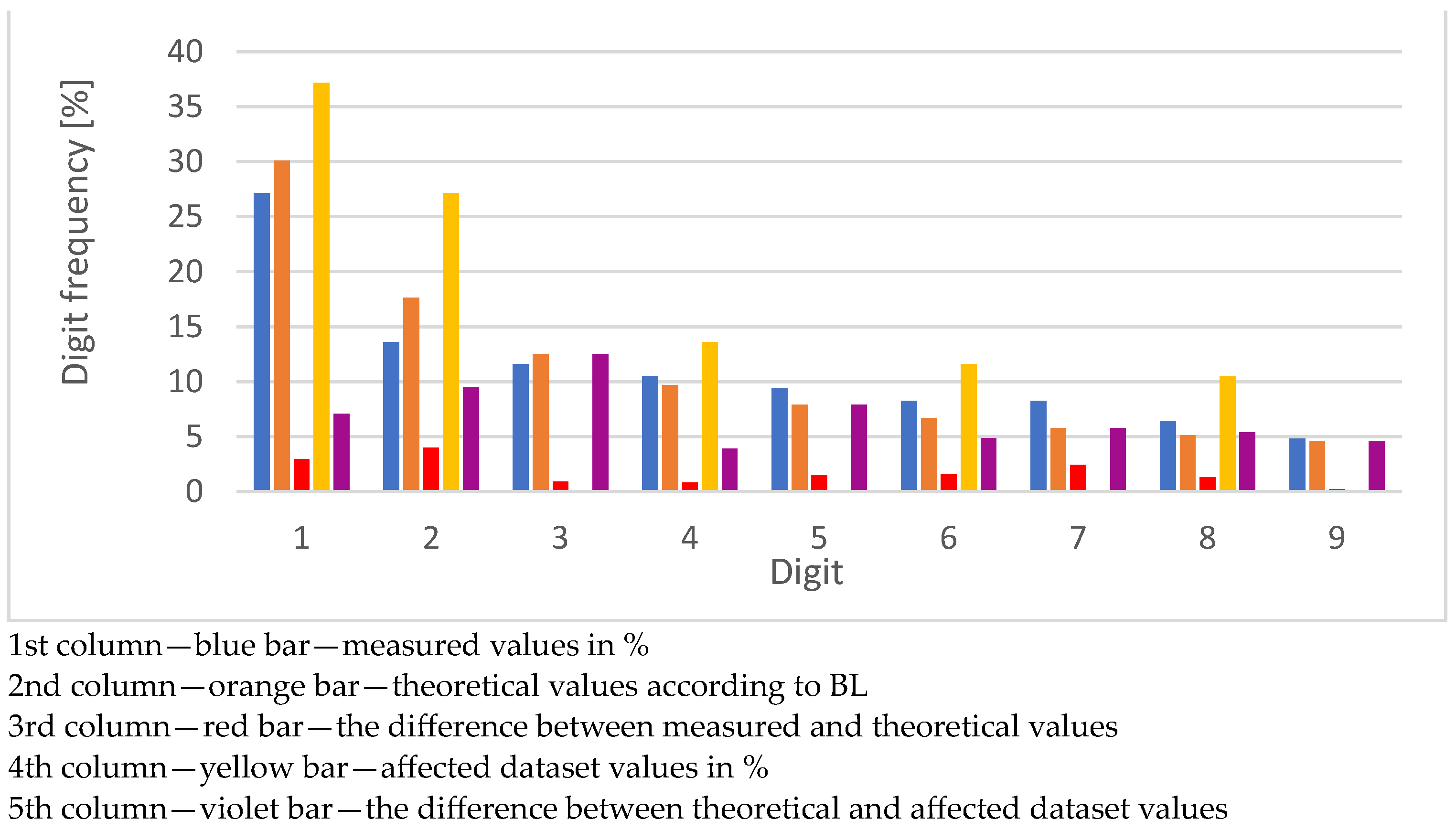
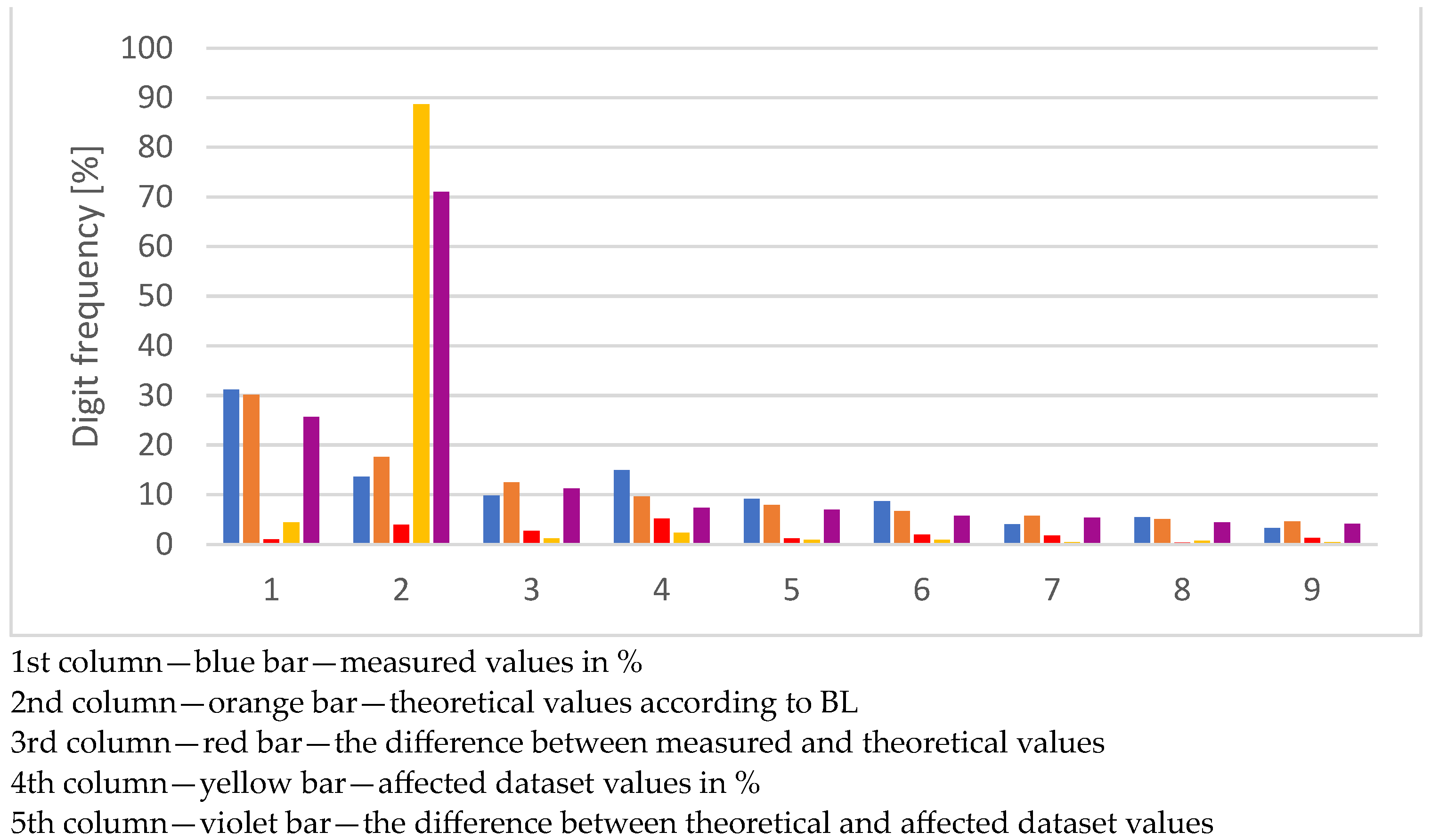
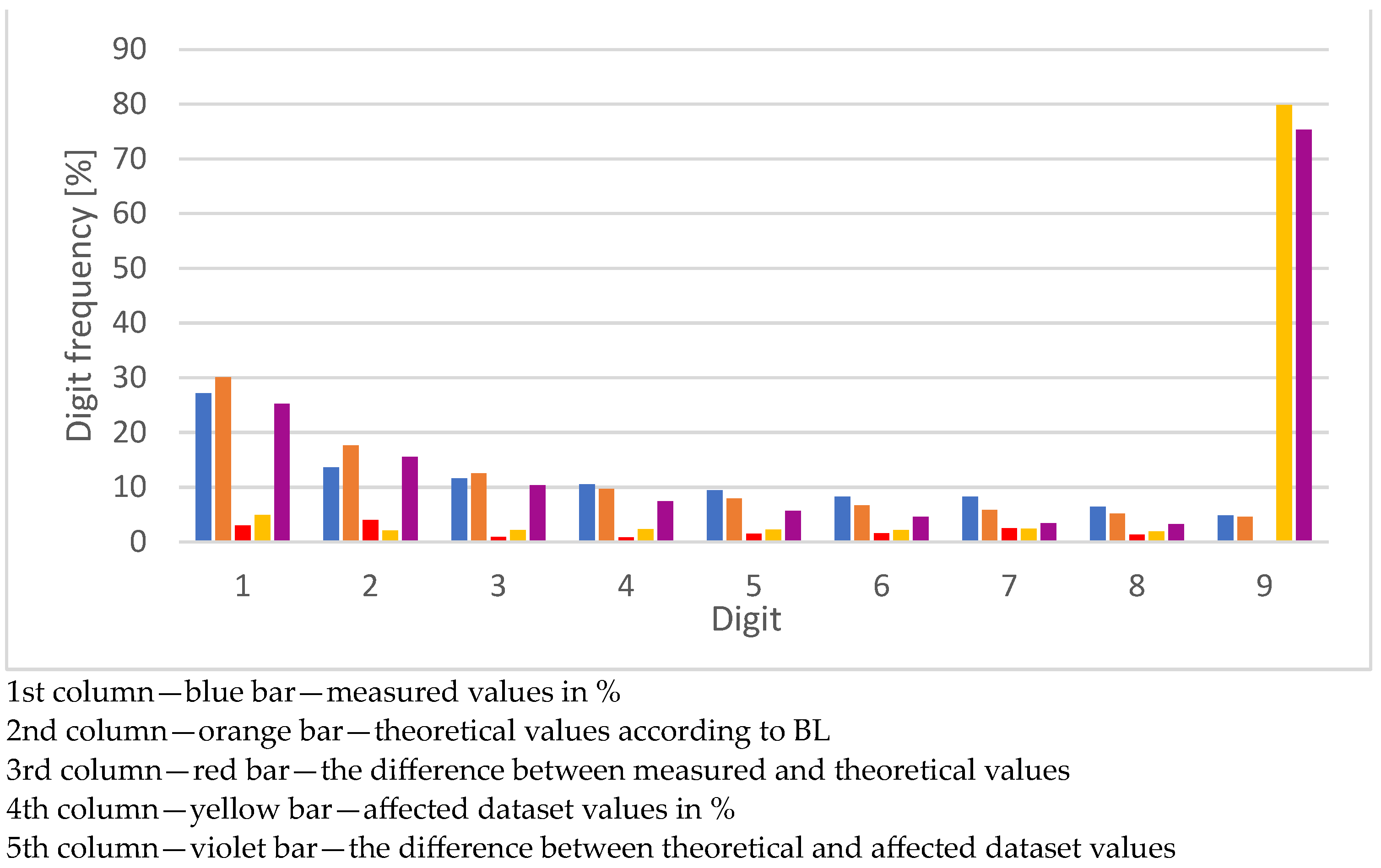
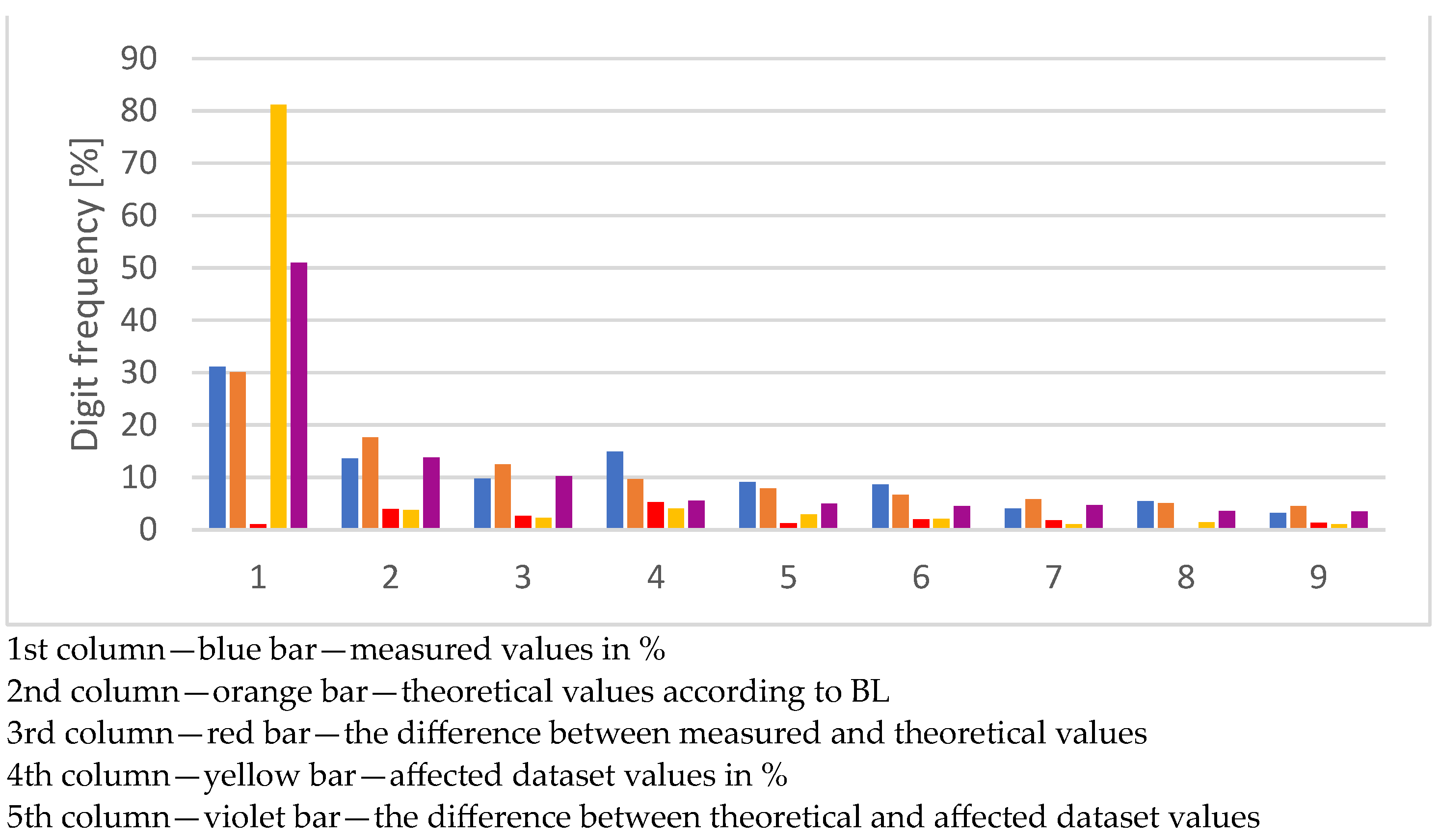
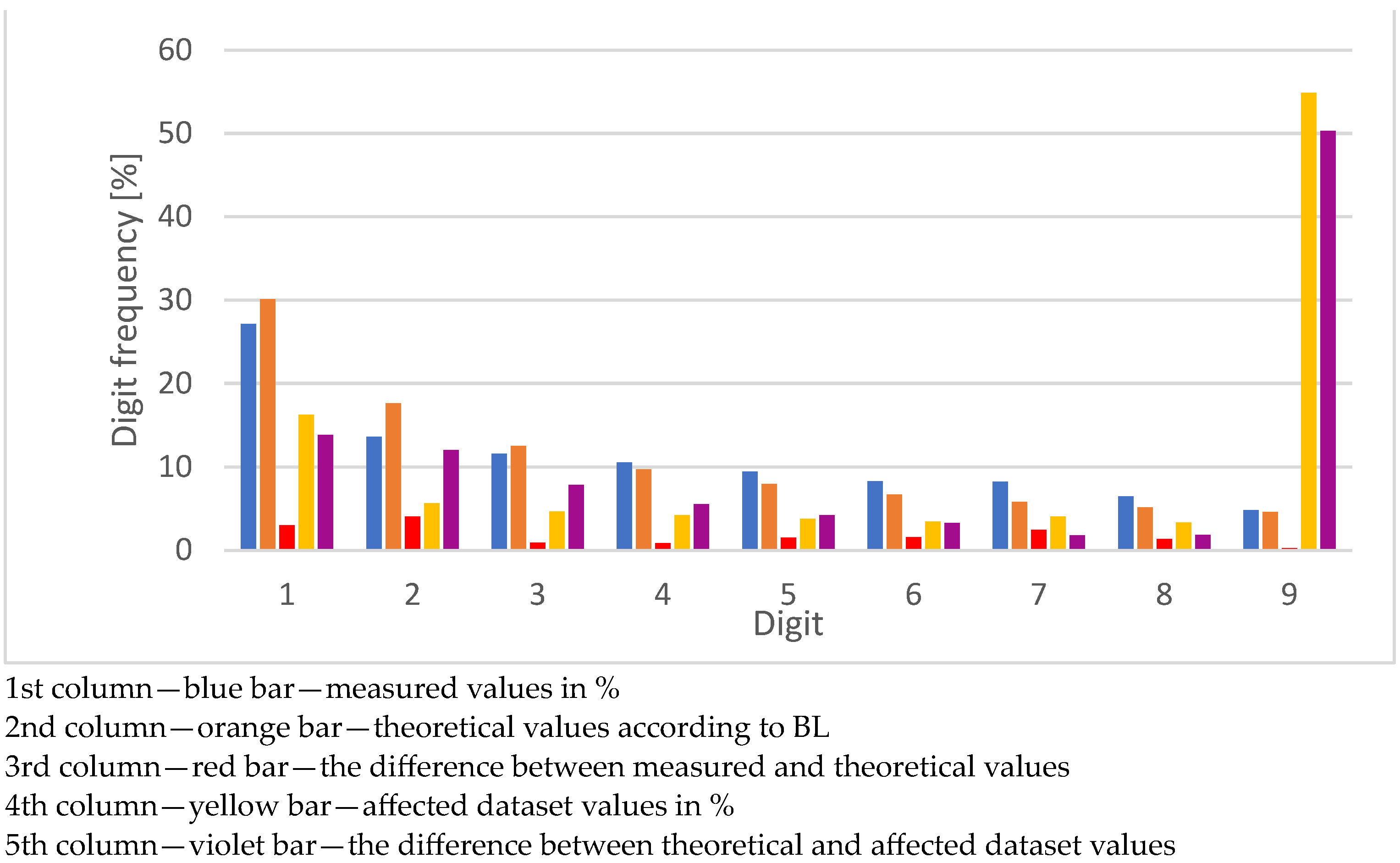
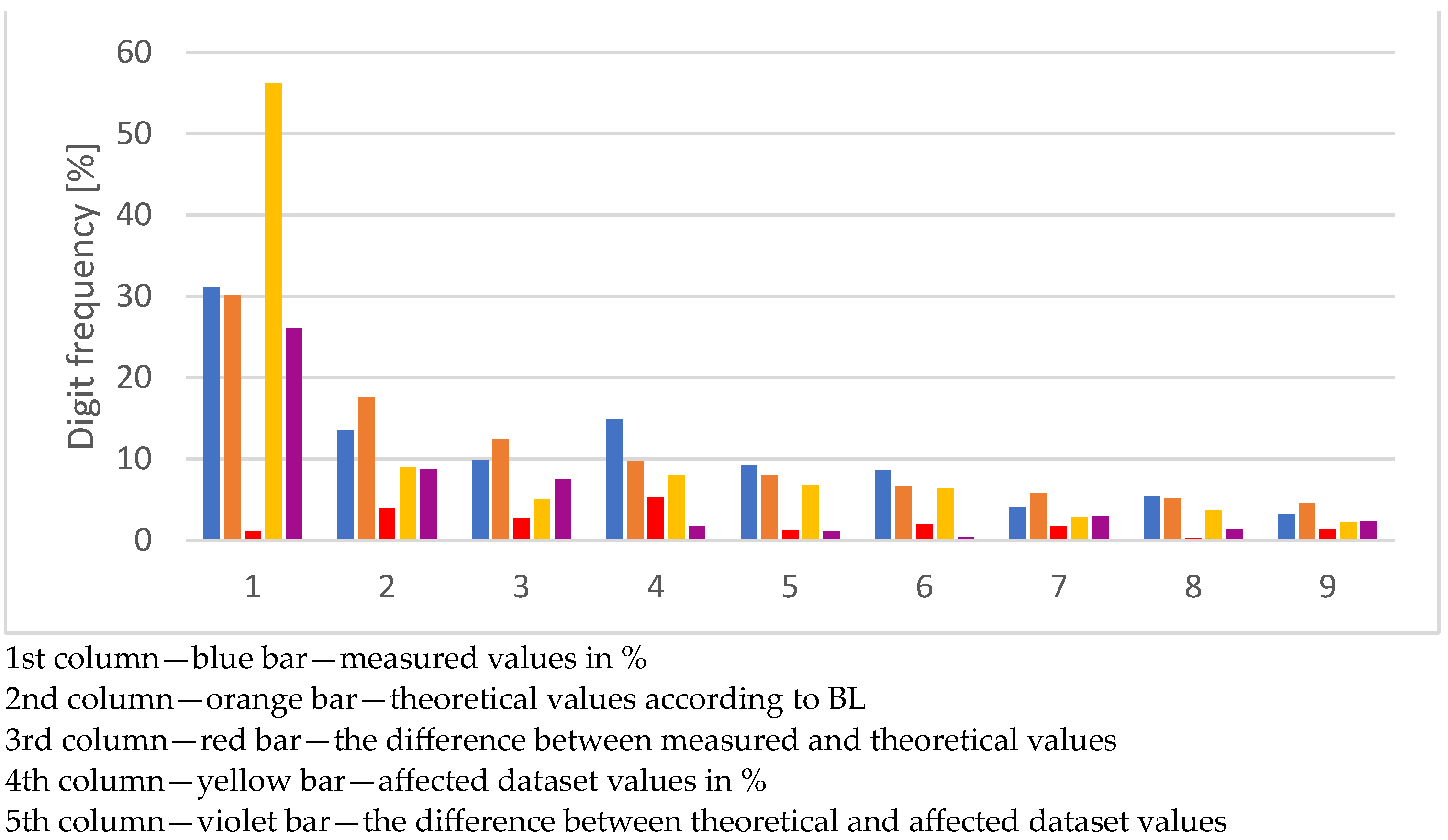
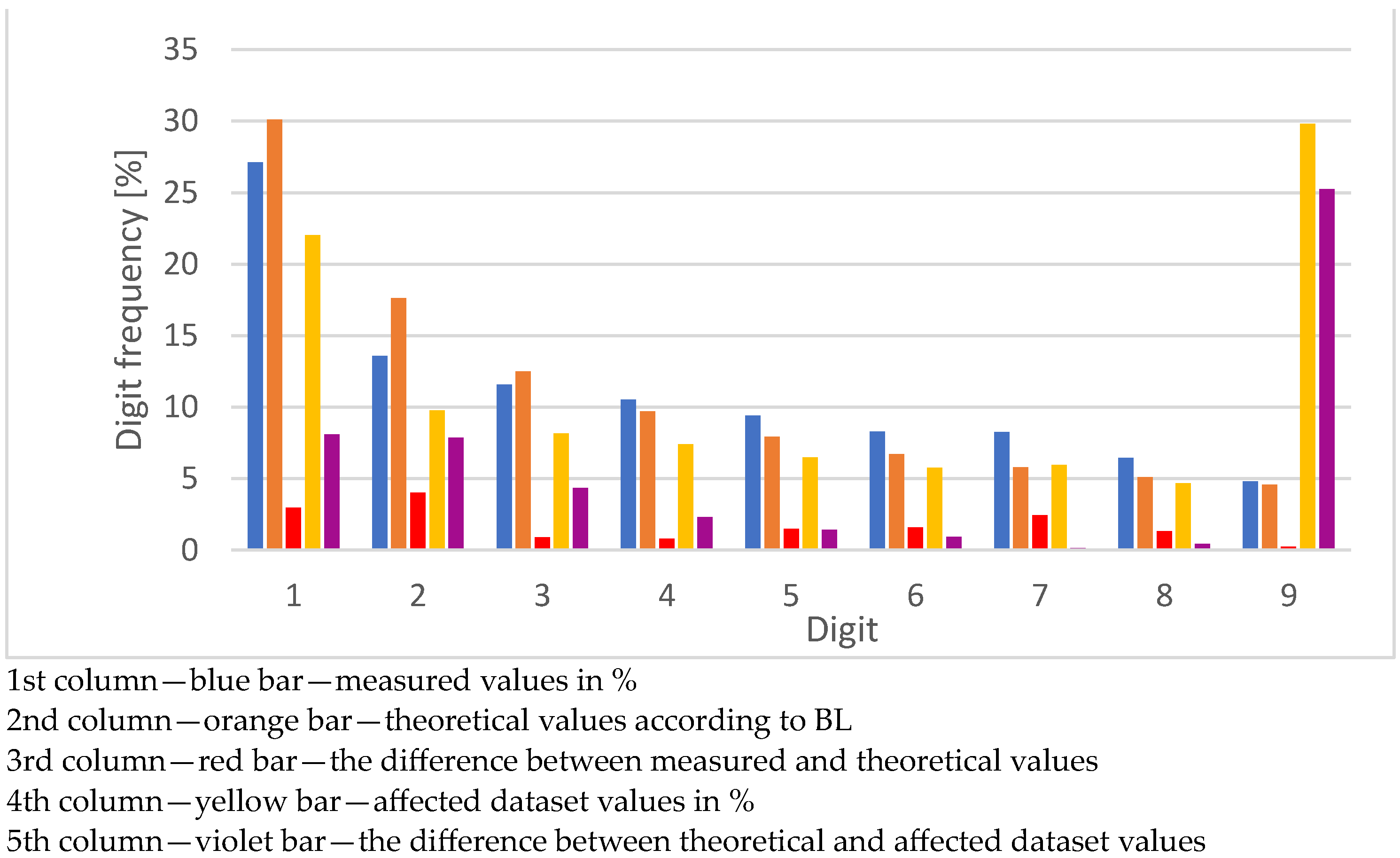
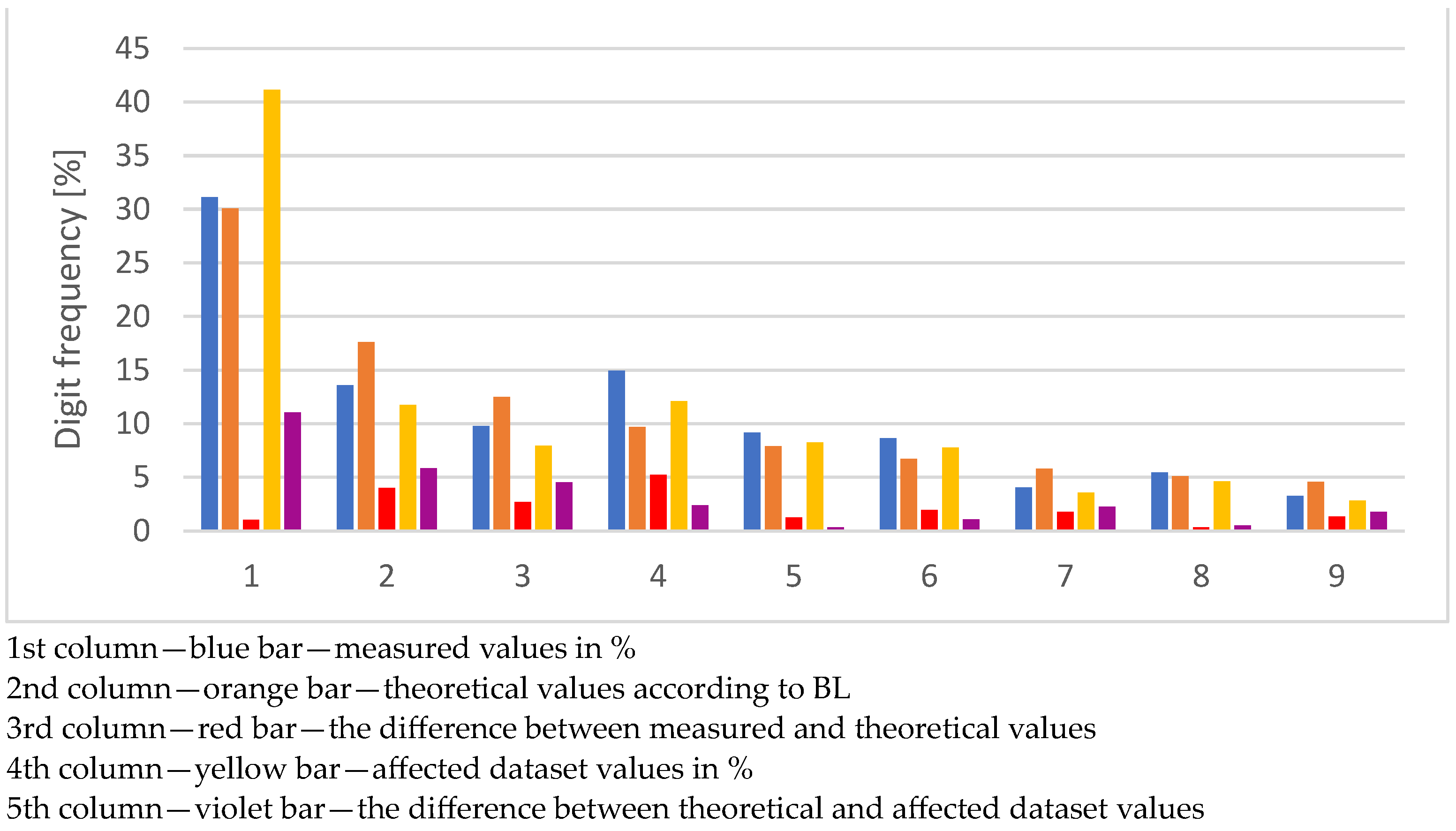

| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 23.4075 | 6.6955 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 24.0830 | 6.4739 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 12.6826 | 0.1887 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 8.6756 | 1.0154 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 31.1513 | 23.2331 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 0.0000 | 6.6947 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 0.0000 | 5.7992 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 0.0000 | 5.1153 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 0.0000 | 4.5757 |
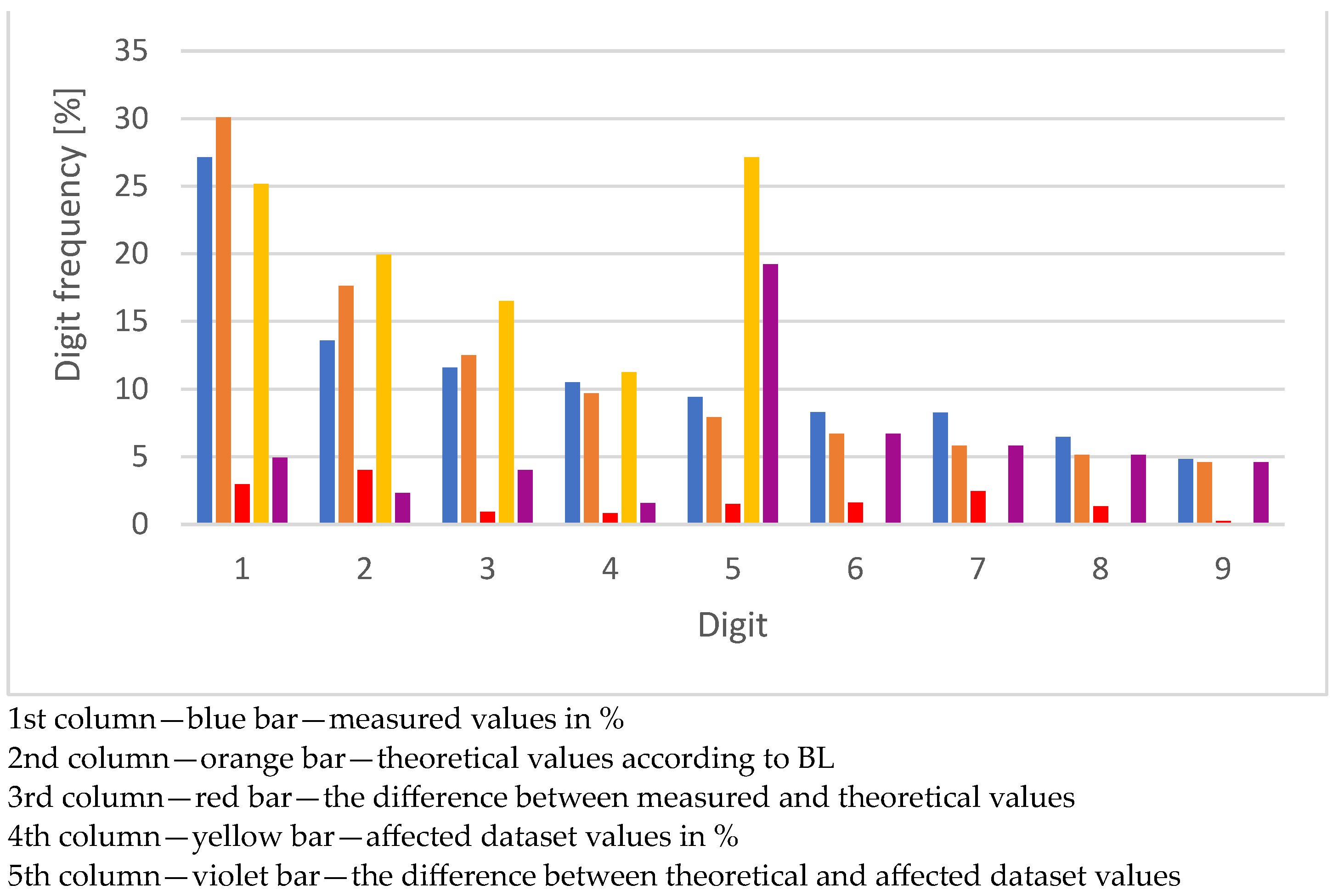
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 4.8585 | 25.2445 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 27.1247 | 9.5156 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 13.5818 | 1.0880 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 11.5716 | 1.8806 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 10.5023 | 2.5842 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 9.4056 | 2.7109 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 25.1655 | 4.9375 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 19.9175 | 2.3084 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 16.5204 | 4.0266 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3158 | 1.8701 | 1.8937 |
| 2 | 7.3884 | 0.8683 | 7.4681 |
| 3 | 5.7579 | 8.3941 | 0.6547 |
| 4 | 2.5972 | 2.1109 | 0.6062 |
| 5 | 29.4182 | 29.4699 | 16.5620 |
| 6 | 6.6947 | 6.6947 | 6.6947 |
| 7 | 5.7992 | 5.7992 | 5.7992 |
| 8 | 5.1153 | 5.1153 | 5.1153 |
| 9 | 4.5757 | 4.5757 | 4.5757 |
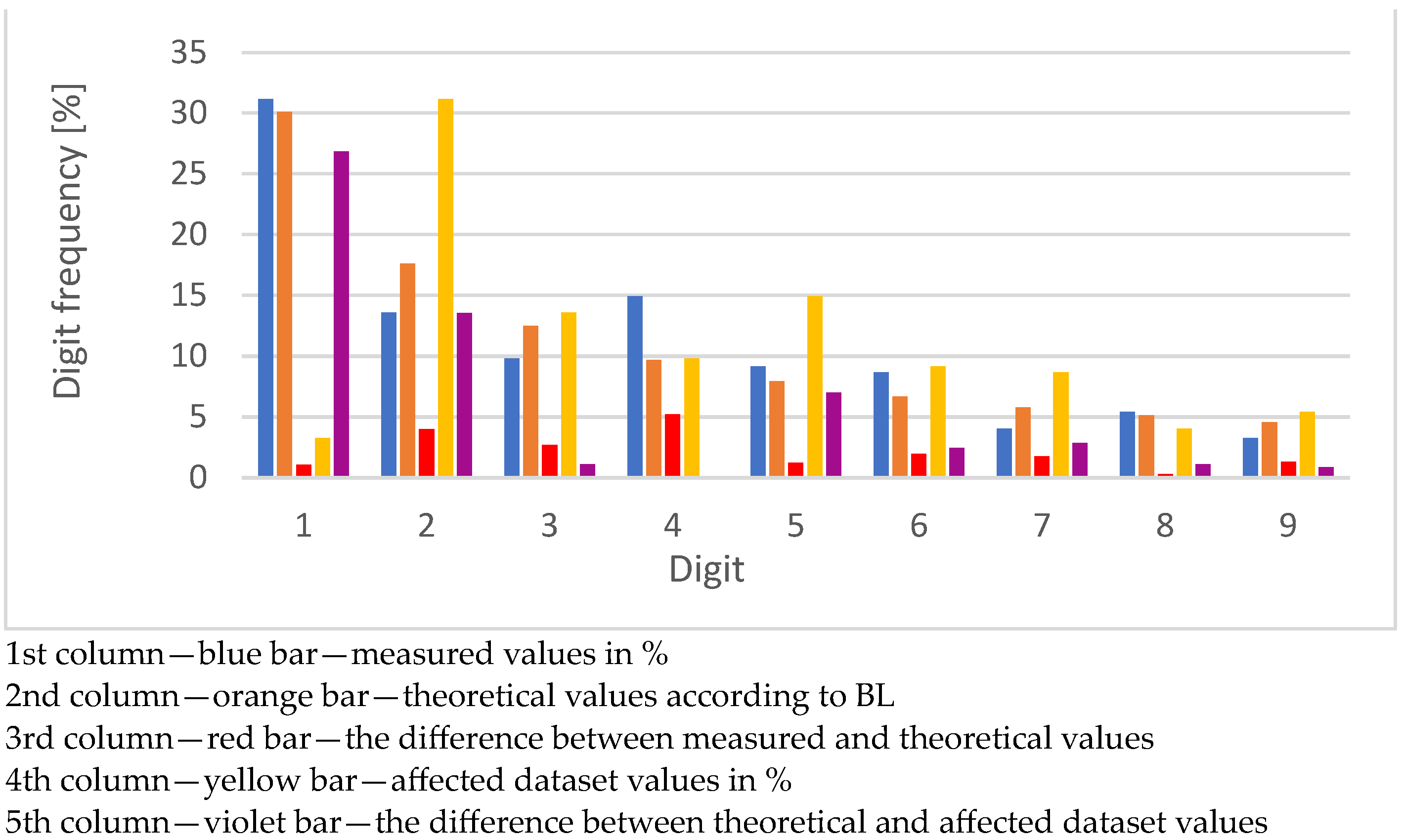
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 3.2535 | 26.8495 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 31.1498 | 13.5407 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 13.6070 | 1.1131 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 9.7994 | 0.1084 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 14.9235 | 7.0054 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 9.1583 | 2.4637 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 8.6546 | 2.8554 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 4.0274 | 1.0879 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 5.4263 | 0.8506 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 4.8585 | 25.2445 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 27.1247 | 9.5156 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 13.5818 | 1.0880 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 11.5716 | 1.8806 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 10.5023 | 2.5842 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 9.4056 | 2.7109 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 8.2746 | 2.4754 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 8.2379 | 3.1227 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 6.4429 | 1.8671 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27.6509 | 28.2553 | 25.5353 |
| 2 | 19.7272 | 19.7455 | 6.5140 |
| 3 | 11.8925 | 6.0953 | 4.5017 |
| 4 | 0.6586 | 0.0724 | 1.1113 |
| 5 | 0.9921 | 7.7999 | 9.1095 |
| 6 | 3.4000 | 3.9518 | 0.9892 |
| 7 | 1.5886 | 3.2600 | 2.2304 |
| 8 | 2.5898 | 3.5583 | 0.1881 |
| 9 | 5.2603 | 5.4572 | 1.2673 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 30.517 | 0.414 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 31.151 | 13.542 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 0.000 | 12.494 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 13.608 | 3.917 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 0.000 | 7.918 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 9.800 | 3.105 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 0.000 | 5.799 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 14.924 | 9.809 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 0.000 | 4.576 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 37.1893 | 7.0863 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 27.1378 | 9.5287 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 0.0000 | 12.4939 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 13.5884 | 3.8974 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 0.0000 | 7.9181 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 11.5771 | 4.8825 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 0.0000 | 5.7992 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 10.5074 | 5.3921 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 0.0000 | 4.5757 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27.6509 | 28.2553 | 25.5353 |
| 2 | 19.7272 | 19.7455 | 6.5140 |
| 3 | 11.8925 | 6.0953 | 4.5017 |
| 4 | 0.6586 | 0.0724 | 1.1113 |
| 5 | 0.9921 | 7.7999 | 9.1095 |
| 6 | 3.4000 | 3.9518 | 0.9892 |
| 7 | 1.5886 | 3.2600 | 2.2304 |
| 8 | 2.5898 | 3.5583 | 0.1881 |
| 9 | 5.2603 | 5.4572 | 1.2673 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 4.4120 | 25.6910 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 88.6070 | 70.9979 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 1.2364 | 11.2575 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 2.3331 | 7.3579 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 0.8952 | 7.0229 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 0.9364 | 5.7582 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 0.4236 | 5.3756 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 0.6983 | 4.4169 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 0.4579 | 4.1178 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 4.8928 | 25.2102 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 2.0547 | 15.5544 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 2.1715 | 10.3224 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 2.3181 | 7.3729 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 2.2609 | 5.6573 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 2.1692 | 4.5254 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 2.3891 | 3.4101 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 1.8966 | 3.2186 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 79.8470 | 75.2712 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.7603 | 20.6101 | 25.4483 |
| 2 | 12.7094 | 13.9494 | 14.2320 |
| 3 | 9.8494 | 10.4716 | 9.9227 |
| 4 | 7.6441 | 6.1961 | 4.2807 |
| 5 | 6.8145 | 7.1005 | 6.1391 |
| 6 | 5.3507 | 5.9229 | 5.0050 |
| 7 | 5.0253 | 5.2702 | 4.6887 |
| 8 | 2.7226 | 2.6830 | 3.8171 |
| 9 | 5.2603 | 5.4572 | 73.5335 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 81.1498 | 51.0468 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 3.8053 | 13.8038 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 2.2781 | 10.2157 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 4.0846 | 5.6064 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 2.9559 | 4.9623 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 2.1339 | 4.5608 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 1.0578 | 4.7414 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 1.4768 | 3.6385 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 1.0578 | 3.5180 |
| Digit | Number of values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 16.2501 | 13.8529 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 5.6053 | 12.0038 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 4.6455 | 7.8484 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 4.1805 | 5.5105 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 3.7430 | 4.1751 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 3.4315 | 3.2632 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 4.0133 | 1.7859 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 3.2940 | 1.8212 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 54.8368 | 50.2610 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13.1326 | 12.3648 | 17.8697 |
| 2 | 5.4377 | 9.1112 | 9.5223 |
| 3 | 7.6193 | 8.3125 | 7.5072 |
| 4 | 6.0322 | 0.6180 | 0.4777 |
| 5 | 6.2078 | 6.5136 | 4.4013 |
| 6 | 4.5951 | 5.3704 | 2.8734 |
| 7 | 4.6223 | 4.9034 | 3.4798 |
| 8 | 0.2293 | 0.0243 | 2.4021 |
| 9 | 47.8764 | 47.2182 | 48.5335 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 56.1524 | 26.0494 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 8.9206 | 8.6885 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 5.0190 | 7.4749 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 8.0093 | 1.6817 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 6.7729 | 1.1452 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 6.3218 | 0.3728 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 2.8323 | 2.9668 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 3.7253 | 1.3899 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 2.2462 | 2.3296 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 22.0250 | 8.0780 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 9.7492 | 7.8600 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 8.1549 | 4.3390 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 7.3852 | 2.3058 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 6.4826 | 1.4355 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 5.7611 | 0.9336 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 5.9375 | 0.1383 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 4.6799 | 0.4354 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 29.8248 | 25.2490 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.8964 | 2.3330 | 11.6512 |
| 2 | 0.4006 | 5.2549 | 5.8590 |
| 3 | 5.5656 | 6.6433 | 5.1832 |
| 4 | 3.8915 | 4.1230 | 3.6184 |
| 5 | 5.2599 | 5.8075 | 1.9560 |
| 6 | 3.3679 | 4.7285 | 0.0984 |
| 7 | 3.9286 | 4.6167 | 1.9344 |
| 8 | 3.4341 | 3.0544 | 0.4697 |
| 9 | 22.8764 | 22.2066 | 23.5335 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,605 | 31.1513 | 30.1030 | 1.0483 | 41.1503 | 11.0473 |
| 2 | 5943 | 13.6076 | 17.6091 | 4.0015 | 11.7690 | 5.8401 |
| 3 | 4280 | 9.7999 | 12.4939 | 2.6940 | 7.9521 | 4.5418 |
| 4 | 6518 | 14.9242 | 9.6910 | 5.2332 | 12.0942 | 2.4032 |
| 5 | 4000 | 9.1588 | 7.9181 | 1.2406 | 8.2658 | 0.3477 |
| 6 | 3780 | 8.6550 | 6.6947 | 1.9604 | 7.7781 | 1.0834 |
| 7 | 1759 | 4.0276 | 5.7992 | 1.7716 | 3.5536 | 2.2456 |
| 8 | 2370 | 5.4266 | 5.1153 | 0.3113 | 4.6252 | 0.4901 |
| 9 | 1419 | 3.2491 | 4.5757 | 1.3267 | 2.8117 | 1.7640 |
| Digit | Number of Values | Number of Values in % | BL | Delta % | Violation % | Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11,847 | 27.1378 | 30.1030 | 2.9652 | 24.9364 | 5.1666 |
| 2 | 5932 | 13.5884 | 17.6091 | 4.0208 | 11.7856 | 5.8235 |
| 3 | 5054 | 11.5771 | 12.4939 | 0.9167 | 10.2760 | 2.2178 |
| 4 | 4587 | 10.5074 | 9.6910 | 0.8164 | 9.3643 | 0.3267 |
| 5 | 4108 | 9.4101 | 7.9181 | 1.4920 | 8.2671 | 0.3490 |
| 6 | 3614 | 8.2785 | 6.6947 | 1.5839 | 7.3966 | 0.7020 |
| 7 | 3598 | 8.2419 | 5.7992 | 2.4427 | 7.4058 | 1.6066 |
| 8 | 2814 | 6.4460 | 5.1153 | 1.3307 | 5.7519 | 0.6367 |
| 9 | 2101 | 4.8127 | 4.5757 | 0.2370 | 14.8162 | 10.2404 |
| Digit | Node. No. 3 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 4 Violation Delta % | Node. No. 5 Violation Delta % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.1670 | 2.8851 | 8.6377 |
| 2 | 4.3526 | 1.3317 | 2.5374 |
| 3 | 4.4414 | 3.9575 | 2.6322 |
| 4 | 3.4656 | 5.2436 | 6.1621 |
| 5 | 4.9760 | 5.3859 | 0.6718 |
| 6 | 2.9375 | 4.3022 | 0.8825 |
| 7 | 3.5806 | 4.3234 | 1.3039 |
| 8 | 4.0065 | 3.9802 | 0.1569 |
| 9 | 7.8750 | 7.1918 | 8.5815 |
| Timestamp | Power [kW] |
|---|---|
| 1 January 2021 00:15:00 | 142.800 |
| 1 January 2021 00:30:00 | 150.400 |
| 1 January 2021 00:45:00 | 146.000 |
| 1 January 2021 01:00:00 | 129.600 |
| 1 January 2021 01:15:00 | 138.000 |
| 1 January 2021 01:30:00 | 126.400 |
| 1 January 2021 01:45:00 | 124.800 |
| 1 January 2021 02:00:00 | 123.600 |
| 1 January 2021 02:15:00 | 119.600 |
| Published Article Contributions | Research Gap |
|---|---|
| BL is a suitable method for original dataset unnatural alteration | Only a minimal amount of research was performed to validate BL for electricity consumption data |
| Articles propose algorithms that identify problematic data and estimate overall electricity consumption through limited datasets | Dataset magnitude determination for applicability of BL |
| BL validity for datasets in different science areas | Experimental research gap for electricity theft detection methods. The lack of sensitivity verification affects different amounts of data in the recorded dataset. The lack of BL validity verification affects different types of alteration operators. |
| One of the basic requirements for datasets to comply with Benford’s Law is the value of the order of magnitude is higher than 3 | Verification gap for this requirement in electricity consumption data, where this order of magnitude is often lower than 3. |
| References provide some simulation tests for altered datasets and the detection of these alterations | No reference tests the sensitivity and alteration detection threshold in combination with different alteration operations. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petráš, J.; Pavlík, M.; Zbojovský, J.; Hyseni, A.; Dudiak, J. Benford’s Law in Electric Distribution Network. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183863
Petráš J, Pavlík M, Zbojovský J, Hyseni A, Dudiak J. Benford’s Law in Electric Distribution Network. Mathematics. 2023; 11(18):3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183863
Chicago/Turabian StylePetráš, Jaroslav, Marek Pavlík, Ján Zbojovský, Ardian Hyseni, and Jozef Dudiak. 2023. "Benford’s Law in Electric Distribution Network" Mathematics 11, no. 18: 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183863
APA StylePetráš, J., Pavlík, M., Zbojovský, J., Hyseni, A., & Dudiak, J. (2023). Benford’s Law in Electric Distribution Network. Mathematics, 11(18), 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183863






