Design of Nonlinear Marine Predator Heuristics for Hammerstein Autoregressive Exogenous System Identification with Key-Term Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
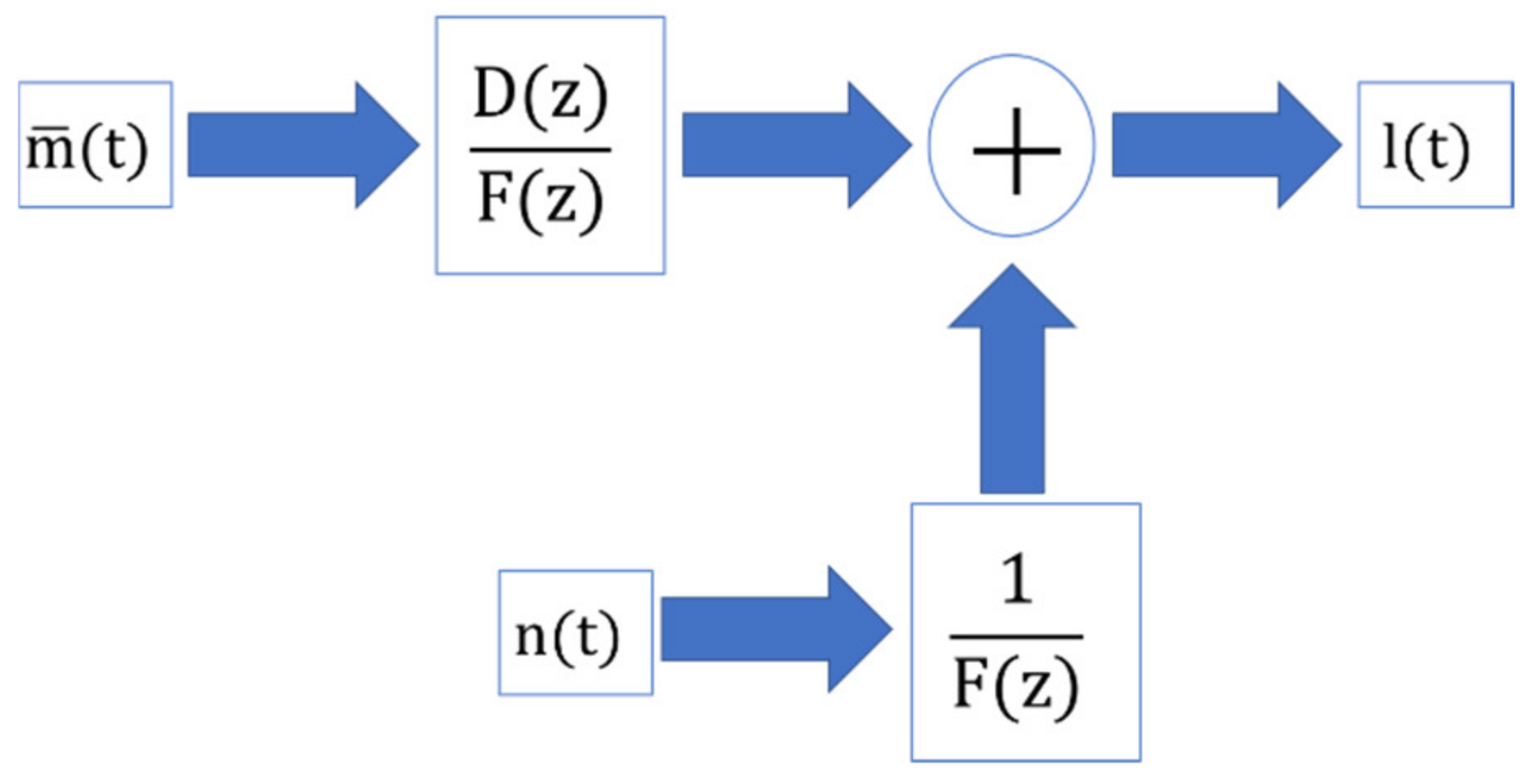
2. Input Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Model Definition
3. Proposed Methodology
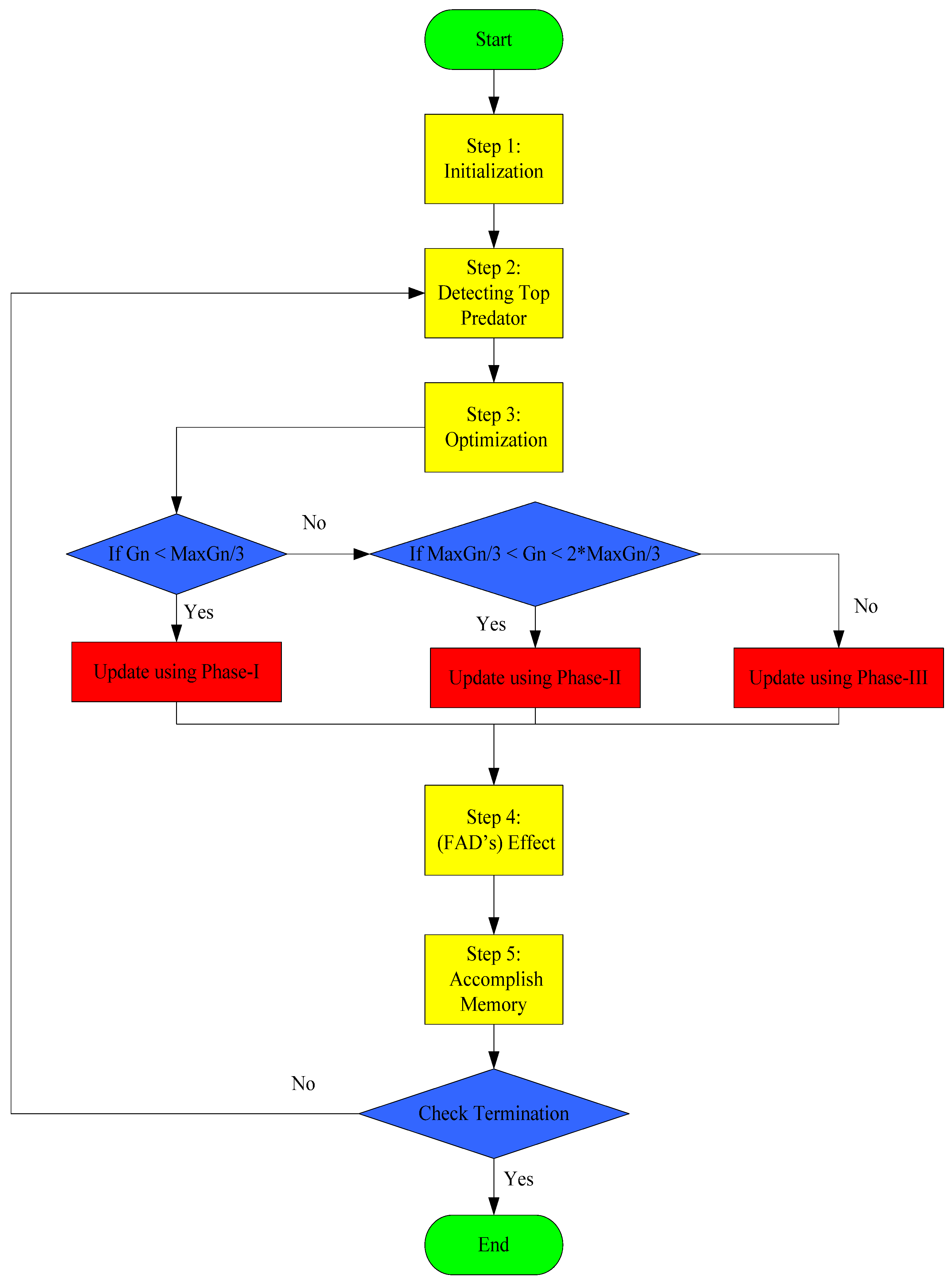
3.1. Nonlinear Marine Predator Algorithm
3.1.1. Step 1: Initialization
3.1.2. Step 2: Detecting Top Predator
3.1.3. Step 3: Brownian Movements and Levy Flight-Based Optimization
Phase I
Phase II
Phase III
3.1.4. Step 4: Fish Aggregating Device (FAD) Effects
3.1.5. Step 5: Marine Memory
| Algorithm 1: Pseudo-code of NMPA |
| Initialize Population () by using (14). while check termination criteria Calculate Fitness value and construct matrices () and () by using (15) and (16). if Update by using (17) and (18). else if Update by using Equations (19) and (20) for first half. Update by using Equations (21) and (22) for other half. else if Update by using Equations (23) and (24). end Update by using Equations (25) and (26). Accomplish memory saving and update. end |
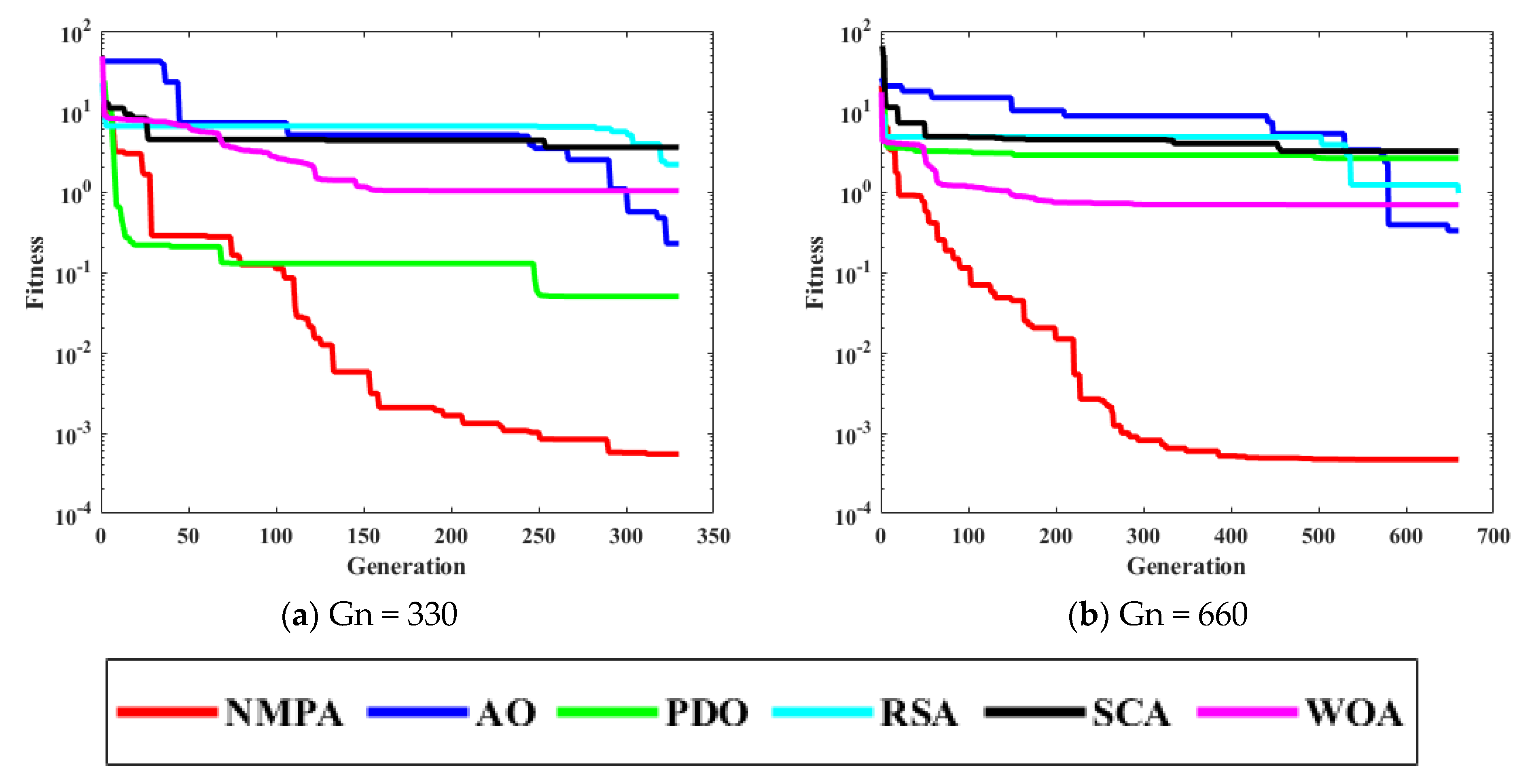
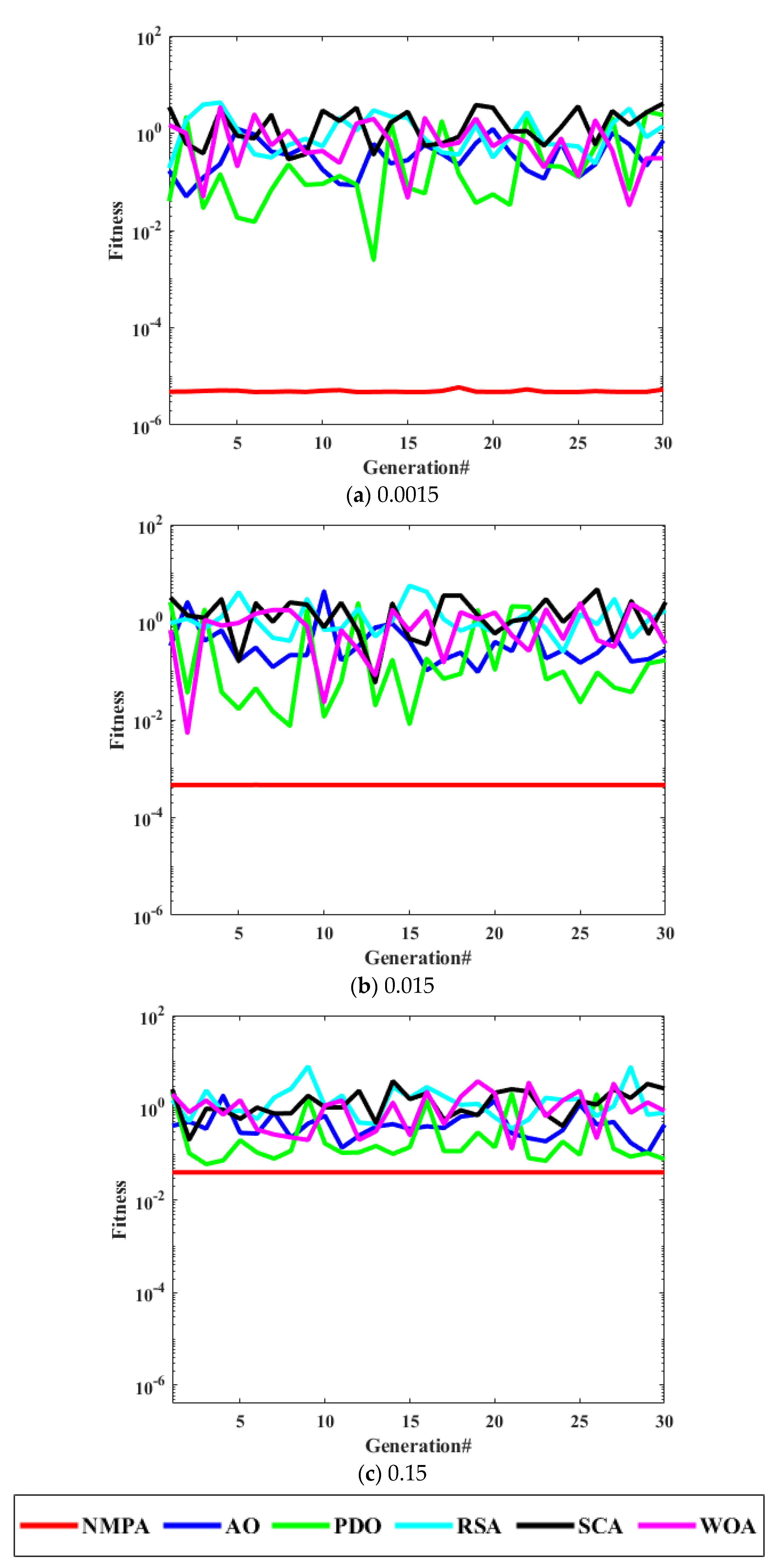
4. Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, G. Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2011, 21, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Ding, R.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, K.; Li, W. Hybrid multi-objective metaheuristic algorithms for solving airline crew rostering problem with qualification and language. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1460–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Kiani, A.K.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Chaudhary, I.I.; Pinto, C.M. Design of auxiliary model based normalized fractional gradient algorithm for nonlinear output-error systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 163, 112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, R.; Kozan, E. A hybrid constructive heuristic and simulated annealing for railway crew scheduling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 70, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, S.Q.; Kozan, E. A hybrid metaheuristic algorithm to optimise a real-world robotic cell. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 84, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ong, H.; Ng, K. Metaheuristics for minimizing the makespan of the dynamic shop scheduling problem. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2005, 36, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Cheema, K.M.; Milyani, A.H. Design of Aquila Optimization Heuristic for Identification of Control Autoregressive Systems. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Ding, F. Least Squares Identification for Hammerstein Multi-input Multi-output Systems Based on the Key-Term Separation Technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 3745–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shi, P.; Chaudhary, N.I. Weighted differential evolution-based heuristic computing for identification of Hammerstein systems in electrically stimulated muscle modeling. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 8929–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Cao, J. Parameter Estimation Algorithms for Hammerstein Finite Impulse Response Moving Average Systems Using the Data Filtering Theory. Mathematics 2022, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.P.; Panigrahi, T.; Wilson, A.M.; Sabat, S.L. Nonlinear channel estimation based on robust distributed Hammerstein spline adaptive technique in wireless sensor network. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 132, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, P.; Guo, H.; Di, Y.; Xu, Q.; Hao, X. Control of Precalciner Temperature in the Cement Industry: A Novel Method of Hammerstein Model Predictive Control with ISSA. Processes 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihi, I.; Sidhom, L.; Kamavuako, E.N. Hammerstein–Wiener Multimodel Approach for Fast and Efficient Muscle Force Estimation from EMG Signals. Biosensors 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, K.; Storn, R.M.; Lampinen, J.A. Differential Evolution: A Practical Approach to Global Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.H.; Mustaffa, Z.; Saari, M.M.; Daniyal, H.; Mirjalili, S. Evolutionary mating algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 487–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Anand, A.; Joshi, D. A Computationally Efficient Evolutionary Algorithm for Real-Parameter Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2002, 10, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.V.; Savsani, V.J.; Vakharia, D.P. Teaching–learning-based optimization: A novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput. Aided Des. 2011, 43, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, Q.; Saeed, M.; Younas, I. Heap-based optimizer inspired by corporate rank hierarchy for global optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, H.; Ghasemian, F.; Vahdat-Nejad, H. Human urbanization algorithm: A novel metaheuristic approach. Math. Comput. Simul. 2020, 178, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-S.; Nguyen, N.-M. FBI inspired meta-optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 93, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, E.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H.; Saryazdi, S. GSA: A Gravitational Search Algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.K.; Eksin, I. A new optimization method: Big Bang–Big Crunch. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2006, 37, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, M.H.; Hasanien, H.M.; Turky, R.A.; Alghuwainem, S.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Jurado, F. Circle Search Algorithm: A Geometry-Based Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.S. Principal components analysis by the galaxy-based search algorithm: A novel metaheuristic for continuous optimisation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Faramarzi, A.; Heidarinejad, M.; Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Marine Predators Algorithm: A nature-inspired metaheuristic. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucherino, A.; Seref, O.; Kundakcioglu, O.E.; Pardalos, P. Monkey search: A novel metaheuristic search for global optimization. AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 953, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. The ant lion optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 83, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.F.; Chang, C.-L.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Kiani, A.K.; Shu, C.-M.; Raja, M.A.Z. Swarming intelligence heuristics for fractional nonlinear autoregressive exogenous noise systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 167, 113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, I.; Pelckmans, K.; Suykens, J.; De Moor, B. Subspace identification of Hammerstein systems using least squares support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.I.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Mehmood, A.; Shah, S.M. Design of fractional hierarchical gradient descent algorithm for parameter estimation of nonlinear control autoregressive systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 157, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.F.; Chang, C.-L.; Aslam, M.S.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Raja, M.A.Z. Fuzzy-Evolution Computing Paradigm for Fractional Hammerstein Control Autoregressive Systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 2447–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Chang, C.-L.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Cheema, K.M.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shu, C.-M.; Milyani, A.H. Novel Fractional Swarming with Key Term Separation for Input Nonlinear Control Autoregressive Systems. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Chang, C.-L.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Cheema, K.M.; Shu, C.-M.; Milyani, A.H. Adaptive Evolutionary Computation for Nonlinear Hammerstein Control Autoregressive Systems with Key Term Separation Principle. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Cheema, K.M.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Milyani, A.H.; Azhari, A.A. Nonlinear Hammerstein System Identification: A Novel Application of Marine Predator Optimization Using the Key Term Separation Technique. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Migallón, H.; Belazi, A.; Sánchez-Romero, J.-L.; Rico, H.; Jimeno-Morenilla, A. Settings-Free Hybrid Metaheuristic General Optimization Methods. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Chauhan, Y.K.; Pandey, A.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Alsaif, F.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Islam, R.; Kannadasan, R.; Alsharif, M.H. A Novel Hybrid MPPT Approach for Solar PV Systems Using Particle-Swarm-Optimization-Trained Machine Learning and Flying Squirrel Search Optimization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakht, K.; Kashif, S.A.R.; Fakhar, M.S.; Khan, I.A.; Abbas, G. Accelerated Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithms Coupled with Analysis of Variance for Intelligent Charging of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2023, 16, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanadath, A.; Jothi, J.A.A.; Urolagin, S. Multilevel Multiobjective Particle Swarm Optimization Guided Superpixel Algorithm for Histopathology Image Detection and Segmentation. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Long, Z. E-Commerce Enterprises Financial Risk Prediction Based on FA-PSO-LSTM Neural Network Deep Learning Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. AWOA: An Advanced Whale Optimization Algorithm for Signal Detection in Underwater Magnetic Induction Multi-Input–Multi-Output Systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Cheema, K.M.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Milyani, A.H.; Azhari, A.A. Dwarf Mongoose Optimization Metaheuristics for Autoregressive Exogenous Model Identification. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.A.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Raja, M.A.Z. Firefly Optimization Heuristics for Sustainable Estimation in Power System Harmonics. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Cheema, K.M.; Raja, M.A.Z. Variants of Chaotic Grey Wolf Heuristic for Robust Identification of Control Autoregressive Model. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sattar, M.A.; Al Sumaiti, A.; Ali, H.; Diab, A.A.Z. Marine predators algorithm for parameters estimation of photovoltaic modules considering various weather conditions. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 11799–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaness, M.A.A.; Ewees, A.A.; Fan, H.; Abualigah, L.; Elaziz, M.A. Marine Predators Algorithm for Forecasting Confirmed Cases of COVID-19 in Italy, USA, Iran and Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssein, E.H.; Abdelminaam, D.S.; Ibrahim, I.E.; Hassaballah, M.; Wazery, Y.M. A Hybrid Heartbeats Classification Approach Based on Marine Predators Algorithm and Convolution Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 86194–86206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.; Kamel, S.; Abualigah, L. Marine predators algorithm for optimal allocation of active and reactive power resources in distribution networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14327–14355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmi, A.M.; Al-Qaness, M.A.; Dahou, A.; Elaziz, M.A. Human activity recognition using marine predators algorithm with deep learning. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 142, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, M.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Hasanien, H.M.; Ezzat, M. Marine predators algorithm for load frequency control of modern interconnected power systems including renewable energy sources and energy storage units. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 3843–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.S.; Dehkordi, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Pham, Q.-V. Nonlinear marine predator algorithm: A cost-effective optimizer for fair power allocation in NOMA-VLC-B5G networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Gan, M.; Qiu, J. A Novel EM Identification Method for Hammerstein Systems with Missing Output Data. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2020, 16, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Yousri, D.; Elaziz, M.A.; Ewees, A.A.; Al-Qaness, M.A.; Gandomi, A.H. Aquila Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 157, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, A.E.; Agushaka, J.O.; Abualigah, L.; Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Prairie Dog Optimization Algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 20017–20065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Sumari, P.; Geem, Z.W.; Gandomi, A.H. Reptile Search Algorithm (RSA): A nature-inspired meta-heuristic optimizer. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 191, 116158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. SCA: A Sine Cosine Algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 2016, 96, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Gholizadeh, H. A comprehensive survey: Whale Optimization Algorithm and its applications. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 48, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B.; Glynn, R.J.; Lee, M.T. Incorporation of Clustering Effects for the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test: A Large-Sample Approach. Biometrics 2003, 59, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Metaheuristics | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| NMPA | FAD = 0.2, |
| AO | alpha = 0.1, delta = 0.1 |
| PDO | rho = 0.005 |
| RSA | alpha = 0.1, beta = 0.1 |
| SCA | a = 2 |
| WOA [60] | a = [2 0] |
| Metaheuristics | Gn | Design Parameters | Best Fitness | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | 330 | −0.8192 | 0.9368 | 0.9891 | 0.4064 | 0.7439 | 1.6007 | −0.2351 | 0.2012 |
| 660 | −0.7755 | 0.9014 | 1.5770 | 1.1252 | 0.4183 | 0.4834 | −0.8811 | 0.0499 | |
| PDO | 330 | −0.8050 | 0.8939 | 1.6015 | 0.8107 | 0.3455 | 0.5423 | −0.7053 | 0.0208 |
| 660 | −0.7903 | 0.8978 | 1.3308 | 0.8973 | 0.4988 | 0.7399 | −0.7047 | 0.0024 | |
| RSA | 330 | −0.7326 | 0.8385 | 1.2840 | 1.7105 | 1.2003 | 0.8957 | −0.9871 | 0.7066 |
| 660 | −0.7421 | 0.8642 | 1.1130 | 0.9510 | 0.8684 | 1.1687 | −0.5634 | 0.1912 | |
| SCA | 330 | −0.7186 | 0.8537 | 0.9150 | 0.6195 | 1.0084 | 2.0000 | 0.0005 | 0.5935 |
| 660 | −0.7648 | 0.9200 | 1.7525 | 2.0000 | −0.2438 | −0.2213 | −1.2119 | 0.2915 | |
| WOA | 330 | −0.8466 | 0.9521 | 0.9878 | 0.6570 | 0.6783 | 1.1143 | −0.6393 | 0.1901 |
| 660 | −0.7862 | 0.9048 | 0.8771 | 0.6877 | 1.3408 | 1.8431 | −0.3522 | 0.0331 | |
| NMPA | 330 | −0.7997 | 0.8997 | 1.1284 | 0.6982 | 0.8521 | 1.2310 | −0.5231 | 2.4132 × 10−5 |
| 660 | −0.8000 | 0.8999 | 1.1067 | 0.6837 | 0.8861 | 1.2821 | −0.5052 | 4.7671 × 10−6 | |
| Actual Values | −0.8000 | 0.9000 | 1.1000 | 0.6800 | 0.9000 | 1.3000 | −0.5000 | 0 | |
| Metaheuristics | Gn | Design Parameters | Best Fitness | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | 330 | −0.7942 | 0.8775 | 1.1663 | 0.7680 | 0.6776 | 0.9902 | −0.6280 | 0.0561 |
| 660 | −0.7945 | 0.9099 | 1.5233 | 1.0325 | 0.0691 | 0.3455 | −0.7981 | 0.0955 | |
| PDO | 330 | −0.7894 | 0.8941 | 1.4523 | 0.9153 | 0.4378 | 0.6399 | −0.7182 | 0.0038 |
| 660 | −0.7959 | 0.8993 | 1.0815 | 0.7327 | 0.8041 | 1.2129 | −0.5317 | 0.0075 | |
| RSA | 330 | −0.7220 | 0.9108 | 1.1243 | 1.0110 | 0.5696 | 1.0461 | −0.5176 | 0.4078 |
| 660 | −0.7712 | 0.8883 | 1.0020 | 0.9802 | 0.8040 | 1.0051 | −0.7028 | 0.2483 | |
| SCA | 330 | −0.7997 | 0.9340 | 1.8997 | 1.4184 | −0.1877 | −0.0817 | −0.9527 | 0.2136 |
| 660 | −0.8026 | 0.8870 | 2.0000 | 1.2379 | 0.0353 | 0.0226 | −0.9581 | 0.0586 | |
| WOA | 330 | −0.8374 | 0.8853 | 1.0703 | 0.2489 | 1.0443 | 1.9562 | 0.0293 | 0.2150 |
| 660 | −0.7864 | 0.8912 | 1.8573 | 1.1397 | 0.0551 | 0.1463 | −0.8773 | 0.0053 | |
| NMPA | 330 | −0.8002 | 0.8988 | 1.1805 | 0.7246 | 0.7452 | 1.1017 | −0.5584 | 4.7301 × 10−4 |
| 660 | −0.8003 | 0.8989 | 1.1751 | 0.7222 | 0.7556 | 1.1140 | −0.5547 | 4.6813 × 10−4 | |
| Actual Values | −0.8000 | 0.9000 | 1.1000 | 0.6800 | 0.9000 | 1.3000 | −0.5000 | 0 | |
| Metaheuristics | Gn | Design Parameters | Best Fitness | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | 330 | −0.7755 | 0.8891 | 1.9109 | 1.8204 | −0.1287 | −0.1344 | −1.0075 | 0.1621 |
| 660 | −0.8177 | 0.9021 | 1.0589 | 0.6413 | 1.1741 | 1.5627 | −0.4029 | 0.1044 | |
| PDO | 330 | −0.8193 | 0.9085 | 0.9650 | 0.6171 | 1.0302 | 1.5850 | −0.3628 | 0.0663 |
| 660 | −0.8218 | 0.8972 | 1.0634 | 0.5911 | 0.8280 | 1.3622 | −0.3971 | 0.0608 | |
| RSA | 330 | −0.7640 | 0.9009 | 1.0093 | 0.9475 | 0.7496 | 1.2128 | −0.5217 | 0.2810 |
| 660 | −0.7809 | 0.9042 | 0.9844 | 0.9097 | 0.5374 | 0.8729 | −0.7874 | 0.3593 | |
| SCA | 330 | −0.7719 | 0.9252 | 1.5129 | 1.7924 | 0.0006 | −0.0261 | −1.1125 | 0.4162 |
| 660 | −0.7868 | 0.9022 | 1.6056 | 1.1461 | −0.2537 | 0.0269 | −0.8898 | 0.2069 | |
| WOA | 330 | −0.7691 | 0.9067 | 1.0330 | 1.1504 | 1.0278 | 1.1263 | −0.7600 | 0.3160 |
| 660 | −0.8086 | 0.9049 | 0.9453 | 0.6698 | 0.7969 | 1.4578 | −0.3311 | 0.1322 | |
| NMPA | 330 | −0.8033 | 0.8948 | 1.9997 | 1.1901 | −0.1187 | −0.0161 | −0.8832 | 0.0405 |
| 660 | −0.8035 | 0.8943 | 2.0000 | 1.1789 | −0.1210 | −0.0139 | −0.8781 | 0.0405 | |
| Actual Values | −0.8000 | 0.9000 | 1.1000 | 0.6800 | 0.9000 | 1.3000 | −0.5000 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehmood, K.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Cheema, K.M.; Khan, Z.A.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Milyani, A.H.; Alsulami, A. Design of Nonlinear Marine Predator Heuristics for Hammerstein Autoregressive Exogenous System Identification with Key-Term Separation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112512
Mehmood K, Chaudhary NI, Cheema KM, Khan ZA, Raja MAZ, Milyani AH, Alsulami A. Design of Nonlinear Marine Predator Heuristics for Hammerstein Autoregressive Exogenous System Identification with Key-Term Separation. Mathematics. 2023; 11(11):2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112512
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehmood, Khizer, Naveed Ishtiaq Chaudhary, Khalid Mehmood Cheema, Zeshan Aslam Khan, Muhammad Asif Zahoor Raja, Ahmad H. Milyani, and Abdulellah Alsulami. 2023. "Design of Nonlinear Marine Predator Heuristics for Hammerstein Autoregressive Exogenous System Identification with Key-Term Separation" Mathematics 11, no. 11: 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112512
APA StyleMehmood, K., Chaudhary, N. I., Cheema, K. M., Khan, Z. A., Raja, M. A. Z., Milyani, A. H., & Alsulami, A. (2023). Design of Nonlinear Marine Predator Heuristics for Hammerstein Autoregressive Exogenous System Identification with Key-Term Separation. Mathematics, 11(11), 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112512








