Artificial Intelligence and Information Processing: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Collection and Methods
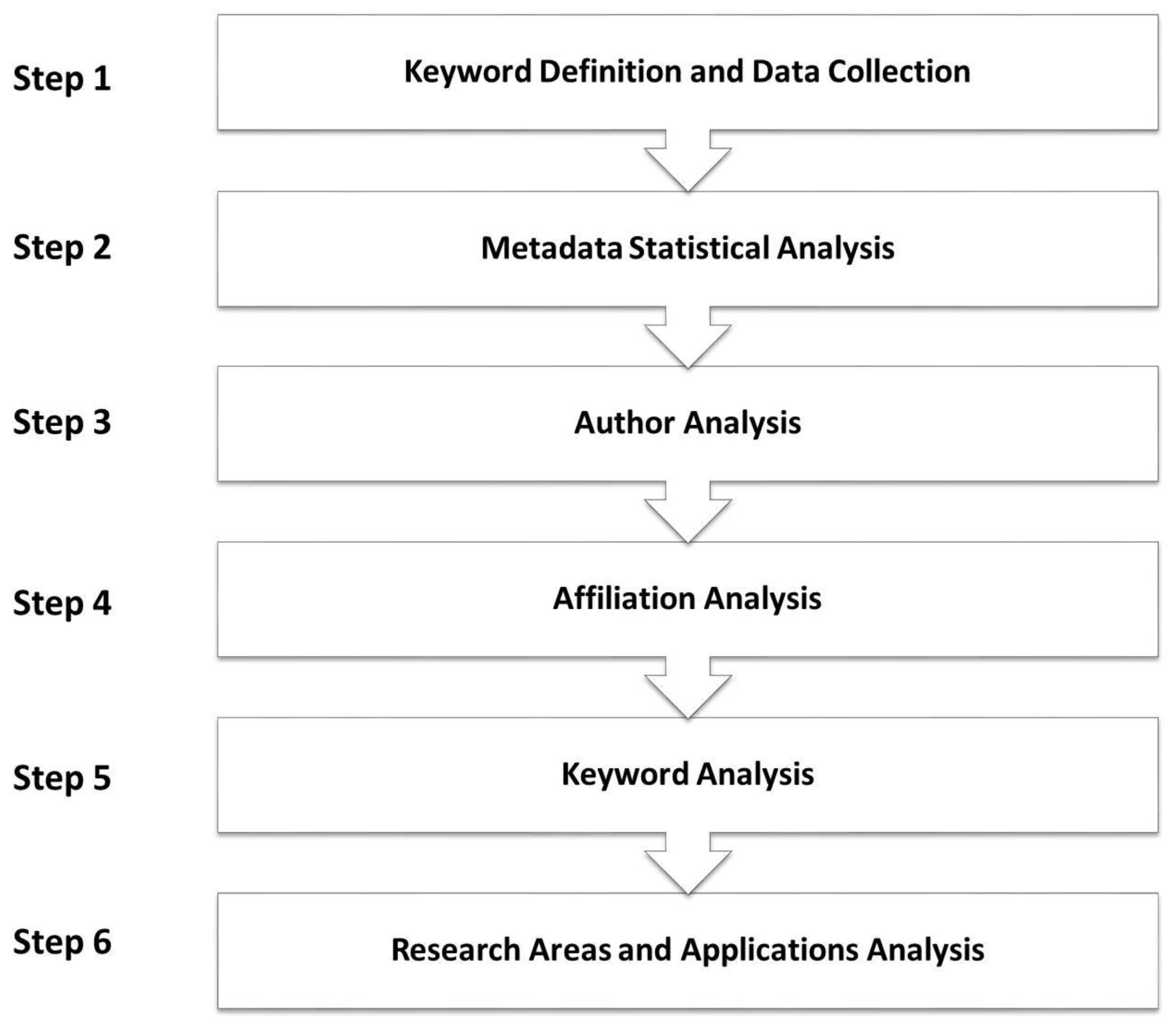
3. Proposed Design
- Step 1: Keyword definition and data collection
- Step 2: Metadata statistical analysis
- Step 3: Author analysis
- Step 4: Affiliation analysis
- Step 5: Keyword analysis
- Step 6: Research areas and applications analysis
4. Analysis Results
4.1. Keyword Definition and Data Collection
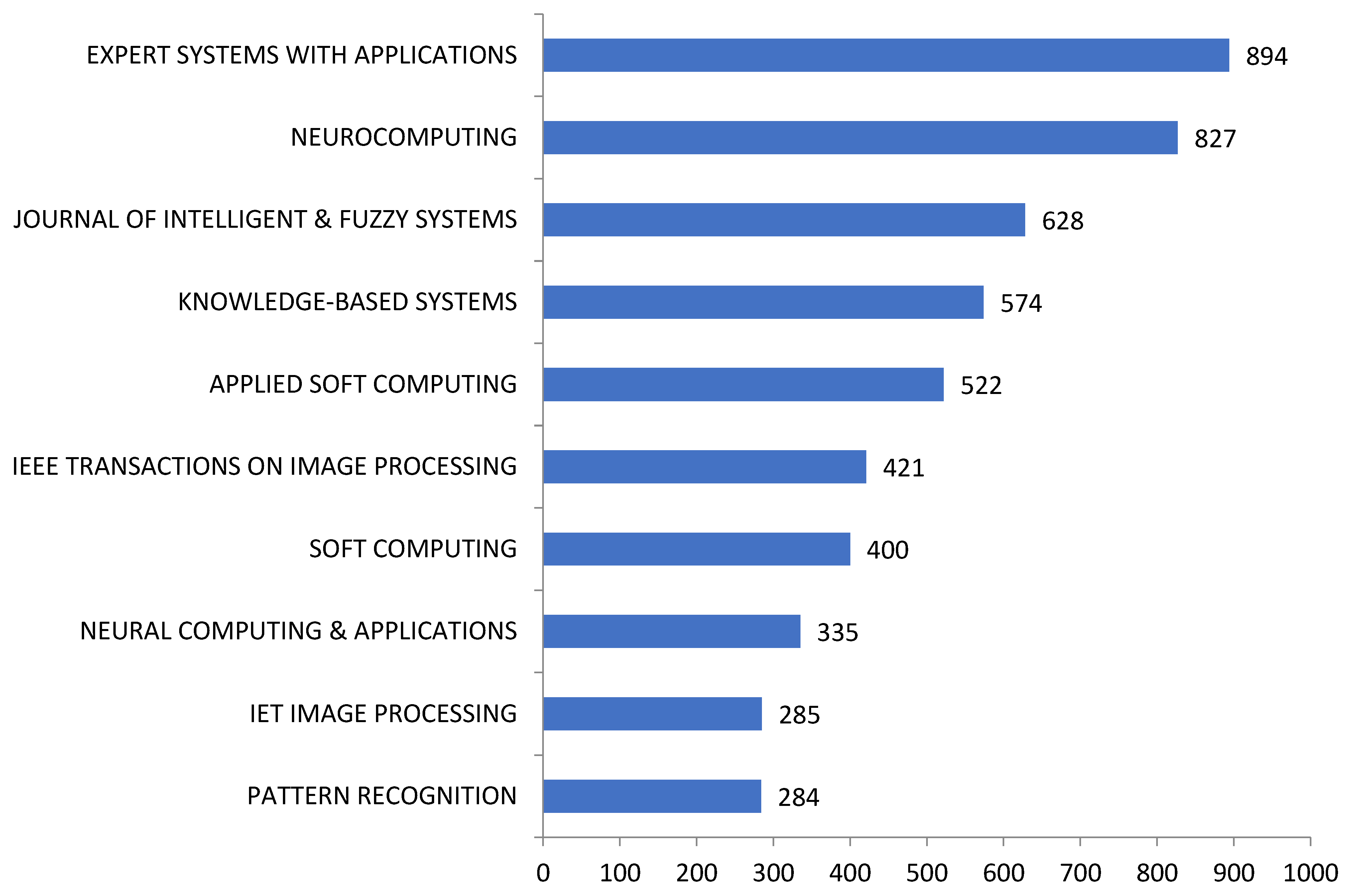
4.2. Metadata Statistical Analysis
4.3. Author Analysis
4.4. Affiliation Analysis
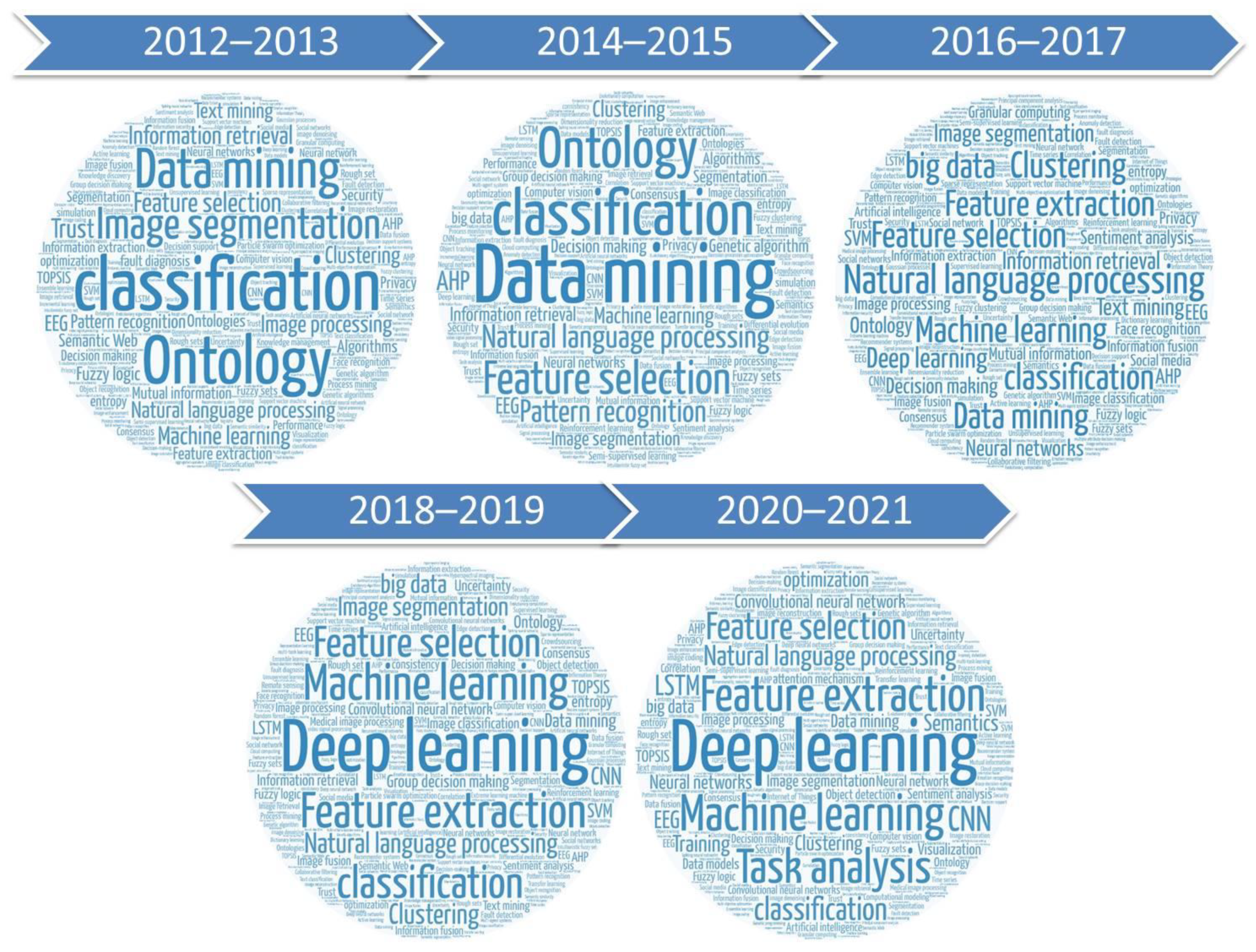
4.5. Keyword Analysis
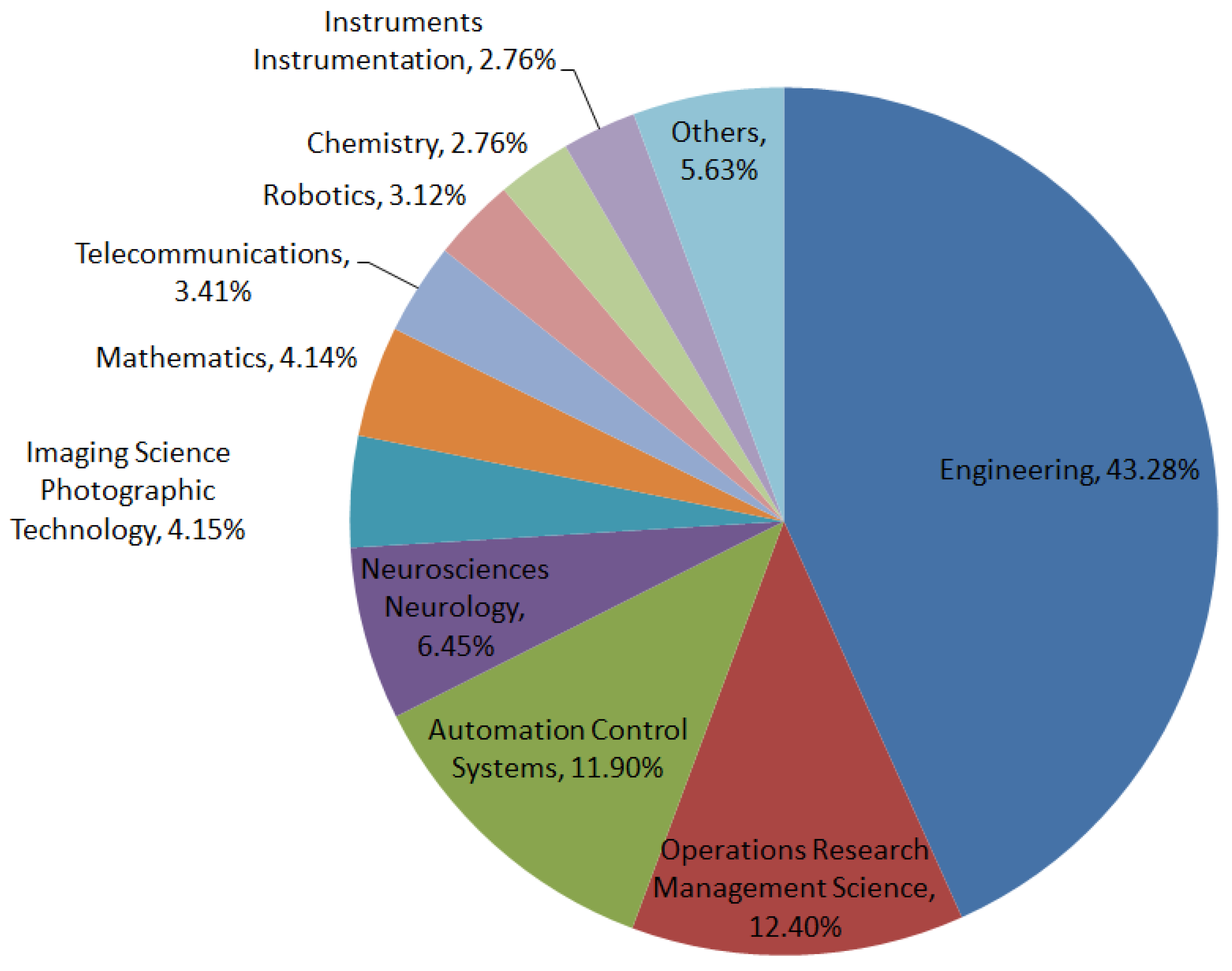
4.6. Research Areas and Applications Analysis
5. Discussion of Gaps and Opportunities
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Sun, A.; Tay, Y. Deep learning based recommender system: A survey and new perspectives. ACM. Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, S.; Islam, M.M.; Sohaib, M. Deep learning aided data-driven fault diagnosis of rotatory machine: A comprehensive review. Energies 2021, 14, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, S.; Wang, B.; Xin, J.; Li, Y.; Du, S. Photovoltaic power forecasting with a hybrid deep learning approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 175871–175880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatur, T.; Onen, F. Computation of design coefficients in ogee-crested spillway structure using GEP and regression models. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Roomi, A.R.; El-Hawary, M.E. Universal functions originator. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 94, 106417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendyk, A.; Pacławski, A.; Szafraniec-Szczęsny, J.; Antosik, A.; Jamróz, W.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. Data-driven modeling of the bicalutamide dissolution from powder systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaci, A.; Ozkaraca, O.; Acar, E.; Demir, A. Prediction of traumatic pathology by classifying thorax trauma using a hybrid method for emergency services. IET Signal Process. 2020, 14, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejnowski, T.J. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep learning in artificial intelligence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30033–30038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Song, K. Fault diagnosis of bearings based on multi-sensor information fusion and 2D convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23717–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chang, K.H.; Meng, H.M.; Chiu, H.C. A novel multi-category defect detection method based on the convolutional neural network method for TFT-LCD panels. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6505372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerini, I.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Maiano, L.; Celsi, L.R. Deep learning for multimedia forensics. Found. Trends Comput. Graph. Vis. 2021, 12, 309–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chang, K.H.; Zheng, C.P. Application of non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm to solving bi-objective scheduling problem of printed circuit board. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. Integrating subjective-objective weights consideration and a combined compromise solution method for handling supplier selection issues. Systems 2023, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. A new emergency-risk-evaluation approach under spherical fuzzy-information environments. Axioms 2022, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.C.; Chang, K.H.; Lai, H.H. Integrating the 2-tuple linguistic representation and soft set to solve supplier selection problems with incomplete information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 87, 103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins-Proulx, P.; Poisot, T.; Gravel, D. Artificial intelligence for ecological and evolutionary synthesis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, O.; Romanov, D.; Drozdov, A.; Gerashchenko, A. Citation-based criteria of the significance of the research activity of scientific teams. Scientometrics 2017, 112, 1179–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Chung, H.Y.; Wang, C.N.; Lai, Y.D.; Wu, C.H. A new hybrid Fermatean fuzzy set and entropy method for risk assessment. Axioms 2023, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.C.; Chung, H.Y.; Chang, K.H.; Li, Z.S. A flexible risk assessment approach integrating subjective and objective weights under uncertainty. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 103, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, H.; Sharma, A. An effective solution for large scale single machine total weighted tardiness problem using lunar cycle inspired artificial bee colony algorithm. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2019, 17, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, J.; Webber, R.J.; Gerber, E.P.; Abbot, D.S.; Weare, J. Learning forecasts of rare stratospheric transitions from short simulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 3647–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierlboeck, M.; Nilchiani, R.R.; Edwards, C.M. The Pandemic Holiday Blip in New York City. IEEE. Trans. Comput. Social Syst. 2021, 8, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalilpourazari, S.; Khalilpourazary, S.; Özyüksel Çiftçioğlu, A.; Weber, G.W. Designing energy-efficient high-precision multi-pass turning processes via robust optimization and artificial intelligence. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 1621–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, V.R.; Özcan, E.; Sichman, J.S. Comparative analysis of selection hyper-heuristics for real-world multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Liu, S. Cooperation search algorithm: A novel metaheuristic evolutionary intelligence algorithm for numerical optimization and engineering optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yang, X. Intelligent recommendation method integrating knowledge graph and Bayesian network. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xin, C.; Zheng, H. Construction of a teaching system based on big data and artificial intelligence to promote the physical health of primary school students. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9777862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Dinesh, P.; Vakula, K.; Rao, B.K.; Ding, W.; Pelusi, D. Intelligent system for COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art survey. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 2908–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Mahmood, A. Review of deep learning algorithms and architectures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 53040–53065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Dahou, A.; Abualigah, L.; Yu, L.; Alshinwan, M.; Khasawneh, A.M.; Lu, S. Advanced metaheuristic optimization techniques in applications of deep neural networks: A review. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14079–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpur, N.; Abdulkadir, S.J.; Alhussian, H.; Hasan, M.H.; Aziz, N.; Bamhdi, A. A comprehensive review of deep neuro-fuzzy system architectures and their optimization methods. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 1837–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Cambria, E.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Gao, J. Deep learning-based text classification: A comprehensive review. ACM. Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Chang, K.H.; Yang, S.C. Integrating corpus-based and NLP approach to extract terminology and domain-oriented information: An example of US military corpus. Acta Sci. -Technol. 2022, 44, e60486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Chang, K.H. A novel corpus-based computing method for handling critical word ranking issues: An example of COVID-19 research articles. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 3190–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, J.; Manning, C.D. Advances in natural language processing. Science 2015, 349, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, A.; Han, J.; Li, C. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, A.; Hartel, T.; Manolache, S.; Ciocanea, C.M.; Miu, I.V.; Rozylowicz, L. Who is researching biodiversity hotspots in Eastern Europe? A case study on the grasslands in Romania. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maditati, D.R.; Munim, Z.H.; Schramm, H.J.; Kummer, S. A review of green supply chain management: From bibliometric analysis to a conceptual framework and future research directions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbat, T.; Chong, H.Y.; Liao, P.C.; Wu, Y.D. A bibliometric review on risk management and building information modeling for international construction. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8351679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Shin, Y.; Hwang, B.G.; Chi, S. Document management system using text mining for information acquisition of international construction. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4791–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Liao, H.; Wang, S.; Lev, B.; Fujita, H. A prospect theory-based group decision approach considering consensus for portfolio selection with hesitant fuzzy information. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2019, 168, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wang, L.; Hou, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y. The optimized GRNN based on the FDS-FOA under the hesitant fuzzy environment and its application in air quality index prediction. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 8365–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liao, H. Expected consistency-based emergency decision making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2019, 176, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Zhan, Q.; Xu, Z. Decision making with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information based on multiplicative consistency. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Xu, Z.; Liao, H.; Herrera, F. Consensus model handling minority opinions and noncooperative behaviors in large-scale group decision-making under double hierarchy linguistic preference relations. IEEE T. Cybern. 2020, 51, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Tang, M.; Qin, R.; Mi, X.; Altalhi, A.; Alshomrani, S.; Herrera, F. Overview of hesitant linguistic preference relations for representing cognitive complex information: Where we stand and what is next. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 12, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Dynamic hesitant fuzzy Bayesian network and its application in the optimal investment port decision making problem of “twenty-first century maritime silk road”. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Mi, X.; Xu, Z. A survey of decision-making methods with probabilistic linguistic information: Bibliometrics, preliminaries, methodologies, applications and future directions. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2020, 19, 81–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liao, H. Managing consensus reaching process with self-confident double hierarchy linguistic preference relations in group decision making. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2021, 20, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; He, Y. A novel weight-derived method and its application in graduate students’ physical health assessment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 200–236. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z. Consensus model based on probability k-means clustering algorithm for large scale group decision making. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2021, 12, 1609–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Fujita, H. Measures of uncertainty based on Gaussian kernel for a fully fuzzy information system. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2020, 196, 105791. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Nie, P.; Zhu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Li, Z. Designing of higher order information granules through clustering heterogeneous granular data. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 112, 107820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Pedrycz, W. Anomaly detection based on a granular Markov model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 187, 115744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Li, Z. A development of hierarchically structured granular models realized through allocation of information granularity. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 3845–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Li, Z. Development and analysis of neural networks realized in the presence of granular data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 3606–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Li, Z. A development of granular input space in system modeling. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Taghavi, A.; Eslami, E.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Ureña, R. Trust based group decision making in environments with extreme uncertainty. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2020, 191, 105168. [Google Scholar]
- Morente-Molinera, J.A.; Wu, X.; Morfeq, A.; Al-Hmouz, R.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A novel multi-criteria group decision-making method for heterogeneous and dynamic contexts using multi-granular fuzzy linguistic modelling and consensus measures. Inf. Fusion. 2020, 53, 240–250. [Google Scholar]
- Zuheros, C.; Martínez-Cámara, E.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Sentiment analysis based multi-person multi-criteria decision making methodology using natural language processing and deep learning for smarter decision aid. Case study of restaurant choice using TripAdvisor reviews. Inf. Fusion. 2021, 68, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Cao, M.; Chiclana, F.; Dong, Y.; Herrera-Viedma, E. An optimal feedback model to prevent manipulation behavior in consensus under social network group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 1750–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Xu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A new multi-criteria decision model based on incomplete dual probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 91, 106237. [Google Scholar]
- Labella, A.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Martinez, L. Extending the linguistic decision suite FLINTSTONES to deal with comparative linguistic expressions with symbolic translation information. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 39, 6245–6258. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Chen, Z.S.; Shuai, B.; Chin, K.S.; Martínez, L. Site selection of high-speed railway station: A trapezoidal fuzzy neutrosophic-based consensual group decision-making approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 5347–5367. [Google Scholar]
- Labella, A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Martinez, L. A consensus reaching process dealing with comparative linguistic expressions for group decision making: A fuzzy approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 38, 735–748. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Labella, Á.; Dutta, B.; Martínez, L. Comprehensive minimum cost models for large scale group decision making with consistent fuzzy preference relations. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2021, 215, 106780. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, Á.L.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L. Computing with comparative linguistic expressions and symbolic translation for decision making: ELICIT information. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 28, 2510–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.S.; Yang, L.L.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Xiong, S.H.; Chin, K.S.; Martínez, L. Power-average-operator-based hybrid multiattribute online product recommendation model for consumer decision-making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 2572–2617. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, H. Sine trigonometric operational laws and its based Pythagorean fuzzy aggregation operators for group decision-making process. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 4421–4447. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.T.; Wang, Z.W.; Garg, H. Extended cumulative residual entropy for emergency group decision-making under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Garg, H. Novel correlation coefficient between hesitant fuzzy sets with application to medical diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Gacek, A.; Liu, X. From numeric data to information granules: A design through clustering and the principle of justifiable granularity. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2016, 101, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W.; Hou, H.; Liu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Zhong, C. Interval kernel fuzzy c-means clustering of incomplete data. Neurocomputing 2017, 237, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Using interval information granules to improve forecasting in fuzzy time series. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2015, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Kou, G.; Li, C.C.; Dong, Y.; Herrera, F. An overview on feedback mechanisms with minimum adjustment or cost in consensus reaching in group decision making: Research paradigms and challenges. Inf. Fusion. 2020, 60, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y. The analytic hierarchy process with personalized individual semantics. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2018, 11, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Dong, Y.; Herrera, F. A consensus model for large-scale linguistic group decision making with a feedback recommendation based on clustered personalized individual semantics and opposing consensus groups. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 27, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chiclana, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. An overview on managing additive consistency of reciprocal preference relations for consistency-driven decision making and fusion: Taxonomy and future directions. Inf. Fusion. 2019, 52, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Triana, J.D.; Charte, D.; Andrés Arroyo, M.; Fernández, A.; Herrera, F. Revisiting data complexity metrics based on morphology for overlap and imbalance: Snapshot, new overlap number of balls metrics and singular problems prospect. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2021, 63, 1961–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ye, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Shang, R.; Jiao, L. Dual-graph convolutional network based on band attention and sparse constraint for hyperspectral band selection. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2021, 231, 107428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, L.; Li, L.; Tang, X.; Guo, Y. Deep multi-level fusion network for multi-source image pixel-wise classification. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2021, 221, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Song, J.; Jiao, L.; Li, Y. Double feature selection algorithm based on low-rank sparse non-negative matrix factorization. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 1891–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Hou, B.; Yang, S.; Jiao, L. GAFNet: Group attention fusion network for PAN and MS image high-resolution classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 10556–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Hou, B.; Yang, S.; Jian, M. DPFL-Nets: Deep pyramid feature learning networks for multiscale change detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6402–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshaghi, A.; Razmjooy, N.; Estrela, V.; Burdziakowski, P.; Nascimento, D.; Deshpande, A.; Patavardhan, P. Image transmission in UAV MIMO UWB-OSTBC system over Rayleigh channel using multiple description coding (MDC). In Imaging and Sensing for Unmanned Aircraft Systems; Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET): Stevenage, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, A.; Razmjooy, N.; Estrela, V.V. Introduction to computational intelligence and super-resolution. In Computational Intelligence Methods for Super-Resolution in Image Processing Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]





| No. | Authors | Country | Organization | Publication Quantity | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xu, Z.S. | China | Sichuan University | 103 | 5177 |
| 2 | Pedrycz, W. | Canada | University of Alberta | 103 | 4621 |
| 3 | Herrera-Viedma, E. | Spain | University of Granada | 40 | 2344 |
| 4 | Martinez, L. | Spain | University of Jaén | 39 | 2208 |
| 5 | Fujita, H. | Japan | Iwate Prefectural University | 34 | 1759 |
| 6 | Garg, H. | India | Thapar Inst of Engn and Technol | 32 | 1543 |
| 7 | Liu, P.D. | China | Shandong University of Finance and Econ | 32 | 1324 |
| 8 | Herrera, F. | Spain | University of Granada | 31 | 1976 |
| 9 | Dong, Y.C. | China | Sichuan University | 29 | 2068 |
| 10 | Jiao, L.C. | China | Xidian University | 28 | 1495 |
| No. | Country | Publication Number | No. | Country | Publication Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 5631 | 6 | Australia | 557 |
| 2 | USA | 1792 | 7 | France | 538 |
| 3 | Spain | 1032 | 8 | Canada | 522 |
| 4 | India | 1008 | 9 | Italy | 499 |
| 5 | England | 851 | 10 | Germany | 481 |
| Country No. | China | USA | Spain | India | England |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | University of California System | University of Granada | Indian Institute of Technology System | University of London |
| 2 | Sichuan University | University of Texas System | Universitat Politecnica de Valencia | National Institute of Technology | Imperial College London |
| 3 | Xidian University | University System of Georgia | Universidad de Jaén | Vellore Institute of Technology | University of Manchester |
| 4 | Zhejiang University | State University System of Florida | Universidad Politecnica de Madrid | Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology | De Montfort University |
| 5 | University of Electronic Science and Technology of China | Georgia Institute of Technology | University of Seville | Anna University | University of Oxford |
| 6 | Xi’an Jiaotong University | State University of New York System | University of the Basque Country | Indian Statistical Institute | University College London |
| 7 | Tsinghua University | University of Illinois System | Universidad de Malaga | VIT Vellore | University of Nottingham |
| 8 | Harbin Institute of Technology | Carnegie Mellon University | Universidad Carlos III de Madrid | Anna University Chennai | University of Sheffield |
| 9 | Northwestern Polytechnical University | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya | Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata | University of Granada |
| 10 | Huazhong University of Science and Technology | Pennsylvania Commonwealth System of Higher Education | Universitat d’Alacant | Shanmugha Arts, Science, Technology and Research Academy | University of Southampton |
| Country No. | Australia | France | Canada | Italy | Germany |
| 1 | University of Technology Sydney | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) | University of Alberta | Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR) | Technical University of Munich |
| 2 | University of Sydney | UDICE—French Research Universities | Concordia University—Canada | University of Salerno | Helmholtz Association |
| 3 | University of New South Wales Sydney | Université Paris-Saclay | Université de Montreal | Sapienza University Rome | University of Erlangen Nuremberg |
| 4 | Queensland University of Technology (QUT) | Université de Toulouse | University of Waterloo | University of Trento | Max Planck Society |
| 5 | Monash University | Institut Mines- Télécom (IMT) | University of British Columbia | University of Naples Federico II | Ruprecht Karls University Heidelberg |
| 6 | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) | Sorbonne Université | University of Toronto | University of Padua | Karlsruhe Institute of Technology |
| 7 | University of Queensland | INRAE | University of Calgary | University of Bologna | Technical University of Darmstadt |
| 8 | Deakin University | Université de Rennes | Toronto Metropolitan University | University of Pisa | Leipzig University |
| 9 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | Université de Lorraine | University of Quebec | Polytechnic University of Milan | Ulm University |
| 10 | University of Adelaide | Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) | Western University (University of Western Ontario) | Polytechnic University of Turin | University of Munich |
| Research Areas | Applications |
|---|---|
| Engineering | Information process |
| Systems | |
| Decision support | |
| Computer engineering | |
| Knowledge management | |
| Control systems | |
| Manufacturing | |
| Sensors | |
| Operations Research and Management Science | Decision making |
| Fuzzy arithmetic | |
| Project management | |
| Classification | |
| Quality control | |
| Big data | |
| Supply chain management | |
| Automation Control Systems | Process control |
| Fuzzy approach | |
| Robotics | |
| Environmental monitoring | |
| Manufacturing | |
| Smart sensors | |
| Energy management | |
| Industry 4.0 | |
| Neurosciences and Neurology | Cognitive architecture |
| Neurorobots | |
| Electroencephalography | |
| Emotion | |
| Imaging Science and Photographic Technology | Medical imaging |
| Image classification | |
| Geophysical imaging | |
| Mathematics | Systems modeling |
| Data science | |
| Optimization | |
| Soft sensors | |
| Fuzzy sets | |
| Telecommunications | Mobile computing |
| Internet of Things | |
| Wireless sensor networks | |
| Robotics | Autonomous |
| Automatization | |
| Service robotics | |
| Chemistry | Chemical process monitoring |
| Operational optimization | |
| Instruments and Instrumentation | Fault detection |
| Autoencoders |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, K.-Y.; Chang, K.-H. Artificial Intelligence and Information Processing: A Systematic Literature Review. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112420
Lin K-Y, Chang K-H. Artificial Intelligence and Information Processing: A Systematic Literature Review. Mathematics. 2023; 11(11):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112420
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Keng-Yu, and Kuei-Hu Chang. 2023. "Artificial Intelligence and Information Processing: A Systematic Literature Review" Mathematics 11, no. 11: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112420
APA StyleLin, K.-Y., & Chang, K.-H. (2023). Artificial Intelligence and Information Processing: A Systematic Literature Review. Mathematics, 11(11), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112420






