Multimedia Applications Processing and Computation Resource Allocation in MEC-Assisted SIoT Systems with DVS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The minimization problem of multimedia application execution latency and energy consumption of IoT devices is studied by the allocation of computing resources in the edge servers while adopting the DVS technology.
- The studied problem of latency and energy consumption is formulated. Due to the formulated problem being an MINP problem, an efficient multimedia applications offloading scheme is proposed, and the solution of it is obtained.
- Simulation results are performed to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed multimedia applications offloading scheme by comparing with the two baseline schemes. The theoretical analysis and simulation results indicate that the multimedia applications’ offloading scheme proposed in this paper can perform better than the baseline methods, which can integrate the dependability aspects into the design of SIoT systems.
2. Related Work
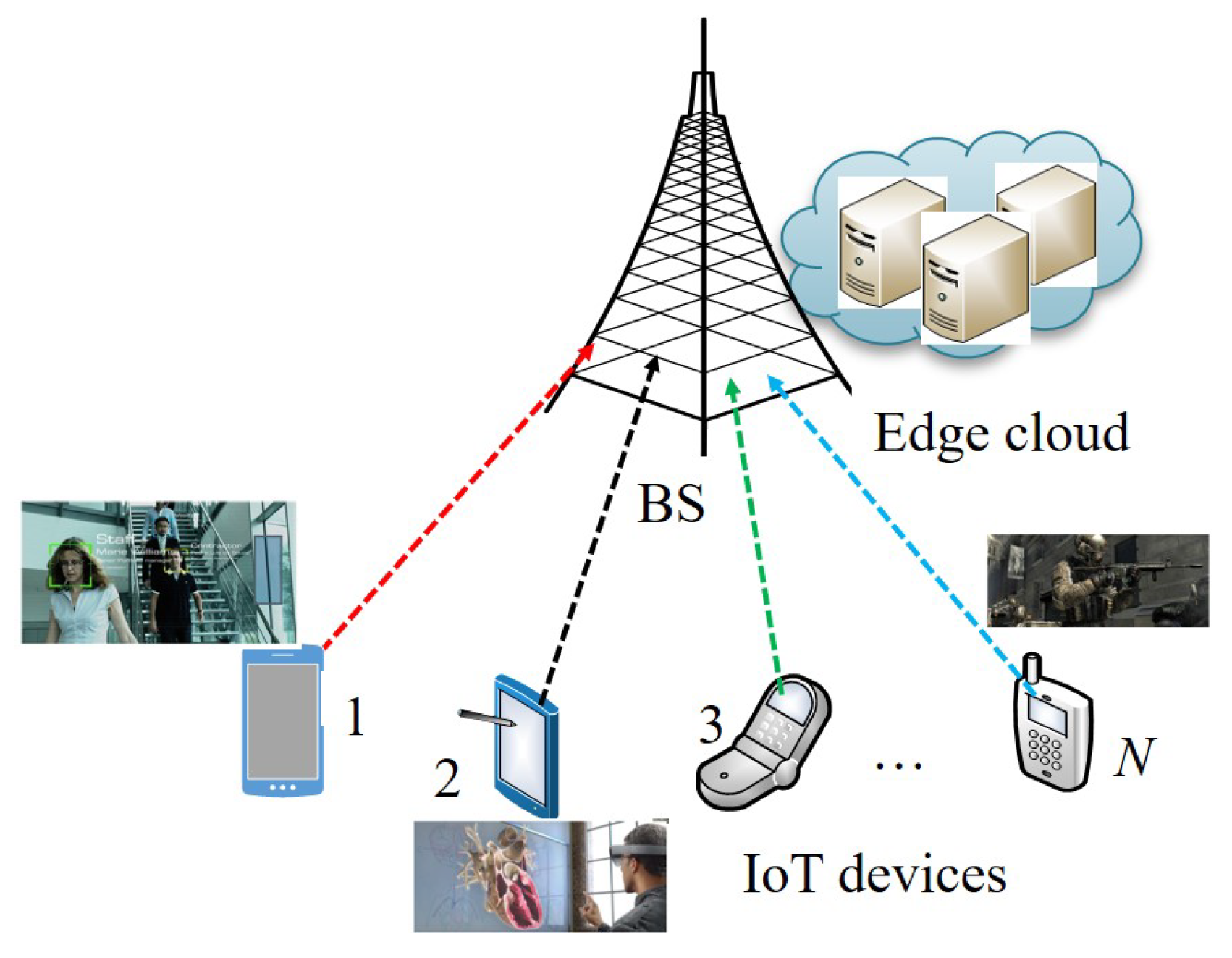
3. System Architecture
3.1. Local Computation Model
3.2. Edge Cloud Model
3.3. Problem Formulation
4. Solution Method
4.1. Solution Method
4.2. Local Computation Problem
4.3. Edge Cloud Computation Problem
4.4. Application Offloading Decision
| Algorithm 1 Computational Resource Allocation and Applications Offloading Algorithm. |
| Input: |
| 1: N applications; |
| Output: |
| 2: The application offloading decision made by each user of IoT device and the system computation overhead; |
| 3: Obtain the optimal resource allocation of each IoT device by solving problem P1; |
| 4: Based on Equation (16), IoT devices make adjustments to their voltage and clock frequency to obtain the adaptive CPU frequency according to the weight coefficient values by applying the DVS technology; |
| 5: Obtain the optimized local computation cost of each IoT device based on Equation (17); |
| 6: Calculate the allocated computational resource of each IoT device by solving problem P2; |
| 7: Obtain the optimal computation cost of the edge cloud computation model from Equation (11); |
| 8: if then |
| 9: ; |
| 10: else |
| 11: ; |
| 12: end if |
5. Simulation Results
5.1. Parameter Setting
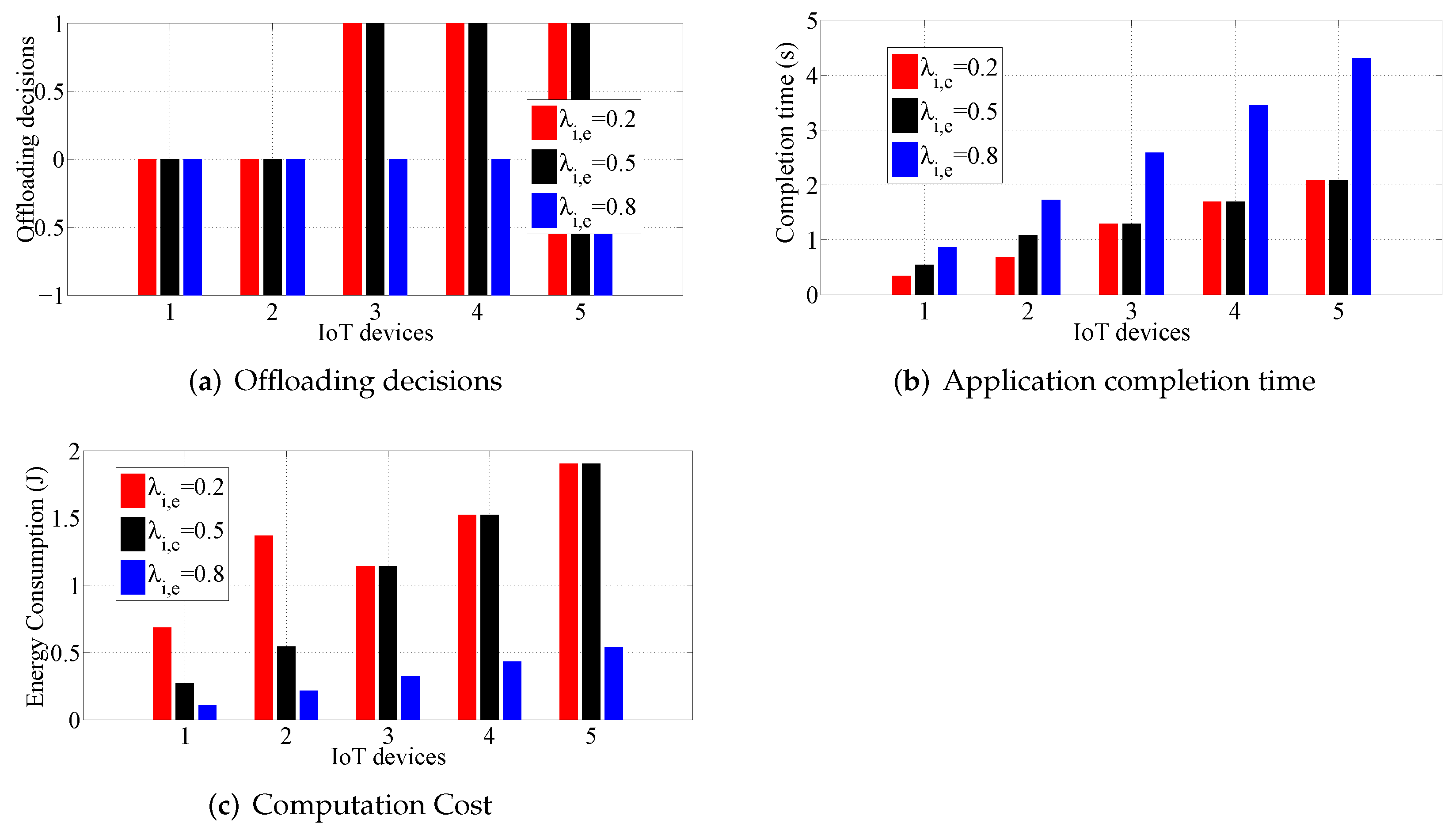
5.2. Effect of Weight Coefficient Values
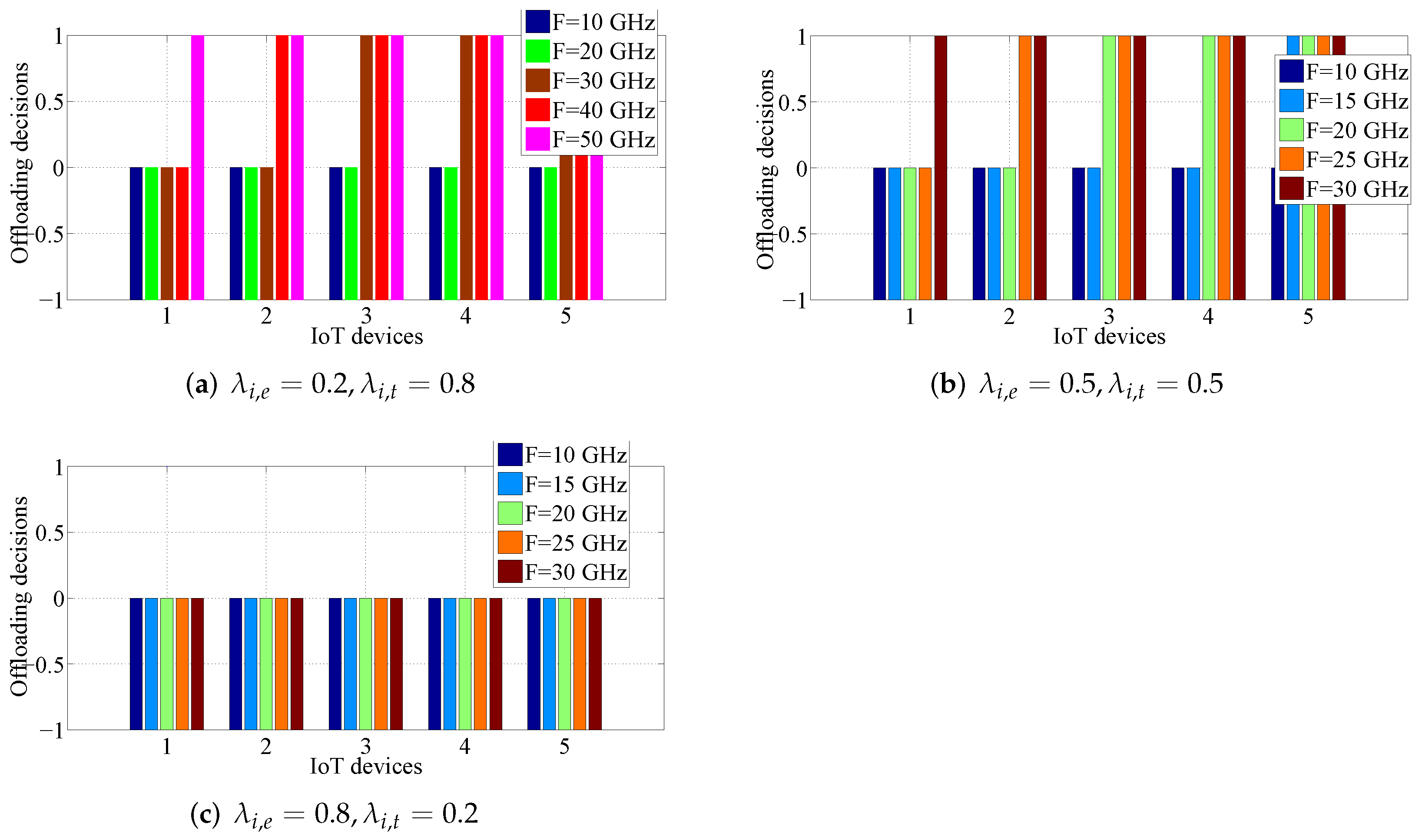
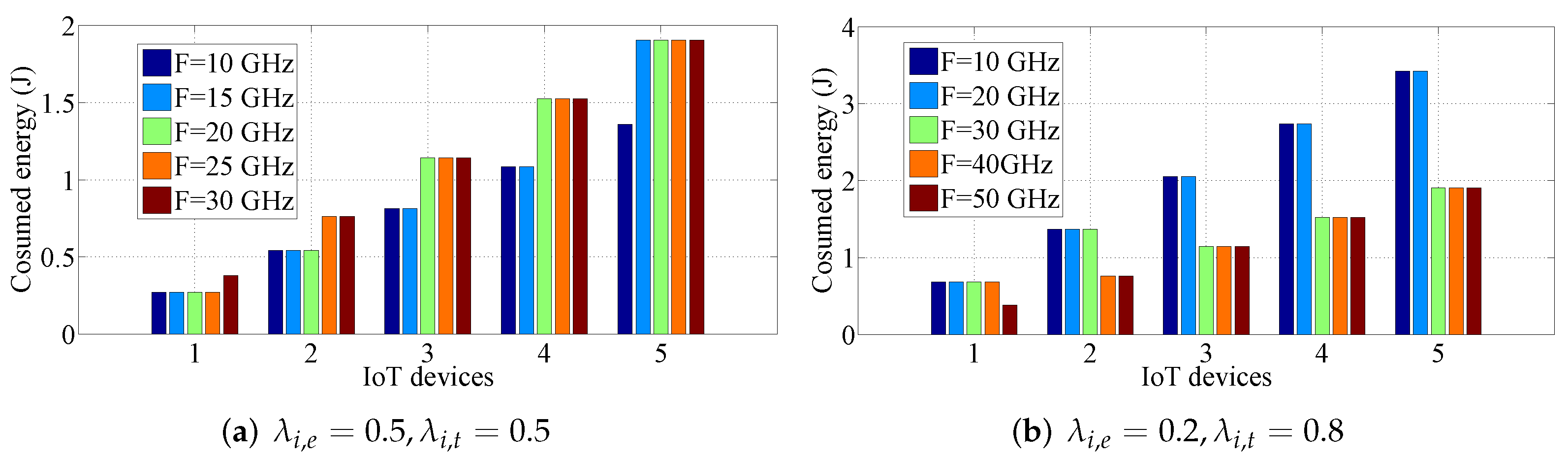
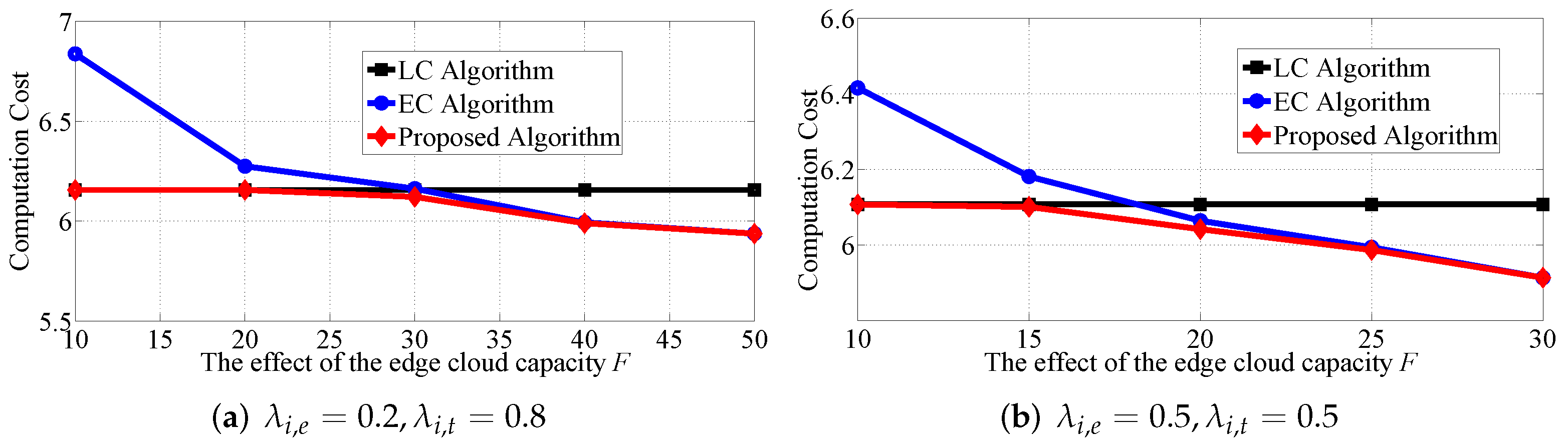
5.3. Effect of the Edge Cloud Capacity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| MCC | Mobile Cloud Computing |
| SIoT | Social Internet of Things |
| DVS | Dynamic voltage scaling |
| MINP | Mixed-integer nonlinear programming |
References
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.P.; Yu, K.; Srivastava, G. Nonlinear mimo for industrial internet of things in cyberphysical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 8, 5533–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhu, G.; Alazab, M.; Li, X.; Yu, K. Deep-learning-empowered digital forensics for edge consumer electronics in 5g hetnets. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 11, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Lin, J.C.-W. Deep Learning-Embedded Social Internet of Things for Ambiguity-Aware Social Recommendations. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yu, K.; Ming, F.; Chen, X.; Srivastava, G. Secure and resilient artificial intelligence of things: A honeynet approach for threat detection and situational awareness. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2021, 11, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, K.; Liu, B.; Feng, C.; Qin, Z.; Srivastava, G. An efficient ciphertext-policy weighted attribute based encryption for the internet of health things. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 26, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, T.; Lin, M.; Hawbani, A.; Shang, J.; Fan, C. SPIDER: A Social Computing Inspired Predictive Routing Scheme for Softwarized Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, K.; Kumar, N.; Barnawi, A.; Xie, Y. Early collision detection for massive random access in satellite-based internet of things. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 5184–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, K.; Tarchi, D.; Wan, S.; Kumar, N. INTERLINK: A Digital Twin-Assisted Storage Strategy for Satellite-Terrestrial Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Liu, B.; Guo, Z.; Yu, K.; Qin, Z.; Choo, K.-K.R. Blockchain-based cross-domain authentication for intelligent 5g-enabled internet of drones. IEEE Internet Things 2022, 9, 6224–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile Data Traffic Forecast Update 2017–2022 White Paper. Available online: http://media.mediapost.com/uploads/CiscoForecast.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, K.; Alazab, M.; Lin, K. Pmrss: Privacy-preserving medical record searching scheme for intelligent diagnosis in iot healthcare. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 18, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.-L.; Chen, J.; Bi, H.; Sui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. Impacts of covid-19 pandemic on user behaviors and environmental benefits of bike sharing: A big-data analysis. Appl. Energy 2022, 285, 116429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Yin, C.; Hu, X.; Yang, S.; Leung, V.C.M. Lightweight management of resource-constrained sensor devices in internet of things. IEEE Internet Things 2015, 2, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, J.; Peng, S.; Jia, W.; Wang, C.; Niu, J.; Yu, S. Energy efficient data collection in large-scale internet of things via computation offloading. IEEE Internet Things 2019, 35, 4176–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yu, K.; Shi, N.; Yang, C.; Wei, W.; Lu, H. Towards secure and privacy-preserving data sharing for COVID-19 medical records: A blockchain-empowered approach. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiao, L.; Li, W.; Fu, X. Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 2795–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Edge computing: Vision and challenges. IEEE Internet Things 2016, 5, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Feng, J.; Pei, Q.; Chen, C.; Ming, Y.; Shang, B.; Dong, M. Blockchain-enabled secure data sharing scheme in mobile-edge computing: An asynchronous advantage actorcritic learning approach. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 4, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.; Yousuf, T.; Aloul, F.; Zualkernan, I. Internet of things (IoT) security: Current status, challenges and prospective measures. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST 2015), London, UK, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bures, M.; Klima, M.; Rechtberger, V.; Ahmed, B.S.; Hindy, H.; Bellekens, X. Review of Specific Features and Challenges in the Current Internet of Things Systems Impacting Their Security and Reliability. In Proceedings of the Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies, Terceira Island, Azores, Portugal, 30 March–2 April 2021; pp. 546–556. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Mobile-edge computing: Partial computation offloading using dynamic voltage scaling. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 10, 4268–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Song, R. Intelligent offloading for noma-assisted mec via dual connectivity. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 4, 2802–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, D.; Zhang, S.; Liu, A.; Xia, X.-G. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation for mec-enabled iot systems with imperfect csi. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 5, 3462–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W. Multi-device task offloading with time-constraints for energy efficiency in mobile cloud computing. Perform. Eval. Rev. 2016, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Huang, K.; Chae, H.; Kim, B.-H. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Mobile-Edge Computation Offloading. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 1397–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Tian, H.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, R.P. Energy-efficient admission of delay-sensitive tasks for mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 6, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Tian, H.; Qin, C.; Nie, G. Energy-saving offloading by jointly allocating radio and computational resources for mobile edge computing. IEEE Access 2017, 11255–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Fodor, V. Energy minimization for delay constrained mobile edge computing with orthogonal and non-orthogonal multiple access. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020, 98, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskar, E.; Todd, T.D.; Zhao, D.; Karakostas, G. Energy aware offloading for competing users on a shared communication channel. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2017, 1, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Yin, C.; Cui, S.; Poor, H.V. A machine learning approach for task and resource allocation in mobile-edge computing-based networks. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 3, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xu, J. Emm: Energy-aware mobility management for mobile edge computing in ultra dense networks. IEEE Trans. J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 11, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.P.; Shi, B.; Wu, Y.; Sun, B.; Tsang, D.H.K. NOMA enabled mobile edge com puting for internet of things via joint communication and compu tation resource allocations. IEEE Internet Things 2020, 7, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, B.; Wu, Y.; Tsang, D.H.K. Latency optimization for computation offloading with hybrid noma-oma transmission. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 8, 6677–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, X. Optimal Resource Allocation for Multimedia Applications Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2021, 2, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W. Cl-admm: A cooperative-learning-based optimization framework for resource management in MEC. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 8, 8191–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Yi, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. NOSCM: A Novel Offloading Strategy for NOMA-Enabled Hierarchical Small Cell Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 10, 8107–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Ning, Z.; Ngai, E.C.-H.; Zhou, L.; Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B. Energy-latency tradeoff for energy-aware offloading in mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Internet Things 2018, 4, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, K.; Aloqaily, M.; Jararweh, Y. A cooperative resource allocation model for IoT applications in mobile edge computing. Comput. Commun. 2021, 173, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.T.; Masouros, C. A scalable energy vs. latency trade-off in fullduplex mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 5848–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Wen, Y. Computing offloading strategy using improved genetic algorithm in mobile edge computing syste. J. Grid Comput. 2021, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadifard, F.; Babamir, S.M. Federated geo-distributed clouds: Optimizing resource allocation based on request type using autonomous and multi-objective resource sharing model. Big Data Res. 2021, 24, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Tang, S.; Li, T.; Chan, A.T. A framework for partitioning and execution of data stream applications in mobile cloud computing. Perform. Eval. Rev. 2013, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochet, Y.; Wolsey, L.A. Production Planning by Mixed Integer Programming; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-G.; Han, S.-F.; Zhao, L.; Gong, C.-Q.; Liu, X.-J. New dandelion algorithm optimizes extreme learning machine for biomedical classification problems. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 4523754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, N.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, L. A novel improved bat algorithm in uav path planning, Computers. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2019, 61, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bu, X.; Yang, K.; Wu, Z.; Han, Z. Green large-scale fog computing resource allocation using joint benders decomposition, dinkelbach algorithm, admm, and branch-and-bound. Comput. IEEE Internet Things 2019, 6, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Computational Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Wen, Y. Efficient caching strategy in wireless networks with mobile edge computing. Comput. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Tan, L.; Lin, L.; Cheng, X.; Yi, Z.; Sato, T. Deep-learning-empowered breast cancer auxiliary diagnosis for 5gb remote e-health. Comput. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 3, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, B.; Hu, R.Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, H. Joint computation offloading and radio resource allocation in MEC-based wireless-powered backscatter communication networks. Comput. IEEE T. Veh. Technol. 2021, 6, 6200–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, W.; Hawbani, A.; Al-Dubai, A.Y.; Min, G.; Zomaya, A.Y.; Gong, C. Novel online sequential learning-based adaptive routing for edge software-defined vehicular networks. Comput. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 5, 2991–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Guo, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, J.C.-W.; Sato, T. Secure artificial intelligence of things for implicit group recommendations. Comput. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 4, 2698–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reference | DVS | Application Execution Time | Energy Consumption | Computation Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [16] | No | No | Yes | No |
| Wang et al. [21] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Wang et al. [30] | No | No | No | No |
| Zhong et al. [35] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Li et al. [22] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Wang et al. [23] | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Liu et al. [33] | No | No | Yes | No |
| Li et al. [14] | No | No | Yes | No |
| Li et al. [38] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Yang et al. [36] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Liu et al. [24] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lyu et al. [26] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| You et al. [25] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Zhao et al. [27] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Kabir et al. [39] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Zhang et al. [37] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Sun et al. [31] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Meskar et al. [29] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Zeng et al. [28] | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Zhu et al. [40] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| This Study | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| The processing rate of the IoT device i | |
| The local processing time of the IoT device i | |
| The local energy consumption of the IoT device i | |
| The transmission time of the IoT device i | |
| The transmission energy consumption of the IoT device i | |
| The application i’s data size | |
| The needed CPU cycles to process application of IoT device i | |
| The weighting parameter of application processing time | |
| The weighting parameter of energy consumption | |
| The channel bandwidth | |
| The transmit power of the IoT device i | |
| The channel gain | |
| The background noise power | |
| The uplink transmission rate for the IoT device i | |
| The application offloading decision that make by the IoT device i | |
| The allocated computational resources in the edge cloud to device i | |
| The maximum processing rate of the IoT device i | |
| F | The total computational resources in the edge servers |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| The number of IoT devices N | 5 |
| The bandwidth allocation | 1.6 MHz |
| The data sizes of multimedia applications | [0.42, 4.2] Mb |
| The transmission power | 1 W |
| The needed computation resources | [0, 1] cycles |
| The channel gain | |
| The maximum processing rate | 1 GHz |
| The background noise power | W |
| The computation capacity of the edge cloud F | 20 GHz |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, L.; Wei, B. Multimedia Applications Processing and Computation Resource Allocation in MEC-Assisted SIoT Systems with DVS. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091593
Li X, Chen G, Zhao L, Wei B. Multimedia Applications Processing and Computation Resource Allocation in MEC-Assisted SIoT Systems with DVS. Mathematics. 2022; 10(9):1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091593
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianwei, Guolong Chen, Liang Zhao, and Bo Wei. 2022. "Multimedia Applications Processing and Computation Resource Allocation in MEC-Assisted SIoT Systems with DVS" Mathematics 10, no. 9: 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091593
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, G., Zhao, L., & Wei, B. (2022). Multimedia Applications Processing and Computation Resource Allocation in MEC-Assisted SIoT Systems with DVS. Mathematics, 10(9), 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091593







