Solving the Eigenfrequencies Problem of Waveguides by Localized Method of Fundamental Solutions with External Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions
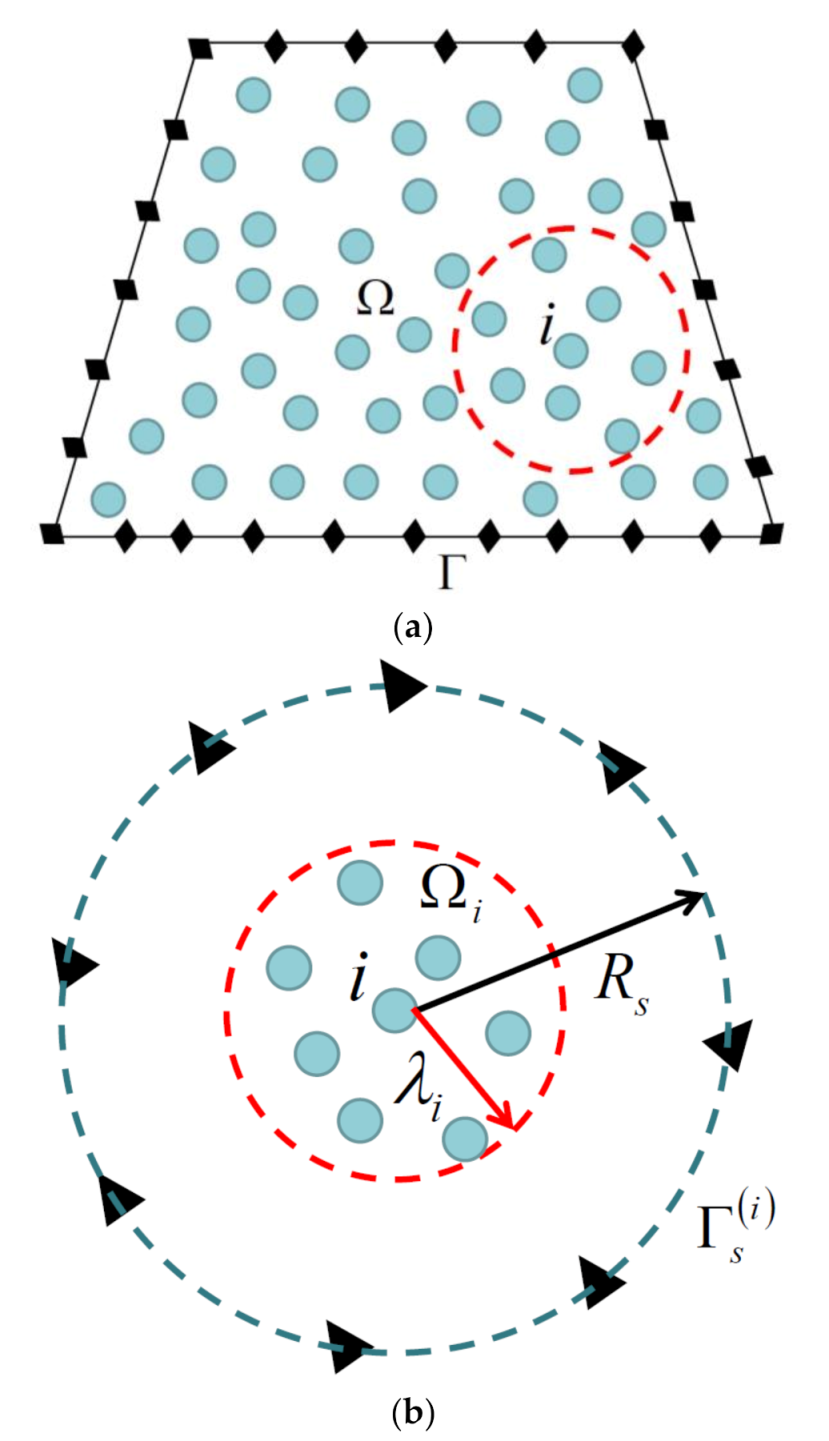
3. Numerical Methods
4. Numerical Results and Comparisons
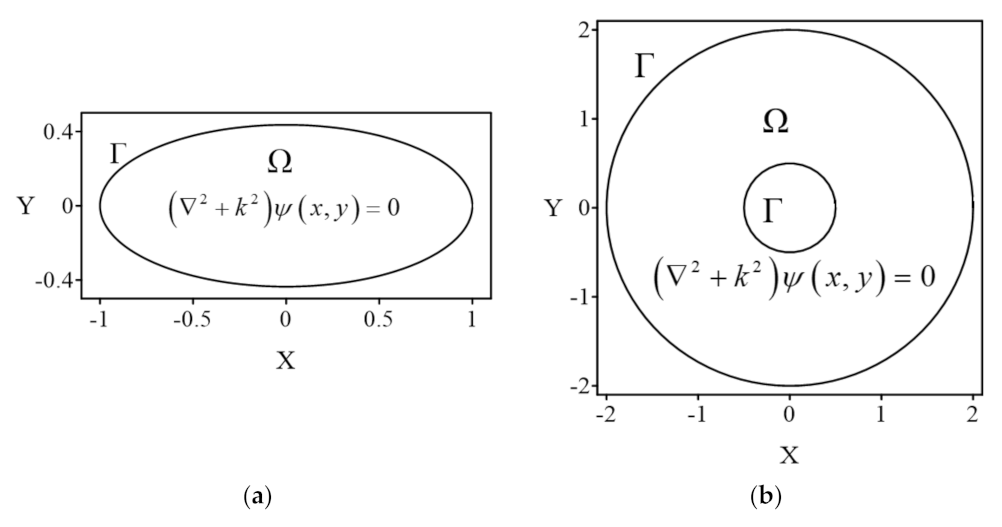
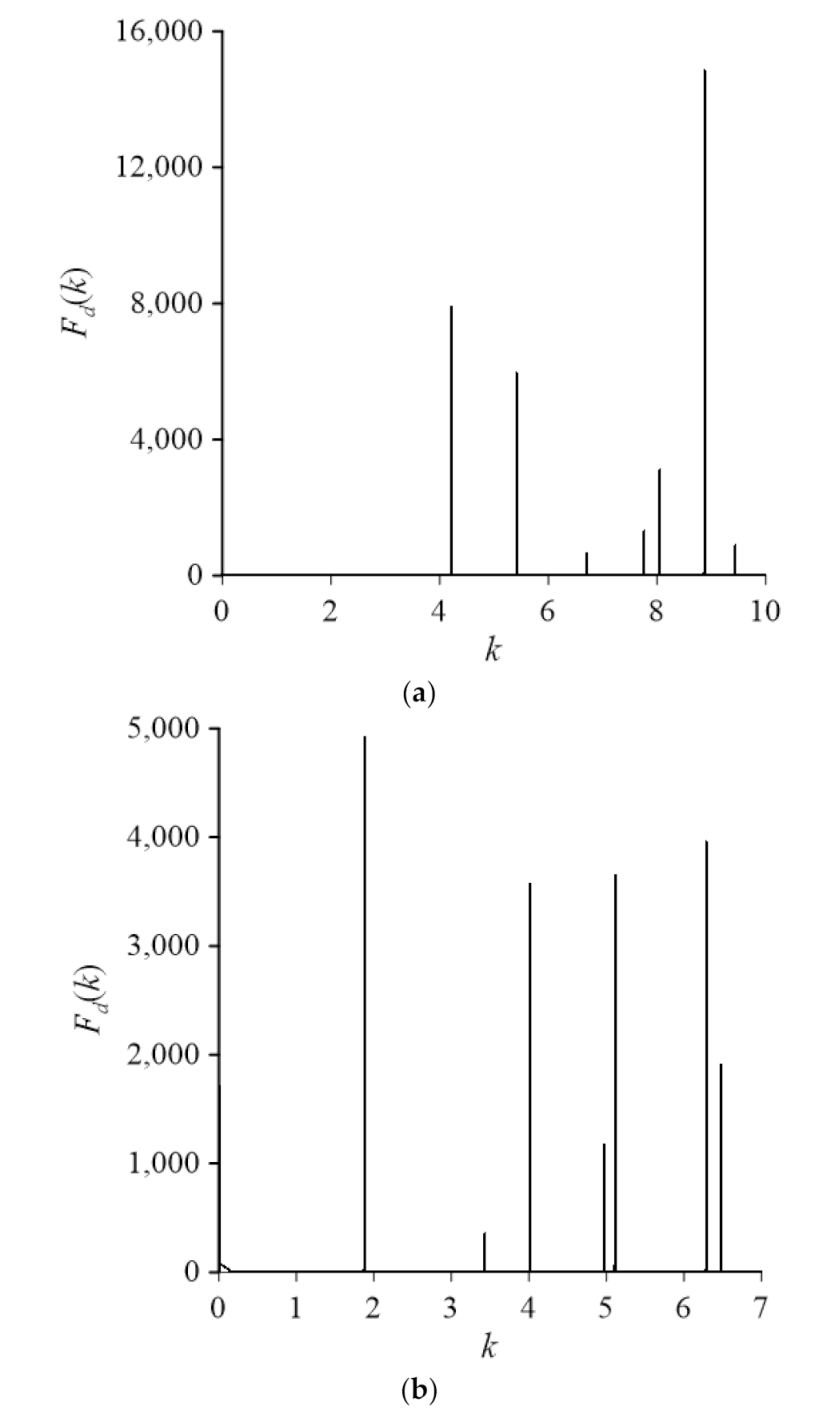
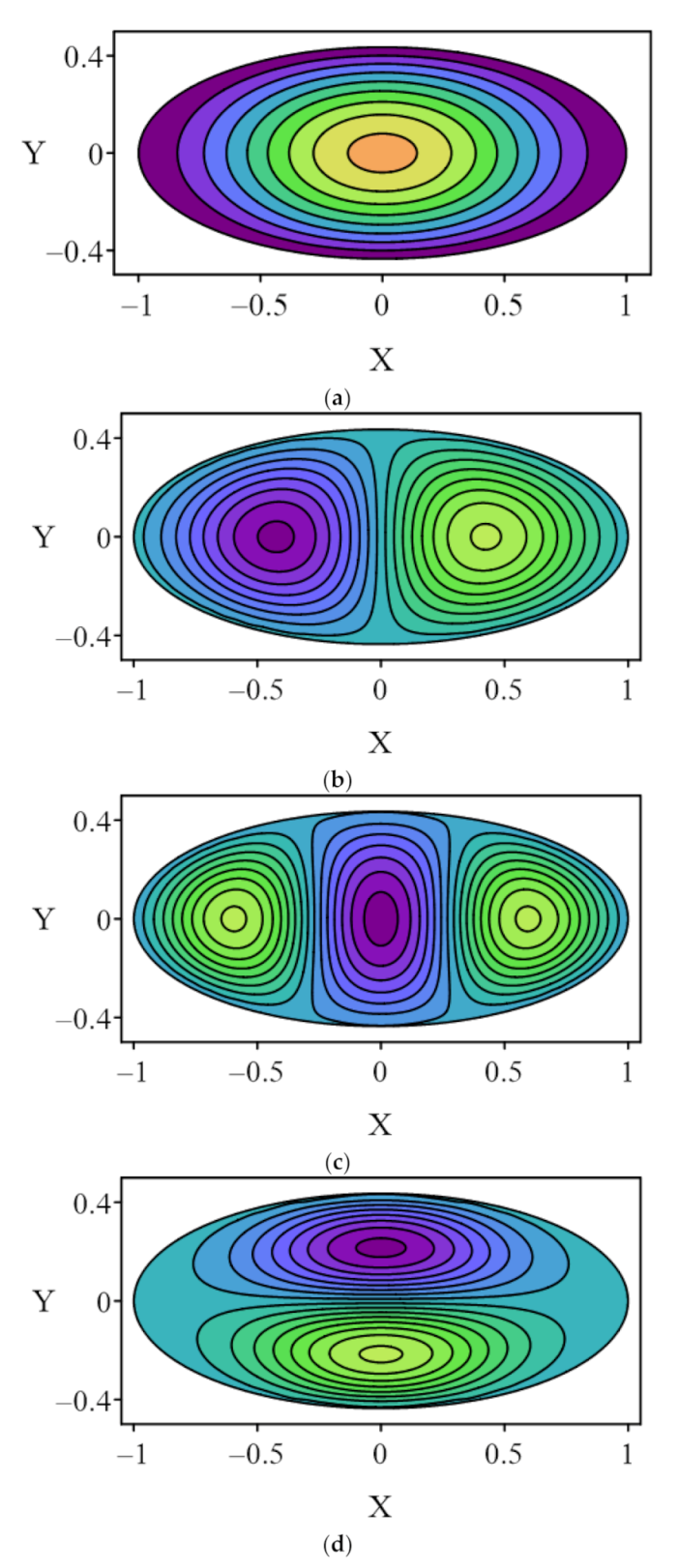
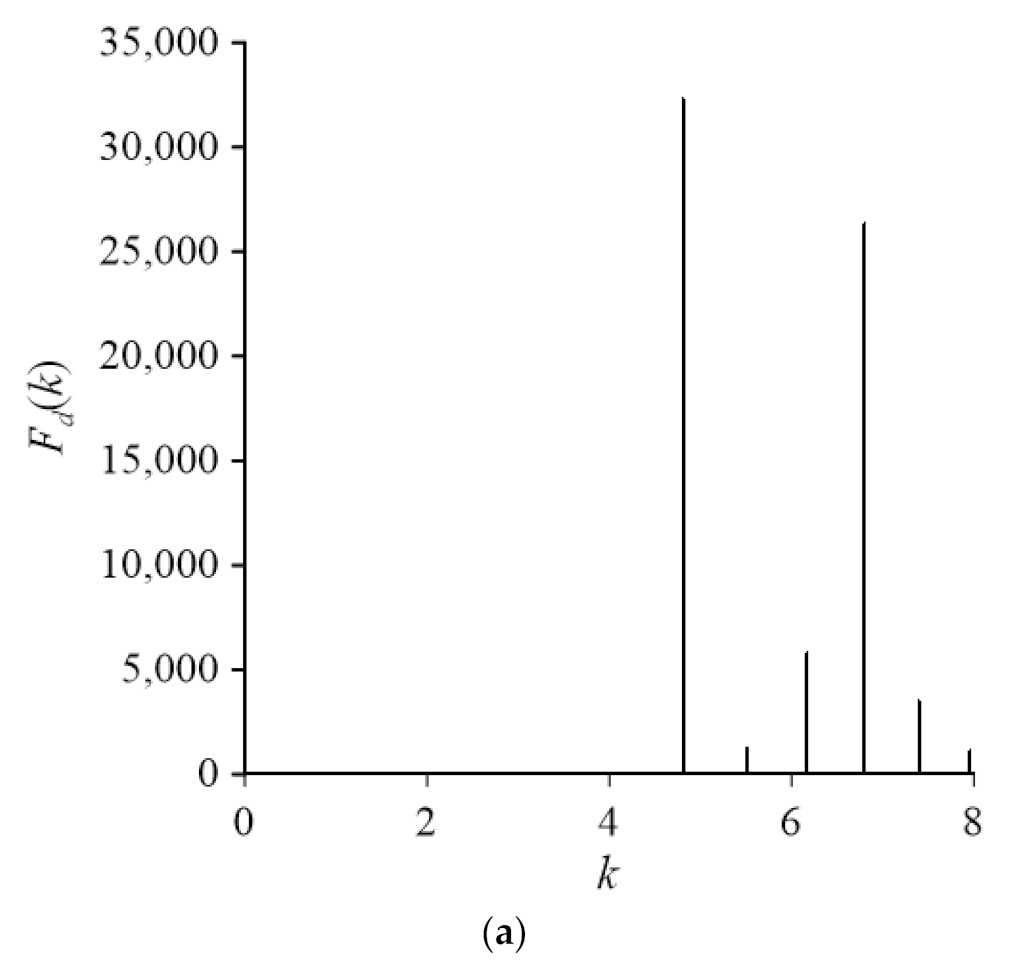
4.1. Case 1
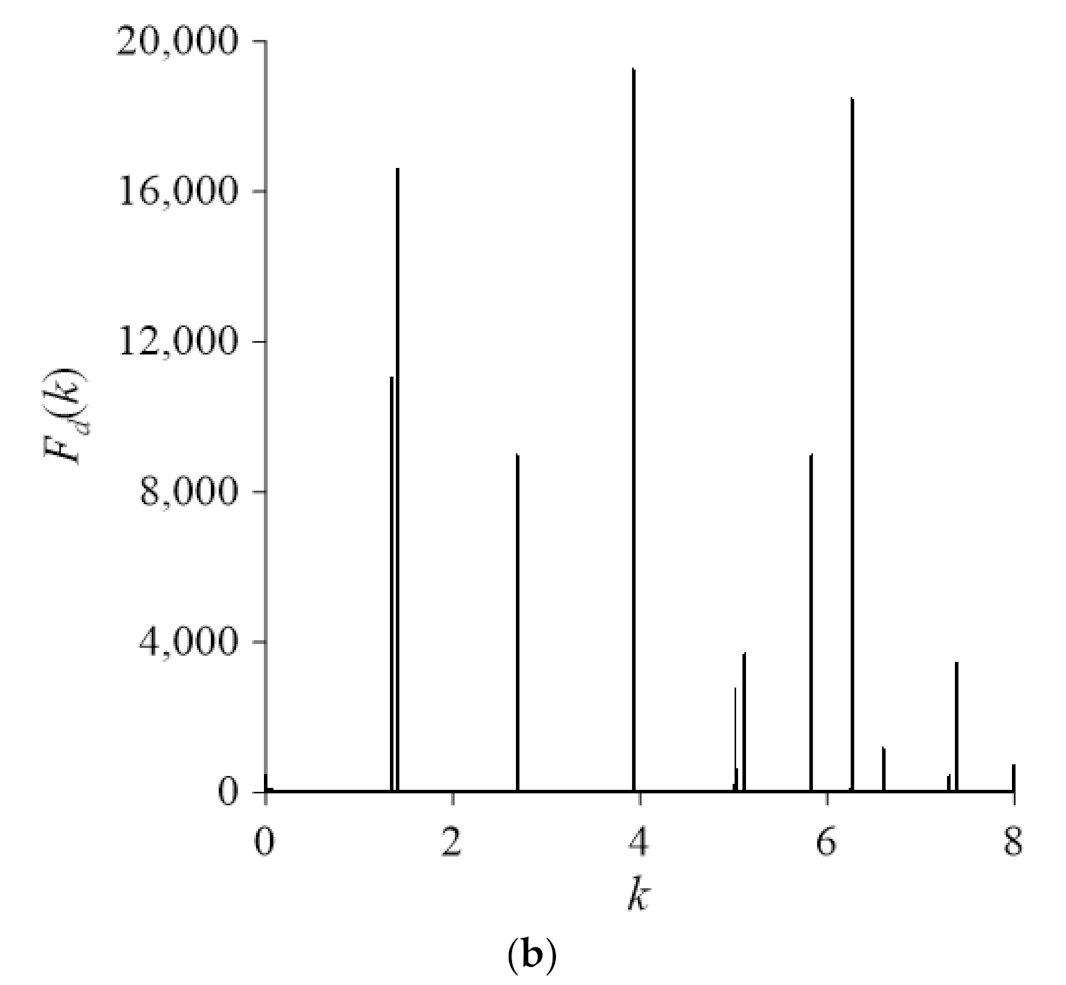
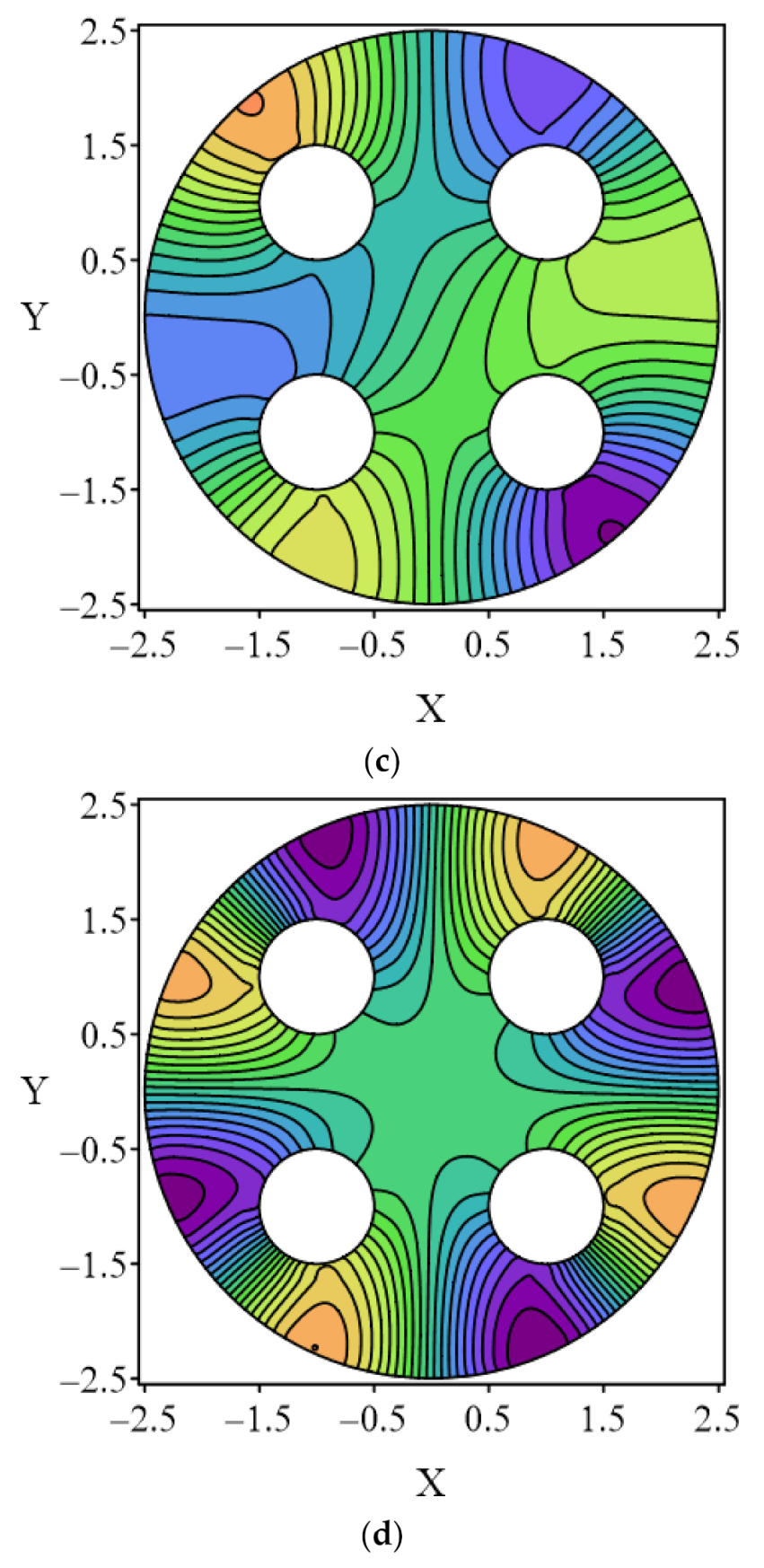
4.2. Case 2
4.3. Case 3
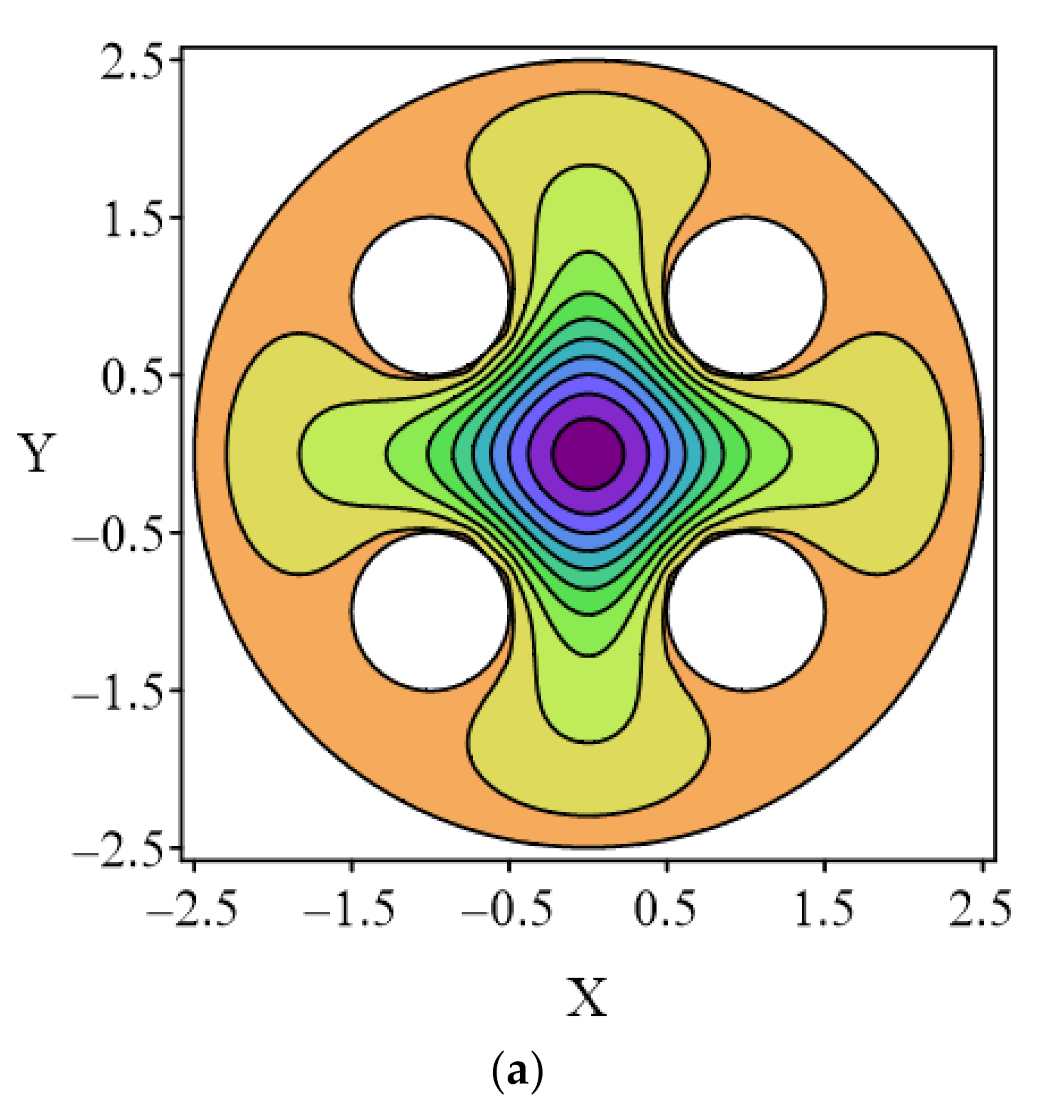
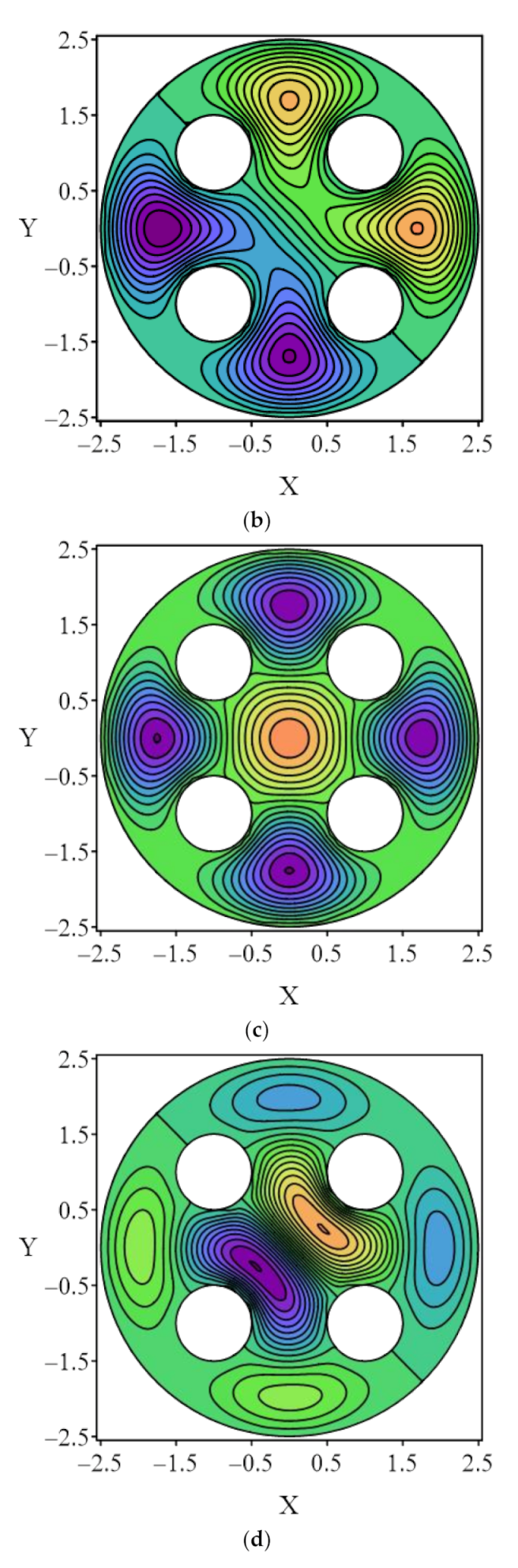
4.4. Case 4
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, D.L.; Hu, S.P.; Chen, C.W.; Fan, C.M.; Murugesan, K. Analysis of elliptical waveguides by the method of fundamental solutions. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2005, 44, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-T.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yu, S.-R.; Shieh, S.-C. Equivalence between the Trefftz method and the method of fundamental solution for the annular Green’s function using the addition theorem and image concept. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2009, 33, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.M.; Chen, C.S.; Monroe, J. The method of fundamental solutions for solving convection-diffusion equations with variable coefficients. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2009, 1, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.P.; Fan, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Young, D.L. Method of Fundamental Solutions for Stokes’ First and Second Problems. J. Mech. 2005, 21, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.; Young, D.; Chiang, J.; Lo, D. The method of fundamental solutions for solving options pricing models. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 181, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.L.; Fan, C.M.; Hu, S.P.; Atluri, S.N. The EulerianLagrangian method of fundamental solutions for two-dimensional Burger’ equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2008, 32, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z. Best estimates of RBF-based meshless Galerkin methods for Dirichlet problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 215, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-M.; Chan, H.-F.; Kuo, C.-L.; Yeih, W. Numerical solutions of boundary detection problems using modified collocation Trefftz method and exponentially convergent scalar homotopy algorithm. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2012, 36, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Dina, M. Implementation of Trefftz method for the solution of some elliptic boundary value problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2002, 127, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lee, Y.; Shieh, S. Revisit of two classical elasticity problems by using the Trefftz method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2009, 33, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-M.; Chan, H.-F. Modified Collocation Trefftz Method for the Geometry Boundary Identification Problem of Heat Conduction. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2011, 59, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. The Trefftz method for the Helmholtz equation with degeneracy. Appl. Numer. Math. 2008, 58, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S. A modified Trefftz method for two-dimensional Laplace equation considering the domain’s characteristic length. CMES Comput. Modeling Eng. Sci. 2007, 21, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.-C. Localized Boundary Knot Method for Solving Two-Dimensional Laplace and Bi-harmonic Equations. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.-L.; Li, S.-Q.; Chan, C.H. Analysis of elliptical waveguides by a meshless collocation method with the Wendland radial basis functions. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2002, 32, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.L.; Fan, C.M.; Young, D.L. Meshless numerical solutions for Burgers equations by Multiquadrics method and Cole-Hopf trans formation. J. Aeronaut. Astronaut. Aviat. Ser. A 2007, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Tan, Y.-J. On condition number of meshless collocation method using radial basis functions. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 172, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, Z.M. Kernel based approximation in Sobolev spaces with radial basisfunctions. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 215, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sladek, J.; Sladek, V. A meshfree local RBF collocation method for anti-plane transverse elastic wave propagation analysis in 2D phononic crystals. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 305, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Sladek, J.; Sladek, V. Band structure computation of in-Plane elasticwaves in 2D phononic crystals by a meshfree local RBF collocation method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2016, 66, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tyrer, M. A local radial basis function collocation method for band structure computation of phononic crystals with scatterers of arbitrary geometry. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 60, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yao, G.M.; Lei, H.K.; Li, X.X. On the selection of a good shape parameter of localized method of approximated particular solutions. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2018, 10, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xiong, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, P. Mixed-mode dynamic stress intensity factors by variation technique with finite block method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2019, 106, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutskiy, S.Y. The method of fundamental solutions for eigenproblems with Laplace and biharmonic operators. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2005, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Reutskiy, S.Y. The method of external sources (MES) for eigenvalues problems with Helmholtz equation. CMES Comput. Modeling Eng. Sci. 2006, 12, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Reutskiy, S.Y. The method of fundamental solutions for Helmholtz eigenvalue problems in simply and multiply connected domains. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2006, 30, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutskiy, S. The method of fundamental solutions for problems of free vibrations of plates. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2007, 31, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-M.; Young, D.-L.; Chiu, C.-L. Method of fundamental solutions with external source for the eigenfrequencies of waveguides. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2009, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.M.; Fan, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-C.; Hsiao, S.-S. The Least Squares Trefftz Method and the Method of External Source for the Eigenfrequencies of Waveguides. J. Mar. Sci. Technol.-Taiwan 2013, 21, 703–710. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.M.; Huang, Y.K.; Chen, C.S. Localized method of fundamental solutions for solving two Dimensional Laplace and bi-harmonic equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2019, 101, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Fan, C.-M.; Yeih, W.; Ku, C.-Y.; Chu, C.-L. Numerical solutions of two-dimensional Laplace and biharmonic equations by the localized Trefftz method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 88, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-M.; Chien, C.-S.; Chan, H.-F.; Chiu, C.-L. The local RBF collocation method for solving the double-diffusive natural convection in fluid-saturated porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarler, B.; Vertnik, R. Meshfree explicit local radial basis function collocation method for diffusion problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2006, 51, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.-F.; Fan, C.-M.; Kuo, C.-W. Generalized finite difference method for solving two-dimensional non-linear obstacle problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2013, 37, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; He, X. Application of the meshless generalized finite difference method to inverse heat source problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Young, D.; Chen, C.; Fan, C.-M. The method of fundamental solutions for eigenproblems in domains with and without interior holes. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. R. Soc. 2006, 462, 1443–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Li, L.-W.; Yeo, T.-S.; Leong, M.-S. Analysis of metallic waveguides of a large class of cross sections using polynomial approximation and superquadric functions. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2001, 49, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttler, J. A New Method for Calculating TE and TM Cutoff Frequencies of Uniform Waveguides with Lunar or Eccentric Annular Cross Section. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1984, 32, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

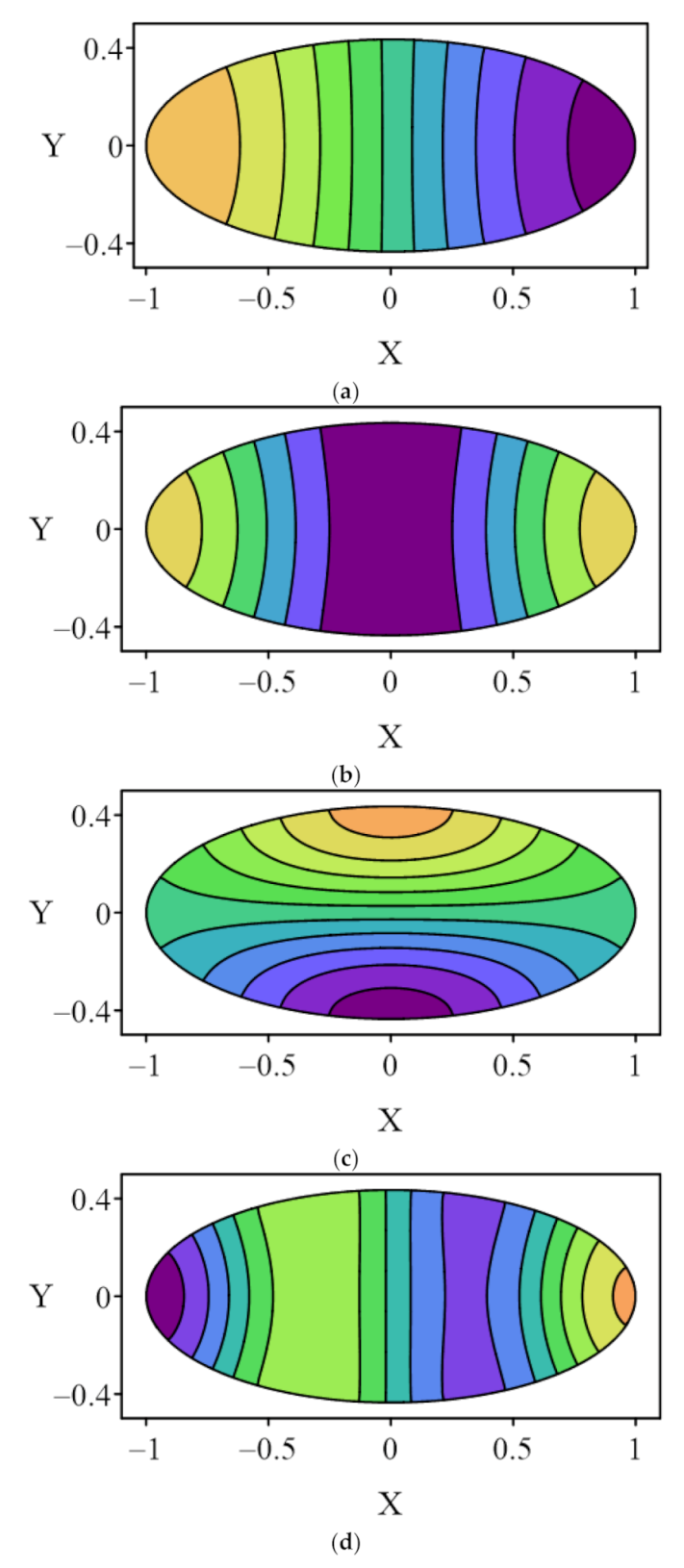
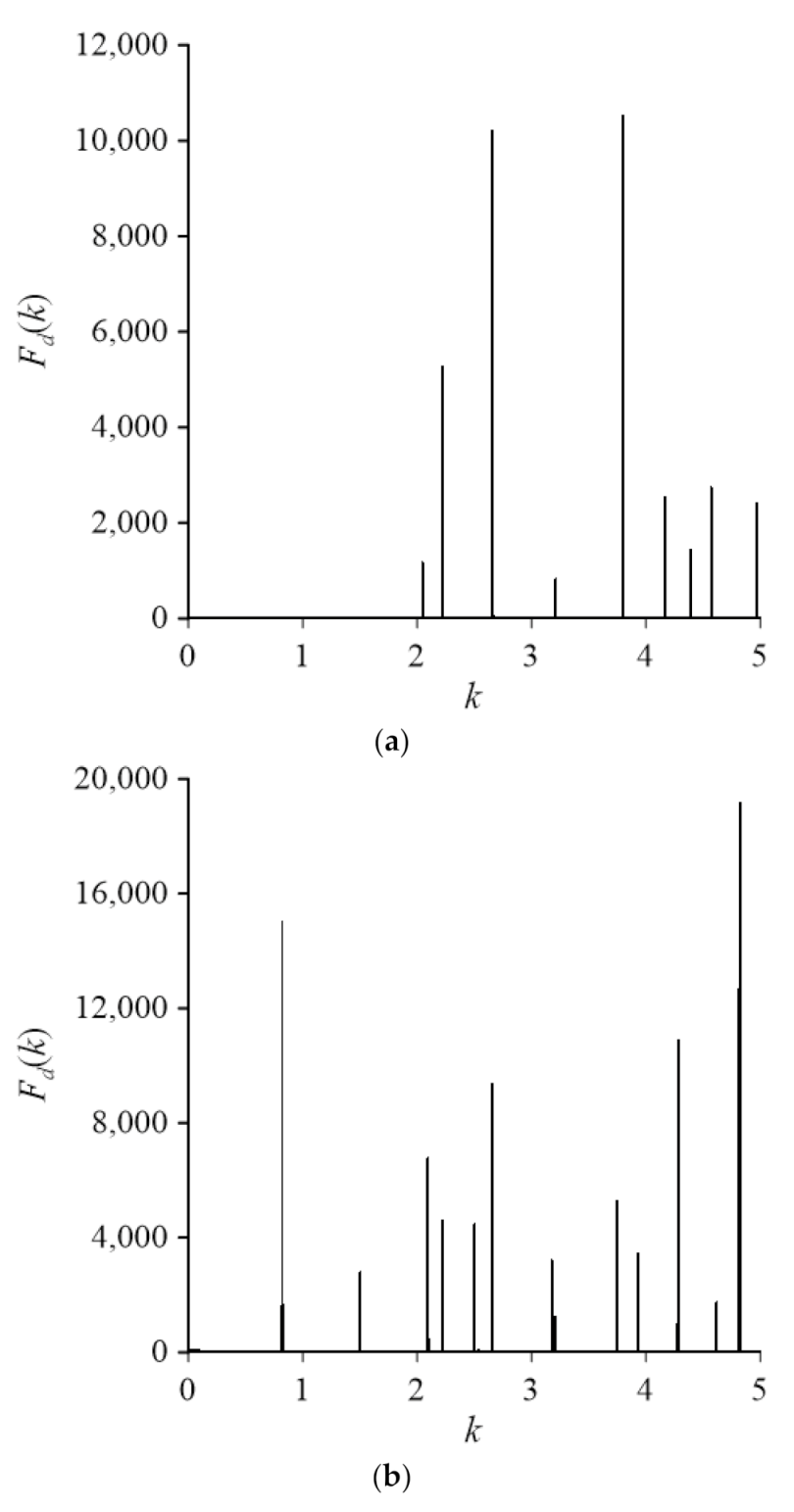

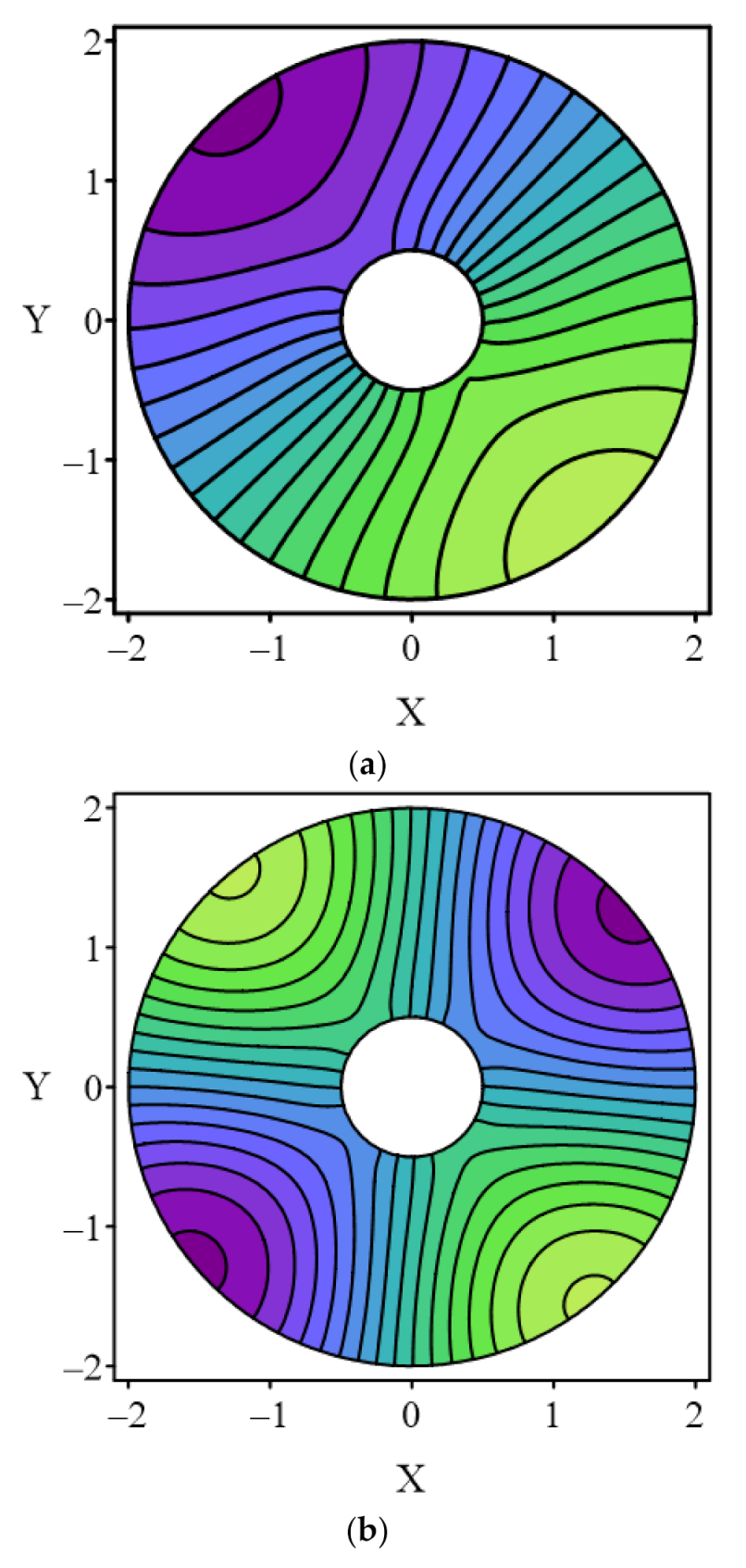
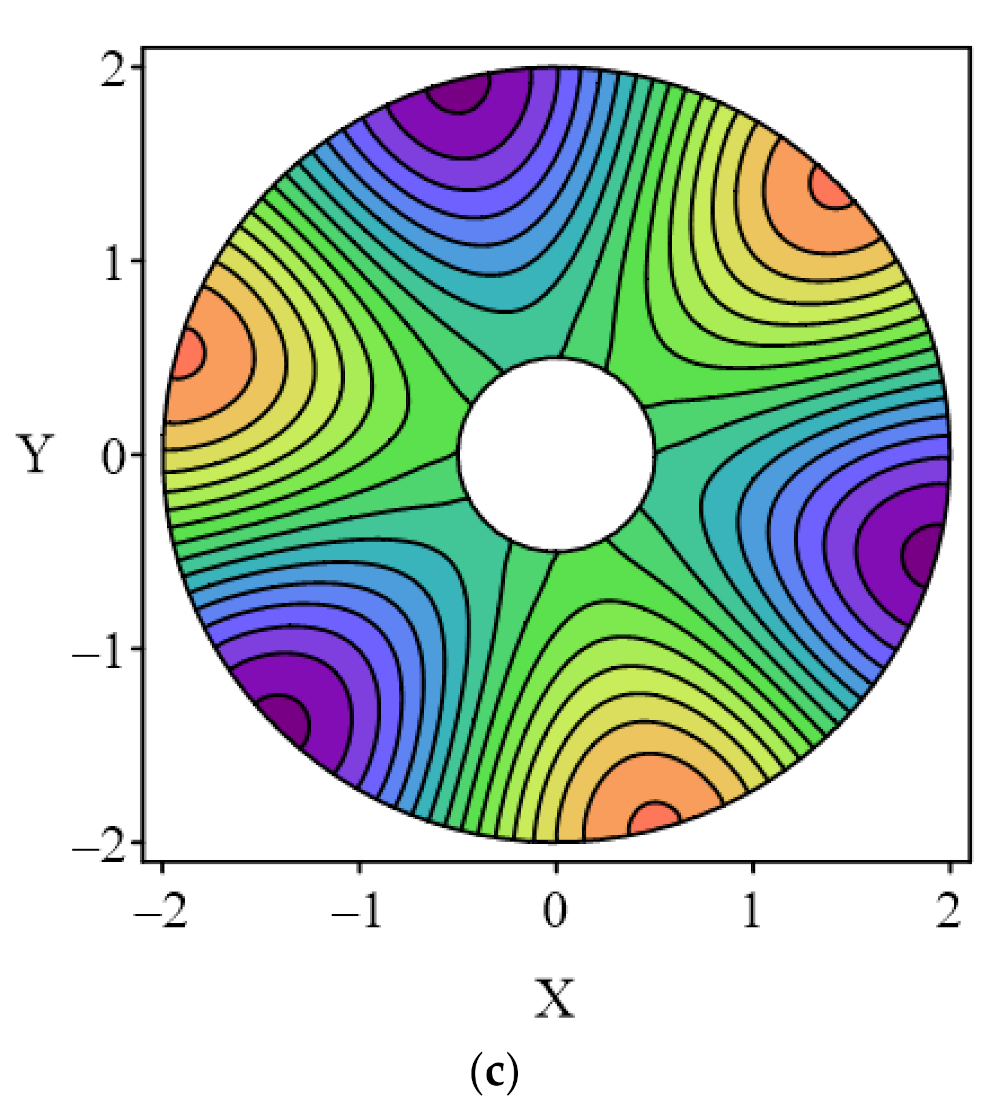






| Mode | LMFS P = 15 | LMFS P = 20 | LMFS P = 30 | MFS-SVD [1] | MFS-ES [28] | RBFCM [15] | Analytical Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.4906 | 1.4906 | 1.4906 | 1.4908 | 1.4906 | 1.4906 | 1.4906 |
| 2 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 | 1.1607 |
| 3 | 0.9375 | 0.9375 | 0.9375 | 0.9375 | 0.9375 | 0.9376 | 0.9375 |
| 4 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 | 0.8093 |
| 5 | 0.7803 | 0.7803 | 0.7803 | 0.7799 | 0.7803 | 0.7804 | 0.7803 |
| 6 | 0.7083 | 0.7083 | 0.7083 | 0.7071 | 0.7083 | 0.7083 | 0.7083 |
| Mode | LMFS P= 20 | LMFS P = 25 | LMFS P= 35 | MFS-SVD [1] | MFS-ES [28] | RBFCM [15] | Analytical Solution |
| 1 | 3.3482 | 3.3482 | 3.3482 | 3.3481 | 3.3482 | 3.3479 | 3.3482 |
| 2 | 1.8287 | 1.8287 | 1.8287 | 1.8287 | 1.8287 | 1.8284 | 1.8287 |
| 3 | 1.5649 | 1.5649 | 1.5649 | 1.5649 | 1.5650 | 1.5650 | 1.5650 |
| 4 | 1.2654 | 1.2654 | 1.2654 | 1.2654 | 1.2654 | 1.2656 | 1.2654 |
| 5 | 1.2292 | 1.2292 | 1.2292 | 1.2292 | 1.2292 | 1.2293 | 1.2292 |
| 6 | 0.9986 | 0.9986 | 0.9986 | 0.9986 | 0.9986 | 0.9984 | 0.9986 |
| Mode | LMFS P = 20 | LMFS P = 30 | LMFS P = 50 | LSTM [29] | MFS-DDSM [36] | Analytical Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0650 | 3.0650 | 3.0650 | 3.0650 | 3.0650 | 3.0650 |
| 2 | 2.8254 | 2.8253 | 2.8254 | 2.8302 | 2.8302 | 2.8176 |
| 3 | 2.3621 | 2.3621 | 2.3621 | 2.3621 | 2.3621 | 2.3621 |
| 4 | 1.9574 | 1.9574 | 1.9574 | 1.9574 | 1.9574 | 1.9574 |
| 5 | 1.6535 | 1.6535 | 1.6535 | 1.6535 | 1.6535 | 1.6535 |
| Mode | LMFS P = 10 | LMFS P = 20 | LMFS P = 30 | MFS-ES [28] | Lin et al. [37] | Kuttler [38] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.3061 | 1.3061 | 1.3061 | 1.3061 | 1.3054 | 1.3057 |
| 2 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.1371 | 1.1398 |
| 3 | 1.0179 | 1.0179 | 1.0179 | 1.018 | 1.0118 | 1.0177 |
| 4 | 0.9241 | 0.9241 | 0.9241 | 0.9241 | 0.9189 | 0.9239 |
| 5 | 0.8497 | 0.8497 | 0.8497 | 0.8497 | 0.842 | 0.8495 |
| Mode | LMFS P= 15 | LMFS P= 25 | LMFS P= 35 | MFS-ES [28] | Lin et al. [37] | Kuttler [38] |
| 1 | 4.6466 | 4.6466 | 4.6466 | 4.6421 | 4.6152 | 4.6466 |
| 2 | 4.4628 | 4.4628 | 4.4628 | 4.4586 | 4.4492 | 4.4571 |
| 3 | 2.341 | 2.341 | 2.341 | 2.3399 | 2.3138 | 2.3409 |
| 4 | 2.3391 | 2.3391 | 2.3392 | 2.338 | 2.2989 | 2.339 |
| 5 | 1.599 | 1.5989 | 1.599 | 1.5984 | 1.5817 | 1.5988 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, K.; Ding, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-C. Solving the Eigenfrequencies Problem of Waveguides by Localized Method of Fundamental Solutions with External Source. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071128
Sun K, Ding S, Zhang J, Liu Y-C. Solving the Eigenfrequencies Problem of Waveguides by Localized Method of Fundamental Solutions with External Source. Mathematics. 2022; 10(7):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071128
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ke, Shuang Ding, Junli Zhang, and Yan-Cheng Liu. 2022. "Solving the Eigenfrequencies Problem of Waveguides by Localized Method of Fundamental Solutions with External Source" Mathematics 10, no. 7: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071128
APA StyleSun, K., Ding, S., Zhang, J., & Liu, Y.-C. (2022). Solving the Eigenfrequencies Problem of Waveguides by Localized Method of Fundamental Solutions with External Source. Mathematics, 10(7), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071128





