Monitoring Sparse and Attributed Network Streams with MultiLevel and Dynamic Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Proposed Methodology
2.1. Zero-Inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Models
2.2. State Space Models and the Extended Kalman Filter
2.3. Monitoring of Dynamic and Multilevel Sparse Network Streams
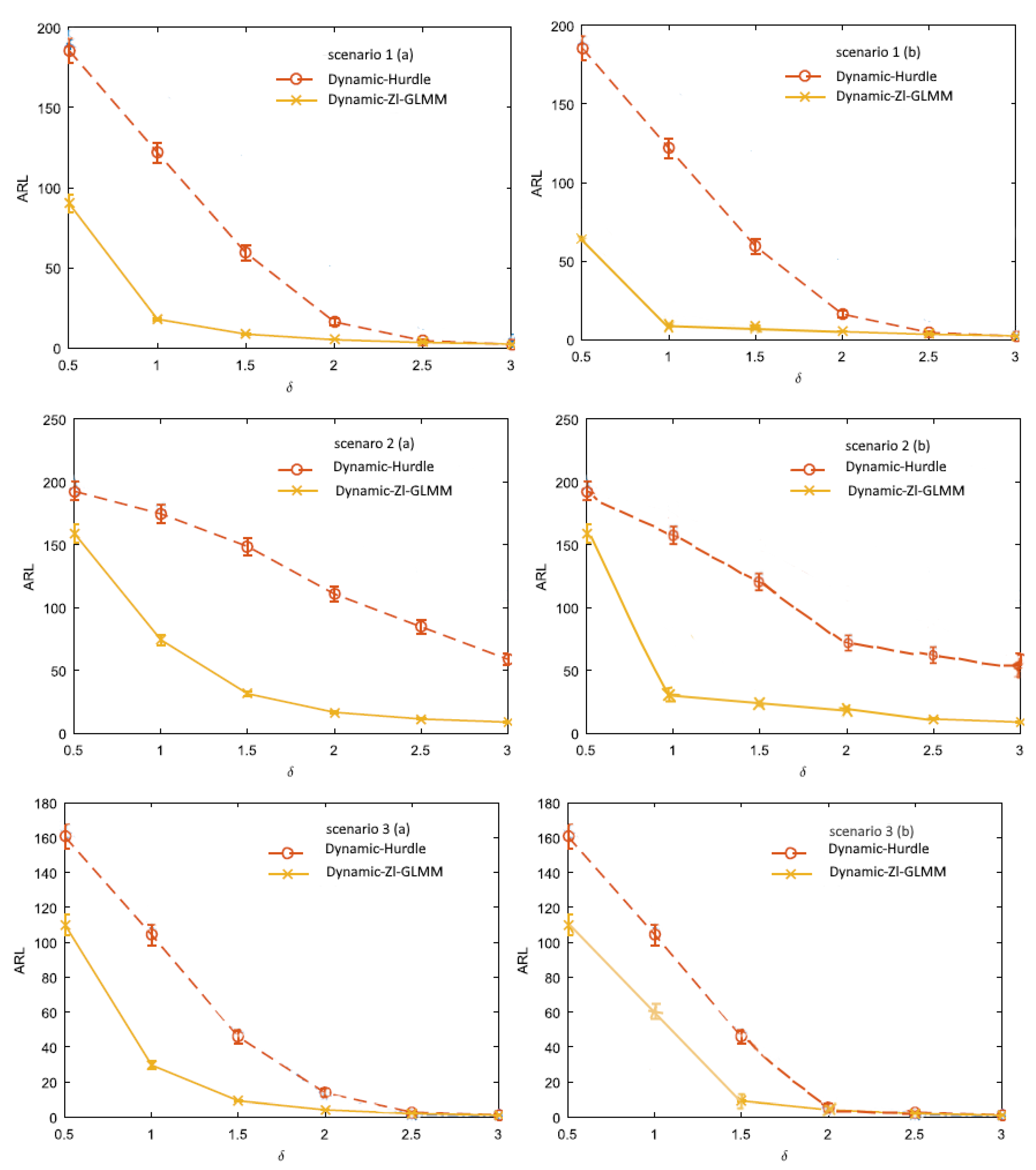
3. Performance Evaluation Using Simulation
Simulation Results
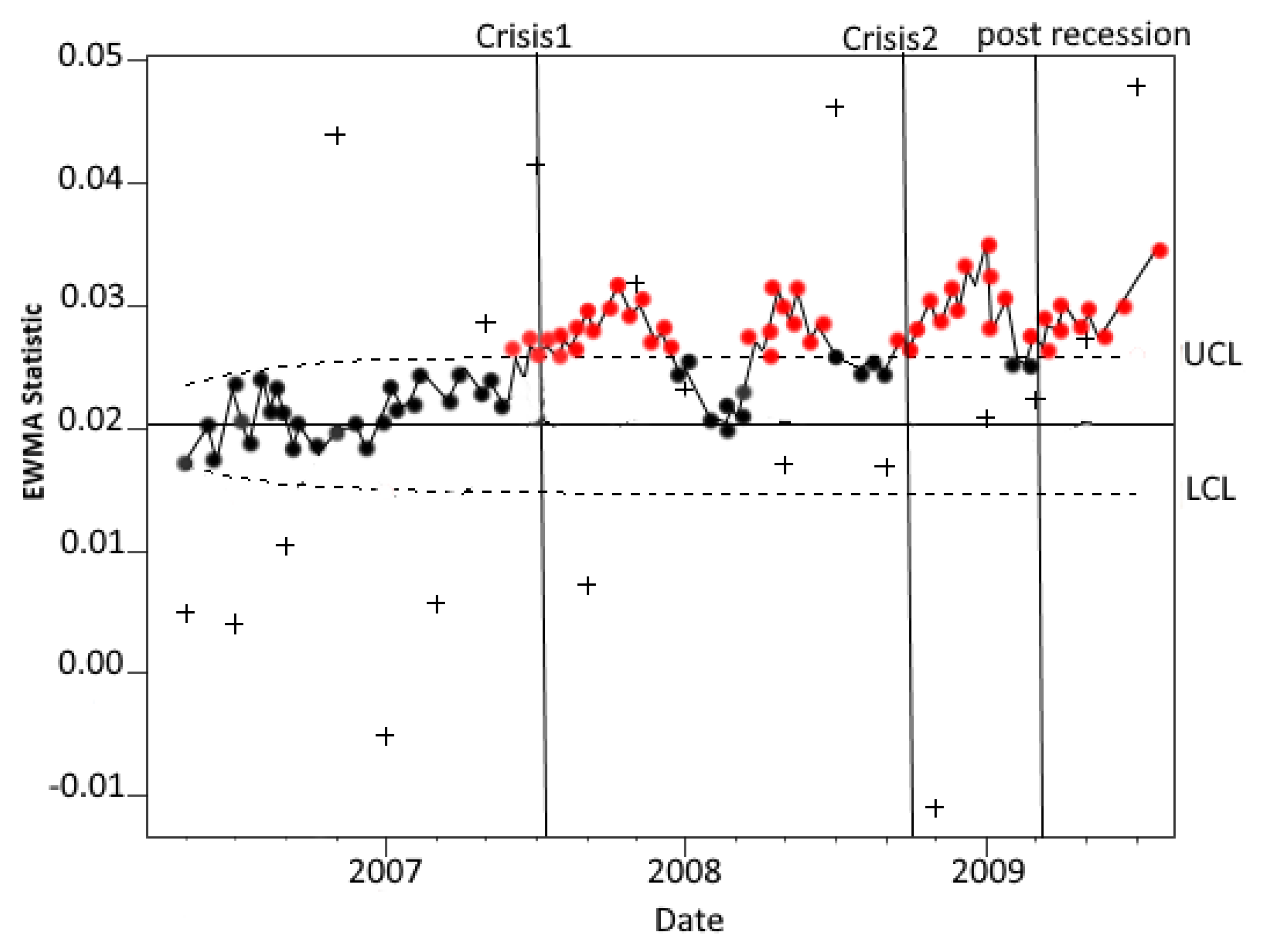
4. Case Study: Change Detection in the Interbank Market during the Financial Crisis
- Overnight (OVN) transactions. Unsecured (U) loans, i.e., without collateral. (OVNU).
- Overnight (OVN) transactions. Secured (S) loans, i.e., with collateral. (OVNS).
- Short-term (ST) transactions, namely those with maturity up to 12 months, excluding overnight. Unsecured (U) loans, i.e., without collateral. (STU).
- Short-term (ST) transaction, namely those with maturity up to 12 months, excluding overnight. Secured (S) loans, i.e., with collateral. (STS).
- Long-term (LT) transactions, namely those with the maturity of more than 12 months of consideration. We distinguish collateralization. Unsecured (U) loans, i.e., without collateral. (LTU).
- Long-term (LT) transactions, namely those with the maturity of more than 12 months of consideration.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mantegna, R.N. Hierarchical structure in financial markets. Eur. Phys. J. B-Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 1999, 11, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, N.; Brandon-Jones, A. Operations and Process Management: Principles and Practice for Strategic Impact; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trier, M. Research note—Towards dynamic visualization for understanding evolution of digital communication networks. Inf. Syst. Res. 2008, 19, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, M. A social network analysis of Twitter: Mapping the digital humanities community. Cogent Arts Humanit. 2016, 3, 1171458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, L.; Keller, T.; Neely, S.; DePaula, N.; Robert-Cooperman, C. Crisis Communications in the Age of Social Media: A Network Analysis of ZikaRelated Tweets. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2018, 36, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, J.; Rank, O. The firm’s knowledge network and the transfer of advice among corporate inventors—A multilevel network study. Res. Policy 2017, 46, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.K.; Luke, D.A.; Zuckerman, R.B.; Shelton, S.C. Forty Years of Secondhand Smoke Research. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 36, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, K.; Fricke, D.; Lux, T. Network analysis of the e-mid overnight money market: The informational value of different aggregation levels for intrinsic dynamic processes. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2013, 10, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarnoush, B.; Paynabar, K.; Bekki, J.; Runger, G. Monitoring Temporal homogeneity in attributed network streams. J. Qual. Technol. 2016, 48, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahrooei, M.R.; Paynabar, K. Change detection in a dynamic stream of attributed networks. J. Qual. Technol. 2018, 50, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Reisi-Gahrooei, M.; Paynabar, K.; Mankad, S. Monitoring sparse and attributed networks with online Hurdle models. IISE Trans. 2021, 54, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, P.J.; Richardson, T.; Macon, K.; Porter, M.A.; Onnela, J.P. Community structure in time-dependent, multiscale, and multiplex networks. Science 2010, 328, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, W.K.; Goh, K.I.; Kim, I.M. Correlated multiplexity and connectivity of multiplex random networks. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 033027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Goh, K.I. Multiple resource demands and viability in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carley, K. A theory of group stability. Am. Soc. Rev. 1991, 56, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollway, J.; Koskinen, J. The case of the global fisheries governance complex. Soc. Netw. 2016, 44, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargigli, L.; di Iasio, G.; Infante, L.; Lillo, F.; Pierobon, F. The multiplex structure20 of interbank networks. Quant. Financ. 2015, 15, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, A.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Moghimbeigi, A.; Rahimi, A.; Mohammad, K.; Fallahigilan, S. Multilevel zero-inflated Generalized Poisson regression modeling for dispersed correlated count data. Stat. Methodol. 2016, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courgeau, D.; Franck, R. Methodology and Epistemology of Multilevel Analysis: Approaches from Different Social Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fávero, L.P.; Hair, J.F.; Souza, R.F.; Albergaria, M.; Brugni, T.V. Zero-inflated generalized linear mixed models: A better way to understand data relationships. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fávero, L.P.L. The zero-inflated negative binomial multilevel model: Demonstrated by a Brazilian dataset. Int. J. Math. Oper. Res. 2017, 11, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D. Zero-inflated Poisson regression, with an application to defects in manufacturing. Technometrics 1992, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Wang, K.; Scott, J.A.; Yau, K.K.; McLachlan, G.J. Multi-level zero-inflated Poisson regression modelling of correlated count data with excess zeros. Stat. Methods Med Res. 2006, 15, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fávero, L.P.L.; Serra, R.G.; dos Santos, M.A.; Brunaldi, E. Cross-Classified multilevel determinants of firm’s sales growth in Latin America. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2018, 13, 902–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yau, K.K.; Lee, A.H. A zero-inflated poisson mixed model to analyze diagnosis related groups with majority of same-day hospital stays. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2002, 68, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younès, M.; Ezzahid, E.H.; Belasri, Y. Operational value-at-risk in case of zero-inflated frequency. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2012, 4, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, R.G.; Hwang, P.Y. Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering: With MATLAB Exercises and Solutions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 12, pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bargigli, L.; di Iasio, G.; Infante, L.; Lillo, F.; Pierobon, F. Interbank markets and multiplex networks: Centrality measures and statistical null models. In Interconnected Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, C.; Harris, J.H.; Mankad, S.; Michailidis, G. Interconnectedness in the interbank market. J. Financ. Econ. 2019, 133, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, K. A comparison of control charts from the viewpoint of change-point estimation. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 1992, 8, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, J.A.; Poldrack, R.A. Modeling group fMRI data. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2007, 2, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafapour, M.; Movahedi Sobhani, F.; Saghaei, A. Monitoring Sparse and Attributed Network Streams with MultiLevel and Dynamic Structures. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234483
Mostafapour M, Movahedi Sobhani F, Saghaei A. Monitoring Sparse and Attributed Network Streams with MultiLevel and Dynamic Structures. Mathematics. 2022; 10(23):4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234483
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafapour, Mostafa, Farzad Movahedi Sobhani, and Abbas Saghaei. 2022. "Monitoring Sparse and Attributed Network Streams with MultiLevel and Dynamic Structures" Mathematics 10, no. 23: 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234483
APA StyleMostafapour, M., Movahedi Sobhani, F., & Saghaei, A. (2022). Monitoring Sparse and Attributed Network Streams with MultiLevel and Dynamic Structures. Mathematics, 10(23), 4483. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234483






